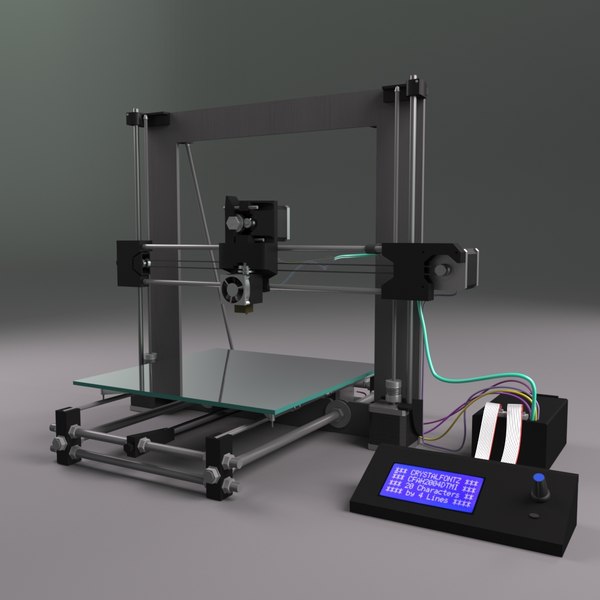
Used 3d printer for sale in india
Buy 3D Printers Online | BuyQuality 3D Printer India |
We sell a carefully curated range of 3D printers. Browse through our range of models below. We are authorized resellers for the machines we sell, and these machines are backed by company warranties.
Not sure which machine is right for you? Call us on 72087-86517 for a free consultation. We will share as much information on 3D printing as you like, and will help you select the best machine for your needs. Do note that there are a very wide range of 3D printers and 3D printing technologies.
Note: Shipping costs not included. Local body taxes like Octroi and West Bengal Entry Tax may apply depending on your location.
Understanding the impact, uses, types and advantages of 3D printing technology is vital for anyone intending to buy 3D printers online India.
A recent report by The McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) ranks 3D printing as one of the top 12 potentially economically disruptive technologies, globally. Projections from that report estimate that approximately 8% of the global workforce (320 million manufacturing workers) would be impacted by this revolutionary technology. Moreover, projections of an estimated $11 trillion worth of global manufacturing GDP would be attributed to the economic value of 3D printing.
Such monumental projections reflect just how significant the impact of this disruptive technology is to the global economy. Indeed, this is a key technology that can drastically disrupt the status quo, rearrange value pools and even alter the manner in which people live and work. Therefore, every business, policy leader and consumer must be acquainted with the workings of such a revolutionary technology.
Overview of 3D Printing
3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing technique that creates objects, based on digital models, through printing layers of special material. In other words, it’s much like what an inkjet printer does in creating images on paper; instead, the 3D printing machine prints objects.
The additive manufacturing process utilized by 3D printers presents a major contrast to traditional subtractive manufacturing techniques. Such a process builds objects sequentially, layer-by-layer. It’s also quite different from molding techniques used in manufacturing.
Modern 3D printers utilize numerous kinds of materials including metal, ceramics, plastic, paper, glass, and even living cells. These materials also come in varying forms, such as liquids, filaments, powders and sheets. The produced objects would feature an even greater diversity of shapes, patterns, colors and even interconnected moving parts.
Whereas some people view it as a mere fad, more and more analysts are beginning to appreciate the potential technological and economic significance of 3D printing. Indeed, it’s hardly possible to ignore all the revolutionary benefits of this new technology when you buy 3D printers online India.
Advantages of 3D Printers
To truly appreciate the value of inherent benefits derived from 3D printing technology, you need to contrast it with traditional methods of manufacture.
1. Mass Customization
Until the advent of 3D printers, it was virtually impossible to personalize products meant for the mass market. Any form of customization would always lead to additional process costs. That changed drastically with the revolutionary additive manufacturing technology.
