Who make 3d printer
5 Biggest 3D Printing Companies
The manufacturing process known as 3D printing is one of the most promising and rapidly developing technologies with applications across a multitude of industries. 3D printing involves the additive layering of thin sheets of material that are fused together to create a physical product from a digital design.
While the industry is currently hampered by relatively slow production times, advocates believe that 3D printing ultimately will have the capability to mass produce everything from medical equipment to automotive parts to airline components.
Below, we look at the 5 biggest 3D printing companies by 12-month trailing (TTM) revenue. This list is limited to companies that are publicly traded in the U.S. or Canada, either directly or through ADRs. Some foreign companies may report semiannually, and so may have longer lag times. All data are from YCharts as of Dec. 15, 2022.
- Revenue (TTM): $659.2 million
- Net Income (TTM): $-31.
4 million
- Market Cap: $818.8 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -47.76%
- Exchange: NASDAQ
Stratasys boasts that its founder created one of the very first 3D printers and says that it continues to evolve. The company's technology provides solutions for various industries, including but not limited to aerospace, health care, and consumer products. Not only does the company produce desktop 3D printers, but it also has systems available for large-scale production that can be used in digital manufacturing. Founded in 1989, the company is based in Eden Prairie, Minnesota, and has another office in Rehovot, Israel.
- Revenue (TTM): $556.2 million
- Net Income (TTM): -$103.4 million
- Market Cap: $1.2 billion
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -15.27%
- Exchange: New York Stock Exchange
3D Systems invented 3D printing in 1989 with the development and patenting of its stereolithography technology, which uses ultraviolet lasers to help create highly precise parts. DDD built on that by developing new technologies, including selective laser sintering, multi-jet printing, film-transfer imaging, color jet printing, direct metal printing, and plastic jet printing. 3D Systems has three business units: products, materials, and services. The products category offers 3D printers and software and includes small desktop and commercial printers that print in plastics and other materials.
DDD built on that by developing new technologies, including selective laser sintering, multi-jet printing, film-transfer imaging, color jet printing, direct metal printing, and plastic jet printing. 3D Systems has three business units: products, materials, and services. The products category offers 3D printers and software and includes small desktop and commercial printers that print in plastics and other materials.
- Revenue (TTM): $496.4 million
- Net Income (TTM): $23.5 million
- Market Cap: $722.1 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -47.65%
- Exchange: New York Stock Exchange
Proto Labs was founded in 1999 with a focus on building automated solutions to develop plastic and metal parts used in the manufacturing process. The company expanded to launch an industrial-grade 3D printing service that allowed developers and engineers to move prototypes into the production process. The company's primary business services include injection molding, sheet metal fabrication, and 3D printing.
- Revenue (TTM): $245.2 million
- Net Income (TTM): $8.0 million
- Market Cap: $562.3 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -57.18%
- Exchange: NASDAQ
Belgian company Materialise has a 30-year history of providing 3D printing solutions and related software. It provides platforms to facilitate the development of 3D printing applications in industries such as healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and art and design. Some of the company's first 3D printing activities included anatomical models in both dental and hearing aid products. Materialise also produces eyewear and automobile products.
- Revenue (TTM): $205.1 million
- Net Income (TTM): $-499.2 million
- Market Cap: $495.4 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -71%
- Exchange: New York Stock Exchange
Desktop Metal was founded in 2015. The company designs and manufactures 3D printing systems. It pairs these systems with performance-driven materials, applications, and technologies, which provide clients with speed and reliability in their 3D printing needs. Desktop Metal serves various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, machine design, and manufacturing tooling. The company is based in Burlington, Massachusetts.
Desktop Metal serves various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, machine design, and manufacturing tooling. The company is based in Burlington, Massachusetts.
The World’s Largest 3D Printing Companies By Market Cap: 3D Systems & Xometry On Top
This is a list of the world’s largest 3D printing companies measured by market capitalisation. Thanks to their resources, these companies dominate the global 3D printing market. The listing is as per the data verified on 4th March 2022.
