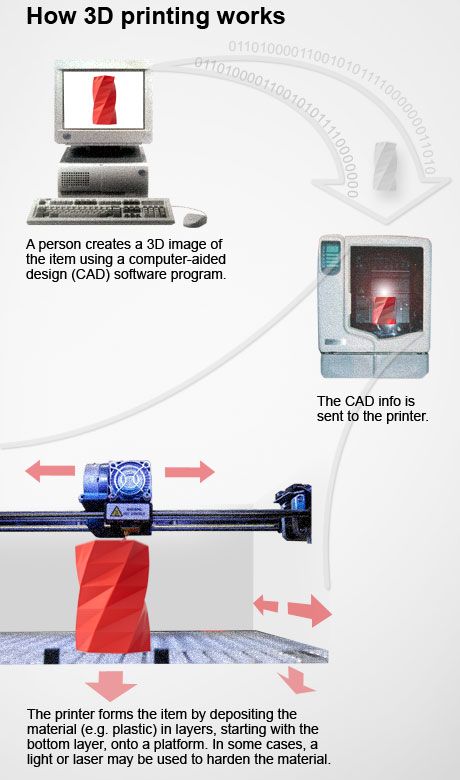
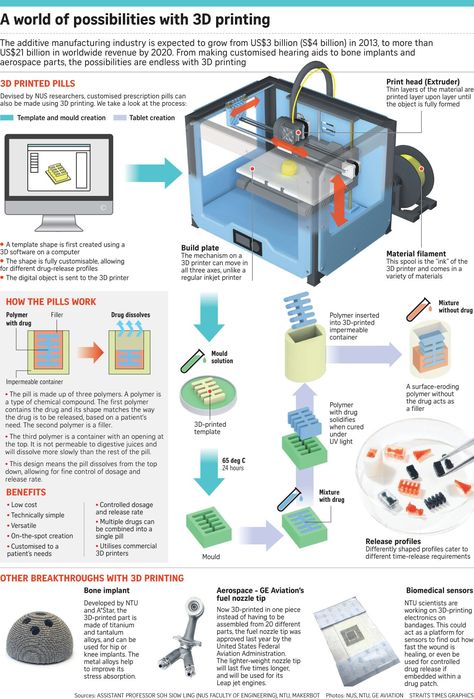
What material does 3d printers use
What Materials Are Used in 3D Printing?
Published Date
Author Jeff Yoders- Plastic is still the most popular material used for 3D printing.
- As the 3D-printing market value increases, the list of what materials can be used also grows.
- Raw materials such as metal, graphite, and carbon fiber are commonly used for 3D printing, though at-home use is mostly limited to PLA for now.
Ice cream. Molecules for medicine. Even human skin. The list of what materials are used in 3D printing grows longer—and much more interesting—by the day. And expanding it is a multibillion-dollar material arms race right now.
A recently released 3D-printing market study found that the worldwide market for 3D-printing products was valued at $12. 6 billion in 2020 and was expected to grow to $37.2 billion by 2036. That means a huge increase in the materials those machines use.
What Is The Most Common Material Used for 3D Printing?
Plastic still reigns supreme in the 3D printing. According to a Grand View Research report, the market size for 3D printing plastics globally was valued at $638.7 million in 2020 and was expected to grow to $2.83 billion by 2027.
This material isn’t just your “everyday” plastic. Two types of plastic are most commonly used in 3D printing:
- PLA: Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) is the most popular 3D-printing material. It’s a biodegradable plastic made from renewables such as cornstarch. Its low melting point makes it easy to use at home.
- ABS: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is best suited for parts that require strength and flexibility, like car components or household appliances. It’s also known for its low cost.
But it doesn’t stop there in the 3D-printing materials world.
1. Metal
Used for: Ready-to-install parts, finished products, prototypes
If there is a runner-up to plastic, it would be metal. Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is the technique and, unlike printing plastics, it can be used to make either a finished industrial product or a prototype. The aviation industry is already an early proponent and consumer of DMLS printing to streamline operations and manufacture ready-to-install parts. There are even already mass-market DMLS printers for creating 3D-printed jewelry.
The growth and popularity of 3D printing metals holds the potential to manufacture and create more effective machine parts that currently cannot be mass-produced onsite. This could lead to better conductors, tensile strength, and other attributes of laboratory metals than “mined-and-refined” metals such as steel and copper.
