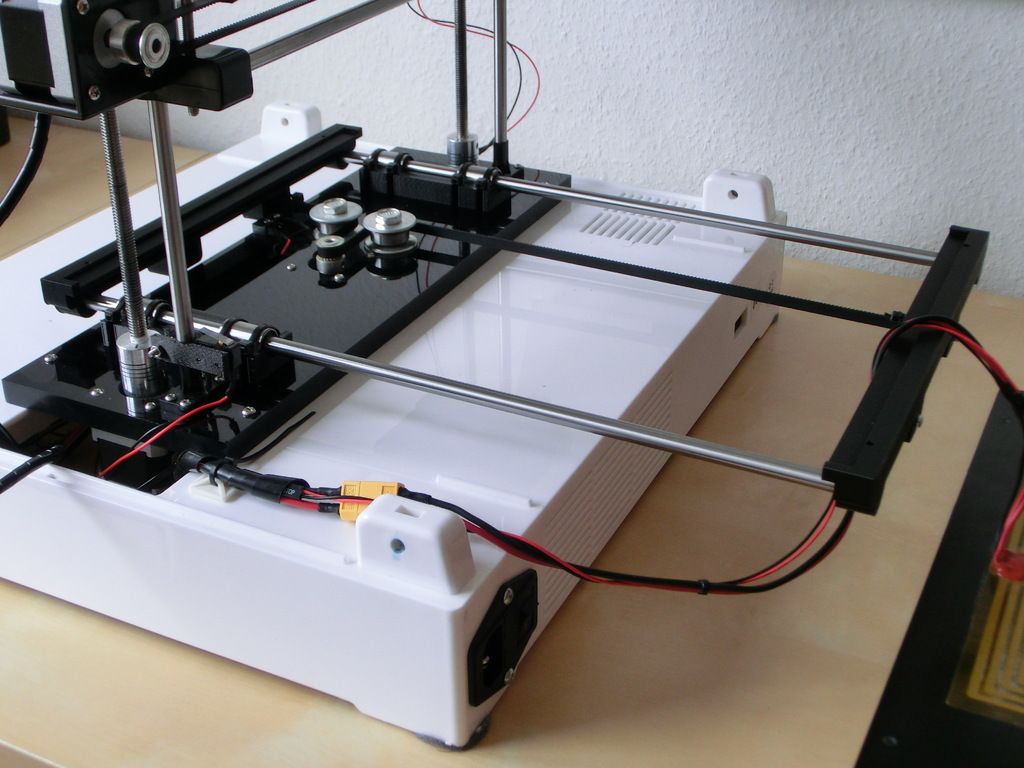
3D printed car part
How To 3D Print Replacement Car Parts [2022 Guide]
If you're looking to create your own car parts, you can do so with ease. Here is a guide on how to 3D print replacement car parts very cheap.
By Justin Evans
As 3D printing technology grows more popular, hobbyists and automotive industry leaders alike are starting to 3D print car parts as an alternative to expensive repairs and manufacturing.
This may seem unbelievable to people outside of the 3D printing space, but it is true. 3D printers can create all kinds of car parts, and they work just as well as traditionally manufactured parts.
There are plenty of reasons why people do this. They may want to personalize their car, make their car lighter, or just replace a part quickly without needing to pay an excessive amount for it.
For people who want to get into it, it is a lot easier than it looks.
Table of ContentsShow
What Kind of Parts Can You Make With 3D Printers?
There are several types of parts that you can use 3D printing to manufacture:
- Cosmetic customization (rear-view mirrors, cup holders, custom frames)
- Small parts (lids, valves, specialized parts)
- Larger parts (grills, dashboards)
While you can make powerful parts with 3D printing (like with carbon fiber), it is not recommended for making internal car parts. These parts must deal with excessive heat or pressure and require a specialized manufacturing process.
So long as you keep the part, your intended material, and what that part is used for in mind, the sky is the limit as far as what you can create.
What Kinds of 3D Printers Are Best for 3D Printing Car Parts?
When 3D printing car parts, the ideal printer can vary depending on what you are trying to print.
