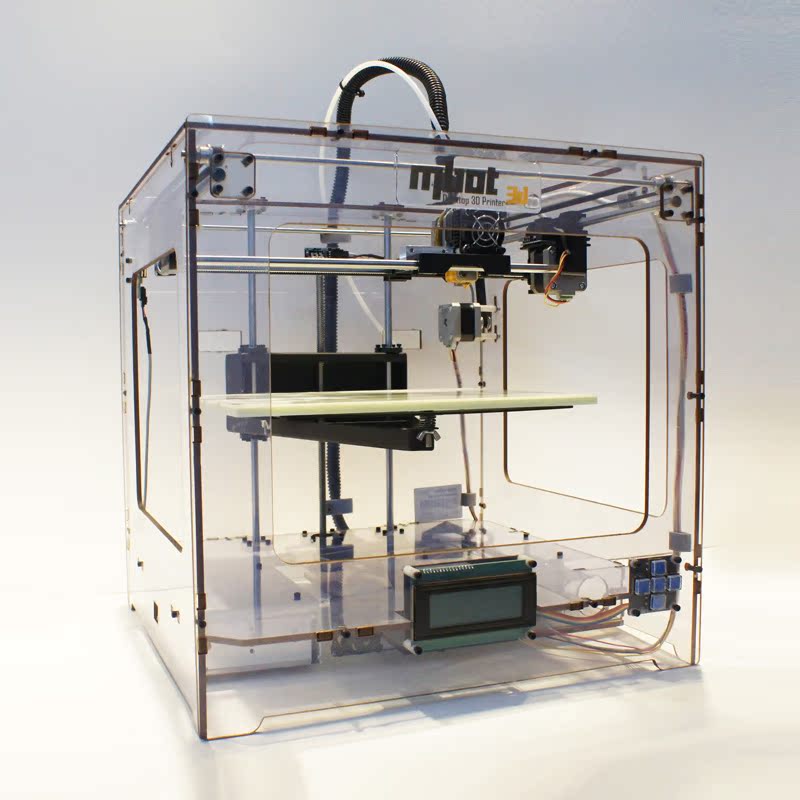
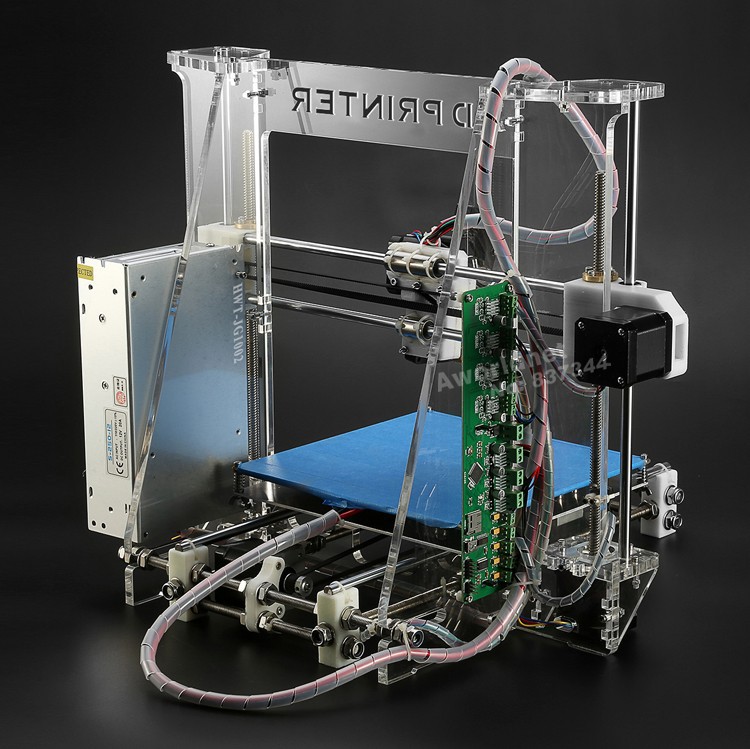
What are the disadvantages of 3d printing
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10 Disadvantages of 3D Printing Technology
3D Insider is ad supported and earns money from clicks, commissions from sales, and other ways.
