3D printer terms
3D Printing Glossary of Terms
Glossary of 3D Printing TermsHere is the glossary from the back of our user manual. We use this vocabulary in our videoconference trainings and tech support.
3D
Three-dimensional
3D Printing
The process of creating a three-dimensional object from a digital file. Usually, it is achieved by stacking two-dimensional layers of material to form a physical 3D object. There are many different 3D printing processes that use many different materials, but the most common process is material extrusion—also known as Fused Deposition Modeling and Fused Filament Fabrication—which uses thermoplastic filament. Also known as additive manufacturing.
3D Printer
A machine tool that creates a three-dimensional object from a digital file by stacking thin, two-dimensional layers of material. This machine usually reads g-code files that give it specific instructions on how to print an object. The most common type of 3D printer uses the process of material extrusion, or fused deposition modeling (FDM), to form parts.
3D Design Program
A type of software used to visualize, design, and manipulate 3D products while providing a test environment for strength and dynamic analysis. Also known as a Computer Aided Design (CAD) program or 3D Modeling Software. Free examples for educators include Autodesk Inventor, Fusion360, SketchUp, Onshape, and Tinkercad.
3D Modeler
A type of multimedia artist or animator who creates three-dimensional models or visuals of items using a variety of different computer software programs and tools. Also, a program used to manipulate 3D shapes to create objects for animation or production.
A5
The A5 is an open source material extrusion 3D printer design that prints 125 x 150 x 100mm. NWA3D heavily modifies this original design to meet the rigorous classroom environment and calls the version an NWA3D A5. We build, modify, and test every printer. We are the sole-source provider of the NWA3D A5. Changes include hardware upgrades, custom operating system, and our unmatched warranty, lifetime training, and support for educators.
We build, modify, and test every printer. We are the sole-source provider of the NWA3D A5. Changes include hardware upgrades, custom operating system, and our unmatched warranty, lifetime training, and support for educators.
A31
The A31 is an open source material extrusion 3D printer design that prints 300 x 300 x 400mm. NWA3D modifies the original design to meet the rigorous classroom environment and calls the version an NWA3D A31. We build, modify, and test every printer. We are the sole-source provider of the NWA3D A31. Changes include hardware upgrades, custom operating system, and our unmatched warranty, lifetime training, and support for educators.
ABS
Stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, which is a thermoplastic used for 3D printing. ABS is a common form of plastic found in most household items that were injection molded.
Additive Manufacturing
The process of creating an object from a digital file by stacking 2D layers to form a 3D object. Also called 3D printing. see also 3D Printing
Also called 3D printing. see also 3D Printing
Axis Binding
A problem associated with the X-, Y-, or Z-axis on a printer, in which the axis is unable to move freely or perform a given movement.
Belt
Toothed gear belt that is used to transfer movement.
Bridging
Bridging occurs in a 3D print when filament is extended across an open area without supports. The distance a print can bridge is determined by the hardware capabilities of the printer and the slicer settings.
Brim
A platform adhesion option whose function is to reduce shrinkage of bottom print layers or better adhere a low surface area object by providing a larger base platform.
Build Plate
The surface where the printer deposits the materials used for printing. Also known as the Print Bed. see also Print Bed
Bowden Extruder
An extruder assembly used pushing filament that uses a tube to feed the filament from the motor to heated areas. This type of extruder assembly reduces heat transfer to filament pressure point, thereby reducing plastic buildup and clogs.
This type of extruder assembly reduces heat transfer to filament pressure point, thereby reducing plastic buildup and clogs.
CAD
Computer Aided Design or CAD is the process of digitally designing 3D models. see also CAM
Calibration
The act or process of adjusting a device or instrument to perform correctly or more efficiently.
CAM
Computer Aided Manufacturing or CAM is the process using digital programs and/or CAD to physically manufacture objects through additive or subtractive manufacturing.
Carriage
The moving assembly that holds the nozzle and hot end of the of the extruder.
CNC
A Computer Numerical Control machine, or CNC, a a machine that uses subtractive manufacturing to create 3D objects. see also Subtractive Manufacturing
Control Screen
LCD screen that displays information and provides an interface to select settings and manipulate the printer.
Cooldown
The process of cooling down the hot end. Cooldown occurs automatically after a print is finished, or can be done manually after changing filament to to prevent filament baking and clogs. Can be controlled using the Control Screen or turning off the 3D printer.
Cura
A 3D printer slicing software. Utilized to transform 3D models into a X, Y, and Z coordinate language called g-code in “.gcode” format.
Endstop
Mechanical switches that indicate where the “home” or “zero” position is on each print axis. see also Limit Switch
Extrude
The act of dispensing build material onto the build platform through a small nozzle commonly referred to as a "hot end.”
Extruder
The assembly that handles feeding and extruding filament during a print. The extruder has two parts: the stepper motor and feeding system that pushes the material into the printer, and a hot end that heats and extrudes the material through a nozzle onto the build surface.
