How to use 3d printers
How to 3D print? The Beginner’s Guide to 3D Printing
Learning how to 3D print has never been easier!3D printing is an ever-evolving and expanding field. If you’re a beginner at 3D printing, the number of possibilities and applications can seem so vast, it can be a bit overwhelming when you’re just starting to know how to 3D print and how to use a 3D printer.
In this beginner’s guide to 3D printing, we’ll explain what exactly 3D printing is, how it works, how to 3D print, the best materials for beginners, and what you need to get started.
What is 3D Printing?3D printing is the process of creating a three-dimensional object, usually done by systematically layering material on top of itself. The printer reads a digital file from the computer which dictates how to layer the material to build the object.
This is why 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing. 3D printing and additive manufacturing are mostly synonymous, although you may hear additive manufacturing used more frequently in the context of mass consumption or mass manufacturing.
Depending on the specific print you are planning to do there could be more or fewer steps in your process. But in general, 3D printing involves the following actions:
Step 1: Create or Find a DesignThe first step of 3D printing typically starts on a computer. You must create your design using a 3D design software, typically a CAD (computer-aided design) software. If you are unable to create the design yourself, you can also find many free resources online with free designs.
Step 2: Export the STL FileOnce you have created or chosen a design, you must either export or download the STL file. The STL file is what stores the information about your conceptual 3D object.
Step 3: Choose Your Materials Typically you may have an idea about what kind of material you will use before you print. There are many different 3D printing materials available, and you can choose them based on the properties that you want your object to have. We will discuss this more in-depth below.
We will discuss this more in-depth below.
The next step is then deciding on the different parameters of your object and the printing process. This includes deciding on the size and placement of your print.
Step 5: Create the GcodeYou will then import the STL file into a slicing software, like BCN3D Cura. The slicing software will convert the information from the STL file into a Gcode, which is a specific code containing exact instructions for the printer.
Step 6: PrintThis is when the magic happens! The printer will create the object layer by layer. Depending on the size of your object, your printer, and the materials used, the job can be done in a matter of minutes or over several hours.
Depending on what you want your final product to be or the material you used, there may be additional post-processing steps after printing, like painting, brushing off powder, etc.
What is 3D Printing Used For?3D printing can be used both recreationally and professionally, across various industries. It has applications in many different fields and sectors, from the healthcare industry to engineering, and even fashion.
It has applications in many different fields and sectors, from the healthcare industry to engineering, and even fashion.
Increasingly, 3D printing is seen as a sustainable and cost-friendly solution for creating prototypes and tools for different manufacturing projects and processes. Traditionally, acquiring prototypes can be time-consuming and costly, requiring companies to depend on outside manufacturers. 3D printing allows companies to quickly make units of an object, tool, or prototype, all in-house.
A great example of this is shoe company Camper. In-house 3D printing has allowed them to transform their nearly month and a half long modeling and designing process into an operation that takes only several days.
3D Printing For Beginners: How To Get Started
So, what do you need to get started with 3D printing? Your specific needs will depend on why and what you want to print, but in general, there are three considerations for getting started:
- A 3D printer
- Filament
- Slicing software
If you plan on creating your own designs you will also need the appropriate designing software. But, as we mentioned earlier, you can also find many free resources online to download designs.
But, as we mentioned earlier, you can also find many free resources online to download designs.
If you have not yet purchased a 3D printer, we have a guide that can help steer you through the most important considerations.
3D printer FilamentsThe material also called filament, you choose for your print will depend on many different factors:
- Do you want your object to be flexible?
- Heat resistant?
- Does it need to be very durable?
These are just some of the factors to consider when choosing your filament.
In general, most beginners start with PLA. This is because PLA is cost-effective and typically easy to print with a standard configuration. Depending on your specific project, PLA could be good starter material.
PET-G is also considered a beginner-friendly material, although it is a bit more technical than PLA. However, it is great for industries like engineering and manufacturing. It is a good material for functional prototypes because it can withstand higher temperatures and has a different chemical makeup that is ideal for these uses.
There are two important pieces of software for 3D printing: CAD and slicing software.
Typically, you can use any CAD system that can create a functional model. CAD is essential if you want to create your own models and objects. You must be able to export an STL file from your CAD software.