With 3D printers, objects can be manufactured en masse based on the requirements of customers. Moreover, unlike traditional manufacturing processes, this doesn’t even necessitate separate build chambers. Instead, tones and tones of unique and varied products are easily manufactured within a single build chamber; thus, drastically cutting down on process costs when you buy 3D printers online India.
2. Lower Production Costs
Low production cost is a significant aspect that would convince many people, especially businessmen, to buy 3D printers online India.
Use of 3D printers in low to medium volume applications can cancel out the need for tool production, leading to lower production cost. This is especially so, since production of tools constitutes the most cost-, labor- and time-intensive stages in product development. Moreover, highly intricate and complex features would be produced without the associated labor cost normally found in traditional assembly processes.
This is especially so, since production of tools constitutes the most cost-, labor- and time-intensive stages in product development. Moreover, highly intricate and complex features would be produced without the associated labor cost normally found in traditional assembly processes.
Printing objects can significantly reduce the steps involved within an entire production process. Such steps involve manufacturing, assembly, transportation and distribution. Cutting down on the overall process would also reduce wastage of materials, unlike subtractive manufacturing techniques. Apart from making the entire production process more efficient, reduced material wastage also has a positive environmental impact.
Application of object printing in medicine offers revolutionary life-saving benefits. This is evident from the potential for improved transplant success rates, on the basis of using body parts produced from a patient’s own cells. Patients would also not have to wait long for donor organs, since such advanced additive manufacturing technologies can be applied.
3. Complex Production
3D printing has created vast opportunities for highly complex designs that were hardly possible in traditional molding and subtractive manufacturing processes. Indeed, truly captivating and impressive visual effects have been produced by designers and artists using this cutting-edge technology. Such complexity in design is also highly beneficial in industrial applications.
Complex internal structures are being applied in object printing to increase functionality, reduce weight and add strength. For instance, metal objects can incorporate internal honeycomb structures; whereas, organs with internal blood vessel networks can be created through bio-printing. Numerous other intricate and complex designs are constantly developed and used in a wide variety of applications.
4. Sustainable / Environmentally Friendly
The efficiency of 3D printing processes makes them much more environmentally friendly than traditional manufacturing processes. Such printing machines have the capacity of using as much as 90% of standard materials; hence, creating significantly lower amounts of waste.
3D printing can also support a local manufacturing model, which has the potential of eliminating unsustainable logistics associated with worldwide shipping of high product volumes. In such a model products are simply made on demand, right where they are needed. This would also cut down on costs of managing huge inventories when you buy 3D printers online India.
Who Uses 3D Printers?
The Mckinsey Global Institute report documents a monumental growth in sales of personal 3D printers at a rate of 200% to 400% yearly, from 2007 to 2011. This is a clear sign of rapid adoption of the technology and its increasing use. Actually, such an object printing technology is already commonplace for many professionals, including engineers, designers and architects.
Professionals, such as designers and architects, normally utilize the object printing technology in creating product designs, as well as prototypes. Other objects being made using the technology include molds, tools and final products in manufacturing processes.
The “democratization” of manufacturing is also a significant aspect, facilitated by 3D printing. This can enable entrepreneurs, as well as consumers to create their own personalized printed products. It is a key feature of mass customization, which leads to less-costly and shrinking supply chains. Bio-printing is also likely to feature in future printer developments that would enable medical professionals to save and extend the lives of many patients using printed organs.
The Mckinsey Global Institute report estimates a yearly economic impact (related to 3D printing) valued at $230 billion to $550 billion by the year 2025. In this estimation, the largest source of impact is expected to come from consumer uses, with direct manufacturing taking second place, followed by use of the technology in creating tools and molds.
