Why use a 3d printer
10 Advantages of 3D Printing
Are you aware of the many advantages of 3D printing technology? Follow along as we break down our top ten here.
There are 3 main methods used for product development, that is, taking a design from idea to a physical, 3-dimensional prototype of the product.
Subtractive manufacturing is a product development process that continuously cuts away material from a solid block, such as metal. This can be done manually or using CNC (Computer Numeric Controlled) machinery.
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used for producing products in large volumes. As the name suggests, parts are produced by injecting heated material into a mold.
So, what is 3D printing? Additive manufacturing, aka 3D printing, is the process of producing 3-dimensional objects from a computer file, where the part is built by adding material layer-by-layer.
Today, more companies in a variety of industries are embracing the 3D printing process as it presents many significant advantages over the more traditional manufacturing methods of subtractive manufacturing and injection molding.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing technology is Rapid Prototyping. Rapid prototyping is the ability to design, manufacture, and test a customized part in as little time as possible. Also, if needed, the design can be modified without adversely affecting the speed of the manufacturing process.
Before 3D printing industry came to flourish, a prototype would take weeks to manufacture. Every time a change was made, another few weeks of time were added to the process. With shipping times figured in, fully developing a product from start to finish could easily take a year.
With 3D printing techniques, a business can design a part, manufacture it in-house on a professional 3D printer, and test it, all within a few days (and sometimes even less).
For small businesses or even individuals, this difference is significant. The freedom and creativity enabled by 3D printing means that almost anything can be created without the need for warehouses full of expensive machinery. There are no long lead times typically associated with having to outsource complex manufacturing projects. It means freedom from the constraints of minimum orders, that parts and products can be created and customized with ease.
There are no long lead times typically associated with having to outsource complex manufacturing projects. It means freedom from the constraints of minimum orders, that parts and products can be created and customized with ease.
For small production runs and prototyping, 3D printing is the best option as far as speed is concerned.
2. CostFor small production runs and applications, 3D printing is the most cost-effective manufacturing process. Traditional prototyping methods like CNC machining and injection molding require a large number of expensive machines plus they have much higher labor costs as they require experienced machine operators and technicians to run them.
This contrasts with 3D printing process, where only 1 or 2 machines and fewer operators are needed (depending on the system) to manufacture a part. There is far less waste material because the part is built from the ground up, not carved out of a solid block as it is in subtractive manufacturing and usually does not require additional tooling.
Another big advantage of 3D printing is that any given printer can create almost anything that fits within its build volume.
With traditional manufacturing processes, each new part or change in part design, requires a new tool, mold, die, or jig to be manufactured to create the new part.
In 3D printing, the design is fed into slicer software, needed supports added, and then printed with little or no change at all in the physical machinery or equipment.
3D printing allows the creation and manufacture of geometries impossible for traditional methods to produce, either as a single part, or at all. Such geometries include hollow cavities within solid parts and parts within parts.
3D printing, in contrast to traditional methods, allows the inclusion of multiple materials into a single object, enabling an array of colors, textures, and mechanical properties to be mixed and matched.
3D printing allows any user, even those with limited CAD experience, to edit designs however they like, creating unique, customized new parts. This also means any given design can be manufactured in a wide range of different materials.
This also means any given design can be manufactured in a wide range of different materials.
Because of the speed and lower costs of 3D printing, product life cycles are reduced. Businesses can improve and enhance a product allowing them to deliver better products in a shorter amount of time.
3D printing allows the physical demonstration of a new product to customers and investors instead of leaving it to their imaginations, therefore reducing the risk of information being misunderstood or lost during communication.
It also allows for cost-effective market testing, obtaining feedback from potential customers and investors on a tangible product, without the risk of large upfront expenditures for prototyping.
5. Tangible Design and Product TestingAs previously described in competitive advantages, seeing a product on a screen cannot compare with actually touching and feeling a prototype. A physical prototype can be tested and if flaws are found, the CAD file can be modified and a new version printed out by the next day.
Why 3D Printing Is Useful and Will Continue to Be Useful
For some, 3D printing might seem childish and toy-like. After all, what can you print in a 3D printer? A whistle or a figurine of a video game character, right? In fact, 3D printing is a powerful technology which is already providing significant savings to companies. Its future is even more promising.
3D printing is taking more and more branches of the economy by storm. Up until recently it has been used only experimentally by universities and large corporations. Today, thanks to companies such as Zortrax, it’s readily available. Just order a 3D printer online today and tomorrow you will be able to enjoy your new device.