As with any emerging technology, 3D printing has disrupted the markets by transforming product development. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing involves joining materials together, layer after layer to make objects from a 3D digital model. It differs from subtractive manufacturing (traditional manufacturing) which comprises cutting away unwanted parts from large pieces of solid material.
The 3D printing process eliminates many steps used in traditional manufacturing and facilitates the manufacture of complex structural components. These features have led to significant success in the areas of rapid prototyping and tool development.
As a result, 3D printing technology has opened new possibilities for industries by enabling faster product design, customization, cost reduction, tangible product testing, and more. For instance, its advances are increasingly becoming relevant in medical and dental industries where customization is essential. We have looked at the advantages of 3D printing here.
However, 3D printing technology has a dark side and is not always the right choice for product development for your development project. 3D machines are still potentially hazardous and wasteful. Moreover, their economic, political, societal, and environmental impacts have not been extensively studied.
Here are ten things about the risks and potentially negative impacts of 3D printing technology.
1. High Energy Consumption
According to research by Loughborough University, 3D printers consume approximately 50 to 100 times more energy than injection molding, when melting plastic with heat or lasers. In 2009, studies at The Environmentally Benign Manufacturing, a research group dedicated to investigating the environmental impacts related to product manufacturing, showed that direct laser metal deposition uses 100 times as much electrical energy as traditional manufacturing. For mass production, 3D printers consume a lot of energy and are therefore better suited for small batch production runs.
In 2009, studies at The Environmentally Benign Manufacturing, a research group dedicated to investigating the environmental impacts related to product manufacturing, showed that direct laser metal deposition uses 100 times as much electrical energy as traditional manufacturing. For mass production, 3D printers consume a lot of energy and are therefore better suited for small batch production runs.
2. 3D Printing Technology is Expensive
3D printing equipment and materials cost make the technology expensive. Industrial grade 3D printers are still expensive costing hundreds of thousands of dollar, which makes the initial expenses of using the technology very high. For a single machine, capital investment starts in the tens of thousands of dollars, and can increase to as high as hundreds of thousands of dollars or more. Also, the materials used in commercial grade 3D printers are costly compared to product materials used in traditional manufacturing.
3. Limited Materials
While 3D printing is a significant manufacturing breakthrough, materials that can be used are still limited, and some are still under development. For example, the 3D printing material of choice is plastic. Plastic is preferred as it can quickly and easily be deposited down in melted layers to form the final product. However, plastic may vary in strength capacity and may not be the best for some components. Some companies offer metal as a material, but final product parts are often not fully dense. Other specialized materials including glass and gold are being used but are yet to be commercialized.
For example, the 3D printing material of choice is plastic. Plastic is preferred as it can quickly and easily be deposited down in melted layers to form the final product. However, plastic may vary in strength capacity and may not be the best for some components. Some companies offer metal as a material, but final product parts are often not fully dense. Other specialized materials including glass and gold are being used but are yet to be commercialized.
4. 3D Printers Aren’t that User-friendly
Because of the excitement and potential around 3D printing technology, 3D printers have come across as easy to use and also sound more useful than they really are. The truth is 3D printers use high-voltage power supplies, specialized equipment, and parts which makes them difficult to use and manage. Some have low resolution and can’t even connect to Wi-Fi. Improvements have been made here and it’s getting easier to 3D print day by day.
5. Harmful Emissions
3D printers used in enclosed places such as homes can generate potentially toxic emissions and carcinogenic particles according to researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology. Their 2013 research study showed that 3D desktop computers could emit large numbers of ultrafine particles and some hazardous volatile organic compounds during printing. The printers emitted 20 billion ultrafine particles per minute using PLA filament, and the ABS emitted up to 200 billion particles per minute. Emitted radiations are similar to burning a cigarette, and may settle in the bloodstream or lungs posing health risks including cancer and other ailments.
Their 2013 research study showed that 3D desktop computers could emit large numbers of ultrafine particles and some hazardous volatile organic compounds during printing. The printers emitted 20 billion ultrafine particles per minute using PLA filament, and the ABS emitted up to 200 billion particles per minute. Emitted radiations are similar to burning a cigarette, and may settle in the bloodstream or lungs posing health risks including cancer and other ailments.
