Wiki 3d printers
3D printing - Wiki | Golden
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing or additive layer manufacturing, is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a digital 3D model. The name additive manufacturing comes from the differentiation of 3D printing, which adds material layers upon each other to build an object, from the more traditional process of subtractive manufacturing, which removes material through milling, machining, carving, and shaping to create an object.
Traditionally, subtractive manufacturing has been used for high production volume manufacturing, while additive manufacturing has been reserved for prototyping and rapid tooling. However, the increased cost-effectiveness of additive manufacturing, the reduction of material waste, and the increased mainstream adoption of 3D printing systems has increased the use of additive manufacturing systems. These, along with the increased precision, repeatability, and material range of 3D printing, have increased the use of the technology for higher volume production.
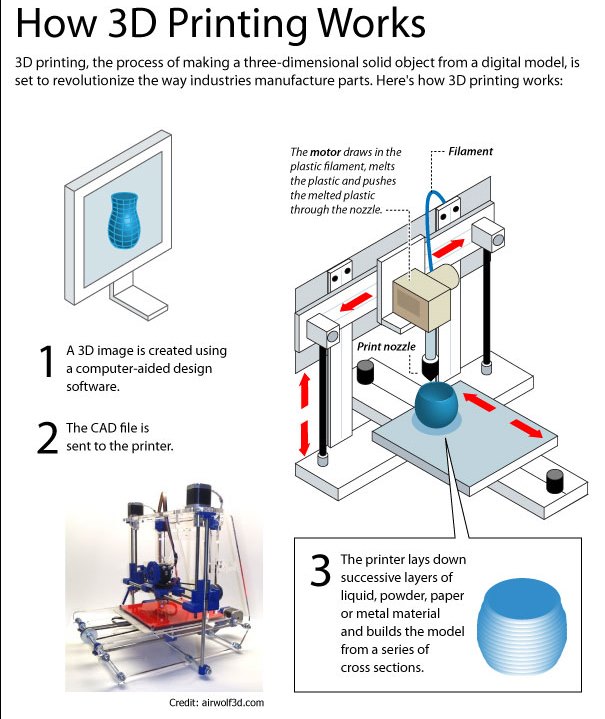
In the case of most 3D printers, a user creates a design using computer aided design software or by scanning an object to print. Software translates the design into the printed layers and framework for the machine to follow. The plan is sent to the printer, which begins creating the object. The materials capable of being printed include polymers, metals, ceramics, foams, gels, and biomaterials.
Processes
Material extrusion
Material extrusion printing, or fused filament fabrication, also known by the trademarked term "fused deposition modeling," is a 3D printing process using a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Through this method, filament is fed through a moving, heated printer extruder head and deposited on a growing work. Printers using this method use a computer to control the printed shape. And printers of this type layer the printed object one horizontal layer at a time before making a small vertical move to start the next layer. The extruder head speed can be controlled to start and stop deposition in order to form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. Fused filament fabrication is the more popular printing process (by number of machines) for hobbyist-grade 3D printing.
The extruder head speed can be controlled to start and stop deposition in order to form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. Fused filament fabrication is the more popular printing process (by number of machines) for hobbyist-grade 3D printing.
The fused deposition modeling technique was developed by S. Scott Crump, the co-founder of Stratasys, in 1988. The patent on the technology expired in 2009 and presented the beginning of people using the type of printing without paying rights to Stratasys. This allowed commercial, hobbyist, and open-source 3D printer applications to grow.
The materials capable of being extruded by fused filament fabrication machines include thermoplastics, such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), polylactic acid (PLA), high-impact polystyrene (HIPS), thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), and aliphatic polyamides (nylon).
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA), also known as optical fabrication, photo-solidification, VAT photopolymerisation, or resin printing, is a 3D printing technology that prints parts in a layer-by-layer fashion using photochemical processes. SLA uses light to cause chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link and form polymers that, in turn, make the body of a three-dimensional solid. The process is fast and can produce almost any design, but can be cost prohibitive. The main fields of application include products in development, medical models, and computer hardware.
SLA uses light to cause chemical monomers and oligomers to cross-link and form polymers that, in turn, make the body of a three-dimensional solid. The process is fast and can produce almost any design, but can be cost prohibitive. The main fields of application include products in development, medical models, and computer hardware.
The materials used in SLA printing are referred to as resins and are thermoset polymers. These resin materials can be soft or hard, filled with secondary materials such as glass and ceramic, or imbued with mechanical properties such as heat deflection or impact resistance. In the post-process of SLA manufacturing, parts need to be removed from a support structure, and alcohol and water rinses are used to remove excess resin. At times, post processing can include scrubbing to remove additional material, and some processes use ultraviolet light for a post-cure process.
Stereolithography was first developed in the early 1980s by Hideo Kodama, who used ultraviolet light to cure photosensitive polymers. French inventors Alain Le Mehaute, Oliver de Witte, and Jean Claude Andre filed an early patent for technology that was later abandoned. The final patent, which gave the process the name "stereolithography," was filed by Chuck Hull in 1984 and granted in 1986. Chuck Hull later founded 3D Systems to commercialize the patented technology.
French inventors Alain Le Mehaute, Oliver de Witte, and Jean Claude Andre filed an early patent for technology that was later abandoned. The final patent, which gave the process the name "stereolithography," was filed by Chuck Hull in 1984 and granted in 1986. Chuck Hull later founded 3D Systems to commercialize the patented technology.
