What is the point of 3d printing
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Purposes and why people should own a 3d printer?? - No category - Talk Manufacturing
Bruce_17
#1
Hi everyone, I am a Junior student studying in Hong kong, also a 3d printing enthusiast. Currently I am doing a personal project on 3d printing. My goal is to promote the 3d printing technology, and I would really want to know what are the purposes of a 3d printer??, specifically in the eyes of a average household. Is it just for business or household? What are some reasons why an average person may want to own a 3d printer?
1 Like
GIFT3D
#2
Hey Bruce,
3D printers can be used for both business purposes and as a hobby. The main purpose is to create items with only minimal material used. In industry products are made cheaply with mass production due to techniques such as injection moulding to ensure there is no material wastage. These moulds are far too expensive for ‘one of products’ and other methods can also be costly like cuttin, sanding and finishing materials like wood, plastic or metal items. 3D printing allows people to create new ideas/ products, construct low cost prototypes and find replacement parts at a low cost.
The main purpose is to create items with only minimal material used. In industry products are made cheaply with mass production due to techniques such as injection moulding to ensure there is no material wastage. These moulds are far too expensive for ‘one of products’ and other methods can also be costly like cuttin, sanding and finishing materials like wood, plastic or metal items. 3D printing allows people to create new ideas/ products, construct low cost prototypes and find replacement parts at a low cost.
Custom designs that can be ‘one of a kind’ and rather cheap construction of items makes 3D printing desirable
Hope this helps. If you have further questions just ask.
RCole
#3
It is amazing how much use a 3D printer is at home. Of course, I do my own design work, but there is so many design files you can download as well.
For a few examples: I built an attachment for tying two wire shelves together (so one doesn’t fall down again). I build an enclosure for my Pine64 that is my new streaming system for the TV. Cell phone stand, mount for an antenna (OTA HD TV antenna in attic), replacement pointer for a weigh scale, book ends and other things.
People also use them for making toys for their kids (until the kids start making their own). RPC gamers are creating miniatures. People are creating costume parts. The possibilities are endless. As the price of printers drops and quality and speed increases, more printers will be showing up in people’s houses. It’s another manufacturing revolution.
Enza3D
#4
Bruce,
An average person won’t have as much use for a 3D printer as a business will. While the price is coming down, and you can print tons of toys/gadgets from pre-made models online (thingiverse, myminifactory, pinshape, etc.), if you truly want to make things for yourself, you have to learn CAD programs. This is one of the biggest bottlenecks to 3D printing really breaking into the consumer market, in my opinion. People see these really cool models they can print, and how people are using them to print replacements for all sorts of home appliances, even car parts and prosthetics, but don’t realize the amount of modeling time and software experience it takes to make said models. Without any CAD knowledge or the time/desire to learn new software, a 3D printer is really just a toy that has very limited use.
While the price is coming down, and you can print tons of toys/gadgets from pre-made models online (thingiverse, myminifactory, pinshape, etc.), if you truly want to make things for yourself, you have to learn CAD programs. This is one of the biggest bottlenecks to 3D printing really breaking into the consumer market, in my opinion. People see these really cool models they can print, and how people are using them to print replacements for all sorts of home appliances, even car parts and prosthetics, but don’t realize the amount of modeling time and software experience it takes to make said models. Without any CAD knowledge or the time/desire to learn new software, a 3D printer is really just a toy that has very limited use.
That being said, if someone is willing to learn some new tricks, they have tons of options and 3D printing opens a lot of doors for them. Free software, like Blender and Onshape, when combined with YouTube and Udemy, allow for makers to learn to model just about anything from home for free (or fairly low cost with Udemy).
Businesses benefit significantly from 3D printing due to reduction in prototyping times and cost. Traditionally, an engineer would model a design then send it to a shop to be fabricated and had to wait for the fabricated model to come back before making any edits to the design. With a 3D printer, you can mock up a design and have a physical model in your hands within hours instead of days.
Garyg
#5
I’ve been wanting to get a 3D printer for the past several years.
I needed to determine how much use I would get out of the printer as I did not want it sitting around gathering dust.
As Bruce said in a previous post, you need to learn CAD.
I’ve been learning to draw over the past 3 years.
I’ve been using printing services like 3D HUBS to get my designs printed.
Once my drawing skills became sufficient and efficient, I keep coming up with 3D printing projects on a quite regular basis.
My designs are small, around the house, automotive, gardening and bicycle repair and invention parts.