The slicing software is the second part of the equation. This software translates the STL file into a language that the printer can understand. The Gcode contains movement information that tells the printer how and where to move its axis, as well as how much material to deposit. The Gcode is sent to the printer via an SD card or wifi.
Final Thoughts3D printing is now more beginner-friendly than it has ever been. In the beginning, many people saw 3D printing as something inaccessible to the major public, but this sentiment is changing, and for good reason. While it takes practice to perfect your prints and technique, learning how to 3D print is an attainable skill.
How to use a 3D printer
David Roberson14 September 2021
Guide
How do you use a 3D printer step by step? Many different technologies share the same basic steps which we’ll cover next, but each 3D printer can also be easier or harder to use depending on its features.
Step 1 – Prepare your design for 3D printingBy this point, it’s important you have a part ready to print and you have chosen your material. This part can be one you designed yourself using CAD (computer aided design), one taken from a 3D scan, or one you have taken from an inventory of existing designs.
Before you start printing, you need to translate your design into ‘coordinates’ the 3D printer can understand, as well as tell it important parameters such as the material you are printing with.
This is known as ‘slicing’, because it involves slicing the 3D design into – you guessed it – layers. This is typically done in a program known as slicing or print preparation software. Our Ultimaker Cura slicing software comes with many preconfigured settings so will normally only take you a matter of seconds to prepare a print. Or if you prefer granular control of the printing process, there are also hundreds of custom settings to use. Once the slicing is done, your file is ready to print.
Our Ultimaker Cura slicing software comes with many preconfigured settings so will normally only take you a matter of seconds to prepare a print. Or if you prefer granular control of the printing process, there are also hundreds of custom settings to use. Once the slicing is done, your file is ready to print.
Preparing a 3D print with Ultimaker Cura software
Step 2 – Set up your printerYou could also do this step first if you like. Or you may not need to at all, for example if you regularly print the same type of parts.
But before you start printing, be sure to check you have the right material loaded. FFF 3D printers like Ultimaker also let you choose different nozzle sizes, with a smaller nozzle giving more detailed prints and a larger nozzle faster print times. If you’re using Ultimaker software together with an Ultimaker 3D printer, it will check your printer configuration and prompt you if anything needs changing.
Step 3 – Send your file to the printerOnce you are ready to go, you need to get the file to your 3D printer.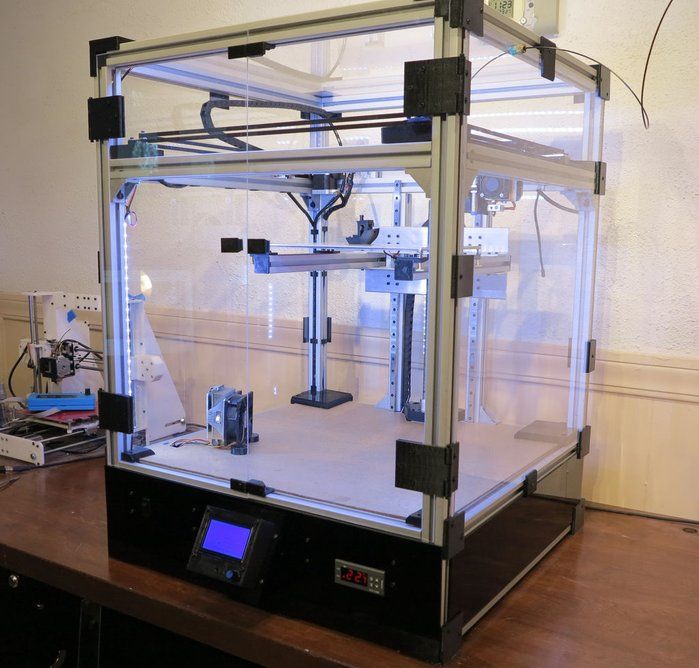 There are two main ways to do this. One is to load the file onto a data storage device (such as a USB drive), put it in the printer, and start your print job via the printer’s interface. The other option is to send the job remotely to a network enabled printer via your local network or the cloud. Remote printing is particularly helpful if you are not in the same location as your 3D printer.
There are two main ways to do this. One is to load the file onto a data storage device (such as a USB drive), put it in the printer, and start your print job via the printer’s interface. The other option is to send the job remotely to a network enabled printer via your local network or the cloud. Remote printing is particularly helpful if you are not in the same location as your 3D printer.