6. Too Much Reliance on Plastic
Popular and cheap 3D printers use a plastic filament. Although using raw plastic reduces waste generation, the machines still leave unused or excess plastic in the print beds. PLA is biodegradable, but ABS filament is still the most commonly used type of plastic. The plastic byproduct ends up in landfills negatively affecting the environment. Furthermore, plastic limits the type of products that can be created from the material. Future 3D printers will need to use other materials such as metal (as some currently do) or carbon composites to become more useful to manufacturers and consumers alike.
7. 3D Printers are Slow
While 3D printers are limitless for mass customization, they are slow when it comes to manufacturing many objects. Depending on printer size and quality, it can take several hours to days to print. The more the work involved with product development, the slower the printers. Companies that receive orders to customize and make 3D prints using a variety of products can take up several weeks to print depending on the materials used.
8. Production of Dangerous Weaponry
With 3D printers, it is easy to create 3D knives, guns, explosives, and any other dangerous items. Criminals and terrorists can, therefore, make such weapons without being detected. Some criminal organizations have already used 3D printing technology to create card readers for bank machines. As time goes on, 3D technology will become more user-friendly and cost-effective, and it is possible that design and production of unlicensed weaponry will increase.
9. Copyright Infringements
Counterfeiting is one the most significant disadvantages of 3D printing. Anyone with a product blueprint can forge products very quickly. Patent violations will increasingly become more common, and identifying counterfeited items will become practically impossible. As 3D printing technology evolves, patents, and copyright holders will have a harder time protecting their rights and companies manufacturing unique products will be significantly affected.
Anyone with a product blueprint can forge products very quickly. Patent violations will increasingly become more common, and identifying counterfeited items will become practically impossible. As 3D printing technology evolves, patents, and copyright holders will have a harder time protecting their rights and companies manufacturing unique products will be significantly affected.
10. Manufacturing Job Losses
3D printing technology can make product designs and prototypes in a matter of hours as it uses only one single step. It eliminates a lot of stages that are used in subtractive manufacturing. As a result it doesn’t require a lot of labor cost. As such, adopting 3D printing may decrease manufacturing jobs. For countries that rely on a large number of low skill jobs, the decline in manufacturing jobs could dramatically affect the economy. It’s likely that robotics will have a much larger impact here.
Conclusion
In a lot of industries, 3D printing provides countless benefits. However, it is not going to replace traditional manufacturing. It is still an emerging technology with some disadvantages that need to be considered when selecting a product development method. Manufacturers and product designers therefore need to see it as a process to complement traditional manufacturing. They can exploit its unique capabilities to improve product design and manufacture entirely new products that could not be otherwise produced.
However, it is not going to replace traditional manufacturing. It is still an emerging technology with some disadvantages that need to be considered when selecting a product development method. Manufacturers and product designers therefore need to see it as a process to complement traditional manufacturing. They can exploit its unique capabilities to improve product design and manufacture entirely new products that could not be otherwise produced.
Warning; 3D printers should never be left unattended. They can pose a firesafety hazard.
3D printers advantages and disadvantages
If you ask any owner of a 3D printer what the main advantage of his device is, he will begin to talk about the high quality of printing and the ability to make any prototypes. When asked about the shortcomings, the answer is usually about some shortcomings in the design of the printer: someone is not satisfied with an insufficiently rigid frame, some complain about too slow printing rates. In the article, we understand what advantages most 3D printers have and find out what disadvantages their owners have to face.
In the article, we understand what advantages most 3D printers have and find out what disadvantages their owners have to face.
Despite a relatively slow start, additive technologies are finally gaining momentum. Now 3D printers have gained well-deserved popularity both in the user environment and in the field of production. We have already appreciated the many benefits of 3D printing, including the ability to print complex models, but the peak of popularity and functionality of 3D technologies is yet to come. We talk about the main advantages and disadvantages of 3D printers.
Benefits of 3D printers
Let's start with the benefits: 3D printing allows you to quickly and relatively inexpensively produce the desired prototypes with high accuracy, independently adjusting the printer settings and choosing the optimal parameters. Let's dwell on each plus of 3D printers in more detail.