Extruder Fan
Fan that cools the heat sink of the extruder.
Extruder Motor
Stepper motor of the extruder assembly.
Extruder Nozzle
A brass or steel funnel-shaped die through which melted plastic is extruded.
Extruder Release Lever
The trigger lever that applies pressure to the extruder gear, which forces filament to flow into the Bowden tube of the extruder to the hot end.
Extrusion Multiplier
A percentage value associated with the flow rate of plastic extrusion. The flow rate can be manipulated by adjusting this multiplier.
Filament
Typically a thermoplastic formed into a continuous wire and wound onto a spool so it is compatible with a 3D printer’s extrusion system. see also ABS, PLA, TPU
Filament Diameter
The size designation of a roll of filament. Usually 1.75mm or 3mm/2.85mm (3mm and 2. 85mm are in the same size filament category are used interchangeably in 3mm and 2.85mm material extrusion 3D printers).
85mm are in the same size filament category are used interchangeably in 3mm and 2.85mm material extrusion 3D printers).
Fill
The area within a 3D-printed object that connects the top, bottom, and side layers. See also Infill
Fill Density
A percentage value that determines how much of the interior volume of a 3D-printed object is filled with material. This value can range from 0–100%, recommended is 5–25%.
Flow
The action of filament moving in a steady continuous stream. see also Extrusion Multiplier
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
FDM is another name for material extrusion and FFF. It is a trade name created by Stratasys, the company that invented and first commercialized the material extrusion process. see also FFF, Material Extrusion
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
FFF is another name for material extrusion and FDM. see also FDM, Material Extrusion
Gantry
The part of the extruder assembly and X-axis motor that moves up and down on the Z-axis of a 3D printer. see also Z-Axis Carriage
see also Z-Axis Carriage
G-code
Coding language that the 3D printer understands. It is used to transmit instructions to a 3D printer’s control system to tell the printer how to print the 3D model. see also Cura, Slicer
Heated Build Plate / Heated Print Bed
The heated surface where the printer deposits the material used for printing. A heated bed can help reduce warping on large prints and help adhere parts better.
HIPS
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a thermoplastic used as a 3D printing material that can be dissolved using limonene and therefore used for dissolvable supports on delicate prints.
Hot End
The heated portion of the extruder assembly that includes the nozzle and heating block.
Infill
The area within a 3D-printed object that connects top, bottom, and side layers. This creates a rigid structure and determines print durability.
Kapton Tape
Heat-resistant polyimide adhesive tape typically used to secure wiring and insulate the hot end of the extruder.
Layer
Extruded plastic of a closed loop, represented as a two-dimensional drawing on the X-Y plane. When replicated over again in the Z direction, it produces a 3D object or multi-layered X-Y drawing. see also Layer Height
Layer Height
Utmost determinant of quality for 3D printing, it defines the distance between lines of extruded plastic in the Z-direction. Material extrusion 3D printers typically print layers between 0.1mm and 0.3mm high. A lower layer height translates to a smoother, higher quality print. A higher layer height translates into a faster, low quality print.
Limit Switch
Mechanical switch that indicates where the “home” or “zero” position is on each print axis. see also Endstop
Material Extrusion
A 3D printing process that dispenses material through a nozzle or orifice. Also known as FFF or FDM. see also FDM, FFF
Also known as FFF or FDM. see also FDM, FFF
Minimal Layer Time
The least amount of time required of the printer to maintain action on any layer of a printed object for the filament to sufficiently cool before fusing a layer on top if it.
Mesh
A collection of polygons attached by edges and vertices that makes up a net-like surface area in CAD.
Motor
In 3D printing, the stepper motor that produces precise movement of the extruder, X-, Y-, or Z-axis. see also Stepper
Nozzle
A brass or steel funnel-shaped die through which melted plastic is extruded. see also Extruder Nozzle, Hot End
OBJ
OBJ stands for Object File, an alternative to the STL file format. OBJ (.obj) files store object exterior pattern and color.
PLA
Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic polymer derived from the starch in plants (normally corn) that is used for 3D printing.
Perimeter
A continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure. In 3D printing, the perimeter is created by the edges of every layer. see also Shell
Preheat
Heating prior to using the device or tool. In 3D printing, the nozzle needs to be preheated before printing or for loading and unloading filament.
Print Bed
The surface where the printer deposits the materials used for printing. Also known as the build plate. see also Build Plate
Print Speed
The rate at which a 3D printer is capable of moving while extruding plastic. A print speed of 50mm/s will be successful on most FDM printers. A print speed of 20–30mm/s will produce higher quality prints.
Print Quality
Refers to the quality of the print and is determined by many factors including mechanical capabilities of the printer, slicer used, layer height, print speed, support, and print orientation.
Printing Temperature
The temperature of the hot end at which the filament is melted and extruded.
