Portland 3d printing lab
▷ portland%203d%20printing%20lab%20logo 【 STLFinder 】
PORTLAND
sketchfab
Indoor playground. ...Amusement park
Portland, Oregon
thingiverse
Just a Topography print of Portland, Oregon
Portland Thorns
thingiverse
This is the logo of the Portland Thorns of the National Women's Soccer League
Fruition PORTLAND
thingiverse
. .. Created with Customizer! ...http://www.thingiverse.com/apps/customizer/run?thing_id=52757 Instructions Using the following options: plate = 155.9 top_word = FRUITION font_scale = 3 text_depth = 6 bottom_word = PORTLAND
Portland Trail Blazers
grabcad
Portland Trail Blazers
Portland Trail Blazers 2
grabcad
Portland Trail Blazers 2
Downtown Portland, Oregon
sketchfab
Downtown Portland, Oregon created from LiDAR data.
Portland Anchor Bolt
grabcad
Parametric (ipart) Portland anchor bolt 36 different sizes.
Portland Oregon Temple
cults3d
Model of the Portland Oregon Temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Portland Oregon Temple
thingiverse
Model of the Portland Oregon Temple of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.
Portland Timbers Logo
thingiverse
Portland Timbers Logo https://www. timbers.com/ 3 color print designed with Adobe Illustrator and Tinkercad. ...Colors were changed manually at the appropriate layer height.
timbers.com/ 3 color print designed with Adobe Illustrator and Tinkercad. ...Colors were changed manually at the appropriate layer height.
Portland Thorns Logo
thingiverse
Portland Timbers Logo https://www.timbers.com/thornsfc 4 color print designed with Adobe Illustrator, Fusion 360, and Tinkercad. Colors were changed manually at the appropriate layer height. ...
Portland Trail Blazers Logo
thingiverse
Portland Trail Blazers Logo https://www.nba.com/blazers/?splash=off 3 color print designed with Adobe Illustrator and Tinkercad. ...Colors were changed manually at the appropriate layer height.
Deephouse Portland 3D model
cgtrader
Deephouse Portland https://deephouse.pro/kresla/kreslo-portlend-vrashchayushcheesya-temno-zelenyy-barkhat-latun/ V-Ray render and materials All textures include in *.rar files Lighting setup is not included in the file! ...
Portland Future Fashion Buttons
thingiverse
I designed this simple 1" button for a fashion designer in need of 1" buttons for Portland's Future Fashion show. ...Friday May 9th at the Museum of Contemporary Craft!
Portland Temple Lithophane
thingiverse
Lithophane of the LDS temple in Portland Oregon. Customized version of http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:74322 Created with Customizer! ...http://www.thingiverse.com/apps/customizer/run?thing_id=74322
Customized version of http://www.thingiverse.com/thing:74322 Created with Customizer! ...http://www.thingiverse.com/apps/customizer/run?thing_id=74322
Portland Trail Blazers Logo
myminifactory
The Portland Trail Blazers, commonly known as the Blazers, are a professional basketball team based in Portland, Oregon. They play in the Northwest Division of the Western Conference in the National Basketball Association (NBA). The Trail Blazers...
Portland Oregon Temple
thingiverse
I wanted to print the Portland, Oregon LDS Temple, but there wasn't one on Thingiverse. So I looked on Google's workshop, and I found one but it had many errors. I have since created a new model using pictures and Google Maps. Here it is for your...
I have since created a new model using pictures and Google Maps. Here it is for your...
The Portland Loo
thingiverse
Providing relief for visitors and residents alike since 2008 -- the Portland Loo is acclaimed as "The Best Public Restroom in Canada!" Now you can print a Loo of your own (but just to look at...for now). Madden Fabrication recently purchased a 3D...
Portland Trail Blazers Stand
thingiverse
Portland Trail Blazers Stand. For the swirl part of the logo I remixed https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2391157 in tinkercad. I grabbed the text off of a google image and converted it to a . SVG file and smashed everything together.
You can use...
SVG file and smashed everything together.
You can use...
Portland Plotter Case
thingiverse
I love my [Portland Plotter](https://www.celestaire.com/product/portland-course-plotter/), but it's inconveniently larger than all the rest of my sailing navigation equipment. This is a case I use to give it some protection in while its sat in my...
