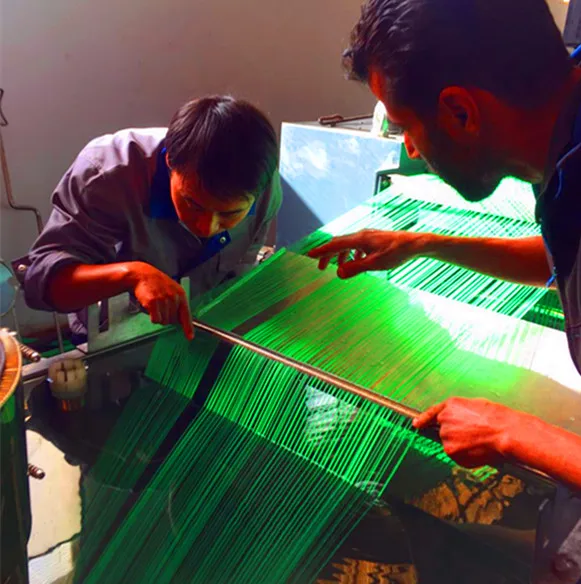
3D printer filament making machine india
Felfil Filament Maker | Make your own 3D printing filament with Felfil Evo
Felfil Evo Extruder
The Perfect Match for your 3d printer
order now
Felfil Shredder
Crush your Plastic Wastes
order now
Felfil Spooler
Easier way to extrude
order now
Our filament maker system
The Felfil filament extrusion line is composed by Felfil Evo, a 3d printer plastic extruder machine, Felfil Spooler which is a winding machine and Felfil Shredder that is a small plastic shredder. This extruding system allows anyone to make custom 3D printing filaments at home or in a lab, starting from industrial pellet or chopped wrong 3D prints, old models and plastic waste.
Using our desktop filament maker you will be able to choose your filament color, diameter and material, day by day, according to your creativity and your needs. In this way you will save over 80% of the price of filaments spools and help to protect the environment.
Recycle
Use failed 3D prints or plastic waste to create your filament
Save money
Save up to 80% of the spool costs starting from our pellets
Experiment
Make your custom 3D printing filament for any 3D printer
Get Your Desktop Filament Extruder
Choose between our different models and start to make your own filament
request a quote
This is the complete filament maker system by Felfil, that includes Felfil Evo Assembled and Felfil Spooler.
You will receive all assembled, ready to make your custom and DIY 3d filament.
A complete solution to make your own filament directly on your desktop.
That’s the full recycling system by Felfil. It includes a plastic shredder, the extruder and the winder. All arrives already assembled and tested.
All three products can be placed on your desktop, and you can start immediately to recycle your old 3d prints or plastic wastes.
The Felfil Evo Complete Kit is the solution for who want to build their own extruder, step by step. Then, it is shortly to begin to extrude.
Buying this package you will get all the components of Felfil Evo, you just have to assemble them following the instruction manuals.
This is the complete filament maker system by Felfil, that includes Felfil Evo Assembled and Felfil Spooler.
You will receive all assembled, ready to make your custom and DIY 3d filament.
A complete solution to make your own filament directly on your desktop.
This solution is perfect for who want to try immediately our extruder! An ideal choice for those who want to begin to extrude easily.
You will receive the filament maker already assembled, ready to make your custom and DIY 3d filament. You have just to unbox it and connect the plug.
The Felfil Evo Complete Kit is the solution for who want to build their own extruder, step by step. Then, it is shortly to begin to extrude.
Then, it is shortly to begin to extrude.
Buying this package you will get all the components of Felfil Evo, you just have to assemble them following the instruction manuals.
ONE SYSTEM, SEVERAL APPLICATIONS
Our filament extruder system is easy to use and suitable for different applications, find out yours
Fablab /Makers
Felfil Evo is an open source project and it is perfect for FabLabs and MakerSpace users: amatorial 3D printers and experts.
It is studied to help Makers recycle plastic waste from 3D printing activities, to save money and try different materials in order to stimulate creativity and innovative ideas.
You can create incredible and original objects from your old 3D prints.