Wider usage of object printers is likely to further accelerate in the coming decade, based on improvements in performance and speed, as well as falling costs of the gadgets.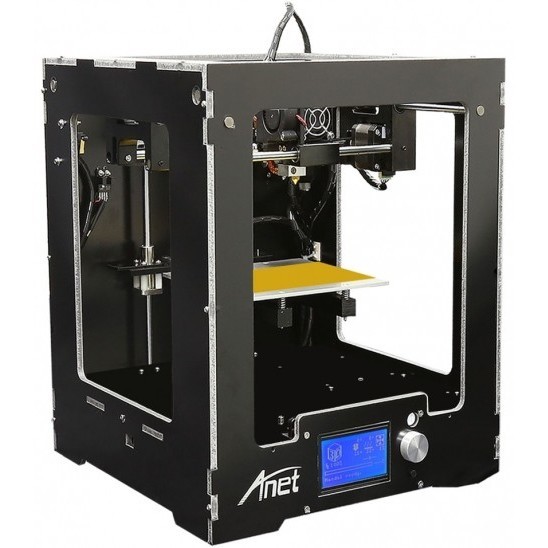 Currently, industrial printers have an average price of approximately $75,000; whereas personal 3D printers can be bought for less than $1,000. However, with increasing production volumes, such costs would decline rapidly; hence making it much more accessible to even more people.
Currently, industrial printers have an average price of approximately $75,000; whereas personal 3D printers can be bought for less than $1,000. However, with increasing production volumes, such costs would decline rapidly; hence making it much more accessible to even more people.
Advancements in 3D technology could also further diversify the use of such a technology; thus enabling penetration into many more user markets. For instance, the Fraunhofer Institute for Laser Technology is undertaking research to achieve fourfold increase in speeds for printing metal objects.
What Can Be Done With 3D Printers?
There is currently a rapid acceleration in 3D printing of complex, highly customizable, yet low volume products. Here is a sample of the numerous applications of 3D printers:
(i) 200 different aircraft parts are being printed for Boeing’s ten aircraft platforms.
(ii) Over one million units of custom printed hearing aid pieces were sold by manufacturers in 2011.
(iii) 3D printing has been used to build 40,000 acetabular hip cups (a term referring to the socket for a hip joint replacement).
(iv) Stereolithorgaphy printers have been extensively utilized by Invisalign, a dental appliance maker, to produce between 50,000 and 60,000 appliances daily.
(v) Numerous 3D printed products, like iPhone cases, are being designed and sold by entrepreneurs. These entrepreneurs normally use such services as Sculpteo or Shapeways, which allow client-end design uploads, that are thereafter printed and shipped over by the company.
Many important needs can be fulfilled when you buy 3D printers online India. This is especially so with regards to expectations for personalization, which can deliver such items as better fitting shoes and helmets.
Multi-material 3D printing offers even greater advantages in production and assembly processes. Unlike use of a single material, this advanced form allows production of objects that possess different properties, without having to bring separate components together.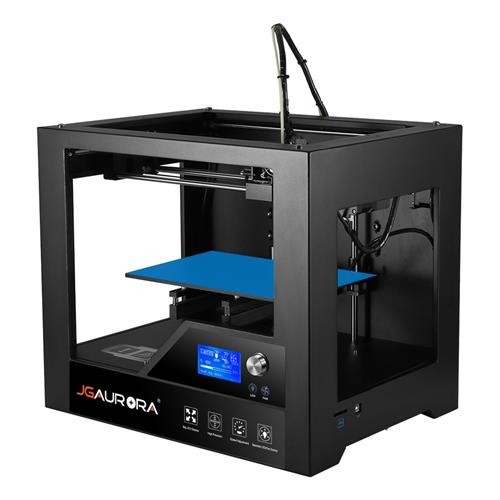 This would effectively reduce the number of steps involved in manufacturing each object.
This would effectively reduce the number of steps involved in manufacturing each object.
The Object Connex range features a sample of multi-material printers. Such systems utilize 120 different printing materials, based on acrylic-based photopolymer resins, which are jetted in liquid form, deposited as a layer and cured by UV light. Although not actually reproducing different materials with unique properties, the printing materials do produce varying characteristics.
Types of 3D Printers
Various types of 3D printing techniques possess particular benefits and shortcomings. You must be well-versed in such differences, so that you can make the most appropriate choice if you intend to buy 3D printers online India. However, all of them follow a similar pattern in the printing process, which involves formation of one layer at a time, with the following layer placed on the previous one.
I. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
The selective laser sintering (SLS) technique makes use of a special powder and laser. A powder layer is first placed on the build platform and thereafter, a laser fuses this powder together into a pre-designed shape by “drawing” a single layer of the object. Once this is done, the platform moves down to allow for depositing of more powder.
A powder layer is first placed on the build platform and thereafter, a laser fuses this powder together into a pre-designed shape by “drawing” a single layer of the object. Once this is done, the platform moves down to allow for depositing of more powder.
An SLS printer has the capacity of producing a range of complex objects, since it doesn’t require supporting structures. The most common use of this printer has been creation of prototypes. However, it has had several practical applications in limited-run manufacturing, during recent years. One example of this is the acquisition of an SLS engineering company by General Electric for the purpose of building parts for its short-haul commercial jet engine.
II. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) printers involve extrusion of wax, plastic, resin or other material through a heated nozzle. Typical of all 3D printers, each layer is placed on the previous one. However, unlike the SLS, a supporting structure may be needed in FDM.
A second nozzle would be used to build any necessary supporting structure, using material that would be discarded later on. Polyvinyl alcohol is one such material, which may be used for the supporting structure. FDM would be used in such applications as low-volume parts manufacturing (includes structural components), as well as single- and multi-part prototyping.
III. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) possesses certain key features similar to selective laser sintering. These include use of laser and powder. However, in the case of DMLS, the powder is completely melted metal.
The melted metal powder used is free of binder or fluxing agent, which facilitates building parts that possess all desirable properties of the particular original material. This type of object printer has a wide range of uses, including: medical implants, aerospace parts used in high-heat applications and rapid tooling development.
IV. Stereolithography (SLA)
The stereolithography (SLA) printer utilizes two key components: a UV light source and a fluid known as photopolymer. A pool of the light sensitive resin (photopolymer) is present on the build platform, when a UV light source, such as a laser, is aimed onto its surface. Once a single layer is drawn on this liquid surface, the platform moves down to facilitate deposition of the next layer.
A pool of the light sensitive resin (photopolymer) is present on the build platform, when a UV light source, such as a laser, is aimed onto its surface. Once a single layer is drawn on this liquid surface, the platform moves down to facilitate deposition of the next layer.
Intricate shapes that possess high-quality finishes can be created using SLA. This includes such items as jewelry. SLA is also useful in rapid prototyping.
V. Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
Laminated object manufacturing utilizes sheets of paper, metal or plastic. Such a sheet is fed over the platform and adhered to a previous layer using a heated roller. An outline of each part in every layer is then cut using a laser.
Unlike stereolithography, LOM would only produce less detailed parts. However, such parts would be in full color. This type of printer is also useful in rapid tooling patterns and form/ fit testing.
VI. Inkjet-bioprinting
The process utilized by inkjet printers is quite similar to bio-printing. This typically involves deposition of one dot of ink after another to form shapes. However, bio-printing replaces ink with human cells.
This typically involves deposition of one dot of ink after another to form shapes. However, bio-printing replaces ink with human cells.
Living cells derived from a patient’s tissue, as well as scaffolding material (include sugar-based hydrogel) make up the object. Since it contains live cells, the printed object is placed in a chamber containing necessary temperature and oxygen conditions that can facilitate cell growth. Once the cells combine and the scaffolding material is extracted, the bio-printed organ can then be transplanted.
Having an in-depth understanding of all these details will help you select the best choice if you want to buy 3D printers online India.
Buy Resin 3D Printers in India with complete after sales support
Buy best Resin 3D printers as they produce incredibly accurate prints, offer a wide variety of materials, and can produce parts relatively quickly. These precision machines used to cost tens of thousands of dollars, but in recent years desktop resin 3D printers have become ridiculously cheap and giving high quality results.
Although SLA and DLP technology are extremely similar in principle, there are slight differences that separate the two.
