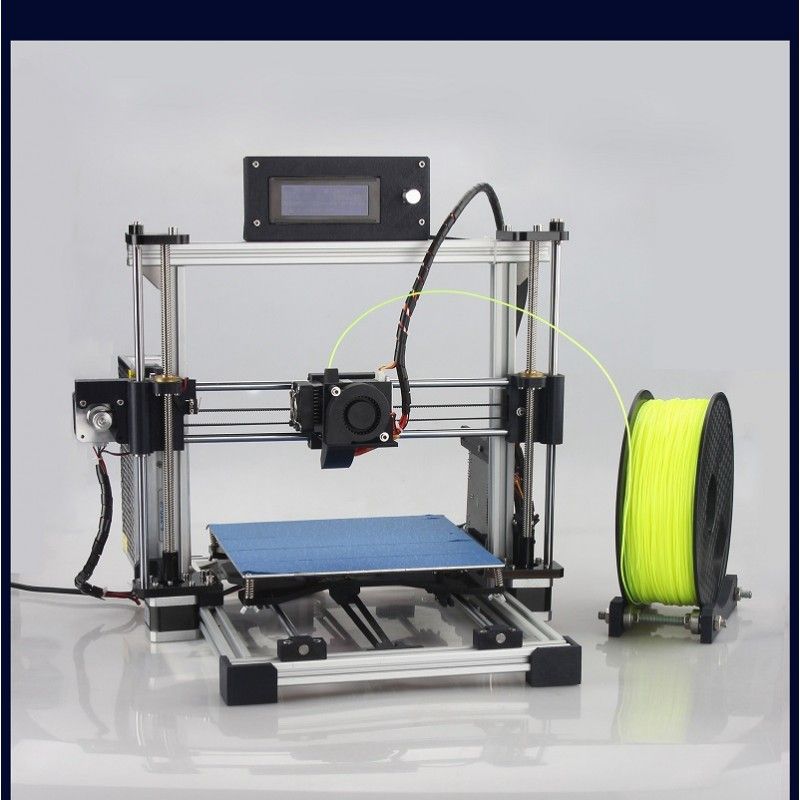
3D printer kit under 100
5+ Best 3d Printer Under 100 USD
3D printing is also called additive printing. It allows for 3D printing by layering materials.
If you get a decent-quality 3D printer, you can make almost anything. Be it toys, cosplay costumes, work prototypes, or even the masks we need for this pandemic.
Modern 3D printers are small, inexpensive, and surprisingly easy to set up and use. As a result, these fun and useful machines are finding their way into schools, design studios, and even into the homes of enthusiasts and amateurs.
Best 3d Printer Under 100 USD
Table of Contents
Some artists even view them as a supplemental income to supplement their income.
The innovations that have emerged from the 3D printer industry over the past decade have been extraordinary: by 2022, the average consumer will be able to purchase a 3D printer for under $100 to $200. You may be surprised.” A legitimate response would be, “That’s a little quirky and absurd.
Yes, you can’t have the most high-end 3D printer on the market. But the ability to experience all the features of 3D printing for under $100 is clearly appealing.
Also Read: Best Printers For Heat Transfers
Can you buy a 3D printer for under $100?
The simple answer to this question is yes, but to some extent it is inevitable. Let’s be clear: a $100 3D printer is not going to print anything large. It won’t have the best technology, and it won’t have the best results when you use it. To be clear, no 3D printer under $100 will give you the same experience as if you bought or used a high-end 3D printer.
Once you understand this and dispel your doubts, you will understand that smaller, less expensive printers are cool and truly exciting technology and that the day will come when they will be twice as efficient for the same price and size.
The future can be seen by these inexpensive models, not to mention the availability to the average consumer. They allow us to see not only what is right in front of us, but also a picture of our imagination. It is a future in which we can have more efficient versions.
They allow us to see not only what is right in front of us, but also a picture of our imagination. It is a future in which we can have more efficient versions.
High-end printers are designed with the best of today’s technology. Conversely, technology products such as these smaller, less expensive models allow us to see the possibilities of a future that makes the most of current technology.
What should we expect from a 3D printer under $100?
First, we must assume that a 3D printer under $100 will have some limitations. You can expect a printer that is no larger than the size of an average jar, made of materials that are not too heavy or too strong. Therefore, it is expected to be somewhat delicate.
What you print will, of course, be the size of the printer, so it will not be very large, to begin with. Most of what you print should fit in the palm of your hand. In addition, printing time is expected to be slower and the finished product less efficient. Unless this is your first experience with 3D printing, in which case you will expect the printer to do something it has never done before.
Also Read: Best Printer For Circut
Best Cheap 3d Printer Under 100 Dollar
The problem with 3D printers under $100 is not that they are less reliable, but mostly about the size of the models and objects that can be printed with them.
Inexpensive 3D printers are certainly a bargain, but they have their own limitations. That is, 3D printers are small compared to other high-end printers and can print relatively small objects.
It may also take a little longer to print moldings than high-end printers. Print quality may be high, but it is not for everyone.
In short, these printers are not intended for industrial use or for making high-quality objects. However, these 3D printers are meant to allow you to marvel at the advances in technology and to experiment with different objects and printed models before investing in a high-quality, premium model.
Best 3d Printer Under $ 100 | Comparison Table 2022
5-Stars Pick | High Quality | Great Prices
Prices and images pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Best 3d Printer Under $ 100 | Products Overview
Check Price
Also Read: Best Sublimation Printer For T-Shirts
Check Price
Check Price
Also Read: 3D Printer Under 150 Dollars of 2022
Error: Unknown Link TypeCheck Price
Also Read: Best Metal 3d Printer
Error: Unknown Link Type Check Price
Also Read: Best Cheap 3d Printer Under $100
Best 3d Printer Under 100 USD | Video Explanation
Best 3d Printer Under 100 USD | Infographic
What are the key factors in choosing a 3D printer under 100 USD | Detailed Guide
Assembly
When choosing a cheap 3D printer, the first thing to check is whether it is pre-assembled, semi-assembled, or unassembled. This will determine your choice of printer, depending on whether you specialize in 3D printers or not. Assembling a semi-assembled or non-assembled printer is not rocket science, but it will definitely test your problem-solving skills. If you want to bypass this process, you can opt for a pre-assembled 3D printer.
It is also important to pay attention to the quality of the printing technology and the number of materials that can be printed. These are just a few of the variable factors that will help you choose a printer that best suits your needs and requirements.