PVA
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a water soluble plastic that is a common ingredient in standard wood glue. It can be used in 3D printing to print dissolvable supports.
Raft
A platform adhesion option in which several layers of printed material are deposited on the build surface to smooth out any irregularities in the build surface and help prevent warping in the model being printed on top of the raft. A raft also helps with bed adhesion of delicate models.
RepRap
An open source 3D printing project, started in 2005, to create the best desktop printers and to make them capable of duplicating themselves.
Repetier Host
An open source slicer program, used for the preparation of STL files prior to 3D printing. Allows manipulation of files prior to printing; rotating, scaling, and duplication.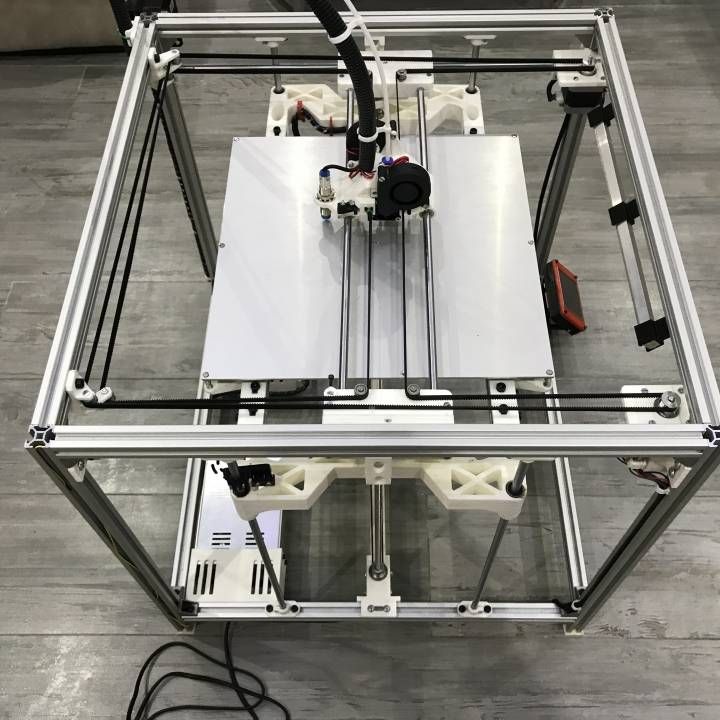
Resolution
The smallest movement a printer’s extruder can make within a single X-Y layer. Often indicates the produced quality of a printed model.
Retraction
Backwards movement of an extruder motor to reduce the amount of material stringing or oozing.
SD Card
A non-volatile memory card for use in portable devices to transfer information, such as .gcode to 3D printers.
Seam
The point at which two layers of 3D-printed material connect.
Shell
The sidewalls of a 3D printed model, created by the exterior edges of every layer. see also Perimeter
Shell Thickness
The total width of an outside wall of a 3D-printed part. Shell thickness should be a multiple of nozzle size. Two shells is typically best. An increased number of shells will lead to a stronger model. see also Shell
Skirt
A platform adhesion option that extrudes an offset outline of the model on the first layer of the print.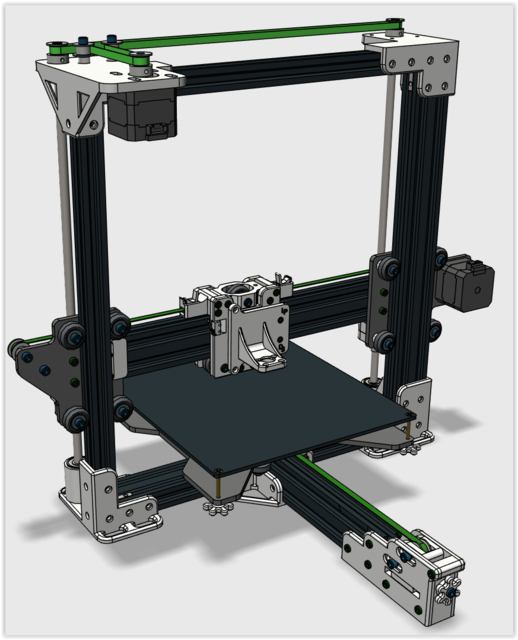 The skirt helps to remove unwanted colors and build pressure for material extrusion. It also checks the accuracy of bed leveling.
The skirt helps to remove unwanted colors and build pressure for material extrusion. It also checks the accuracy of bed leveling.