SLA 3D printing utilizes two motors known as galvanometers. These motors, placed on the X and Y axis, work together to rapidly angle a pair of mirrors to aim a laser beam across the print area, solidifying resin into a 3D model. The layers of the model are broken down into a series of points and lines, which the galvos use to direct the laser beam.
On the other hand, DLP technology uses a digital projector screen to flash a single image of each layer across the entire platform at once. Each layer of the 3D model is displayed as square pixels, meaning that the print is comprised of voxels. Flashforge Hunter is using DLP Technology
As for LCD 3D printing, the process is nearly identical to DLP in that it utilizes projected light to solidify resin layer-by-layer until a 3D model is built. The main difference is that LCD 3D printers use a bank of UV LEDs to project light through a mask of the layer on an LCD panel. In contrast, DLP 3D printers utilize an array of micro-mirrors (each mirror corresponding to a pixel) to either project light, or not, thus creating a mask. Itech 3D Printers uses the LCD technology
In contrast, DLP 3D printers utilize an array of micro-mirrors (each mirror corresponding to a pixel) to either project light, or not, thus creating a mask. Itech 3D Printers uses the LCD technology
Showing 12 of 16 results
PopularityAverage ratingLatestPrice: low to highPrice: high to lowSold
out
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Sold
out
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Sold
out
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Sold
out
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
Add to wishlist
Compare
Quick view
Add to cart
High Quality Products
Total product quality control for peace of mind
Affordable Prices
Factory direct prices for maximum savings
Express Shipping
Fast, reliable delivery from global warehouses
Worry free
Instant access to
professional support
- +91 9969 555 777
- [email protected]
- Orange Door by WOL3D (Head Office) 19/B(1), Ground Floor, Hakoba Compound, Bombay Cotton Mill, Dattaram Lad Marg, Kalachowky, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400033
Email *
* By Signing up here i agree to receive Minigear’s email newsletter.
© 2022 WOL 3D. All rights reserved.
Read an article about the first 3D printed houses?
3D printing has been used in construction for several years now. In this article, you will learn about the first real houses printed on 3D printers.
3D printing of houses is still quite new to the layman. While construction 3D printing technologies have been developed for many years, only a few "real" projects have already seen the light of day. We are still far from technology taking over conventional construction methods. But with each new project, she is getting closer to becoming mainstream.
There are many benefits to 3D printing. For example, the cost of a 3D printed house can be much lower. And it will take much less time to build.
In order to draw a line under what has already been achieved in this area and show some interesting projects, we have devoted an article to the "first" and the best. These projects will always remain milestones in the 3D construction printing industry as they set the stage for future advances in the field.
These projects will always remain milestones in the 3D construction printing industry as they set the stage for future advances in the field.
First 3D printed house in Germany
Germany is a country often associated with cutting edge engineering, so let's start our list with Germany's first ever 3D printed house.
The house itself is located in Beckum, a city that is partly located in North Rhine-Westphalia, next to Holland and Belgium. This is the first 3D printed house to be fully certified to official building codes. This project will give way to many other 3D printed construction projects in Germany as well as the rest of Europe.
The project is the result of a collaboration between German construction company Peri and Danish construction 3D printing firm COBOD. Peri is a large corporation that operates not only in Germany, but throughout the EU. Its portfolio includes many products, including scaffolding and formwork solutions that every construction site needs.
Peri followed the construction 3D printing segment for years before acquiring a stake in COBOD in 2018. Now they are pushing the technology together and further. The construction of the house in Beckum began two years after the acquisition of the share.
For 3D printing at home, a BOD2 modular 3D printer from COBOD was used. The printing itself took just over 100 hours.
• Built: (started) September 17, 2020
• Commissioned: summer 2021
• Where: Beckum, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany
• By: Peri, COBOD
First occupied 3D printed home in the US
Several homes have been printed in the US, but this home is the first officially occupied home, according to CNN. Its creators: the construction company Alquist and the humanitarian organization Habitat for Humanity Peninsula.
