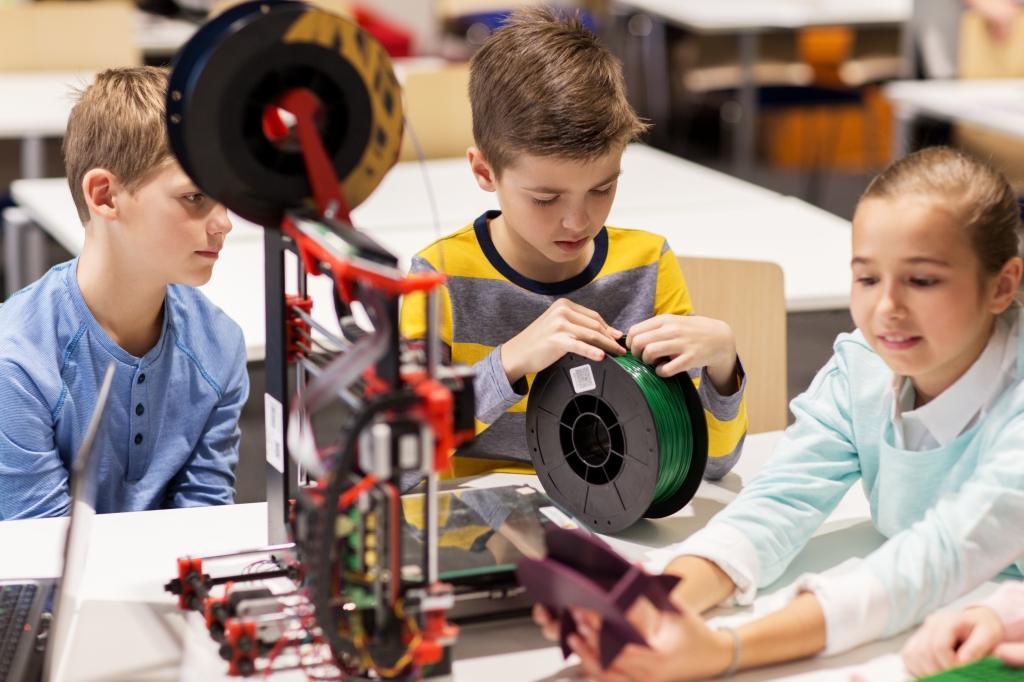
3D printer in the classroom
How to Get Started With 3D Printing for the Classroom
3D printing has taken off in the past few years. Advancements in the 3D printing industry have made a technology that was once prohibitive far more intuitive for teachers and students. 3D printing has transformed a wide range of industries: engineering, manufacturing, dental, healthcare, entertainment, jewelry, audiology, and education. And now, it is time for schools to embrace 3D printing so that the students of today can become the innovators of tomorrow. In addition to helping with job readiness, 3D printing is an incredibly useful learning tool that encourages creativity.
How can educators teaching all levels get started with 3D printing in the classroom? In this blog post, we cover the following:
Classrooms need to modernize. This means equipping students with basic resources like modern laptops and audiovisual tools like projectors and smartboards. Instead of banning technology in the classroom, educators should enable students to learn with the help of technology. 3D printers may not sound basic, but they have proven themselves to be foundational tools. 3D printers have recently generated plenty of interest for education purposes. According to a Department for Education report, “3D printers have significant potential as a teaching resource and can have a positive impact on pupil engagement and learning.”
3D printing makes learning active, giving students hand-on experience and bringing their CAD projects to life. In addition to reading books and taking notes on lectures, students can apply academic concepts to 3D printing, helping them absorb the information better. This is exceptionally helpful for tactile learners. For example, in human anatomy classes, students can print bones and organs to better understand the human body. By 3D printing, students also gain analytical skills--they interpret the size, shape, movement, and relationships between objects.
Furthermore, 3D printing supports real-world understanding. Through learning by doing, students are able to see the impact their 3D printed parts can have in the real world. Educators play an important role in helping students understand the impact 3D printing has in daily life.