The advantage is the speed of production
3D printers can significantly reduce the time spent on each project. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, when using additive technologies, the entire printing process will take from several weeks or days, and the bulk of the models can be printed in a matter of hours. Some manufacturers have decided to optimize their inventory by starting to make parts to order. This approach allows you to take mass production to a new level: now you do not need to store a lot of parts in stock, because you can simply print them as needed, immediately sending them to sale.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, when using additive technologies, the entire printing process will take from several weeks or days, and the bulk of the models can be printed in a matter of hours. Some manufacturers have decided to optimize their inventory by starting to make parts to order. This approach allows you to take mass production to a new level: now you do not need to store a lot of parts in stock, because you can simply print them as needed, immediately sending them to sale.
Advantage - cost of production
Large-scale projects with a large number of 3D printed parts are not cheap, but additive manufacturing still remains more profitable than traditional technologies. Many manufacturers use 3D printing for short runs or prototyping. For example, it is much more profitable for jewelers to print wax prototypes of jewelry than to cast them from metal. The plastic used in 3D printing is relatively inexpensive, and even the simplest printer can help save money.
Product quality
Modern 3D printers demonstrate high product quality. In our opinion, the quality depends on the following characteristics of the device:
- Photopolymer printing. This technology allows you to get the highest possible quality of the finished product.
- FDM technology. Despite the fact that FDM printers are in demand, they simply cannot create detail above 100 microns.
- Metal body. When choosing FDM printers, you should give preference to models whose body is made of metal. Such printers demonstrate the best quality of products at high print speeds.
- Regardless of which printer model is chosen, the finished product printed at low speed and quality materials is almost the same as that produced on high speed equipment.
Thus, it is possible to achieve decent print quality on inexpensive printers using high-quality filament at low speeds.
Copy Accuracy
3D Printing Accuracy is the minimum layer height allowed. Modern devices can produce high quality down to 20 microns, but in order to actually obtain prototypes of such accuracy, the user will need to meet certain conditions.
Modern devices can produce high quality down to 20 microns, but in order to actually obtain prototypes of such accuracy, the user will need to meet certain conditions.
First of all, the accuracy of the finished copies depends on the 3D printer itself - on its technical characteristics, layout, etc. You should not rely only on the layer height value that is indicated in the device description.
The accuracy of prototypes depends on many factors. For example, printers made in a closed case are able to produce much better model accuracy than their counterparts in an open case, due to the uniform temperature regime inside the printer.
In addition, it is required to correctly set all print settings, monitor the calibration of the table, the operating conditions of the device, and the temperature regime. High-quality plastic plays an important role in the accuracy of the copies made.
Production flexibility
The introduction of 3D printing in various areas of production is due to the fact that the technology makes it possible to create geometric shapes of almost any size and unlimited complexity.
Printers print with a wide variety of materials, making the production process as flexible as possible. For example, on the same device, you can create both waxes for jewelers and dentures for dentists. Such versatility cannot be achieved using standard production equipment. 3D printers open up new horizons and prospects for the development of their own business and additive technologies for engineers, designers and device owners.
Availability
The availability of 3D printing makes it possible to experiment using printers both at home and at work. Even the most inexpensive 3D printer can be used in architecture, construction, small-scale production, medicine, education, jewelry, printing, souvenirs, and advertising. A standard spool of filament will last for a long time, and almost everyone can afford to buy a 3D printer. One of the most budget models costs about $100.
Any technique has its downsides, and 3D printers are no exception. Therefore, today additive technology has a certain number of significant drawbacks.
Therefore, today additive technology has a certain number of significant drawbacks.
Minus - the small size of the camera
Perhaps the most significant drawback of printers are the small size of the print area. Look at any 3D printer, evaluate its dimensions - that's it, everything is limited to them. The device can only print the model that will fit on its platform. If you need to create a larger prototype, you will have to resort to various tricks: for example, you can print the model in parts, and then assemble them in some way. Despite the fact that there is already a prototype of a 3D printer with an unlimited size of the working platform, it is not yet possible to talk about the mass introduction of such a technology.
Minus - inaccuracies of the part
It is impossible to completely get rid of thermal contraction or shrinkage of the finished model. This is a physical process - you can only compensate for it. The layers floated, the vertical is not observed, the layers do not lie exactly on top of each other. The protrusions on the top layer of the part can be either open or closed. Essentially, this is due to the sagging of the plastic, which does not have time to cool when printed in the air without supports.