For most things, an inexpensive basic printer is fine. Plenty of car parts are small and simple and should not need a heavy-duty machine to do the lifting.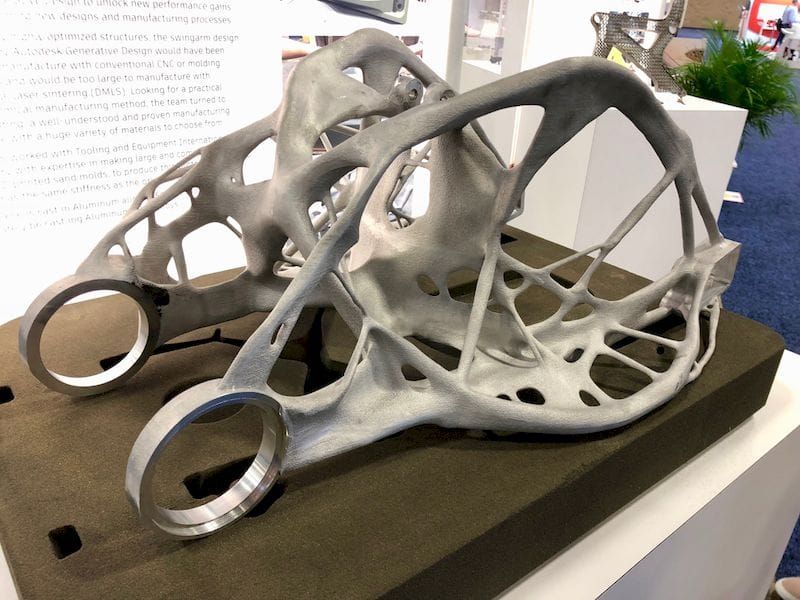
If you plan on printing more complex parts or want intricate engravings on your customized parts, you may want to use a higher-end model that can handle that.
What Materials Should You Use?
There are plenty of materials you can use to 3D print your car parts, but the rule of thumb is they should be durable, lightweight, and flexible.
A few standout materials are:
- TPU (shock-absorbent, flexible, and durable)
- Polypropylene (great for airflow and fluid systems)
- Nylon PA11 (great if you are worried about sustainability)
- Polyamide 6 (heat resistant)
What material you use depends entirely on what part you want to make, so always do your due diligence and research what materials work best for each part before you start printing.
How Do You Go About 3D Printing Car Parts?
3D printing car parts seems complex, but when you get down to it, it is a simple process that only requires a few steps.
Make or Find a Scale Model
This is the most important step of the entire process.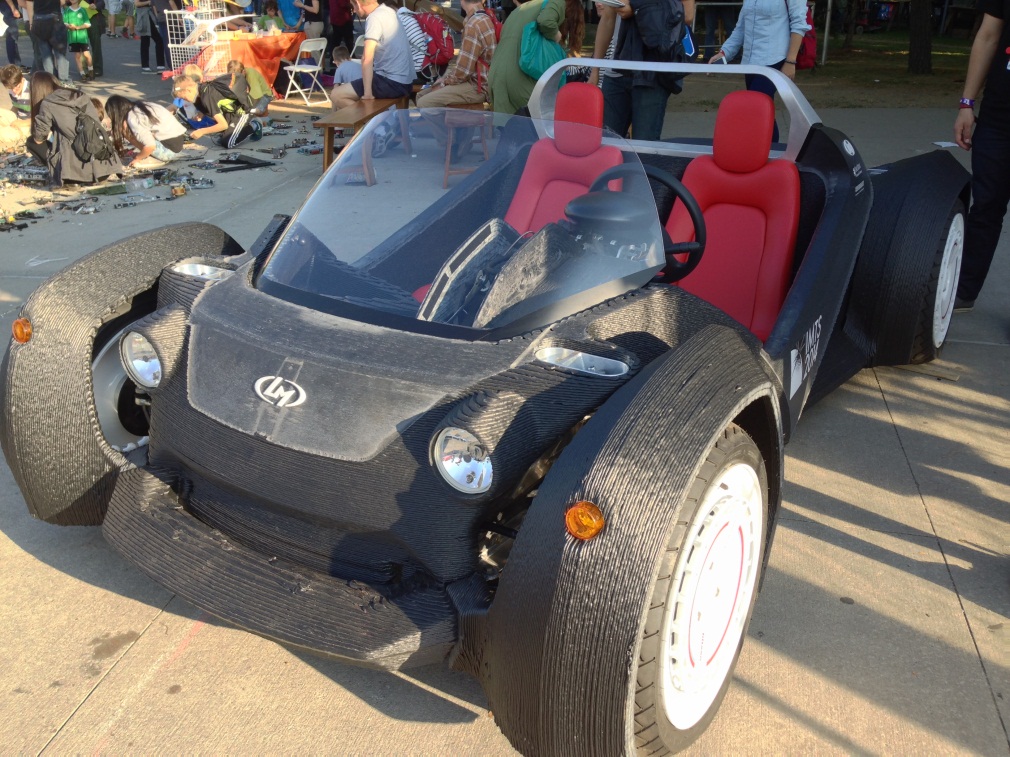 A high-quality 3D printed car part relies on using the proper material and creating it from a good model.
A high-quality 3D printed car part relies on using the proper material and creating it from a good model.
You can set up your scale model in one of two ways. You can make the model yourself using a 3D modeler or find a model online. If you are not confident in your 3D modeling skills, it may be best to find an online model rather than make it yourself.
Many websites offer 3D models for parts that you can download and use with your 3D printer. Make sure the model is from a reputable source for the best results.
Pick Your Material
After picking out your model, the next step is to pick what material you want to use. This will depend entirely on what part you are making and your specific needs.
Remember, materials are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Make sure the material you choose matches your part’s use (heat resistance or flexibility, for example). If you make a part with the wrong material and install it, it can break or damage your car.