Educators play an important role in helping students understand the impact 3D printing has in daily life.
3D printing in the classroom has applications that extend beyond STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) subjects. 3D printers are creative tools that expand imaginations. There is practically no limit on what students can print. Students without CAD skills can create 3D objects in VR then print them.
How can educators incorporate 3D printing in the classroom? They will need to learn 3D printing themselves. While there is a learning curve, Formlabs’ resources can help educators get started. Our Learning Pathways provide all the information you need, customized to your industry. You’ll acquire basic knowledge of scanning and design, print preparation, printing, and post-processing. Specific education topics include:
-
Unboxing, printing, and post-processing.
-
Making 3D models printable.
-
Implementation advice and curriculum examples.

The next step is to design a curriculum that incorporates 3D printing. 3D printing is suitable for any level of education: K-12, community colleges and technical schools, and higher education.
K-12 Schools
Some schools have already successfully integrated 3D printing in their curriculum. For example, University of Florida started a program for middle and high school students called iDigFossils that uses 3D printed fossils. iDigFossils brings the museum to middle and high school classrooms. Teachers designed activities that enabled students to explore fossils through the lens of evolution, biology, and climate change. Researchers at the program are also working on computer applications that can let students examine 3D images in layers. Educators at K-12 schools should evaluate how 3D printing can best fit into the subjects they’re teaching. At its core, 3D printing is about designing and making. Educators can apply 3D printing to a wide range of subjects and activities: recreate historical buildings, create human skeletons and internal organs, build math experiments, and make jewelry, to name a few examples.
Community colleges and technical schools
Community colleges and technical schools also leverage 3D printing. At Morrison Tech, students learn by doing, and 3D printing is a critical part of that ethos. Nearly all Morrison Tech’s engineering courses include 3D printing and the projects students work on address real-world problems. Students learn 3D printing for product development and prototyping--they’ve created functional parts like gears that are cured with the Formlabs Form Cure. Technical schools like Morrison Tech incorporate 3D printing to help students become acclimated to jobs that will heavily use 3D printing.
Higher education
3D printing has become increasingly common in higher education. According to a Deloitte study, here are the top 3D printing needs for higher education:
-
A multidisciplinary understanding of key Additive Manufacturing (AM) (related knowledge areas—material science, design, engineering, etc.
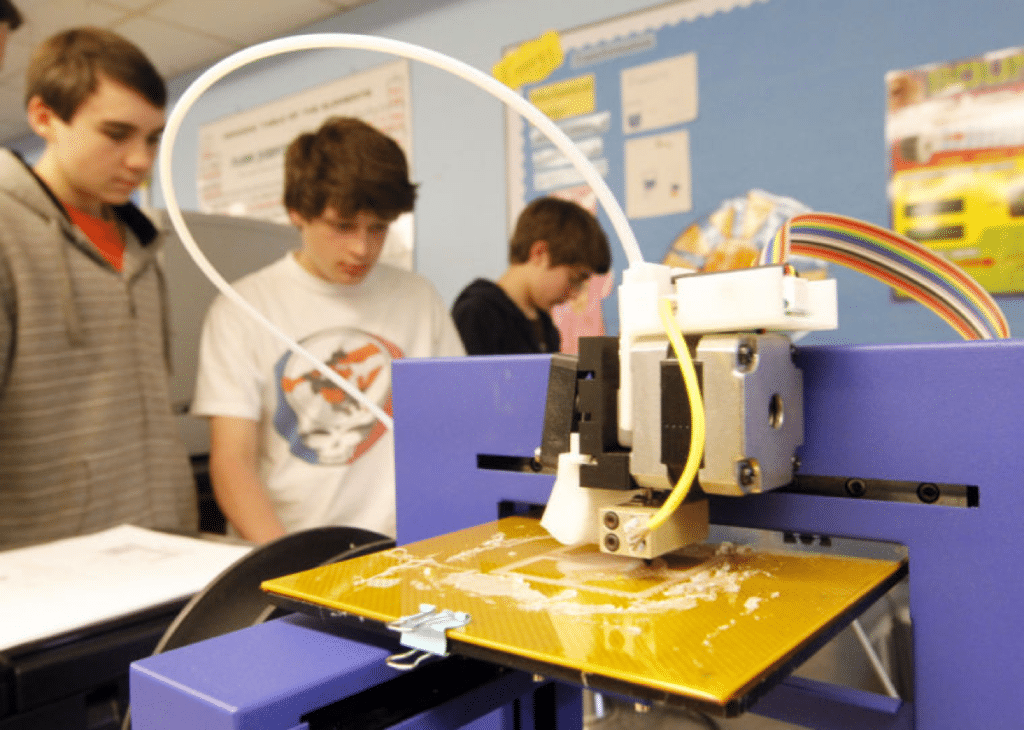

-
Better design knowledge, specifically design-for-AM skills.