As a result of my 3D printing experiences so far, I’m planning on purchasing a 3D printer for home use.
I’m still unsure if my 3D printer purchase will happen this year or next, but I’m getting very close to purchase time.
…
I hope this helps you in some manner.
kr0sh2
#6
Like your shelf scenario, my primary use is repair and sometimes prototyping. Steam valve on my Gaggia Classic snapped off, made a new one in Tinkercad and printed it off in polycarbonate in about two hours flat. An official replacement would have cost me £20. One thing I think that’s an even bigger bottleneck is the price of a decent scanner - if someone could just scan their favourite mug and print twenty more we wouldn’t have to rely on CAD so much IMO.
One thing I think that’s an even bigger bottleneck is the price of a decent scanner - if someone could just scan their favourite mug and print twenty more we wouldn’t have to rely on CAD so much IMO.
kr0sh2
#7
Here’s that handle if anyone likes their coffee with steamed milk. http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:1671472
InsaneCheese
#8
As an average user with a 3d printer, at the moment I just print up stuff I can find models for. I can at best resize them using the slicer. I’ve found a bunch of neat stuff and mostly print for the sake of making stuff - I pulled 40 smileys off my printer last night for tokens represent civilians in Infinity. I think the biggest thing that’s need to be pushed is that CAD abilities are insanely useful for making anything more than what you find online. It doesn’t help when you’re reading a 3d printing blog and the guy says “oh and then I whipped up this nifty bracket/holder/whosawhatsit in 15mins” which makes it sound easy - if you read the guys bio you find out he’s being doing CAD stuff for 15 years. Which I suppose it’s like computer science at high school. 15 years ago I got a crash course in Visual Basic, now I’d imagine it’s significantly more than an introduction for 14 y.o’s.
I think the biggest thing that’s need to be pushed is that CAD abilities are insanely useful for making anything more than what you find online. It doesn’t help when you’re reading a 3d printing blog and the guy says “oh and then I whipped up this nifty bracket/holder/whosawhatsit in 15mins” which makes it sound easy - if you read the guys bio you find out he’s being doing CAD stuff for 15 years. Which I suppose it’s like computer science at high school. 15 years ago I got a crash course in Visual Basic, now I’d imagine it’s significantly more than an introduction for 14 y.o’s.
Enza3D
#9
This is unrelated to the original post, but how many of you guys would be interested in learning some CAD skills using free software (OnShape) and videos I post here? Like make talk posts once a week going over different skills starting from very basic to advanced? The comments can serve as kind of a forum.
I’ve been kicking around the idea of doing a Udemy series for CAD, and think doing this first would be a great starting point. Yes, no, maybe?
RCole
#10
It is true that the CAD programs are not keeping up with the speed that 3D Printing is evolving. But as CAD gets better and easier, this will change. Right now, yes, I’ll agree that most people would find a printer of limited utility. Remember when computers were thought of that way?
Take a look at some of the new devices like Microsoft’s HoloLens if you want to see where 3D is going in the computing world. Their design program allows the user to walk around a model and push and prod it to change a design. Sure, HoloLens is still only available to developers and expensive, but that will change too.
So, I think, as the CAD gets easier, 3D printers will be much more useful and be in more homes.
InsaneCheese
#11
I’d be interested, as long as I get to ask stupid questions. I’m sure there’s a bunch of other people who would be if you started it up.
Enza3D
#13
No such as thing as stupid questions when you’re learning something new!
RCole
#14
As a personal request - if you’re doing a tutorial, please make sure that there is good closed captioning. I’m happy to say that most of the existing OnShape tutorials have good captions and the ones produced by the OnShape team have transcripts available as well. Yay.
I’m happy to say that most of the existing OnShape tutorials have good captions and the ones produced by the OnShape team have transcripts available as well. Yay.
Enza3D
#15
The OnShape team is fantastic, and really do care about their users! This is definitely easy to implement and I myself get annoyed when videos don’t include this.
What is 3D printing and how it can be used! Interesting!
