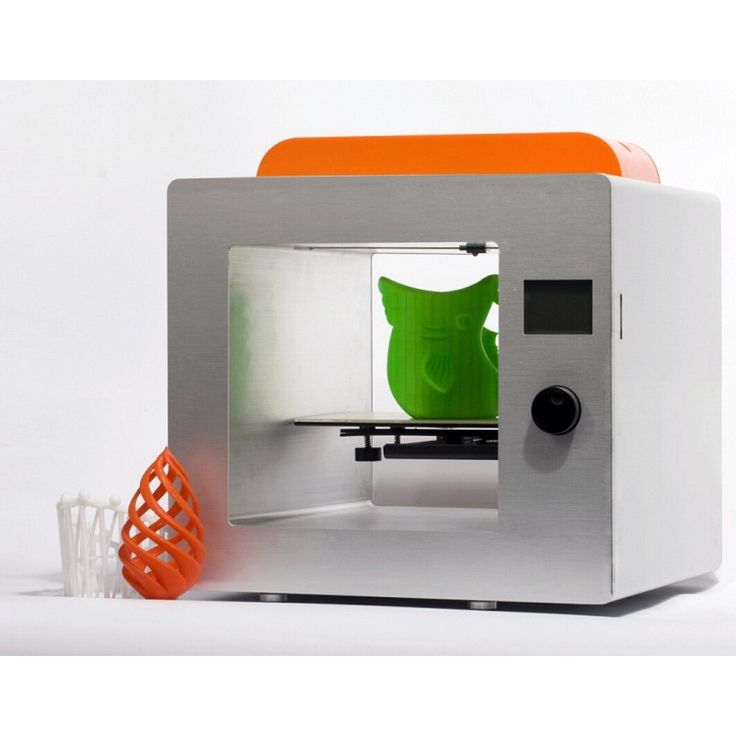
How small can 3d printers print
How Small Can a 3D Printer Print? – The 3D Bros
Printing small-scale 3D models with a 3D printer may be challenging because resolutions are not the same as the resolutions you use for two-dimensional pictures and for printing images on paper. Using your 3D printer in creating very small models or models with very fine features and details may involve a steep learning curve for new users. But as to how small your 3D printer can go, it depends mainly on its technology.
An FDM 3D printer can print 3D models as small as its nozzle diameter, which is at least 0.15 millimeters. Resin 3D printers like DLP and SLA can print much smaller details as it offers very fine Z resolutions. With resin printers, you can choose layer height options from 25 to 300 microns.
This article will discuss the differences in various types of 3D printers, especially in terms of their printing accuracy and their ability to print fine details. You will understand how their different 3D printing technologies and mechanisms affect the quality of their print output.
Most Common Types of 3D Printers
Different types of 3D printers use different printing technologies, processes, and materials, influencing their print accuracy and minimum feature size. The most common are:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printers, also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers
- Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers
- Digital light processing (DLP) 3D printers
FDM/FFF 3D Printers
FDM or FFF 3D printers extrude thermoplastic filaments like polylactic acid (PLA) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) through a heated nozzle, which melts the plastic and applies layer upon layer of the molten material to create a form. The FDM printing process is widely used at the consumer level.
One advantage of using FDM is that three-dimensional printing models are easy. Once you calibrate your printer and upload your CAD file, the printing process begins with just a push of a button. FDM printing is also a speedy process, and the technology can cost-effectively print objects in low quantities.
However, FDM 3D printing is not known for turning in long-lasting and durable products because each one is created in multiple layers instead of a single piece. There are bound to be weak spots in applying the layering technique. Additionally, FDM’s thermoplastics cannot withstand extreme conditions, so they would melt or deform when exposed to hot environments and crack when exposed to cold.
FDM 3D printing is also not able to produce models at a fine resolution. Because of the layering method, the output tends to have rough edges and surfaces and may require sanding and other finishing to smoothen them out. The tolerances are larger, too, which could lead to multiple prints of similar parts having inconsistencies and significant differences.
SLA 3D Printers
Dental technician removing jaw model from a 3d printer at the laboratory, modeling frame for implant productionAn SLA 3D printer is a resin 3D printer that produces high-accuracy, watertight, and airtight prototypes and models in advanced plastic materials. It is known to print 3D models with smooth surface finish, fine features, and highly detailed designs.
It is known to print 3D models with smooth surface finish, fine features, and highly detailed designs.
