3D printer extruder definition
essential part of a 3D Printer
While using additive manufacturing, and especially when you are 3D printing by yourself with a desktop 3D printer, you might be confronted with an extruder. This component of 3D printers plays a great role in your additive manufacturing projects, that is why we think you should know everything about it!
The 3D extruder is the part of the 3D printer that ejects material in liquid or semi-liquid form in order to deposit it in successive layers within the 3D printing volume. In some cases, the extruder serves only to deposit a bonding agent used to solidify a material that is originally in powder form. Let’s discover the function of the 3D printer extruder, a little but essential part, required for some additive manufacturing processes
3D extruder depositing plastic filament on a 3D printing platformWhat is an extruder?
The 3D extruder is the part of the 3D printer that ejects material in liquid or semi-liquid form in order to deposit it in successive layers within the 3D printing volume. In some cases, the extruder serves only to deposit a bonding agent used to solidify a material that is originally in powder form.
The different 3D printing technologies that require an extruder
Found in 3D Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printers, the extruder is also required for proper operation of machines using Binder Jetting or Polyjet technologies, and even 3D Systems’ CPX machines. These are additive manufacturing machines that need to deposit material before transforming it either by adding a bonding agent to it (Binder Jetting) or by changing the chemical properties (Polyjet and CPX). These technologies are explained in our guide about the different kinds of 3D printing.
What are the differences and advantages of 3D printer nozzles, depending on the 3D printing technologies?
- For FDM / FFF printers
The filament extruder on a FDM printer is the part that extrudes the plastic filament in a liquid form and deposits it on a printing platform by adding successive layers. The printing head is made of many distinct parts including a motor to drive the plastic filament and a nozzle (or extruder) to extrude the plastic.
The printing head is made of many distinct parts including a motor to drive the plastic filament and a nozzle (or extruder) to extrude the plastic.
Some 3D FDM / FFF printers are now equipped with two extruders. This enables you, in particular, to print two materials simultaneously in order to obtain 3D prints in two colours. The presence of two extruders also allows support material to be extruded, which can be removed afterward using a solvent.
To regulate the plastic cooling process, some printers are enclosed. This helps maintain a uniform temperature in the manufacturing chamber, ensuring greater consistency in the print result.
- For printers operating with Binder Jetting
The most common kinds of Binder Jetting printers are probably the Projet printers from 3D Systems. These printers have an extruder that projects a bonding agent (or colour) onto a powder material. It’s the action of projecting this bonding agent onto successive layers of powder that creates the object.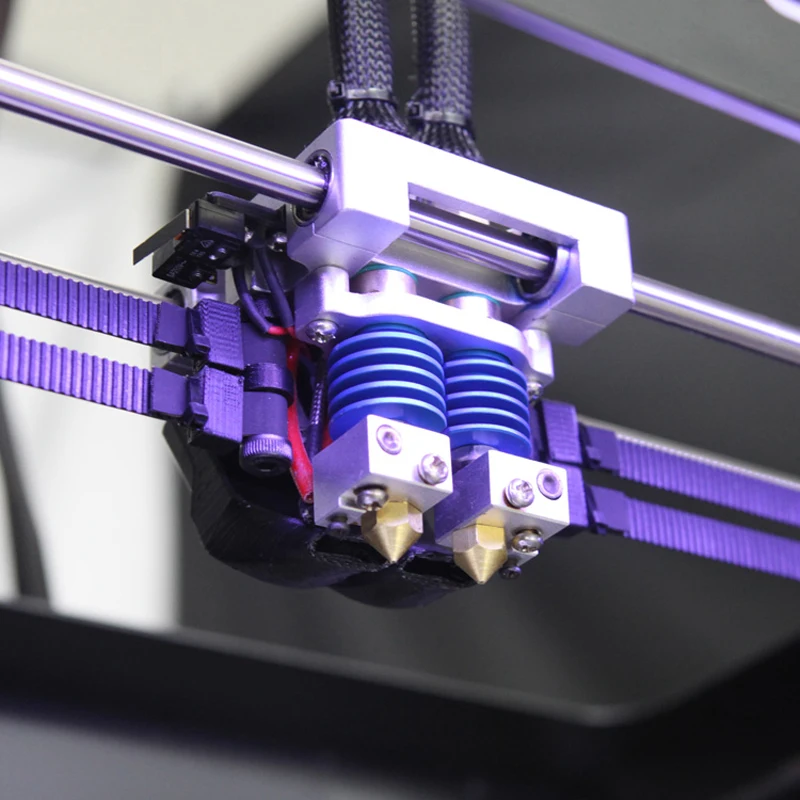
- For Polyjet printers
Polyjet technology, originally developed by Objet (which is now owned by Stratasys), is also based on the projection of resin in the form of droplets onto the printing platform. Once the droplets are projected, UV polymerises the resin.