PORTLAND Armchair 3D model
cgtrader
Size (cm): H 102 x W 80 x D 98 Weight: 24 kg http://www.maisonsdumonde.com/FR/fr/produits/fiche/fauteuil-portland-121846.htm ref 121846, ⬠249 Polygons: 1160 Textures can be found in .skp file How to extract textures from . skp file? If you have...
skp file? If you have...
Portland Timbers Axe in Stump
thingiverse
Go Portland Timbers!!!!
Portland 3D Printing Lab logo
thingiverse
This is a printable logo for the Portland 3D Printing Lab meetup. It's intended for members that want to print giveaways, etc. ...for the meetup.
Portland concrete Floor Tile Texture
cgtrader
Portland floor tile 21 faces of texture: light grey, grey, dark grey matt tile concrete and decoration collection Portland by Terragres 600x600x10mm Matt concrete material is created with corona multimap, includes 22 different HD texture No Plugins!
Portland Aparments Free 3D model
cgtrader
This 3D model was originally created with Sketchup 13 and then converted to all other 3D formats. ...Native format is .skp 3dsmax scene is 3ds Max 2016 version, rendered with Vray 3.00 Apartment building in downtown Portland
...Native format is .skp 3dsmax scene is 3ds Max 2016 version, rendered with Vray 3.00 Apartment building in downtown Portland
Portland Tower Free 3D model
cgtrader
This 3D model was originally created with Sketchup 8 and then converted to all other 3D formats. ...Native format is .skp 3dsmax scene is 3ds Max 2016 version, rendered with Vray 3.00 A new apartment building in Portland. ...
Portland Tower Free 3D model
cgtrader
This 3D model was originally created with Sketchup 13 and then converted to all other 3D formats. ...Native format is .skp 3dsmax scene is 3ds Max 2016 version, rendered with Vray 3. 00 Portland Tower
00 Portland Tower
"The Forbidden City" of Portland
sketchfab
A lot of effort went in to the exercises to make them as real-to-life as possible with casualties even sporting fake blood and broken bones.” https://www.theurbanexplorer.co.uk/east-weare-batteries-distex-site-portland-dorset/...
Iris, Rodin, Portland Art Museum
thingiverse
We call ourselves Layer Geeks and even have a club on meetup.com called the “Portland 3D printing lab” We Love to talk about 3D printing and challenge each other to make. We also do fun projects like 3D print a life size cow #crowdcow. This project. ..
..
NW Noggin & PDX3DP Lab: 3D Printing Brain Models for Students in Oregon - 3DPrint.com
3D printing is very helpful when used to make teaching tools and visual aids for the classroom. When I was scrolling through my Twitter feeds recently, I came across a good example of this application when I saw an interesting tweet from Portland, Orgeon-based nonprofit neuroscience outreach group NW Noggin, or Northwest Neuroscience Outreach Group: Growing in Networks.
Thank you @skjain2 & @pdx3dplab 🧠🎨🙏❤️! They’re #3Dprinting #brains for #nwnoggin delivery to teachers @PPSConnect 🏃🏽♀️🚲🛴🧠😃 We’ll (virtually!) visit 6th-8th graders in May 🗓 to talk #neuroscience #research & make #art 🤝😍 #teaching #outreach 👉🏾 https://t.co/lgXpeK2jxt pic.twitter.com/ncET0MiklJ
— N.W. Noggin (@NWNoggin) May 1, 2020
The NW Noggin organization sends its award-winning graduate and undergraduate art and neuroscience volunteers to work in classrooms and at community events.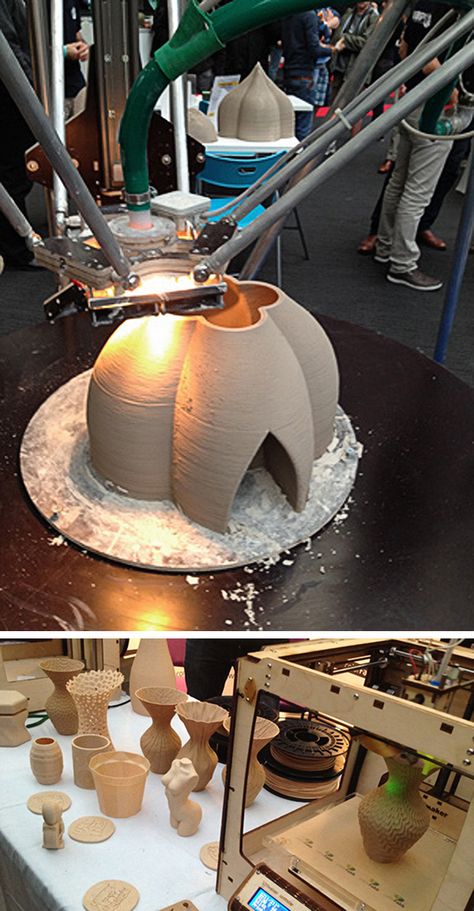 These artists, students, and scientists share their expertise and area educational resources in order to get young people excited about art and science, and teach the public about continuing taxpayer-supported neuroscience research in a fun way.