On the other hand, the question that’s often asked is: why 3D printing, what can this technology be used for? Pessimists like to show examples of minor, simple 3D printed items which could have easily been manufactured with a different method and maybe would’ve even been cheaper. However; 3D printing is very useful when you know how to utilize it and what you want to achieve. The technology has a wide range of prospects, therefore more and more universities are establishing departments focused on 3D printing and skills related to 3D printing are valued by many companies. Experts in the field of 3D printing are in high demand.
The technology has a wide range of prospects, therefore more and more universities are establishing departments focused on 3D printing and skills related to 3D printing are valued by many companies. Experts in the field of 3D printing are in high demand.
Multitude of Useful Applications
3D printing technology is utilized in many fields. One of them is medicine. 3D printers such as the Zortrax M200 create models of hearts and other organs as training aids for surgeons. Such a printer was also used to create the first winch that facilitates the procedure of varicose vein removal. These are just a handful of examples from one field. Another field which is aware of the potential of 3D printing is the automotive industry. The technology allows for rapid prototyping of not only elements of the body, but also of individual components. The future of 3D printing in manufacturing cars is looking brighter and brighter. Experts predict that it will be possible to easily print spare parts, personalize your car and increase the speed of production.
Industrial Powerhouse
A 3D printers can also be the basis of significant economizing in manufacturing plants. Bosch uses Zortrax 3D printers in its plant to create spare parts for machines as well as solutions which facilitate work. 3D printing is becoming indispensable in R&D departments and design departments. Wherever the technology is introduced, it accelerates work and cuts down costs.
3D printing is useful to architects for creating mockups and to mechanics for creating tools. It has found a place in media houses for manufacturing personalized promo gadgets. It’s also a wonderful tool for start-ups when they need to create prototypes of casing or even the casings themselves in low-volume production. 3D printing offers a chance to people who want to start their own business as well. You can use it as a basis and build your business around it: make 3D printed models on demand or earn money through printing specific projects.
We’re still at the very first stages of the development of 3D printers. The technology is evolving rapidly, new, larger devices, such as the Zortrax M300 3D printer, are being introduced, new materials are appearing and people are coming up with new ideas of how to use a 3D printer. Nowadays, desktop 3D printing is mainly a hobby, but soon you’ll likely be able to print items that you happen to lack at the moment you need them. In many fields of the economy, however, development without 3D printing is almost unimaginable. 3D printing is an innovation which fuels more innovation. 3D printing is inexpensive prosthetics, creating spare parts, rapid prototyping, creating personalized items and manufacturing with minimum waste. The technology is useful and thanks to its widespread availability as well as further development will be even more useful in the future.
The technology is evolving rapidly, new, larger devices, such as the Zortrax M300 3D printer, are being introduced, new materials are appearing and people are coming up with new ideas of how to use a 3D printer. Nowadays, desktop 3D printing is mainly a hobby, but soon you’ll likely be able to print items that you happen to lack at the moment you need them. In many fields of the economy, however, development without 3D printing is almost unimaginable. 3D printing is an innovation which fuels more innovation. 3D printing is inexpensive prosthetics, creating spare parts, rapid prototyping, creating personalized items and manufacturing with minimum waste. The technology is useful and thanks to its widespread availability as well as further development will be even more useful in the future.
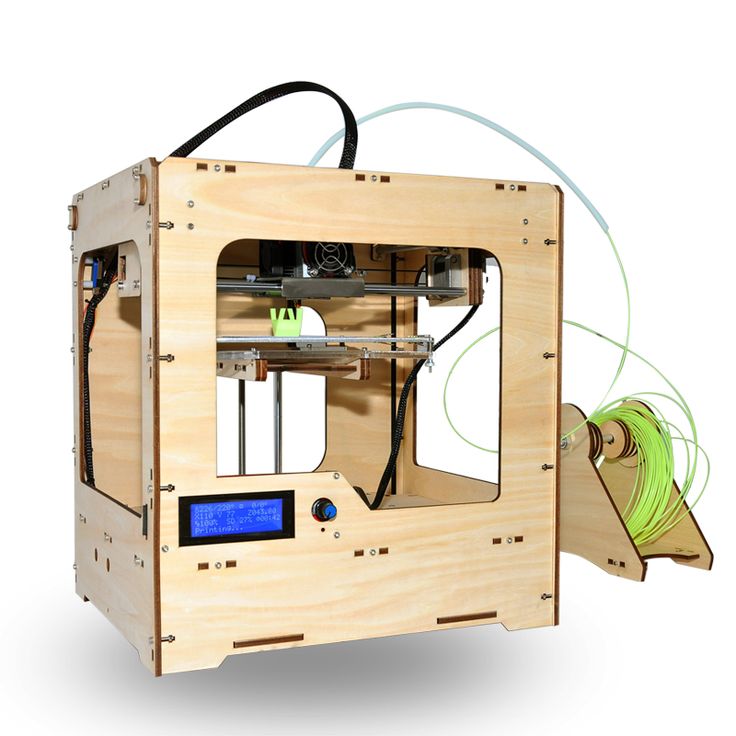
What is a 3D printer and why is it needed? / Amperka
Additive technologies have been going to the masses for a long time: institutes and research centers have been closely involved in them since the 80s, and now the moment has come when you can touch high-tech and master 3D printing right at home. You don’t even have to break the bank to do this: the prices of 3D printers have caught up with average smartphones. We understand how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts!