Now you can sit back and relax! Or if you’re at work, get on with something else while the printer does its job.
Printing times vary depending on the size and detail level of your printed object and your 3D printer type. On an FFF 3D printer such as Ultimaker, a small component or rough prototype may only take a few hours. Most parts will be ready the next day if you leave the printer running overnight. And if you need a very large, detailed print, you may have to wait a couple of days.
Some 3D printing platforms enable you to monitor your print job.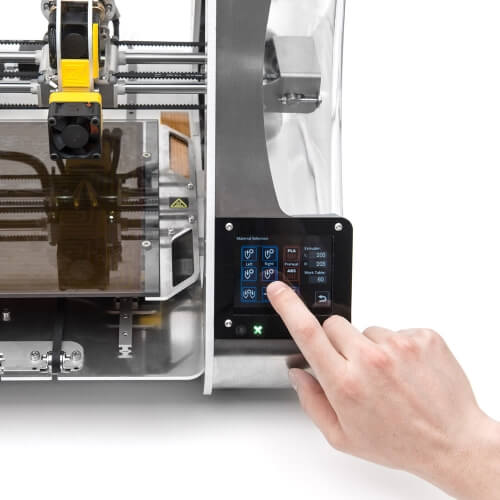 You can do this via the Ultimaker Digital Factory – and with an Ultimaker S3 or Ultimaker S5 printer, even view progress via a webcam feed.
You can do this via the Ultimaker Digital Factory – and with an Ultimaker S3 or Ultimaker S5 printer, even view progress via a webcam feed.
When the print is finished, remove from the printer. Depending on your chosen material and printing process, some final manual steps may be needed before it’s ready to use. With an FFF 3D printer, this ‘post-processing’ is often little more than peeling off a small brim of material around the part. Other methods like SLA or SLS typically need more intricate post-processing, for example removing the loose powder from the chamber of an SLS printer.
With the Ultimaker platform you can prepare a print, choose a printer with your required setup, then send the print job – all remotely. Just collect it when it’s done
Are 3D printers easy to use?
This can depend on a lot of factors, but in general 3D printing is one of the most accessible manufacturing processes available. Compared to injection molding or CNC machining, 3D printers are a much easier way to make parts and models, which is why it works as a desktop technology everywhere from schools to offices.
But, there are a few things to be aware of that will help make your experience of 3D printing hassle-free:
Material choice – Perhaps the key area where all 3D printers are not created equal. Check which materials a 3D printer can print or you may end up surprised to discover you are limited to only one or two. Even worse, some printer manufacturers only let you print with their own material products, so you’re locked into using these forever. Look for a 3D printer that’s compatible with a wide range of materials, including those made by third parties, so you can leverage the near endless options on the market and benefit from open innovation
Automation – There are potentially hundreds of parameters and configurations involved every time you 3D print, such as printer temperatures or how the nozzle will travel to build up the print. But at Ultimaker, we don’t believe this should mean complexity for the user. For example, our material spools come with embedded NFC chips so the printer knows what’s loaded, preconfigured printing profiles in our software dramatically reduce setup time for each print, and you can manage the whole end-to-end process in one place via the Ultimaker Digital Factory
Support and service – If things do go wrong, it can be frustrating and impact your productivity.
 So be sure to check your 3D printer comes with comprehensive support and a warranty. Check for troubleshooting, FAQs, and other resources so you can easily solve problems yourself and stay productive
So be sure to check your 3D printer comes with comprehensive support and a warranty. Check for troubleshooting, FAQs, and other resources so you can easily solve problems yourself and stay productive
What do you need to 3D print?
Your 3D printer should come with everything you need to get started out of the box. Below we list the essentials, as well as the optional extras it’s good to know about:
A 3D printer – OK, this one’s obvious
Material – Your printer should include some in the box or it can be bought from 3D printing vendors
Software – Some printer brands supply their own, or you may have to find a compatible program. Note that there are two types of 3D printing software – print preparation (or slicing) software and printer (or print job) management software
Consumables – In addition to materials, your 3D printer may require or come with other consumables. For example, oil or grease for maintenance, or adhesive aids for the build surface.
