Peek filament 3d printer
PEEK 3D Printing Filament from 3DXTECH
$195.00 – $1,175.00
4 interest-free payments with Learn More
ThermaX™ PEEK (PolyEtherEtherKetone) is one of the highest-performance polymers in world. PEEK has exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties making it a go-to material in some of the most demanding applications.
[yith_wcwl_add_to_wishlist]
SKU: Select options above Brand: ThermaX™ Categories: PEEK, PEEK Family
- Description
- Reviews
- Questions & Support
ThermaX™ PEEK (PolyEtherEtherKetone) is one of the highest-performance polymers in world. In fact, it’s one of the highest-performance plastics ever invented. PEEK has exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties making it a go-to material in some of the most demanding applications where failure is not an option.
Gearbox HT2™ 3D Printer:
Print industrial-grade parts using our PEEK and more with the new Gearbox™ HT2 High-Temp 3D Printer.
Extruder Temp
375-410°C
Bed Temp
130-145°C
Heated Chamber
Recommended
70-140°C if possible
Nozzle Specs
No special concerns
Bed Adhesion
Nano Polymer Adhesive
Layer Height
No special concerns
Drying Specs
120°C for 4 hours
Supports
Break-Away Support
Benefits of PEEK Include:
- Inherently flame resistant and self-extinguishing
- Long-term hydrolytic stability even above 250°C
- Outstanding resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including automotive fluids, fully halogenated hydrocarbons, alcohols, and aqueous solutions
- Low smoke and toxic gas emissions
- Excellent dimensional stability with low heat creep, low and uniform coefficient of thermal expansion, giving PEEK highly reproducible part-to-part dimensions
- High thermal properties with a Tg of 143°C, CUT of 240-260°C, and Tm of 343°
Typical PEEK Applications Include:
- Seals, Gears, Bushings, Bearings, Pump and Compressor Components
- Industries Served: Auto, Aerospace, Defense, Semi-conductor, Oil & Gas
Filament Specifications:
1. 75mm and 2.85mm +/- 0.05mm in diameter
75mm and 2.85mm +/- 0.05mm in diameter
Recommended Print Settings:
- Extruder: 375-410°C
- Bed Temp: 130-145°C
- Bed Prep: Nano Polymer Adhesive gives us the best results
- Heated Chamber: Recommended, an enclosure helps reduce warping and improves print success. 70-140°C if at all possible
- Supports: ThermaX™ HTS High-Temp Support is designed to work with complex, high-temp materials just like this
- Drying Instructions: 120°C for 4 hours
Questions?
Send us a message and we'll reach out as soon as we can!
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form.Name *
Business / Organization
Email *
Phone
What can we help you with? *
Newsletter Signup
- Sign me up for the 3DXTECH newsletter
PEEK Filament | 3D4Makers | 3D Printing
Roll over image to zoom in Click on image to zoom
Save €-299.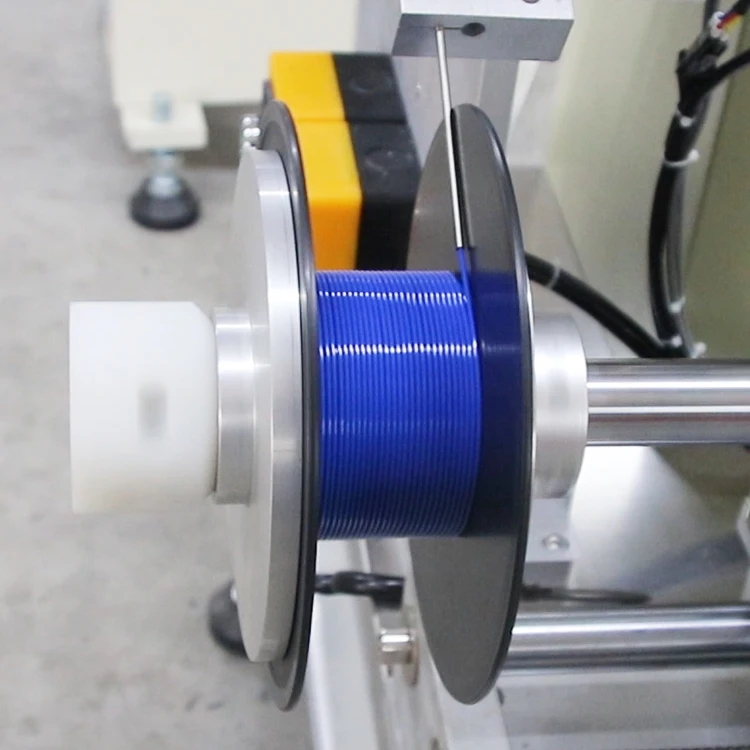 00
00
3D4MakersSKU: PEEKX-0000-175-500-3D4M
6 reviews
Color: Natural
Natural
Diameter: 1.75mm
1.75mm
2.85mm
Weight: 500 gram
500 gram
750 gram
200 gram
Variant
Natural / 1.75mm / 500 gram - €299.00Natural / 1.75mm / 750 gram - €399.00Natural / 1.75mm / 200 gram - €150.00Natural / 2.85mm / 500 gram - €299.00
The 3D4MAKERS PEEK Filament will be delivered in a vacuum packaging in our recyclable box.