What is 3D printing
3D printing technology was patented in the 80s of the last century, but gained popularity relatively recently. New, promising techniques have been developed and the possibilities of 3D technologies have reached a completely new level. However, to this day, the technique is not known in all circles, and not everyone is aware of what 3D printing is.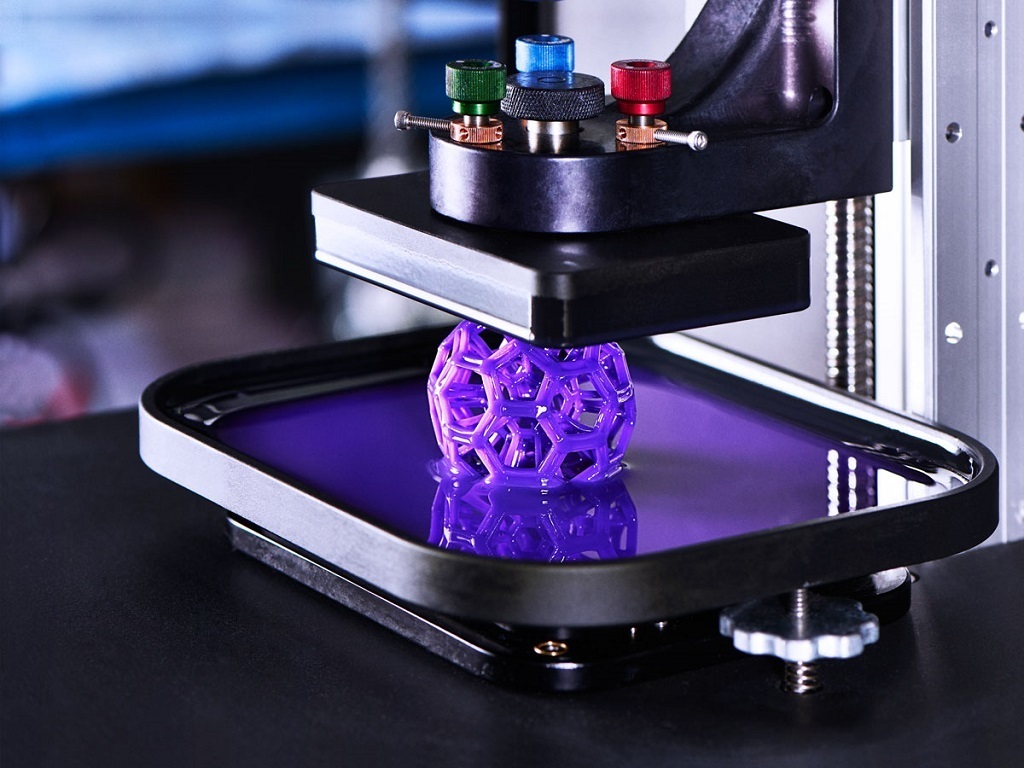 In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used.
In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used.
In short, 3D printing is a technique for manufacturing three-dimensional products based on digital models. Regardless of the specific technology, the essence of the process is the gradual layer-by-layer reproduction of objects.
This process uses a special device - a 3D printer, which prints certain types of materials. More details about it are written here. Other names for the technology are rapid prototyping or additive manufacturing. Often the phrase "additive technologies" is used in the meaning of "3D technologies".
3D printing steps
To make it clearer what 3D printing is, let's take a look at the playback process step by step. Below are the specific stages of 3D printing. How it works:
- 3D modeling of the required object is performed according to certain rules;
- The file with the digital model is loaded into the slicer program, which generates the control code for the 3D printer;
- Sets required 3D printing options;
- The code is written to a removable memory that connects to the 3D printer;
- 3D model reproduced.

Objects are reproduced gradually. According to the required shape, the selected material is applied layer by layer, forming the finished product. It is worth noting that the possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless, that is, anything can be made. In some technologies, very thin overhanging elements are provided with supports, thanks to which they can be avoided from sagging.
Naturally, this is a very simplified description of the stages of 3D printing, but they give a very clear idea of the essence of the technique.
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Basics What is 3D scanning?
- Basics What is a 3D model?
3D Printing Technologies
Different 3D printing technologies are used to reproduce different objects. They differ both in the consumables used, and in the speed and accuracy of printing. Here are the main 3D printing technologies:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) .