You don’t even have to break the bank to do this: the prices of 3D printers have caught up with average smartphones. We understand how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts!
Everything for 3D printing ❯
Why you need a 3D printer
The printer is very useful for do-it-yourself engineers. You no longer have to look for a universal case for the project, and then drill additional holes in it. 30 minutes of design, a few hours of printing - and you already have a case that is perfect for your device. Assembly of 5 shields does not fit anywhere? Forget about such problems.
The printer is sure to help you repair gizmos around the house. Everyone has had a situation in life when a thing had to be thrown away, although only one plastic part was broken in it. With the help of 3D printing, you can easily replace rare plastic parts in appliances that are difficult to find separately.
Until you learn how to model plastic parts yourself, you can simply download them on the Internet. There are many sites with millions of ready-made free models that are freely exchanged by users. We devoted a separate article to the search for models.
There are many sites with millions of ready-made free models that are freely exchanged by users. We devoted a separate article to the search for models.
Types of 3D printers
There are several main types of 3D printers that differ fundamentally in terms of how they work.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM printers are the most common type. They work due to a movable print head with a heating element. Plastic is fed into it in the form of a rod, which melts and is squeezed out in liquid form onto the printing table. At the same time, the plastic is blown by a fan and instantly freezes, and the head begins to squeeze out a new layer over the frozen one.
SLA technology (Stereolithography Apparatus)
SLA printers work on the basis of stereolithography: instead of plastic, a special photopolymer resin is used, which cures under the influence of ultraviolet rays. For printing, the resin is filled into a tray, below which there is a display with ultraviolet pixels. A drawing of the lower layer of the model is displayed on it for several seconds. In this case, the resin above the display solidifies in the form of a displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table from above. After that, the table with the first layer rises, and the next layer polymerizes in the resin.
A drawing of the lower layer of the model is displayed on it for several seconds. In this case, the resin above the display solidifies in the form of a displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table from above. After that, the table with the first layer rises, and the next layer polymerizes in the resin.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) Technology
SLS printers use selective laser sintering technology, which uses a special plastic powder. During the printing process, a thin layer of powder is poured, and the printer processes it with a laser so that the layer hardens according to the model. Then the next layer of powder is poured and fused with the previous one - and so on in a circle. At the end, it remains only to clean the finished part from the remnants of the powder, which can then be reused.
Technology comparison
Each type of 3D printer has its advantages and disadvantages.
- SLS printers are large and require expensive raw materials.
 They are often used in high-tech industries for piece parts.
They are often used in high-tech industries for piece parts. - SLA printers are much more widespread. The UV display improves accuracy, but working with toxic photopolymer resin at home is difficult.
- FDM printers are the most popular among hobbyists. A plastic rod is much cheaper than a special powder or photopolymer resin. However, to print complex geometry on such a printer, you will have to take care of auxiliary support. And the print speed is on average lower than on other technologies. But FDM printers are the easiest and safest to maintain.
How to prepare a print
The process from conception of an idea to the production of a finished plastic part is simple - a schoolboy can handle it. We've broken it down in a 3D printing guide using the Flying Bear Ghost 5 printer as an example, but here we'll show you the general principle.
Initial model
First you need to create or download a 3D model of the future part. As a rule, sources are stored in the STL format, which describes the polygonal structure of the model as a set of triangles. But it will not be possible to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break the detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle.
But it will not be possible to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break the detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle.
Slicing
The program for cutting models (slicer) will require you to enter the model of your printer and set the print settings: layer thickness, percentage of internal filling of the part, auxiliary supports and the like. Based on this data, the slicer will automatically prepare a special code for the printer - G-Code, which describes how to move the print head, to what temperature it should be heated and at what speed to extrude plastic in order to get the desired model layer by layer. Then it remains to load this code into a 3D printer and be patient until the end of printing.