Contents
- 1 3D Systems (NASDAQ: DDD)
- 2 Xometry Inc. (NASDAQ: XMTR)
- 3 Stratasys Ltd. (NASDAQ: SSYS)
- 4 Protolabs (NASDAQ: PRLB)
- 5 Velo3D Inc. (NYSE: VLD)
- 6 Desktop Metal Inc. (NYSE: DM)
- 7 Materialise N.V. ADR (NASDAQ: MTLS)
- 8 Nano Dimension (NASDAQ: NNDM)
- 9 Markforged Holding Corp. (NYSE: MKFG)
- 10 Shapeways Holdings Inc.: (NYSE: SHPW)
- 11 MeaTech 3D Ltd. (NASDAQ: MITC)
- 12 Organovo Holding Inc.
 (NASDAQ: ONVO)
(NASDAQ: ONVO) - 13 Voxeljet AG ADR (NASDAQ: VJET)
- 14 Final Thoughts
Market Capitalisation: $2.2B
3D Systems is the most valuable and biggest 3D printing companies in the world, with a market capitalization of $2.2 billion. The company sells a variety of items, including 3D printers, printing materials, digital design tools, and more. Manufacturing, 3D scanning, and healthcare are among the industries where the company’s 3D printing services are used.
With the acquisitions of Titan Additive and Kumovis, it is now expanding into extrusion-based 3D printing technologies.
Share Price (March, 2022): $17
Xometry Inc. (NASDAQ: XMTR)
Market Capitalisation: $2.17B
Xometry, which debuted on the stock market less than a year ago in June 2021, is now second on the list of the top 3D printing companies. Xometry is an on-demand manufacturing company that was founded in 2013 as a convenient marketplace for products people to make and use. Xometry digitised manufacturing by starting from 3D printing but expanding to include much of the conventional manufacturing processes as well. Today, it is one the world’s biggest on-demand manufacturing platform. To understand Xometry better, think of it as the Airbnb of On-demand manufacturing.
Xometry is an on-demand manufacturing company that was founded in 2013 as a convenient marketplace for products people to make and use. Xometry digitised manufacturing by starting from 3D printing but expanding to include much of the conventional manufacturing processes as well. Today, it is one the world’s biggest on-demand manufacturing platform. To understand Xometry better, think of it as the Airbnb of On-demand manufacturing.
Share Price (March, 2022): $49
Stratasys Ltd. (NASDAQ: SSYS)
Market Capitalisation: $1.55B
Israel-based Stratasys is on the third spot in the list of world’s largest 3D printing companies as per market capitalisation (rising from 5th position last year to the third position). It also ranks high among the biggest 3D printer companies across the world. With a market cap of $1.55 billion, the company is undeniably a force to be reckoned with in the global 3D printing market.
Share Price (March, 2022): $23. 97
97
Market Capitalisation: $1.51B
With a market cap of $1.51 billion Protolabs stands fourth in the list of largest companies in the global 3D printing market. Specialising in rapid prototyping, the company is known to offer the fastest source for and customised custom prototypes production parts. The company uses three additive processes namely stereolithography, selective laser sintering (SLS), and one of the metal 3D printing technologies such as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). With more than half a dozen manufacturing locations across three continents, the company is known to produce and assemble custom parts in just one day.
Share Price (March, 2022): $54.93
Velo3D Inc. (NYSE: VLD)
Above: Velo3D team at the New York Stock Exchange/Image Source: Velo3DMarket Capitalisation: $1.47B
Velo3D is a new entrant to the list as it debut as a publicly-traded company in October 2021. Velo3D is a leading additive manufacturing technology company for mission-critical metal parts. It has quickly rose to prominence due to its proprietary Sapphire® system. Velo3D’s reputation can be gauged by the fact that its AM systems are used by some of the most innovative companies in the world, including SpaceX, Honeywell, Boom Supersonic and more. Velo3D is said to be effective in producing mission-critical parts and that too at fraction of time and cost required by conventional technologies.
Velo3D is a leading additive manufacturing technology company for mission-critical metal parts. It has quickly rose to prominence due to its proprietary Sapphire® system. Velo3D’s reputation can be gauged by the fact that its AM systems are used by some of the most innovative companies in the world, including SpaceX, Honeywell, Boom Supersonic and more. Velo3D is said to be effective in producing mission-critical parts and that too at fraction of time and cost required by conventional technologies.
Share Price (March, 2022): $7.78
Desktop Metal Inc. (NYSE: DM)
Market Capitalisation: $1.27B
Desktop Metal became a publicly listed company on December 10, 2020 after going through a SPAC deal. There was much excitement as Desktop Metal went public but for multiple reasons the DM stock has continued to fall. From the stock hitting an all-time high of $35 per share last February, it has plummeted to $4 per share (March 3rd, 2022).