Cold end and hot end: What are these components?
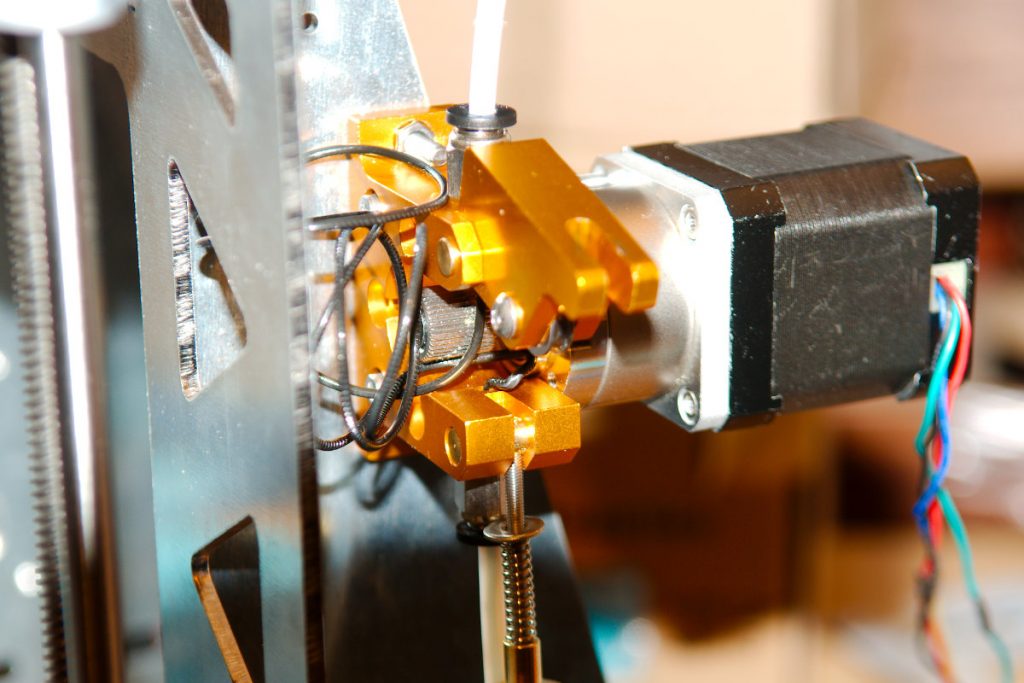
The cold end is the cold part in the upper portion of the 3D printer extruder. At this point, there is no heating of the filament. This is just the part with the motor and gearing, pushing the 3D printer filament into the hot end. Different systems actually exist, there is usually a combination of gears and hobbed bolts, dictating the movement of the printing filament.
The hot end is the part where the filament is transitioning from solid to liquid, while extruded on the building plate. But how is the filament melting? Indeed, something has to be hot enough to melt materials and as we want to print an accurate part, the temperature between the cold filament, the hot end, and the final cold and solid part has to be perfectly managed.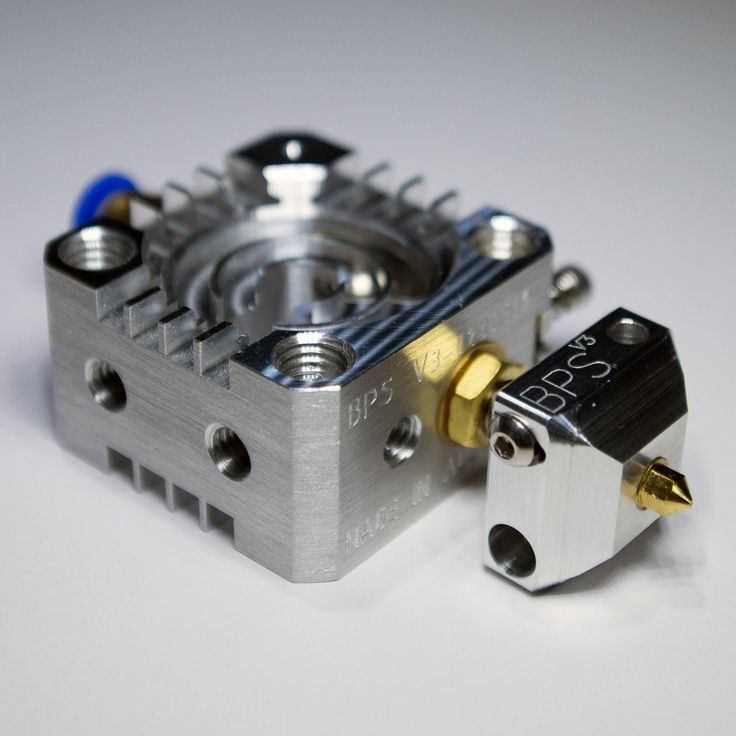 The heat break, in combination with the heat sink, maintains a boundary at which the filament is confronted with high temperatures. There is, in the system, a heater cartridge that is getting hot, transferring heat to the nozzle via the heater block in aluminum.
