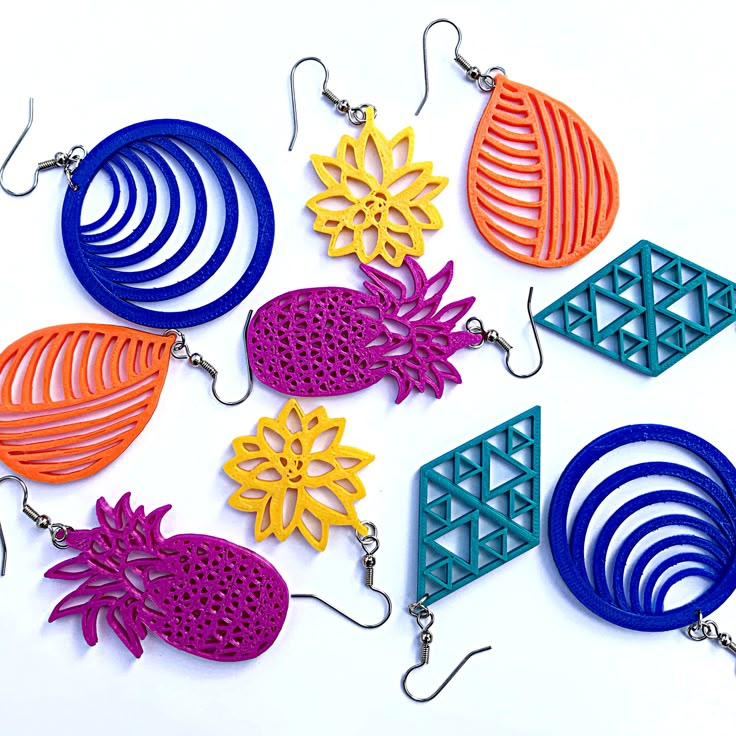
3D print flower stl
Flower Stl Model - Etsy.de
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
( 808 relevant results, with Ads Sellers looking to grow their business and reach more interested buyers can use Etsy’s advertising platform to promote their items. You’ll see ad results based on factors like relevancy, and the amount sellers pay per click. Learn more. )
3d Printed Flowers - Etsy.
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
( 1,000+ relevant results, with Ads Sellers looking to grow their business and reach more interested buyers can use Etsy’s advertising platform to promote their items. You’ll see ad results based on factors like relevancy, and the amount sellers pay per click. Learn more. )
Requirements for 3D Models for 3D Printing and CNC Machining
01/16/2017 in 3D Modeling Instructions
Contents:
- Introduction
- Product creation process.

- Requirements for models for 3D printing and CNC processing.
- Fixing non-critical bugs with NetFabb.
- Fixing non-critical bugs with MeshMixer.
- Fixed non-critical bugs with Materialize Magic.
- Examples of the most common errors.
Introduction.
In this article, we will talk about the basic and general parameters that a model must meet in order to obtain high-quality 3D printed products. Let's discuss common errors that occur in the process of creating three-dimensional models in terms of a high-quality polygonal mesh and how to quickly fix them. Requirements for 3D models and quality issues in terms of the accuracy of manufactured parts are described in another article: The actual size of the product after 3D printing.
The process of creating a product.
Structure of the additive manufacturing process for the production of products:
| Designer / 3Dartist | 3D printing service | Discussed errors |
1. Creating a 3D model Creating a 3D model | ||
| 2. Export/convert 3D model to required format | 3. Model validation | 4. Compliance / non-compliance with the minimum allowable thicknesses. |
| 6. Preparation of control program for 3D printer (GCode) | 5. Compliance / non-compliance with the requirements for the polygonal mesh of the 3D model. | |
| 7. 3D printing process. | ||
| 9. Quality control. | 8. Post-processing process. |
In accordance with the presented algorithm, at the first stage of product creation, a 3D model is developed using modeling programs in accordance with the terms of reference and the requirements of standards. After that, it is necessary to export the data of the simulation result program file to a format accepted by the program of the additive manufacturing control machine (for example, “STL”). The modeling process can now be done not only in solid format, but also immediately in STL. Before the next stage, possible defects in the model are identified. A model intended for 3D printing must be hermetic, monolithic and not contain cavities and gaps in the walls, which is ensured using special programs. Next, the information from the STL file is converted into commands, following which the 3D printer produces a product, this is the so-called GCode.