Though the picture seems dark, Desktop Metal is betting big on its flagship Production System P-50 printer. The company shipped its first P-50 printer on 28th February. So, there is something to look forward to.
Share Price (March, 2022): $4.03
Materialise N.V. ADR (NASDAQ:
MTLS)Image Source: MaterialiseMarket Capitalisation: $1.17B
With a market capitalisation of $1.17B, Belgium-based Materialise NV comes at number seven this year. The company has more than two decades of 3D printing experience and offers a host of software solutions and 3D printing services to a variety of industries such as automotive, art and design, consumer goods, and healthcare.
The Materialise stock is steady at $19 per share. Though it reached a 52-week high of $77 per share in February last year, but has seen a downturn since then.
Share Price (March, 2022): $19.34
Nano Dimension (NASDAQ: NNDM)Image Credit: Nano DimensionMarket Capitalisation: $890. 02M
02M
Israel-based Nano Dimension is the next on the list of the world’s largest 3D printing companies with a market cap of $890.02M. The company has registered exponential growth recently and has emerged as a leader in additive electronics and nanotechnology-based ink products. Its products include the award-winning DragonFly Pro 2020 3D printer known to 3D print a variety of functional electronics such as sensors, antennas, moulded connected devices, printed circuit boards, and other devices. By easing the process of manufacturing such complex electronic devices, the DragonFly 2020 Pro 3D printer is transforming the electronic additive manufacturing market and allowing companies to take charge of their entire development cycle.
Share Price (March, 2022): $3.41
Markforged Holding Corp. (NYSE: MKFG)
Image Source: MarkforgedMarket Capitalisation: $691.37M
Markforged is an American public additive manufacturing company that debuted on the NYSE last year in July 2021. It designs, develops, and manufactures The Digital Forge — an industrial platform of 3D printers, software and materials that enables manufacturers to print parts at the point-of-need.
It designs, develops, and manufactures The Digital Forge — an industrial platform of 3D printers, software and materials that enables manufacturers to print parts at the point-of-need.
Markforged was valued at $2.1 billion at the time of its debut but has seen a downfall in stock prices like almost every 3D printing company and especially those going public via SPAC deals. One of the reason for the fall in prices is likely due to the SPAC deals going out of favour among many other.
Share Price (March, 2022): $3.57
Shapeways Holdings Inc.: (NYSE: SHPW)
Market Capitalisation: $155.51M
Shapeways is the Dutch-New York counterpart of the Belgian Materialise. It is a digital manufacturing platform offering customers access to high-quality part manufacturing from a wide selection of processes and materials through automation, innovation and digitisation.
It also offer ready-made products from its marketplace like an E-commerce store catering to B2C clients who can place an order and get it delivered to their doorstep.
Share Price (March, 2022): $3.13
MeaTech 3D Ltd. (NASDAQ: MITC)
Market Capitalisation: $82.49M
MeaTech4D is also among the biggest 3D printing companies in the world. MeaTech 3D Ltd. is an Israeli food technology company, that promotes and focuses on developing alternative option to industrialised farming. It does this to circumvent the ethical and environmental issues surrounding conventional animal husbandry by developing an industrial cultured meat production process with integrated 3D printing technology. It aims to develop a customised process to manufacture protein without animal slaughter.
MeaTech was also among the companies that went public last year in 2021.
Share Price (March, 2022): $5.15
Organovo Holding Inc. (NASDAQ: ONVO)
Image Source: OrganovoMarket Capitalisation: $32.82M
San Diego-based Organovo is at the 12th position in the list of the world’s largest 3D printing company with a market cap of $76. 65 million. Known to transform the future of regenerative medicine with its 3D bioprinting technology, the company has partnered with several pharmaceuticals, medical centers and develops 3D human tissue models that could be used for different medical purposes such as biological research, predictive preclinical testing of drug compounds, therapeutic implants and even to treat damaged or degenerating tissues and organs.
65 million. Known to transform the future of regenerative medicine with its 3D bioprinting technology, the company has partnered with several pharmaceuticals, medical centers and develops 3D human tissue models that could be used for different medical purposes such as biological research, predictive preclinical testing of drug compounds, therapeutic implants and even to treat damaged or degenerating tissues and organs.