The heat break, in combination with the heat sink, maintains a boundary at which the filament is confronted with high temperatures. There is, in the system, a heater cartridge that is getting hot, transferring heat to the nozzle via the heater block in aluminum.
Most desktop 3D printers ship with 0.4mm nozzles as standard, but there are many other sizes available. Brass is usually used for 3D printer nozzles, but there are also several options. For some materials, stainless steel can be prefered.
Direct or Bowden extruder: Which one to choose?
There is not a single extruder type, your choice will depend on the kind of 3D printer that you have, on the materials that you will use, and on the printing speed and accuracy that you need.
There are two different possibilities: Direct or Bowden extruders. The nature of your projects will determine which extruder you need to use. First, all extruders have motors, but there are also geared extruders to control your print speed. It is not essential, but it can help you to customize your setups in order to improve your print quality.
It is not essential, but it can help you to customize your setups in order to improve your print quality.
Direct extruders are directly attached to the hot end, while a Bowden extruder (or remote extruder) has a tube to link the hot end and the extruder body. For direct extruders, the gear rotates by a stepper motor driving directly the filament to the extruder hot end. The filament path is shorter, that is why Direct extruders are better to 3D print flexible materials than Bowden extruders You can totally 3D print flexible filament with a Direct extruder, but it is not really convenient.
With Bowden extruders you can 3D print your projects faster. It is easier to accelerate or decelerate because there is just the printing head to move, not the whole extruder hot end.
They both can have a direct drive system. Indeed, for both of them the filament drive mechanism can be mounted to the motor shaft, directly.
Moreover, keep in mind that there are extruders for all filament thickness, for 3mm filament, 1.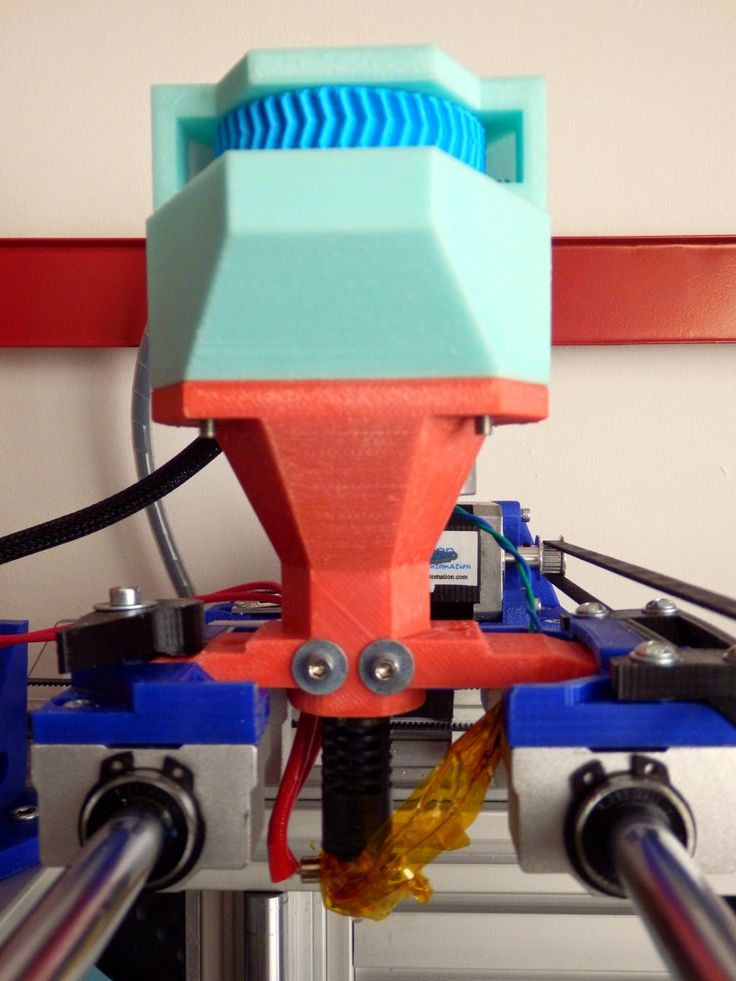 75mm filament, etc.