From a distance, you might think that this is an ordinary house. However, when approaching it, the layered structure of the concrete walls becomes noticeable.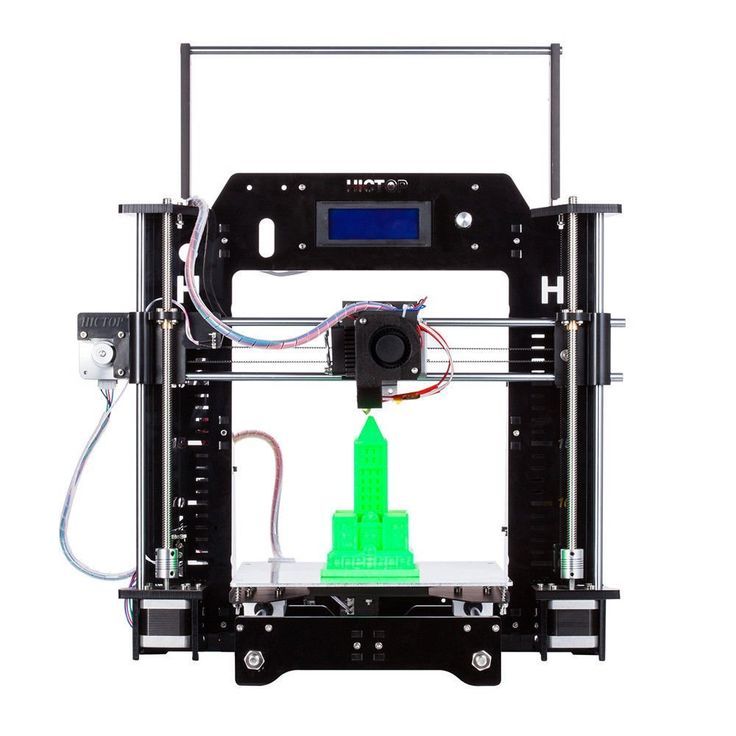 After all, 3D printing creates an object in layers.
After all, 3D printing creates an object in layers.
Surprisingly, the 111.5 square meter concrete structure of the house (was printed in about 12 hours, significantly faster than traditional construction methods would allow.
The house was reportedly purchased by April Springfield, who lives there with her son and dog She bought the house through Habitat for Humanity's housing program, and given that the nonprofit's goal is to help solve the global housing crisis, it makes sense to use 3D printing to create affordable homes that will make many people's dreams of home ownership come true.0005
• Built: 2021
• Commissioned: December 22, 2021
• Where: Williamsburg, Virginia, USA
• By: Alquist 3D, Habitat for Humanity Peninsula, Greater Williamsburg
The first five-story 3D printed house
This project, made by the Chinese company WinSun, is a real record holder. It is a 3D printed five-story residential building with a height of 10 meters - the tallest 3D printed building so far.
The house is located in Suzhou Industrial Park in Jiangsu province in eastern China. It stands next to a mansion that was also built by WinSun using a concrete 3D printer.
Looking at the WinSun designs, you can't help but notice that they don't look like they've been 3D printed. Usually 3D printed structures are gray in color, the layer lines are clearly visible. But WinSun adds color and makes walls smoother. Nowhere is it stated how the company achieves the smoothness of the walls, but we assume that the workers smooth them by hand. WinSun projects are not like the ones we're used to.
• Built: Winter 2014
• Commissioned: Not specified
• Where: Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
• By: WinSun
First 3D printed biodegradable house
Can you guess that there is rice in the walls of this house?
Most 3D printed buildings are made from concrete mix. But this project is different from the rest. With the aim of creating housing solutions with little to no environmental impact, Italian company WASP 3D printed Gay's house using soil and agricultural waste.
WASP developed the sustainable blend in collaboration with Ricehouse, a company that specializes in using natural and agricultural materials such as clay and rice in construction.
The house is named Gaia in honor of the ancient Greek goddess of the earth. In fact, 25% of the mixture contains local soil, 10% hydraulic lime, 25% rice husks and 40% crushed rice straw (a by-product of rice production at harvest).