Also Read: Best 3d Printer Under 500 Dollar
Print bed
If you’ve ever used a 3D printer with a heated bed, you’ll never go back. The first few layers of the print are the basis of the formatting and are very important to the final look. The heated bed provides a stable base for the assembly and allows it to adhere to the bed. The larger the print bed, the better. It is possible to create large objects with a large build area. But at the same time, it means you have to pay more.
The first few layers of the print are the basis of the formatting and are very important to the final look. The heated bed provides a stable base for the assembly and allows it to adhere to the bed. The larger the print bed, the better. It is possible to create large objects with a large build area. But at the same time, it means you have to pay more.
Printing speed
Most low-cost printers operate at a speed of 50 mm/second. This means that printing a design takes longer. This doesn’t mean you should look for the fastest printer on the market. Fast printers tend to have thicker layers, resulting in a lack of detail. Therefore, a slow and steady print is better in this regard. Some printers have two extruders to increase speed. In this way, different materials can be used simultaneously.
Also Read: Best 3D Printers Under $300
Materials
3D printers work by heating different types of filament and forming them into different shapes. There are many types of filament materials, but not all printers can handle all of them. The most commonly used filaments are ABS and PLA. If you need a specific material, check to see if your printer can handle it. Some printers are also compatible with clay and Sugru.
The most commonly used filaments are ABS and PLA. If you need a specific material, check to see if your printer can handle it. Some printers are also compatible with clay and Sugru.
Also Read: Best 3D Printer Under $ 400
Other Features
Always use caution when handling hot or electrical equipment. Find out which printers have safety measures for safe use. Choose a printer that automatically cools the nozzle at the end of printing. If you purchased a printer with a heater, look for a feature that automatically turns off the heater when printing is complete.
It’s always a good idea to invest in a printer that has a print playback feature. A print playback option is essential if you don’t want your beautiful prints to be half-finished. It ensures that your printing will not be interrupted at an unexpected time. Printing will pick up where it left off.
When you receive your printer, you may need to set it up. Look for a printer that allows you to easily adjust the belt tension. This will save you time and unnecessary headaches.
This will save you time and unnecessary headaches.
Also Read: Best 3D Printers Under $ 200
Is a less than $100 3D printer worth its money?
Buying a 3D printer for under $100 is fine, but keep in mind that most cheap 3D printers usually use cheap components that are not very durable, so it’s worth lowering your expectations when ordering.
The answer to the question in the title of this article is not so simple. If you are very interested in 3D printers and would like to buy one, but you are on a very tight budget, I would suggest you try one of the 3D printers for under $100 and see what happens.
However, if you have a bit more of a budget, I would recommend that you don’t buy a cheap printer right away just because the price is attractive.
Conversely, if you’re on a budget, we think it’s a good decision to choose a more expensive printer (price range around $250), as the quality of the components and the printer as a whole will often be better.
The final answer is that yes, a $100 3D printer is almost always worth the money, especially for those on a very tight budget, but if you plan to buy one, make sure your expectations are not too high and be prepared to experience disappointment as we did
As we said before, cheap printers usually come with cheap electronic components that may not be very durable, as they may fail after a while.
Buying a 3D printer for less than $100 can be either a good or a bad move. It all depends on the product you choose and what you expect from such an inexpensive printer.
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things. And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
If you're in the market for a beginner or low-cost 3D printer, it's important to know how lower-end models differ. Read on for mini-reviews of the top budget 3D printers we've tested. After that, we go into more detail on understanding the 3D printer specs and tech relevant to beginning buyers. Ready to take the plunge? Read on.
Original Prusa Mini
Best Overall Budget 3D Printer
4.5 Outstanding
Bottom Line:
It requires assembly and calibration care (plus shipping from the Czech Republic), but the Original Prusa Mini is a compact, open-frame 3D printer that consistently produces superb-quality output for a great price.
PROS
- Top-notch object quality
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Useful, professionally printed user guide
- Great support resources
- Versatile, user-friendly software
CONS
- First-layer calibration can be tricky
- Only includes starter packets of filament
- Requires monitoring if young children or pets are around
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | $399. 00 00 | $399.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Original Prusa Mini Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
Best Budget 3D Printer for Schools, Community Centers
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Mini is a consumer-oriented 3D printer that provides a winning combination of low price, ease of setup and use, solid print quality, and smooth, misprint-free operation.
PROS
- Very low price.
- Reasonably priced filament.
- Good print quality.
- No misprints in testing.
- Easy setup and operation.
- Quiet.
- Prints over a USB or Wi-Fi connection.
CONS
- Occasional problems in trying to launch prints.
- Removing printed objects from the print bed is sometimes tricky.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | $199. 95 95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Amazon | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Mini Review
Toybox 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Children
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The Toybox 3D Printer works well as a model designed for children, offering reliable printing from a browser or mobile device and a few thousand toys to print, plus creative options to output drawings or photos. Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
PROS
- Reliable, misprint-free printing
- Easy setup
- One-touch operation
- Well-composed help resources
- Access to more than 2,000 printable toys and projects
- Lets you create your own printable designs
CONS
- Tiny build area
- Not ideal for importing 3D files created elsewhere
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299. 00 00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Toybox Labs | $379.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Toybox 3D Printer Review
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Beginners, Non-Techies
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
3D printing gurus will be intrigued by the Monoprice Mini Delta V2's use of the delta rather than Cartesian coordinate system, but beginners will just enjoy its low price, ease of use, and speedy printing.
PROS
- Sub-$200 price
- Quick, nearly misprint-free printing
- Easy setup and operation
- Sturdy steel-and-aluminum frame
- Supports multiple filament types
CONS
- Tiny build area
- So-so print quality
- Mere one-year warranty
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $179. 99 99 | $179.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer Review
Anycubic i3 Mega S
Best Budget 3D Printer With an Open Design, Big Build Area
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Anycubic i3 Mega S, an inexpensive open-frame 3D printer, produced decent-quality prints in our testing. To get the most out of it, though, may require precise calibration.