Powder bed fusion
The powder bed fusion manufacturing process includes the printing techniques of direct metal laser sintering, electron beam melting, selective heat sintering (SLS), selective heat sintering, and selective laser melting (SLM). All methods use either a laser or an electron beam to melt and fuse material powder together. The methods involve spreading the powder material over previous layers, using either a roller or a blade while a hopper or reservoir provides fresh material supply. In all methods, a layer, typically 0.1 millimeters thick, of material is built over the platform and the laser or electron beam fuses new material in layers or cross-sections. Materials capable of being used in powder bed fusion manufacturing processes include nylon, stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, cobalt chrome, steel, and copper.
Materials capable of being used in powder bed fusion manufacturing processes include nylon, stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, cobalt chrome, steel, and copper.
In direct metal laser sintering, metal powders are sintered layer by layer with a range of metals available.
In electron beam melting (EBM), layers are fused using an electron beam to melt metal powders. In the EBM process, a vacuum is required with a pressure of 1×10-5 mba, and electromagnetic coils are used to control the beam. The EBM process also produces better strength properties due to even temperature during fusion. These strength properties with the high quality and finish of the product suits it to manufacturing of parts for aerospace and medical applications.
In selective laser sintering (SLS), machines are made up of three components: a heat source, a method to control the heat source, and a mechanism to add new layers of materials. The SLS process requires no additional support structure for the product being printed. In the SLS chamber, nitrogen is often used to maximize the oxidation and end quality of the model. A cool-down period is also required to ensure high tolerance and quality of fusion. Some SLS machines monitor the temperatures layer by layer and adapt the power to improve quality. SLS processes use plastic powders, rather than metal powders used in direct metal laser sintering.
The SLS process requires no additional support structure for the product being printed. In the SLS chamber, nitrogen is often used to maximize the oxidation and end quality of the model. A cool-down period is also required to ensure high tolerance and quality of fusion. Some SLS machines monitor the temperatures layer by layer and adapt the power to improve quality. SLS processes use plastic powders, rather than metal powders used in direct metal laser sintering.
Selective heat sintering uses a heated thermal printhead to fuse powder material. Layers are added with a roller between fusion of layers. The use of a thermal printhead reduces the heat and power levels required for printing. Selective heat sintering systems use thermoplastic powders and require support materials in the process of printing. The process is often used to create concepts prototypes rather than structural components.
Selective laser melting (SLM) is similar to selective laser sintering, except it is faster while requiring the use of an inert gas and requiring higher energy use with poor overall energy efficiency. Through the process, a roller or blade is used to spread new layers of powder over previous layers. In cases when a blade is used, the blade is often vibrated to encourage a more even distribution of powder.
Through the process, a roller or blade is used to spread new layers of powder over previous layers. In cases when a blade is used, the blade is often vibrated to encourage a more even distribution of powder.
Material jetting
Material jetting, also known as multi-jet modeling, creates objects in a similar method to an inkjet printer. The process uses droplets to build a material on a support structure, while ultraviolight light or heat cures the droplets to create a 3D object. In the technique, droplets are selectively deposited on an X, Y, and Z axis controlled by computer and based on computer-aided designs. Common materials used in material jetting machines include polymers and waxes, due to their viscous nature that can form droplets. Overall, the materials suitable for use in material jetting machines are limited. And the parts printed through material jetting printers are mainly suitable for non-functional prototypes, as the printed parts often have poor mechanical properties.
The types of material jetting technologies include PolyJet technology, NanoParticle Jetting, and Drop On Demand. PolyJet technology jets thin layers of photopolymer material onto a build tray, in which each layer is cured by ultraviolet light. PolyJet technology was the first material jetting technology introduced. The PolyJet process was developed by Object and was later bought by Stratasys.
NanoParticle jetting technology was developed by XJet and uses a dispersion methodology to deposit solid nanopoarticles suspended in a liquid and jetted onto the build tray. In the system, two printheads and thousands of nozzles spray ultrafine drops that both build and support materials onto the build trays, while high temperature in the build area evaporates the liquid jacket around the nanoparticles. The remaining nanoparticles are sintered and the support material is removed, with a thin and smooth surfaced product capable of fine details remaining.
Drop on demand (DOD) technology is a process typically used for viscous materials, and consists of deposits tiny dots of material instead of continuous lines. The printers consist of two heads for each build and support material and are often used for make wax patterns for investment casting. In the printing process, wax material is printed in layers with the support material automatically laid down and eliminating the need for designers to create support structures. The finished part is placed in a liquid bath which dissolves the support material away.
Binder Jetting
Binder jetting is a manufacturing technique in which a binding liquid is selectively deposited to join powder material to form a 3D part. The process does not require heat during the printing process. Exon, an early developer of the binder jetting technique, uses furan binder, silicate binder, phenolic binder, and aqueous-based binder for their binder jetting printers. Regardless of binder, the process of a binder jetting printer sees the application of a layer of material powder, followed by a printhead depositing the binder adhesive on the powder where required until a 3D model is finished. The unbound powder remains until it is removed.
Regardless of binder, the process of a binder jetting printer sees the application of a layer of material powder, followed by a printhead depositing the binder adhesive on the powder where required until a 3D model is finished. The unbound powder remains until it is removed.
Binder jetting processes can manufacture in a range of different colors and in a range of metal, polymers, and ceramics. The two-material process allows for many different binder-powder combinations with various mechanical properties. However, often, through the use of specific binder materials, binder jetting printed materials are not always suitable for use as structural parts.