Before the next stage, possible defects in the model are identified. A model intended for 3D printing must be hermetic, monolithic and not contain cavities and gaps in the walls, which is ensured using special programs. Next, the information from the STL file is converted into commands, following which the 3D printer produces a product, this is the so-called GCode.
During this procedure, you should select the desired scale of the part, the correct position in space, and accurately position the model on the work surface. The result of the whole process, strength, surface roughness of the part and material consumption depend on this . After the settings are made, the model is divided into layers of material, which are “fitted” into the body of the part in one working cycle of the additive machine. This process is called slicing. Slicing is done using the software supplied with the machine, or using special tools (Simplify, Skein-forge, Slic3r, KISSlicer, MakerWare, etc. ). The G-code obtained in the previous step is transferred to the 3D printer via flash memory or via a USB cable. In the process of preparing and setting up the additive machine, calibration, preheating of the working bodies, selection of the model material and setting the parameters of the equipment operation modes that depend on it are performed. On professional level devices, this step can be combined with the slicing process procedures. After all the preparatory operations are completed, the printing process starts, that is, the layer-by-layer combination of materials. Its duration depends on the type of technology and the selected parameters for the accuracy and quality of the part.
). The G-code obtained in the previous step is transferred to the 3D printer via flash memory or via a USB cable. In the process of preparing and setting up the additive machine, calibration, preheating of the working bodies, selection of the model material and setting the parameters of the equipment operation modes that depend on it are performed. On professional level devices, this step can be combined with the slicing process procedures. After all the preparatory operations are completed, the printing process starts, that is, the layer-by-layer combination of materials. Its duration depends on the type of technology and the selected parameters for the accuracy and quality of the part.
Requirements for models for 3D printing and CNC processing.
- List of file formats by 3D technologies.
- FDM (ABS, PLA, FLEX, HIPS, etc.): .STL .OBJ
- SLS (polyamide): .STL .OBJ
- SLA, DLP (photopolymer): .
 STL .OBJ
STL .OBJ - SLM (metal): .STL+STP(STEP) .OBJ+STP(STEP)
- Multicolour plaster: .OBJ+texture .WRL+texture
- Polygon mesh.
- The mesh must be uniform and closed. A model consisting of several polygonal meshes is not allowed! Intersection of polygonal meshes is not allowed! Holes in the grid are not allowed!
- Multiple models in one file are not allowed. Each object needs to be saved as a separate file.
- The number of polygons must not exceed 500,000.
- Wall thickness must be at least the specified values for each technology.
- Inverted normals are not allowed! The outer normal should face outward. This problem is especially common when mirroring the model in some 3D modeling programs.
- The dimensions of the model must correspond to the dimensions of the real object.
In 95% of cases, errors in files are not critical and can be easily fixed using specialized programs that can be easily found on the Internet. Even if you are sure that everything is in order with the model, it does not hurt to check it once again for correctness.
Even if you are sure that everything is in order with the model, it does not hurt to check it once again for correctness.
NETFABB - as a solution to most file errors.
MESHMIXER is a powerful and convenient alternative.
- Wall thickness analysis of the model.
It should be understood that there are several 3D printing technologies. They differ not only in the materials used, but also in the accuracy of the equipment. Different equipment has its own resolution. Therefore, before sending the file for printing, it is necessary to make sure the quality of the model in terms of the specified thicknesses in the walls, rods, mesh ceilings. Detailed article about checking models for thickness.
Fixing non-critical bugs with NetFabb.