Also, keep in mind that just because you can theoretically make engine parts with 3D printing does not mean that you should.
Print the Part
After you have your model and material, it is time to make your part. Make sure the parameters are set the way you want them and double-check everything before printing. Follow the instructions based on your specific printer.
Finishing Touches
Once your part is printed, it is time to add any finishing touches. This is when you paint any small details, like numbers on a knob, or coat the part in another material for a better finish.
You should also use this time to check over the part and make sure everything is up to standard. If there are any defects or issues with the part, you will need to start over.
Install the Part
After printing the part, it is time to install it. This is simple for a part like a cup holder or knob — just pop it in and see if it fits.
If you 3D printed a part like a grill or a dashboard, try going on a test drive first and see how it holds up under a stress test. If it looks like it is not holding up well, it’s time to go back to the drawing board.
What if You Don’t Want to Do It Yourself?
Sometimes 3D printing car parts is not feasible for everyone. A person may want to 3D print a part, but they do not have access to a printer or are not confident in their 3D modeling skills.
In this case, you may want to consider hiring a business that specializes in 3D printing car parts. Be sure to check the business’ rates, selection, and reviews before committing.
Conclusion
3D printing car parts is an easy way to customize and repair your car without breaking the bank. With the right model, materials, and plenty of patience, 3D printing your own parts is a reliable way to take care of your car and make it your own.
There are no limits to what can be done with 3D printing, whether you do it yourself or hire someone else to make the parts for you.
3d Printed Car Parts - Etsy.de
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
(1,000+ relevant results)
5 ways 3D printing is changing the automotive industry / Sudo Null IT News
You can't buy a fully 3D printed car in a car dealership yet, but additive technologies have been used in car design for many years.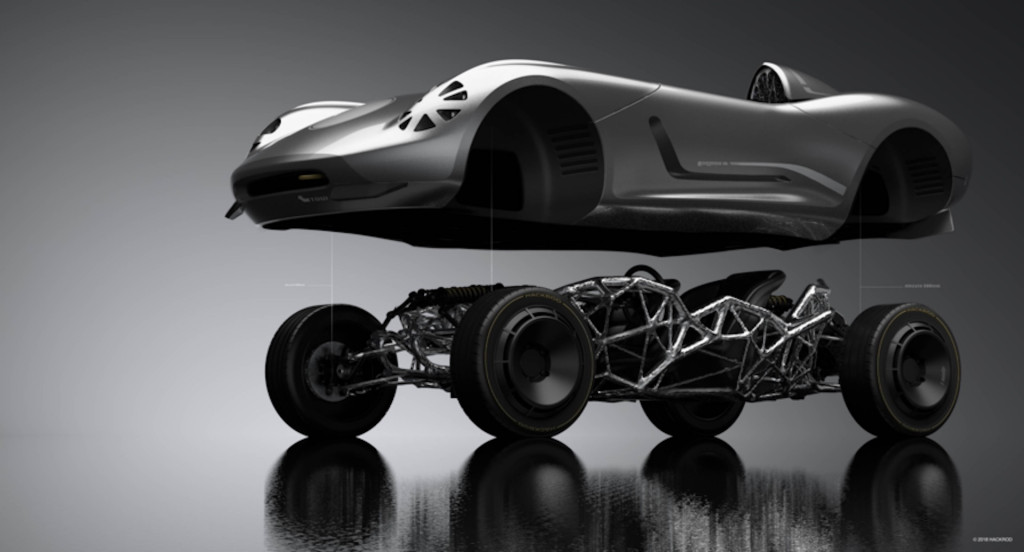 Every year, especially in recent years, 3D printing is taking an increasingly important place at all stages of production. This is evidenced by the rapid growth of 3D printing market share in automotive manufacturing, which is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2023. nine0005
Every year, especially in recent years, 3D printing is taking an increasingly important place at all stages of production. This is evidenced by the rapid growth of 3D printing market share in automotive manufacturing, which is projected to reach $2.5 billion by 2023. nine0005
For example, luxury car companies including Bentley, Porsche, BMW and Ferrari are using 3D printing to create custom car interior parts. GM, Volvo, Ford are using 3D printing to produce tooling to save money, improve designs and reduce delivery times. 3dprinting.com If the first 3D printers cost about $20,000, now you can find 3D equipment for $100. Now companies can, with the help of additive technologies, produce the necessary components directly at their own enterprises and not depend on suppliers. nine0005
With new materials, 3D printers can print high-precision, functional end parts. Additive technologies facilitate the production of custom products and increase productivity.
But this is only the beginning of the journey. Here are five key ways 3D printing is driving innovation in the automotive industry, from car design to production. Plus one bonus.
Here are five key ways 3D printing is driving innovation in the automotive industry, from car design to production. Plus one bonus.
1. Changing the prototyping process
It was with the manufacture of prototypes that the use of 3D printers in the automotive industry began. 3D printed prototypes took much less time than traditional methods required.