Lean more
Laboratories
With our system it is possible to experiment new material, test their features and study their application. Felfil Evo and Felfil Spooler can be used in many sectors for prototyping activities.
Felfil Evo and Felfil Spooler can be used in many sectors for prototyping activities.
With our desktop filament maker, research laboratories can be independent creating and testing small quantities of filament and have an immediate experience with the new materials.
Lean more
Education
Felfil helps students to learn about new technologies and additive manufacturing.
Thanks to our filament recycler system it is possible to learn about plastic materials for 3D printing and their potential for reuse culture.
The educational potentials of Felfil project concerns recycling and reuse, maker philosophy and application sectors of 3D printing.
Lean more
Our Clients
Born as open hardware but ready to make filament easily and safely at home. It’s a desktop 3d printer filament extruder able to produce custom filaments for your 3D printer.
Meet Felfil Evo
Meet
Make your choice
You can choose between three different version of Felfil Evo filament maker
DIY Project
Discover how to customize Felfil Evo
More
Make 3D Print Materials - Desktop Filament Maker and Shredder
Innovate right from your desk
REDEFINING EXTRUSION
Filament Makers
Our Composer and Precision filament makers help you break new ground in the development, production and recycling of 3D printing materials. Find out more..
Learn More
MISSION: ZERO
Upcycling is Off To a Promising Start at Audi.
AUDI is leaping into a new era of sustainability as they create new components from plastic packaging waste. How are they doing this? Through their pilot 3D printing and upcycling project incorporating our solution.
Learn More
NEW PRODUCT LAUNCH
GP20 Shredder Hybrid.
Introducing the most innovative autonomous plastic shredder. A modular dual-part system with an intelligent interactive display, allows you to truly tailor your material settings..
Learn More
EXTREME E
Extreme E is partnering with 3devo.
The first all-electric racing to highlight the climate change challenges has just started, and we just couldn’t miss it!
Learn More
A full recycling ecosystem
From design to development and production, 3devo creates the most complete filament extrusion machines and tools. Using cutting-edge technology, and high-quality European standards, our goal is to make filament extrusion simple for everyone!
Filament Makers
Plastic Shredder
Polymer Dryer
Our Process
Customer Care
Customer care is always the first priority for us. On our online help platform, you will find video tutorials, troubleshooting steps and solutions, and everything else you may need to know about filament extrusion.
Knowledge base
Forums
Videos
Visit Help Center
Quality
3D Printing is a demanding procedure with a focus on detail and we know that. By using the highest quality standards, we make sure that you will be able to recycle your plastics for a long time.
Support
Durable
About Us
Evolution
We are never standstill. Innovation is the reason
3devo was born, thus it is always at the center
of our core values.
Innovation
Production
About Us
Materials Made Simple
Our mission is simple – to streamline the process of material research and development. How do we do this? By providing you with the best accessible features with the highest quality components. Are you ready to join the revolution in material development?
“All-in-All, the extruder is a cost-saving alternative for our 3D printing needs, as it cuts out expensive purchases and deliveries of ready-made filament.”
Svein A. Hjelmtveit
Hjelmtveit
Laboratory Manager
“Navigating the menu was intuitive and the pre-set list is adequate for the first steps of processing.”
Pere Castell
Nanotechnology Manager
“As of this moment, we are extruding a new type of material weekly.”
Martin Olofsson
Laboratory Engineer
“It is a lot more flexible than our big extruder. Quick to use and doesn’t need lots of material. This device allows us to conduct most tests as part of research projects with other companies.”
Kurt van Houtte
Coordinator Fablab
“The machine is perfectly suitable for small batch extrusion in short time-frames, and allows you to immediately proceed with material testing and analysis.”
Mathias Czasny
Materials Scientist
“The Composer 450 is ideal for proceeding with immediate testing and analysis as it requires the minimum amount of input material, unlike the other extruders which require a minimum input of one kilogram.”
Corinne van Noordenne
Researcher and Lecturer
Latest Blog Posts
We're here to help
Contact Sales
Contact Sales
Source 3D Printer Filament Making Machine, 3D Printing Filament Extruder on m.
 alibaba.com
alibaba.com Overview
Details
Inquire
Start Chat
Trade Assurance
Trade Assurance
Integrated Service for Orders on Alibaba.com
Product quality
Timely delivery
Learn more about shipping and other trade services.