NETFABB (download for PC or download for Mac) is a program that allows you to solve almost any issue related to 3D printing. Let's go through the main functions of this software, which AutoDesk itself bought at one time.
The program shows the outer part of the polygon in green, its inner normal in red. Ideally, the model should be all green. If you observe red spots, then these are polygons that are turned outward. If the entire model is highlighted in red, then the entire mesh is turned inside out.
Even if the model is green, but there are errors in your file, the program will display a big exclamation mark in the lower right corner of the screen, and will also not be able to calculate the volume of your model.
To treat the model, click on the red cross on the toolbar at the top of the screen. The program will put you into the treatment mode, and will indicate in yellow the breaks in the polygonal mesh, if any.
This program has functions for removing or adding polygons, changing sizes or proportions. (I will leave these functions for independent study). I recommend that you study the entire toolbar in order to easily understand how, where and which polygons we can select and what we can change.
To invert normals, select the polygons that look “in the wrong direction” and click on the “invert normals” button. Then click on the “Apply Repair” button.
If your model was initially all green or inverting the normals didn't remove the exclamation mark, and the volume has not yet been calculated, you need to apply automatic treatment. To do this, go back to the treatment mode by clicking on the red plus. In the treatment mode, select "Automatic treatment", then select "Default Repair" and click "Extrude".
The program has now done its best to repair the model automatically. Click "Apply Repair".
Typically, these steps should have fixed your model. If after the performed operations an exclamation mark is on and there is still no volume, then you are among those 5% when the model has critical errors and errors are laid down at the modeling stage.
Fixing non-critical bugs with MeshMixer.
Autodesk MeshMixer is a free program for working with 3D mesh models. You can download the program from the link. The program does not have tools for creating 3D models, but a wide range of tools for modifying them and preparing them for 3D printing. The main difference between this software and NETFABB is that MESHMIXER officially supports the latest versions of macOS. For me, this is a decisive factor, because I always carry a MacBook with me, and a Windows computer is only in the office. In turn, NetFabb stopped supporting software for macOS.
You can download the program from the link. The program does not have tools for creating 3D models, but a wide range of tools for modifying them and preparing them for 3D printing. The main difference between this software and NETFABB is that MESHMIXER officially supports the latest versions of macOS. For me, this is a decisive factor, because I always carry a MacBook with me, and a Windows computer is only in the office. In turn, NetFabb stopped supporting software for macOS.
As in the case of Netfabb, you need to drop the model in STL format into the MeshMixer program window.
At first glance, the model looks good, but let's try to test it for suitability for 3D printing (mesh requirements). To do this, you need to analyze the model for errors. To do this, go to the “Analisis” section, then click on the “Inspector” button.
On the screen, we see how the program has highlighted areas on the model with bright colors that do not meet the requirements, which means they have errors.
In order to fix (cure) these errors, click on the “Auto Repair All” button. The program will try to remove errors automatically. Checking before 3D printing is a must. Even if outwardly the model seems suitable to you, it is still worth checking. In the picture below, you can see the errors that are inside the mesh, although everything looks good with the model.
However, this treatment does not always help. For example, if the model has a huge number of errors that the program is not able to remove automatically, then you will have to correct the model yourself in the program where the model was originally created. In case of a large number of errors, the program will indicate their presence even after you have tried to do automatic treatment. The picture below is an example of a very large number of shortcomings and errors that the program is not able to remove by itself.
This usually happens when the model is being prepared for rendering rather than 3D printing. That is, there is a huge number of surfaces, but they are not connected into a single grid.
That is, there is a huge number of surfaces, but they are not connected into a single grid.
Fixing non-critical errors with Materialize Magic
The 3D model healing feature in Materialize Magic is located in the Fix tab.
After that, select the “Correction Wizard” command. Next, you need to alternate the “Update” and “Autocorrect” buttons.
Do this several times. Sometimes for a long time. Until the moment when the number of errors becomes minimal or disappears altogether.