With a highly precise laser, an SLA 3D printer delivers light to form and cure thin layers of liquid resin that stack up to form one solid object. The process of curing resin into hardened plastic is called photopolymerization. SLA resin formulations boast a broad range of thermal, optical, and mechanical properties that make them ideal for industrial and engineering thermoplastics applications.
Using light instead of heat to print prototypes make SLA reliable. By printing three-dimensional parts at close to room temperature, you don’t have to worry about thermal expansion and contraction, which can be prevalent when printing via FDM.
These parts and prototype printing using the SLA process are also isotropic, which means that they have high lateral strength levels that don’t alter with orientation.
DLP 3D Printers
Like an SLA printer, a DLP 3D printer also uses resin. It creates parts and models upside down, layer by layer, as its build platform goes down into a resin tank. And while an SLA 3D printer uses a laser as its light source, a DLP 3D printer uses a digital projector screen. An image of a layer’s pattern or shape is flashed across the build platform, and this light cures the liquid resin.
It creates parts and models upside down, layer by layer, as its build platform goes down into a resin tank. And while an SLA 3D printer uses a laser as its light source, a DLP 3D printer uses a digital projector screen. An image of a layer’s pattern or shape is flashed across the build platform, and this light cures the liquid resin.
The light gets reflected onto microscopic-sized mirrors that are arranged on a semiconductor chip. This digital micromirror device (DMD), in turn, points the light to the bottom of the resin tank, defining the coordinates where the resin hardens in a particular layer.
DLP 3D printers are among the most precise and accurate 3D printers around, so they are great for highly detailed models. And like SLA printers, they create objects with a smooth surface finish.
How Small Can Your 3D Printer Print?
The different types of 3D printing technology have different minimum feature sizes.
How Small Can FDM 3D Printers Print?
FDM 3D printers can print features as small as the diameter of their printing nozzles. The most common nozzle size for these printers is 0.4 millimeters, so that means the smallest feature they can print is that same size, too. However, third-party nozzle upgrades are available. You can get a 0.15-millimeter nozzle and swap your printer’s old nozzle with it so you could print smaller features.
The most common nozzle size for these printers is 0.4 millimeters, so that means the smallest feature they can print is that same size, too. However, third-party nozzle upgrades are available. You can get a 0.15-millimeter nozzle and swap your printer’s old nozzle with it so you could print smaller features.
However, you have to keep in mind that how well a model or 3D figure turns out is also heavily influenced by its shape and the movements that the FDM printer needs to make to print it.
One major problem regarding printing small details with an FDM printer is that you have limited control over when the thermoplastic material starts to flow out from the nozzle and exactly when it stops. As such, an FDM printer will have an easier time creating fine details that are part of a larger object than creating a similar-sized detail on a much smaller object.
How Small Can SLA 3D Printers Print?
The minimum feature resolution for SLA 3D printers relies on the spot size of the laser beam. Because SLA technology does not involve thermal stresses like FDM, it is easier to print tall and thin shapes and very small features.
Because SLA technology does not involve thermal stresses like FDM, it is easier to print tall and thin shapes and very small features.
In 3D printing, you will need to get acquainted with the three dimensions: the X and Y dimensions, the two-dimensional planes, and the vertical Z dimension. The Z resolution is the thickness or height of a layer that the printer can produce.
The laser spot size of the SLA printer determines the XY resolution. The increments by which the laser beam is controlled also affects the XY resolution. As for the Z resolution, resin printers offer a layer height of between 25 to 300 microns.
How Small Can DLP 3D Printers Print?
Just like SLA printers, DLP printers offer a fine resolution. You can also pick a layer height option or Z resolution of anything between 25 and 300 microns. Meanwhile, the XY resolution is defined by pixel, which is the tiniest feature that the projector can print within a particular layer.
However, with DLP printers, there is a trade-off between build volume and resolution. The projector dictates the number of voxels or pixels available. The closer the projector is moved to the optical window, the smaller the pixels get, which increases the resolution of your print. As a result, the available build area also gets limited.
The projector dictates the number of voxels or pixels available. The closer the projector is moved to the optical window, the smaller the pixels get, which increases the resolution of your print. As a result, the available build area also gets limited.
Calibration also plays a crucial role. Unlike SLA printers with the same light source throughout, with DLP projectors, you will need to factor in the non-uniform distribution of light on the build platform and lenses’ optical distortion. This means that the pixels right in the middle of the print object are not of the same shape and size as the pixels on its edges.
Final Thoughts
Generally, SLA and DLP printers can print much smaller features and details than FDM printers. More importantly, SLA and DLP are known for more accurate, precise, and more durable prints of industrial and engineering quality. But that is not to say that FDM technology doesn’t have its own strengths. That is why thorough research needs to be done on the pros and cons of each of these types of 3D printers to know which one suits your specific printing requirements.