These artists, students, and scientists share their expertise and area educational resources in order to get young people excited about art and science, and teach the public about continuing taxpayer-supported neuroscience research in a fun way.
“NW Noggin is a locally sourced, 501(c)(3) shoestring nonprofit organization. Your tax-deductible contribution supports the purchase of sheep brains, pipe cleaners, electrodes and clay for innovative, arts-integrated outreach, and helps send volunteers from local universities (including Portland State University, OHSU, and other area institutions) to public school classrooms and free community events…” the website states.
The organization got started in the Pacific Northwest in 2012, and has since expanded to holding events in places like Chicago and even Washington D.C. NW Noggin claims that integrating art into science education can make “learning personally relevant” for students, especially when it’s focused on the organization’s specialty – brains.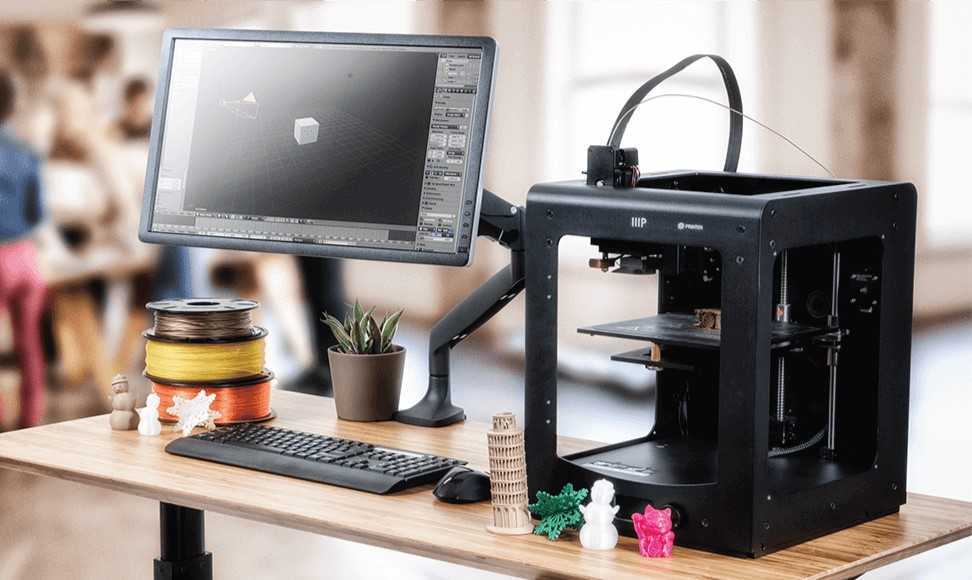
The website explains that “Noggin volunteers now regularly visit K-12 classrooms throughout the academic year, and arrange public, semi-monthly collaborative presentations on research and art.”
This brings me back to the interesting tweet I saw from NW Noggin. One part was the picture you see above, and the second was a screenshot, which you can see below, from Shashi Jain, an e-NABLE volunteer, instructor at TYE Orgeon, and the organizer of the PDX 3D Printing Lab, a group of 3D printing enthusiasts in Portland who meet monthly to talk about their 3D printing projects and businesses, collaborate, and learn from each other. PDX3DP LAB is also a partner organization of, you guessed it, NW Noggin.
That’s right – NW Noggin teaches kids about neuroscience by having them touch brains. Jain offered to 3D print brain models for NW Noggin’s roadshow, which is coming (virtually, of course, thanks to COVID-19) to Oregon’s largest school district, Portland Public Schools (PPS), later this month.
On three consecutive Thursdays – May 14, 21, and 28 – from 10-10:45 am, the NW Noggin Online team will conduct Google Hangouts for students in 6th-8th grade at the PPS Creative Science School. The volunteers will be answering questions from students, and they’ll show 3D printed brains and real animal brains on the screen, in addition to hosting a talk with neuroscience graduate students and providing some interesting at-home art project ideas.