75mm filament, etc.
Extruder-related problems in 3D printers
The main problems encountered with 3D printer extruders are the same as with inkjet printers, which is poor maintenance or the use of the wrong materials leading to deterioration or fouling the nozzle that projects the material.
In the particular case of 3D FDM printers, the main problem stems from print nozzles that are blocked by hardened plastic unable to leave the extruder or by slack or space in the plastic extrusion axis, causing discontinuous extrusion.
Sculpteo provides a 3D printing service that enables you to verify your file and order a 3D print in a few clicks. To try our service, begin by uploading a 3D file.
Related glossary pages
5 things to learn on Extruder – Core part of a 3D printer
Extruder is considered as one of the important components of a 3D printer. It is the part of the 3D printer responsible for drawing in, melting and pushing out the filament.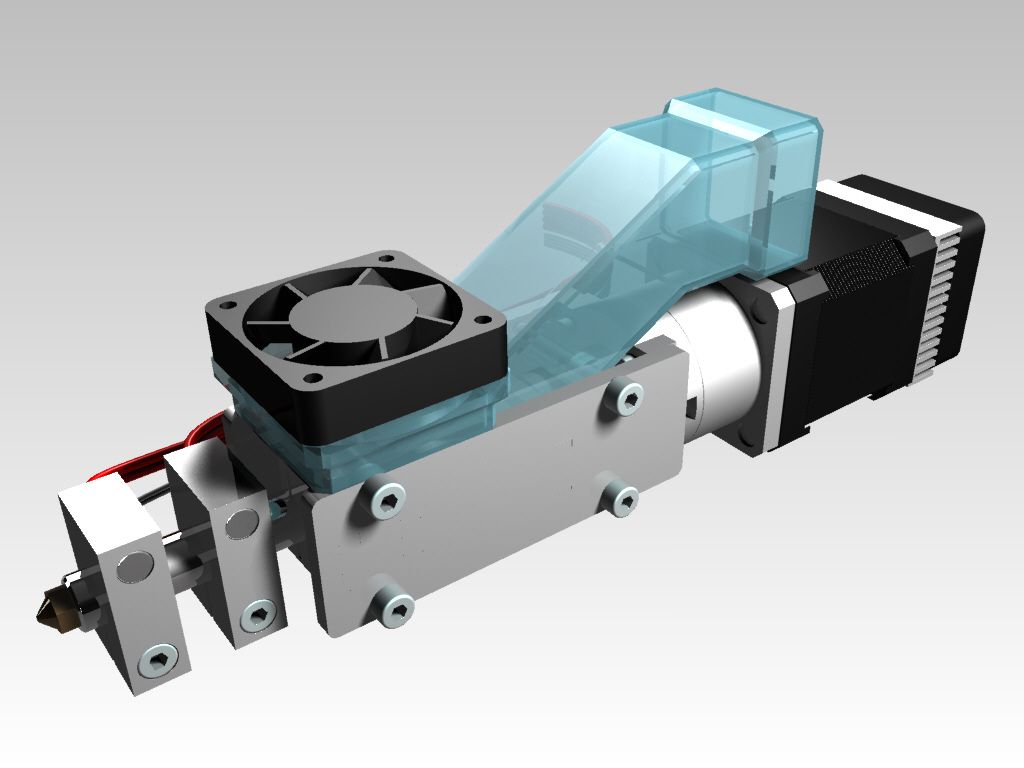
It is often called a “fancy hot glue gun”. In some cases, it serves to deposit a bonding agent to solidify the material that is in powder form. It is small but it is where the “main” printing procedure happens.
Since the extruder is the core part of a 3D printer, it is beneficial for you to understand the basics of an extruder. Hence, here is a blog post on the 5 things about 3D printer extruder.
- What is an extruder
The extruder is a part of a 3D printer where material is ejected in liquid or semi-liquid form. It is deposited in successive layers within the 3D printing volume. At times, the extruder only serves to deposit a bonding agent. This bonding agent is also used to solidify the material which is originally in powder form.