Slice
The action of changing a model file (STL, OBJ, etc.) into a a G-code file. The coordinate type can vary depending upon setting selection. The most common type uses cartesian coordinates on an XYZ plane. see also Slicer
Slicer
A type of program, such as Cura or Repetier Host, that allows manipulation of a 3D model and converts the file type into a coordinate system (usually .gcode) the printer follows to create a model. see also Cura, Repetier Host
Soft Pull/Soft Removal
The process of heating filament to the phase transition temperature (solid to liquid) and removing it from the extruder assembly. The process helps to remove unwanted material and can assist in the removal of nozzle blockage. NWA3D recommends to always remove filament using the soft pull method as preventive maintenance for your 3D printer.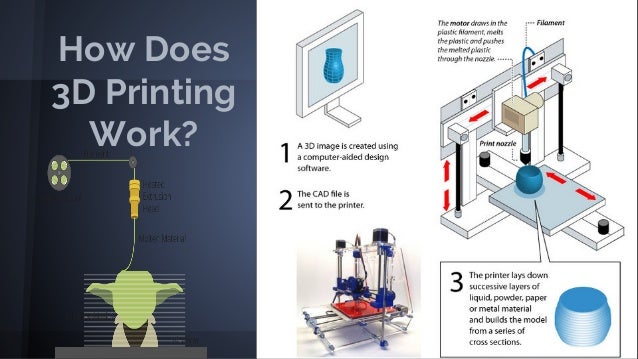
Stepper/Stepper Motor
An electric motor that moves in discrete movements, or steps, to allow more precise regulation of its movement. see also Motor
STL
The STL file format (STL stands for stereolithography) is the recommended file format for 3D models for 3D printing. The filetype contains the best mesh for solid 3D-printed objects. see also Mesh
Support
Additional removable structures that are printed to support overhangs or other parts of a model that do not make contact with the build plate during printing.
Subtractive Manufacturing
Manufacturing techniques that remove material to create an object. Common types are CNC routing and laser cutting.
Tension Arm
Arm that presses the filament into the gear of the extruder motor. see also Extruder Lever
TPU
Thermoplastic urethane (TPU) is a semi-flexible plastic that is used in 3D printing.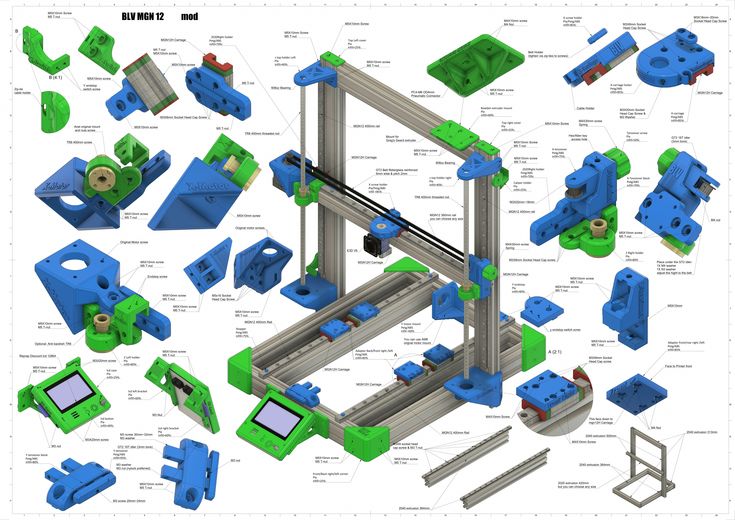
Travel Speed
The rate at which the nozzle assembly will move to a new position when not extruding.
USB Connection
USB, short for Universal Serial Bus, is a connection type to send files from a slicer on a computer to a 3D printer via a USB cable.
Viscosity
A measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow. The higher the viscosity, the more resistant the fluid is to flowing.
Vitamin
A part for a 3D printer or 3D printing project that isn’t 3D printable.
X-Axis
The principal or horizontal axis of a system of coordinates.
Y-Axis
The secondary or vertical axis of a system of coordinates.
Z-Axis
The axis in three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates which is usually oriented vertically.
Z-Lift
The process that a printer uses to lift the hot end upward prior to retraction and moving.
Z-Axis Carriage
The part of the extruder assembly and X-Axis motor that moves up and down on the Z-Axis of a 3D printer.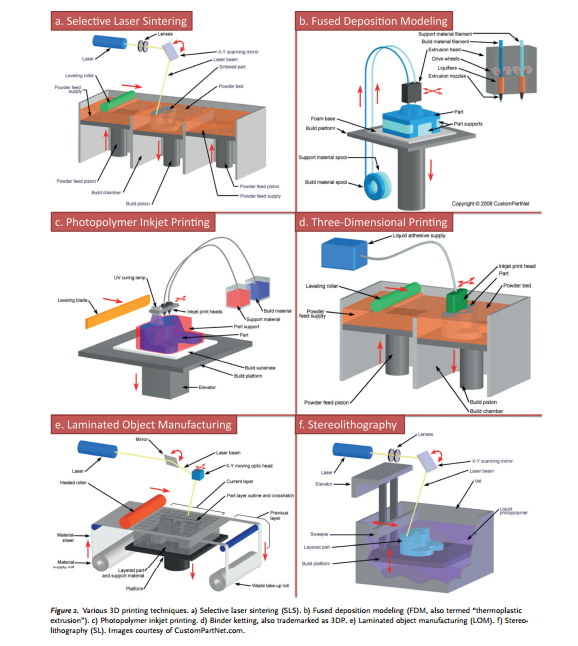 see also Gantry
see also Gantry
500 - Stratasys
500 - Stratasys Stratasys Invests in Axial3D to Make Patient-Specific 3D Solutions Available to All - Learn MoreUSA & Canada
Select your country and region
- Americas
- English
- Español (México)
- Português (Brasil)
- EMEA
- English (United Kingdom)
- Deutsch
- Español
- Français
- italiano
- APAC
- 中文(简体)
- 日本語 (日本)
- 한국어(대한민국)
- English (India)
USA & Canada
Challenges We Solve
Gain a competitive edge through 3D printing solutions
Challenges We Solve
Manufacturing Solutions
Bringing an idea to life is no longer bound by traditional constraints.