-
A broader, more creative, and innovative mindset.
-
A better understanding of AM’s ties to existing manufacturing processes, not just AM.
-
A commercial mindset to understand the AM business case.
Colleges and universities seeking to incorporate 3D printing should assess their programs and how 3D printing can fit in. The key to implementing successful 3D printing programs is through a multidisciplinary approach that emphasizes experiential learning.
At UMass Lowell, that meant upgrading its sculpting and 3D design courses for the 21st century. Professor Yuko Oda uses 3D printing to modernize 3D Design, Sculpture, and 3D Modeling and Animation courses at the college with great results.
Educators of all subjects can seamlessly weave 3D printing into their lesson plans. With programs like Pinshape and Thingiverse, students can access a wide range of ready-to-print files.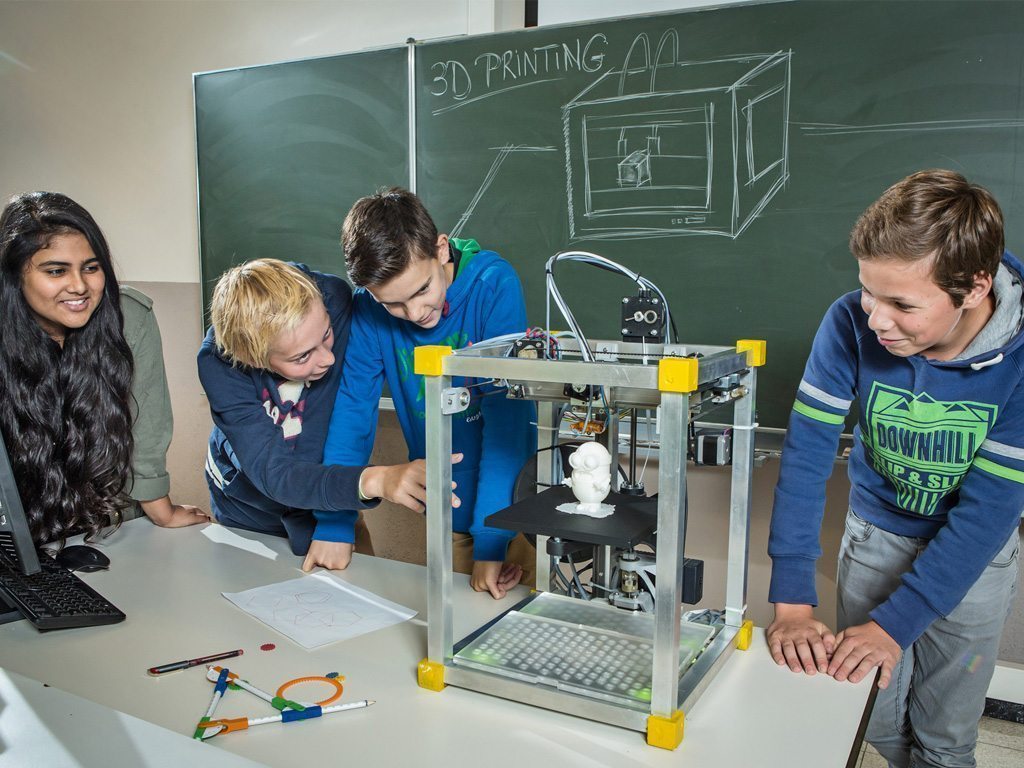 Easy-to-use CAD programs like Tinkercad enable students to design their own prints. With these free sources available, educators can elevate their lesson plans with 3D printing.