- Main elements of an extruder
An extruder has two main elements. These are the cold end and hot end. The cold end refers to the upper portion of the 3D printer extruder system where the filament is fed.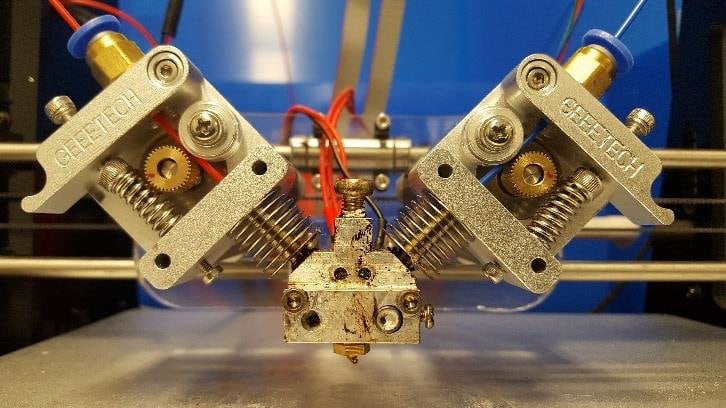 On the contrary, the hot end is where the filament gets melted and squirted out.
On the contrary, the hot end is where the filament gets melted and squirted out.
- Cold end
The cold end consists of stepper motor, some toothed gearing, hobbed bolt or gear, spring loaded idler to hold the filament and PTFE tubing to guide the filament.
In the cold end, the stepper motor drives the motion and extrusion of the filament for most of the desktop 3D printers. It is a brushless DC motor that is responsible for achieving high level of precision. It works on small movements and imparts full torque at low speeds.
- Hot end
If the cold end manipulates the filament as required by the 3D printer, the hot end, on the other hand, is where the filament passed for melting and extrusion onto the print end.
In the hot end, the filament should pass into a heated chamber where it transitions from solid to liquid. For a Bowden 3D printer extruder, a filament feed tube inserts the filament directly into the heat break through the heat sink.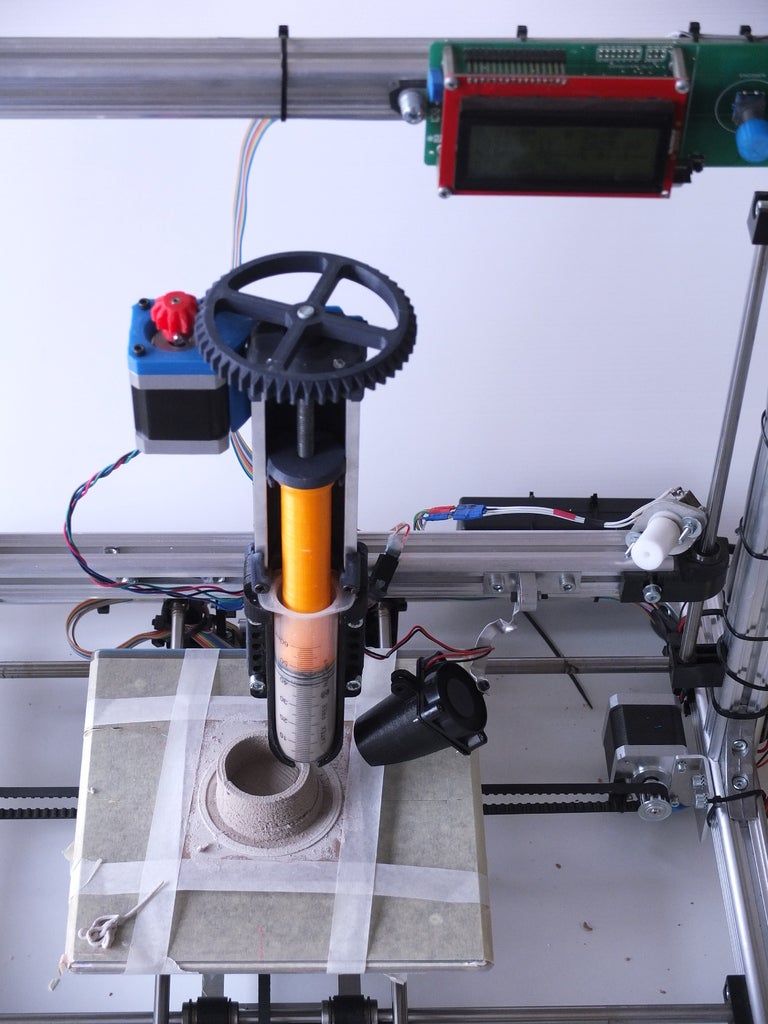
During the printing process, the filament travels from the cold end into the hot end. It will then go through the heat break where it meets the nozzle. This is where the filament liquifies.
One of the integral components of the hot end is the nozzle. It is a small piece with a hole where the melted filament comes out. It is usually screwed into the hot end heater block. Nozzles are typically interchangeable. It comes in various sizes but the normal size is 0.4mm.