Sources
- MH Manufacturing: Benefits and Disadvantages to 3D Printing in Manufacturing
- Pinshape Blog: 4 Things You Need to Know About 3D Printing Resolution
- Quora: How small of an object can a 3D printer print?
- All3DP: How Small Can You Go?
- All3DP: SLA vs. DLP: The Differences – Simply Explained
- Dummies: How to Print Tiny or Highly Detailed 3D Objects
- 3D Printing: How small can I expect FDM 3d printers to print?
- Formlabs: FDM vs. SLA: Compare the Two Most Popular Types of 3D Printers
- Formlabs: SLA vs. DLP: Guide to Resin 3D Printers
- Xometry: What is the smallest feature that you can print?
- Make Parts Fast: What is a DLP 3D Printer?
How Small Of An Item Can A 3D Printer Make? – 3dprintscape.com
One of the most amazing things about 3D printers is that they are capable of creating things out of what seems to be nothing. This means that what they do is that they create different objects using a bottom-up approach by putting together different small particles. But how small of an item can a 3D printer actually print?
But how small of an item can a 3D printer actually print?
In most cases, 3D printers can print as small as their nozzles allow them to do so. Some 3D printers can print at least 0.15 millimeters. However, it usually really all depends on the manufacturing specifications of the 3D printer and the type of 3D printer we are talking about here.
3D printers come in all shapes and sizes, and that means that there are also different types of 3D printers. In that case, the smallest thing that 3D printers can print will mostly depend on how small the 3D printer’s nozzles or manufacturing capabilities are. And there are also cases where it can depend on the type of 3D printer that you have.
What are the different types of 3D printers?
3D printers are amazing in the sense that they use a bottom-up approach when it comes to creating different designs. What they do is that they put together smaller particles that form one bigger structure. However, what you should know is that different 3D printers work differently. So, if we are to talk about how small of an item a 3D printer can print, it is equally important to talk about the different types of 3D printers.
So, if we are to talk about how small of an item a 3D printer can print, it is equally important to talk about the different types of 3D printers.
FDM/FFF 3D Printers
Some of the most common types of 3D printers are FDM/FFF 3D printers. What these 3D printers do is that they extrude thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle so that the plastic material melts. In a sense, what happens is that these 3D printers put together small particles of heated plastic to create the form you want at the end of the 3D print job. This is the most common type of 3D printer in consumer markets.
The best part about FDM/FFF type of 3D printers is that they are very easy to use when creating three-dimensional printing models as you simply need to calibrate the machine and then upload your CAD file. From there, the printing process can be done with a simple push of a button. It’s that easy and speedy.
But the problem with these 3D printers is that they are not known for creating products that are quite durable because you need to know that what they do is that they put together several layers of plastic instead of printing one single piece. That means that there are going to be a few weak spots on the final product. Of course, you also need to consider that thermoplastics aren’t exactly the best when it comes to extreme conditions as they can easily melt or deform when exposed to heat or crack when exposed to cold.
That means that there are going to be a few weak spots on the final product. Of course, you also need to consider that thermoplastics aren’t exactly the best when it comes to extreme conditions as they can easily melt or deform when exposed to heat or crack when exposed to cold.
And, in connection to our topic, FDM 3D printers are unable to produce models at the smallest scale possible. That is because, as mentioned, they rely on a method of layering plastics together. That means that it might be difficult to produce a really small product using an FDM printer.
SLA 3D Printers
SLA 3D printers are resin 3D printers that use a method that is quite different from what FDM printers do. What these 3D printers do is that they produce high-accuracy and water and airtight 3D models using plastic materials. In most cases, they are more accurate than FDM 3D printers as they are capable of producing models with fine features and accurate details.
Using a precise laser, SLA printers are capable of creating accurate models as they deliver light to form and cure layers of resin. What happens is that these thin layers of resin stack up to one another to form one solid object.
What happens is that these thin layers of resin stack up to one another to form one solid object.
So, the difference here is that these 3D printers use light instead of heat to print 3D models. This is why SLA 3D printers are widely used in a lot of industries that require their pinpoint accuracy and detailed printing. And you don’t even have to worry about the resin warping or cracking because of how heat isn’t in the equation here.
DLP 3D Printers
DLP 3D printers are like SLA printers in the sense that they also use resin. What they do is that they create parts and models layer by layer from top to bottom. But the difference here is that DLP 3D printers use a digital projector screen instead of using laser as their light source. The image of the model’s shape or pattern is flashed, and this is the light that cures the liquid resin to form the 3D model.