Sheet Lamination
Sheet lamination is a process of building a 3D object by stacking and laminating thin sheets of material. The lamination method can be bonding, ultrasonic welding, or brazing while a final shape is achieved through laser cutting or CNC machining. Sheet lamination produces parts with the least additive resolution compared to other additive manufacturing processes; however, it is a low cost and offers fast manufacturing times from easily available low-cost material.
The materials involved in sheet lamination include paper, plastic, metal, and woven fiber composites. Forming methods include CNC milling, laser cutting, and aqua blasting. And the lamination techniques include adhesive bonding, thermal bonding, and ultrasonic welding. The process either follows a form then bond process, in which sheet material is cut into shape and then bonded layer on layer to create a 3D object. Or it follows a bond then form process, in which the material layers are bonded and then cut into the desired shape. Sheet lamination types, each offering some kind of variation of the above methods, can be categorized into seven types:
- Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
- Selective lamination composite object manufacturing (SLCOM)
- Plastic sheet lamination (PSL)
- Computer-aided manufacturing of laminated engineering materials (CAM-LEM)
- Selective deposition lamination (SDL)
- Composite based additive manufacturing (CBAM)
- Ultrasonic additive manufacturing (UAM)
Directed Energy Deposition
Directed energy deposition is an additive manufacturing process that forms 3D objects by melting material as it is deposited using focused thermal energy such as laser, electron beam, or plasma. Both energy source and the material feed nozzle are manipulated using a gantry system or robotic arm. Due to the nature of direct energy deposition, even though it is possible to create 3D objects from scratch, the process is generally used for adding to an existing part or repairing existing parts. Direct energy deposition systems are used in hybrid manufacturing, in which a substrate bed is moved to create complex shapes.
Both energy source and the material feed nozzle are manipulated using a gantry system or robotic arm. Due to the nature of direct energy deposition, even though it is possible to create 3D objects from scratch, the process is generally used for adding to an existing part or repairing existing parts. Direct energy deposition systems are used in hybrid manufacturing, in which a substrate bed is moved to create complex shapes.
Direct energy deposition systems can be used to make metal, ceramic, and polymer parts, although they are primarily used to make metal parts. The types of systems include laser-based systems, such as Optomec's laser engineering net shape system, which uses a laser as the main energy source. An electron beam based system, such as Sciaky's electron beam additive manufacturing system, uses electron beams to melt the powdered material feedstock. And the plasma or electric arc based system, such as Wire's arc additive manufacturing process use electric arcs to melt wire.
The suitable materials for direct energy deposition systems include niobium, titanium and titanium alloys, inconel, stainless steels, hastelloy, aluminum alloy, tantalum, zinc alloy, tungsten, and copper-nickel alloys. Direct energy deposition systems are used in industries such as aerospace, defense, oil and gas, and the marine industry.
Applications
The applications for 3D printing are various across industries and for hobbyist uses with the introduction of lower cost printing technology.
Housing
3D printing is being explored as a construction method that reduces the costs of on-site construction and time-to-build of a home. The application of 3D printing in home construction has been explored as an affordable housing solution for urban areas.
3D printing companies in housing industry
Aerospace
Additive manufacturing systems are capable of producing lightweight parts with complex geometric designs useful for the aerospace industry. In 2013, NASA tested SLM-printed rocket injector during a hot fire test generating 20,000 pounds of thrust. In 2015, the FAA cleared 3D-printed parts for use in commercial jet engines. In the 2017 Paris Air Show, the Boeing 787 displayed FAA-certified structural parts fabricated from 3D printing of titanium wire.
In 2013, NASA tested SLM-printed rocket injector during a hot fire test generating 20,000 pounds of thrust. In 2015, the FAA cleared 3D-printed parts for use in commercial jet engines. In the 2017 Paris Air Show, the Boeing 787 displayed FAA-certified structural parts fabricated from 3D printing of titanium wire.
3D printing companies in aerospace industry
Automotive
The automotive industry has used 3D printing processes for rapid prototyping. As manufacturing techniques have advanced, 3D printing has been used for developing automotive parts. This includes the McLaren Formula 1 racing team using 3D printed parts in their race cars, including a rear wing replacement that took ten days to produce using 3D printers, instead of the five weeks subtractive manufacturing can take. In 2014, Koenigsegg, Swedish supercar manufacturer, used 3D printing for many components. Most of the manufacturing processes extend to the bodywork and related elements, but do not extend to the powertrain.
Healthcare
Additive manufacturing has been used in the healthcare industry to produce medical items and prosthetics. This has included medical device manufacturing company Stryker using additive manufacturing technology to create surgical implants for patients suffering from bone cancer. A clinical study done by the New York University School of Medicine is looking into the use of patient-specific, multi-colored kidney cancer models and whether they can effectively assist surgeons with pre-operative assessments.
There have been studies into the viability of 3D bio-printing for use in tissue engineering applications, including the printing of organs and body parts. In the process, layers of living cells are deposited onto a gel medium or sugar matrix to build a three-dimensional structure, including vascular systems. In May 2018, a 3D printing system was used for a kidney transplant to save a three-year-old boy.
In the pharmaceutical industry, 3D printing systems are being used by researchers as a new way to develop formulations of materials and compounds not possible with conventional techniques such as tableting or cast-molding. One of the possible uses of 3D printing in pharmaceuticals is to print personalized dosages to better target patient needs.
One of the possible uses of 3D printing in pharmaceuticals is to print personalized dosages to better target patient needs.