- Types of extruder
The extruder has two different types depending on the drive. These are Direct extruder and Bowden extruder.
- Direct extruder
In direct extruders, the hot end and cold end are simply attached together. In this setup, the filament goes straight down through the cold end and into the hot end.
One of the main benefits of a direct extruder is the very short distance between the drive mechanism and the hot end.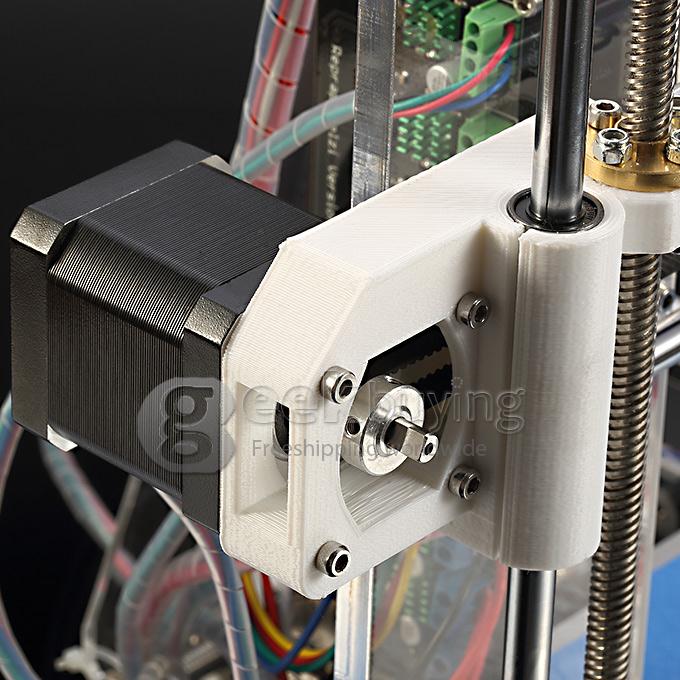 This means that it more responsive to extrusion and retraction. As a result, it can produce clearer prints with less stringing and oozing.
This means that it more responsive to extrusion and retraction. As a result, it can produce clearer prints with less stringing and oozing.
Moreover, the shorter distance between the drive mechanism and hot end can make printing with flexible materials a lot easier.
However, because direct extruders are directly attached to its hot end, there is also a possibility that its mass will be moved along with the hot end. This means that as more mass are moved around, it will likely to backlash, overshoot and frame wobble.
- Bowden extruder
In Bowden extruder, the hot end and cold end are not directly attached to each other. Instead, there is a tube that extends from the extruder to its hot end.
With this setup, the printer will be able to print faster, more accurately and more precisely than 3D printers with direct extruder.
Nevertheless, the most common weakness of Bowden extruder is that it is prone to retraction and stringing. Additionally, since the idler/gear pinch point and hot end are far from each other, there is a chance that the hysteresis (lag) of the system will increase.
- 3D printing technologies that require an extruder
3D printing uses different methods in printing. Some of these 3D printing technologies require an extruder while others don't. Below are some printing technologies that will require an extruder for printing.
- FDM/FFF
FDM printers use material extrusion process wherein the material is being melted and extruded through a nozzle to print a cross-section of an object. This is done layer by layer at a time.
- Binder Jetting
There are some Binder Jetting printers that have extruder which projects a bonding agent onto a successive layer of powder material to create a 3D object.
- Common extrusion problems that you might encounter
Here are the common extrusion-related problems that you might encounter while printing.
- Under-extrusion
Under-extrusion happens when the 3D printer cannot supply or extrude the right amount of material. Most of the time, it will result in missing layers, little dots or holes in layers or unwanted gaps which make the design incomplete. Print quality and print strength are sometimes compromised when under-extrusion happens.
Most of the time, it will result in missing layers, little dots or holes in layers or unwanted gaps which make the design incomplete. Print quality and print strength are sometimes compromised when under-extrusion happens.
- Over-extrusion
Over-extrusion occurs when the 3D printer supplies more material than needed. This will result in dimensional inaccuracy, layer drooping, stringing, oozing, etc. thus, ruining the quality of 3D prints.
ConclusionKnowing the basic things about 3D printer extruder is important since it is where the “actual printing” happens. Most specifically, it is where the filament gets drawn in, melted and pushed out. Moreover, 3D printers with extruders (material extrusion method) are what the majority of 3D makers and hobbyists used nowadays.
If you are interested in trying new things with 3D printing, you can ask for help from a 3D printing service provider. They can offer services according to your 3D printing requirement.
