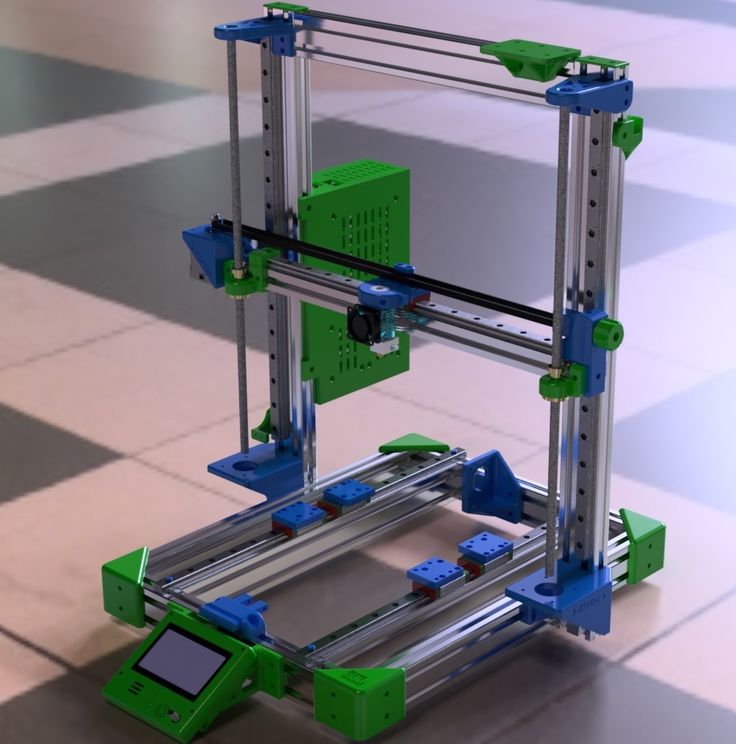
Helix 3d printer
Helix best 3D printer models・Cults
5 GHz Helix antenna
Free
Helix
€2.12 -15% €1.80
Fixed Fishbone Gears (47/9 double helix). Wade-Greg-Jonas Kuehling extruder
Free
(SPIRAL) SPEEDSOFT HANDGUARD M4 PLATFORM
€5.82
FGC-68 MKII tipx edition: Helix DMAG UAL (UPPER and Lower) set
Free
MXR Modular Pedalboard enclosure
€2
RGB DOUBLE HELIX DNA LAMP - Micro USB Socket & Closed Bottom - with Arduino Code
Free
RGB DOUBLE HELIX DNA LAMP - Micro USB Socket & Closed Bottom - with Arduino Code
Free
FGC-68 tipx edition: Helix/ Dmag lower for roundball
Free
Propeller, Propeller
€2
Archimedes screw auger
€3. 84
Propeller
€2.17
Rook (With Resin Drain Relief)
Free
Sphere with Rombs CNC
€2
Windmill D145 / Helix Vertical Windmill
Free
GUITAR & BASS MODULAR MINI PEDALBOARD
€2
Grenade - Keychain
Free
DNA Incense Holder
Free
DNA Helix
€1.20
Helix lampshade
Free
GUITAR & BASS MODULAR PEDALBOARD LARGE
€4
SCAR STOCK / STOCK HURRICANE / X7 CLASSIC , X7 PHENOM
€39.66
RNA model
€1. 99
99
Helix Vial Small
€5
Fridge Propeller Helix
Free
Xmas tree decoration spherical helix ball
Free
DoubleHelix Stand with Ball Joint
Free
Triple helix
Free
Smoking piece
€1.20
RGB DOUBLE HELIX LAMP - easyprint (diffusors needs verry slow print)
Free
Airsoft Mock Suppressor Caliber Customs Osprey-style
€7.69
Pineapple vase set
€1.50
Helix Fossil - FAN ART - POKÉMON FIGURINE - 3D PRINT MODEL
€1.90
Propeller for electric motor
€11. 53
53
Helix Pencil Holder
€0.94
Customizable Double Helix
Free
Wacom Feel IT_SAMSUNG_S-PEN_Rubber Grip Adjuster
Free
Helix helix helix Superzing 7 series
€1.25
Helix in different shapes
Free
Twisted Helix Ring
Free
Wind turbine
€1.25
Slinky
Free
Helical Ribbed Pencil Container
Free
Rounded bar helical pattern large statement ring 3D print model
€7.69
Simple spiral bevel gear set-2 gears-t24m1deg60
Free
Spring (made of heat-treated filament)
Free
Diamond helix and drum ring 3D print model
€7. 69
69
Helix penholder
€1.59
Printing a Helix successfully... Possible? - Software - Talk Manufacturing
lagarkane
#1
Hi!
I am struggling in trying to print a fairly simple part: a simple helix. In this picture, you can see how Cura (in this case, but I tried Slic3r and Simplify3d with the same result…) slices my model and computes the paths:
Oscar_svensson
#2
It looks like you model doesn’t have any thickness set in the middle part. Would you mind sharing the STL so we can have a look?
keebie81
#3
That section missing is most likely thinner than the nozzle diameter. So it doesnt show up. Or theres a problem with the geometry of the stl. What program was used to create this?
So it doesnt show up. Or theres a problem with the geometry of the stl. What program was used to create this?
9 Likes
lagarkane
#4
Hi and thanks for your replies!