Share Price (March, 2022): $4.67
Voxeljet AG ADR (NASDAQ: VJET)
Market Capitalisation: $30.57M
The next on this list of the world’s largest 3D printing companies with a market cap of $96.59 million is Voxeljet. A manufacturer of 3D printing systems for industrial applications, Voxeljet is known for its large-format production and a chemical 3D printing process. The company caters to industries that range from automotive, aerospace to architecture and design.
Share Price (March, 2022): $4.60
Final Thoughts
The list of 13 of the largest and the best 3D printing companies around the world also offer a great representation of the entire 3D printing ecosystem. This list has some of the biggest 3D printer manufacturers, 3D printing service providers, software manufacturers and also one of the top medical/healthcare 3D printing company.
This list has some of the biggest 3D printer manufacturers, 3D printing service providers, software manufacturers and also one of the top medical/healthcare 3D printing company.
Note: The article is for informational purposes only. Manufactur3D does not offer personalised investment recommendations or views about any particular company or stock of a company
About Manufactur3D Magazine: Manufactur3D is an online magazine on 3D printing. which publishes the latest 3D printing news, insights and analysis from all around the world. Visit our 3D Printing Education page to read more such informative articles. To stay up-to-date about the latest happenings in the 3D printing world, like us on Facebook or follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter.
How a 3D printer works, what can be printed on a 3D printer
The 3D printer is a technology that allows you to create real objects from a digital model. It all started in the 80s under the name "rapid prototyping", which was the goal of the technology: to create a prototype faster and cheaper. A lot has changed since then, and today 3D printers allow you to create anything you can imagine.
It all started in the 80s under the name "rapid prototyping", which was the goal of the technology: to create a prototype faster and cheaper. A lot has changed since then, and today 3D printers allow you to create anything you can imagine.
Contents:
- What is 3D printing? nine0012
- How does a 3D printer work?
- What can be printed?
The 3D printer allows you to create objects that are almost identical to their virtual models. That is why the scope of these technologies is so wide.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process because, unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, 3D printing does not remove material, but adds it, layer by layer—that is, it builds or grows. nine0005
- In the first step of printing, the data from the drawing or 3D model is read by the printer.
- Next is the sequential overlay of layers.
- These layers, consisting of sheet material, liquid or powder, are combined with each other, turning into the final form.
With limited production of parts, 3D printing will be faster and cheaper. The world of 3D printing does not stand still and therefore there are more and more different technologies competing with each other on the market. The difference lies in the printing process itself. Some technologies create layers by softening or melting the material, then they provide layer-by-layer application of this same material. Other technologies involve the use of liquid materials, which acquire a solid form in the process under the influence of various factors. nine0005
In order to print something , you first need a 3D model of the object, which you can create in a 3D modeling program (CAD - Computer Aided Design), or use a 3D scanner to scan the object you want print. There are also easier options, such as looking for models on the internet that have been created and made available to other people.
Once your design is ready, all you need to do is import it into the Slicer, a program that converts the model into codes and instructions for a 3D printer, most of the programs are open source and free. The slicer will convert your project into a gcode file ready to be printed as a physical object. Simply save the file to the included SD card and insert it into your 3D printer and hit print. nine0005
The slicer will convert your project into a gcode file ready to be printed as a physical object. Simply save the file to the included SD card and insert it into your 3D printer and hit print. nine0005
The whole process can take several hours and sometimes several days. It all depends on the size, material and complexity of the model. Some 3D printers use two different materials. One of them is part of the model itself, the other acts as a prop that supports parts of the model hanging in the air. The second material is subsequently removed.
How does a 3D printer work?