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
We all know that precise calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them. Many will say that it is wrong to compare them or Read more→
XYZprinting, best known for its daVinci line of desktop 3D printers, is bringing five new devices to the professional and industrial environment. One will use laser sintering technology, the second full color inkjet printing and three DLP machines.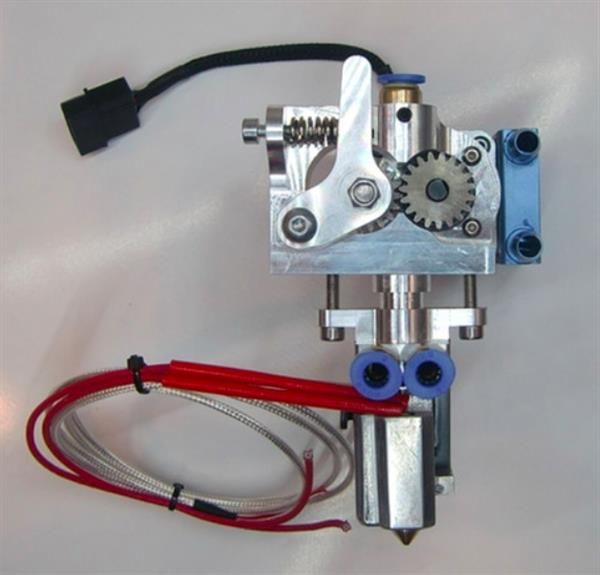 First of all, the novelties will be of interest to dentists and jewelers. Read more→
First of all, the novelties will be of interest to dentists and jewelers. Read more→
Cleaning the nozzle of a 3D printer is a fairly common process that any user of such a device has to deal with. This is not at all a complicated procedure that anyone can handle. You can complete this task in 15 minutes, using only handy tools and accessories. Read more→
Acetone steam polishing of ABS plastic is a process for smoothing the surface of 3D printed models. The result of this treatment makes your printed products look as if they were made by a professional mold casting method. If you want to understand how this is done correctly, then read this article. Aceto Read more→
How to choose an extruder for a 3D printer
3DPrintStory 3D printing process How to choose an extruder for a 3D printer
Hello friends. Today we will talk about choosing an extruder.
Today we will talk about choosing an extruder.
In simple terms, an extruder is a mechanism whose task is to feed molten plastic into the printing zone. It consists of a feeding mechanism and a print head.
Two types of extruders
There are two main types of extruders: bowden (bowden) - in the picture on the left and direct (direct) extruder - in the picture on the right. With a direct extruder, the plastic feed mechanism is located in close proximity to the print head. In bowden - at some distance, connected by a Teflon tube.
The main advantages and disadvantages of the two types of extruders
Both have their advantages and disadvantages.
In direct extruders, the weight of the stepper motor with the plastic feed mechanism is added to the weight of the printhead. Excess weight will increase the inertial forces when stopping and accelerating the print heads, which can adversely affect the quality of 3D printing, especially at high speeds, and also causes increased wear of the kinematics of the shafts and bearings.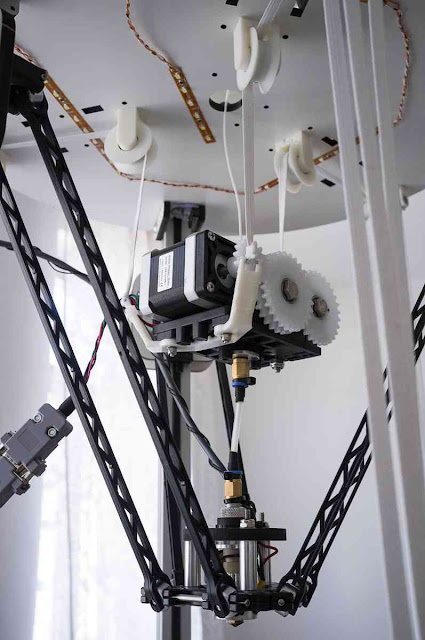 But the supply and rollback of plastic (the so-called retract) is more accurate, which makes tuning easier.
But the supply and rollback of plastic (the so-called retract) is more accurate, which makes tuning easier.
Bowden eliminates the disadvantages of direct extruders regarding extra weight, since only the print head runs along the carriage, which makes it possible to print at higher speeds. But in return, we get problems with the exact dosage of plastic, which will complicate tuning and calibration.
Extruder design
All extruders are similar in design and differ only in execution. Let's look at what the extruder consists of using the well-known e3dv6 model as an example.