The whole process of model preparation is clearly illustrated by the program and provided with intuitive tips for novice users. In general, slicing is not as scary as it is painted!
Finishing
After the model is ready, it can be further processed with sandpaper or a chemical solution. This will smooth out the unevenness between the layers, and the part will look just like the factory. There are a lot of life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look.
This will smooth out the unevenness between the layers, and the part will look just like the factory. There are a lot of life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look.
Printing consumables
The properties of the printed item largely depend on the raw material. As we said before, FDM 3D printers use plastic filament as a consumable, and you have a lot of room to experiment with different types of plastic.
- PLA is highly extrudable and allows complex shapes to be printed at relatively low head operating temperatures of 190°C. The biodegradability of PLA plays into the hands of the environment, but at the same time, things from it are not very durable.
- PETG plastic is stronger than PLA, but also well suited for printers with temperatures around 200 °C. Varieties of PET plastic are well known to you from bags and plastic soda bottles.
- ABS plastic is more durable than other types.
 However, your printer will need an elevated extrusion temperature of around 250°C and a heated bed up to 120°C to print quality ABS plastic, so not every model aims to support it.
However, your printer will need an elevated extrusion temperature of around 250°C and a heated bed up to 120°C to print quality ABS plastic, so not every model aims to support it. - HIPS plastic is close in temperature properties to ABS, but has low caking with it and is easily removed with an organic solvent. Because of this, HIPS plastic is often used for printing composite models and supports for ABS models.
- Wood plastic is produced with the addition of wood dust. Finished models from it imitate wood not only in appearance, but also in smell.
Plastic spools are available everywhere - it will not be difficult for you to choose the right consumables and combine different properties and colors of parts when printing.
In conclusion
Home 3D printing is easier than you think. With a 3D printer at hand, you can create any plastic parts you can think of: cases, mock-ups, figurines, and more. Do not forget that you have at your disposal a huge library of models that are shared on the Internet. Broken vacuum cleaner nozzle or window opening limiter? No problem! Having your own 3D printer, you just need to take the finished model from the Internet, run it through the slicer program in a couple of clicks and send it to print.
Broken vacuum cleaner nozzle or window opening limiter? No problem! Having your own 3D printer, you just need to take the finished model from the Internet, run it through the slicer program in a couple of clicks and send it to print.
Useful Links
- Where to Download Free 3D Models of
- Flying Bear Ghost 5 3D Printing Manual
- Creality Ender-3 V2 3D Printing Manual
Why do you need a 3D printer at home? Application examples
3D printer: application
Just a few years ago, few people heard about 3D printers in Ukraine, but today they are already gaining popularity. But while in other countries 3D printing conquers production, we are at the stage of mastering desktop 3D printers. Due to their relatively high cost, it is too early to talk about the wholesale distribution of the latter, but we are definitely moving towards the popularization of 3D technologies. So, in today's article we will try to understand in detail why a 3D printer is needed.
You have probably already heard a lot of information on this topic and you know that a 3D printer, which is used in almost every area, is an extremely useful device. So, SLA 3D printers are indispensable in the field of dentistry and jewelry creation, and metal 3D printers find themselves in large factories producing components for aircraft and cars. And that's not to mention how many benefits 3D printing brings to medicine. But this is a conversation about global opportunities. As for private use, everything is no less interesting here.
Why you need a 3D printer at home
So why do you need a 3D printer at home? It has a lot of applications, and here are the main ones:
Repair and restoration of damaged parts
Desktop 3D printer will help you save time and money in case of breakage of any parts. All that is needed is a 3D model of the required component and the optimal material to recreate it.
Design
3D printing is a recognized tool for designers to take their creativity to the next level. What craftsmen do not print: amazing designer musical instruments, jewelry, home decor items, clothing items, etc. With endless modeling possibilities and a wide variety of print materials available, any task can be brought to life.
What craftsmen do not print: amazing designer musical instruments, jewelry, home decor items, clothing items, etc. With endless modeling possibilities and a wide variety of print materials available, any task can be brought to life.
Prototyping of engineering instruments
The main task of 3D printing is precisely rapid prototyping, therefore it can easily cope with any project in this direction. A variety of 3D plastic will only contribute to the fulfillment of the tasks.
Gift & Toy Making
Many fans use the 3D printer to create figurines of characters and paraphernalia from their favorite games and movies. 3D models of popular media elements can already be found in the public domain. And in addition, you can always model something of your own.
Printing useful little things for the home
You yourself know what things would make your life easier and imagine how best to turn them into reality. A 3D printer can help with this.