Product features
Yield (kg/h): 2, Models: 1
| Port: | Shanghai Port | ||||||
| Payment Terms: | L/C,Western Union,D/P,D/A,T/T,MoneyGram | ||||||
| Delivery Ability: | 8 sets For MONTH 3D printers of threads machine | ||||||
| Name: | ACC | ||||||
| screw diameter: | 45 | ||||||
| Voltage: | |||||||
| Vint:0027 | |||||||
| Showroom Location: | Egypt,Turkey,United Kingdom,United States,France,Saudi Arabia,Indonesia,India,Thailand,Morocco,Chile,United Arab Emirates,Colombia,South Africa,Kazakhstan,Uzbekistan,Tajikistan | ||||||
| The screw ratio L/D: | 28: 1 | ||||||
| Temperature controller: | OMRON | ||||||
| Color: | on an individual order | ||||||
| Power (BCW): | 15 | ||||||
| Key point for sale: | Sustainable | ||||||
| screw design: | Class -wires | ||||||
| COMPLEDERY LEARALISTION OF LEARAGED OFFICAL ACTIVITY ACTIVITY ACTIVITY ACTIVITY OFFICALLY LEARAL | |||||||
| Test Report Production Equipment: | Provided | ||||||
| Size: | Mini | ||||||
| Propeller speed (rpm): | 60 rpm | ||||||
| Treated plastic: | PE,ABS,WPC,Polyacrylamide,EVA,PPS,PET,ABC,PVC Machine for the production of PND/PP, ABS PLA | ||||||
| Guaranteed: | 4 years old | ||||||
| Size (L*W*H): | 1 m | ||||||
| Video-SPIRITION: | FACTION|||||||
| Contactor: | German "Siemens" | ||||||
| Marketing type: | New product 2020 | ||||||
| raw materials: | Pla ABS granules | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year | 1 year |
| Application: | Profile, Granulation, Straw hat, Incandescent lamp | ||||||
| Origin: | Jiangsu, China0026 The main components: | Bearing, engine, pump, gear, PLC, pressure vessel, engine, gearbox, screw | |||||
| Use: | Production 3D | ||||||
| applicable industries: | GOODS, CLOSE OF GOODS OF GODS ,Manufacturing Plant,Farm,Retail,Grocery Store,Construction Works,Energy & Mining,Food & Drink Stores,Advertising Company | ||||||
| Inverter: | ABB | ||||||
| Type: | 3D Printer Filament Extruder | ||||||
| Packing Information: | 3D Printer Filament Machine Packed in the Standard Wooden Box | ||||||
| Preview Package: |
1 set
Subject to agreement
1+ set
Suzhou ACC Machine Co. , Ltd.
, Ltd.
CNTrading Company
≤6hResponse time
US $ 70,000+10 sales
100.0%number of orders delivered timely
500 General area
0-4 controllers of quality
0-4R & D Employees
90,000 Russian scientist-about the prospects of 3D-printing-RT in Russian Using materials from other planets for 3D printing is an important step in the development of space manufacturing. This was stated in an interview with RT by Vladimir Kuznetsov, Associate Professor of the Department of Materials Science of Non-Ferrous Metals at NUST MISiS, Head of the FabLab Digital Production Laboratory. So the scientist commented on the recent statement by the European Space Agency about plans to use lunar metals for 3D printing. He noted that parts printed on 3D printers are already being sent into space. The scientist also spoke about the types of 3D bioprinting and the properties of materials created using additive technologies.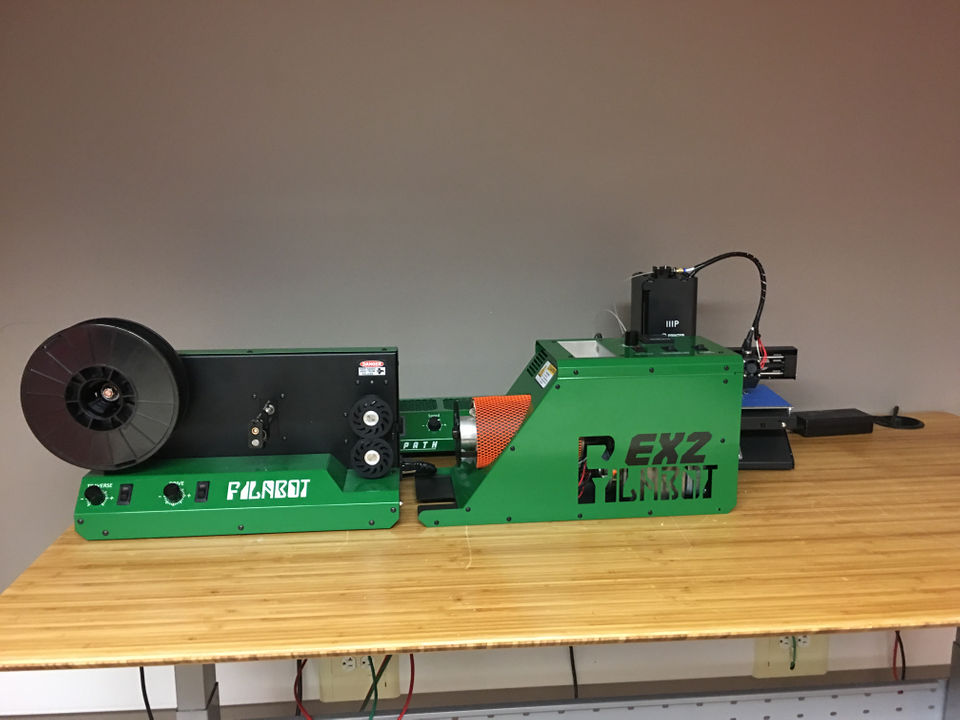 According to him, the most important prospect for the development of 3D printing is its use in personal production.