PROS
- Modestly priced
- Large build area for an inexpensive printer
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Generally solid print quality
- Uses well-known Cura software
CONS
- Finicky print-platform alignment
- Supported coils of filament are small
- Poorly placed spool holder
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $229.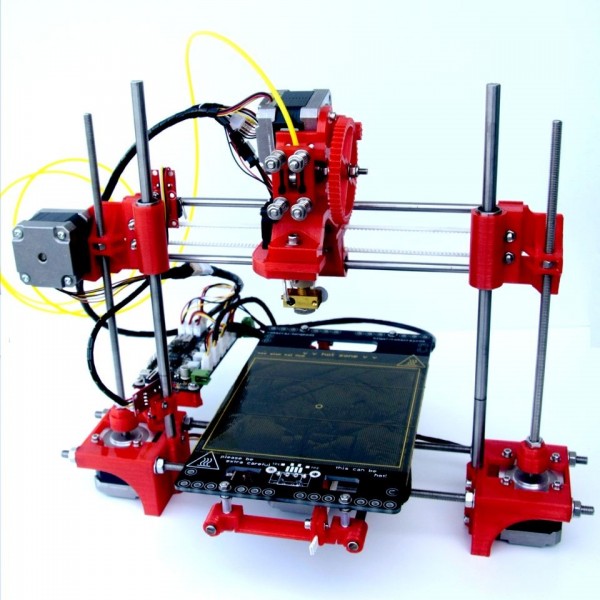 98 98 | $229.98 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic i3 Mega S Review
Anycubic Vyper
Best Budget 3D Printer for the Biggest Build Area Possible
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Anycubic's modestly priced Vyper whips up large 3D prints on its open-frame design, and provides automatic print-bed leveling. Just know that some minor assembly is required—and printed objects may require a bit of cleanup.
PROS
- Relatively large build area
- Automatic bed leveling
- Simple assembly
CONS
- Short (one-year) warranty
- Includes only a small starter filament coil
- Using Cura software with the Vyper requires tweaking a couple of settings
- Test prints showed some "hairy" filament residue
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $429. 99 99 | $429.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $369.00 | $319.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic Vyper Review
Creality Ender-3 V2
Best Budget 3D Printer for Tinkerers and DIY Types
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Hands-on tweaking defines Creality's budget-price Ender-3 V2, an open-frame 3D printer that you build from a kit. It produces generally above-par prints, but its print bed can be tricky to keep leveled.
PROS
- Inexpensive
- Slightly above-average print quality
- Good-size build area for its price
- Supports several filament types
CONS
- Manual print-bed leveling can be tricky
- Setup instructions could be deeper, more legible
- Questionable quality control on some parts
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299. 00 00 | $246.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Creality Ender-3 V2 Review
Flashforge Finder 3D Printer
Best 3D Printer for the Very Tightest Budgets
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Flashforge Finder 3D Printer is moderately priced and offers good print quality, but it proved tricky to get up and running in our tests.
PROS
- Quiet.
- Good print quality.
- Connects via USB 2.0 cable, USB thumb drive, or Wi-Fi.
- Reasonably priced.
CONS
- Some objects pulled off the platform during testing.
- Poor documentation.
- Modest build volume.
- Limited to printing with polylactic acid filament (PLA).
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $729.00 | $729.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Flashforge Finder 3D Printer Review
Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Dabbling in Small Objects
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer is a compact, stylish 3D printer with above-par overall print quality, but, alas, a tiny build area for the money.
PROS
- Small, lightweight for a desktop 3D printer.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Supports PLA, PETG, and wood composite filaments.
- Multiple-color support.
- Wi-Fi camera monitors print jobs.
- Prints from USB drives, SD cards, or mobile devices.
CONS
- High price for its capabilities.
- Small build area.
- Too-brief warranty.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $699.00 | $699.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro
Best Budget 3D Printer With Closed Design, Roomy Build Area
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro is a moderately priced closed-frame 3D printer with a large build volume and overall good performance, but a potentially balky filament-feeding system.
PROS
- Spacious build area
- Works with third-party filaments
- Self-leveling print bed
CONS
- Build plate is not heated
- Limited to PLA- and PETG-based filaments
- Guide tube is prone to detaching
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Best Buy | $449.95 | $449.95 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro Review
Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Cheap Filament