What happens is that the light gets reflected onto very small mirrors that are microscopic in size. These mirrors are arranged on a semiconductor chip and will point the light to the bottom of the resin tank while defining the coordinates where the resin should harden to form the layers of the 3D model.
Because of the way DLP 3D printers work, they are considered some of the most precise and accurate 3D printers. They are so accurate that they are capable of printing fine details and even smaller objects that other types of 3D printers cannot print.
How small of an item can a 3D printer make?
Now that you know the different types of 3D printers, let us now look at how small of an item these 3D printers can make. And it is important to know how these 3D printers work because you need to understand that different methods of 3D printing can make big differences in how small of an item they can print.
FLM 3D printers, for the most part, are highly dependent on their nozzles in the sense that they can print as small as what the nozzles allow them to do so. In most cases, these 3D printers have nozzle sizes that are 0.4 millimeters, but it isn’t rare for some nozzles to be as small as 0.15 millimeters. You can even get a 0.15-millimeter and then swap out your old one for the newer and smaller nozzle so that you can 3D print smaller and more accurate features.
But the problem here is that, because FDM 3D printers rely on thermoplastic, you don’t have any control as to how the plastic flows out from the nozzle. This means that it would be very difficult to 3D print something that is as small as 0.4 millimeters.
Meanwhile, for SLA 3D printers, the size of the item will depend on the spot size of the laser beam. So, when the spot size is quite small, it would be easier for you to 3D print a model that is quite small. It will also be easier to print tall and thin shapes with amazingly accurate features using SLA 3D printers.
When dealing with SLA 3D printers, you need to know the X, Y, and Z dimensions. The laser spot size of the SLA printer is what determines the XY resolution of the 3D printer. Then, for the Z resolution, these printers can offer heights between 25 to 300 microns, and that means that you can 3D print smaller and finer models.
Finally, DLP printers are similar to SLA printers in the sense that they are capable of producing materials with amazing resolution and detail. The size of the 3D print will once again rely on the XYZ resolutions, but the difference here is that the XY resolution is defined by pixels, which are tiny spots that you can see on the projector.
The size of the 3D print will once again rely on the XYZ resolutions, but the difference here is that the XY resolution is defined by pixels, which are tiny spots that you can see on the projector.
So, in a way, both SLA and DLP 3D printers rely mainly on how the machines are calibrated and on the manufacturing settings of these printers. And the consensus is that SLA and DLP 3D printers are much more capable than commercialized FDM printers when producing smaller materials.
Related Articles
- What Is the Size Limitation of 3D Printing?
- Best 3D Printing Infill Pattern – Complete Details Inside!
- Why Is 3d Printing Slow?
- Do 3D Printers Use a Lot of Power? (The Numbers Inside)
- Create a Temperature Tower Using Cura – The Easy Way
- 3D Printing Blobs and Zits: Tips to Avoid Them
Make sure you check out our YouTube channel, and if you would like any additional details or have any questions, please leave a comment below. If you liked this article and want to read others click here.
If you liked this article and want to read others click here.
Is it possible to print 10 times faster on a 3D printer? Tips for increasing the speed of your 3D printer
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Is it possible to print 10 times faster on a 3D printer? Tips for Increasing 3D Printer Speed
From time to time, all 3D printing enthusiasts think about increasing the speed of a 3D printer and creating figures and models in a matter of hours, not days. Wouldn't it be great if you could 3D print 10 times faster than you can now? This article provides tips on how to increase the speed of your 3D printer without losing quality.
Before we take a closer look at the secrets that will help you print faster and share ideas for fast 3D printing, it's worth a little imagination about the incredible future. Maybe one day you will buy an affordable and fast device that turns STL files into detailed figures and models from your favorite video games and movies in just a couple of hours or even faster... And this one will really happen. But! Now let's put aside the fantasies and return to the current reality. The reality is that the following tips will actually help you speed up your 3D printing, so let's get started.
Maybe one day you will buy an affordable and fast device that turns STL files into detailed figures and models from your favorite video games and movies in just a couple of hours or even faster... And this one will really happen. But! Now let's put aside the fantasies and return to the current reality. The reality is that the following tips will actually help you speed up your 3D printing, so let's get started.
There are great guys - John Hart and Jamison Goh from MIT - the real geniuses of modernizing technology. According to MIT news, these two professors, along with their colleagues, have been working to increase the speed of a 3D printer and have developed an innovative model called Fast FFF.
