How much does it cost to 3d print at staples
3D Printing in 3 Steps (Yes, Only 3!)
3D Printing in 3 Steps (Yes, Only 3!) | Staples.comby Kevin Ackerman, Staples® Contributing Writer
Since it gives computer users the ability to produce tangible objects in a variety of materials and colors right from their desktop, 3D printing seems as if it would be technically complicated (or just magical). But in reality, it’s not all that different from printing in two dimensions on paper.
To produce a printed page, all computer users need is a document, a computer and access to a printer — and, of course, ink and paper. Likewise, printing in 3D only requires three similar things. Sure, the technologies differ, but that’s the basic gist, as these three steps explain.
Step 1: Develop a Concept
If you were to open a document file on your computer, hit some random keys on your keyboard and press Print, you’d have a paper printout — though it wouldn’t make much sense. With 3D printing, you can’t make a shape that easily, not even a poor one, so it’s worth beginning the process by putting some thought into your object.
Start by knowing what you’d like to print in three dimensions. If you don’t have an idea or concept, there are plenty of free suggestions online to get you started. Web sites like Thingiverse.com offer a library of pre-designed objects that you can print with any 3D printer to gain experience. Or you can be inspired by people who are already using 3D printing technology.
Phoenix-based sculptor Kevin Caron uses 3D printing to refine his artwork before making full-sized versions. "Mostly what I'm doing is proof of concept designs. You know, will it stand up, does it look right and are the proportions correct on it?” he says.
And Chris Considine, CEO and founder of Los Angeles–based CXC Simulations, uses 3D printing to prototype custom-designed parts for racing simulators that are so realistic, they are used by professional race car drivers. "We need 3D orienting to see if the part feels exactly how we want it to feel,” he says.” We went through about 30 versions before we found the one that was perfect for us. Other than 3D printing, there’s truly no way you could have done that without building it over and over again."
"We need 3D orienting to see if the part feels exactly how we want it to feel,” he says.” We went through about 30 versions before we found the one that was perfect for us. Other than 3D printing, there’s truly no way you could have done that without building it over and over again."
Step 2: Hop on a Computer
Once you know what you want to produce, it’s time to sit down at a computer and make it happen. 3D prints are most commonly generated from an STL or .stl file. Standing for “stereolithography” (what 3D printing was named when it was first invented), this file format is to 3D printing what the .doc file is to document output.
To open and manipulate an STL file, you’ll need computer-aided design (CAD) software. For decades, these programs have been used by everyone from architects to product designers, so there are many kinds of CAD software available.
SketchUp is a free modeling program designed to be straightforward and allow anyone to create three-dimensional renderings, whether simple or complicated. Likewise, Tinkercad keeps the design process easy by providing just three simple tools. It also runs in a Web browser and offers step-by-step design lessons to demonstrate how easy 3D printing can be.
Likewise, Tinkercad keeps the design process easy by providing just three simple tools. It also runs in a Web browser and offers step-by-step design lessons to demonstrate how easy 3D printing can be.
Meanwhile, programs like AutoCAD are favored by many experienced professionals, having been used in the design and prototyping of millions of products throughout the years.
To run these programs, you don’t need a particularly powerful computer. Caron uses an HP desktop machine to create his digital sculptures. "It's not a big screaming gaming computer by any means,” he says. "It's just a small office computer and it handles the CAD program just fine.”
Step 3: Get Access to a 3D Printer
Most people assume they need to own a 3D printer to produce digitally rendered objects, but that isn’t true. Sure, owning a desktop 3D printer can put your designs within arm’s reach. But driving across town to pick up your objects at a Staples 3D printing service location or having them delivered by mail can be just as convenient for some businesses.
For example, Caron owns a CubeX™ commercial 3D printer. With the ability to print objects up to the size of a basketball, this device produces designs in plastic and in more than 4,000 different colors. He’s also used print-on-demand services to produce sculptures that he couldn’t make on his office’s machine.