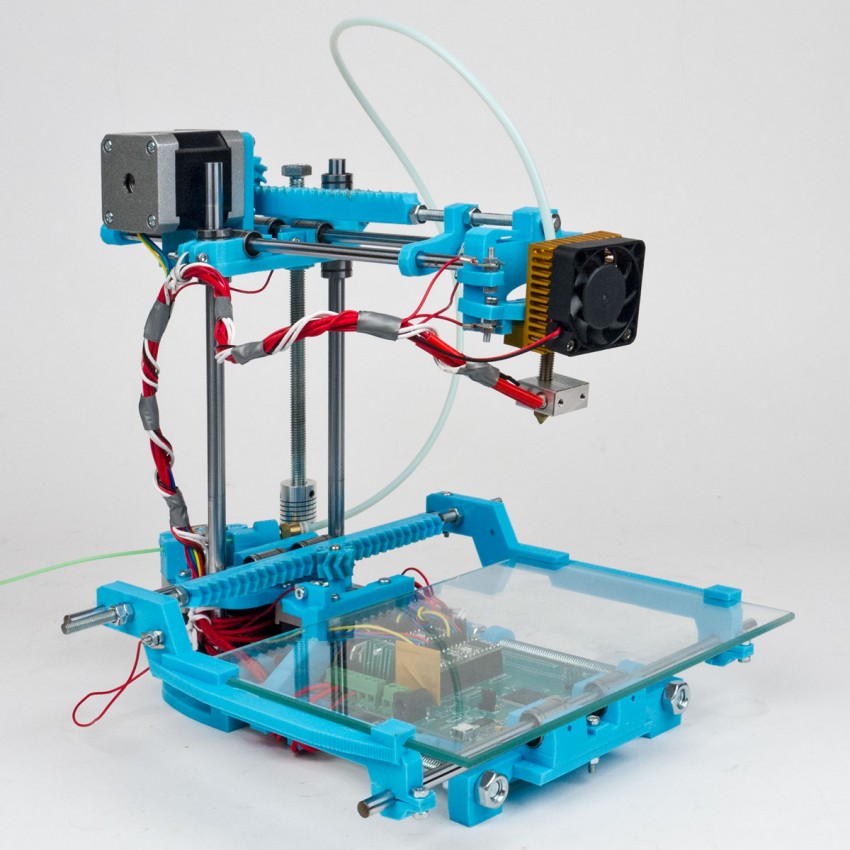 One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic;
One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic; - Laser stereolithography (SLA) . The formation of the object occurs due to the layer-by-layer illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin by a laser, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage;
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) . Reproduction is performed by layer-by-layer melting of a special powder under the action of laser radiation. This 3D printing method is widely used in the industry for the manufacture of durable metal elements
3D Printing Applications
As you may have guessed by now, 3D printing is extremely versatile. The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent.
The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent.
Well, that was a brief description of what 3D printing is. We hope we were able to provide the necessary information in an accessible way. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
We also want to remind you about the possibility to order 3D printing, 3D scanning, 3D modeling services or purchase of related equipment and consumables with delivery throughout Ukraine in 3DDevice. If you have any questions, please contact us at one of the phone numbers listed here. We look forward to collaborating!
Back to homepage
3D printing: the possibilities of additive technologies
Additive technologies or 3D printing is the process of creating an object that exactly corresponds to a three-dimensional model by applying material layer by layer. This innovation has become a global trend. The main advantage of the technology is resource saving. Losses of useful substance tend to zero.
Losses of useful substance tend to zero.
Area of use
3D printers have not yet penetrated into every home, but they are already present in all key areas of human life. 3D printing is in demand in the automotive industry, energy, medicine, food industry, construction/design, fashion industry.
In resource- and labour-intensive industries, the development of a product prototype costs a lot of money. With traditional casting or machining technologies, this takes weeks, months. Using the possibilities of volumetric printing, the work is done many times, and sometimes dozens of times, more quickly. At the same time, the quality does not suffer at all and the parameters of the product remain extremely accurate. By the way, the strength of the prototype is more than 20% higher than that of the classic production.