Manufacturing
Rapid Prototyping
Create. Test. Refine. Repeat. Prototyping with 3D printing accelerates business.
Rapid Prototyping
Contact Us for Help
Need a little help in bringing your vision to life? Our team of experts are always here for you.
Contact Us
Terminology/slang in 3D printing in Russian
Hi all. I want to share my experience of my research in terms of 3D printed terminology. I myself am still a beginner in both 3D modeling and 3D printing, and at the beginning of studying the issue, I came across an abundance of terms unknown to me before. In order to ease the thorny path of the pioneers of 3D printing, I decided to create a list of terms / slang with a little interpretation (I took something from this site, something from WIKI, I interpreted something myself). I propose, within the framework of this entry, to limit ourselves to the FDM type of printing and not to interfere with the rest. I hope you throw those 9 in the comments0% of the article that I missed, well, correct me if I made a mistake somewhere.
I want to share my experience of my research in terms of 3D printed terminology. I myself am still a beginner in both 3D modeling and 3D printing, and at the beginning of studying the issue, I came across an abundance of terms unknown to me before. In order to ease the thorny path of the pioneers of 3D printing, I decided to create a list of terms / slang with a little interpretation (I took something from this site, something from WIKI, I interpreted something myself). I propose, within the framework of this entry, to limit ourselves to the FDM type of printing and not to interfere with the rest. I hope you throw those 9 in the comments0% of the article that I missed, well, correct me if I made a mistake somewhere.
The 3D Printer is a peripheral that uses a layer-by-layer method to create a physical object from a 3D digital model.
FDM (Fused deposition modeling)
Filament (plastic rod) (from English filament - thread) is a consumable used for printing on a 3D printer.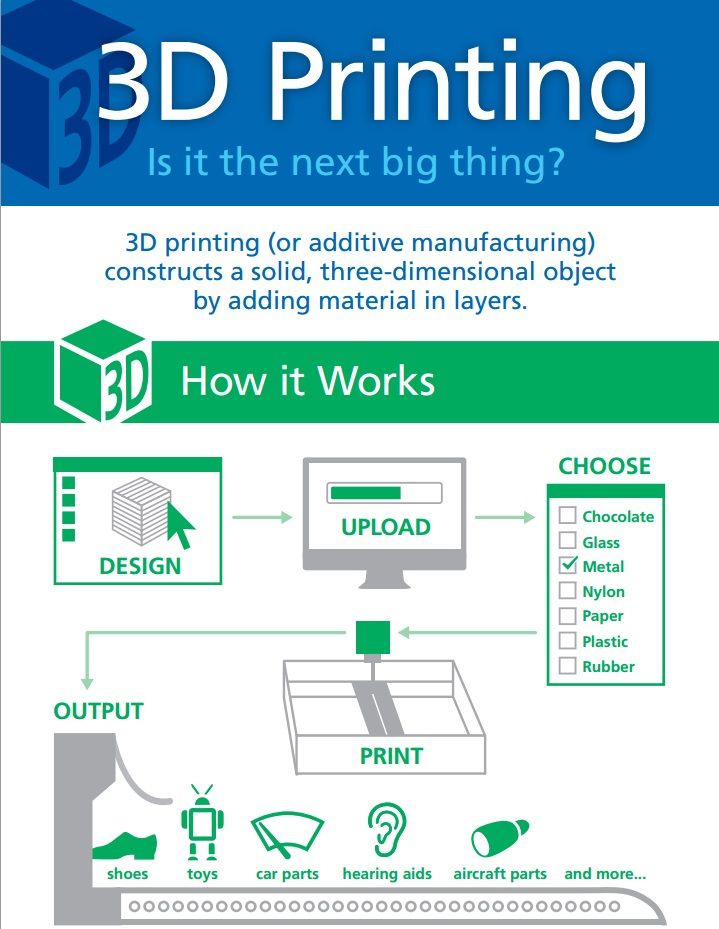 It is a plastic thread with a cross section of 1.75 or 3 mm.