3D printing companies in healthcare industry
Clothing
In the clothing and fashion industry, designers and manufacturers have experimented with 3D printed clothing items, including Nike using 3D printing to prototype and manufacture their 2012 Vapor Laser Talon football shoes and New Balance 3D manufacturing custom-fit shoes for athletes.
Shoes
In 3D printing for shoes, the additive manufacturing techniques offers a chance for creators and designers in the fashion industry to create designs and collections with shapes or designs that could be otherwise unable to create in subtractive manufacturing methods. As well, there are many projects launching to develop new speakers, futuristic lightweight footwear, and customer printed shoes for specific athletes.
Food
Additive manufacturing systems, or analogues, are also being used in the manufacturing of food. The foods printed have included chocolate, candy, crackers, pasta, and pizza. NASA has pursued research into the technology to reduce food waste and design foods to fit astronauts' dietary needs. And in 2018, Giuseppe Scionti developed technology to generate fibrous plant-based meat analogues using a custom-built 3D bioprinter.
The foods printed have included chocolate, candy, crackers, pasta, and pizza. NASA has pursued research into the technology to reduce food waste and design foods to fit astronauts' dietary needs. And in 2018, Giuseppe Scionti developed technology to generate fibrous plant-based meat analogues using a custom-built 3D bioprinter.
Often 3D printing in foods describes an additive manufacturing process, such as an automated pizza vending machine that is capable of extruding dough, topping the dough with tomato sauce and cheese, and sending that to an oven. Food can, especially in the case of viscous foods, be printed fairly easily. 3D printing has been used for decorating and deserts where the accuracy of the printer can create complex designs. However, in the case of other types of food, 3D printing can be more restrictive. As well, in the case of 3D printing new or novel foods, the technology is further behind its peers, as the technology can be prohibitively expensive and often is not scalable.
Firearms
Additive manufacturing has been used in the firearms industry to offer a new manufacturing method for established companies, and has produced possibilities for the do-it-yourself manufacturing of firearms.
All 3D printing companies
3d Printer Tips and Mods Wiki
What’s New
- See the donations page for information of helping support this cause (web hosting, products to review, etc).
- We have added a Review section where we will be posting reviews of boards, printers, upgrades, filament and resins.
- Added a SLA Resin information database for the Wanhao D7 where users can add curing times for others to lookup.
About Us
- Who we are and why we are doing this
Articles
The Articles page is where we will be posting any 3d printer related news, information or stories.
Safety Notices
- Wanhao I3 Plus Bed Notice
- Wanhao first batch (alpha testers) D7 LED Power Driver Fix
- Wanhao D7 Printer check on Unboxing (for common problem areas)
- Wanhao D7 v1 and v1.
 2 Fan Upgrade Kit
2 Fan Upgrade Kit
Resources
- 3d Printing Products Store (being updated) – Parts for building 3d printers and cnc. Tools and filaments also available.
- Amazon Subscriptions and Deals
Printers
This is a list of common 3d printers and will be adding any documentation we can find along with mods and tips for these printers.
-
Wanhao Duplicator i3 (also rebranded as the Monoprice “Maker Select” and Aldi “Cocoon Create”)
-
Wanhao Duplicator i3 Plus
- Wanhao Duplicator I3 Mini
-
Wanhao Duplicator 4
-
Wanhao Duplicator 5 Series (DS/D5S/D5S Mini)
- Wanhao Duplicator 6 Series
- Wanhao Duplicator 7 Resin Printer
- Wanhao Duplicator 9 Series
-
Raise 3D N series
- Tiko3d Delta Printer
- Ultimaker
- Phrozen Resin Printer
- Flashforge Hunter Resin Printer
- Voxelab Aquila
- Zortrax
-
Cubicon Single (3DP-110F)
-
Cubicon Style (3DP-210F)
-
Makerbot TOM
-
Makerbot Replicator
-
Makerbot Replicator Mini
-
Type-A clone (Jetguy modification)
-
Kossel Mini
-
CNCMe Rostock MAX
-
Rostock custom (original Rostock design)
-
Cube Gen3 (2x)
-
New Matter Mod-t
-
M3D
-
Makerbot Replicator clone Tall
-
CoreXY Ultireplicator (Jetguy custom 4’x4’x4′)
-
CoreXY (Jetcuy custom 24“ bed)
-
CoreXY (Jetguy custom 16” bed)
-
CoreXY (Jetguy custom 13″ bed)
-
CoreXY custom
-
mUVe SLA Printer (custom build)
-
FlashForge Dreamer
-
Printrbot Metal
Printer Boards
3D Object / STL Resource List
- Sources for 3d Printable Objects
Reviews
We are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.
 com and affiliated sites.
com and affiliated sites. Encyclopedia of 3D printing
Welcome to the help section of our portal!
As you can see, the world of 3D printing deserves the title of "mysterious". The rapid development of technology gives rise to a lot of all kinds of terms, concepts and designs, whose essence is far from obvious to a simple layman. The main task of our site is to acquaint you with the latest news from the world of 3D printing, tell you about technological innovations and help you with the purchase of the necessary equipment.
The task is complicated by the fact that currently in Russia there is no official standard for terms related to 3D printing. As a result, many of them are differing translations of the originals, somewhat confusing to the reader. In addition, 3D printer manufacturers themselves often try to monopolize parts of the market by making fairly minor changes to existing technologies in order to obtain a patent, and supplying “new” products with new names, thereby only exacerbating the confusion.