In the aerospace industry, the materials question is largely answered, and creating volume of parts is the Holy Grail. GE Aviation began printing fuel nozzles for its LEAP jet engine in 2016, ramping up to 30,000 parts in less than three years and printing its 100,000th nozzle in 2021. The LEAP’s successor, the RISE, will also incorporate 3D-printed parts.
GE Aviation began printing fuel nozzles for its LEAP jet engine in 2016, ramping up to 30,000 parts in less than three years and printing its 100,000th nozzle in 2021. The LEAP’s successor, the RISE, will also incorporate 3D-printed parts.
Used for: Electronics, lighting
Australian-listed graphite and nickel miner Kibaran Resources has partnered with 3D-printing company 3D Group to share development costs on a research-and-development venture called 3D Graphtech Industries.
The partnership is pursuing patents to investigate 3D printing graphite and graphene, a pure form of carbon first created in a laboratory in 2004. Graphene conducts electricity better and is stronger, easier to insulate, and lighter than other conductors on the market today. It outperforms even the best conductors several times over. Because it must be created in a lab, it is a good case study for just what kind of mass production of metals additive manufacturing can accomplish.
Because it must be created in a lab, it is a good case study for just what kind of mass production of metals additive manufacturing can accomplish.
Materials for research and development are sourced from Kibaran’s Tanzanian mines, where graphite with high crystallinity and a purity of 99.9% carbon has been found. This is incredibly well-suited to the production of graphene.
The semiconductor industry is interested in producing large quantities of graphene, as well. For example, IBM found a way to use it for LED lighting in 2014. The ability to 3D print sheets of material for use in LEDs could seriously cut lighting production costs.
3. Carbon FiberUsed for: Bearings, parts, electrical cable installation
Related to graphite, carbon fiber (which undergoes an oxidation process that stretches the polymer) can be added to the more traditional plastic to create a composite that can be as strong as steel but less intensive to use than aluminum, says Markforged. The company’s large-format 3D printers are designed to print stronger parts more quickly and at significantly lower costs.
The company’s large-format 3D printers are designed to print stronger parts more quickly and at significantly lower costs.
Meanwhile, startup Impossible Objects has also been exploring carbon fiber, as well as glass, Kevlar, and fiberglass. The company’s printer can also work with PEEK (polyether ether ketone) thermoplastic polymers, which are typically used for bearings, piston parts, and electrical cable installation.
New 3D Printing Materials
The 3D-printing industry is experimenting with a wide variety of innovative, novel approaches such a bio-based resins made from corn and soybean oil, powders, nitinol, and even paper.
Do I Need a New 3D Printer for These Materials?As the list of materials grows, what does this mean for the actual hardware? Right now, on the consumer level, plastic is about as good as it gets. For example, the $1,399 Dremel 3D40 Flex is limited to PLA.
Today, several printers are focused entirely on DMLS, including the 3DSystems DMP Flex 350 and several models from Stratasys, but these currently cost upward of $100,000 each because DMLS printers burn much hotter than their plastic counterparts, as the powders and metals they create have higher melting points. Stronger housings and more powerful industrial smelting tools increase their costs significantly.
Stronger housings and more powerful industrial smelting tools increase their costs significantly.
Although many 3D-printer manufacturers are offering metal 3D-printing services, it will be some time before the economies of scale that helped bring down the cost of plastic 3D printing affect the DMLS market. And 3D-printing systems with graphite/carbon fiber are just now starting to gain traction in the marketplace.
The diversity of applications that industries are exploring for 3D printing makes for an exciting but tumultuous time. From jet parts to lighting to rapid prototyping, the new (and “old”) 3D printing materials will deliver even more opportunities for how and what industries print.
This article has been updated. It was originally published in November 2014.
About the Author
Jeff Yoders has covered IT, CAD, and BIM for Building Design + Construction, Structural Engineer, and CE News magazines. He has won six American Society of Business Publications Editors awards and was part of the reporting team for the 2012 Jesse H. Neal Award for best subject-related series of stories.
Neal Award for best subject-related series of stories.
Follow on Twitter More Content by Jeff Yoders
Top 10 Materials Used For Industrial 3D Printing
Over the years, 3D printing industry has been growing and new advancements are being introduced. New 3D printing machines are also being developed to print different kinds of materials such as plastics, metals, composites and many more.