The name Fast FFF stands for "Production of Fast Fibers". This model is capable of stacking material 10 times faster than any existing desktop 3D printer. In addition, the print head with fantastic 3D printing speed can work with renewable materials.
As the engineers noted, in order to increase the speed of 3D printing, three main factors had to be taken into account:
- The force applied by the print head when pushing the 3D printing material through the nozzle;
- The time required to heat up the material so that it melts and can flow through the nozzle;
- Print head movement speed.
All these things have been improved in the Fast FFF prototype. As a result, it was possible to 3D print two simple eyeglass frames in less than 4 minutes and a complex bevel gear in about 10 minutes. These models were printed with a 0.2mm layer and proved to be strong and durable.
Fast FFF prototype 3D printer cost about $15,000. This is a good price compared to expensive commercial 3D printers that cost over $100,000 and are about three times slower. But if you compare the price with an affordable home 3D printer under $300 or $500, the Fast FFF is clearly too expensive, even though it can 3D print 10 times faster than a regular FDM 3D printer. And it's currently unclear if an affordable ultra-fast 3D printer for home use will hit the market...
While you can't get your home 3D printer to 3D print 10 times faster than it is now, or beat the innovative Fast FFF machine, there are secrets :).
Most of the tips that can help improve your 3D printing speed can also affect the quality of your figurine or model.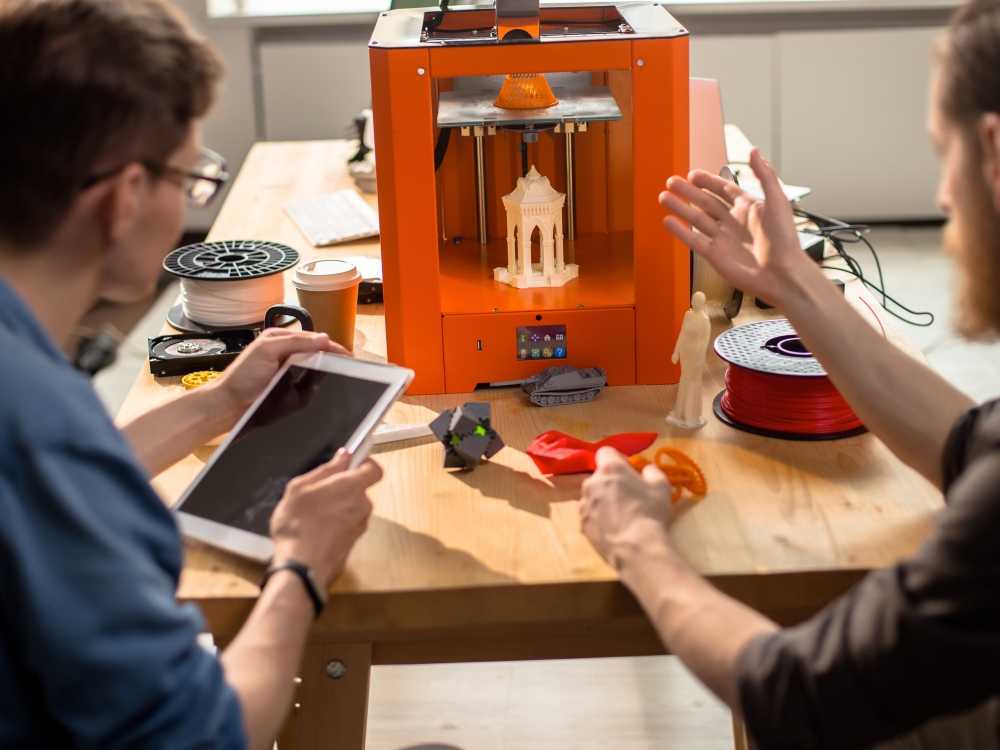 However, sometimes it's worth it.
However, sometimes it's worth it.
Adjust 3D print speed
Settings is the first thing you can try if you want to increase your 3D print speed. Every hobbyist likes to work with certain slicing software. It is worth exploring all the possibilities and changing the settings to suit your needs.
The ability to control the speed of the print head is amazing. Sometimes this does not negatively affect the quality of a complex 3D printed model. And when you do something simple, you can significantly increase the speed without losing quality.
Replace nozzle
Sometimes you don't care about 3D printing accuracy. In this case, a larger nozzle may suffice. For example, you can change the nozzle on your 3D printer from 0.4mm to 0.8mm. Or you can choose even 1.0mm print head.