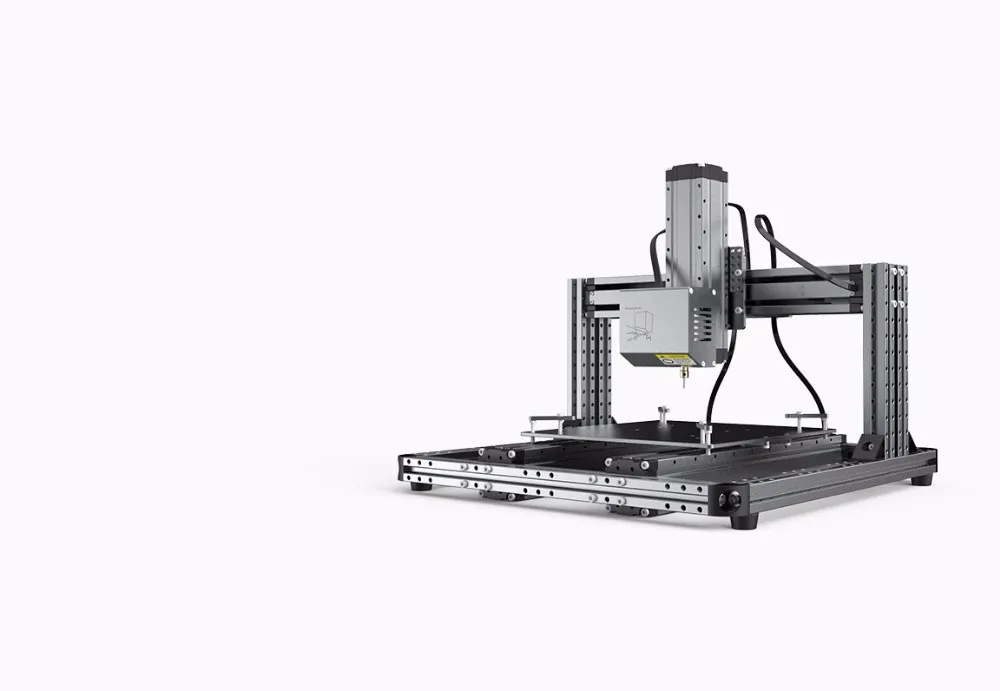
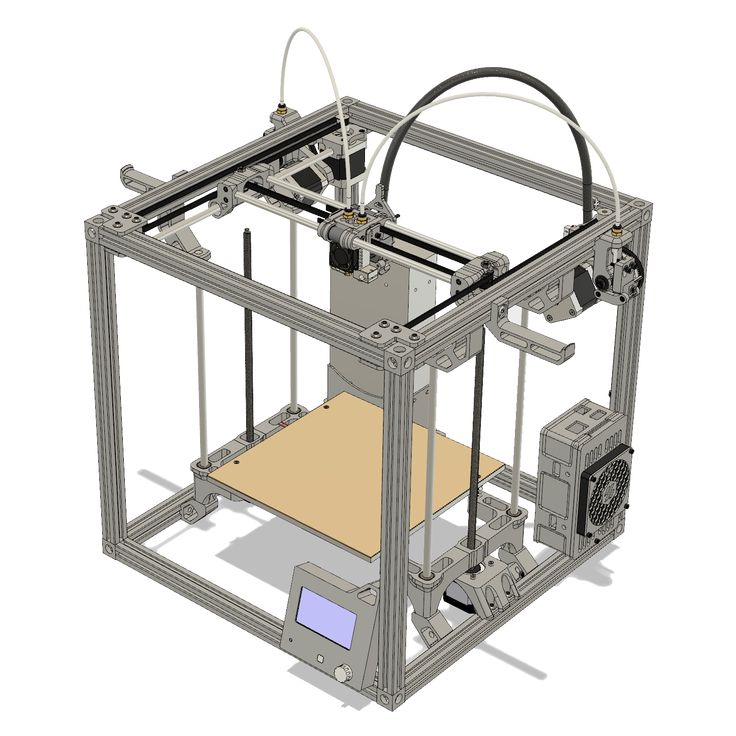
Although there are several 3D printing technologies, most create an object by building up many successive thin layers of material. Typically desktop 3D printers use plastic filaments (1) which are fed into the printer by the feeder (2) . The filament melts in the print head (3) which extrudes the material onto the platform (4) creating the object layer by layer.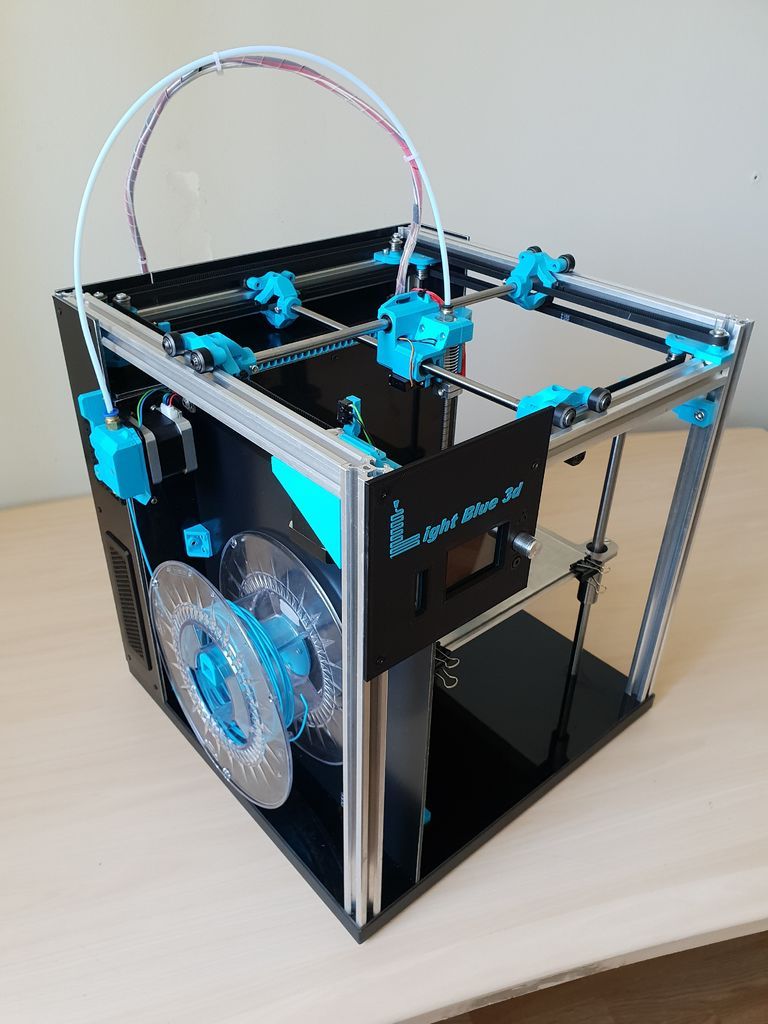 Once the printer starts printing, all you have to do is wait - it's easy.
Once the printer starts printing, all you have to do is wait - it's easy.
Of course, as you become an advanced user, playing with the settings and tweaking your printer can lead to even better results.
What can be 3D printed? nine0021
The possibilities of 3D printers are endless and they are now becoming a common tool in fields such as engineering, industrial design, manufacturing and architecture. Here are some typical usage examples:
Custom Models
Create custom products that perfectly match your needs in terms of size and shape. Do something that would be impossible with any other technology.
Rapid Prototyping
3D printing allows you to quickly create a model or prototype, helping engineers, designers and companies get feedback on their projects in a short time.
Complex geometry
Models that are hard to imagine can be easily created with a 3D printer. These models are good for teaching others about complex geometry in a fun and useful way.