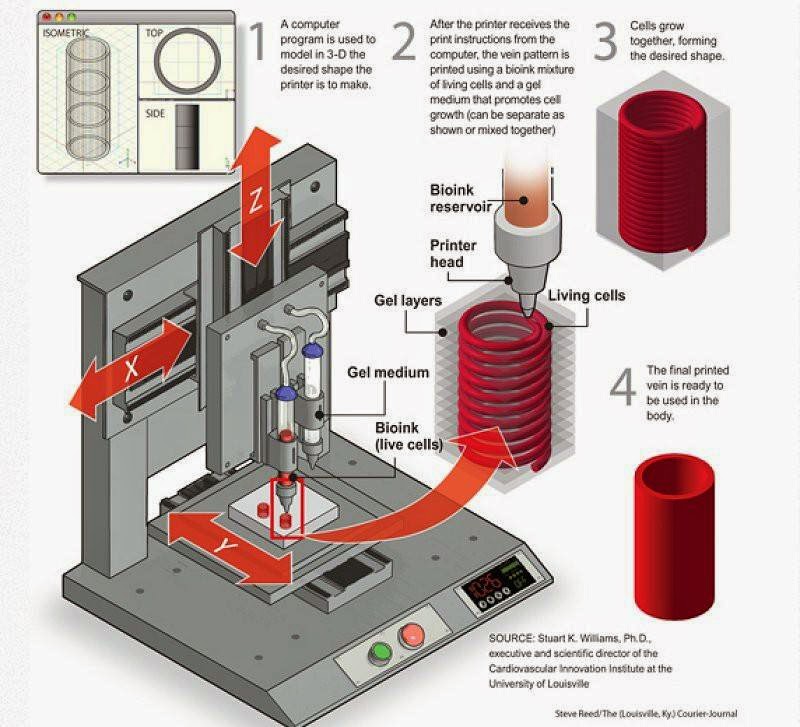
In medicine, the possibilities of 3D printing are used to design dentures, skeletons, and even internal organs. Additive technologies make it possible to create a medical instrument with certain parameters for specific patients with pathologies and anatomical features. This allows you to take a huge step forward in training and preparation for operations.
This allows you to take a huge step forward in training and preparation for operations.
In 2011, a kidney was “drawn” on a 3D printer. Scientists have created an exoskeleton to support atrophied muscles. There are even special “pens” that “draw” living cells on injured skin areas.
On 3D printers, models of premises are created with a visual study of interiors, buildings and entire residential areas with details of houses, utilities, and infrastructure facilities.
In the field of science and education, the benefits of 3D printing are expressed in the creation of visual aids with which the learning process becomes easier and more efficient.
3D printing is in demand in the fashion world. On the printer, you can create shoes, clothes, perfume bottles. While this process is expensive, therefore, it is not used in mass production. However, piece products made on 3D printers are already presented on the catwalks.
Creative 3D Printed Sandals
The advantage of introducing AF technologies into the light industry is the ability to create products for a specific physique/foot shape.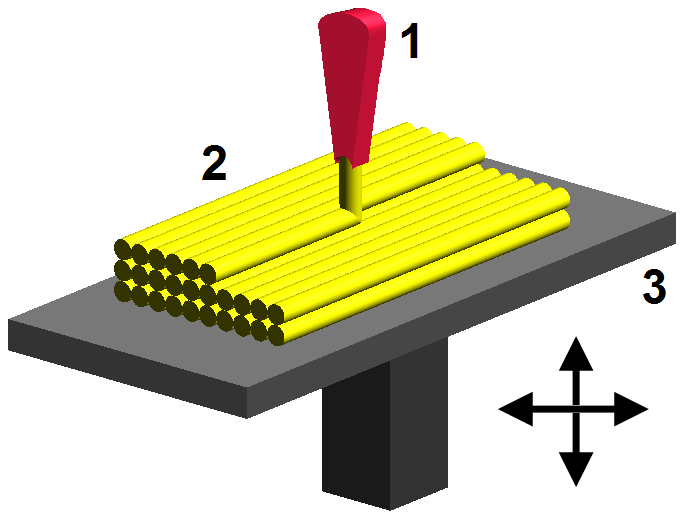 This is especially true for athletes, people with deviations of the anatomical structure. For example, designer Ross Berber introduced the world to shoes printed on a 3D machine. His collection includes 5 pairs.
This is especially true for athletes, people with deviations of the anatomical structure. For example, designer Ross Berber introduced the world to shoes printed on a 3D machine. His collection includes 5 pairs.
3D printing allows for a breakthrough in innovation. Before a product can be mass-produced, a prototype must be tested and repeatedly tested. This is done on 3D models. You can create them in minutes.
Three-dimensional technologies are used in jewelry, when creating maps of the area, making souvenirs, customizing finished products (applying a pattern, logo).
How does a 3D printer work?
A classic 3D printer is a 3D printing device that works on the principle of FDM (Fusion Deposition Modeling). On three-dimensional equipment, you can create an object of almost any shape, with curves, a relief surface. The product "increases" simultaneously in the horizontal and vertical directions.
Printers work with various materials: plastic, metal, and so on. With their help, you can create parts that can withstand a significant load. In order for the printer to print three-dimensional figures, it is equipped with:
With their help, you can create parts that can withstand a significant load. In order for the printer to print three-dimensional figures, it is equipped with:
- extruder - for heating and forcing plastic through the printheads;
- motors (usually linear) - set in motion the mechanisms;
- work surfaces - the platforms on which everything happens;
- sensors for fixing moving parts;
- Cartesian robots - devices moving along three axes.