Much depends on your current nozzle size. Standard printheads are 0.2mm and 0.4mm. But choosing a larger size can save time and speed up 3D printing.
Increase layer height
If you increase the speed of the 3D printer by changing the nozzle to a larger diameter, you will also have to increase the layer height of the 3D print. The maximum height you can select is approximately 75% of the current nozzle diameter.
The maximum height you can select is approximately 75% of the current nozzle diameter.
So if you change the nozzle from 0.4 mm to 0.8 mm, you can increase the layer height to 0.6 mm. These settings will affect the quality of your 3D model and cause you to lose a lot of impressive detail because the layers will be thinner and the speed will be much faster. Keep this in mind when experimenting with nozzle size and layer height.
Reduce wall thickness of 3D models
100% infill models and figurines take longer to print, but are durable when finished. You've probably guessed how to make 3D print faster by playing with wall thickness and reducing infill. But in this case, you need to be careful, because the thin walls of the 3D model and less infill can lead to poor quality 3D printing.
If you have a resin based 3D printer, you can save resin and increase 3D printing speed by working with the appropriate DLP/SLA Eco version of STL files offered by Gambody - Premium 3D Printing. The Eco version ensures that your walls are thick enough to make your 3D model strong, detailed and of the highest quality.
The Eco version ensures that your walls are thick enough to make your 3D model strong, detailed and of the highest quality.
Print two 3D models at the same time
Another way to speed up your 3D printer without sacrificing product quality is to work on two projects at the same time. This is only possible if both models or figurines are small and can fit on the same 3D printer table without interfering with each other.
This option can be set in the slicing software. Select centering and place both models for 3D printing on the work surface. The main disadvantage of this method is that both models will be printed from the same material, but the final print speed will be significantly increased.
Do not use supports
When a large amount of support material is needed to 3D print a complex model, printing time will increase. This way, whether you choose to do projects with fewer supports or learn how to 3D print without supports, you can speed up and print the prototypes and figures you need faster.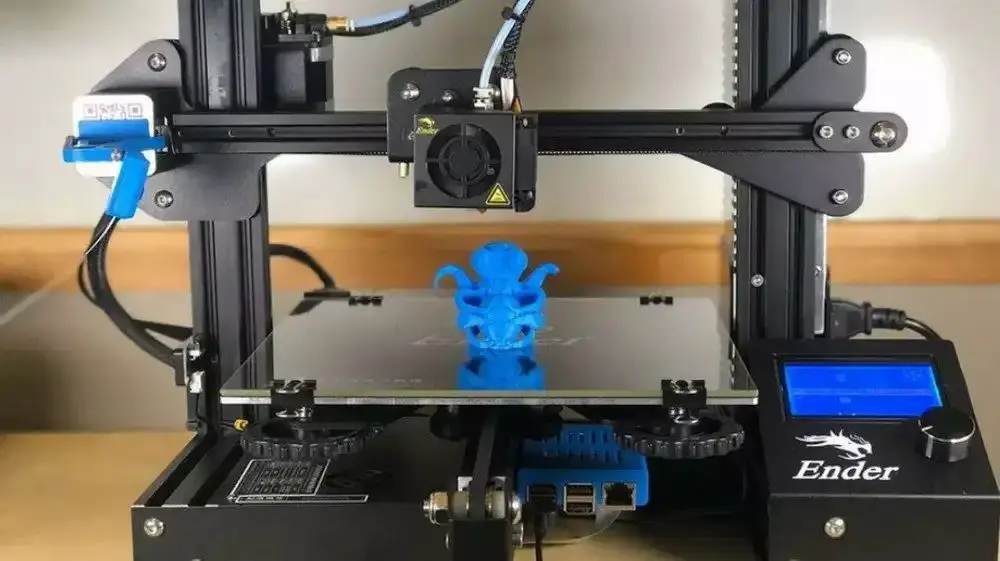
Change the infill pattern of a 3D model
If you don't want to adjust the infill density, but still want to improve 3D printing speed, try adjusting the infill pattern in the slicer settings. People work with different patterns, but the most popular version for speed optimization is "lines" or "straight lines".
Filling in a line pattern is very simple. Your 3D printer will make fewer moves when creating a straight infill figurine and can reduce print time by up to 20%-25%. But the models will not be as durable as those with a triangular or mesh pattern.
Adjust the jerk and acceleration settings
After making changes to the slicing software in the hope of increasing the speed of 3D printing, you can also try changing the jerk settings. They are responsible for how fast the print head can move. Of course, the print head must move smoothly, because increasing the speed can negatively affect the quality of the 3D print and even lead to problems with the mechanical part of the 3D printer.