 With Ultimaker, everything you need to get started comes in the box
With Ultimaker, everything you need to get started comes in the boxTools (largely optional) – Some 3D printers may require one or two basic tools for configuration changes or maintenance. (Again, with Ultimaker everything essential comes in the box.) Otherwise, if you’re going to be using your 3D printers a lot and will need to do some post-processing of prints, it’s useful to keep a few tools handy. We created a guide to tools for FFF 3D printers
Peripherals (optional) – These can add more functionality to your 3D printer. For example, for some of our printers you can also add an Air Manager, which encloses the 3D printer and filters up to 95% of UFPs (ultrafine particles), or Material Station which stores filament in an optimal environment and automatically loads material when a spool runs out
Next to this, all you need is a power supply and a clean, safe workspace for your 3D printer. You can find more advice on these topics in our free, in-depth white papers.
How do you use a 3D printer at home?
Hobbyists and entrepreneurs have been using desktop 3D printers at home for years, but at a time when remote working is more common than ever, this is an important question.
Generally, the same setup advice as above for a workplace is recommended. But think carefully about two key considerations – safety and space. SLS and SLA printers require careful processing of hazardous chemicals before unused resin or powder can be disposed of with your household waste. And as space is likely at a premium in the home, choosing a large format printer like the Ultimaker S5 Pro Bundle may not be practical compared to a smaller unit like an Ultimaker 2+ Connect or Ultimaker S3.
3D printers vary in size. Check the dimensions before installing it in your chosen location
There's more to discover...
Explore the wider world of 3D printing by checking out our answers to these common questions:
What is 3D printing?
What can you 3D print?
How much does 3D printing cost?
instruction how to work from scratch for beginners and dummies, how
looks like Three-dimensional printing has become increasingly introduced into our daily lives. Thanks to new technologies, it has become possible to easily print from a small detail to a large building. The range of products is also pleasing - today you can find a lineup that includes both affordable devices and more expensive ones. But how to work with a 3D printer? This is a completely normal question that any beginner will have, it is for this reason that we will try to answer it as simply and accessible as possible.
Thanks to new technologies, it has become possible to easily print from a small detail to a large building. The range of products is also pleasing - today you can find a lineup that includes both affordable devices and more expensive ones. But how to work with a 3D printer? This is a completely normal question that any beginner will have, it is for this reason that we will try to answer it as simply and accessible as possible.
What is a 3D printer and how does it work?
The 3D device consists of the printer itself and a computer that controls all processes. The principle of operation of such a design is to create 3D models by superimposing layers of liquid material. There are a large number of printer models - from large industrial ones to compact ones, but they all have the same principle of operation and component parts:
- Extruder - the print head through which the thread passes. The head heats the thread to a semi-liquid state and evenly supplies the material to the working surface.
- Work surface - a printing platform on which a 3D model is formed.
- Motors - mechanisms responsible for the accuracy of movement and speed of printing.
- Sensors are electronic devices that limit moving parts to specified coordinates.
- The frame is the structure that connects all parts of the printer.
How a 3D printer works: features
Work with the aim of building a three-dimensional model begins with a sketch, which is created in a special program. After that, the software independently generates a plan for the movement of the print head and a print sequence. The 3D model is reproduced by strongly heating the plastic and distributing it evenly.
3D printers are used in many areas. Let's list some of them:
- Architecture - creation of models of buildings.
- Medicine - dental prosthetics, making models of organs for study.
- Construction - production of houses using 3D printing technology.

- Education - a visual aid for learning 3D printing.
- Automotive - creation of tuning parts, prototype layouts and other products.
This is a small list of industries where 3D printing is actively used. Today, almost every entrepreneur and just an enthusiastic person can afford a printer.
The following printers are distinguished by design features:
- RepRap - self-reproducing printers that can create their own copies.
- DIY-kit - the device comes disassembled with instructions, the assembly of which will take a sufficient amount of time.
- Completed - Models are delivered assembled and ready to use.
- Commercial and Industrial - devices capable of printing metal, concrete, polymers and other materials.
How to use a 3D printer: tips for beginners, where to start
Mastering the technique of 3D printing is not difficult if you follow the recommendations and tips. Especially for those who plan to learn the basics of 3D modeling, an up-to-date list of questions and detailed answers to them has been prepared.
Especially for those who plan to learn the basics of 3D modeling, an up-to-date list of questions and detailed answers to them has been prepared.
Printer Installation
To begin, you will need to carefully unpack the box and remove any stops. The next step is to install the printer on the surface using the building level. This will allow you to place the device as evenly as possible, which will provide better printing.