3. 0 Average
0 Average
Bottom Line:
The Monoprice Voxel is an under-$400 3D printer that's easy to set up and use. It exhibits generally good print quality, but it was unable to print two of our test objects.
PROS
- Easy to set up and use.
- Budget price for printer and filament spools.
- Supports PLA, ABS, and several composite filament types.
- Versatile software.
- Prints over Ethernet or Wi-Fi, or from a USB thumb drive.
CONS
- Frequent misprints on certain test objects.
- Slightly balky touch screen.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $449.99 | $329.46 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Walmart | $429.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer Review
Buying Guide: The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
How to Buy a Cheap 3D Printer
The biggest changes to 3D printers over the last few years have come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.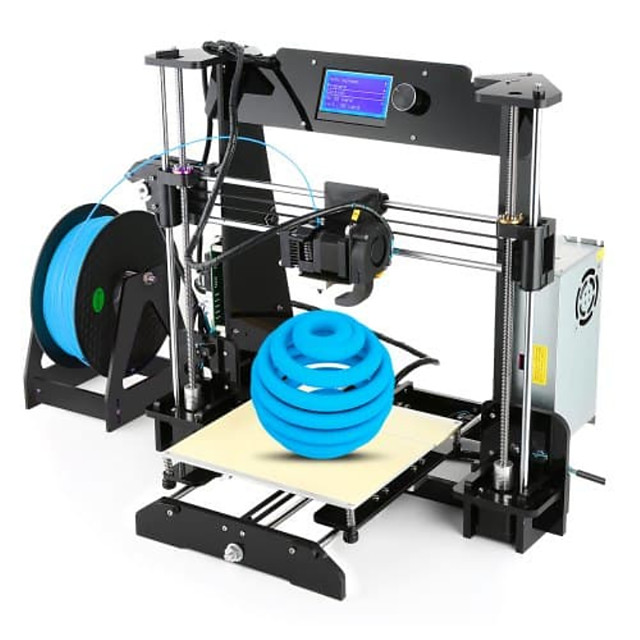
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.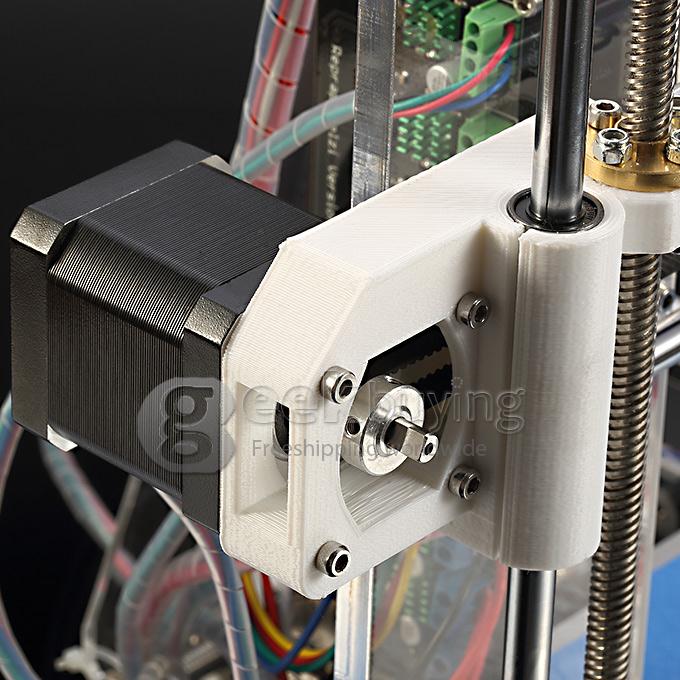
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones.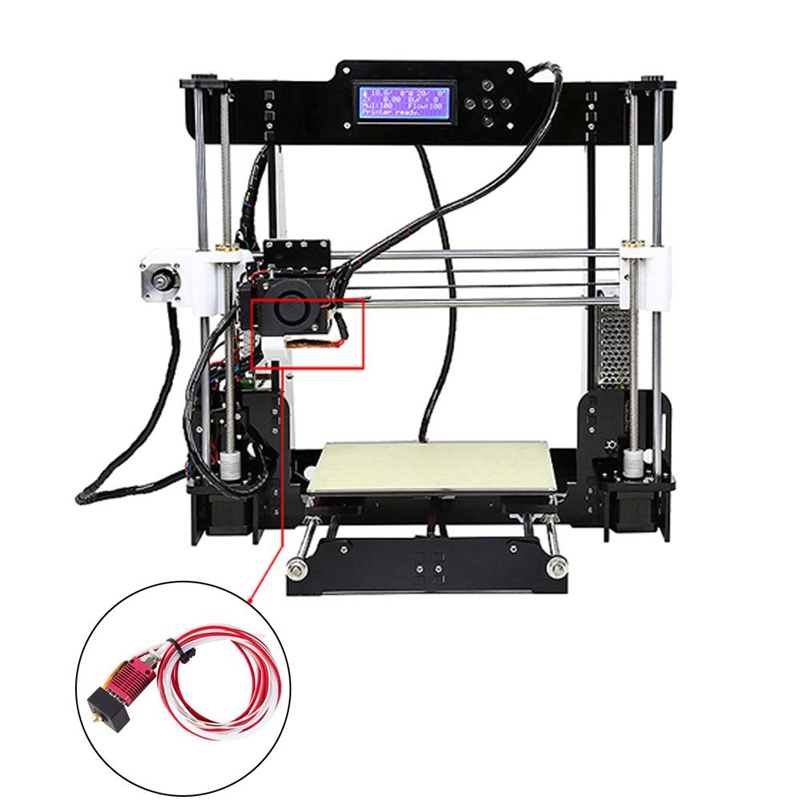 (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
(See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
Recommended by Our Editors
3D Printing: What You Need to Know
3D Printer Filaments Explained
(Credit: Molly Flores)
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
(Credit: 3Doodler)
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, What Is the Best Cheap 3D Printer to Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Below, check out a spec breakdown of the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed, paralleling our picks above. Also, for a look at the broader market, see our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
instruction how to work from scratch for beginners and dummies, how
looks like Three-dimensional printing has become increasingly introduced into our daily lives. Thanks to new technologies, it has become possible to easily print from a small detail to a large building. The range of products is also pleasing - today you can find a lineup that includes both affordable devices and more expensive ones. But how to work with a 3D printer? This is a completely normal question that any beginner will have, it is for this reason that we will try to answer it as simply and accessible as possible.
Thanks to new technologies, it has become possible to easily print from a small detail to a large building. The range of products is also pleasing - today you can find a lineup that includes both affordable devices and more expensive ones. But how to work with a 3D printer? This is a completely normal question that any beginner will have, it is for this reason that we will try to answer it as simply and accessible as possible.
What is a 3D printer and how does it work?
The 3D device consists of the printer itself and a computer that controls all processes. The principle of operation of such a design is to create 3D models by superimposing layers of liquid material. There are a large number of printer models - from large industrial ones to compact ones, but they all have the same principle of operation and component parts:
- Extruder - the print head through which the thread passes. The head heats the thread to a semi-liquid state and evenly supplies the material to the working surface.
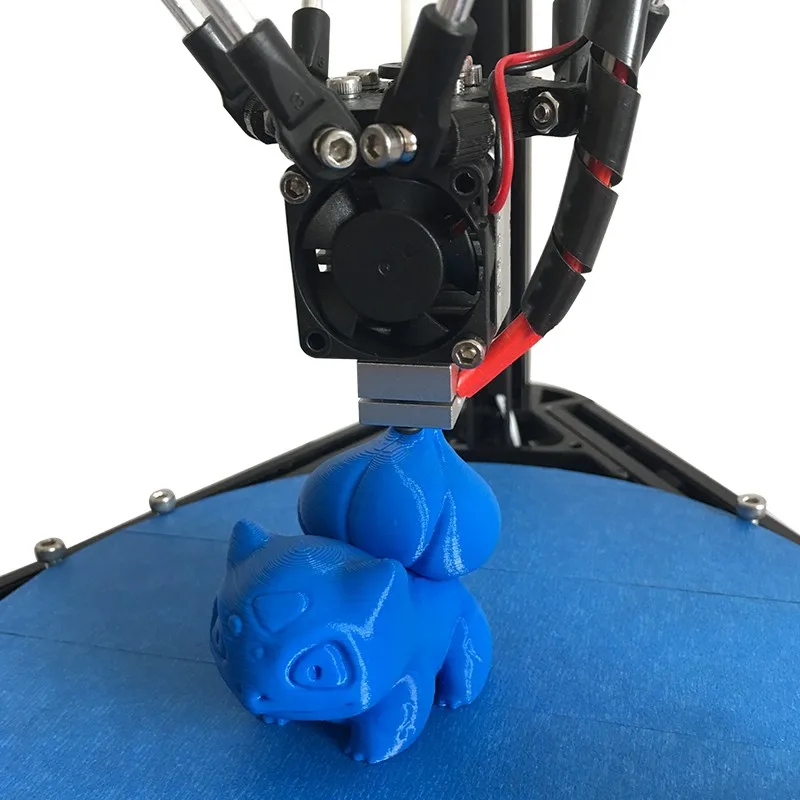
- Work surface - a printing platform on which a 3D model is formed.
- Motors - mechanisms responsible for the accuracy of movement and speed of printing.
- Sensors are electronic devices that limit moving parts to specified coordinates.
- The frame is the structure that connects all parts of the printer.
How a 3D printer works: features
Work with the aim of building a three-dimensional model begins with a sketch, which is created in a special program. After that, the software independently generates a plan for the movement of the print head and a print sequence. The 3D model is reproduced by strongly heating the plastic and distributing it evenly.