When it comes to industrial 3D printing, there is a wide range of materials to choose from. These materials have their own unique features, strengths and weaknesses. Moreover, there are important factors such as material type, texture, cost, etc. that need to be considered to avoid mistakes in 3d printing. It can be difficult to choose the most suitable material for a specific project.
To guide designers and engineers, listed below are the Top 10 materials used for industrial 3D printing.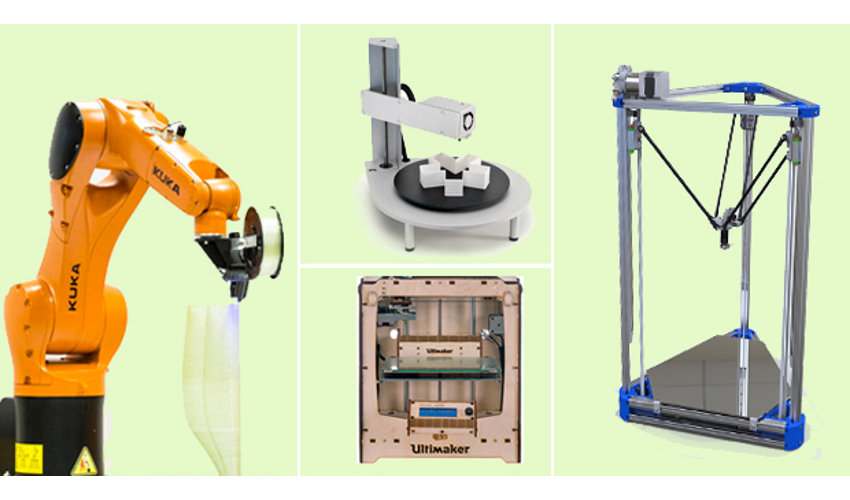
- Nylon
Nylon (known as polyamide) is a synthetic thermoplastic linear polyamide and is the most common plastic material. It is a well-known 3D printing filament because of its flexibility, durability, low friction and corrosion resistance. Nylon is also a popular material used in manufacturing of clothes and accessories.
Nylon is suitable to use when creating complex and delicate geometries. It is primarily used as filaments in FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) or FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) 3D printers. This material is inexpensive and recognised as one of the toughest plastic material.
Distinct Characteristics:
- Nylon is known for its durability.
- It has an excellent strength to flexibility ratio.
- Nylon has a very little warpage.
- This type of material can be easily dyed or coloured.
Disadvantages:
- Since nylon is hydroscopic, it should be kept dry.
- It has a shelf life of 12 months.
- This material can shrink during cooling, thus, prints may be less precise.
- Printer suitability also varies.
- ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a thermoplastic that is commonly used as a 3D printer filament. It is also a material generally used in personal or household 3D printing and is a go-to material for most 3D printers.
Distinct Characteristics:
- It is one of the most accessible and cheap materials for 3D printing.
- ABS is highly available and has a wide variety of colours.
- This material has a longer lifespan compared to Nylon.
- It is also mechanically strong.
- This material is not suitable for hobbyists. It is only used for manufacturers and engineers who are looking for high-quality prototype production.
Disadvantages:
- It requires heated bed when printing.
- Since ABS materials have high melting point, it has a tendency to experience warping if cooled while printing.
- This type of filament is a non-biodegradable toxic material that releases toxic fumes with awful smell at high temperature.
- Resin
Resin is one of the most used material in 3D printing. It is mainly used in technologies such as SLA, DLP, Multijet or CLIP technologies. There are various types of resins that can be used in 3D printing such as castable resins, tough resins, flexible resins, etc.
Distinct characteristics:
- It can be used in many applications.
- It has low shrinkage.
- Resin materials have high chemical resistance.
- This material is rigid and delicate.
Disadvantages:
- It is expensive.
- This type of filament also expires.
- It needs to be stored securely due to its high photo-reactivity.
- When exposed to heat, it can cause premature polymerization.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA or Polylactic Acid are made from renewable resources such as sugarcane or cornstarch. It is also called “green plastic”. It is mostly used in primary and secondary schools since it is safe to use and easy to print with. It is also used in FDM desktop printing.
It is also called “green plastic”. It is mostly used in primary and secondary schools since it is safe to use and easy to print with. It is also used in FDM desktop printing.
Distinct characteristics:
- PLA is easy to print since it has low warping.
- It can also be printed on a cold surface.