According to him, the most important prospect for the development of 3D printing is its use in personal production.
— It was recently revealed that the European Space Agency (ESA) is planning to test 3D printing technologies using metals from the Moon's surface. What can be printed in space and what materials will be used for this?
- The European Space Agency is now very far from the Moon. It is important to understand that the now popular term "3D printing" is often applied too loosely. The last high-profile European project related to the Moon and 3D printing involved the construction of a lunar base using regolith (the surface layer of loose lunar soil. - RT ). The project with the lunar base involved the use of elements of additive technologies (technologies for building up and synthesizing objects. - RT ), but the label “3D printing” glued to it is completely illegal.
At the same time, the very idea of using local materials for the production of anything on the Moon, Mars or Pandora is the only correct one. 3D printing will certainly play an important but not exclusive role in these projects. The European Space Agency with such conceptual projects makes a kind of reserve for the future.
3D printing will certainly play an important but not exclusive role in these projects. The European Space Agency with such conceptual projects makes a kind of reserve for the future.
Also related
From a 3D printer to an airplane: which industries use Russian innovations most actively
Aviation, pharmaceuticals, chemical industry, production of electronic and optical equipment are leading in Russia in terms of number... threads - RT ) is quite ready to work on the space station and in zero gravity conditions and can be used, for example, for the manufacture of fixtures and experimental equipment on the ISS. The problem is the material that will have to be delivered from Earth. The question is what is more efficient: to deliver finished parts from Earth or to deliver the printer and consumables into space.
— When will 3D technologies be launched in space and how will the use of 3D printers on the Moon differ from their use on Earth?
— Rockets with 3D printed parts are already being launched into space today. On the Moon, different 3D printing technologies can be used, both adapted from the Earth and specially developed for new missions. To solve the problems of building outer shells of lunar bases, for example, selective sintering technology can be used (the process of obtaining solid and porous materials from fine powdery or dusty materials at elevated temperatures and (or) high pressure. - RT ), in which the material will be lunar soil, and the energy source will be sunlight.
On the Moon, different 3D printing technologies can be used, both adapted from the Earth and specially developed for new missions. To solve the problems of building outer shells of lunar bases, for example, selective sintering technology can be used (the process of obtaining solid and porous materials from fine powdery or dusty materials at elevated temperatures and (or) high pressure. - RT ), in which the material will be lunar soil, and the energy source will be sunlight.