These are three main nodes: cold end (cold part), hot end (hot part), which are connected by a thermal barrier.
Hot end consisting of:
- Heating element to melt plastic.
- Measuring element (thermistor) for maintaining the desired temperature.
- Aluminum heating block to house them.
- Nozzle with calibration hole from 0.1 to 0.8 millimeters.
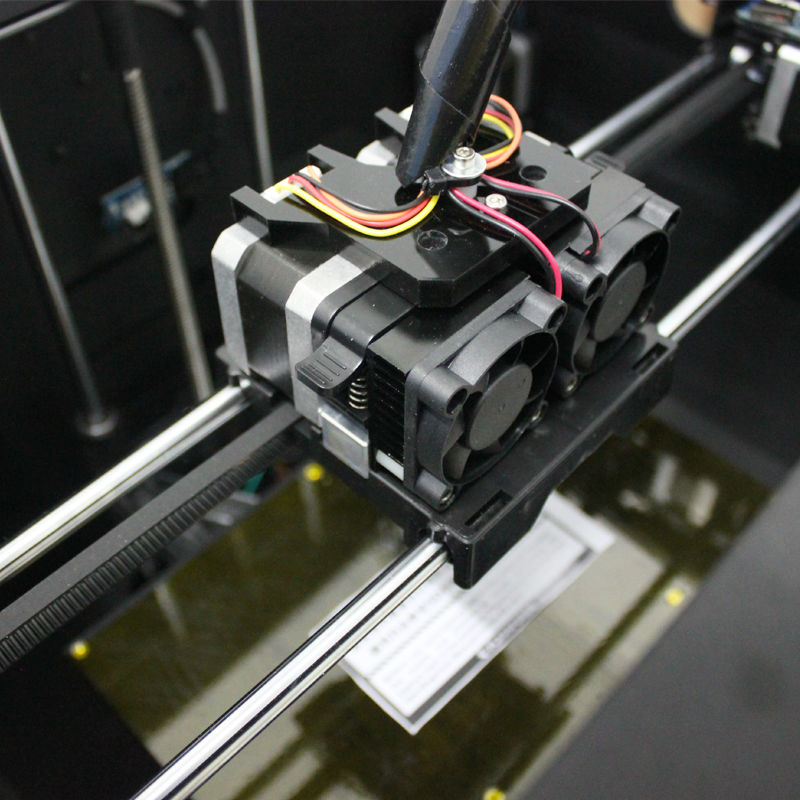
Cold end is:
- Aluminum heatsink with fan, which serves to cool the plastic, preventing it from melting prematurely.
- Thermal barrier that serves to isolate these two elements from each other. Usually it is a stainless steel sleeve, and sometimes plain steel. Stainless steel is still preferable, since it is no worse than ordinary steel in thermal conductivity. By the way, when buying, pay attention to this! Easy to check with a magnet. With a relatively similar weight, stainless steel is not magnetic. The nozzle, on the contrary, should be made of a material that conducts heat well.
Detailed construction and features of the e3dv6 extruder
In our case, we will consider a bowden extruder based on a Chinese copy of e3dv6.
The Chinese copy works as well as the original, but costs several times cheaper. The difference is only in the quality of processing and the materials used. Please note that there is also an older version of e3dv5. They are very similar in appearance, but still have significant differences. I do not recommend taking e3dv5, since e3 dv6 is an improved version of it. The e3dv5 has a larger heatsink and a slightly different heating block. In e3dv6, the thermistor is placed closer to the nozzle than to the heater relative to e3dv5, which provides more accurate control and maintenance of temperature in the area of \u200b\u200bthe plastic, and not the heater.
They are very similar in appearance, but still have significant differences. I do not recommend taking e3dv5, since e3 dv6 is an improved version of it. The e3dv5 has a larger heatsink and a slightly different heating block. In e3dv6, the thermistor is placed closer to the nozzle than to the heater relative to e3dv5, which provides more accurate control and maintenance of temperature in the area of \u200b\u200bthe plastic, and not the heater.
There are versions for different plastic diameters. 1.75 millimeters, which most print or 3 millimeters.
To avoid traffic jams, choose a thermal barrier with a Teflon tube insert for PLA printing. It is smoother and slipperier.
Solid metal is more suitable for printing with nylon, ABS or other plastics that require a higher printing temperature, since the Teflon tube in the middle is already destroyed at a temperature of about 200 degrees. On the Internet they write that the all-metal barrier in the original prints with all types of plastic, since the hole in the middle is well polished and smooth, unlike the Chinese counterpart, in which the hole was drilled with a conventional drill without additional post-processing.