- It can print with sharper corners and features compared to ABS material.
- This material is available in different colours.
Disadvantages:
- PLA materials are not very sturdy and can deform when exposed to extreme heat.
- This type of material is less sturdy.
- Gold and silver
Today, it is possible to 3D print using gold and silver. These filaments are sturdy materials and are processed in powder form. These materials are generally used in the jewellery sector. These metal use the DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) or SLM process for printing.
Distinct Characteristics:
- It has high electrical conductance.
- It is heat proof.
Disadvantages:
- Printing with gold and silver are expensive.
- It takes a lot of effort and time to get it right.
- Both gold and silver are difficult to work with lasers because of its high reflectivity and high thermal conductivity.
- Since extremely high temperature is needed to print these materials, a regular FDM 3D printer is not suitable to use.
- Stainless steel
Stainless steel is printed by fusion or laser sintering. There are two possible technologies that can be used for this material. It can be DMLS or SLM technologies. Since stainless steel is all about strength and detail, it is perfect to use for miniatures, bolts and key chains
Distinct Characteristics:
- Stainless steel can be heat treated in order to improve strength and hardness.
- It performs well in high strength applications.
- It provides strong resistance against corrosion.

- It has high ductility.
Disadvantages:
- Building time for 3D printing using these metals are much longer.
- Printing with stainless steel is expensive.
- Printing size is limited.
- Titanium
Titanium is the strongest and the lightest material for 3D printing. It is used in the process called Direct Metal Laser Sintering. This metal is mainly used in high-tech fields such as space exploration, aeronautics and medical field.
Distinct Characteristics:
- It provides greater complexity and resolution in design.
- It offers industrial designers precision in design.
- It has an average surface roughness.
- Titanium is also biocompatible and resists corrosion.
Disadvantages:
- Titanium 3D printing is expensive.
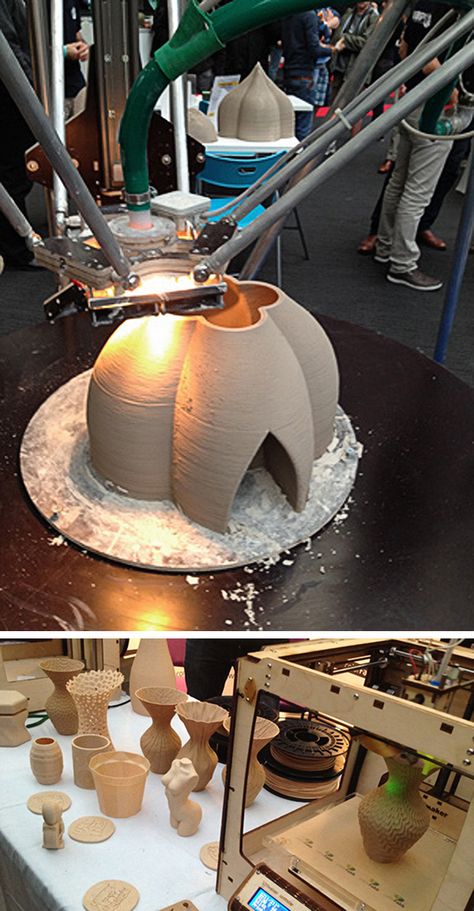
- Ceramics
Ceramics is one of the newest material that is used in 3D printing. It is more durable than metal and plastic since it can withstand extreme heat and pressure without even breaking or warping it. Moreover, this type of material is not prone to corrosion like other metals or wear away like plastics do.
It is more durable than metal and plastic since it can withstand extreme heat and pressure without even breaking or warping it. Moreover, this type of material is not prone to corrosion like other metals or wear away like plastics do.
This material is generally used in Binder Jetting technology, SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing).
Distinct characteristics:
- It has high-precision components with a smooth and glossy surface.
- It has also resistance to acid, heat and lye.
- It has a wide range of colour
Disadvantages:
- Ceramic requires great amount of temperature to melt.
- It is not suitable for glazing and kilning processes.
- Since it is fragile, it has limitations in printing objects with enclosed and interlocking parts.
- It is not ideal for piece assembly process.
- PET/PETG
Like Nylon, PET or Polyethylene terephthalate is also one of the frequently used plastic. This material is used in thermoforming processes. It can also be combined with other materials like glass fiber to create engineering resins.
This material is used in thermoforming processes. It can also be combined with other materials like glass fiber to create engineering resins.