Technical information:
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) PEEK polymers are obtained by step-growth polymerization. PEEK is a semicrystalline thermoplastic with excellent mechanical and chemical resistance properties that are retained to high temperatures. PEEK is regarded as one of the highest performing engineering thermoplastics in the world together with other polymers of the PAEK family such as PEKK. PEEK is used to fabricate items used in demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, oil and gas and medical industries. This PEEK filament is based on the VICTREX® PEEK 151G grade.
PEEK is a semicrystalline thermoplastic with excellent mechanical and chemical resistance properties that are retained to high temperatures. PEEK is regarded as one of the highest performing engineering thermoplastics in the world together with other polymers of the PAEK family such as PEKK. PEEK is used to fabricate items used in demanding applications in aerospace, automotive, oil and gas and medical industries. This PEEK filament is based on the VICTREX® PEEK 151G grade.
The 3D4MAKERS PEEK Filament has unique properties because it does not come into contact with water during the production process and is directly packaged in a vacuum packaging. These properties make the 3D4MAKERS PEEK Filament particularly suitable for usage in FDM and FFF 3D printers. The material has an excellent adhesion between layers which results in great improvement of the impact resistance, strength, durability and the printing process.
The PEEK Filament produced by 3D4MAKERS meets the European regulations EC No. 1935/2004, EC No. 2023/2006 and EC No. 10/2011 concerning plastic materials and articles coming into contact with food and is also compliant with the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for food contact. The colorants used by 3D4MAKERS to colour the Filament also meet these European regulations.
1935/2004, EC No. 2023/2006 and EC No. 10/2011 concerning plastic materials and articles coming into contact with food and is also compliant with the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for food contact. The colorants used by 3D4MAKERS to colour the Filament also meet these European regulations.
Measurements & Tolerance
| Size | Diameter tolerance | roundness |
|---|---|---|
| 1,75 mm Filament | +/- 0,05mm | 95% |
| 2,85 mm Filament | +/- 0,10mm | 95% |
Physical properties
| Description | Value | Test method |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1,26 g/cm3 | ISO 1183 |
| Tensile Modulus | 4.1 GPa | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Strength | 105 MPa | ISO 527 |
| Impact strength Notched Izod | 5 Kj/m² | ISO 180/A |
Printer settings
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Printer nozzle temperature | 370 - 420°C |
| Heated bed temperature | 120°C + |
| Drying Recommendations | 120°C, 2-4 hours |
| Print Speed | 15-30 mm/s |
| Adhesion | Magigoo HT on glass or a PEI Sheet |
To get the best results while printing we advise you to keep the 3D printer in a room where there is hardly any draft and/or temperature fluctuations. Keep the 3D printer out of the sun. This cannot be a room where people sleep.
Keep the 3D printer out of the sun. This cannot be a room where people sleep.
When the 3D printer is not being used it is important to keep the 3D4MAKERS PEEK Filament in a bag and stored in a cool, dry and dark place until it is used again.
Please also try our Luvocom 3F PEEK 9581 Filament.
Exposure controls / Personal protection
Local Exhaust Ventilation at the workplace or on the 3D printer is required.