There are also acceleration settings that need to be adjusted. They control the speed at which the print head reaches its maximum speed. It's worth playing around with these settings to find a balance between the jerk and acceleration settings to slightly increase print speed without affecting the quality of the 3D model or 3D printer.
For example, if you work with the jerk setting at 10 (low) and select a speed of 60mm/sec, you won't save much time in 3D printing, but the print quality will be ok. Increasing speed to 120mm/s and jerk to 40 will cut 3D printing time by 25%! However, the quality of the printed 3D model will also be greatly reduced.
Replace 3D printer
If you are not satisfied with your current 3D print speed capabilities, you can always look for another 3D printer with higher speed. However, such a device can be expensive. Most printers designed for home use are not as fast as industrial 3D printers.
For example, the cheapest FDM printers can cost as little as $300 or even $200, and they typically print at 60mm/sec. They will never reach the speed of industrial equipment such as the Massivit 1800 which can reach speeds of 1000mm/s.
They will never reach the speed of industrial equipment such as the Massivit 1800 which can reach speeds of 1000mm/s.
Select objects for 3D printing quickly
Another way to increase the speed of 3D printing is to search for new ideas for 3D printing as quickly as possible. It is ideal for beginners who want to learn on the go and improve their skills as they progress from simple models to more complex figures.
How a 3D Printer Works and What It's Used for - Code Magazine
There has been a lot of news over the past couple of years that someone has printed something with a 3D printer:
- hearing aid,
- milk products,
- residential building,
- robo-finger,
- brain implants,
- 1mm statue of David,
- prefabricated electronic devices.
Let's see how this technology works, what its limitations are and whether it has a future.
Why you need a 3D printer
3D printers print three-dimensional things from plastic or other materials. They can be used at home or in production. For example, here is what you can print on a 3D printer:
They can be used at home or in production. For example, here is what you can print on a 3D printer:
How it works
Usually a 3D printer uses special plastic to print. It comes in the form of powder, liquid resin or plastic wire in coils. It is from this material that the printed part will consist.
Further, roughly speaking, the process looks like this:
- this plastic is either applied using a moving nozzle;
- or "baked" with a laser;
- or the excess is cut out from the array of the finished material using a movable cutter (but this is more like turning and is often not attributed to 3D printing).
Material takes the shape you want, layer by layer. When all layers are passed, the detail turns out.
Fast 3D printing with moving nozzle:
Due to the fact that the printer needs to constantly heat the plastic, 3D printers do not print very quickly: a part the size of a phone can take 15-20 minutes. The speed also depends on the thickness of the layer: the thicker the layer, the faster the print. But with a large layer thickness, the part may turn out to be sloppy: layers will be visible:
The speed also depends on the thickness of the layer: the thicker the layer, the faster the print. But with a large layer thickness, the part may turn out to be sloppy: layers will be visible:
Printing technologies
3D printing is very important in industry and industrial design, so there is a whole zoo of printing technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Stereolithography . Instead of plastic, a special resin is used here, which hardens in the light. The detail is also formed in layers, but the layers themselves are almost invisible - the resin fills the relief and the detail seems to be a single whole even from a very close distance.