After the update, the result shown below can be considered successful. All checkboxes must be green.
Complete the treatment by following the recommendations and save the corrected model!
A very important point! Treatment in automatic mode occurs according to the principle of adding or removing polygons. Therefore, after automatic treatment, fully check the model for the correct form. Suddenly, the program removed something or added something superfluous.
Suddenly, the program removed something or added something superfluous.
Finally, the final model must be checked for wall thickness. All programs described in this article support this feature.
Let the video card help you in learning 3D modeling programs. =)
Examples of the most common mistakes.
Too thin walls in the 3D model on extruded parts.
Multiple sections less than 1 mm thick
Reversed polygons, infinitely thin walls
Error converting to STL format, low polygonality
Inverted polygons, infinitely thin walls
Inverted polygons, polygons overlapping each other
Extra garbage from polygons
Poor quality 3D scanning without result processing
Tags: 3D printing, 3D printer, 3D printers, 3D scanning, netfabb, Additive technologies, Parts, Inventions, Hardware
20 best and free 3D printing and 3D printer software
Looking for 3D printing software? We've rounded up the top 20 software tools for beginners and professionals alike. Most slicers are free.
Most slicers are free.
What is a slicer? This is a program for preparing a digital model for printing. Models for 3D printing are usually distributed in STL files. To turn an STL file into G-code (a language that a 3D printer understands), a slicer program is required. It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
Which slicer should I choose? In this article, we will tell you which slicer is best for 3D printing for each stage of your work. Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Don't be afraid: we've answered all of these questions, including the required skill level for each program and where you can download it. The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
- Cura
- CraftWare
- 123D Catch
- 3D Slash
- TinkerCAD
- 3DTin
- Sculptris
- ViewSTL
- Netfabb Basic
- Repetier
- FreeCAD
- SketchUp
- 3D Tool
- Meshfix
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
- Blender
- MeshLab
- Meshmixer
- OctoPrint
#1: Cura
For beginners who need a slicer to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Cura is the default slicer software for all Ultimaker 3D printers, but can be used with most others , including RepRap, Makerbot, Printrbot, Lulzbot and Witbox. The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
This program is very easy to use and allows you to manage the most important 3D printing settings through a clear interface. Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings./cncBR62-500x500.jpg) If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Cura can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: Cura
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No.2: CraftWare
For beginners to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Another manufacturer developed slicer software 3D printers by the Hungarian startup CraftUnique to support their CraftBot crowdfunding machine. However, the program works with other printers.
Like Cura, CraftWare allows you to switch from "Easy" to "Expert" mode, depending on how confident you feel. It's a colorful app that features a visual G-code visualization with each function represented by a different color. But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
Please note, however, that this program is still in beta, so bugs may occur.
Download: CraftWare
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#3: 123D Catch
-systems, smartphones and tablets, which allows you to convert images of objects into a 3D model. Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
You need many photos of the object from different angles - the more the better - after which they will be compiled into a 3D model.
123D Catch is more of a fun app than a professional 3D printing tool, but after some tambourine dancing, you can get good results, especially when paired with an STL editor like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Android, iOS, Windows Phone
#4: 3D Slash
and surprisingly simple, and refreshingly new. With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
You can start with a large block and, like a virtual sculptor, remove small cups from it with tools such as a hammer or drill, or start from empty space and build a model from cubes and other shapes. You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
Other features worth mentioning are tools for creating logos and 3D text. The Logo Wizard imports an image and creates a 3D model, while the Text Wizard allows you to enter and format text, and then turn it into 3D.
Recommended!
Download: 3dslash.net
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux, Browser
#5: TinkerCAD
- A computer-aided design (CAD) system for 3D printing, which is a good starting point for beginners. Since its capabilities are limited compared to Blender, FreeCAD and SketchUp, many users switch to more powerful tools after some time.