But don't despair. In this section, we will try to explain all the nuances of the world of 3D printing: the technologies used, how they work, terminology options, and so on. Keep in mind that the world of 3D printing does not stand still, and therefore we will constantly update and supplement our help section with new information.
Reference sections:
- 1 3D printing
- 2 3D printing technologies
- 3 Consumables for 3D printers
- 4 3D equipment
- 5 SLISERS
- 6 Articles about 3D printing
- 7 Our reviews about 3D printers and about 3D printing 9002
- 9 Literature
- 10 Work with the 3DTODAY portal. Reference
3D printing
- What is a 3D printer.
- All about 3D printing. additive manufacturing. Basic concepts.
- 3D printing for dummies or "what is a 3D printer?"
- How to build a 3D printer with your own hands"
- 3D Printer & 3D Printing FAQ"
3D Printing Technologies
- Mask Stereolithography (SGC)
- Multi-Jet Modeling Technology (MJM)
- Color Inkjet (CJP)
- Digital LED Projection (DLP)
- 3D Inkjet Printing (3DP)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Selective laser melting (SLM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Selective heat sintering (SHS)
- Lamination Object Manufacturing (LOM)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
- Electron Beam Fusion Manufacturing (EBFȝ)
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Selective Deposition Lamination (SDL) Technology
3D Printer Consumables
- FDM/FFF Consumables
- 3D Printing Consumables Chart.
 Melting Points and Extrusion Rates
Melting Points and Extrusion Rates - Photopolymer consumables
- PLA plastic for 3D printing
- ABS plastic for 3D printing
- Printable PVA
- PET plastic for printing
- 3D Printable Nylon
- Laywoo-D3 for 3D printing
- NinjaFlex for 3D printing
- Laybrick for 3D printing
- Stratasys Photopolymer Resins
- 3D Ink Photopolymer Resins
- Photopolymer resins Asiga
- Photopolymer Resins Digital Wax Systems
- RapidShape 9 Photopolymer Resins0021
- MadeSolid Photopolymer Resins
- 3D Systems Photopolymer Resins
- Fun To Do Photopolymer Resins
- Polystyrene for 3D printing
- 3D printed polycarbonate
- Portable bar extruders.
 Filament manufacturing. How To Make Your Own 3D Printing Consumables
Filament manufacturing. How To Make Your Own 3D Printing Consumables
3D equipment
- 3D pen
- 3D printer FDM
- Catalog of DIY and OpenSource 3D printers
- Photopolymer 3D printer
- Metal 3D printing
Slicers
- All versions of CURA - download
3D printing articles
- How to avoid deformation of models when 3D printing
- How to choose high quality filament
- Processing of 3D printed models
- How to clear a clogged extruder nozzle
- "Rescue" of the product using the Repetier-Host program when 3D printing is stopped
- 3 Commandments to make 3D printed products cheaper
- Photoshop CS6 modeling and 3D printing tutorial
Our reviews about 3D printers and 3D printing
- We bought a 3D printer and decided to make money.
 What's next?
What's next? - Cheap 3D printers for every taste
- Household 3D printers for your home
- Jewelry 3D printers or what to give your beloved man
- Metal 3D printing on a home 3D printer. Technology Today and Immediate Prospects
- 3D printer and metal - the present and future of metal 3D printing
- ChefJet Confectionery 3D Printers – The End of the Sugar Cube Era
- MBot Home 3D Printer Review
- 3D printing with chocolate or how to organize your sweet business
- 3D Printers for Jewelers - Unparalleled Print Quality
Technical
- Set up the Marlin firmware and upload it to the 3D printer
- We print with ABS plastic without cracks and heat chambers
Literature
- Book: 3D printing - short and clear
Working with the 3Dtoday portal.
 Handbook
Handbook - 3Dtoday: portal visitor guide
What is a 3D printer?
Popular articles
Bad advice for beginner 3D printers.
11/06/2022
6903
So, after reading all sorts of articles and comments on them, you have finally made a decision for yourself...
Again "BLUE TRACTOR"
11/12/2022
1299
Hello! Not so long ago, about a year and a half ago, I drew and printed out this "blue tra...
for my grandson Voron 2.4 R2: Path of the Jedi
11/11/2022
1755
Greetings, dear reader! In this article, I will try to share my experience in creating...
Wiki section. - 3D printers
Creality ender 3
For questions related to the Creality Ender 3 3D printer family
Marlin
Questions about the firmware for the Marlin 3D printer.
Print quality
Questions about troubleshooting and achieving a specific print quality. Please include pictures of your…
Ultimaker cura
Questions about a cutting program called Ultimaker Cura.
Troubleshooting
Use this tag when you need a logical or systematic search for the source of a problem in order to solve it.
Pla
Polylactic acid, also known as PLA, is a common biodegradable thermoplastic polymer.
3d models
Use this tag for questions about 3D models.
Extruder
Questions about 3D printer extrusion equipment.
Filament
For questions about the various filaments used as printing media.
Prusa i3
Prusa i3 is the third iteration of Josef Pruša's RepRap 3D printer design. This is an open source design, the tag should…
3d design
3D design (or modeling) is the process of creating a three-dimensional digital representation of some object that…
Bed leveling
Use this tag for questions regarding manual or automatic leveling of the build platform. Diy 3d printer
Diy 3d printer
Heated bed
Use this tag for questions about the heated build platform or plate (HBP) for 3D printers.
Firmware
In electronic systems and computing, firmware is a type of software that…
Slicing
Slicing questions. Problems and problems in the process of slicing models should use this tag.