Easy-to-use CAD programs like Tinkercad enable students to design their own prints. With these free sources available, educators can elevate their lesson plans with 3D printing.
Science
An example of how educators can incorporate 3D printing into a science lesson plan is with earth science. Students can print layers of the earth, piece them together, and paint them. By printing the layers themselves, they can better familiarize themselves with the structure of the earth. Students can also print 3D molecular models for chemistry.
Engineering
In engineering, students can build their own structures by 3D printing separate parts. For example, they can make a functional 3D printed clock.
Math
3D printing is very well suited for geometry lessons. Students can 3D print all kinds of shapes, from simple to complex. They can also familiarize themselves with patterns. The Tessellation Escher Project encourages students to print tessellation shapes, then piece them together.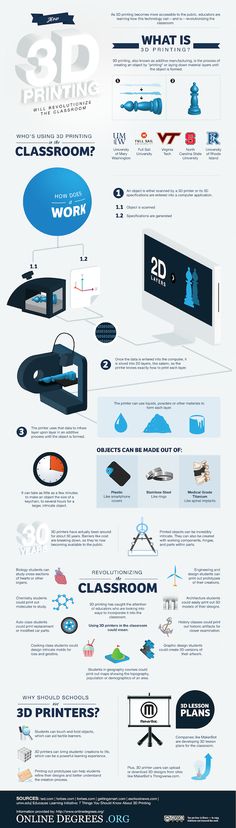 Students can also create scale models that help them understand ratios and proportions.
Students can also create scale models that help them understand ratios and proportions.
Architecture
3D printing can help architecture students design and build prototypes of buildings. By 3D printing different components of a building, students can better understand how their design can be brought to life.
Art
The possibilities of 3D printing in art are endless. Students can make 3D snowflakes, musical instruments, and more.
History
Students can recreate historical landmarks and buildings by 3D printing them. For example, students can print Aztec and Mayan structures.
3D printing may seem like a luxury addition at first glance, but it has already become a key technology multidisciplinary education tool. An incredibly versatile technology, 3D printing has many applications in education, spanning education levels and subjects. In order for the students of today to become the innovators of tomorrow, educators should get started with 3D printing in the classroom.
Learn more about 3D printing for the classroom with our whitepaper FDM vs. SLA: Compare the Two Most Popular Types of 3D Printers For Education
How to use 3D printers in the classroom
3D printers are receiving a lot of interest in the educational space, and are frequently cited as a new catalyst for learning. Certainly, this revolutionary technology is helping teachers to reach a level of student engagement that is almost impossible to recreate from a textbook.
But its not just about engagement. In fact, a report from the Department for Education (DfE) found that 3D printing in schools offers a number of compelling benefits for teachers and students.
3D printers have significant potential as a teaching resource and can have a positive impact on pupil engagement and learning
3D printers in schools: uses in the curriculum, DfE
The benefits of using 3D printers in the classroom
3D printers are helping to inspire a new generation of STEM learners by combining problem-solving skills with creativity and innovation. But this nifty tech also has the potential to support pedagogy across all disciplines.
But this nifty tech also has the potential to support pedagogy across all disciplines.