Cost reduction
The cost of 3D printing end-use parts and prototypes is low due to the materials and technology used. Reduced production time and material consumption as you can print models multiple times using only the material you need. nine0005
How to choose and buy a 3D printer? →
What is a 3D printer and why is it needed? / Amperka
Additive technologies have been going to the masses for a long time: institutes and research centers have been closely involved in them since the 80s, and now the moment has come when you can touch high-tech and master 3D printing right at home. You don’t even have to break the bank to do this: the prices of 3D printers have caught up with average smartphones. We understand how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts! nine0005
Everything for 3D printing ❯
Why you need a 3D printer
The printer is very useful for do-it-yourself engineers. You no longer have to look for a universal case for the project, and then drill additional holes in it.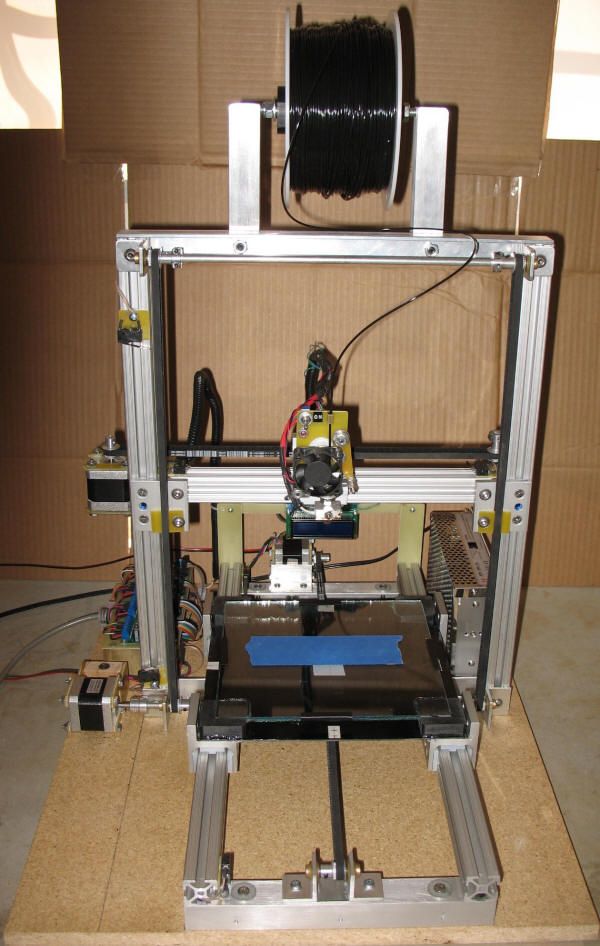 30 minutes of design, a few hours of printing - and you already have a case that is perfect for your device. Assembly of 5 shields does not fit anywhere? Forget about such problems.
30 minutes of design, a few hours of printing - and you already have a case that is perfect for your device. Assembly of 5 shields does not fit anywhere? Forget about such problems.