Hotend
Questions about standard extrusion mechanisms used in FDM/FFF technology in 3D printers.
Z axis
Use this tag for questions related to a specific Z-direction of the printer-Questions about the Z axis of the machine…
Extrusion
Questions about the extrusion mechanisms in different types of 3D printers or the extrusion process.
Calibration
Questions about calibrating various 3D printers
Bltouch
Questions about the BLTouch auto leveling sensor for 3D printers.
Nozzle
Questions about the
nozzle extrusion assembly componentSoftware
Questions about slicing systems or 3D modeling programs.
Adhesion
Questions about part-in-platform or layer-on-layer adhesion in 3D printing.
Anet a8
This tag should be used for specific questions about specific issues with Anet A8 printers.
Resin
For questions about resin printers
Print material
Print material, compared to the tag "material", helps to indicate that the question is about the material from which ...
Slic3r
Questions related to a software slicing engine called Slic3r
Ramps 1.4
For questions specifically related to the RAMPS 1.6 controller board - RepRap Arduino Mega Pololu Shield, or for short…
Electronics5 questions
Electronics5
Electronics5 electronic components for 3D printers and electronic components for 3D printing.
Creality cr 10
For questions about the Creality CR-10 3D Printer Family
Abs
Use this tag for questions about Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, also known as ABS, commonly used…
Fdm
Questions about Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) as an additive manufacturing technology.
Creality ender 5
For questions about the Creality Ender 5 family of 3D printers
Printer building
Questions about building your own printer.
Post processing
Use this tag for questions about post processing, that is, additional methods and processes after printing is complete.
Stepper driver
Questions related to different types of stepper drivers
Support structures
Questions about a technique or help with a 3D printing problem.
Stepper
Questions about stepper motors, a type of motor commonly used in 3D printers.
Petg
Use this tag for questions about PETG.
Stl
For questions regarding .stl files and the STL file format.
Reprap
For questions related to the RepRap project (repicating rapid prototyper), its firmware of the same name and related topics,…
Safety
For questions about immediate safety and security precautions when working with a 3D printer or…
Filament choice
Questions about which filament to choose for a particular application refer here.
Desktop printer
General questions about desktop 3D printers.
Octoprint
Octoprint is a web interface for 3D printers. It is hosted at http://octoprint.org/ and programmed by Gina Heusge.
Sla
Questions about stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing.
Delta
Questions about Delta style 3D printers.
Heat management
Temperature management in 3D printers. This includes heaters, heated print beds, chambers with…
Build plate
The build plate describes the flat piece of material you are printing on. The heated mounting plate is called…
Material
For questions about materials in general. For questions related to filaments, please use the print tag…
Infill
Questions about the internal structure of 3D printed parts.
Motor
Any questions about the various motors on the 3D printer
Makerbot
Questions about the 3D printer manufacturer MakerBot Industries
Z probe
Use this tag for questions related to switches or sensors to manually level the table …
Speed
For questions regarding the execution of a 3D printing operation, or to increase the speed of the operation being performed.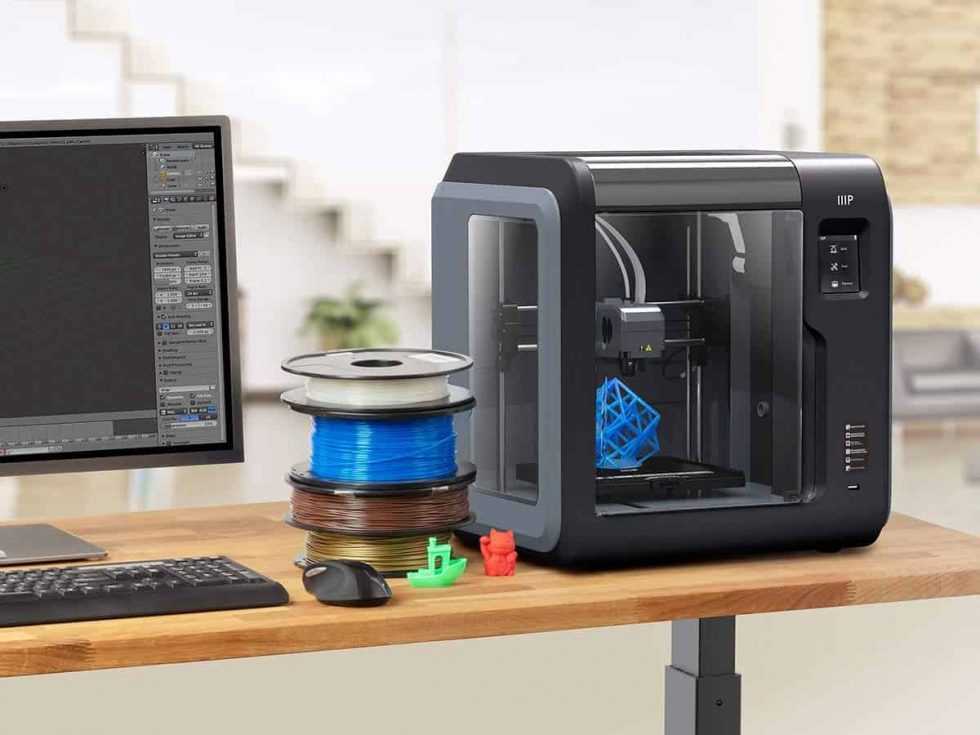
Maintenance
General maintenance and printer maintenance questions.
Thermistor
Thermistor is an electronic component often used to measure temperature.