It is a plastic thread with a cross section of 1.75 or 3 mm.
Extruder (from extrude - extrude) - a device that feeds a plastic rod into a heating block, in which a melt occurs under the influence of temperature and is squeezed out through a nozzle. A tube of toothpaste, a glue gun, a silicone sealant syringe work in a similar way. In a broad sense, this is a block consisting of a cold and a hot end.
Hot end (hot-end) — includes in the classical sense a nozzle, a heating block, a thermal barrier and an extruder heat sink. It is inside this block that the filament melts and is molded by welding.
Cold end (cold-end) is a device responsible for feeding the filament to the hot end, in the classical sense it consists of a feed gear, a pressure roller and a stepper motor. Often an intermediate reduction gear is used between the feed gear and the stepper motor to improve the accuracy of material feeding when printing thin layers or when printing at low speed.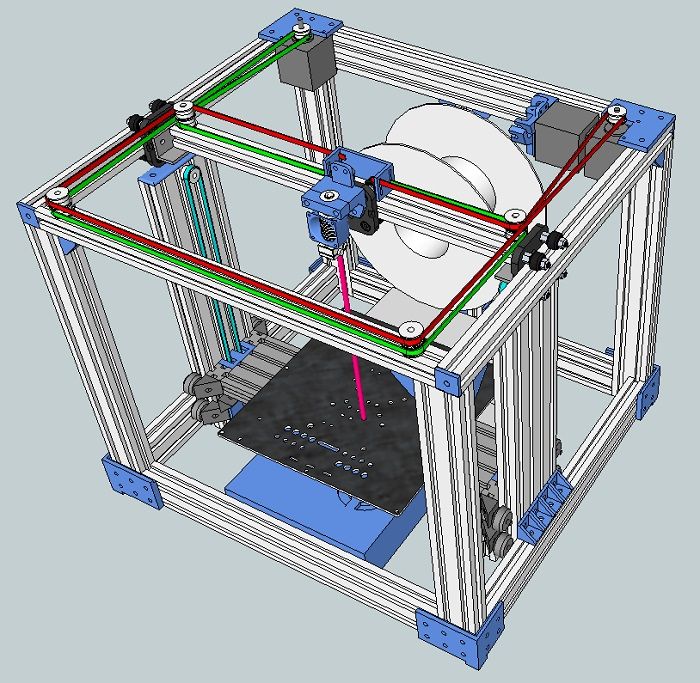
Nozzle (nozzle) — metal, ceramic or ruby hairpin with a longitudinal hole, this element is responsible for the shape and size of the extrusion melt at the outlet of the extruder.
Heating block - a block consisting of a heater (heater), thermistor (thermocouple, temperature sensor) and the block itself, which depletes these elements in itself.
Extruder heater (extruder heater) is an element that converts electric current into thermal energy and is responsible for heating the filament melt chamber inside the heating block.
Thermistor (thermocouple, temperature sensor) - takes temperature readings to control the voltage supply to the heating element to hold the temperature within the specified intervals. It is used both in an extruder and in a hot table.
Thermal barrier - a device whose task is to reduce the distance between the two phases of plastic - liquid and solid, in other words, does not allow the plastic to melt above what is needed, usually connects the heating block and the extruder radiator.
The extruder heat sink is a device designed to remove excess heat from the thermal barrier, usually through an air-cooled jacket, but liquid-cooled models are also available.
Worktable (print bed, platform, bed) - a platform on which the material is directly melted from the extruder. The surface of the table can be either perfectly smooth or perforated / corrugated in both cases, it is required to improve adhesion with the print object.
Hot bed (hotbed) - the same as the work table, only with the heating function, which allows to reduce the distortion of the deposited model, due to the gradual decrease in the temperature of the object. It also improves adhesion with the deposited object to the platform.
The stepper motor is a multi-winding synchronous brushless motor in which a current applied to one of the stator windings causes the rotor to lock. Sequential activation of windings of the motor causes discrete angular movements (steps) of the rotor.
Driver - microcircuit, the purpose of which is to convert the commands of the stepper motor controller into pulses applied to the windings of the Stepper motor and amplify them.
Direct Feed Extruder (direct) is a type of extruder where the cold end is located immediately before the hot end. Used for printing flexible plastics, rubber. The main disadvantage of this design is a lot of weight.
Bowden extruder ('Bowden extruder', Bowden extruder) is an extruder whose filament supply unit and nozzle are spaced apart: the cold end is rigidly fixed to the frame of the 3D printer, and the hot end is located on the movable print head. The filament, in this case, is fed into the nozzle through a long Teflon tube. Used for printing with rigid/elastic plastics.