As in 3D Slash, here you can build models from basic shapes. At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
Come in: Autodesk TinkerCAD
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#6: 3DTin
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
another easy and intuitive online tool choice for beginners in 3D modeling. All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
Choose from a huge library of 3D shapes and add them to your sketch. All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
Enter: 3DTin
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#7: Sculptris
clay. This is a fantastic 3D modeling program if figurines are your main task. For example, you can make a bust of your favorite video game or comic book character. Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Download: Pixologic Sculptris
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#8: ViewSTL
For beginners who want to view STL files
Using ViewSTL is the easiest way to view STL files . Simply open a web page and drag the STL onto the dotted box.
The STL online viewer allows you to display the model in one of three views: flat shading (for a quick view), smooth shading (for a high-quality image), and wireframe.
Enter: ViewSTL
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#9: Netfabb Basic
some nice features that allow you to analyze, "repair" and edit STL files before moving on to the model cutting stage.
A good choice if you need more than just a slicer and want to be able to quickly fix STL files without having to learn programs like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Don't let the 'Basic' in the name fool you, Netfabb Basic is actually a very powerful 3D printing tool. It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
Download: netfabb.de
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No. 10: Repetier
For advanced to prepare STL files for 3D printing
9002 the next level of 3D printer slicer software, but if you want to stay open source, you should look into Repetier. It is the great grandfather of 3D printing software and a favorite of the RepRap community. Today the program is moving by leaps and bounds from the level for beginners to advanced users. Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
What's more, Repetier Host works remotely via Repetier Server, so that the 3D printer can be controlled via a browser, tablet or smartphone.
Download: Repetier
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#11: FreeCAD
The program is a great option for developing your design skills. More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
Download: freecadweb.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#12: SketchUp
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
SketchUp is the perfect combination of simplicity and - the perfect combination functionality, with a user-friendly interface and a relatively flat learning curve (i. e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
The Make SketchUp version is free and will have everything you need for 3D modeling if you also download and install the free STL exporter. There is also a professional edition for architects, interior designers and engineers.
Download: sketchup.com
Price: Free (SketchUp Make), $695 (SketchUp Pro)
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#13: 3D-Tool Free Viewer
view and check STL files
3D-Tool Free Viewer is a sophisticated tool that, among other things, allows you to check the structural integrity and printability of your file. With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
Download: 3D-Tool
Price: Free
Systems: PC
#14: Meshfix
your model for errors.
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#15: Simplify3D
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing print. A flexible algorithm checks the model for problems, fixes them, shows a preview of the printing process (ideal for identifying potential problems), and then slices it.
This slicer offers the best infill pattern options in the competition. For models that require supports, Simplify3D will create the appropriate structures on its own and give you full control over their placement. For printers with a dual extruder, when printing with different materials, the Dual Extrusion wizard will help, as a result of which, for example, it will be easier to remove the dissolving filament.
Simplify3D supports 90% of today's commercially available desktop 3D printers and is compatible with Marlin, Sprinter, Repetier, XYZprinting, FlashForge, Sailfish and MakerBot firmware. Simplify3D can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: simplify3d.com
Price: $149
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#16: Slic3r
source code, which has a reputation as a carrier of super new functionality, which you will not find anywhere else. The current version of the program is able to show the model from multiple angles, so that the user gets a better preview experience.
There's also an incredible 3D honeycomb infill, the first of its kind that can extend over multiple layers rather than repeating itself like a stamp. This significantly increases the strength of the internal filling of the model and the final printout.
Another option is direct integration with Octoprint. Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Download: Slic3r
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#17: Blender
For professionals who want to create 3D printable models
Blender is a popular computer-aided design (CAD) system with a steep learning curve. Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
In short, Blender is one of the most powerful tools in existence. Its community is always ready to help, there are a lot of educational materials. It's also open source, so enthusiasts often write extensions to make it even better and more powerful.
Download: blender.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#18: MeshLab
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing
MeshLab - advanced editor. It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#19: Meshmixer
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing files. It's especially good for identifying potential problems and fixing them automatically.