Using Raise3D 3D printers and ideaMaker software, Crazy Grandpa Garage was able to automate the process of creating custom car parts. Production costs have been reduced by 50%, design reliability has improved significantly, and lead time has been reduced by 83%. The parts now come out very well fitted to the car. nine0005
Source: facebook.com
Using 3D printing, car designers can quickly prototype individual parts or assemblies, from interior detail to dashboard, or even full-size car models. Thanks to 3D prototyping, the initial idea quickly turns into a physical embodiment of the concept - a conceptual model. The concept can then be developed into full-featured, high-fidelity prototypes, and after several validation steps, mass production begins. For the automotive industry, getting through these steps quickly is vital, and the entire downtime of an automobile production line in just an hour is very costly for the company. nine0005
The concept can then be developed into full-featured, high-fidelity prototypes, and after several validation steps, mass production begins. For the automotive industry, getting through these steps quickly is vital, and the entire downtime of an automobile production line in just an hour is very costly for the company. nine0005
For example, the assembly plant of the US car manufacturer General Motors claims to have saved more than $300,000 by purchasing a 3D printer in 2016.
Ringbrothers designers and engineers are not dependent on third parties to implement laser stereolithography (SLA) in their facility. The cost is reduced, the development time is reduced. Source: formlabs.com
Hose for Eventuri BMW M4, Source: ultimaker.com
Traditional prototyping was time-consuming and costly, in part because the product went through more iterations. With 3D printing, you can create high-quality prototypes in one day and at a much lower cost.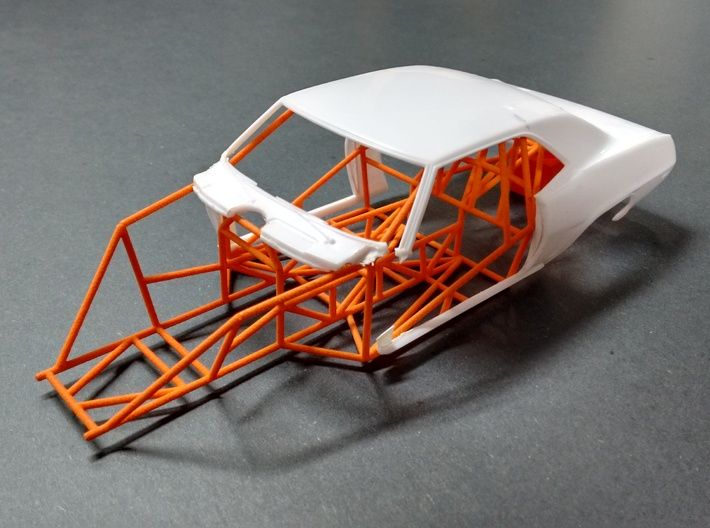 More examples.
More examples.
The Ford Fiesta ST with 3D printed parts, ext. SEMA 2016, ultimaker.com
For example, General Motors has partnered with Autodesk to produce low cost, lightweight automotive parts using 3D printers. Tools, fixtures and fittings can now be produced at a fraction of the cost, according to Autodesk. For example, a 3D printed tool used to align engine and transmission ID numbers costs less than $3 at General Motors. A traditionally produced instrument will cost $3,000. In addition, downtime due to faulty tools can be significantly reduced as new tools are produced in-house. nine0005
2. Creation of non-standard and complex parts
Daihatsu, Japan's oldest car manufacturer, launched a project in 2016 to customize its Copen model.
Source: 3dprint.com
In partnership with Stratasys, Daihatsu customers can design and order custom 3D printed panels for their front and rear bumpers with a choice of over 15 basic patterns in 10 different colors. nine0005
nine0005
Source: 3dprint.com
In Europe, the BMW MINI brand also uses 3D printing to create personalized car parts. Since the beginning of 2018, MINI customers have been able to personalize various trim elements such as the instrument panel, LED treadplates and illuminated bumpers, as well as choose from different colors and textures. These parts are then 3D printed using a range of technologies from DLS Carbon to SLS.
Source: formlabs.com
Volkswagen Motorsport's I.D. R Pikes Peak is designed with over 2000 3D printed test parts.
Source amfg.ai
The use of 3D printers makes it possible to experiment in the development of non-standard designs, reduces the cost of their production. Long production processes for custom-made products are becoming much shorter.
Ringbrothers uses 3D printing to create customized end pieces such as ventilation grilles. Source: formlabs.com
Large companies are merging 3D printing technologies with traditional manufacturing methods. Volkswagen has recreated its iconic 1962 Microbus by replacing the petrol engine with a 120 hp electric one. The Type 20 concept electric minivan has received many improvements using 3D printed parts. These improvements include cast aluminum wheels. Even the wheel hubcaps, while looking like stamped steel, are actually printed on a Formlabs SLA 3D printer, then electroplated and polished. nine0005
Volkswagen has recreated its iconic 1962 Microbus by replacing the petrol engine with a 120 hp electric one. The Type 20 concept electric minivan has received many improvements using 3D printed parts. These improvements include cast aluminum wheels. Even the wheel hubcaps, while looking like stamped steel, are actually printed on a Formlabs SLA 3D printer, then electroplated and polished. nine0005
Source: formlabs.com
Formlabs Form 2 SLA 3D printer specifications
Bentley has used cutting-edge metal 3D printer technology to produce a grille, side vents, door handles and exhaust pipes much more complex than those used on current production models.