The protrusions on the top layer of the part can be either open or closed. Essentially, this is due to the sagging of the plastic, which does not have time to cool when printed in the air without supports.
Disadvantage - post-processing
Most finished products printed on a 3D printer require post-processing and cleaning. The process helps to achieve the best look and smoothness of the model. Finished models are processed in various ways. Users grind parts, chemically process them, cut supports, dry products. The need for post-treatment depends on many factors. For example, the scope of work varies depending on the size of the model, the material, the type of technology chosen in the manufacture of the prototype. Thus, given that 3D printing allows fast production of parts, the speed of production can be reduced through subsequent post-processing.
Strength properties of models
As a rule, the production of a three-dimensional model using additive technologies occurs by layer-by-layer application of a filament. Despite the fact that the layers are well glued together, this is not a guarantee of the perfect solidity of the finished product, and it can delaminate under certain loads. This problem is especially common when using FDM printers. Experienced users advise using injection molding to improve the strength properties of parts. Using this method, the structure of the finished part is more uniform and less brittle.
Despite the fact that the layers are well glued together, this is not a guarantee of the perfect solidity of the finished product, and it can delaminate under certain loads. This problem is especially common when using FDM printers. Experienced users advise using injection molding to improve the strength properties of parts. Using this method, the structure of the finished part is more uniform and less brittle.
3D printers are not user-friendly
Manufacturers claim that 3D printers are easy to use. Some companies produce devices specifically for beginners. However, even for the initial assembly and preparation of the printer for operation, the user will need certain skills. Calibrating the desktop on your own, setting up the slicer program, and setting the desired print settings is not as easy as the manufacturers assure. Some models are delivered already assembled - we advise you to choose them as your first printer.
Harmful emissions
The size of the device and the amount of thermoplastic produced by the printer greatly affect the amount of harmful aerosol emissions into the atmosphere. The chemicals settle in our lungs and also contribute to the increase in the size of the ozone hole. A team of researchers led by Professor Brent Stevens conducted their own experiment, which tested five models of 3D printers. As a result, scientists were able to calculate the concentration of nanometer particles that are formed during the 3D printing process.
The chemicals settle in our lungs and also contribute to the increase in the size of the ozone hole. A team of researchers led by Professor Brent Stevens conducted their own experiment, which tested five models of 3D printers. As a result, scientists were able to calculate the concentration of nanometer particles that are formed during the 3D printing process.
The results of the experiment did not please either printer manufacturers or device owners and users. The fact is that 3D printers using polylactic acid (PLA) in printing have demonstrated extremely high levels of ultrafine particles - from 20 billion per minute. Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)-powered gadgets emit up to 200 billion particles per minute into the atmosphere.
Scientists have stated that harmful emissions in such quantities are similar to emissions into the atmosphere from burning tobacco or scented candles, burning natural gas. In addition, when using a laser printer using powder as a printing material, no less harmful emissions are produced.
Slow
3D printers are actually very slow. Some manufacturers claim high print speeds, but this figure is relative. Especially when it comes to making a lot of prototypes. Many users who own budget printers leave them running all night to have a small finished model by morning. Depending on the dimensions and quality of the printed product, the process may be delayed. On average, the process of creating a model can take from several hours to several days. The duration is directly proportional to the size of the object: the larger the future prototype, the more time it will take to print.
Environmental pollution
Waste plastic by-products of additive printing have long been of interest to conservationists. Production waste ends up in landfills, creating a negative additional burden on the environment. Scientists believe that the ABS plastic used in most 3D printers is quite toxic. This type of filament has a long period of decomposition in the soil. However, ABS is the most common type of material used in additive printing. PLA is a greener alternative to ABS. This material is more biodegradable and less toxic. The problem of environmental pollution can be solved with the spread of household plastic convertors into 3D printing filament.
PLA is a greener alternative to ABS. This material is more biodegradable and less toxic. The problem of environmental pollution can be solved with the spread of household plastic convertors into 3D printing filament.
Three-dimensional printers open up a wide range of possibilities for their owners. The list of advantages of such devices is endless, but we have chosen only the main ones. In our opinion, one of the main advantages of 3D printers is their affordability. Finished models are of sufficient quality even on budget models. The main thing is that the user sets the correct settings and fills the printer with good material.