3D printers are used in many areas. Let's list some of them:
- Architecture - creation of models of buildings.
- Medicine - dental prosthetics, making models of organs for study.
- Construction - production of houses using 3D printing technology.

- Education - a visual aid for learning 3D printing.
- Automotive - creation of tuning parts, prototype layouts and other products.
This is a small list of industries where 3D printing is actively used. Today, almost every entrepreneur and just an enthusiastic person can afford a printer.
The following printers are distinguished by design features:
- RepRap - self-reproducing printers that can create their own copies.
- DIY-kit - the device comes disassembled with instructions, the assembly of which will take a sufficient amount of time.
- Completed - Models are delivered assembled and ready to use.
- Commercial and Industrial - devices capable of printing metal, concrete, polymers and other materials.
How to use a 3D printer: tips for beginners, where to start
Mastering the technique of 3D printing is not difficult if you follow the recommendations and tips. Especially for those who plan to learn the basics of 3D modeling, an up-to-date list of questions and detailed answers to them has been prepared.
Especially for those who plan to learn the basics of 3D modeling, an up-to-date list of questions and detailed answers to them has been prepared.
Printer Installation
To begin, you will need to carefully unpack the box and remove any stops. The next step is to install the printer on the surface using the building level. This will allow you to place the device as evenly as possible, which will provide better printing.
Note. Some 3D printers come with a level for installation.
Next, you will need to connect the printer to your computer and install the necessary drivers. The software disc comes with the 3D device.
Preparation for work
To get started, you need to calibrate the working surface - without this, printing quality products is impossible. This process is carried out automatically or manually. The attached instructions have detailed information on how to perform manual calibration.
Extruder patency test
The next important step is setting up the extruder.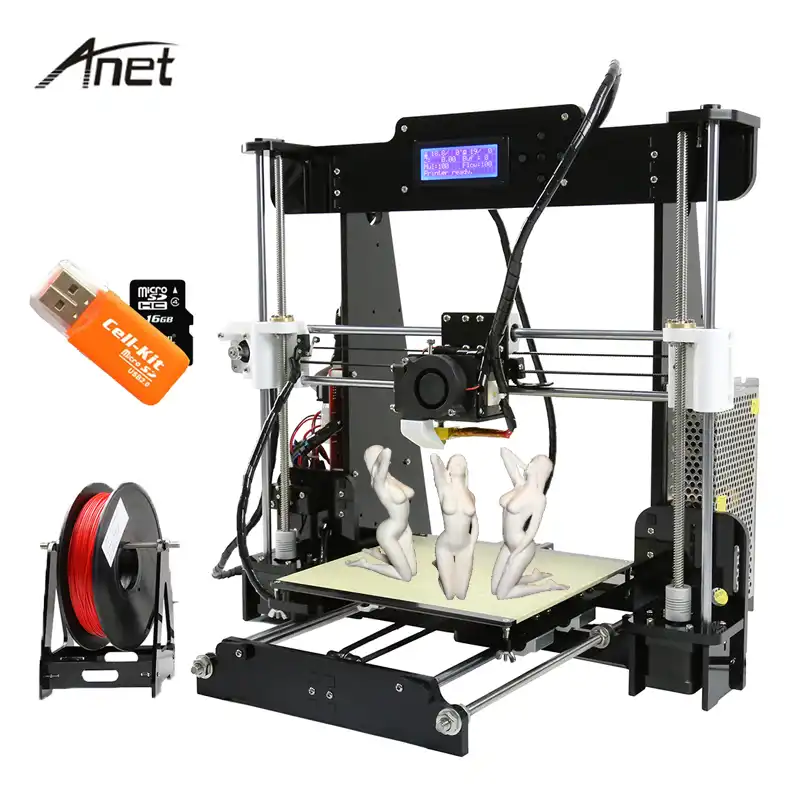 First of all, you will need to check its nozzle. If the printer has already been used, the nozzle should be cleaned of solidified particles that will interfere with the throughput of the material. Refueling the 3D printer The thread is fed into the extruder directly from the spool. But there is one caveat - for this you must first warm it up. To thread the thread, you will have to make a small effort in order to loosen the presser mechanism.
First of all, you will need to check its nozzle. If the printer has already been used, the nozzle should be cleaned of solidified particles that will interfere with the throughput of the material. Refueling the 3D printer The thread is fed into the extruder directly from the spool. But there is one caveat - for this you must first warm it up. To thread the thread, you will have to make a small effort in order to loosen the presser mechanism.
Working with models
Models can be created using a variety of 3D modeling programs. The process of manufacturing three-dimensional parts is creative, requiring careful preparation. The better and more detailed the model is drawn, the better the 3D layout will be at the output.
Start printing
After creating the model in the program and preparing the printer for work, you need to send the file for printing and wait for the result. The print speed varies depending on the printer model and specifications, as well as the media used.
Processing the finished product
3D printed products usually do not please the user with an ideal appearance: the parts have an uneven surface. But this is typical for models of 3D printers on FDM, SLA and DLP devices, which are distinguished by higher print quality. Owners of FDM printers should not despair - a simple processing of products will give products an attractive appearance and make the surface smooth.
Several powerful ways to post-process 3D printed parts:
- Mechanical - carried out by sanding the surface with sandpaper or a special sponge for grinding.
- Chemical - Surface treatment with aggressive solvents such as acetone and dichloroethane.
- Mixed - In this case, the above two processing methods are used.
What are the possible errors and how to avoid them?
Even a novice can master the technology of 3D printing, but, despite this, the production of the first products causes excitement for the user. Simple operation, detailed instructions and recommendations on the Internet will allow everyone to deal with almost any printer model. But there are a few useful life hacks, the knowledge of which will help you avoid typical beginner mistakes:
Simple operation, detailed instructions and recommendations on the Internet will allow everyone to deal with almost any printer model. But there are a few useful life hacks, the knowledge of which will help you avoid typical beginner mistakes:
- Calibrate and test the 3D printer before starting work.
- Be sure to use the correct file extension for quality printing.
- Do not remove the finished product from the printer immediately after it has been processed: this may damage the part and cause defects.
- If errors occur during the 3D printing process, try restarting the device - this usually helps.
- If restarting the printer still does not help, try changing the settings or re-entering the model.
- When assembling the 3D printing devices, follow the enclosed instructions carefully.
- Use only the correct materials for your 3D printer.
- Subscribe to useful 3D printing channels and articles.