In 3D printing, PETG is used. It is a modified version of PET where G stands for “glycol-modified”. As a result, a filament that is less brittle, clearer and easier to use than PET is formed. This filament is applicable in FDM or FFF technologies.
Distinct characteristics:
- This material is durable.
- It is impact-resistant and recyclable.
- It can also be sterilised.
- It has an excellent layer adhesion.
- It has a combined functionality of ABS (temperature resistant, stronger) and PLA (easy to print).
Disadvantages:
- The material can be weakened by UV light.
- It is prone to scratching.
- More testing with 3D printing parameters is needed.
- HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
HIPS or High Impact Polystyrene are plastic filaments that are used for support structures in FDM printers. It comparable to ABS when it comes to ease of use. The only difference is its ability to dissolve. HIPS is completely soluble to a liquid hydrocarbon called limonene.
It comparable to ABS when it comes to ease of use. The only difference is its ability to dissolve. HIPS is completely soluble to a liquid hydrocarbon called limonene.
Distinct Characteristics:
- It has good machinability. It can also be used to make complex structures.
- It is very smooth and lightweight.
- It is water resistant and impact resistant.
- It is inexpensive.
Disadvantages:
- It produces strong fumes. Thus, it is recommended to be used in a ventilated area.
- Without constant heat flow, this material can clog up nozzle and delivery tubes of the printer.
With proper knowledge equipped and the right materials being used, industrial 3D printing can be done efficiently. As the 3D printing industry grows, more and more materials will be used for making prototypes and will be compatible with different 3D printers. As with any new processes and equipment there is a steep learning curve and this increases as you move from plastic to metal 3D Printing.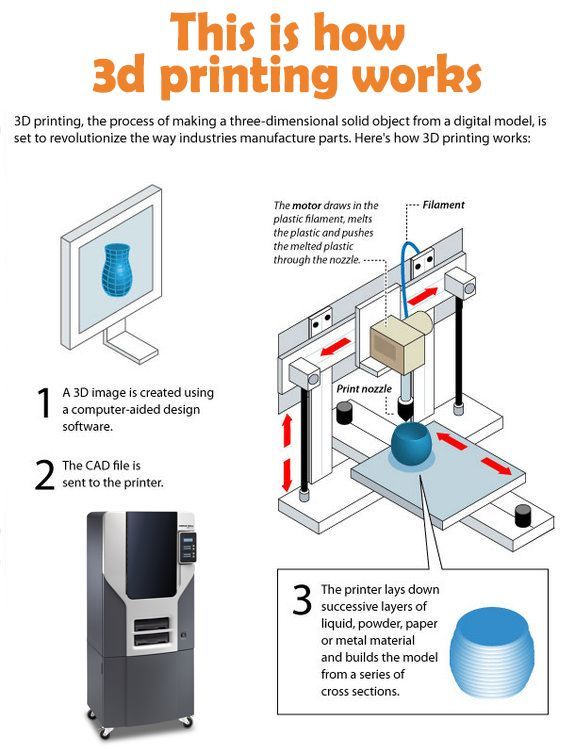
If you want to enjoy the ease of 3D printing, you can just outsource to a reliable 3D printing service provider. Your company actually doesn't need to do 3D design and printing, mechanical design and drafting, 3D design modelling services and in-house as they all can be done professionally with quality and accuracy by a local 3d printing company.
What material does the 3D printer print with? Plastic for 3d printer.
Layer-by-layer printing of three-dimensional models is made from a variety of materials, be it plastic, concrete or metal, and even hydrogel, chocolate and living cells.
For 3D printing, the use of ABS plastic is most optimal. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (official name ABC plastic ) is valued for the absence of foreign smell, toxicity, in addition, it is impact resistant, flexible and elastic. The material begins to melt from 240 to 248 degrees Celsius. Plastic goes on sale in a powdered state, or in the form of bobbins with plastic threads wound around them. Despite the fact that plastic does not tolerate direct sunlight, models made from it are famous for their durability. Plastic for a 3D printer can be bought in our online store.
Despite the fact that plastic does not tolerate direct sunlight, models made from it are famous for their durability. Plastic for a 3D printer can be bought in our online store.