Note. Some 3D printers come with a level for installation.
Next, you will need to connect the printer to your computer and install the necessary drivers. The software disc comes with the 3D device.
Preparation for work
To get started, you need to calibrate the working surface - without this, printing quality products is impossible. This process is carried out automatically or manually. The attached instructions have detailed information on how to perform manual calibration.
Extruder patency test
The next important step is setting up the extruder. First of all, you will need to check its nozzle. If the printer has already been used, the nozzle should be cleaned of solidified particles that will interfere with the throughput of the material. Refueling the 3D printer The thread is fed into the extruder directly from the spool. But there is one caveat - for this you must first warm it up. To thread the thread, you will have to make a small effort in order to loosen the presser mechanism.
First of all, you will need to check its nozzle. If the printer has already been used, the nozzle should be cleaned of solidified particles that will interfere with the throughput of the material. Refueling the 3D printer The thread is fed into the extruder directly from the spool. But there is one caveat - for this you must first warm it up. To thread the thread, you will have to make a small effort in order to loosen the presser mechanism.
Working with models
Models can be created using a variety of 3D modeling programs. The process of manufacturing three-dimensional parts is creative, requiring careful preparation. The better and more detailed the model is drawn, the better the 3D layout will be at the output.
Start printing
After creating the model in the program and preparing the printer for work, you need to send the file for printing and wait for the result. The print speed varies depending on the printer model and specifications, as well as the media used.
Processing the finished product
3D printed products usually do not please the user with an ideal appearance: the parts have an uneven surface. But this is typical for models of 3D printers on FDM, SLA and DLP devices, which are distinguished by higher print quality. Owners of FDM printers should not despair - a simple processing of products will give products an attractive appearance and make the surface smooth.
Several powerful ways to post-process 3D printed parts:
- Mechanical - carried out by sanding the surface with sandpaper or a special sponge for grinding.
- Chemical - Surface treatment with aggressive solvents such as acetone and dichloroethane.
- Mixed - In this case, the above two processing methods are used.
What are the possible errors and how to avoid them?
Even a novice can master the technology of 3D printing, but, despite this, the production of the first products causes excitement for the user. Simple operation, detailed instructions and recommendations on the Internet will allow everyone to deal with almost any printer model. But there are a few useful life hacks, the knowledge of which will help you avoid typical beginner mistakes:
Simple operation, detailed instructions and recommendations on the Internet will allow everyone to deal with almost any printer model. But there are a few useful life hacks, the knowledge of which will help you avoid typical beginner mistakes:
- Calibrate and test the 3D printer before starting work.
- Be sure to use the correct file extension for quality printing.
- Do not remove the finished product from the printer immediately after it has been processed: this may damage the part and cause defects.
- If errors occur during the 3D printing process, try restarting the device - this usually helps.
- If restarting the printer still does not help, try changing the settings or re-entering the model.
- When assembling the 3D printing devices, follow the enclosed instructions carefully.
- Use only the correct materials for your 3D printer.
- Subscribe to useful 3D printing channels and articles.
Following the above tips will allow you to set up your 3D printer, get it ready for operation and, most importantly, print your first 3D products. Choose a model according to your budget and capabilities, and it will not be difficult to master the basics of 3D modeling and get the first details if you follow the instructions and recommendations.
Choose a model according to your budget and capabilities, and it will not be difficult to master the basics of 3D modeling and get the first details if you follow the instructions and recommendations.
- March 21, 2021
- 5816
Get expert advice
How a 3D printer works, what can be printed on a 3D printer
The 3D printer is a technology that allows you to create real objects from a digital model. It all started in the 80s under the name "rapid prototyping", which was the goal of the technology: to create a prototype faster and cheaper. A lot has changed since then, and today 3D printers allow you to create anything you can imagine.
Contents:
- What is 3D printing?
- How does a 3D printer work?
- What can be printed?
The 3D printer allows you to create objects that are almost identical to their virtual models. That is why the scope of these technologies is so wide.
That is why the scope of these technologies is so wide.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process because, unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, 3D printing does not remove material, but adds it, layer by layer - that is, builds or grows.
- In the first step of printing, the data from the drawing or 3D model is read by the printer.
- Next is the sequential overlay of layers.