Legally Obliged Information
1 Specific safety, health and environmental regulations and legislation for the substance or mixture.
Classification of the substance or mixture
The substance is not classified as dangerous according to Regulation (EC) no 1272/2008 (CLP/GHS) and Directive 67/548/EEC.
2 Chemical safety assessment: Does not apply
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals).
Recommended restrictions
Do not use in medical applications involving permanent implantation in the human body. The PEEK Filament produced by 3D4MAKERS meets the European RoHS and REACH guidelines.
AmazonAmerican ExpressApple PayDiners ClubGiropayGoogle PayiDEALJCBMaestroMastercardPayPalPaySafeCardShop PaySOFORTVisaYour payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Country
NetherlandsGermanyItalyAustria---AfghanistanÅland IslandsAlbaniaAlgeriaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntigua & BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAscension IslandAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBosnia & HerzegovinaBotswanaBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBritish Virgin IslandsBruneiBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape VerdeCaribbean NetherlandsCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongo - BrazzavilleCongo - KinshasaCook IslandsCosta RicaCroatiaCuraçaoCyprusCzechiaCôte d’IvoireDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEswatiniEthiopiaFalkland IslandsFaroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHondurasHong Kong SARHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKosovoKuwaitKyrgyzstanLaosLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacao SARMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmar (Burma)NamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorth MacedoniaNorwayOmanPakistanPalestinian TerritoriesPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairn IslandsPolandPortugalQatarRéunionRomaniaRussiaRwandaSamoaSan MarinoSão Tomé & PríncipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint MaartenSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSouth Georgia & South Sandwich IslandsSouth KoreaSouth SudanSpainSri LankaSt. BarthélemySt. HelenaSt. Kitts & NevisSt. LuciaSt. MartinSt. Pierre & MiquelonSt. Vincent & GrenadinesSudanSurinameSvalbard & Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandTaiwanTajikistanTanzaniaThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad & TobagoTristan da CunhaTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks & Caicos IslandsTuvaluU.S. Outlying IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVatican CityVenezuelaVietnamWallis & FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabwe
BarthélemySt. HelenaSt. Kitts & NevisSt. LuciaSt. MartinSt. Pierre & MiquelonSt. Vincent & GrenadinesSudanSurinameSvalbard & Jan MayenSwedenSwitzerlandTaiwanTajikistanTanzaniaThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad & TobagoTristan da CunhaTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks & Caicos IslandsTuvaluU.S. Outlying IslandsUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVatican CityVenezuelaVietnamWallis & FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabwe
Zip code
Returns
Our policy lasts 30 days. If 30 days have gone by since your purchase, unfortunately we can’t offer you a refund or exchange.
To be eligible for a return, your item must be unused and in the same condition that you received it. It must also be in the original packaging.
To complete your return, we require a receipt or proof of purchase.
Any item not in it's original condition, is damaged or missing parts for reasons not due to our error.
Any item that is returned more than 30 days after delivery
Refunds
Once your return is received and inspected, we will send you an email to notify you that we have received your returned item. We will also notify you of the approval or rejection of your refund.
If you are approved, then your refund will be processed, and a credit will automatically be applied to your credit card or original method of payment, within 14 days.
Late or missing refunds
If you haven’t received a refund yet, first check your bank account again.
Then contact your credit card company, it may take some time before your refund is officially posted.
Next contact your bank. There is often some processing time before a refund is posted.
If you’ve done all of this and you still have not received your refund yet, please contact us at [email protected].
Sale items
Only regular priced items may be refunded, unfortunately sale items cannot be refunded.
Exchanges
We only replace items if they are defective or damaged. If you need to exchange it for the same item, send us an email at [email protected] and send your item to: Oudeweg 91-95 Haarlem NL 2031CC.
If you need to exchange it for the same item, send us an email at [email protected] and send your item to: Oudeweg 91-95 Haarlem NL 2031CC.
Gifts
If the item was marked as a gift when purchased and shipped directly to you, you’ll receive a gift credit for the value of your return. Once the returned item is received, a gift certificate will be mailed to you.
If the item wasn’t marked as a gift when purchased, or the gift giver had the order shipped to themselves to give to you later, we will send a refund to the gift giver and he will find out about your return.
Shipping
To return your product, you should mail your product to: Waarderweg 56 Haarlem NL 2031BP
You will be responsible for paying for your own shipping costs for returning your item. Shipping costs are non-refundable. If you receive a refund, the cost of return shipping will be deducted from your refund.