Unlike ABC plastic, which models are opaque, acrylic is used to create transparent objects. But acrylic is more capricious in the process of use: the melting point of acrylic is reached later, which means that it will take more time and energy to heat up, and at the same time it quickly cools and hardens. The very process of manufacturing the product is laborious, since heated acrylic contains a lot of air bubbles that can distort the finished product.
Concrete applied for 3D printing , improved, and has a formula that differs from the formula of conventional cement by 5%. The “printing” of a residential building with an area of 230 m2 on a 3D printer will take no more than 20 hours, during which it carefully “lays out” building blocks and structures from concrete.
The use of hydrogel for 3D printing was successfully tested by scientists from the University of Illinois, who used a 3D printer to print miniature (5-10 mm) biorobots. Living cells isolated from the tissue of the heart muscle were placed on them, which, spreading through the hydrogel, set the biorobot in motion. The speed of such a biorobot is 236 µm/s. As planned by scientists, in the future, with the help of such biorobots, tumors and toxins in the body will be detected and neutralized, and they will also be used to deliver medications to diseased human organs.
Living cells isolated from the tissue of the heart muscle were placed on them, which, spreading through the hydrogel, set the biorobot in motion. The speed of such a biorobot is 236 µm/s. As planned by scientists, in the future, with the help of such biorobots, tumors and toxins in the body will be detected and neutralized, and they will also be used to deliver medications to diseased human organs.
There are 3D printers that use ordinary office paper as a material. Pre-cut layers of paper are applied one on top of the other and attached with glue. Paper models are cheap enough that they are accessible to users, but at the same time, paper models are not durable and not aesthetically pleasing. Models created in this way are ideal for prototyping in computer projects.
Gypsum used for 3D printing is a fragile, short-lived material, but at the same time it has a low cost. Therefore, models made of plaster are mainly suitable for presentations, perfectly conveying the shape, structure and size of the original product.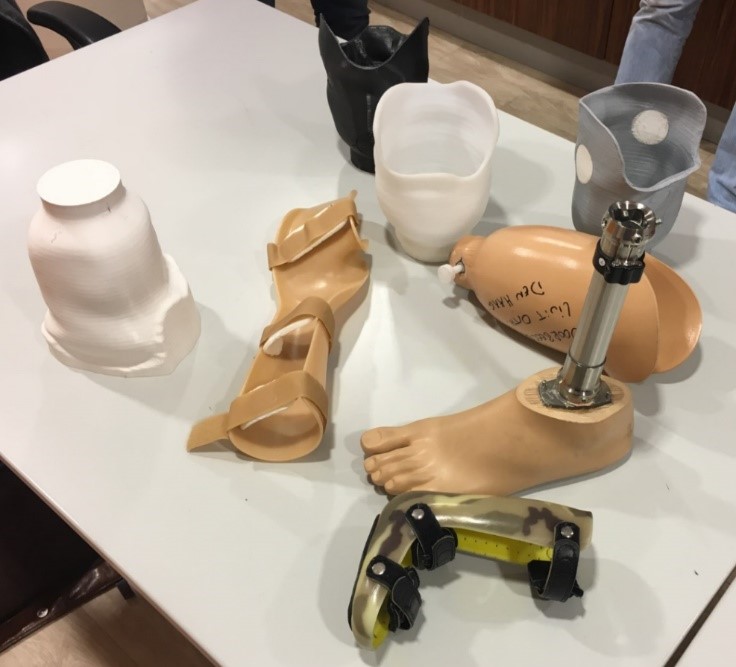 The resistance of gypsum to heat treatment makes it possible to use it in the foundry as samples for casting.
The resistance of gypsum to heat treatment makes it possible to use it in the foundry as samples for casting.
Fans of natural wood and products made from it will also enjoy 3D printing, as there is a specially designed “wood” fiber that contains wood and a polymer, and its properties are similar to polyactide (PLA). Outwardly looking like natural wooden models with the smell of fresh wood, they are quite strong and durable. Currently, the material can only be used in the RepRap self-replicating printers.
3D printing with ice is perhaps the most exotic way of making small figures today. The temperature at which the figures are printed is quite low and is -22 degrees Celsius, and the printing material is water and methyl alcohol heated to 20 degrees Celsius.
The pleasant soft sheen and high strength of the metal are far ahead in quality of any plastic used in 3D printing, therefore light and precious metal powders are successfully used in this area. Copper, aluminum and its alloys, gold and silver in powder form are used for printing, adding fiberglass and ceramic inclusions to them.