Bentley used metal 3D printing to create intricate micron precision parts. Source: formlabs.com
Source: youtube.com
3D printing has also made it possible to create parts that could not be made in any other way.
Bugatti's monobloc brake caliper is a prime example. For some components, Bugatti would have preferred titanium due to its high performance, but processing this metal with traditional methods is expensive and difficult. 3D printing has allowed Bugatti to produce a titanium alloy brake caliper. Due to the thin walls, the caliper turned out to be very light - almost two times lighter than forged aluminum. At the same time, the strength of the 3D-printed monoblock is superior to that of aluminum. The 3D printed titanium monoblock has a tensile strength of 1250 N/mm2. This means that a force of just over 125 kg will be applied per square millimeter of this titanium alloy without tearing the material. The new titanium caliper is 41 cm long, 21 cm wide and 13.6 cm high and weighs only 2.9kg compared to currently used aluminum, which weighs 4.9 kg.
Source: youtube.com
The Bugatti brake monoblock is the industry's largest functional 3D printed titanium component for a car. Source: formlabs.com
Source: formlabs.com
3. Tool making
Various devices help to facilitate and speed up the production and assembly processes, improve the safety of workers. Automotive factories and component suppliers use a large number of non-standard tooling that is specifically designed and optimized for end use. As a result, a lot of non-standard equipment and tools are made, which increases production costs. nine0005
This 3D protective wheel disc was purchased for 800 euros but can now be printed for just 21 euros. Tool development time has been reduced from 56 to 10 days.
Source: ultimaker.com
Delegating custom tooling and fixtures to service providers who machine parts from solid metal or plastic stock can delay production by weeks.
For example, the development and prototype of a commutator motor using traditional manufacturing methods can take up to four months and cost about half a million dollars. Thanks to 3D printing, Ford was able to develop several variants in just 4 days and 99.4% cheaper - only $3,000.
Thanks to 3D printing, Ford was able to develop several variants in just 4 days and 99.4% cheaper - only $3,000.
Source: youtube.com
Additive technologies allow you to complete the task in a few hours and significantly reduce costs compared to ordering from a third-party enterprise. Since increasing the complexity of a 3D printed model does not incur additional costs, products can be better optimized for their application. New elastic materials for 3D printing in many cases allow you to print plastic parts instead of metal or create prototypes on a 3D printer to test the tool before using it in production
Gradually, the production of 3D printed accessories and tools is becoming one of the largest applications of additive technologies.
Pankl Racing Systems uses 3D printed fixtures to fasten workpieces to a conveyor belt. Source: formlabs.com
For example, Pankl Racing Systems uses a stack of multiple Formlabs SLA 3D printers to make critical manufacturing tools. The multi-stage production of parts for transmissions on automatic lathes requires a series of fixtures and tools designed for each specific part. nine0005
The multi-stage production of parts for transmissions on automatic lathes requires a series of fixtures and tools designed for each specific part. nine0005
With the help of 3D printing, Pankl's engineers have reduced the production time for the aids by 90%, from 2-3 weeks to around 20 hours. Costs were also reduced by 80-90%, saving $150,000.
The transition to 3D printing has enabled Volkswagen Autoeuropa to cut tooling development costs by 91% and cut tooling times by 95%.
4. Troubleshooting spare parts
Spare parts have always been a problem for the automotive industry. The demand for them is either there or not, so the production of spare parts is not economically viable, and the storage of pre-fabricated replacement components is also costly. But if there are no repair parts available, difficulties arise and the main product becomes less valuable. nine0005
3D printing could solve the problem of parts in the automotive industry in many ways. The main factors are printed materials, which can match the characteristics of traditional materials used in parts and be cost-effective. There are prerequisites for this.
The main factors are printed materials, which can match the characteristics of traditional materials used in parts and be cost-effective. There are prerequisites for this.
Using computer-aided design, drawings of all parts can be stored digitally, so there is no need to store the parts themselves. The parts needed by the client can be printed on a 3D printer right in the workshop. nine0005
Even obsolete parts whose blueprints have not survived can in principle be recreated by making a 3D scan of existing parts of this type and applying reverse engineering (reverse engineering). You can read more about this on our blog. Old projects can take on new life. There are many lovers of vintage cars, with the help of 3D printing it would be possible to create parts for them.
Ringbrother 3D printed the Cadillac emblem for a custom built old car. Source: formlabs.com
5. Production of standard parts
As 3D printers and materials for 3D printing become more affordable, a gradual transition to the production of mass-produced automotive parts using additive technologies is possible.