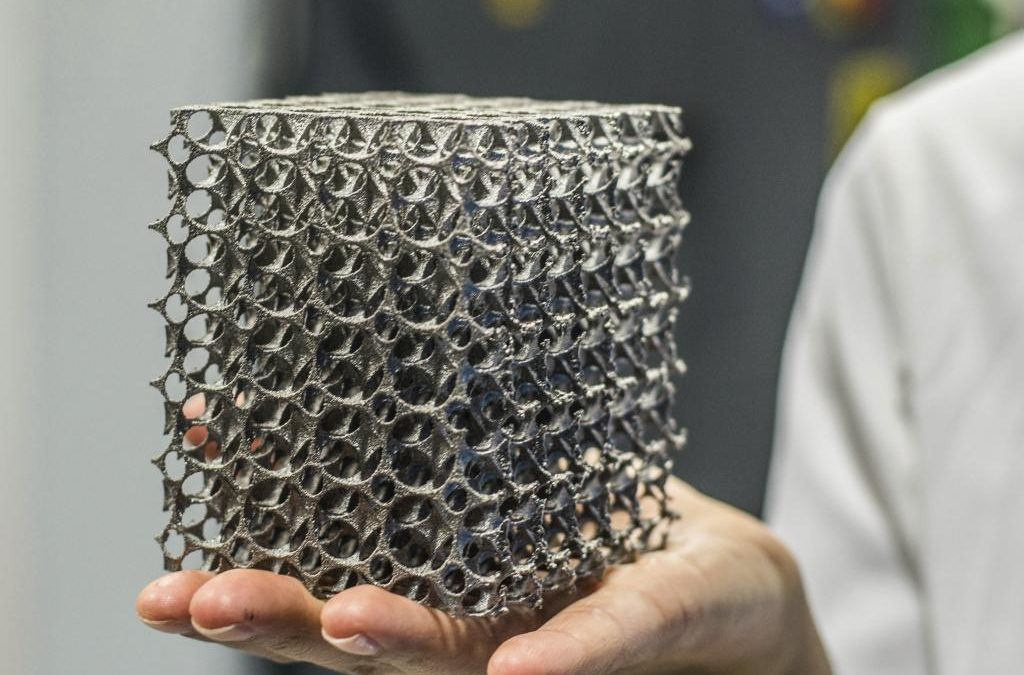
Polymer synthesis (SLS) . This type of printing uses powder, which is then baked with a laser beam. Since the laser beam can be focused anywhere with the desired accuracy, very complex models with high detail can be obtained in this way of printing:
Polyjet. The peculiarity of this technology is that it can print objects simultaneously from different materials. This allows you to create almost any thing of the most complex shape, which immediately have the desired properties. On such a printer, you can even print sneakers that you can wear:
The peculiarity of this technology is that it can print objects simultaneously from different materials. This allows you to create almost any thing of the most complex shape, which immediately have the desired properties. On such a printer, you can even print sneakers that you can wear:
What can be printed
Anything can be printed on a 3D printer, as long as you have the right media, a finished model, and a large enough printer.
Prototypes. Often, before starting production, a company needs to understand how comfortable a thing will turn out to be in use. In order not to launch a line for the sake of one product, it is printed on a 3D printer and they look at what needs to be changed or finalized. On such prototypes, you can see, for example, that the buttons turned out to be too small and it would be inconvenient to press them, or that the buttons turned out to be very far from the fingers and you will need to reach them specially.
Parts and parts. Sometimes it is difficult or almost impossible to find a spare part for a tool: the manufacturer does not produce them or the model has been out of production for a long time. In this case, you can find a three-dimensional model of the desired part on the Internet or draw it yourself in the editor, so that you can then send it to print.
Medicine. Three-dimensional printing is actively used in medicine to create new joints, tissues and treat patients. The difference from traditional printing is that instead of plastic, they print with special “living” solutions that interact with each other and behave like real organs and tissues. Thanks to this technology, it is now easy to print a joint that a surgeon can put on a person instead of a damaged one.
Hobbies and modeling. It is easy to print various miniatures, collectible figures and models on a 3D printer.
Manufacture of other robots. 3D printers do not yet know how to produce servos and microprocessors, but they already know how to print bodies and frames of robots.
3D printers do not yet know how to produce servos and microprocessors, but they already know how to print bodies and frames of robots.
Houses and buildings. We take hefty rails with motors and controllers. We install a movable nozzle, on which you can supply a building mixture (concrete or polymers). You can print the walls of buildings. Unlike traditional brick, panel and block construction technologies, the shape of the walls and the building as a whole can be any. The foundation, floors and roof are not yet printed, but this is for now.
Imagine: we send fifty 3D printers on a mobile basis to Mars. For a year, each of them prints another 100 printers. Then all these 5,000 printers disperse around Mars and begin to build the first colony. While they are building, we order furniture from Ikea, arrange delivery, and just in time for delivery, our robots will finish printing everything. Apple trees on Mars are unlikely to bloom, but five-story buildings can.
While they are building, we order furniture from Ikea, arrange delivery, and just in time for delivery, our robots will finish printing everything. Apple trees on Mars are unlikely to bloom, but five-story buildings can.
Criticisms and issues
❌ Slow and no guarantees: printing is quite slow, not accurate enough. A huge problem in amateur printers is marriage. For example, a part can peel off the substrate right during printing, and hell will happen. Or the motors will decalibrate, and the nozzle will begin to miss the right places.
❌ Low efficiency: to print a 10 x 10 cm part, you need a printer that is at least 50 x 50 cm, which will cost several hundred dollars.
❌ Not the strongest materials: 3D printing is currently limited to plastics and resins. There are separate printing technologies based on metal powder, but if you need a steel part, you don’t need a 3D printer, but a normal turner and machine tool. But not every detail can be made on the machine.