Following the above tips will allow you to set up your 3D printer, get it ready for operation and, most importantly, print your first 3D products. Choose a model according to your budget and capabilities, and it will not be difficult to master the basics of 3D modeling and get the first details if you follow the instructions and recommendations.
Choose a model according to your budget and capabilities, and it will not be difficult to master the basics of 3D modeling and get the first details if you follow the instructions and recommendations.
- March 21, 2021
- 7180
Get expert advice
How to build a home 3D printer: recommendations from personal experience
3D printing and assembly of 3D printers is my hobby and passion. Here I will not share detailed diagrams and drawings, there are more than enough of them on specialized resources. The main goal of this material is to tell you where to start, where to dig and how to avoid mistakes in the process of assembling a home 3D printer. Perhaps one of the readers will be inspired by applied engineering achievements.
Why do you need a 3D printer? Use cases for
I first came across the idea of 3D printing back in the 90s when I was watching the Star Trek series. I remember how impressed I was by the moment when the heroes of the cult series printed the things they needed during their journey right on board their starship. They printed anything: from shoes to tools. I thought it would be great someday to have such a thing too. Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few.
I remember how impressed I was by the moment when the heroes of the cult series printed the things they needed during their journey right on board their starship. They printed anything: from shoes to tools. I thought it would be great someday to have such a thing too. Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few.
Years passed, everything changed. Around 2010, the first working models of 3D printers began to appear on sale. Yesterday's fantasy has become a reality. However, the cost of such solutions, to put it mildly, discouraged. But the IT industry would not be itself without an inquisitive community, where there is an active exchange of knowledge and experience and who just let them dig into the brains and giblets of new hardware and software. So, drawings and diagrams of printers began to surface more and more often on the Web. Today, the most informative and voluminous resource on the topic of assembling 3D printers is RepRap - this is a huge knowledge base that contains detailed guides for creating a wide variety of models of these machines.
I assembled the first printer about five years ago. My personal motivation to build my own device is quite prosaic and based on several factors. Firstly, there was an opportunity to try to realize the old dream of having your own device, inspired by a fantasy series. The second factor is that sometimes it was necessary to repair some household items (for example, a baby stroller, car elements, household appliances and other small things), but the necessary parts could not be found. Well, the third aspect of the application is "near-working". On the printer, I make cases for various IoT devices that I assemble at home.
Agree, it is better to place your device based on Raspberry Pi or Arduino in an aesthetically pleasing "body", which is not a shame to put in an apartment or take to the office, than to organize components, for example, in a plastic bowl for food. And yes, you can print parts to build other printers :)
There are a lot of scenarios for using 3D printers. I think everyone can find something of their own.
I think everyone can find something of their own.
A complex part in terms of drawing that I printed on my printer. Yes, it's just a figurine, but it has many small elements
Ready solution vs custom assembly
When a technology has been tested, its value in the market decreases markedly. The same thing happened in the world of 3D printers. If earlier a ready-made solution cost simply sky-high money, then today acquiring such a machine is more humane for the wallet, but nevertheless not the most affordable for an enthusiast. There are a number of solutions already assembled and ready for home use on the market, their price range ranges from $500-700 (not the best options) to infinity (adequate solutions start from a price tag of about $1000). Yes, there are options for $150, but we, for understandable, I hope, reasons, will not dwell on them.
In short, there are three cases to consider a finished assembly:
- when you plan to print not much and rarely;
- when print accuracy is critical;
- you need to print molds for mass production of parts.
There are several obvious advantages to self-assembly. The first and most important is cost. Buying all the necessary components will cost you a maximum of a couple of hundred dollars. In return, you will receive a complete 3D printing solution with the quality of manufactured products acceptable for domestic needs. The second advantage is that by assembling the printer yourself, you will understand the principles of its design and operation. Believe me, this knowledge will be useful to you during the operation of even an expensive ready-made solution - any 3D printer needs to be serviced regularly, and it can be difficult to do this without understanding the basics.
The main disadvantage of assembly is the need for a large amount of time. I spent about 150 hours on my first build.
I spent about 150 hours on my first build.
What you need to assemble the printer yourself
The most important thing here is the presence of desire. As for any special skills, then, by and large, in order to assemble your first printer, the ability to solder or write code is not critical. Of course, understanding the basics of radio electronics and basic skills in the field of mechanics (that is, "straight hands") will greatly simplify the task and reduce the amount of time that needs to be spent on assembly.
Also, to start we need a mandatory set of parts:
- Extruder is the element that is directly responsible for printing, the print head. There are many options on the market, but for a budget build, I recommend the MK8. Of the minuses: it will not be possible to print with plastics that require high temperatures, there is noticeable overheating during intensive work, which can damage the element. If the budget allows, then you can look at MK10 - all the minuses are taken into account there.

- Processor board. Well known to many Arduino Mega. I didn't notice any downsides to this solution, but you can spend a couple of dollars more and get something more powerful, with a reserve for the future.
- Control board. I'm using RAMPS 1.4 which works great with the Arduino Mega. A more expensive but more reliable board is Shield, which already combines a processor board and a control board. In modern realities, I recommend paying attention to it. In addition to it, you need to purchase at least 5 microstep stepper motor controllers, for example - A4988. And it's better to have a couple of these in stock for replacement.
- Heated table. This is the part where the printed element will be located. Heating is necessary due to the fact that most plastics will not adhere to a cold surface. For example, for printing with PLA plastic, the required surface temperature of the table is 60-80°C, for ABS - 110-130°C, and for polycarbonate it will be even higher
There are also two options for choosing a table - cheaper and more expensive. Cheaper options are essentially printed circuit boards with preheated wiring. To operate on this type of table, you will need to put borosilicate glass, which will scratch and crack during operation. Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table.
Cheaper options are essentially printed circuit boards with preheated wiring. To operate on this type of table, you will need to put borosilicate glass, which will scratch and crack during operation. Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table. - Stepper motors. Most models, including the i2 and i3, use NEMA 17 size motors, two for the Z axis and one each for the X and Y axes. Finished extruders usually come with their own stepper motor. It is better to take powerful motors with a current in the motor winding of 1A or more, so that there is enough power to lift the extruder and print without skipping steps at high speed.
- Basic set of plastic fasteners.
- Belt and gears to drive it.
Examples of elements appearance: 1) MK8 extruder; 2) Arduino processor board; 3) RAMPS control board; 4) motor controllers; 5) aluminum heated table; 6) NEMA 17 stepper motor; 7) a set of plastic fasteners; 8) drive gears; 9) drive belt
This is a list of items to be purchased. Hardcore users can assemble some of them themselves, but for beginners, I strongly recommend purchasing ready-made solutions.