"They’re breathtaking when you see them,” he says of the two acrylic sculptures. "The detail that I could view on the computer came out in the print — it just blew me away.” Caron is planning to scale his designs down and turn them into jewelry to sell. "I've gotten one back in a polished glass and it's stunning. You can’t tell it from gold other than by the weight."
If you are interested in using 3D printing but need help with these steps, visit one of our stores that offers 3D printing services (currently in Los Angeles and New York City). There, we can help you with all the steps, from getting in touch with designers to actual 3D printing. You can even get in our 3D printing photo booth and have your face put on a figurine.
You can even get in our 3D printing photo booth and have your face put on a figurine.
Go from Concept to Reality
Some businesses would argue that 3D printing, whether it’s done in the office or at an outside service, is worth its weight in gold. "I can go from concept in my head to holding the part in sometimes as quickly as an hour,” says Considine. "It’s a very powerful thing for an engineer to have. It's liberating."
Related Articles
7 Things You Didn't Know About 3D Printing
In the ever-expanding universe of 3D printing, no one knows it all. Though the technology has been around since the 1980s, it’s only recently... Read more
8 Tips from MakerBot for Making Better 3D-Printed Objects for Your Small Business
Both an art and a science, 3D printing is actually easy to do, but difficult to master. The experts at MakerBot have seen... Read more
The experts at MakerBot have seen... Read more
Carrie Mae Rose
Does mankind’s destiny lie in the stars? Artist Carrie Mae Rose thinks so. Her show... Read more
How Much Does 3d Printing Cost At Staples
3D printing technology has come a long way in recent years, and it is now possible to purchase a wide variety of 3D printers for both personal and commercial use. One of the most popular brands of 3D printers is Staples, and many people are wondering how much it will cost to print with one of their machines. The cost of 3D printing at Staples will vary depending on the specific printer that you choose and the size of the object that you want to print. However, you can expect to pay between $50 and $200 for most 3D printing projects at Staples.
For a fee, customers can print an unlimited number of items. For smaller, simpler items, prices will range from a few dollars to thousands of dollars. For the second time in Europe, the Staples brand will provide 3D printing services.
For smaller, simpler items, prices will range from a few dollars to thousands of dollars. For the second time in Europe, the Staples brand will provide 3D printing services.
How Much Is It To Get An Item 3d Printed?
3D printing is a process of making a three-dimensional solid object of almost any shape from a digital model. 3D printing is achieved using an additive process, where successive layers of material are laid down in different shapes.
The cost of 3D printing depends on a few factors, such as the price of the printer, the cost of the filaments, and the time it takes to print the object. Generally, the cost of 3D printing an object is between $0.10 and $0.30 per hour of printing.
The price of 3D printing is influenced by a number of factors. It includes the time spent printing, the type of material used, and how the work is completed. The shape of a part’s layers is primarily determined by its geometry. It is also common for tall parts to take a long time to build because they require more layers of construction. Materials can be classified in four types based on their properties: thermoplastics, photoplastics, polymers, and metals. The 3D printer’s resolution is primarily determined by the layer height it employs, which can be adjusted to achieve a finer resolution. thermoplastic filament costs between $6.50 and $7.50 per cubic inch on average.
Materials can be classified in four types based on their properties: thermoplastics, photoplastics, polymers, and metals. The 3D printer’s resolution is primarily determined by the layer height it employs, which can be adjusted to achieve a finer resolution. thermoplastic filament costs between $6.50 and $7.50 per cubic inch on average.
Thermoset photopolymers, which are liquid resin thermosets, must be cured with UV light. Metals, like polymers, are powdered and melt together using a laser during 3D printing. Labor will be required to complete additional steps such as priming, dyeing, painting, and coating.
For commercial printing, you must consider the cost of the 3D printer, the materials, and the labor costs. The cost of 3D printing services may be higher than for an entry-level 3D printer, but they also provide more control, flexibility, and speed. You can get a 3D printer that works for you no matter how small or large your budget. It is critical to remember that the price of a 3D printer will vary depending on the model, the material used, and the complexity of the project.
How Much Does It Cost To 3d Print Per Inch?