Make learning active
Pupils learn best through interaction and application. By doing rather than by reading a book or listening to a lecture. As such, 3D printers are an excellent way to deploy experiential learning and give pupils more hands-on experiences. With 3D printers, teachers can create activities that take academic concepts from the theoretical to the practical. For example, in biology lessons, students could create an anatomical heart. Such active learning also ensures that pupils retain information with greater ease.
Encourage real-world understanding
3D printers help to put learning into context, so students see the value of lessons in the form of real-world problem-solving. For example, one trainee teacher has developed an amazing 3D bee prototype which he hopes will allow the bee population to increase.
Augment the educational process
Students can easily spot where they have made mistakes, discuss these errors with the class, learn from these mistakes, and rectify them.
Fire imaginations
3D printers and design software inspires creativity and ignites young imaginations. In fact, the possibilities of what students can create through 3D printing are infinite; and it’s remarkable how creative children can be when empowered with the ability to turn their 3D designs into real physical objects!
Instil spatial intelligence
Spatial intelligence involves analysing and interpreting the size, shape, movement and relationships between objects; it’s the ability to draw correct conclusions from observing three-dimensional environments. According to studies, the use of 3D printers in lessons enhances a student’s spatial intelligence, with such intelligence an important predictor of achievement in STEM subjects.
Boost digital engagement
3D printing is a hands-on, fun activity. So, by incorporating this technology into lessons, teachers can uncover fresh ways to keep pupils engaged; adding extra value and relevance to lessons in a way that is both mentally stimulating and enjoyable. What’s more, 3D printers are applicable across education levels; making them a natural starting point for early years digital engagement.
What’s more, 3D printers are applicable across education levels; making them a natural starting point for early years digital engagement.
Help students prepare for the future
The ability to innovate in our digital world is becoming increasingly important, so encouraging pupils to explore tools that help them to think differently will prepare them for life after education. That said, it’s not about technology for technology’s sake. Global revenue for 3D-printing spending is projected to reach $35.4 billion in 2020. In response, schools should use 3D printers as a way to expose students to this soon to be widely used-tech, and get them future ready.
Boost computational thinking
Computational thinking and skills such as decomposition, pattern recognition, logical thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving are becoming increasingly important. 3D printers (and other tools such as micro:bits and Raspberry Pi) are helping to make computational thinking a key part of the modern curriculum.
Create new learning materials
If your school doesn’t have access to specific learning materials, a 3D printer could help you to make them instantly!
The opportunity to realise a concept or idea quickly into a 3D product is an incredibly powerful teaching tool
David Jermy, head of DT at Settlebeck High School, Sedbergh, Cumbria
How teachers are already using 3D printers in the classroom
Integrating a 3D printer into the classroom is affordable, despite increasingly squeezed academic budgets. In fact, 3D printers often come in cheaper than laptops and computers. Nevertheless, most teachers are still reluctant to use one in their lessons.
Despite the reported benefits, while over 70% of schools have access to a 3D printer, only 9.04% of teachers use this technology frequently.
State of Technology in Education Report: 2016
Here are just some examples of how you can use 3D printers in your classroom:
- Create interactive maps.
 3D printers can be used to design and build interactive maps. These can be of real-life modern cities, maps setting out what pupils think the city of the future will look like, historical locations (e.g. a Roman settlement), or even fictional places from books students are reading.
3D printers can be used to design and build interactive maps. These can be of real-life modern cities, maps setting out what pupils think the city of the future will look like, historical locations (e.g. a Roman settlement), or even fictional places from books students are reading. - Create decorations. Younger children can use 3D printing to create their own seasonal decorations.
- Recreate real-life structures. Create models of world-famous buildings such as the Empire State Building or the Taj Mahal. You can also recreate historical ruins such as the Colosseum in all its former glory.
- Get musical. Ask a class to design and create a new musical instrument.
- Consider the tools for a job. For example, you could ask pupils to print out what they think an astronaut needs in space.
- Bring back the dinosaurs. Use a 3D printer to create a sculpture of a T-Rex or other dinosaur.