Layer height
Questions regarding the resolution of print layers, i.e. printing parallel to the Z plane.
Cad
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Repetier
Repetier (Repetier) and repetier.com are 3D printer software related projects.…
Arduino mega 2650
Arduino Mega 2560 is one of the most common microprocessor boards used to control 3D printers.…
Homing
For questions regarding "pointing" (positioning in a known place) of 3D printing devices.
Y axis
Use this tag for questions related to specific printer movement in the Y direction - Questions about…
Quality
For questions about the quality or durability of the finished 3D print, print media, or 3D printing machine.
Warping
Warping refers to the phenomenon of raised edges during printing.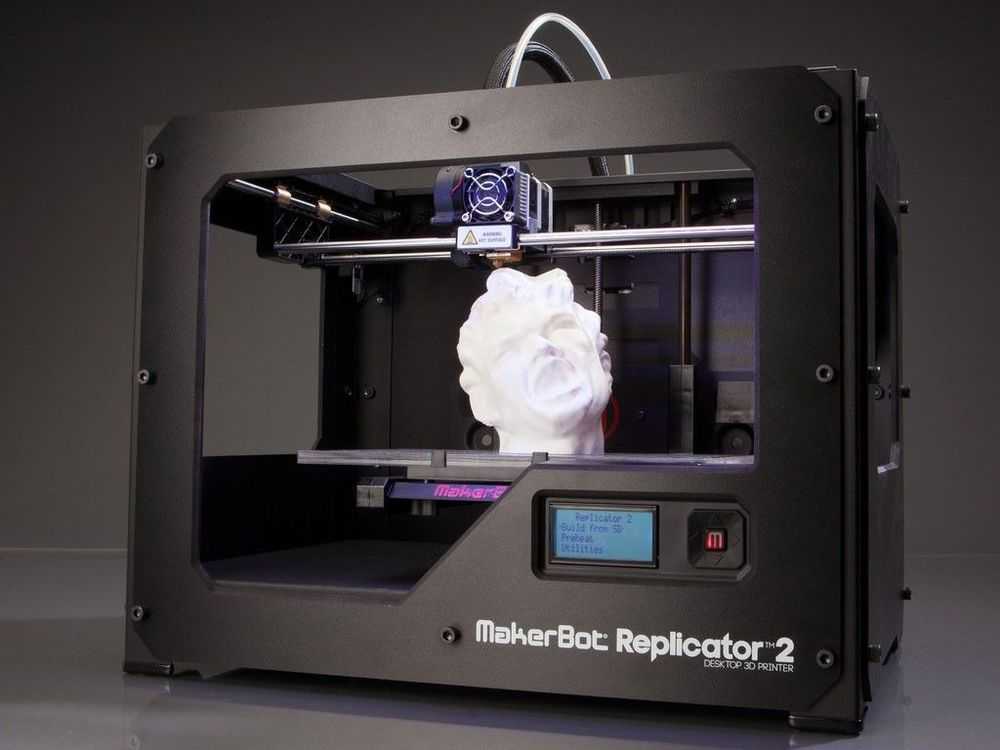 Deformation is the effect of thermal expansion due to…
Deformation is the effect of thermal expansion due to…
Openscad
Questions related to using the OpenSCAD program and how it relates to creating 3D printed parts
Prusaslicer
For questions about the slicer serviced by Prusa Research.
Bowden
Questions using this tag should include a Bowden extruder - a type of FDM extruder that does not have a motor,… leads to…
Knowledgebase
For FAQs or questions that discuss the basics of 3D printing.
Hardware
Any questions related to the hardware of the 3D printer, implying the physical parts of the 3D printer or located in…
Simplify3d
Questions related to the software slicing program called Simplify3D which converts the current of the electrical network into the properties required by the device.
Bigtreetech
For bigtreetech displays, drivers, modules, motherboards.
Retraction
Use this tag for questions about filament retraction.
Endstop
Switch used to notify the controller that the printer has completed its movement in the direction of…
Cooling
Questions about cooling 3D printers and 3D printed parts.
Anet a6
This tag should be used for specific questions about specific problems with Anet A6 printers.
Glass bed
Use this tag for questions related to glass slates used as a build platform…
Anycubic i3 mega
For any question about 3D printers Anycubic Mega series
Monoprice maker select
Questions using this tag must be about a 3D printer made by Monoprice and branded…
Fusion360
For related questions CAD related to Autodesk's use of Fusion 360
Scanning
Questions about 3D scanning.
Replacement parts
For 3D printer spare parts
Dual nozzle
Questions about FDM/FFF printing with two extrusion units.
File formats
Questions about 3D printing of various file formats.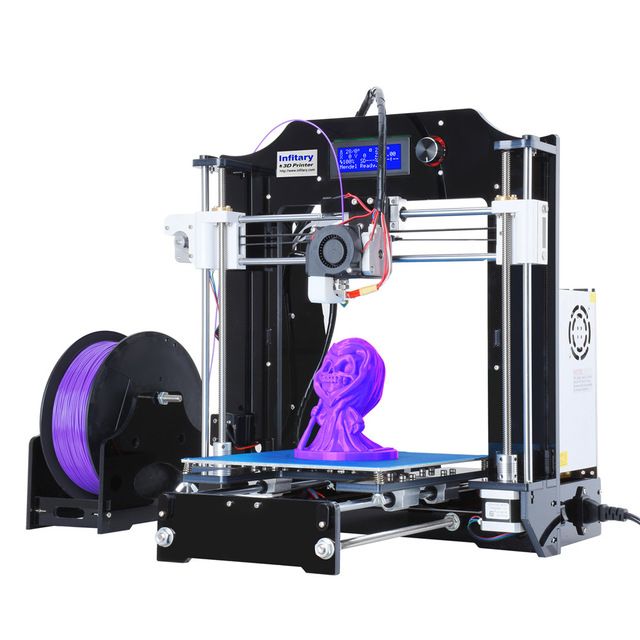
Mechanics
For questions regarding the mechanical parts of 3D printing such as frames, axles, pulleys, belt tensioners, etc.