Credit: VentureBeat
The average price for thermoplastic filament ranges from $3.50 to $7.50 per cubic inch. Because of the need for support material in FDM printers, filament for a FDM printer will be around the same price as model filament.
Many people wonder about the cost of 3D printing an object, whether that be a miniature figure or a large object like a helmet or mask. Let’s take a closer look at the costs of 3D printing as a general starting point. Because materials are relatively inexpensive, there is no fluctuation in costs. A filament 3D printer is an excellent choice with the Artillery Sidewinder X1 V4. When it comes to 3D printing, filament and resin are the two most common materials. Filament is usually packaged in plastic tubes that have round ends. This resin is packaged in a dark bottle with UV protection and contains resin as well as resin in the form of a liquid.
filament will cost between $20 and $30 per kg if you purchase a standard spool. The Elegoo Rapid Resin and Anycubic UV Curing Resin are two of the most popular resin brands. When it comes to premium resins, you can expect more strength and durability. These include both high-quality mechanical resins and high-quality dental resins. There are costs associated with other devices after purchasing a 3D printer and filament. It is no secret that Elmer’s disappearing glue is the best glue for 3D printing. This sandpaper is made of silicon carbide and offers the benefits of wet and dry sanding.
This water-based primer is ideal for use on wood, laminate, PVC, railings, galvanized steel, and thermoplastics. Using acryllic paints and paint brushes is the most effective way to color your printed models. It is ideal for use in high-temperature environments due to its high friction coefficient. The Rustark 42-piece 3D Print Tool Kit includes a variety of 3D printer parts, including pliers and flush cutters. The 3-in-One Multipurpose PTFE Lubricant is an excellent choice for 3D printer lubrication. After a few years, it is common practice to replace FDM printer parts. filament, which costs around $25 per KG for plastic, is the most expensive component of 3D printing.
The 3-in-One Multipurpose PTFE Lubricant is an excellent choice for 3D printer lubrication. After a few years, it is common practice to replace FDM printer parts. filament, which costs around $25 per KG for plastic, is the most expensive component of 3D printing.
It is advantageous to maintain your 3D printer on a regular basis in order to lower your overall costs because you will not have to replace parts so frequently. Errors in bed leveling, slicer settings, or filament tangled around the bed are all likely to lead to failures among beginners. For a list of some common objects that people 3D print, the average cost per KG is $25. How Much Does It Cost To 3D Print a Miniature? A standard tabletop miniature costs around $0.12 and uses 5 g filament rather than 28mm scales like the Elf Ranger. To adjust the price, you may need to use more or less filament for some miniatures. A full-sized Stormtrooper helmet has 1.5 grams of filament, which equates to around $37.50 on average.
XEV started producing a $7,500 electric car in 2019, which weighs 450 kilograms. Bioprinters are said to be able to 3D print organoids for as little as $10,000. PLA filament will cost you $0.98 per piece when used in conjunction with a full Nintendo Headrest Prototype measuring 94.7 x 86.9 x 121.9mm. A 3D printed shoe made from 114g of filament would use about $2.85 to make. The CR-10 filament is approximately 20kg in size when used with a Full MK6 Iron Man suit. Anatomical heart PLA filament costs approximately $3.65 and uses 146g of filament. A SQ4D home can be made in just 48 hours and use less than $6,000 in materials; they are at the forefront of the 3D printed home industry. As the economy improves, affordable housing is becoming more readily available in the United States and Mexico.
Bioprinters are said to be able to 3D print organoids for as little as $10,000. PLA filament will cost you $0.98 per piece when used in conjunction with a full Nintendo Headrest Prototype measuring 94.7 x 86.9 x 121.9mm. A 3D printed shoe made from 114g of filament would use about $2.85 to make. The CR-10 filament is approximately 20kg in size when used with a Full MK6 Iron Man suit. Anatomical heart PLA filament costs approximately $3.65 and uses 146g of filament. A SQ4D home can be made in just 48 hours and use less than $6,000 in materials; they are at the forefront of the 3D printed home industry. As the economy improves, affordable housing is becoming more readily available in the United States and Mexico.