But 3D printers also have their drawbacks. In addition to the fact that they are not very easy to calibrate and prepare for work, they produce harmful emissions into the atmosphere, and production waste in the form of plastic practically does not decompose, polluting the environment. Another disadvantage of the devices is the low print speed. However, 3D printing is too useful to pass up. In our opinion, printers are being improved every year, and very soon their shortcomings will be minimized.
In our opinion, printers are being improved every year, and very soon their shortcomings will be minimized.
- May 18, 2020
- 14705
Get expert advice
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing. All subtleties and nuances in one post
Introduction.
The invention of 3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing and product development.
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, entails combining multiple layers of material one after the other until you create a 3D printed model.
It has become so popular among many manufacturers due to its innovative features that far exceed those of traditional production.
However, like any other manufacturing method, 3D printing has many disadvantages.
Therefore, in this article, we will tell you about the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing so that you can learn more about this groundbreaking technology.
Benefits of 3D printing.
The reason 3D printing has become so popular is because of its advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Here we look at the most significant benefits of 3D printing.
This is available.
3D printers are more affordable than ever. One of the most popular Creality Ender 3 V2 models is available for just $300.
In addition to the bestseller Ender 3 V2, we have a selection of kits for building 3D printers in our catalog, and all of them impress with their price-quality ratio.
Only 5 years ago it was impossible to buy ready-made equipment at such a low price.
3D printing is a one-step manufacturing process, so it not only saves you the cost of using different manufacturing processes and machines, but also saves you valuable time.
3D printers don't need constant supervision as they can perform certain tasks once set up; so you don't have to be around all the time.
For example, they can be left to work at night without resorting to expensive night shifts to watch them.
In addition, 3D printing saves on overall material costs by using only the material needed to produce a particular part with no or minimal wastage.
Buying 3D printing equipment can be expensive if you only have one part to make, so it may be cheaper to outsource a project to a 3D printing service company.
3D4U engineers have hands-on experience in providing custom 3D printing services. You can contact us in any convenient way and we will provide you with support, both in choosing equipment and consumables, and in printing your products.
Rapid prototyping.
Using 3D printing equipment, you can create prototypes in a couple of hours. This greatly speeds up the design process, meaning you can get parts within hours and be ready for your next project.
In addition, you can cheaply and quickly create a new prototype with each design modification, as opposed to the costly and time-consuming prototyping process with traditional methods.
Strong and lightweight parts.
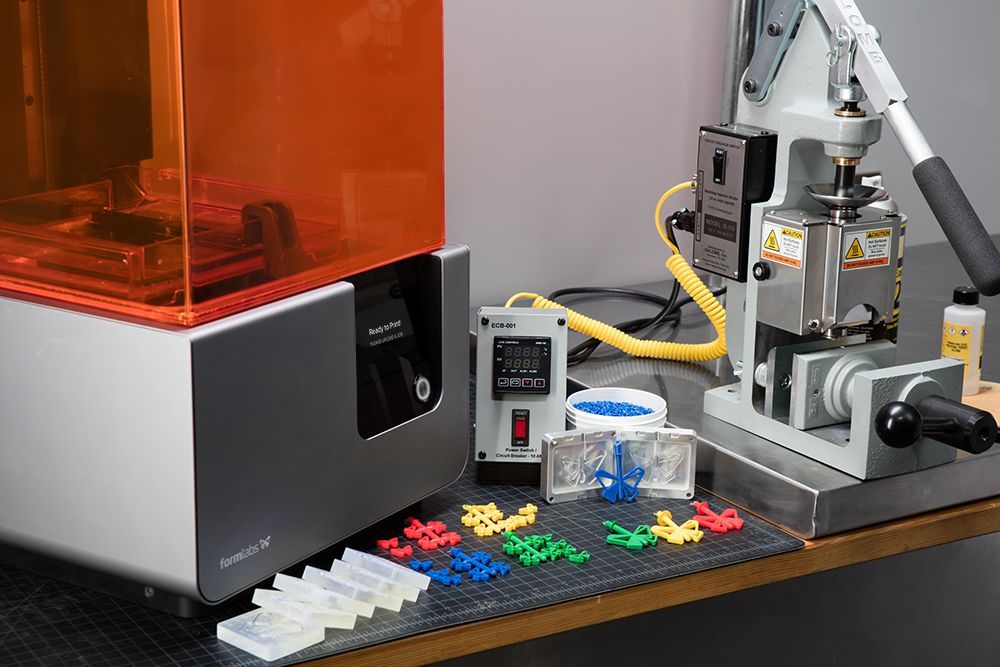

Plastic is the main material used in 3D printing, although there are a number of materials available for 3D printing.