3D printing makes it possible to combine components into a single whole. Let's say there is a mechanism assembled from six or seven car parts that can be combined into one printed part. It will save time and assembly costs. With 3D printing, it is also possible to reduce the weight of the combined assembly, as a result, the car will use fuel more efficiently. nine0005
3D Systems has designed an advanced exhaust pipe for a sport bike. In the image below, you will see 20 sheet metal and hydroformed parts needed to assemble the original exhaust pipe. On the right is a monolithic exhaust pipe that does not require assembly, made using metal 3D printing.
Source designnews.com
The 3D printed tube was produced using Grade23 titanium in just 23 hours, compared to three weeks for traditional production. Design development time reduced from 6 weeks to 6 days. Additive manufacturing also eliminates the need for tooling, fixtures, multiple welding and multiple inspections. nine0005
nine0005
Geometry optimization has reduced the amount of material needed for maximum productivity. All elements of the original exhaust pipe are incorporated into the new design and, when printed with a typical wall thickness of 0.5mm, the 3D printed exhaust pipe is about 25% lighter than the original one.
A wide range of 3D printing materials is starting to meet the requirements of various vehicle components. Since additive methods reduce costs compared to traditional methods (such as molding and injection molding), it makes a lot of sense from a production and financial point of view to further introduce 3D printing into the production of basic parts. nine0005
Volkswagen, one of the world's largest and most innovative car manufacturers, is using an HP Metal Jet 3D printer to produce high-performance functional parts with special design requirements, such as shift knobs and mirror mounts. Volkswagen's long-term plans to work with HP include accelerating the production of mass-customized parts such as key rings and exterior nameplates.
Source: youtube.com
+1. 3D printed cars
While 3D-printed cars have yet to hit the market, there are some interesting designs and concepts that can suggest a possible direction for the automotive industry.
Light Cocoon . German engineering firm EDAG was clearly inspired by nature to create the 3D printed supporting structure of the Light Cocoon concept car. The frame resembles the veins of a tree leaf or its branch. Despite the fact that the design of the EDAG took less material than a conventional frame, all the strength requirements for structurally significant components are met. Outside, the case is covered with a lightweight and durable waterproof fabric. nine0005
The cover protects the EDAG Light Cocoon from bad weather and gives the car a unique personality. Source: formlabs.com
Blade . Blade ("Blade") announced as "the world's first 3D-printed supercar. " It meets supercar standards but is made from inexpensive materials: carbon fiber tubes and aluminum rods, combined with 3D printed metal parts. Blade turned out to be very light and does not take long to assemble. nine0005
" It meets supercar standards but is made from inexpensive materials: carbon fiber tubes and aluminum rods, combined with 3D printed metal parts. Blade turned out to be very light and does not take long to assemble. nine0005
The world's first 3D printed Blade supercar. Source: formlabs.com
Strati . The American company Local Motors 3D printed and assembled the Strati electric car right at the exhibition stand, in just 44 hours. Most of the components were printed - the body, seats, interior parts. A car is made up of less than 50 assemblies, far fewer than the thousands of parts that go into a traditional car. The company intends to reduce the print time to 10 hours. nine0005
The Strati from Local Motors consists of less than 50 individual parts*. Source: formlabs.com
LSEV. Developed by the Italian company XEV, the LSEV could be the first in the 3D printed electric vehicle market when it goes on sale. The 3D printed chassis, seats, windshield and all visible parts of the LSEV. Thanks to the active use of 3D printing, the number of components was reduced from 2000 to just 57, resulting in a very lightweight design. The electric car weighs only 450 kg. nine0005
Thanks to the active use of 3D printing, the number of components was reduced from 2000 to just 57, resulting in a very lightweight design. The electric car weighs only 450 kg. nine0005
The LSEV is the first 3D printed electric vehicle to hit the market in 2020. Source: formlabs.com
While most of these and many other 3D printed car projects remain at the concept stage, the extent to which 3D printing has penetrated various areas of the automotive industry is striking. In some cases, additive technologies provide new opportunities for design and production, in others they reduce production costs and save time. nine0005
See also:
3D printer and CNC race car manufacturing
3D scanning of cars in tuning and repair
Printed parts: can auto parts from a 3D printer replace traditional ones?
It's the 21st century - technological progress in the automotive industry is advancing by leaps and bounds and adjusting the world of auto parts production for itself. Even 30 years ago, we could not even imagine that we would be able to order parts for cars via the Internet and pick them up online in a matter of minutes, but today we have already found a lot of shortcomings in this. Parts often turn out to be not what we expect, spare parts of poor quality, fakes come across. In addition, you often have to wait a long time for an order or until the desired product appears at the seller, etc. nine0005
Even 30 years ago, we could not even imagine that we would be able to order parts for cars via the Internet and pick them up online in a matter of minutes, but today we have already found a lot of shortcomings in this. Parts often turn out to be not what we expect, spare parts of poor quality, fakes come across. In addition, you often have to wait a long time for an order or until the desired product appears at the seller, etc. nine0005
But this situation is about to change thanks to the invention of the 3D printer. Surely, many have already heard about 3D printing technology, and so - today it is already successfully used to create auto parts from plastic and metal. But if plastic parts have been mass-printed for a long time, then in the recent past, at the factories of the Daimler-Benz automobile concern, 3D printing was used for the industrial production of metal parts, and today thermostat housings are produced using this method. nine0005
It turned out that the new technology is much more efficient than the traditional one, since the part does not require additional processing, and, accordingly, the time and financial costs for its production are reduced. It seems that soon the technology will become more accessible and will be used everywhere, so we decided to discuss this issue in more detail.