- These layers, consisting of sheet material, liquid or powder, are combined with each other, turning into the final form.
With a limited number of parts, 3D printing will be faster and cheaper. The world of 3D printing does not stand still and therefore there are more and more different technologies competing with each other on the market. The difference lies in the printing process itself. Some technologies create layers by softening or melting the material, then they provide layer-by-layer application of this same material. Other technologies involve the use of liquid materials, which acquire a solid form in the process under the influence of various factors.
Other technologies involve the use of liquid materials, which acquire a solid form in the process under the influence of various factors.
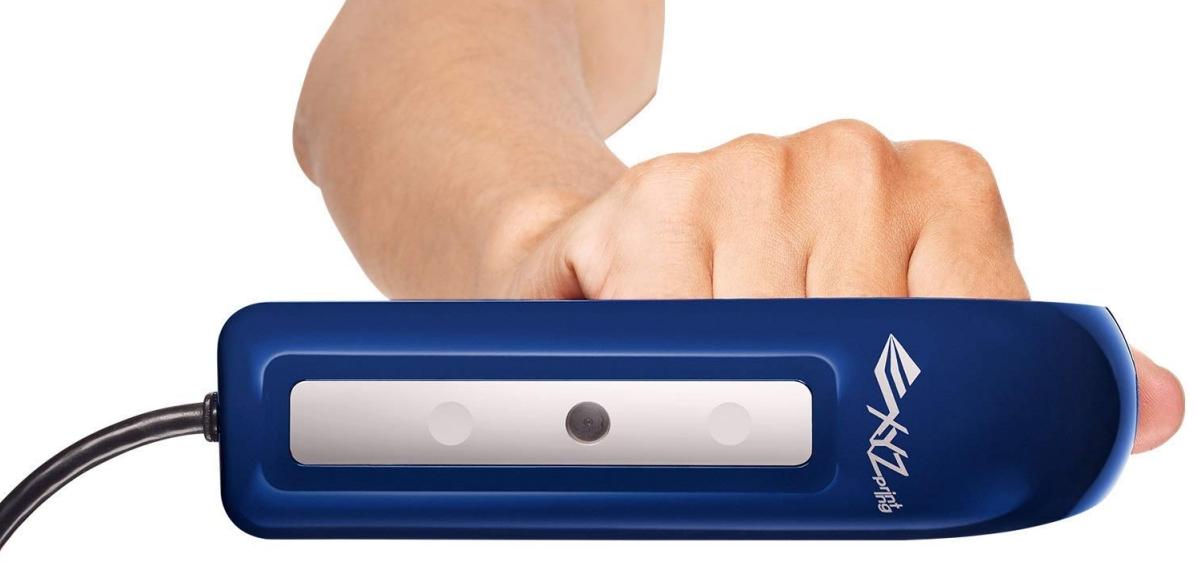
In order to print something , you first need a 3D model of the object, which you can create in a 3D modeling program (CAD - Computer Aided Design), or use a 3D scanner to scan the object you want print. There are also easier options, such as looking for models on the internet that have been created and made available to other people.
Once your design is ready, all you need to do is import it into the Slicer, a program that adapts the model into codes and instructions for a 3D printer, most of the programs are open source and free. The slicer will convert your project into a gcode file ready to be printed as a physical object. Simply save the file to the included SD card and insert it into your 3D printer and hit print.
The whole process can take several hours and sometimes several days. It all depends on the size, material and complexity of the model. Some 3D printers use two different materials. One of them is part of the model itself, the other acts as a prop that supports parts of the model hanging in the air. The second material is subsequently removed.
It all depends on the size, material and complexity of the model. Some 3D printers use two different materials. One of them is part of the model itself, the other acts as a prop that supports parts of the model hanging in the air. The second material is subsequently removed.
How does a 3D printer work?
Although there are several 3D printing technologies, most create an object by building up many successive thin layers of material. Typically desktop 3D printers use plastic filaments (1) which are fed into the printer by the feeder (2) . The filament melts into the print head (3) which extrudes the material onto the platform (4) creating the object layer by layer. Once the printer starts printing, all you have to do is wait - it's easy.
Of course, when you become an advanced user, playing with the settings and tweaking your printer can lead to even better results.
What can be 3D printed?
The possibilities of 3D printers are endless and they are now becoming a common tool in fields such as engineering, industrial design, manufacturing and architecture.