End switch - a sensor responsible for finding the carriage in the dimensions of the printer structure, in other words, limiters at the ends of the axles. They are created both on button sensors and on optical or based on the Hall sensor. When this sensor is triggered, the printer control board resets the position of the carriage, and then counts the position from this starting point.
They are created both on button sensors and on optical or based on the Hall sensor. When this sensor is triggered, the printer control board resets the position of the carriage, and then counts the position from this starting point.
Slicer - software that converts a 3d model (usually from STL format) into gcode with specific print settings and for a specific material and printer.
Gcode ( G-code) - conditional naming of the programming language (markup) of devices with numerical control (CNC).
Retract - reverse filament withdrawal from the hot end, used to prevent plastic melt from flowing out of the nozzle at the moments of idle movement of the extruder over the model to be welded.
Raft (raft, raft) - horizontal filament mesh located under the model. The rafts are designed to increase the level of adhesion, and level out the unevenness of the bed and poor calibration of the extruder relative to the table.
Brim (border) - a skirt around the object of printing associated with the object itself, used to improve adhesion and entrainment of the plane of contact with the bed.
Support - additional printing elements not part of the model, designed to support overhanging elements. The printer simply cannot print through the air, it needs a base where to fuse the material.
Adhesion (from Latin adhaesio - sticking) in physics - adhesion of surfaces of dissimilar solid and / or liquid bodies.
Delamination (stratification) - the term is borrowed from biology, simply splitting the cell into two layers, in 3D printing it means both peeling off the part from the bed and splitting the print object itself into layers due to warpage of the object.
Juice (ABS Juice) - ABS solution in acetone with a consistency similar to baked milk, used to improve the adhesion of the printed object to the crib.
Post-processing - model processing after printing, grinding, heat treatment, chemical treatment, painting, gluing, etc.
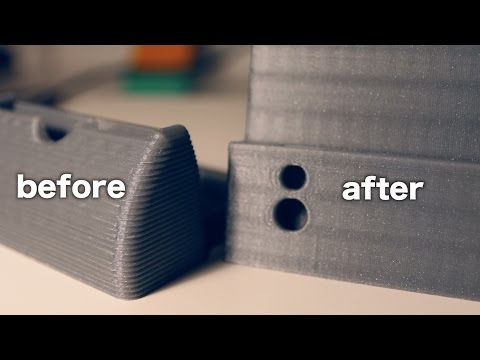
Acetone (Dichloromethane, Dichloroethane) bath - a method of post-processing of the print object, in which the product is placed in an environment of saturated vapor of one or another chemical compound for a smooth effect on the model, after which the model changes its properties. Acetone bath for ABS makes the part smooth, glossy. The dichloromethane bath for PLA turns it into a kind of flex/rubber.
Acetone bath for ABS makes the part smooth, glossy. The dichloromethane bath for PLA turns it into a kind of flex/rubber.
Hygroscopicity (from other Greek ὑγρός - wet and σκοπέω - observe) - the ability of some substances to absorb water vapor from the air, in our case, the ability of the filament to absorb moisture from the environment.
Drying - drying process of 'raw' plastic, printing with raw plastic is difficult due to water boiling inside the material and foaming as it exits the nozzle. Drying of plastic can be carried out both on the battery and in special heat chambers. In some cases, it is sufficient to store the materials together with silica gel in one package.
Warping - distortion of the product shape due to internal stresses caused by uneven heating or cooling.
I hope it will be useful to someone.
Please write in the comments on the merits, namely the interpretation of the missing terms (with images) and comments regarding my interpretations.
Thank you for your attention.
3D Printers and Scanners - Glossary of Terms and Definitions
Lamination Object Printing (LOM) - Laminated Object Manufacturing - a rapid prototyping technology developed by Cubic Technologies (formerly Helisys). It consists in layer-by-layer gluing of sheet material (paper with an adhesive coating, plastic, foil) with the formation of the contour of each layer using laser cutting. Cubic Technologies has already discontinued its plastic-handling machine, but Mcor recently offered a similar machine that works with colored paper.
PC-ABS - Polycarbonate-acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene - a thermoplastic that has the best characteristics of two FDM thermoplastics: the strength and heat resistance of PC and the flexibility of ABS.