The printer is sure to help you repair gizmos around the house. Everyone has had a situation in life when a thing had to be thrown away, although only one plastic part was broken in it. With the help of 3D printing, you can easily replace rare plastic parts in appliances that are difficult to find separately. nine0005
Until you learn how to model plastic parts yourself, you can simply download them on the Internet. There are many sites with millions of ready-made free models that are freely exchanged by users. We devoted a separate article to the search for models.
Types of 3D printers
There are several main types of 3D printers that differ fundamentally in terms of how they work.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM printers are the most common type.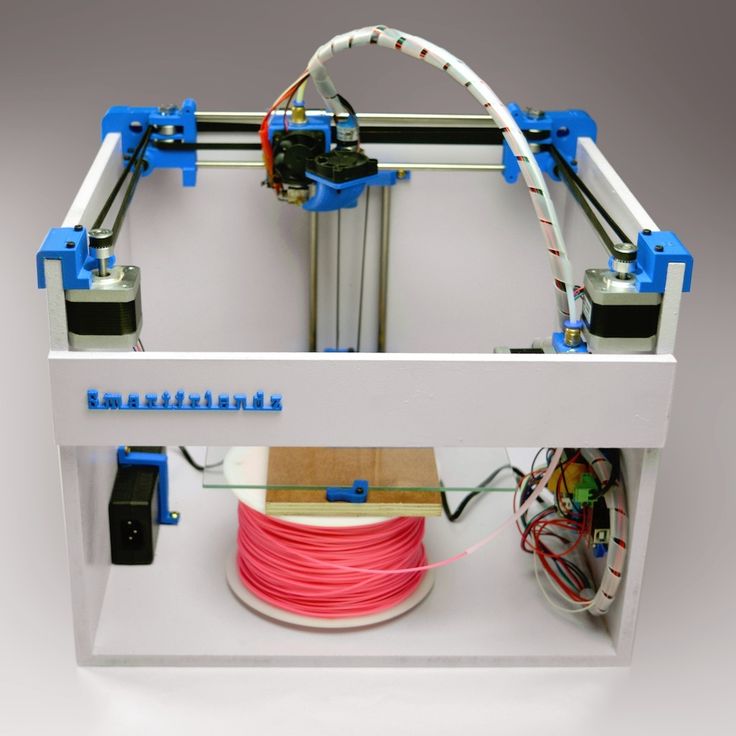 They work due to a movable print head with a heating element. Plastic is fed into it in the form of a rod, which melts and is squeezed out in liquid form onto the printing table. At the same time, the plastic is blown by a fan and instantly freezes, and the head begins to squeeze out a new layer over the frozen one.
They work due to a movable print head with a heating element. Plastic is fed into it in the form of a rod, which melts and is squeezed out in liquid form onto the printing table. At the same time, the plastic is blown by a fan and instantly freezes, and the head begins to squeeze out a new layer over the frozen one.