Hardcore users can assemble some of them themselves, but for beginners, I strongly recommend purchasing ready-made solutions.
Yes, you will also need various small things (studs, bearings, nuts, bolts, washers ...) to assemble the case. In practice, it turned out that using a standard m8 stud leads to low printing accuracy on the Z axis. I would recommend immediately replacing it with a trapezoid of the same size.
M8 trapezoid stud for the Z axis, the use of which will save you a lot of time and nerves. Available for order on all major online marketplaces
You also need to purchase customized plastic parts for the X axis, such as these from the MendelMax retrofit kit.
Most parts available at your local hardware store. On RepRap you can find a complete list of necessary little things with all sizes and patterns. The kit you need will depend on the choice of platform (we'll talk about platforms later).
What's the price
Before delving into some aspects of the assembly, let's figure out how much such entertainment will cost for your wallet.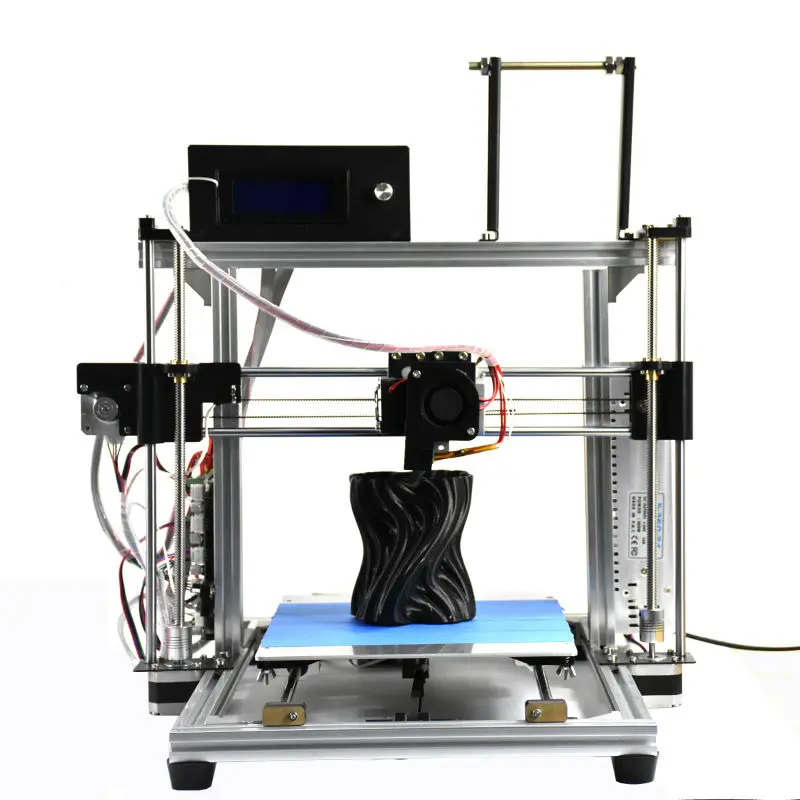 Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price.
Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price.
Platform selection
The community has already developed a number of different platforms for assembling printers - the most optimal case designs and the location of the main elements, so you do not have to reinvent the wheel.
i2 and i3 are key platforms for self-assembly printer enclosures. There are also many modifications of them with various improvements, but for beginners, these two classic platforms should be considered, since they do not require special skills and fine-tuning.
Actually, illustration of platforms: 1) i2 platform; 2) i3 platform
On the plus side of i2: it has a more reliable and stable design, although it is a little more difficult to assemble; more opportunities for further customization.
The i3 variant requires more special plastic parts to be purchased separately and has a slow print speed. However, it is easier to assemble and maintain, and has a more aesthetically pleasing appearance.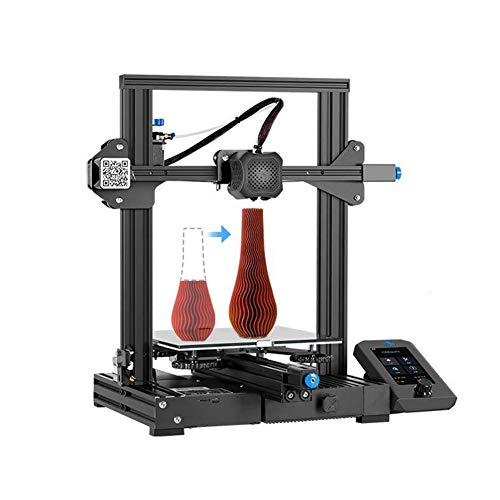 You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy.
You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy.
Personally, I started my experiments in assembling printers from the i2 platform. She will be discussed further.
Assembly steps, challenges and improvements
In this block, I will only touch on the key assembly steps using the i2 platform as an example. Full step by step instructions can be found here.
The general scheme of all the main components looks something like this. There is nothing particularly complicated here:
I also recommend adding a display to your design. Yes, you can easily do without this element when performing operations on a PC, but it will be much more convenient to work with the printer this way.
Understanding how all components will be connected, let's move on to the mechanical part, where we have two main elements - a frame and a coordinate machine.
Assembling the frame
Detailed frame assembly instructions are available on RepRap.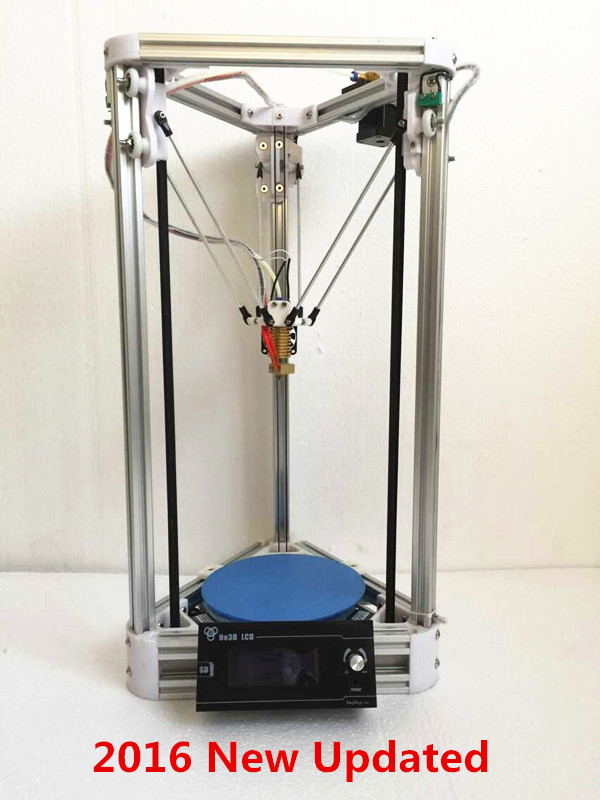 Of the important nuances - you will need a set of plastic parts (I already talked about this above, but I'd better repeat it), which you can either purchase separately or ask your comrades who already have a 3D printer to print.