- Create a human skeleton and/or internal organs. Create anatomical models to teach pupils about the human body.
- Build maths experiments. Design larger experiences to facilitate mathematical thinking.Here are some real-life examples of how 3D printing in being used in maths education
How are you using 3D printers in your classroom? Tell us on Twitter!
Rather than just being a cool piece of tech, 3D printing has significant educational benefits and practical applications for the next generation of engineers, architects, designers, and creatives. However, digital leaders in education must do more to ensure teachers are comfortable enough with the technology to use it successfully in the classroom.
we print ornaments, birdhouses and schools
March 17, 2021
Education in the world: figures and trends
3D printing has become a breakthrough in many manufacturing processes: thanks to it, it is possible to visualize various objects, as well as speed up production. This technology has not bypassed the field of education: now students can take part in protecting the environment by creating solar-powered devices, see and touch something very rare, and even study at a school printed on a 3D printer.
This technology has not bypassed the field of education: now students can take part in protecting the environment by creating solar-powered devices, see and touch something very rare, and even study at a school printed on a 3D printer.
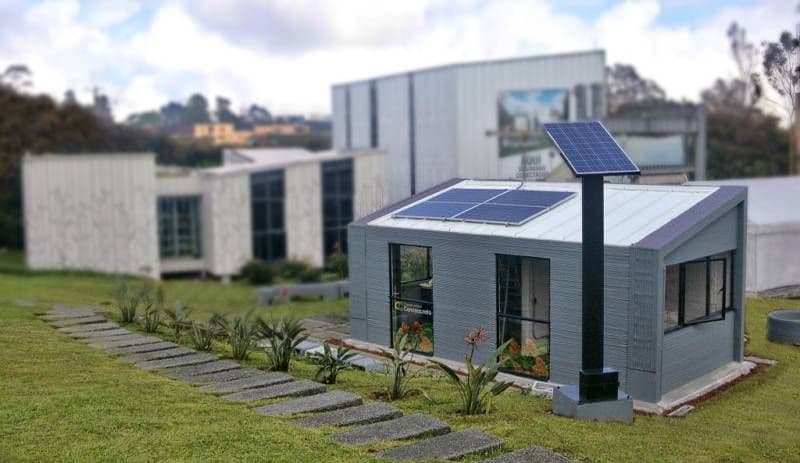
A solid building with solar panels and rainwater tanks that can be built in three weeks with a 3D printer sounds like a fantasy story. However, this is not an ecological house of the future, but a school project, the construction of which will begin in a few months.
In the summer of 2021, on the island of Madagascar, the non-profit organization Thinking Huts and its partners intend to begin construction of the world's first school created with the 3D printer. The main goal of the project is to solve the problem of the lack of educational infrastructure, which leads to the inaccessibility of education in many countries that lack qualified labor and resources for construction. According to Thinking Huts, the construction of such schools will increase access to education, which is especially important after the COVID-19 pandemic, when children and adolescents will return to school en masse. Externally, the building resembles a beehive, consisting of blocks, which allows you to expand the structure if necessary. “These blocks are valuable because we can build them endlessly on campus,” says Amir Mortazavi, founder of Studio Mortazavi, an architectural firm and partner at Thinking Huts, . "Because 3D printing is limited in size, adding blocks is the most efficient and flexible way to build" . At the same time, the 3D-printed construction process is much more sustainable than traditional construction: Thinking Huts claims that 3D-printed buildings use less concrete and emit less carbon dioxide during construction. 3D printing will be used to build walls, while doors, roofs and windows will be made from local materials.
Externally, the building resembles a beehive, consisting of blocks, which allows you to expand the structure if necessary. “These blocks are valuable because we can build them endlessly on campus,” says Amir Mortazavi, founder of Studio Mortazavi, an architectural firm and partner at Thinking Huts, . "Because 3D printing is limited in size, adding blocks is the most efficient and flexible way to build" . At the same time, the 3D-printed construction process is much more sustainable than traditional construction: Thinking Huts claims that 3D-printed buildings use less concrete and emit less carbon dioxide during construction. 3D printing will be used to build walls, while doors, roofs and windows will be made from local materials.