- An employee of the Moscow laboratory of 3D Bioprinting Solutions holds a thyroid gland printed on a 3D printer.
- RIA News
- © Kirill Kallinikov
— What is the difference between 3D printed models and parts made using traditional technologies?
- There are many 3D printing technologies, and there are different materials for them. For these technologies and materials, it is more correct to use different references from the world of traditional technologies. In general, the strength of printed products, with rare exceptions, is noticeably inferior to the strength of products made from the same or similar materials, but obtained by traditional methods. In the most common technology (Fused Filament Fabrication), one of the key features is a strongly pronounced anisotropy of properties (a characteristic of a physical body, which consists in the fact that its various properties in different directions manifest themselves quantitatively differently. - RT ).
For these technologies and materials, it is more correct to use different references from the world of traditional technologies. In general, the strength of printed products, with rare exceptions, is noticeably inferior to the strength of products made from the same or similar materials, but obtained by traditional methods. In the most common technology (Fused Filament Fabrication), one of the key features is a strongly pronounced anisotropy of properties (a characteristic of a physical body, which consists in the fact that its various properties in different directions manifest themselves quantitatively differently. - RT ).
This means that the properties of the product depend on the direction of the applied external forces relative to the orientation of the product when printed. The printed product is not monolithic, it is formed by polymer threads laid in parallel layers. Along the layers, the properties are one, across - others. As a rule, the strength across the layers is about 40% of the strength along the layers, but this difference can be significantly reduced or even eliminated.
— In the coming decades, bioprinting could be the next major milestone in healthcare and personalized medicine. Advances in 3D bioprinting have included the creation of human skin, cartilage, bones, blood vessels, and internal organs such as the heart and kidneys. How safe are printed organs and can they be transplanted into humans? Can organ printing replace traditional transplantation?
— Traditional transplantation has never been and probably will not be safe. The transplanted organ is perceived by the body as a foreign object and is subjected to constant attacks by the immune system. In this sense, artificial organs grown from the host organism's own stem cells and printed on a 3D bioprinter can become safer than "traditional" solutions.
- 3D printing can produce products such as chocolate, pasta, sugar and more. Recently, Japanese scientists have 3D printed a piece of beef using genetic modification technologies. Why print products?
— In edible 3D printing, it is important to distinguish between two completely different directions. The first is shaping the edible material into the desired shape, such as printing edible cake decorations.
The first is shaping the edible material into the desired shape, such as printing edible cake decorations.
- 3D printer prints a snowflake out of chocolate
- globallookpress.com
- © ZUMA Press / Rodrigo Reyes Marin
The second direction, which has a very indirect relation to 3D printing in its classical sense (toolless production of simple and complex forms by layer-by-layer addition of material), implies not so much giving the product the necessary shape, but rather the synthesis of the material. Many of these technologies are close to bioprinting technologies. Why grow a whole cow when you can only "grow" a steak from stem cells?
— In the modern world, 3D printers are used in various fields: mechanical engineering, architecture, small-scale production and many others. What are the prospects for this area?
What are the prospects for this area?
- Digital additive technologies complement subtractive (traditional methods of production and processing, where the appearance of the product is formed by removing excess material. - RT ) and deformation (traditional methods of processing materials by pressure. - RT ) in all branches of modern industry. We are currently experiencing major changes in the industrial order, but it is a mistake to link this solely to the advent of 3D printing. The revolution lies in the replacement of digital manufacturing technologies with analog ones, and not in the replacement of 3D printers with milling machines or stamping presses.
The most important development of 3D printers, as well as other modern digital production machines, is personal production, and this concept has two meanings. First, with the help of digital machines, it is possible to efficiently produce personal products - products in a single copy, needed by a single person. And secondly, a 3D printer is a personal means of production.
And secondly, a 3D printer is a personal means of production.
For several centuries the world was divided into those who own the means of production and everyone else, but today this boundary is blurring. An inexpensive home (personal, desktop, amateur) 3D printer has very low productivity, but it is easily compensated by a large number of these printers, which allows you to start moving in the direction from mass production, which cannot exist without mass consumption, to distributed personal production.