It is possible to save a significant amount on this purchase, not just on houses. It is a versatile tool that can be used to build anything from a bed to a car. The cost of this technology will only increase in the future as it grows rapidly. If you want to save money on your next project, you should consider 3D printing.
3d Printing: The Future Of Manufacturing
3D printing is a technology that allows users to rapidly create objects from digital models by printing them layer by layer. There are frequently comparisons between this process and traditional printing, which entails printing one piece of paper at a time. In general, there are several distinctions between traditional printing and 3D printing. There is a significant distinction between 3D printing and traditional printing in that 3D printing allows it to print multiple objects on a single sheet of paper. In other words, 3D printers can use digital models rather than physical objects. As a result, the size and shape of the object that you intend to print are not restricted by 3D printers. In addition to printing in multiple colors, 3D printing is a distinct departure from traditional printing. The reason for this is that 3D printers use plastic filament instead of ink. A plastic filament is made of small pieces of plastic that are melted and then extruded into a strand. As a result, 3D printers are capable of producing objects with a wide range of colors. A 3D printer is still in its infancy in terms of its application. However, it has the potential to greatly alter the way we manufacture goods. There is no such thing as 3D printing the size or shape of an object. Because traditional printers can print objects of a larger size or complexity, they can print even larger items. A 3D printer can also print in a wide range of colors. A three-dimensional object can be created with a variety of colors.
As a result, 3D printers are capable of producing objects with a wide range of colors. A 3D printer is still in its infancy in terms of its application. However, it has the potential to greatly alter the way we manufacture goods. There is no such thing as 3D printing the size or shape of an object. Because traditional printers can print objects of a larger size or complexity, they can print even larger items. A 3D printer can also print in a wide range of colors. A three-dimensional object can be created with a variety of colors.
How Much Does It Cost To 3d Print Per Hour?
What is the cost per hour of 3D printing? It costs around $0.15 per hour to print 3D models, which includes a 0.4mm nozzle, a 0.2mm layer height, and standard electricity and maintenance costs.
Using melted materials, we can create 3D models in the real world using 3D printing. It is made up of time, labor, and electricity. For filaments, power, and labor, the hourly wage can be calculated. The price per hour for 3D printing will be 17. 08 US dollars. Depending on the model, there are several 3D printers on the market with different power consumptions. By calculating the power consumption of your 3D printer, you can calculate how much it costs per hour. The labor costs associated with 3D printing are listed here. It’s quite different than what you’d expect in this apartment. If we need to 3D print and ship, we must also pay for shipping.
08 US dollars. Depending on the model, there are several 3D printers on the market with different power consumptions. By calculating the power consumption of your 3D printer, you can calculate how much it costs per hour. The labor costs associated with 3D printing are listed here. It’s quite different than what you’d expect in this apartment. If we need to 3D print and ship, we must also pay for shipping.
It is easy to create custom objects using 3D printing. Although it is not always the most inexpensive hobby, it is something you can do. A standard 3D printer can cost anywhere from $1,000 to $10,000, depending on the model. However, if you are willing to spend a little more, you can get much more powerful printers capable of printing objects at much faster speeds, potentially saving you a lot of time and money.
Staples Printing
Staples printing is a great way to get your documents and photos printed quickly and easily. You can bring your own documents and photos to Staples to be printed, or you can print from a variety of online sources. Staples offers a variety of printing options, including color printing, black and white printing, and large format printing.
Staples offers a variety of printing options, including color printing, black and white printing, and large format printing.
The printing needs of businesses and educational institutions can be met by Staples. As an instant copy center, use the self-service machines in any Staples store. By ordering online, you can get it delivered to your door the same day that Curbside pickup is available. We offer free shipping for orders over $50K. We provide full-service printing.
3d Printing Industry
3D printing technology has been around for several decades, but it was only recently that the industry has begun to take off. 3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The objects are created by successively layering material until the desired shape is achieved. There are a variety of applications for 3D printing technology. In the medical field, 3D printers are being used to create prosthetic limbs and organs. In the automotive industry, 3D printers are being used to create prototype parts and tools. In the aerospace industry, 3D printers are being used to create fuel nozzles and engine parts. The 3D printing industry is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. This is due to the decreasing cost of 3D printers and the increasing availability of 3D printing materials.