It seems that soon the technology will become more accessible and will be used everywhere, so we decided to discuss this issue in more detail.
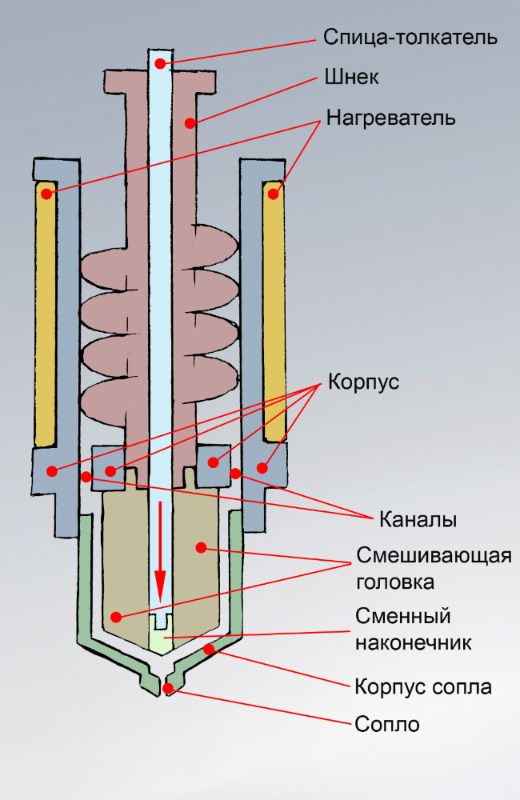
How does the technology work?
The principle of operation of a 3D printer is to create a three-dimensional object by repeatedly layering the material. In order to obtain the desired shape, it is necessary to build a computer model of the future part. You need highly specialized knowledge and appropriate software. A model created on a computer is a kind of pattern; it serves as the basis for creating a finished product. nine0005
In this way, it is possible to manufacture new parts with improvements and modifications, based on old parts, the main thing is that there is a drawing of them. However, with the help of 3D scanning, you can quickly and easily recreate a computer model of a part from an existing part or part. Using technology, you can add or remove some elements of the part, strengthen weak points, etc.
It turns out that 3D technologies will help to simplify production, as many of the additional steps used in traditional methods (in particular, casting and machining) will be skipped. This means that in such production, the cost of a part can be even lower than in traditional production. And now we smoothly approached the issue of price. nine0005
This means that in such production, the cost of a part can be even lower than in traditional production. And now we smoothly approached the issue of price. nine0005
Will printed parts be more cost effective?
3D printing technology has not yet found wide application in the modern car market, so its cost is initially much higher than traditional. However, with the development of this method, it is becoming cheaper. And now the price of such a seal is rapidly approaching the public.
Why is it more profitable than the traditional method of manufacturing auto parts?
First, as we said, some steps in production are skipped. Casting and machining require additional time and money. And 3D printing makes it easy. nine0005
Secondly, in traditional manufacturing, a lot of factors affect the final cost of a part: cost, expected margin, various logistics costs, storage. The price is rising. Traditional production can be profitable with large volumes of output. But niches remain where it is much more efficient to produce a small number of parts “here and now”.
All you need for this production:
- Material,
- Printer, nine0302 Computer 3D model of the part.
The ideal scheme is brought to life - from the drawing directly into the finished product. Creating plastic or thin-walled metal parts on a printer is also more profitable than casting them. 3D technologies are able to completely turn the usual vision of the process of manufacturing auto parts.
Minimal production costs and low alloy wastage make 3D printing very profitable, even though alloys are more expensive than traditional printing. The finished part is cheaper, but its characteristics are the same as the usual one, or even better, depending on the technology. nine0005
What materials are used for 3D printing?
Of course, most of the 3D printers today create plastic parts. But in different areas, a wide variety of metal alloys and even some types of concrete are used. In the automotive industry, of course, the most interesting materials are plastic and metal: steel, aluminum, copper.
Consider all the metals that are successfully used for 3D printing today.
Titanium
This is one of the most popular metals in 3D printing because of its high strength. It is especially in demand in the field of creating prostheses, as well as in the space and aircraft industries. It is these areas that are the most progressive in terms of the application of this technology. nine0005
Stainless steel
This material is great for 3D printing. Compared to non-ferrous metals, it is advantageous in price, although it remains more expensive than cheap steel. It is a very durable metal, due to which it is actively used in a variety of fields.