The simplicity and environmental friendliness of 3D printing opens up great opportunities for using this technology in education. In October 2018, the Idaho Science Center launched a competition in which teams of high school students use digital manufacturing and 3D printing to design a product that addresses the state's natural resource challenges. The Center has previously trained team mentors, educators from 19 state schools and libraries. The final stage of the competition was the FabSLAM exhibition, where the participants presented their inventions. At the end of the show, the team that used a 3D printer to create a solar-powered motion sensor designed to keep deer and elk out of the fields won first place. The students created a website where they noted the stages of sensor development - from discussing the idea and creating a test model from cardboard to presenting the finished product. It took them 18 weeks in total. The second and third places in the competition were taken by the development of a set of firefighters' tools and a solar-powered birdhouse with a temperature control system.
The Center has previously trained team mentors, educators from 19 state schools and libraries. The final stage of the competition was the FabSLAM exhibition, where the participants presented their inventions. At the end of the show, the team that used a 3D printer to create a solar-powered motion sensor designed to keep deer and elk out of the fields won first place. The students created a website where they noted the stages of sensor development - from discussing the idea and creating a test model from cardboard to presenting the finished product. It took them 18 weeks in total. The second and third places in the competition were taken by the development of a set of firefighters' tools and a solar-powered birdhouse with a temperature control system.
A 3D printer can also be used to help children themselves: for example, Yahoo Japan's Sawareru Kensaku, which means "search that can be touched" in Japanese, is designed to be used by blind and visually impaired children in schools. The product is a 3D printer that prints models of various objects based on voice search. The device is designed to expand the understanding of children with disabilities about the world around them, primarily about those objects that can rarely be touched. Using the device is very easy: there are only two buttons on its body - to activate voice search and start the printing process. The finished model of the desired object comes out of the window below.
The product is a 3D printer that prints models of various objects based on voice search. The device is designed to expand the understanding of children with disabilities about the world around them, primarily about those objects that can rarely be touched. Using the device is very easy: there are only two buttons on its body - to activate voice search and start the printing process. The finished model of the desired object comes out of the window below.
Of course, the introduction of 3D technologies can not only improve the conditions of education, but also expand its content, developing creative skills and even critical thinking in children. This is evidenced by a study by Macquarie University (Sydney, Australia). In a study of 27 teachers and more than 500 students, 3D printer classes showed almost 100% student engagement, with 94% saying they would like to continue using 3D printing outside of class. Also, in 71% of the lessons conducted during the study, an increase in the creativity of students was noted, in 64% of the lessons - an increase in project thinking, in 58% of the lessons - an increase in critical thinking.
Special cases of using a 3D printer also show the positive impact of this practice on the learning process. One of the schools in St. Petersburg shared its experience in using a 3D printer. The device was assembled by students and teachers themselves: “It was educational: assembly was not an easy test, but we learned so much about 3D printing and printers that it was no longer scary at all.” In the process of using the device, two vectors of application of 3D printing have been outlined: extracurricular project activities and educational, when a 3D printer is used as an applied tool when mastering the material. Teachers note that this greatly increases the interest and motivation of children, and also enlivens the lessons. For example, the theme of studying ornaments at technology lessons, in addition to searching for information and preparing reports, now includes drawing in a vector editor, programming and printing an ornament on a 3D printer. Moreover, the school is open to cooperation with other educational institutions - from discussing possible ideas and projects to exchanging devices. “How much we like the idea of openness and cooperation between schools, and not only schools. Together we can do so much more.”
“How much we like the idea of openness and cooperation between schools, and not only schools. Together we can do so much more.”