NW Noggin is providing the teachers with kits for their virtual activities, and PDX3DP LAB is providing ten full-size, 3D printed human brains for the occasion. The 3D printable brain models can be found on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) 3D Print Exchange website, which was launched back in 2014 as a way for people to download, edit, and create health and science-related 3D printing files for free.
This is what I love about the 3D printing and maker communities – the desire to help others by sharing knowledge.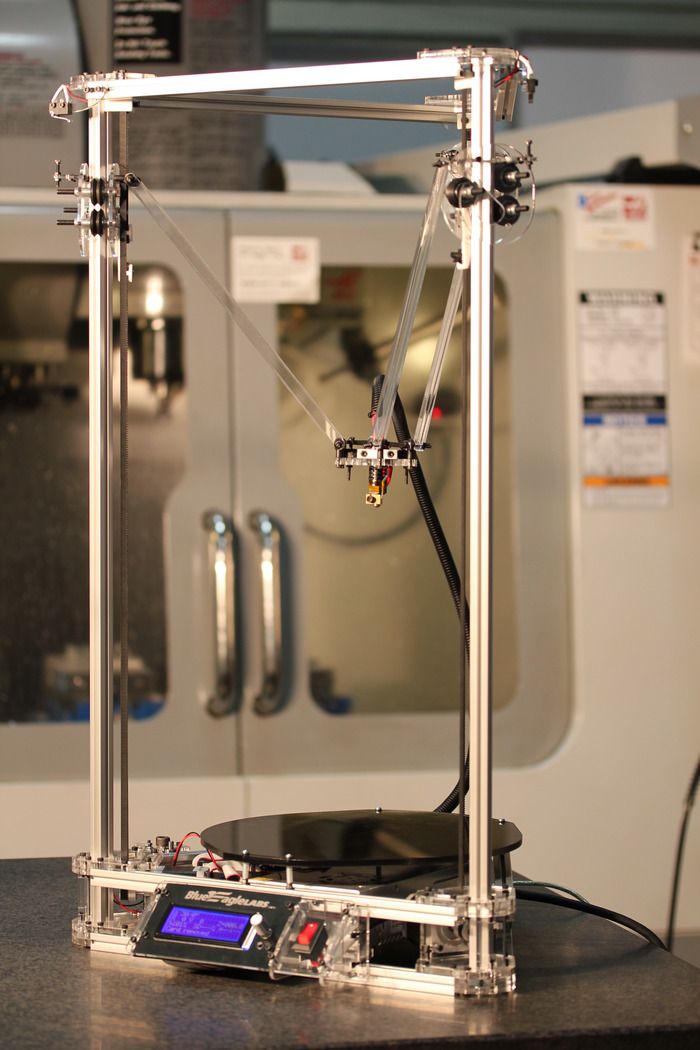
To learn more about 3D printing brains, check out this post by NW Noggin about a previous partnership with Jain at the Portland Mini-Maker Faire.
“These models always attract student and public interest, and are tangible, graspable objects that help teach through visual inspection, direct touch – and discussion about research related to the brain and behavior,” the post states.
“We handled our cerebrums, crafted pipe cleaner neurons, considered intriguing questions about making and brains, and enjoyed discovering the motivating, innovative, creative work and play of Portland’s thriving maker community!”
What do you think? Discuss this story and other 3D printing topics at 3DPrintBoard.com or share your thoughts in the Facebook comments below.
Stay up-to-date on all the latest news from the 3D printing industry and receive information and offers from third party vendors.
Tagged with: 3d printed brain • 3d printed brain model • 3D printed educational products • 3D printed student projects • brain • brain model • google hangout • NIH 3D Print Exchange • non-profit • NW Noggin • oregon • PDX3DP Lab • Portland 3D Printing Lab
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
3D printing laboratory - All about plastics - education, technology, perspectives
Prototyping and modeling using 3D printers has recently become more and more widespread. This is due not only to the development and cheapening of equipment for creating three-dimensional models, the emergence of new polymeric materials for three-dimensional printing, but also the emergence of the need for such modeling for medical products, aircraft parts, instrumentation, automotive and aircraft manufacturing, as well as souvenirs. and other areas. The use of polymeric materials for structural purposes for prototyping made it possible to produce not only models, but also small batches of technical products.