Aluminum
Allows for lightweight, corrosion resistant parts. It is easy to process, cheap, and therefore is actively gaining popularity as a material for three-dimensional printing. It is important that inexpensive printers that are available to many small businesses today work with it. Its only disadvantage is the explosiveness in the form of a powder. nine0005
nine0005
Cobalt Chromium and Inconel
These alloys are highly specialized. They are designed for printers used in dentistry, medicine, and aerospace. New specialty materials are emerging as 3D printing technologies evolve and provide opportunities for different business areas.
Copper, gold, silver
Common in the jewelry industry. Copper and silver are used in electronics.
Technologies for 3D printing of auto parts
There are several technologies. Each of them has a different principle of operation, cost and gives a different quality of parts at the output. But all of them are successfully used in modern automotive industry.
EBM and DED
The most commonly used technologies in mass production. They are also the most expensive. EBM stands for Electron Beam Melting - electron beam melting. During this process, the metal powder is exposed to a controlled electron beam. This flow melts the powder exactly along the contour of the model, thus forming the part.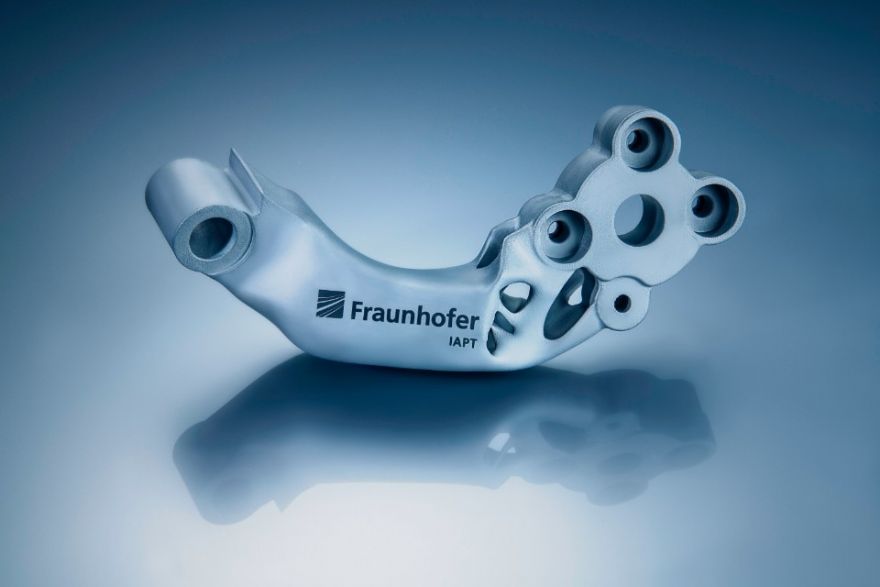 nine0005
nine0005
DED stands for Directed Energy Deposition and translates as "direct deposition". With this technology, the building material (metal powder) and the energy for its fusion are supplied simultaneously to the place where the model is built. The energy is a laser or electron beam.
What can be achieved with these technologies:
- High strength parts;
- Metal quality better than cast;
- Ideal homogeneous structure; nine0303
- High manufacturing precision;
- Ability to create a part from scratch or restore an existing one;
- Ability to change and modify the product.
SLM and SLS
SLM stands for selective laser melting. This technology is used more widely, although it is less accurate than the previous two.
Interesting fact: Mercedes-Benz uses this technology to manufacture many spare parts. Moreover, the automaker plans to create parts in this way not only for new car models, but also for existing lines. Thus, replacing old spare parts for foreign cars, you get an original created using the latest technology. nine0005
Thus, replacing old spare parts for foreign cars, you get an original created using the latest technology. nine0005
SLS, or selective laser sintering, is the same technology, only it is used for plastic parts and translates as "laser sintering".
Both technologies work on the same principle: layer-by-layer melting of the powder under the influence of a laser beam. What is the result:
- Homogeneous composition of the part;
- Mechanical characteristics as cast;
- High precision geometrically complex parts.
DMLS
Direct Metal Laser Sintering The laser acts on the metal powder, the layer of which is leveled in the working chamber, melting it and creating the necessary geometric shape. Then the next layer of powder is fed, it melts, connecting with the previous one. This is how the detail is created layer by layer. The unmelted powder remains in the chamber and can then be collected and reused, making the technology waste-free. nine0005
nine0005
Advantages:
- Allows the creation of geometrically very complex parts;
- It is possible to manufacture several parts at the same time;
- High precision finished products;
- There is no need to build supports for overhanging elements - its role is performed by unspent powder in the chamber;
- The process takes less time compared to previous technologies.
This technology is used to build some parts in the Super Draco engine from Elon Musk's company. Inconel alloy powder was used as the material. nine0005
Binder Jetting (DoP)
Also known as Drop on Powder. Its principle of operation differs significantly from those listed above. Thin layers of powder are interconnected by a special binder, that is, the particles of the material are simply glued together.
This 3D printing is much cheaper and suitable for small production volumes. It is effective not only in working with metals and plastics, but also, for example, with gypsum and sand.