Laser Engineered Net Shape Melting (LENS) – Laser Engineered Net Shape is an additive manufacturing method in which a product is created layer by layer by continuously feeding metal powder or metal wire fused into a laser beam.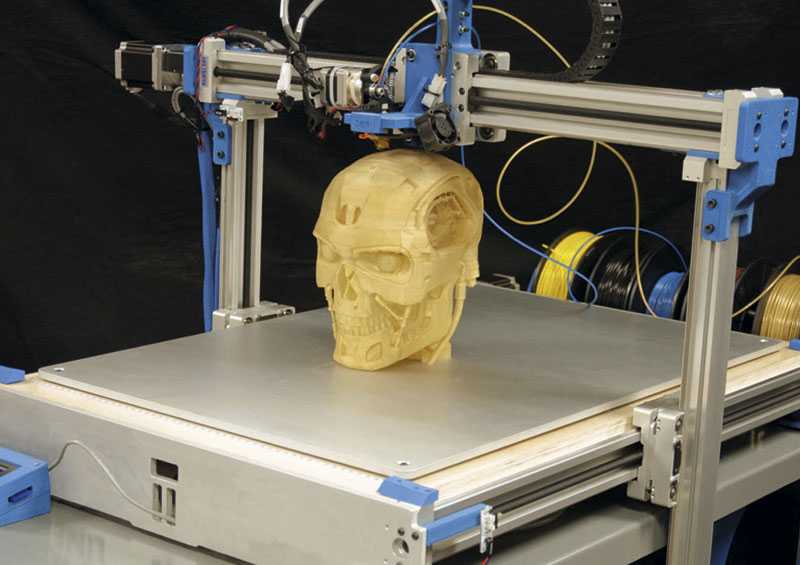 The laser creates a melting pool on the print platform, into which the printer nozzle ejects the powder material. In the melting bath, the material solidifies, forming a layer.
The laser creates a melting pool on the print platform, into which the printer nozzle ejects the powder material. In the melting bath, the material solidifies, forming a layer.
Plastic Inkjet (PJP) - 3D printing technology that uses heat and pressure to extrude a continuous bead of material. Thermoplastics are the only material used in PJP 3D printing.
Assembly surface is the surface on which the printed object is created. Often different types of build surfaces are placed on or attached to the printer bed to improve adhesion.
Support (support structure) is a low density material used in 3D printing to support any raised or undercut sections present in the model. The low density of the material makes it easy to remove it from the finished model after processing.
Backing is a layer or layers of extruded thermoplastic used to stabilize the printed object. The backing helps the object adhere to the print bed.
Polyamide is a tough and flexible thermoplastic that can withstand small impacts and resist some bending pressure. The surface has a sandy, grainy appearance and a slightly porous structure.
Polylactide (PLA) - Polylactic acid, Polylactic acid - biodegradable plastic of plant origin. It is the most popular FDM 3D printing material available.
Polypropylene (PP, polypropylene) is a semi-crystalline material belonging to the family of polyolefins, also known as polyalkenes. Widely used in plastic injection molding industry. Flexible and durable material for FDM printing with excellent physical and mechanical properties. Physiologically inert, which may come into contact with food.
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) is an engineering thermoplastic with good dimensional stability, good impact resistance, excellent machinability and good aesthetic qualities. It combines the hardness of polystyrene with the elasticity of rubber to produce an impact-resistant thermoplastic that is tough and strong without being brittle. In 3D printing, HIPS is an excellent soluble support material. HIPS dissolves in limonene, a readily available solvent derived from the peel of lemons.
In 3D printing, HIPS is an excellent soluble support material. HIPS dissolves in limonene, a readily available solvent derived from the peel of lemons.
Powder Fusion SAF - Selective Absorbction Fusion is the 3D printing technology behind Stratasys' new H Series manufacturing platform. SAF is one category of powder coated 3D printing processes that uses an infrared absorbing liquid to melt polymer powder. This fluid is precisely placed layer by layer to create the shape of the part. When the infrared sensitive liquid is exposed to the printer's fusing lamps, it heats up to a higher temperature than the surrounding material, which "selectively" fuses the powdered particles together but leaves the adjacent material unmelted.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) –Direct Metal Laser Sintering is a metal additive manufacturing technology that uses a fiber optic laser as the energy source. Focusing on a three-dimensional model in STL format, it sinters the powder material at the right points, forming an integral structure.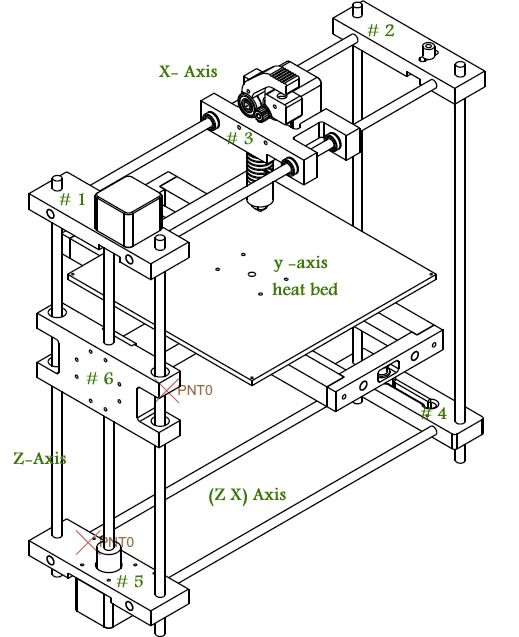





_RlfzhrZzWj.jpg?auto=compress&w=900&h=675&fit=min&fm=jpg)