- 3D printed face shields
- RIA News
- © Ekaterina Chesnokova
In the midst of the first wave of the global coronavirus pandemic, when the epidemic and related restrictive measures instantly destroyed the logistics chains of production and supply of goods, the whole world faced a shortage of personal protective equipment: masks, face shields, gloves. These products were not enough for doctors and medical staff, and “makers” came to the rescue - the owners of home 3D printers. They worked as volunteers and set up the production of various funds and their donation to doctors. Thousands of amateur 3D printers went online across the world - in the US, India, Peru and Russia - and, according to statistics from the non-profit organization Open Source Medical Supply, produced more than 40 million units of scarce products before the system of global distribution and mass production was restored.
These products were not enough for doctors and medical staff, and “makers” came to the rescue - the owners of home 3D printers. They worked as volunteers and set up the production of various funds and their donation to doctors. Thousands of amateur 3D printers went online across the world - in the US, India, Peru and Russia - and, according to statistics from the non-profit organization Open Source Medical Supply, produced more than 40 million units of scarce products before the system of global distribution and mass production was restored.
— How are Russian 3D printing technologies developing and what 3D printers are used in Russia?
- 3D printing technologies have been developing since the mid-1980s, serious progress came in the 1990s. At that time, both the USSR and Russia had very limited opportunities to create new science-intensive technology. However, the Institute for Problems of Laser and Information Technologies of the Russian Academy of Sciences after 1991 produced a stereolithography installation (an additive manufacturing process, the result of which is achieved through the photopolymerization of resin. - RT ). In the last decade, there have been enough large and small developers and manufacturers of 3D printers in Russia, many solutions are competitive on the global market.
- RT ). In the last decade, there have been enough large and small developers and manufacturers of 3D printers in Russia, many solutions are competitive on the global market.
- Recently, the AMT company, a resident of the Skolkovo Foundation, announced that it will build a village of 12 houses in the Yaroslavl region using a 3D printer. How will printing be carried out and will it be possible to live in such houses?
— Construction printing is a separate area of digital additive technologies, and it is also developing in different ways. The most popular scheme now is printing with concrete or geopolymer concrete. Another scheme developed in Russia is printing with a special polymer gel that hardens under ultraviolet illumination.
There are two different approaches. In the first, a mobile 3D printer is deployed on a construction site and prints the walls of a building directly onto the foundation. The second approach is to print the modules of the future building in the factory with their subsequent delivery to the construction site. People already live in houses of both types.
People already live in houses of both types.
Related
Eco-friendly and safe: Russian scientists have created invisible labels to protect goods from fakes
Russian scientists have created invisible polymer gel tags that can be used to protect against counterfeiting. They represent...
— Researchers from Loughborough University (UK) have developed a new 4D printing method. What kind of print is this?
- 4D printing is a popular and common term that can mean very different solutions. The most popular interpretation: 4D printing is the printing of products whose shape is not static. An example of 4D printing is the simultaneous printing of materials with different properties. Rigid and elastic sections are formed in the product, thus the behavior of the product under load is programmed. 4D printing allows you to print objects with dimensions larger than the printer on which it is carried out. The object extracted from the printer unfolds, increasing in size. A possible end goal for the development of 4D printing is the printing of a robot that can itself get out, drive out, crawl out or fly out of the printer that printed it.
The object extracted from the printer unfolds, increasing in size. A possible end goal for the development of 4D printing is the printing of a robot that can itself get out, drive out, crawl out or fly out of the printer that printed it.
- Parts printed on a 4D printer
- © Legion-media.ru / Xinhua/Sipa USA
Can 3D printers help us explore other planets like Mars? Is it possible that during colonization we will be able to create 3D parts directly from the useful resources found on the planet?
- We need to stop dreaming about colonization and terraforming (the theory of the hypothetical possibility of changing climatic conditions on space bodies. - RT ) other planets. It is necessary to work on terraforming our native Earth. The Industrial Revolution and its main achievements - mass production and consumption - have led to the fact that our environment has become toxic to life.