Blender
For questions about the free 3D design software blender in its use for 3D printing.
Filament quality
Questions about the quality of media for FDM printers that come in filament form
Wiring
Wiring describes the electrical connection between components.
Dlp
Issues Digital Light Processing (DLP) 3D printing method.
Enclosure
3D Printer Enclosures can include simple homemade soundproof enclosures up to professional…
Wanhao
3D Printer manufacturer from China since 2011.
Print strength
Issues related to the mechanical strength of the print, such as the strength of the material or the strength of the finished part
Repair
Use this tag to indicate the action or action to be taken to correct an element or…
Prusa i3 rework
Prusa i3 Rework is a third generation redesign of the renowned RepRap Prusajr…
Food
Questions about 3D printed food or 3D printed food processing objects.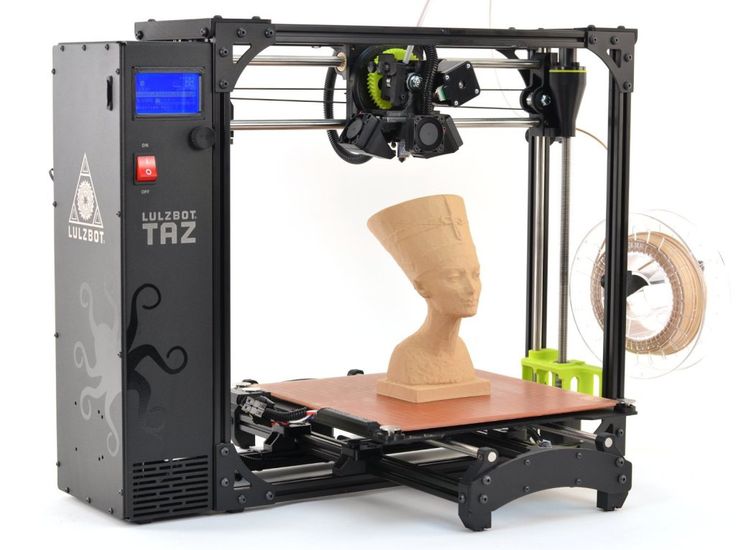
Surface
Questions about the surface of the 3D printed object
Resolution
Questions about the resolution of the 3D printer or 3D print object
Monoprice select mini Monoprice and is called…
Tevo tarantula
This tag should be used for specific questions about specific issues related to the TEVO Tarantula 3D printer.
Switching power supply
Switched power supply (also called SMPS or “switch”) converts electrical energy…
Multi material
Questions about 3D printing with multiple materials.
Raspberry pi
Questions related to the Linux computer "Raspberry Pi" and how it can be used with or for 3D printers. threads, powders or resins
Linear motion
Use this tag for questions about 1D motion in a straight line.
Rafts
For questions about rafts, usually layers of plastic are applied before the print operation to facilitate removal…
Kossel
For questions about the Kossel family of printers in particular. Questions about Delta printers in general have their own tag.
Questions about Delta printers in general have their own tag.
Axis
Use this tag for questions related to a specific printer direction
Ramps
For questions related to the RAMPS controller board - The RepRap Arduino Mega Pololu Shield, or RAMPS for short, presents…
Flashforge adventurer 3
Questions using this tag should be about the Adventurer 3 3D printer manufactured by FlashForge Corporation
Arduino
Use this tag for questions about 3D printing with the Arduino microcontroller hardware platform. For general…
Lulzbot
Questions using this tag must be about the LulzBot line of 3D printers manufactured by Aleph Objects, Inc.
Print fan
Questions regarding print cooling fans used to cool extruded material in…
Support material
Support material determines the type of material used in the support structure. Usually the supporting material is the same…
Laser
Low power lasers can be used as measuring instruments in 3D printer environment, but more powerful…
Usb
Universal Serial Bus; interface standard for connecting computers and electronic devices for communication…
X axis
Use this tag for questions related to specific printer movement in the X direction - Questions about the X axis of the machine…
Flashforge creator
Questions using this tag must be about the Creator series of 3D printers manufactured by FlashForge Corporation
Print preparation
Questions about setting up the machine for printing.
Repetier host
For questions about the repetier-host software used to send g-code commands to 3D printers
Belt
Use this tag for questions related to the mechanical movement of a loop or strip of material that causes…
Ramps 1.6
For questions specifically related to the RAMPS 1.6 controller board - RepRap Arduino Mega Pololu Shield, or for short…
Geeetech
Geeetech is a Chinese manufacturer of 3D printers and printer parts
Freecad
FreeCAD is an open source 3D modeling software application for parts design.
Ptfe tube
Use this tag for questions that use low friction tubing to transport the filament…
Inductive sensor
For questions about installing or using inductive sensors
Pronterface
Use this tag for questions associated with the use of the work of a program called Pronterface.
Metal printing
Questions regarding 3D printers that create all-metal parts.