Depending on where you live, the time it may take for your exchanged product to reach you, may vary.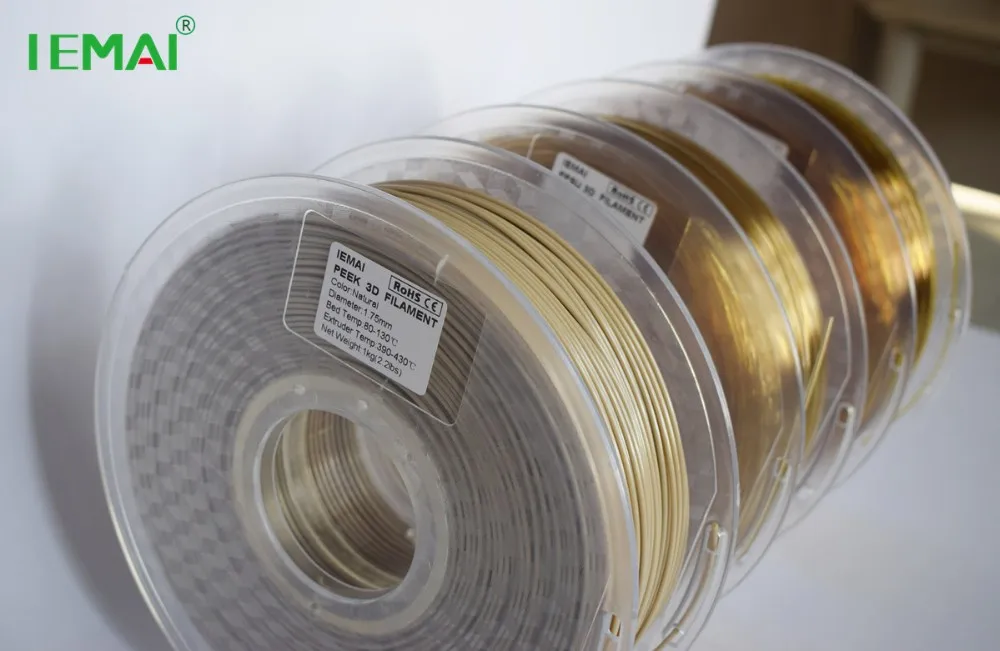
If you are shipping an item over €75, you should consider using a trackable shipping service or purchasing shipping insurance. We don’t guarantee that we will receive your returned item.
3D printer printed multi-colored filament from different materials
19:01 10/30/20 1.7 3D printing materials
Roman Kolesov
Engineers have presented a new technique for printing colored plastic objects on a simple 3D printer with a single nozzle without the use of additional devices. To do this, it is necessary to print a thread consisting of colored segments in the right places in several steps, and then you can use this filament for conventional printing by layer-by-layer deposition.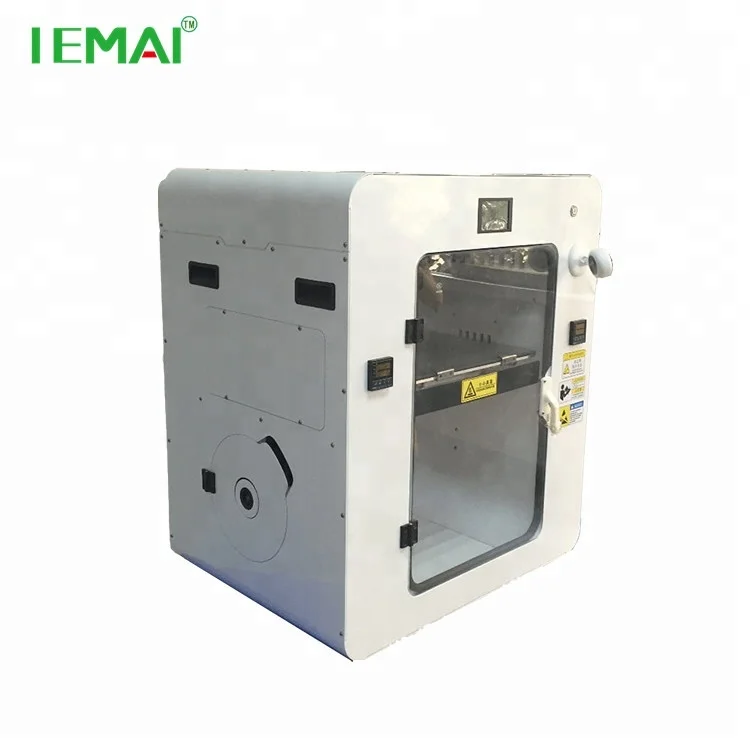 In addition to color, the method also allows you to create a thread from different materials. Article published at ACM Digital Library .