An innovative solution not only in terms of material, but also in the design of the walls themselves. The specific corrugated structure was used to provide ventilation on warm days as well as insulation on cold periods, virtually eliminating the need for air conditioning.
Gay's house is small - about 20 square meters. The wall printing took only 10 days, while the estimated materials cost is just under $1,000.
• Built: not specified
• Commissioned: October 7, 2018
• Where: Massa Lombarda, Ravenna, Italy
• By: WASP, Ricehouse
AirBnB's first 3D printed house
The perfect weekend getaway.
You can find many different types of accommodation on AirBnB, but what about a 3D printed home?
The so-called Fibonacci house is the first 3D printed house to be offered for booking through AirBnB. Considering that it is located in rural British Columbia, it will be a wonderful place to stay.
Although the Fibonacci house looks small, it has a lot to offer vacationers. About 35 square meters is enough to accommodate up to four people.
The concrete walls of the house were designed and printed by Dutch 3D printing firm Twente. 20 concrete parts were produced offsite in just 11 days. The material was produced by Laticrete. The parts were later transported and assembled at their current location.
• Built: 2020
• Commissioned: Not specified
• Where: Kootenays, British Columbia, Canada
• By: Twente Additive Manufacturing
First 3D printed houseboat
Prvok is not only the first 3D printed house in the Czech Republic, but the world's first floating 3D printed house on a pontoon.
The project was implemented by the start-up company Scoolpt. The concrete structure of the houseboat took only 22 hours to print.
Approximately 43 square meters of living space divided into bathroom, bedroom and living room with kitchen. Weight isn't usually discussed in the context of houses, but given that this one is on water, it's interesting to note that Prvok weighs 43 tons.
The house is equipped with a built-in recirculating shower and tanks for drinking and municipal water and has a service life of at least 100 years.
• Built: June 2020
• Commissioned: August 18, 2020
• Where: Prague, Czech Republic
• By: Scoolpt
Europe's first 3D printed residential house
Not every 3D printed house has visible line layers.
More often than not, 3D printed houses are demos made to show what the technology can do. For most of them there is no information about the actual residents. But in 2017, the couple did move to live in a 3D printed house located in Nantes, France. Thus, the house of "Yanov" became the first of its kind, which was inhabited in Europe.
Thus, the house of "Yanov" became the first of its kind, which was inhabited in Europe.
The house is a project of the University and the Laboratory of Digital Sciences of Nantes. An interesting aspect of the project is the special technique used in its construction by BatiPrint3D. Instead of 3D printing a concrete structure, the robotic arm created wall shells using polyurethane, a material used for insulation. Later, these membranes were filled with concrete.
It took a total of 54 hours to print. It took a little over 4 months to complete the construction. Mainly due to the fact that the rest of the components were created using conventional means. House area - 95 square meters.
• Built: 2017
• Commissioned: March 2018
• Where: Nantes, France
• By: University of Nantes, Nantes Digital Science Lab
India's first 3D printed house
This building was built in a couple of days.
India's first ever 3D printed house was completed back in 2020. The project was carried out by construction startup Tvasta, founded by graduates from the Indian Institute of Technology Madras. In fact, the institute's Chennai campus was chosen as the location of the building.
The project was carried out by construction startup Tvasta, founded by graduates from the Indian Institute of Technology Madras. In fact, the institute's Chennai campus was chosen as the location of the building.
The significance of this project lies in its possible impact on the solution of the housing crisis worldwide and in India in particular. The ability to build such a house within a few days and at a low cost cannot be underestimated.
House 55.7 sq.m. with a spacious layout, one bedroom, combined kitchen and living room.
The concrete structure of the house was 3D printed off site and the parts were later transported and assembled on campus. The foundation, meanwhile, was built using the conventional method of pouring concrete into the ground.
• Built: 2020
• Commissioned: Not specified
• Where: Chennai, India
• By: Tvasta Construction
Africa's first 3D printed house
Back in 2019, in the Moroccan city of Ben Guerir, Spanish firm Be More 3D created Africa's first 3D printed house. The project originated during the team's participation in the Solar Decathlon in Africa. This is an international competition during which teams design and build solar-powered houses.