According to the recent study “3D Printing Market (2013-2020)” published by Markets and Markets (“M&M”), between 2013 and 2020, the annual growth of the 3D printing market will be 23%, resulting in will grow to 8.4 billion US dollars by 2020 (http://www.orgprint.com/wiki/3d-pechat/obzor-tehnologij-3D-pechati).
3D printing is a technology for creating three-dimensional objects from a digital sample (CAD) by layer-by-layer application of additive materials. 3D printing methods include stereolithography (SLA), powder laser sintering (SLS), electron beam melting (EBM), layer-by-layer printing with molten polymer thread (FDM), formation of three-dimensional models from layer-by-layer sheet material (LOM) and others.
Initially, 3D printing was used exclusively for prototyping objects, but recently a radical step has been taken towards production. Automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer products are among the industries that are actively embracing 3D printing. According to M&M, 3D printing in medicine and aerospace will grow exponentially in the near future. 3D printing has significant growth potential, it is indispensable where piece production of personalized products is needed.
This article touches upon some aspects of 3D printing, which is carried out by layer-by-layer printing with a melted polymer thread (rod).
Layer-by-layer printing with a molten polymer thread , also known as Fused Deposition Modeling or simply FDM, is used to obtain single products that are close in their functional characteristics to serial products, as well as for the manufacture of investment molds for casting metals.
The main polymer materials used in FDM technology in Russia are ABS plastic, PLA (polylactide), to a lesser extent polyamide (PA-12 or PA-11), TPU, PET-G and a number of other polymers. Almost all polymeric materials are imported.
High impact polystyrene (HIPS) is used as support polymers. This material is used for printing ABS plastic, PMMA, PET-G. Polyvinyl alcohol PVA (PVOH, PVA or PVAL) is also used as a support polymer, however, due to the water solubility of this polymer, it is more difficult to obtain a thread from it, modification of the standard technology is required.
At the Interplastica-2018 exhibition, work was announced on the synthesis of special grades of structural polymer materials for 3D printers at the Kabardino-Balkarian State University (PSU, PFS, etc.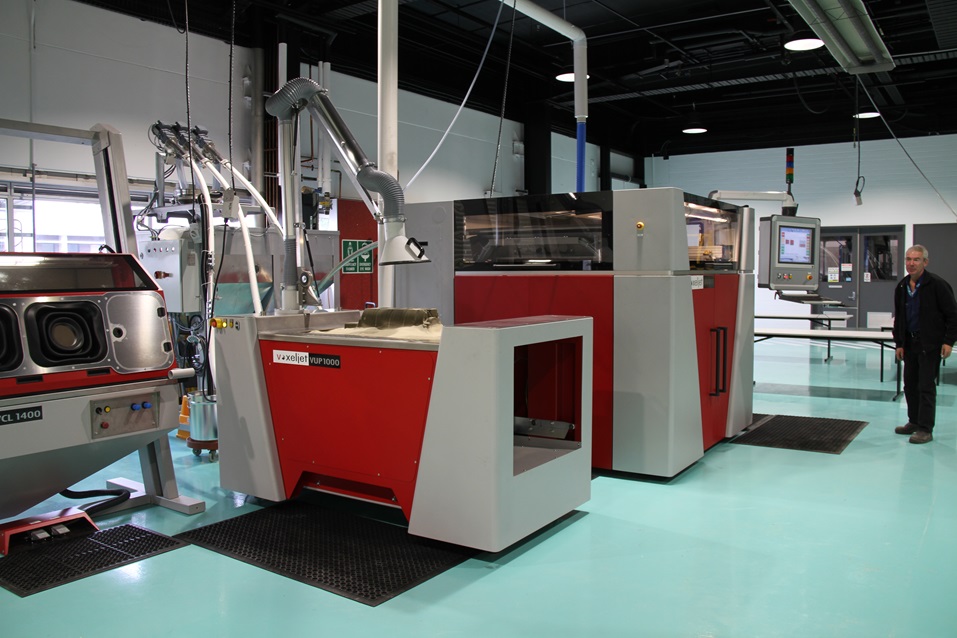 ). In the report of KNRTU (Kazan), the topic of using PP filament for 3D printing was mentioned, which is not surprising, since in the Republic of Tatarstan a wide range of PP grades is produced by Nizhnekamskneftekhim PJSC. The problem with polyolefins in printing is associated with poor adhesion to the 3D printer substrate and high shrinkage when cooled.