3D printing makes it possible to create complex organic shapes that are much lighter than traditionally created parts.
In the aerospace and automotive industries this is a vital factor as the use of lightweight materials helps improve fuel efficiency.
3D printed parts can be made from custom-made materials that have special characteristics such as water repellency, higher strength, and heat resistance.
Plastics such as PLA can be combined with metals or even wood for unique finishes and properties.
3D printing technology is environmentally friendly.
The use of 3D printing technology reduces the amount of waste generated during the production process.
What's more, this technology helps to improve the environment even further, as lightweight 3D printed models can make cars or planes significantly more fuel efficient.
You can 3D print with materials that are either recycled or made from plant-based organic materials.
Easy access.
The use of 3D printing equipment has increased in recent years due to greater availability.
Finding a local 3D printing service provider is now easier than ever.
3D printing has become a popular hobby due to its low cost and easy access.
Many people have integrated 3D printing into their hobbies such as games, fan art or cosplay.
For people who can't afford to buy a 3D printer, there are many so-called manufacturing facilities where sharing a 3D printer is free or inexpensive.
Manufacturers are also turning to 3D printing to save on shipping costs. With most of the traditional manufacturing methods used overseas in countries such as China, 3D printed parts can be made closer to where they are needed for fast response.
Waste reduction.
3D printing uses only the required material to make certain parts, as it is an additive manufacturing process.
This is different from traditional processing, in which huge masses of non-recyclable materials are cut to form three-dimensional parts.
The total cost of 3D printing is therefore lower because less material is used and you only pay for what you need.
Improvements in the medical sector.
3D printing has revolutionized the medical sector as it is now possible to print human body organs such as the heart, kidneys and liver.
Printing prostheses or hearing aids is no longer a novelty.
In addition, more research is being done on how 3D printing technology can further help the healthcare sector.
Print on demand.
Unlike subtractive manufacturing, 3D printing technology does not take up much inventory space as parts can only be printed when ordered or needed.
Not only will you save on costs, but you will also save space as you only print in bulk when needed.
All 3D design files are stored in a virtual library, from where you can then print them with a 3D model as an STL or CAD file.
Quality and consistency.
Old production methods are usually characterized by poor design, which can lead to poor quality prototypes.
This means that the quality of the product cannot be guaranteed.
However, this is not the case when 3D printing technology is used, since the assembly of the product is carried out in a strict step-by-step process, which ensures outstanding product design and quality.
3D printing technology also allows for greater consistency than traditional manufacturing, while still producing consistently high quality parts.
This is possible because errors are detected immediately, helping to reduce the overall number of wasted materials and defective parts.
Therefore, this technology ensures that parts in a batch are not defective or incompatible when compared to other parts.
Open design and product testing.
The visual appearance of a product, either virtually or on screen, cannot be compared to the actual feel of a prototype that you can experience with 3D printing technology.
In this way, you can physically touch and feel the product prototype and check if there are any flaws in its design.
In case of an error, you can edit the CAD file and print a new version later.
A physical prototype is invaluable for demonstrating a product to clients or executives who would otherwise find it difficult to validate a product based on a 3D CAD model.
This is one of the main applications of 3D printing in the industry, and it's worth remembering that 3D printing was originally called "rapid prototyping" for this very reason!
Faster production.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods such as CNC machining and injection molding, 3D printing is significantly faster.
This is because this technology allows you to quickly test designs and ideas, from prototype to final product.
Therefore, this allows you to spend more time in the market and attract customers before your competitors have finished producing their final products.
Endless geometry and shapes.
Conventional manufacturing methods rely on cutting and shaping techniques to create the desired shapes, which is not only difficult but also expensive.
Luckily, you won't have this problem with 3D printing technology, and all you need is the right supports.
You can create supports yourself or automatically using the software.