The project originated during the team's participation in the Solar Decathlon in Africa. This is an international competition during which teams design and build solar-powered houses.
Be More 3D printed house 32 sq.m. in about 12 hours, took first place and received the title of the most innovative startup.
Be More 3D didn't stop building in Africa and later created the first 3D printed house in Spain and developed its own concrete 3D printer in partnership with several corporations from the automation and materials industries.
• Built: 2019
• Commissioned: Not specified
• Where: Ben Guerir, Morocco
• By: Be More 3D
First 3D printed home for sale in the US
Last on our list is the first 3D printed home for sale in the US.
This house was printed in the same place by SQ4D, a company specializing in the development of robotic building systems. The building was printed with SQ4D's Arcs concrete extrusion system and has a 50-year warranty on the printed structure.
Living area of 130.7 sq.m. with three bedrooms and two bathrooms. There is also a garage for 2 cars.
The house was listed for sale in January 2021 for $299,999. Considering the size of the house and the fact that it is priced 50% below the cost of comparable newly built houses in the same area, the deal is pretty good.
• Built: 2020
• Commissioned: 2021
• Where: Riverhead, New York, USA
• By whom: SQ4D
Translation source: https://m.all3dp.com/2/first-3d-printed-house/
On our website you can choose and order a construction 3D printer for both building construction and small building forms. To do this, go to the catalog of construction 3D printers. "Tsvetnoy Mir" is a reliable supplier of 3D printers with many years of experience, supplying directly from manufacturers and guaranteeing their quality.
Voxeljet Systems VOXELJET- VX200 3D Printer 3D Printer Used equipment
- Description
- Detailed information
- About this seller
We have Voxeljet industrial 3D printer for sale: VOXELJET - VX200 3D printer.
* Model No.: VOXELJET-VX200 3D printer.
Manufactured in: VOXELJET
Dimensions / weight:
* External dimensions LxWxH: 1700 x 900 x 1500 mm
* Installation location LxWxH *: 3500 x 2500 x 2000 mm
* Weight: 450 kg
VX200 is one of the most compact voxeljet 3D printing systems. Thanks to its optimized dimensions, this entry-level 3D printing system can be easily installed in small spaces. This is especially useful for research and development. The VX200 prints small prototypes and design details efficiently and is very easy to operate. The practical option: With the open source software voxeljet, various machine settings can be individually adjusted to customize the printing process. This optimizes the interaction between the printing system and the 3D printing material.
Condition: excellent.
This description can be translated automatically. Please contact us for more information. The information in this announcement is for guidance only. Exapro recommends that you check with the seller before buying a machine.
Exapro recommends that you check with the seller before buying a machine.
| Approval | 300dpi |
| ------------------- | |
| L x W x H | 3500.0 x 2500.0 x 2000.0 |
| Weight | 450kg |
| Operating hours | |
| Switching hours | |
| Condition | in excellent condition |
| CE marked | --------- |
| Status |
| Customer type | Dealer |
| Active with | 2017 |
| Offers online | 1 |
| Last activity | June 15, 2022 |
Description
We have Voxeljet industrial 3D printer for sale: VOXELJET - VX200 3D printer.
* Model No.: VOXELJET-VX200 3D printer. VOXELJET -print voxeljet. Thanks to its optimized dimensions, this entry-level 3D printing system can be easily installed in small spaces. This is especially useful for research and development. The VX200 prints small prototypes and design details efficiently and is very easy to operate. The practical option: With the open source software voxeljet, various machine settings can be individually adjusted to customize the printing process. This optimizes the interaction between the printing system and the 3D printing material.
Condition: excellent.
This description can be translated automatically. Please contact us for more information. The information in this announcement is for guidance only. Exapro recommends that you check with the seller before buying a machine.
Details
| Approval | 300dpi |
| ------------------- | |
| L x W x H | 3500. |