). In the report of KNRTU (Kazan), the topic of using PP filament for 3D printing was mentioned, which is not surprising, since in the Republic of Tatarstan a wide range of PP grades is produced by Nizhnekamskneftekhim PJSC. The problem with polyolefins in printing is associated with poor adhesion to the 3D printer substrate and high shrinkage when cooled.
FDM printing technology is as follows: a polymer thread is fed into a heated head with a controlled temperature, in the head it is heated to a melt state and the resulting thermoplastic modeling material is fed with high precision in thin layers onto the working surface of a 3D printer. The layers are applied on top of each other, joined together and cooled, gradually forming the finished product.
The diameter of the nozzle through which a thread with a diameter of 3 or more often 1.75 mm is fed is 0.3-0.4 mm in the first case, and 0.1-0.3 mm in the second case. Therefore, the requirements for a polymer thread should be quite stringent in terms of sizing (thickness variation), stability of rheological properties (melt flow), melt purity (presence of impurities or contaminants).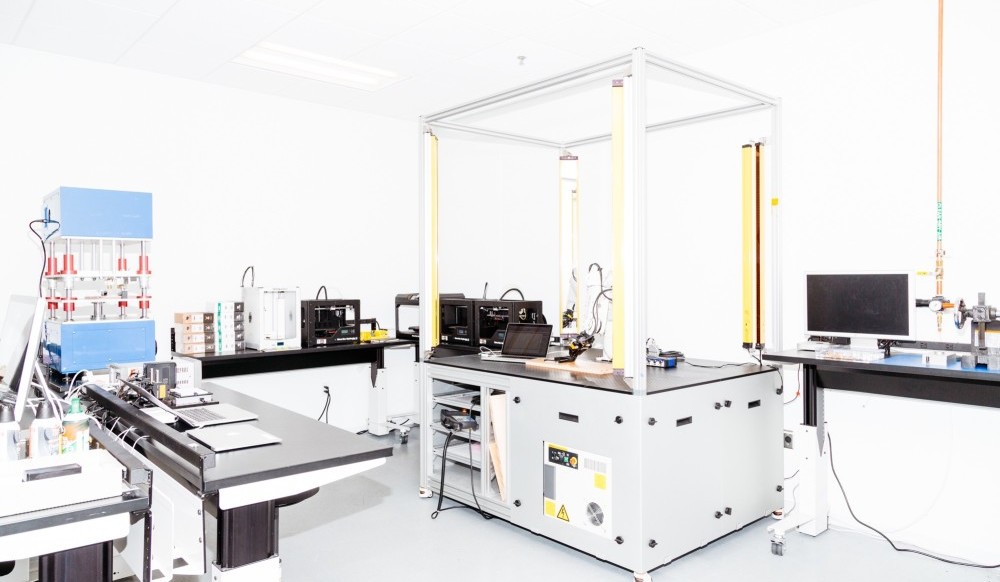
1 shows the scheme of printing polymer thread FDM
1. Flow chart of 3D printing by FDM polymer filament printing.
The production of thread (rod) for FDM technology is carried out on extrusion plants for extruding rod, including a dryer, an extruder, usually a single-strand extrusion head, a calibrator (if necessary), a cooling bath, a gauge for the thickness (diameter) of the thread, 2 (rarely 4 -x positional) bar winder on the coil. There is a lot of information on the Internet about homemade filament extruders, as a rule, of low productivity and low quality filament. However, the production of thread must be carried out on specialized extrusion lines.