3D printing allows you to create hollow shapes without holes, have extreme undercuts that are impossible with any other production method.
Disadvantages of 3D printing.
Of course, everything will always have its disadvantages! While there are many advantages to 3D printing, there are also disadvantages. Here are the main ones.
Limited build size.
The size of the camera built into 3D printers is usually relatively small, which limits the size of the parts you can print.
Therefore, any larger item must be printed piece by piece and then reassembled after production.
This increases the time it takes to print because the 3D printer needs to print more parts before you can go ahead and manually join the parts.
The designer must decide where to place these breaks so that they do not weaken the surface and ruin the finish of the final piece.
Structure Detail.
In 3D printing, parts are usually created one layer after another, which is why it is also called additive manufacturing. This means that although the layers are firmly held together, they are susceptible to splitting when subjected to loads at certain orientations or stresses.
This is a problem that is often encountered in products created using fused deposition modeling. In addition, Multijet and Polyjet parts tend to be more fragile.
In this regard, it may be better to use injection molding in the manufacture of homogeneous parts, since they are stronger and less likely to fail when the structure is loaded.
Loss of jobs in the manufacturing sector.

The use of 3D printing allows you to create prototypes and product designs within hours with one simple step.
Most subtractive manufacturing steps are eliminated, and this helps save on labor costs as fewer people need to be hired to complete the manufacturing process.
Ultimately, this leads to a reduction in manufacturing jobs, which can be especially detrimental in countries where the majority of citizens depend on low-skill jobs.
Of course, operators and manufacturers of 3D printers are required, which partially compensates for these losses.
3D printing technology is not very user friendly.
Despite the hype about the potential of 3D printing technology, using 3D printers is not as easy as you might think. Since this is a new technology, trial and error is often required when creating parts on a 3D printer.
Those with previous experience with this technology can fix this problem.
However, until 3D printing becomes widespread, it should be viewed as a technology with a potentially steep learning curve.
Limited materials.
Since 3D printing technology is a recent innovation, the materials needed in the manufacturing process are limited and some are still being developed.
The material of choice for 3D printing is plastic as it melts quickly in layers to make the final item. However, plastic is not the strongest material for all requirements and its strength varies making it not an ideal choice for certain components.
Metal 3D printing is gradually gaining momentum as a viable technology, but at the moment it is quite expensive.
Other specialized materials are also used, including gold and glass, but have yet to be commercialized.
3D printers are expensive.
Of course, we are talking about the industrial sector and industrial 3D printers. At the beginning of the article, we already mentioned that the growth in the production of desktop printers is now at its peak and anyone with an average income can afford to buy a 3D printer. Modern printers for the home are cheaper than laptops, TVs and smartphones.
Modern printers for the home are cheaper than laptops, TVs and smartphones.
The materials and equipment used in industrial 3D printing are expensive, and industrial printers cost hundreds of thousands. Since the initial capital required to use 3D printing technology is prohibitive, many people are unable to enjoy this innovative technology.
What's more, the materials needed to use 3D printing technology can be expensive compared to materials used in traditional manufacturing.
To get around these costs, many companies rent 3D printing equipment or use a third party to gain access to 3D printers from so-called 3D printing shops.
Copyright infringement.
The development of 3D printing technology has led to an increase in counterfeiting cases. This is because now anyone with access to a product blueprint can quickly copy existing products. Because of this, the number of patent infringements has increased, and it is almost impossible to identify a counterfeit product. The development of 3D printing technology has made life difficult for copyright and patent holders to protect the rights to their unique products.
The development of 3D printing technology has made life difficult for copyright and patent holders to protect the rights to their unique products.
As with other industries such as the music industry, this is likely to be an ongoing battle with many innovations and legislative changes to combat it.
Manufacture of hazardous goods.
Making explosives, guns, knives, and other dangerous weapons is theoretically more accessible thanks to 3D printing technology. This is because it gives people access to a method of producing items in their own homes, which was previously not possible.
This has made it difficult for the relevant security authorities to determine when terrorists and criminals are manufacturing weapons. As 3D printing technology becomes cheaper and more user-friendly, the development and production of unlicensed weapons is expected to increase.
Of course, media reports of 3D printed weapons have been exaggerated, and in fact any weapon made from plastic that melts at 200°C will not be very effective.