Of the important nuances - you will need a set of plastic parts (I already talked about this above, but I'd better repeat it), which you can either purchase separately or ask your comrades who already have a 3D printer to print.
The frame of the i2 is quite stable thanks to its trapezoid shape.
This is how the frame looks like with parts already partially installed. For greater rigidity, I reinforced the structure with plywood sheets
Coordinate machine
An extruder is attached to this part. The stepper motors shown in the diagram above are responsible for its movement. After installation, calibration is required along all major axes.
Important - you will need to purchase (or make your own) a carriage for moving the extruder and a mount for the drive belt. Drive belt I recommend GT2.
The carriage printed by the printer from the previous picture after it has been assembled. The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
Calibration and adjustment
So, we completed the assembly process (as I said, it took me 150 hours) - the frame was assembled, the machine was installed. Now another important step is the calibration of this very machine and extruder. Here, too, there are small subtleties.
Setting up the machine
I recommend calibrating the machine with an electronic caliper. Do not be stingy with its purchase - you will save a lot of time and nerves in the process.
The screenshot below shows the correct constants for the Marlin firmware, which must be selected in order to set the correct number of steps per unit of measure. We calculate the coefficient, multiply it, substitute it into the firmware, and then upload it to the board.
Marlin 9 firmware constants0179
For high-quality calibration, I recommend relying on larger numbers in measurements - take not 1-1. 5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
Calibrating the extruder
When the frame is assembled, the machine is calibrated, we start setting up the extruder. Here, too, everything is not so simple. The main task of this operation is to correctly adjust the supply of plastic.
If underfeeding, the printed test item will have noticeable gaps, like test die 1. Conversely, the result will look bloated if plastic is overfed (dice 2)
Getting Started Printing
It remains for us to run some CAD or download ready-made .stl, which describe the structure of the printed material. Next, this structure needs to be converted into a set of commands understandable to our printer. For this I use the Slicer program. It also needs to be set up correctly - specify the temperature, the size of the extruder nozzle. After that, the data can be sent to the printer.
Slicer interface
As a raw material for printing, I recommend starting with regular ABS plastic - it is quite strong, products made from it are durable, and it does not require high temperatures to work with. For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
Some important little things. Before printing, calibrate the machine along the Z axis. The extruder nozzle should be approximately half a millimeter from the table and ride along it without distortion. For this calibration, a regular sheet of A4 paper inserted between the nozzle and the surface of the heated table is best suited. If the sheet can be moved with little effort, the calibration is correct.
Another thing to keep in mind is the surface treatment of the heated table. Usually, before printing, the surface of the table is covered with something that hot plastic sticks to well. For ABS plastic, this can be, for example, Kapton tape. The disadvantage of adhesive tape is the need to re-glue it after several printing cycles. In addition, you will have to literally tear off the adhering part from it. All this, believe me, takes a lot of time. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it.
All this, believe me, takes a lot of time. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it.
An alternative option that I use instead of scotch tape is to apply several layers of ordinary light beer, followed by heating the table to 80-100 ° C until the surface is completely dry and re-applying 7-12 layers. It is necessary to apply the liquid with a cloth moistened with a drink. Among the advantages of this solution: ABS plastic separates from the table on its own when it cools down to about 50 ° C and is removed without effort, the table does not have to be peeled off, and one bottle of beer will last you for several months (if you use the drink only for technical purposes :)).
After we have collected and configured everything, we can start printing. If you have an LCD screen, then the file can be transferred for printing using a regular SD card.
The first results may have bumps and other artifacts - do not worry, this is a normal process of "grinding" the printer elements, which will end after a few print cycles.
Tips to make life easier (and sometimes save money)
In addition to the small recommendations given in the text above, in this section I will also give a short list of tips that will greatly simplify the operation of a 3D printer and the life of its owner.
- Do not experiment with nozzles. If you plan to immediately print from materials that require high temperatures, then it is better to immediately take the MK10 extruder. On MK8, you can "hang" special nozzles that support high-temperature conditions. But such modifications often cause difficulties and require special experience. It is better to avoid this fuss on the shore by simply installing the right extruder for you.
- Add starter relay for heated table. Improving the power supply system of this important part for printing with a starter relay will help solve the known problem of RAMP 1.4 - overheating of the transistors that control the power of the table, which can lead to failure of the board.
 I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s.
I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s. - Select the correct filament diameter for printing. I recommend using 1.75mm plastic for MK8 and MK10. If we take plastic, for example, 3 mm, then the extruder simply does not have enough strength to push it at an acceptable speed - everything will be printed much longer, and the quality will drop. ABS plastic is ideal for MK8, MK10 will be able to produce products from polycarbonate.
- Use only new and precise X and Y guides. Print quality will be affected. It is difficult to count on good quality with bent or deformed guides along the axes.
- Take care of cooling. During my experiments with various extruders, the MK10 showed the best results - it prints quite accurately and quickly. The MK10 can also print plastics that require a higher print temperature than ABS, such as polycarbonate. Although it is not as prone to overheating as its younger brother MK8, I still recommend taking care of its cooling by adding a cooler to your design.
 It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling.
It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling. - Consider heat retention. Yes, on the one hand, we are struggling with overheating of the elements. On the other hand, a uniform temperature around the printer will contribute to high-quality printing (the plastic will be more pliable). To achieve a uniform temperature, you can put our printer, for example, in a cardboard box. The main thing is to connect and configure the coolers before that, as described above.
- Consider insulating your desk. Heated table heats up to high temperatures. And if part of this heat leaves properly, heating the printed part, then the second part (from below) just goes down. To concentrate the heat from the table onto the part, you can perform an operation to insulate it.
 To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips.
To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips.
Pins
I am sure that during the assembly process you will encounter a number of difficulties specific to your project. Neither this text nor even the most detailed guides will insure against this.
As I wrote in the introductory part, the above does not claim the status of a detailed assembly manual. It is almost impossible to describe all the stages and their subtleties within the framework of one such text. First of all, this is an overview material that will help you prepare for the assembly process (both mentally and financially), understand whether you personally need to bother with self-assembly - or give up on everything and buy a ready-made solution.
For me, assembling printers has become an exciting hobby that helps me solve some issues in home and work affairs, take my mind off programming and do something interesting with my own hands. For my children - entertainment and the opportunity to get unusual and unique toys.