A diagram of such a line is shown in fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Extrusion plant for the production of polymer thread
I would like to note that for the wide development of FDM technology in our country, it is necessary to clearly define the characteristics of polymer materials that determine the possibility of their use in 3D printing technology with a polymer thread, as well as to synthesize or modify industrial polymers in order to obtaining material with the required characteristics.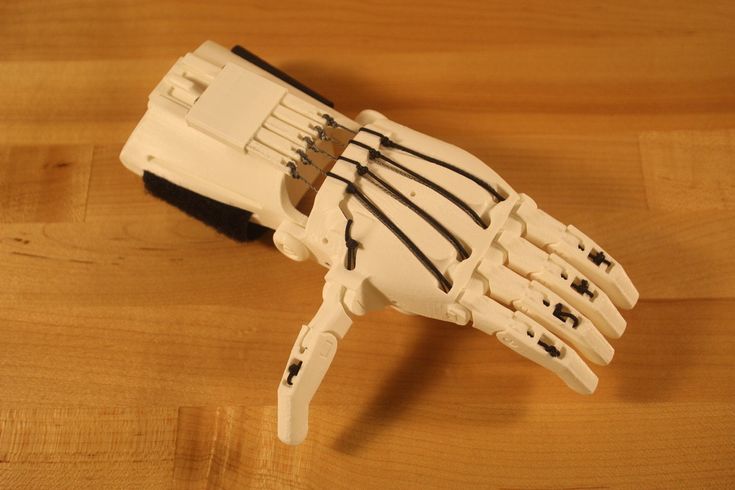 In particular, both thermophysical properties (for example, the thermal diffusivity coefficient, which determines the cooling rate of the material), and rheological properties (fluidity at different temperatures), as well as temperature parameters of the weldability of layers depending on the properties of the feedstock, etc., should be taken into account.
In particular, both thermophysical properties (for example, the thermal diffusivity coefficient, which determines the cooling rate of the material), and rheological properties (fluidity at different temperatures), as well as temperature parameters of the weldability of layers depending on the properties of the feedstock, etc., should be taken into account.
3D printing in Moscow at the 3D printing laboratory
Application of 3d printing
Gaining popularity and being in great demand, 3d printing on order is becoming an integral and indispensable part of life in our time.
The manufacture of cases and volumetric products is a very profitable solution when small-scale production is spreading.
Layer-by-layer material growth technologies (or fabber technologies) for creating physical objects came to Russia not so long ago, but their popularity is growing rapidly. Performing 3D printing - in Moscow or in any other city - is not a problem today. Products for various purposes - from prostheses to parts for cars and aircraft - can be made on the basis of the fabber method.
The term “additive manufacturing” is accepted in industry guides, however, this technology has become commonly referred to as “3d printing” and it is in this version that it is used in the startup environment, between entrepreneurs and journalists.
Layer-by-layer build-up is applicable both for creating prototypes, prototypes of a future product, and for direct manufacturing of parts and solid objects.
Where is the 3d printer used
In what case may 3D printing be required? At the stage of product development, when it is required to visualize it and determine the likelihood of defects or unsatisfactory quality during production. It is also in demand for creating prototypes of architectural objects, as well as for prototyping.
Prototyping of parts, production of tooling - for example, molds for casting; assembly tools - this is not a complete list of cases when they decide to use 3D printing on order. Moscow in this regard is in a much more advantageous position compared to other Russian regions, since ideas and technologies, for the most part, are concentrated here.
We use additive technologies and high-quality materials to make your models, which will then be presented in many industries after printing: medicine, science and education, architecture and construction, energy and oil and gas industry, automotive and mechanical engineering, aerospace industry, jewelry manufacturing .
3D printing, ordering the release of a single item or a series is possible only on the basis of three-dimensional modeling based on special software products - this is where work on a separate project begins. If you want to create a copy or form of an existing object, you will need to apply three-dimensional scanning.
The principle of operation of a 3d printer
Ordering 3d printing means placing an order for the reproduction of a digital three-dimensional model of an object in physical form by horizontal layering of a substance. Layering is carried out using additive installations or three-dimensional printers, the variety of which is quite large today.
For each of the layering methods, including lamination, fusion, sintering, extrusion, jet spraying, UV curing, there is a separate category of devices. To create an accurate three-dimensional geometric product (3d model) that can perform any function, "3D printer" is used - this is the general name for a whole family of equipment capable of performing 3d printing on order (Moscow). At its core, each device is a numerically controlled machine that performs layering operations.
To reproduce the desired objects, it is necessary to use different 3D printing technologies that differ from each other.
Here are the main 3D printing technologies:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM). ABS and PLA printing with this technology is the most popular of all 3D printing technologies. It is used in most desktop 3D printers and represents an ideal price / quality ratio, which allows printing by layer-by-layer supply of a filament of molten plastic;
- Laser stereolithography (SLA).
 Photopolymer printing using SLA technology allows you to form an object by layer-by-layer laser illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage;
Photopolymer printing using SLA technology allows you to form an object by layer-by-layer laser illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage; - Selective laser sintering (SLS). Reproduction is performed by layer-by-layer melting of a special powder under the action of laser radiation. This 3D printing method is widely used in the industry for the manufacture of durable metal elements.