In addition to color, the method also allows you to create a thread from different materials. Article published at ACM Digital Library .
The most common and affordable 3D printing method is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). FDM printers have one (sometimes more) extruder that supplies filament to the substrate, and to print multi-colored objects, you either need to change the filament spool manually, stopping the printing process, or print on a printer with several extruders, or use additional devices to thread several threads at once. Printing with two extruders increases the chance of shearing, welding and other defects, and these defects are also difficult to avoid when manually changing the filament. In addition, manual replacement may be required several times during the printing process, which can greatly increase the time spent and increase the likelihood of printing defects. Accessories, on the other hand, need to be bought separately, and they often require certain skills and training, complicate and increase the cost of printing. There are also multi-color threads and materials that can change their color and properties, but these are not universal solutions that are usually not available to the average user.
There are also multi-color threads and materials that can change their color and properties, but these are not universal solutions that are usually not available to the average user.
Haruki Takahashi of Meiji University and colleagues have come up with a low-cost method for printing different colors and even materials on a printer with just one extruder. The method involves the creation of a programmable thread for each individual project using a 3D printer, which is then fed into the 3D printer as a regular filament. The length and number of required segments is generated in G-code format from a 3D model or 2D image using printer software.
A program developed by scientists uses this G-code to design a future thread and offers optimal printing options. The printer sequentially prints the filament in the form of a spiral, starting from the edge towards the center. First, all segments of one color are printed, and only then another, which significantly reduces the number of manual filament changes. The ends of the segments are cut diagonally during the printing process to increase the contact area between the segments, and are additionally fused with stitches - additional layers of filament. Fusing the stitch and simultaneously passing a hot nozzle at the point of contact increases the strength of the connection.
The ends of the segments are cut diagonally during the printing process to increase the contact area between the segments, and are additionally fused with stitches - additional layers of filament. Fusing the stitch and simultaneously passing a hot nozzle at the point of contact increases the strength of the connection.
The scientists tested their technique on four different printers using filaments of different colors and different materials: polylactide, thermoplastic polyurethane, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, polyvinyl acetate, nylon. One of the samples printed with the programmable filament consisted of five colors, which is difficult to achieve using even multi-extrusion machines. In addition, the engineers printed a mock-up of a watch that combines a solid base and a flexible strap, proving the possibility of using dissimilar materials in their technique.
The researchers plan to refine their method in further studies and study the mechanical behavior of composite structures in more detail, as well as increase the strength of connections between heterogeneous materials.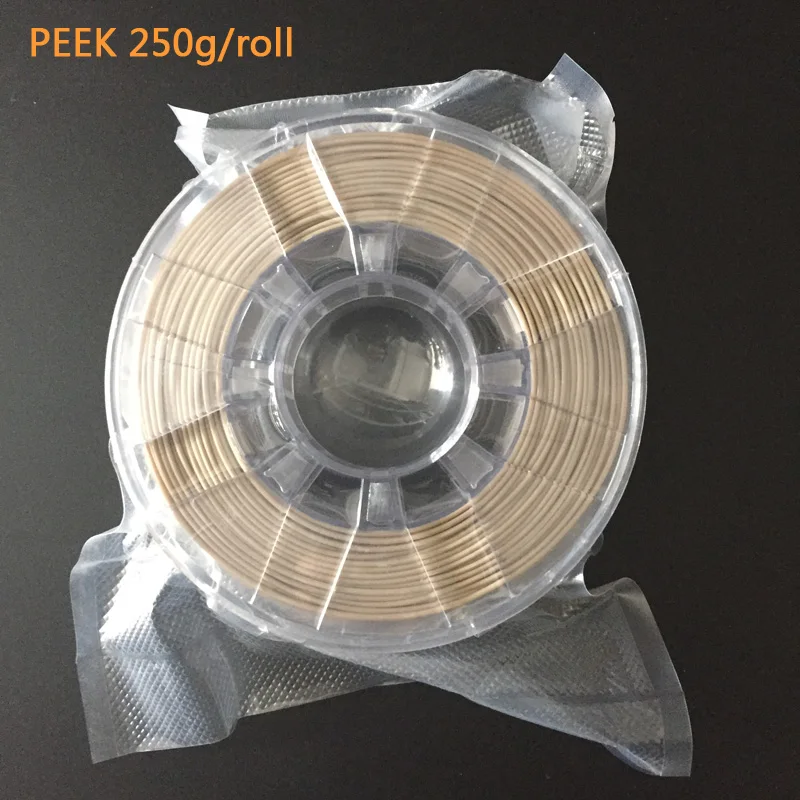 Already at this stage, the filament stitching technique provides good joint strength, reduces the cost and simplifies the printing process.