Printers work differently, but the classic sequence of actions can be described by a single algorithm. First, a 3D image is created. This requires specialized software. After that, the model is “cut” into horizontal layers. A special program (G-code generator) is also provided for this. The computer converts the codes into information that the 3D printer can recognize. The next step is to recreate the model.
Smartprint HB-8 3D printer
3D printing technologies
There is monochrome and color 3D printing - more than a dozen technologies (plus their modifications). Among the most common:
Among the most common:
- SLA - stereolithographic laser printing. The technology provides the creation of models with high detail. Its essence is the layer-by-layer application of a photopolymer material. It hardens under the influence of a laser. Then the working platform is lowered. A translucent composition is used as a photopolymer: it is easy to process, paint, glue.
- SLS - the technology is suitable for working with plastics and metals. The reagent is sintered under the laser beam. The products are very durable.
- HPM - printers work with thermoplastic, auxiliary soluble materials. The latter are used to create complex multilevel models with cavities and functional holes. Finished products may have a different shape. They are durable, resistant to stress, mechanical and chemical stress.
- DLP is a relatively new 3D modeling technology. The printers that support it print with photopolymer resin. The material hardens when exposed to light.
The most progressive technologies are EBM and SLM. The first involves the impact on the material with an electron beam, and not with a laser, the second works with metals.
Equipment for 3D printing is produced by companies from the USA, Europe, and Asia. Among the famous ones are Photocentric, 3D systems, Makerbot, Azuma Engineering Machinery Inc. and others.
3D model of the ship strikes with realism
Advantages of additive technologies
The advantages of 3D printing include:
- Resource efficiency. Products are "grown" from scratch, that is, the production is completely waste-free. For comparison: when creating a blank using traditional methods, material losses sometimes reach up to 85%.
- Efficiency. The time from the development of the layout to the receipt of the product can be reduced several times, or even tens of times, without compromising quality.
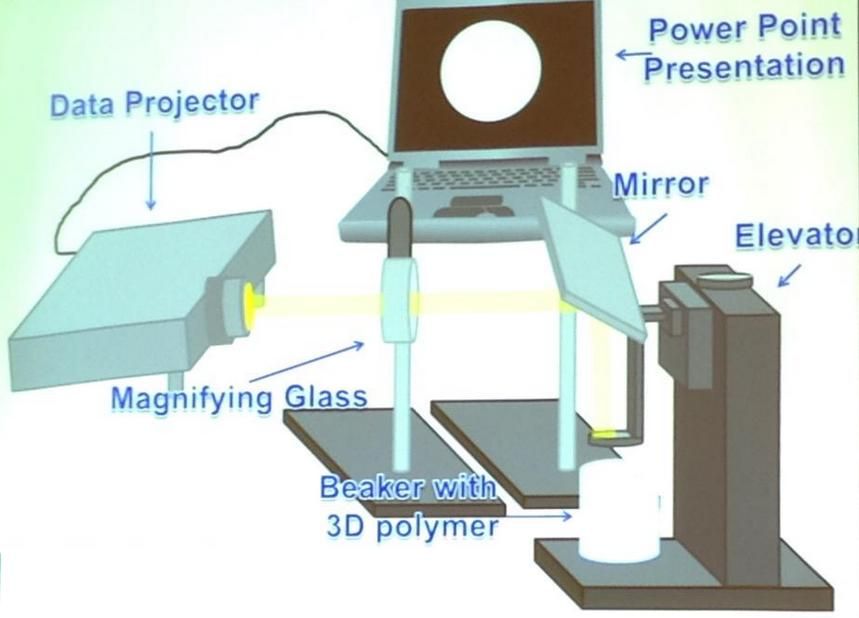
- Mobility. The equipment is compact, layouts can be transferred online.
- Precision. Layered synthesis ensures absolute compliance with specified technical parameters.
- Strength. The indicator is 25–30% higher than that of products obtained by traditional methods (forging, casting).
- Weight. This is an important advantage for industry, aircraft and mechanical engineering. The mass of individual products is reduced by 40–50% without loss of strength.
Souvenirs and toys are successfully printed in Russia using 3D printing technology
3D printing is also used in advertising printing. For example, for the production of souvenirs. Advertising agencies involved in cross-marketing willingly order a range of services, which includes both traditional production of business cards or flyers, as well as innovative solutions.