In the aerospace industry, 3D printers are being used to create fuel nozzles and engine parts. The 3D printing industry is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years. This is due to the decreasing cost of 3D printers and the increasing availability of 3D printing materials.
Part performance in the aerospace industry is of the highest level. It is now possible to print in thermoplastics reinforced with continuous fiber reinforcement (CFR) for professional 3D printers. For example, at Garry Rogers Motorsport, a professional 3D printer can be used to print a variety of end-use parts, such as steering wheels. The industrial 3D printer revolution has completely transformed the manufacturing industry from the ground up. Custom, low-volume tooling and fixtures are created for a fraction of their traditional cost. As a result, designers and engineers have more time to devote to revenue-generating equipment. Colleges and universities are rushing to keep up with the rapid growth of the 3D printing industry. Colleges such as Oklahoma State University and Purdue University are investing heavily in teaching students about additive manufacturing materials and technologies, and Haddington Dynamics has used its four printers to create robot arms for NASA and GoogleX.
Colleges such as Oklahoma State University and Purdue University are investing heavily in teaching students about additive manufacturing materials and technologies, and Haddington Dynamics has used its four printers to create robot arms for NASA and GoogleX.
The AM process is the process of creating products from the first layer of data. Although it has not yet been invented, it has seen a recent resurgence in popularity as a result of its potential to overcome a number of production hurdles. For large-scale manufacturing, AM has been a time-consuming and costly process in the past. Recent advances in technology, on the other hand, are changing this.
The cost of AM technologies such as laser sintering and 3D printing is falling. This method enables mass production of products, which is a significant advance in terms of speed and cost. Despite its practical applications, AM is still too slow for mass production in the majority of cases. However, with continued innovation, this process is expected to become faster and less expensive, making it a viable manufacturing option for large businesses.
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong. In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product. nine0003
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.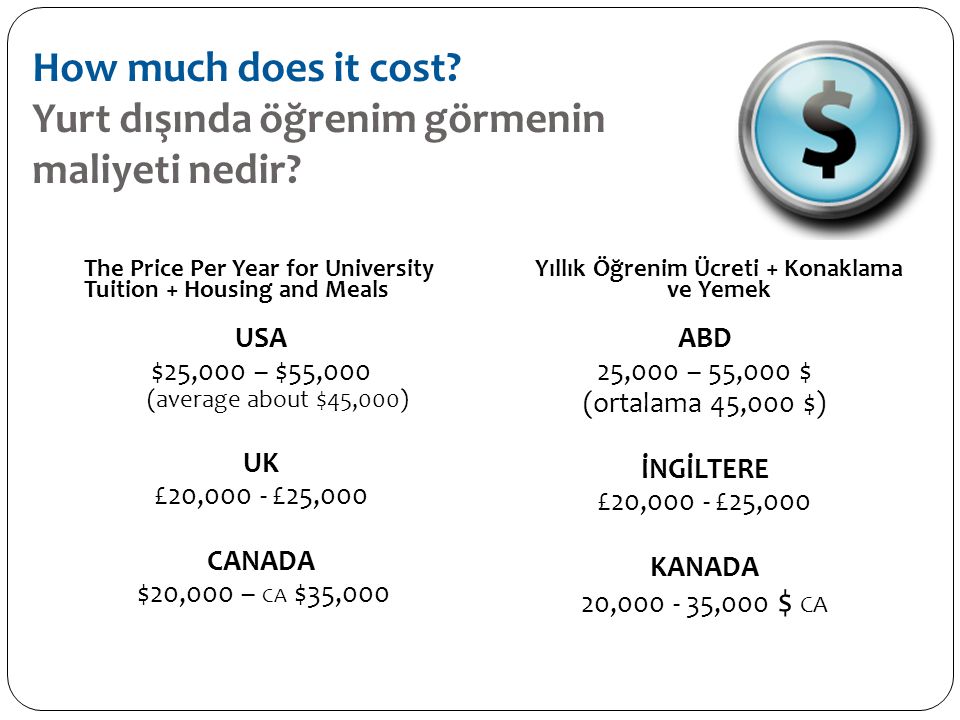
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details. nine0003
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
nine0060 -
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy. They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more. nine0003
nine0003
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
nine0021 CreatBot F160-PEEK designed to work with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model. nine0003
In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model. nine0003
Prismlab Large Area Industrial Resin Printer Family
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored. nine0003
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support. nine0003
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc. nine0003
nine0003
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model. Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.). nine0003
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder). The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype. nine0003
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale. You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model. nine0003
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin. nine0003
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull (quick release loop) for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles. nine0015
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products). nine0003
Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products). nine0003
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
nine0003
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burnout resin rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product. nine0003
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different. nine0003
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.

Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling. Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make. nine0003
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
nine0167What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer.
For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D printed model
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
If the item is only sold as an assembly. For example, a small gear broke in the mechanism, but the mechanism is sold only “assembly”. It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism. nine0003
A small batch of parts. Small batches, especially models with complex geometry, are more profitable to produce on a 3D printer than by casting or other methods.
Totals
If you need several models or a small project, sometimes it will be more expedient to outsource manufacturing.
After all, in addition to buying equipment and materials, you will have to understand the nuances of the settings and the characteristics of various materials. nine0003
Buying a 3D printer for commercial use is justified if you can fully load it with work or then it can be used for other purposes.
To print to order, you need to have several printers working on different technologies. It is better to get several devices with a smaller print area than to buy just one printer, albeit with a large working area.
Order stapled brochure with 3D cover trim
- Home
- Products
- Brochures
- Staple Brochures with 3D Finished Cover
Staple Brochure is a popular type of printed matter that is used for business, education, promotional purposes and services. The FineArtPrint printing house offers customers to order brochures with 3D finishing and a unique cover design.
Technologies
We use modern technologies to manufacture our products:
- 3D varnish;
- 3D foiling.

They allow you to create an original, presentable design, thanks to which the brochure will be of interest to those for whom it is intended.
The number of sheets in a classic stapled brochure must be a multiple of 4. This product has a maximum of 60 pages. Our company prints brochures with 3D finishes in Moscow and offers the services of professional designers to create an original, attractive cover. nine0003
Circulation (pcs)
500 pcs.
1000 pcs.
Date of manufacture 11.01.2330.12.22
500 pcs.
1000 pcs.
Format (mm)
A4 vertical (210x297 mm) A5 vertical (148x210 mm) A6 vertical (105x148 mm) A4 horizontal (297x210 mm) A5 horizontal (210x148 mm) A6 horizontal (148x105 mm) EURO (100x2010 mm)010 mm120x120 mm150x150 mm200x200 mm
1
Select cover characteristics
Specify the type of 3D finish - varnished, foiled or both. Cover includes 4 pages and is added to the block automatically
Paper
Coated matt
Density
170 g
200 g
250 g
300 g
Color
4+0 (CMYK)
4+4 (CMYK)
1+0 (Black)
1+1 (Black)
Laminating film
Matt Velvet (Soft Touch)
Thickness
0.
028 mm
Thickness
0.03 mm
Lamination sides
Front side only
3D varnishing
front side, varnish thickness 29 µm, sheet filling area up to 15%. The price includes drawing files under varnish - 1500 rubles. nine0003
3D foiling
front side, rise height 29 µm, sheet filling area up to 15%. The price includes drawing files under the foil - 2500 rubles.
Foil
Golden-stain-red-red linen-shaped green
density
density
density
density
density
2 9000 ATTENTION! In the "Number of pages" field, specify the number of pages in the block, excluding the cover. Maximum number of pages - 60
Number of pages
Paper
Coated matt Coated glossy Offset
Weight
130 g
150 g
170 g
200 g
250 g
300 g
Density
150 g
170 g
200 g
250 g
300 g
Density
80 g
120 g
Color
4+4 (CMYK)
Additional services
Design check by designer (from +500.

Learn more