Already at this stage, the filament stitching technique provides good joint strength, reduces the cost and simplifies the printing process.
Recently, we wrote about another way to simplify the post-processing of 3D printed materials - this is the addition of a catalyst to the plastic to facilitate subsequent metallization.
Roman Kolesov
Found a typo? Select the fragment and press Ctrl+Enter.
15:51 07/22/21 2.9 Robots and drones 3D printing
3D-printed robotic arm passed the first level in Super Mario
Andrey Fokin
American engineers used PolyJet 3D printing technology to build robot prototypes from polymer materials. Thanks to the ability to print simultaneously with several photopolymers, this technology allows you to create complex designs from several polymer materials with different properties in one print session, which reduces the amount of subsequent manual work and increases the speed of development.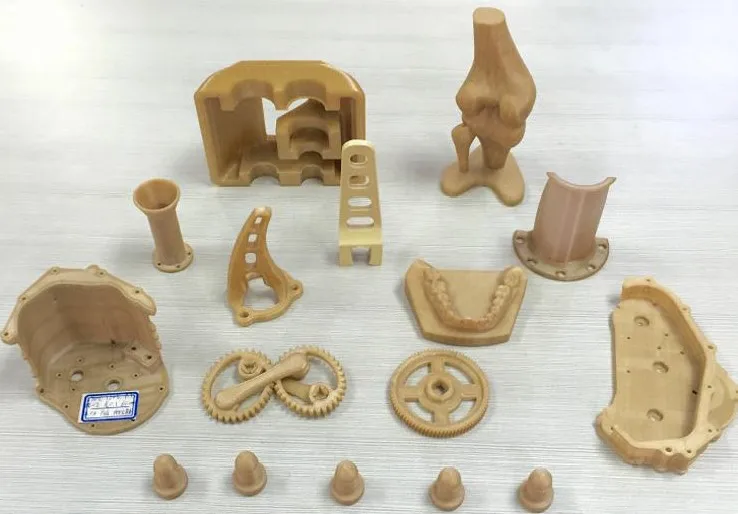 First, the engineers designed and printed several inkjet logic elements: a diode and transistors powered by hydraulics and pneumatics, and then demonstrated their use in the control circuits of hydropneumatic turtle-like robots and in a three-fingered robotic arm, which the engineers used to control the gamepad of the NES game console. Using a pre-written program that controls the pressing of the fingers of the robotic arm on the buttons of the controller at given points in time, the engineers were able to complete the first level of Super Mario Bros. The article was published in Science Advances.
First, the engineers designed and printed several inkjet logic elements: a diode and transistors powered by hydraulics and pneumatics, and then demonstrated their use in the control circuits of hydropneumatic turtle-like robots and in a three-fingered robotic arm, which the engineers used to control the gamepad of the NES game console. Using a pre-written program that controls the pressing of the fingers of the robotic arm on the buttons of the controller at given points in time, the engineers were able to complete the first level of Super Mario Bros. The article was published in Science Advances.
Read more
How is filament (material) made for 3D printing?
3DPrintStory News How is filament (material) made for 3D printing?
Filament is a necessary part of the 3D printing process, if you draw an analogy - it is the "food source" for FDM 3D printing. As the industry develops, so does the variety of materials available. Nowadays, there are many brands, different sizes and a wide range of new types of materials for 3D printing. Have you ever wondered where these filament spools come from?