Copper, aluminum and its alloys, gold and silver in powder form are used for printing, adding fiberglass and ceramic inclusions to them.
Nylon printed parts are similar in many ways to ABS plastic parts, but are softer and more practical. Nylon manufacturing technology is more capricious, in particular, it has a longer curing period, the printing temperature reaches 320 degrees Celsius, and it is more toxic.
The 3D printers of the near future will print shaped chocolate molds, which should be in great demand in restaurants and pastry shops.
It is also impossible not to mention polycaprolactone, the most popular consumable for 3D printing. This material is so valued for its excellent physical properties and the possibility of being used in various printing technologies.
Of the plastic materials for printing, it is also worth highlighting polycarbonate (hard plastic), polylactide material obtained from biomass, sugar beet or corn silage, polypropylene, polyphenylsulfone, which came from the aviation industry, and an unsurpassed leader in the field of 3D printing, used in any of its areas - polyethylene low pressure.
Among other things, there are also printers that carry out 3D printing with mixtures of clay, lime powder, food, cells from living organic matter. And what exotic materials will be printed 3D printers in the future, one can only guess.
3D printing materials | A wide variety of materials
Materials for 3D printing! To date, the main materials for printing on a 3D printer are PLA and ABS plastic. Both materials have long established themselves on the market and are used for printing on a 3D printer using layer-by-layer material build-up technology.
ABS (ABS) plastic is a plastic formed during the polymerization of substances such as acrylonitrile (A) with butadiene (B) and styrene (S).
PLA plastic, or as it is also called biodegradable plastic, is an aliphatic polyester with a monomer in the form of lactic acid. The materials for the production of such plastic are rapidly renewable resources - corn or sugar cane, that is, starch or cellulose.
PVA plastic. The well-known PVA glue is transferred from a dry state to a liquid of the desired consistency, then melted using special equipment and formed into PVA threads or special granules that are used for 3D printing.
An even newer material, Nylon, is resistant to a wide range of chemicals and solvents. The materials discussed above are known to everyone who is associated with the 3D technology market.
These are the most commonly used materials. But manufacturers have stepped far ahead, and are already using a wide variety of materials for printing on a 3D printer, for example, clay, resin, seaweed, and more. etc.
Here is a list of the most unexpected and creative materials for 3D printing:
White Resin from Formlabs:
3D Printing Materials
3D printing equipment manufacturer Formlabs introduces a new material - White Resin. The company has recently launched two new 3D printing materials, Clear Resin and Gray Resin. The main feature of the White Resin material is the striking white and opaque color of the material, as well as the exceptional smoothness of the surface of the printed object. In addition, this material is ideal for subsequent staining.
The main feature of the White Resin material is the striking white and opaque color of the material, as well as the exceptional smoothness of the surface of the printed object. In addition, this material is ideal for subsequent staining.
Titanium Powder for 3D Printing Auto Parts:
British metalworking company Metalysis has released a new cheap titanium powder that is suitable for 3D printing of auto parts and parts. Until now, the most popular materials for 3D printing have been plastics, due to the high cost of producing titanium powders. But recently, Metalysis has found a new, low-cost way to produce titanium powder, which could become the most sought after in the manufacture of equipment and machinery in the aerospace, defense and automotive industries.
For the production of titanium powder, Metalysis uses rutile, which is electrolyzed directly into titanium powder. This method of obtaining a powder makes it possible to change, if necessary, the size of the powder granules, its purity, morphology and the proportion of the content of alloying elements in the composition.
Metal plastic for ColorFabb 3D printer:
Materials for 3D printing
BronzeFill and CopperFill are two new filaments from the premium Dutch manufacturer colorFabb. Their key feature is the addition of bronze and copper powder to the plastic, which gives the filament additional rigidity, as well as a pleasant metallic sheen and smoothness. To the touch, the model obtained as a result of printing will very much resemble a metal one.
Bronzefill and CopperFill can be polished to a beautiful metallic sheen just like any other hard bronze and copper items. After polishing, the visible streaks that remain after printing disappear, and the bronze or copper item begins to shine.
Bronze and copper plastic for 3d printing is ideal for prototyping metal products and obtaining very durable models in industry, architecture, design and other fields.