Perhaps the secret of the success of the considered projects lies in openness and cooperation. Unfortunately, at the moment, 3D printers are quite expensive equipment that not all schools can afford, but there is the possibility of cooperation with manufacturers or other schools that already have such equipment. In the end, everyone has the same goal – to expand access to education and at the same time improve its quality. With these trends in mind, the future looks to be even more creative and effective ways to use 3D printing devices in schools.
3D printer at school, everything you need to know
top sellers
-
Bearing 604UU U604ZZ
U-bearing U604ZZ 604UU 4*13*4
35.
 00 UAH
00 UAH Thermal mat for 3D printing 200 x 200 mm
3D printing thermal mat
150.00 UAH
-
Buy epo3d+ 3D printer
Epo3d+ Ukrainian FDM 3D printer on HIWIN rails. Thanks to reliable...
UAH 35,000.00
-
ABS granules
ABS granules for extrusion
400.00 UAH
-
PLA
PLA environmental plastic from Plexiwire.
 100% advance payment....
100% advance payment.... UAH 375.00
-
Buy ABS plastic (ABS)
ABS plastic from Plexiwire. 100% prepayment. Free shipping...
UAH 220.00
-
Mini motor reducer 12v 100 rpm
high torque mini electric motor. Its size...
150.00 UAH
-
Nozzle for 3D printer 1.75 mm, for E3D and MK8 hotends
Nozzle for 3D printer 1.75 mm 0.2/0.3/0.4/0.5
35.00 UAH
-
PETG plastic for 3D printer
PETG plastic from Plexiwire.
 100% prepayment. Free...
100% prepayment. Free... UAH 360.00
-
SHF-20 shaft support
SHF-20 shaft support is used for CNC
60.00 UAH
-
A4988 stepper motor driver
35.00 UAH
-
Buy epo3d 3D printer
Ukrainian epo3d 3D printer built on the basis of modern kinematics...
UAH 18,000.00
All best sellers
Information
3D printer at school, everything you need to know
Just think, you could use a 3D printer to physically shape each lesson plan. Which 3 D printer is ideal for working with children.
Which 3 D printer is ideal for working with children.
3D printing provides a whole new level of creative learning and understanding for students. And thanks to its affordability, 3D printers in the classroom are no longer a fantasy.
3D printing can be used at all levels of education, from elementary schools to universities. Not to mention the fact that almost any object, with the help of a 3D printer, becomes more understandable and interesting. And it's not as hard to integrate 3D printing into the curriculum as you might think...
A 3D printer in the classroom solves a number of important problems at once, such as:
- Capture the interest of students
3D printing has the added benefit of keeping young learners interested with a visual aid. The process of designing and then printing their creations is stimulating, but the feedback from idea to creation makes the learning experience enjoyable, but more importantly, makes learning effective.
- Encourage interaction during class
Using a 3D printer instantly turns any classroom into an interactive learning experience. Whether it's printing skeletal parts for use in biology classes or creating prototypes for engineering classes, the process requires learning through interaction and encourages learning.
- Create material assets
Complex concepts become not only visible, but also tangible. Whatever you normally draw on the board, you can explain with models that students can touch and explore from any angle.
- Practical training through 3D models
Especially for arts and technology, it is very useful to use prototyping capabilities to bring students' creative ideas and designs to life.
Here are some more ideas to use 3 D printers in the learning process:
- .
 Engineering design students can print prototypes of
Engineering design students can print prototypes of - Architecture students can print 3D models of structures
- History classes can print historical artifacts for study
- Graphic design students can print 3D versions of their work
- Geography students can print topographic, demographic or population maps.
- Cooking students can create food molds
- Automotive students can print replacement parts or modified samples of existing parts for testing.
- Chemists can print 3D models of molecules
- Biologists can create cells, viruses, organs and other important biological artifacts.
When buying a 3D printer for your school, pay attention to its key features.
The first is, of course, safety. The case of the 3D printer for the school must be completely closed. An exhaust hood or a filter can be connected to such a case, which will eliminate the problem of evaporation when the plastic is heated.