As the industry develops, so does the variety of materials available. Nowadays, there are many brands, different sizes and a wide range of new types of materials for 3D printing. Have you ever wondered where these filament spools come from?
The filament manufacturing process can be broken down into five steps, from harvesting the raw material to having the spool at your doorstep. In this article, we will take a detailed look at the process of making material for 3D printing. Given the variety of material types and the differences in how they are made, we will only focus on the basic steps that are common to all filaments.
Step 1: Plastic
The first step in the filament production process is the production of plastic. During refining, crude oil is heated in an industrial furnace that separates its many different components. One of the components, naphtha (naphtha), is most used in the production of plastic for 3D printing.
Naphtha, catalysts and other chemical components are chemically bonded in the polymerization reactor. The polymerized naphtha products are then compounded and processed. This process involves melting the products and mixing them with other materials to form the plastic. The resulting plastic is then granulated into small pieces known as pellets or resin.
The polymerized naphtha products are then compounded and processed. This process involves melting the products and mixing them with other materials to form the plastic. The resulting plastic is then granulated into small pieces known as pellets or resin.
Plastic suppliers typically produce clear or white granules and resins. This allows their users, such as material manufacturers, to have more control over the dyeing process.
Compared to filament spools, pellets are very inexpensive: you can buy 1 kg of pellets for a fraction of the cost of 1 kg of finished filament. This, of course, is due to the fact that filament companies turn raw materials into finished products.
If you're up to the challenge, you can save a lot of money by buying pellets directly from a plastic supplier and making your own 3D printing material. There are even commercial products that make the filament manufacturing process easier.
Step 2: Preparation
In the second step of the process, the granules are prepared for the next step, molding, where they harden into a filamentous shape. The granules are placed in an industrial blender and mixed with additives to create a homogeneous mixture and give the material special properties.
The granules are placed in an industrial blender and mixed with additives to create a homogeneous mixture and give the material special properties.
Additives may include colorants or other elements that affect properties such as impact resistance, strength, structural integrity, and even magnetic properties. Exotic materials such as wood are produced by mixing special additives such as sawdust or wood particles with plastic granules.
Drying
After the granules are properly mixed, they enter the drying phase. Like the filament, the granules are hygroscopic. This means that they absorb moisture from the air. This can deform or break the plastic, so removing moisture from the pellets is essential to ensure the production of quality filament. Drying usually takes place at 60°C to 80°C for several hours, but the process depends on the manufacturer.
Step 3 Shaping
The third step in the 3D printer filament production process is the string-shaping of the granules. This step includes the heating and cooling process. This is one of the most important and responsible steps.
This step includes the heating and cooling process. This is one of the most important and responsible steps.
Heating
In the first molding step, the pellets are fed into a material extruder which includes a heating chamber. In this chamber, the individual granules are melted into a sticky substance so that they can be easily shaped.
In this state, the granules are joined together and form a continuous twisted material. The bonded string material, better known as filament, leaves the heating chamber through a round nozzle and enters the cooling section.
Cooling
After the thread leaves the heating section, it passes through several water chambers. The first chamber is filled with warm water, which is an important factor in obtaining a rounded thread. Setting the right temperature for the material helps prevent oval-shaped filament from forming, which can cause problems for 3D printing.
The second chamber is filled with cool water, which cools the thread and reshapes it. The speed at which the thread is pulled determines the diameter of the thread. A lower speed produces a larger diameter, and a higher speed does the opposite.
The speed at which the thread is pulled determines the diameter of the thread. A lower speed produces a larger diameter, and a higher speed does the opposite.
Step 4 Winding
In this step of making the 3D printable material, the motors pull the filament from the cooling chamber to the winding mechanism. The winding process begins by measuring the filament diameter with a laser device to ensure that it is within the tolerance of the final required diameter, most likely 1.75 mm or 2.85 mm.
The thread is then attached to the spool and wound around it. As soon as the sensors detect that the spool is full, the thread is cut and secured. The process starts again, filling the next spool until a batch of filament runs out.
Step 5 Packing
The last step is the process of preparing the filament spools for sale. Vacuum packaging, boxes, barcodes, barcodes, all this is completed at this stage. Once the filament is properly packaged, it is ready to ship to customers.