To order printing on a 3d printer using any of the above methods, you must select the material in which the product will be made. What will be the composition of the product, such will be the cost of the work.
Printing on a 3D printer is possible using powder forms of gypsum, polystyrene, polyamides, metal alloys; liquid photopolymers, wax and other materials.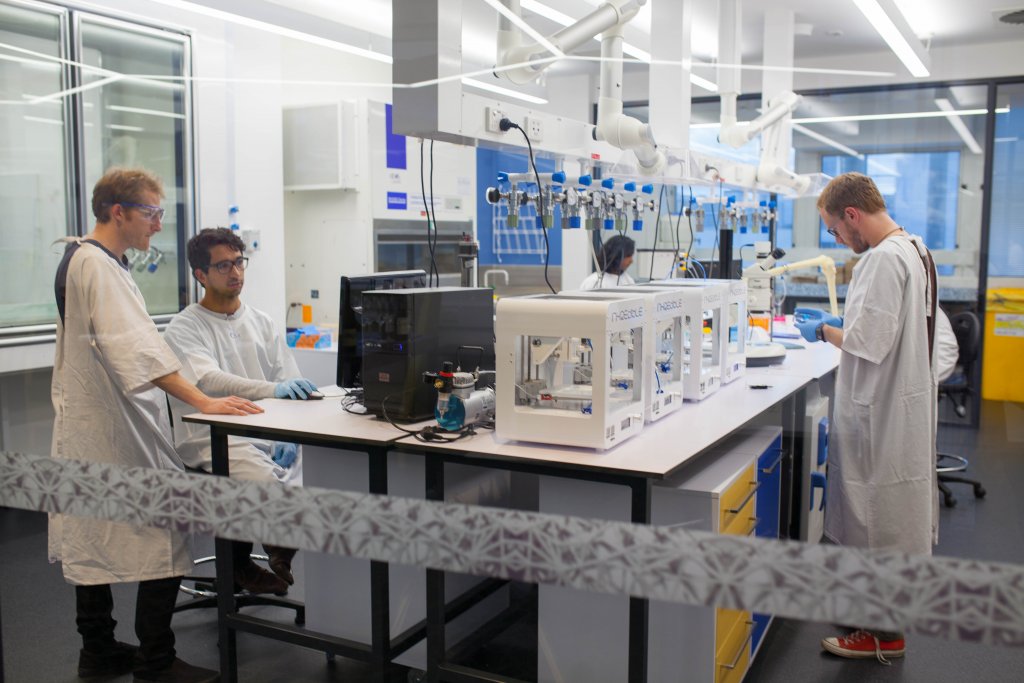 The specific task and requirements for the final product depend on which consumables are selected. It is important that with this production method, whatever you choose, there is almost no mechanical post-processing required.
The specific task and requirements for the final product depend on which consumables are selected. It is important that with this production method, whatever you choose, there is almost no mechanical post-processing required.
In order to understand the principle of 3D printing, it is necessary to reproduce the step-by-step process of creating models.
Let's describe some stages of 3D printing:
- 3D modeling of the required object according to the specified parameters;
- loading a file with a digital model into a slicer program that generates a control code for a 3D printer;
- setting the required 3D printing parameters;
- writing a code to a removable memory that connects to a 3D printer;
- 3D model reproduction.
Objects are reproduced progressively in the desired shape, the selected material is applied layer by layer, forming the finished product.
The possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless, that is, you can make anything you want and this is a huge advantage of this type of printing. In some technologies, for very thin overhanging elements, supports are provided, thanks to which, sagging can be avoided.
In some technologies, for very thin overhanging elements, supports are provided, thanks to which, sagging can be avoided.
Such a brief description of the stages, where there is no ready and detailed analysis of the complete picture of the 3D printing process, gives only an idea of the essence of the technique.
What equipment does LAB3DPrint 9 have0045
Due to the fact that 3D printers are quite expensive equipment, and not everyone can use 3D technologies, but there is a need, our company provides printing services quickly, efficiently and in accordance with your wishes, will complete your task.
The high speed and accuracy of printing, as well as the maximum reliability of our 3D printers, reduce the cost of all types of 3D printing.
We can order a full range of preparatory work and the actual printing on a 3D printer (Moscow) using various methods and materials. We have all the necessary equipment and software.
Our company works with professional equipment, so the quality of the finished product is guaranteed and the result exceeds all expectations.