SLA technology (Stereolithography Apparatus)
SLA printers work on the basis of stereolithography: instead of plastic, a special photopolymer resin is used, which cures under the influence of ultraviolet rays. For printing, the resin is filled into a tray, below which there is a display with ultraviolet pixels. A drawing of the lower layer of the model is displayed on it for several seconds. In this case, the resin above the display solidifies in the form of a displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table from above. After that, the table with the first layer rises, and the next layer polymerizes in the resin. nine0005
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) Technology
SLS printers use selective laser sintering technology, which uses a special plastic powder. During the printing process, a thin layer of powder is poured, and the printer processes it with a laser so that the layer hardens according to the model. Then the next layer of powder is poured and fused with the previous one - and so on in a circle. At the end, it remains only to clean the finished part from the remnants of the powder, which can then be reused. nine0005
During the printing process, a thin layer of powder is poured, and the printer processes it with a laser so that the layer hardens according to the model. Then the next layer of powder is poured and fused with the previous one - and so on in a circle. At the end, it remains only to clean the finished part from the remnants of the powder, which can then be reused. nine0005
Technology comparison
Each type of 3D printer has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- SLS printers are large and require expensive raw materials. They are often used in high-tech industries for piece parts.
- SLA printers are much more widespread. The UV display improves accuracy, but working with toxic photopolymer resin at home is difficult.
- FDM printers are the most popular among hobbyists. A plastic rod is much cheaper than a special powder or photopolymer resin. However, to print complex geometry on such a printer, you will have to take care of auxiliary support.
 And the print speed is on average lower than on other technologies. But FDM printers are the easiest and safest to maintain. nine0012
And the print speed is on average lower than on other technologies. But FDM printers are the easiest and safest to maintain. nine0012
How to prepare a print
The process from the idea to the finished plastic part is simple - a schoolboy can handle it. We've broken it down in a 3D printing guide using the Flying Bear Ghost 5 printer as an example, but here we'll show you the general principle.
Initial model
First you need to create or download a 3D model of the future part. As a rule, sources are stored in the STL format, which describes the polygonal structure of the model as a set of triangles. But it will not be possible to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break a detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle. nine0005
Slicing
The program for cutting models (slicer) will require you to enter the model of your printer and set the print settings: layer thickness, percentage of internal filling of the part, auxiliary supports and the like. Based on this data, the slicer will automatically prepare a special code for the printer - G-Code, which describes how to move the print head, to what temperature it should be heated, and at what speed to extrude plastic in order to get the desired model layer by layer. Then it remains to load this code into a 3D printer and be patient until the end of printing. nine0005
Based on this data, the slicer will automatically prepare a special code for the printer - G-Code, which describes how to move the print head, to what temperature it should be heated, and at what speed to extrude plastic in order to get the desired model layer by layer. Then it remains to load this code into a 3D printer and be patient until the end of printing. nine0005
The whole process of model preparation is clearly illustrated by the program and provided with intuitive tips for novice users. In general, slicing is not as scary as it is painted!
Finishing
After the model is ready, it can be further processed with sandpaper or a chemical solution. This will smooth out the unevenness between the layers, and the part will look just like the factory. There are a lot of life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look. nine0005
Printing consumables
The properties of the printed item largely depend on the raw material. As we said before, FDM 3D printers use plastic filament as a consumable, and you have a lot of room to experiment with different types of plastic.
As we said before, FDM 3D printers use plastic filament as a consumable, and you have a lot of room to experiment with different types of plastic.
- PLA is highly extrudable and allows complex shapes to be printed at relatively low head operating temperatures of 190°C. The biodegradability of PLA plays into the hands of the environment, but at the same time, things from it are not very durable. nine0012
- PETG plastic is stronger than PLA, but also well suited for printers with temperatures around 200 °C. Varieties of PET plastic are well known to you from bags and plastic soda bottles.
- ABS is more durable than other types. However, your printer will need an elevated extrusion temperature of around 250°C and a heated bed up to 120°C to print quality ABS plastic, so not every model aims to support it. nine0012
- HIPS plastic is close in temperature properties to ABS, but has low caking with it and is easily removed with an organic solvent. Because of this, HIPS plastic is often used for printing composite models and supports for ABS models.

Learn more