One of the most amazing materials is graphene:
3D Printing Materials
A 3D printable material with incredible potential for applications in various fields (molecular programming, solar energy, etc. ), it can change the lives of many people. In this regard, the Canadian research company Lomiko Metals Inc. announced the opening of a new special laboratory Graphene 3D Labs Inc., which will focus on the development of high-performance materials based on graphene. Information about the material: graphite or graphene is entirely composed of carbon atoms, but 1 mm of graphite contains about 3 million layers of graphene. Graphite has a three-dimensional crystal structure, while graphene is a two-dimensional crystal 1 atom thick.
), it can change the lives of many people. In this regard, the Canadian research company Lomiko Metals Inc. announced the opening of a new special laboratory Graphene 3D Labs Inc., which will focus on the development of high-performance materials based on graphene. Information about the material: graphite or graphene is entirely composed of carbon atoms, but 1 mm of graphite contains about 3 million layers of graphene. Graphite has a three-dimensional crystal structure, while graphene is a two-dimensional crystal 1 atom thick.
3D Printer Wood Filament:
3D Printing Materials
Dutch 3D printing material company colorFabb has launched WoodFill wood filament. Wooden threads WoodFill are available in two types - Fine (Delicate) and Coarse (Rough). The main difference between these threads is the quality of processing of wood fibers. WoodFill Fine uses finely ground wood particles, WoodFill Coarse threads are thicker - based on coarsely ground wood particles..jpg) Wooden threads allow you to print beautiful and original vases, decorative elements and interior items. Finished objects are highly durable and produced in a short time. WoodFill filaments are made up of 30% pine wood fibers and 70% PLA plastic.
Wooden threads allow you to print beautiful and original vases, decorative elements and interior items. Finished objects are highly durable and produced in a short time. WoodFill filaments are made up of 30% pine wood fibers and 70% PLA plastic.
Seaweed 3D Printer Filament:
3D Printing Materials
Le Fabshop is the first company in the world to introduce SWF filaments - "green" filaments based on seaweed.
New materials from Proto-Pasta:
Recently, scientist Aaron Crum and mechanical engineer Dustin Crum launched the Proto-Pasta project, which developed three new materials for use in a desktop 3D printer: Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA ( PLA reinforced with carbon fiber), High Temperature PLA (high temperature PLA) and Polycarbonate-ABS (ABS with polycarbonate alloy). Compared to all known types of plastic - ABS and PLA, the presented materials have improved performance characteristics and are affordable. Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA is more resistant to high temperatures than regular PLA. Polycarbonate-ABS (PC-ABS) is characterized by high elasticity and bending strength.
Polycarbonate-ABS (PC-ABS) is characterized by high elasticity and bending strength.
Rubber material for stereolithography:
Materials for 3D printing
This is a rubber based material ideal for stereolithography printing, the new material has a wide color gamut, allows you to print objects in high resolution, odorless, easy to peel, available from price.
3D printing material based on silk:
3D printing materials
Another 3D printing material was created from raw silk. The raw silk has been sourced from sustainable sources and treated with epoxy. The silk-based material is flexible and highly durable, thin and light, ideal for 3D printing applications.
Polished and Raw Brass for 3D Printing:
3D Printing Materials
Shapeways has introduced two new materials to the world at once - Polished Brass and Raw Brass. Polished Brass is a material with a smooth, glossy bright yellow surface. Products printed with its help, then covered with 22 carat gold, are almost indistinguishable from real gold jewelry. Raw Brass is ideal for 3D printing antique or antique-style objects, and is also useful for jewelry prototyping and functional parts.
Products printed with its help, then covered with 22 carat gold, are almost indistinguishable from real gold jewelry. Raw Brass is ideal for 3D printing antique or antique-style objects, and is also useful for jewelry prototyping and functional parts.
Shapeways Soft Plastic:
3D Printing Materials
Shapeways has developed a new soft plastic, Elasto Plastics, for use in summer footwear. Elasto Plastics has a milky white color, the material is very flexible, has an uneven grainy surface and is quite strong.
In our online store ac5ffgxkeg.lceqo.ccwc.finefive.ru there is an excellent analogue of Elasto Plastics - this is a unique flexible plastic from a Ukrainian manufacturer - PLASTAN 9 plastic0003
The second analogue - FlexibelPolyEster (FPE) - is a rubber-like elastic plastic thread designed specifically for printing on a 3D printer
Transparent resin for a 3D printer:
Materials for 3D printing stereolithography, according to the technology of layering transparent resin and strengthening the layers with a special laser.