It was designed using FreeCAD (I am a beginner in 3D design -> less than a week, basically, when I got my printer… ) So Maybe I forgot to handle something.
I thought it could be because of too thin walls, or too large nozzle. I tried different layer heights in Cura, I even changed my nozzle to a .2mm and printed with the finest settings possible
I tried using Slic3r, I tried with some online slicing software I forgot the name…
I also added a central rod to my design, hoping it would solve the issue, but the gcode puts some kind of v-shaped crack in the rod, so one side of the helix is never connected to it… (c.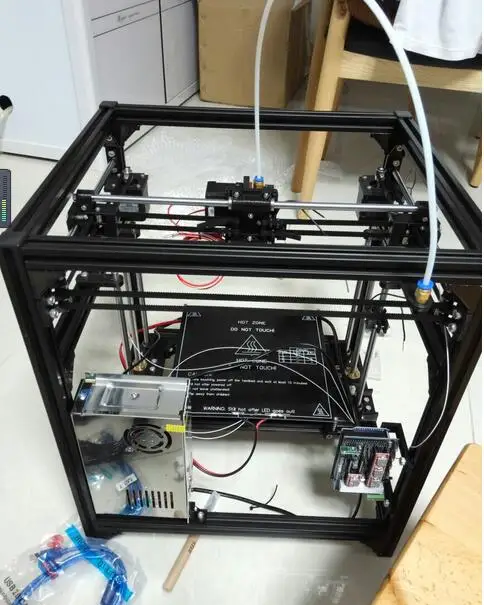 f. picture)
f. picture)
I’m really looking to your feedback at this point!
19_helix_norod.obj (55.8 KB)
19_helix.obj (64.4 KB)
lagarkane
#5
Hi again!
Actually @Oscar_svensson, your comment got me on the right track thanks!
I redesigned the part in FreeCAD. This time though, instead of drawing the whole helix at once, I started with one side of the helix (the radius instead of the whole diameter) and then the second part. This way, the solids that are generated both have no areas without a thickness, and put together, they merge just fine when generating the STL!
A not-so-obvious workaround maybe but it did the job
Thanks again!
how food is printed using a 3D printer Now you will not surprise anyone with a 3D printer for printing metal or plastic with the properties of rubber.
 It's time for food 3D printers. The technology is still in its infancy, but entrepreneurs have embraced it. Already in many restaurants around the world you can taste printed dishes.
It's time for food 3D printers. The technology is still in its infancy, but entrepreneurs have embraced it. Already in many restaurants around the world you can taste printed dishes. We tell you what 3D food printers exist and how they print food.
How is food printed?
To put it simply, 3D printed food is food prepared using an automated food pairing process. For example, in European countries you may have seen pizza or yogurt vending machines. The machine takes the prepared dough, drizzles it with tomato sauce, adds chunks of other ingredients and sprinkles cheese on top, and then bakes it in the oven. This process can be called primitive food 3D printing.
3D printed food is still in its infancy and has a long way to go before being widely adopted by professionals and consumers. However, this does not prevent us from marveling at these fascinating machines and enjoying the results.
However, this does not prevent us from marveling at these fascinating machines and enjoying the results.
Food 3D printer works on the principle of the classic one, which prints with plastic. The extruder (the part that extrudes the food product onto the table) is fed with pasty material such as puree, mousse, chocolate ganache, and so on. In the program, the dish is divided into layers, each of which is printed separately. The most difficult thing is to combine several materials at the same time. Users either combine multiple extruders or produce a complex system of gradual feeding of multiple materials into one extruder.
The use of spreadable materials may seem somewhat limited in terms of versatility, but think of all the possible combinations with doughs, purées, processed cheeses, glazes, and even raw meats.
Other additive processes are still at the research stage. These include jet application of liquid food or handling powdered food products.
Do 3D food printers cook food?
3D food printers are mostly suitable for creating complex shapes and designs, not for preparing full-fledged meals. Usually, after creating a food “mockup” on a 3D printer, it is baked in the oven or on the grill.
Usually, after creating a food “mockup” on a 3D printer, it is baked in the oven or on the grill.
This technology is of interest to restaurants that want to decorate a banquet table, impress customers, or who are into molecular cuisine. It is still not scalable, since very little time has passed since its inception. However, this does not prevent pioneers and innovators from using it.
Back in 2016, two world-class chefs created a new restaurant concept in London called Food Ink. At first the idea was to serve 3D printed food, but eventually they ended up with only 3D printed furniture in the restaurant.
It's not just in fine restaurants that 3D printed food can be found. Bakers are actively using 3D printed lettering. In general, this technology greatly facilitates the tasks for confectioners. By the way, when you use a piping bag, you are actually 3D printing decorations for cakes, cookies, and more by hand.
In general, this technology greatly facilitates the tasks for confectioners. By the way, when you use a piping bag, you are actually 3D printing decorations for cakes, cookies, and more by hand.
In 2016, Ukrainian developer Andrey Barna created a 3D chocolate printer in Dnepropetrovsk. By that time it was only the fifth such development in the world. The printer can reproduce the form of any complexity. Printing accuracy - from 0.6 to 1 mm. Printing one sweet takes from 14 minutes to several hours.
Andrey uses special Spanish chocolate in “coins” as a material, but he says that any other high-quality chocolate will do.
Also last year, startup Alt-Steak showed off 3D printed vegetable steaks that closely resemble real animal meat. In addition, the German company Biozoon is printing food for the elderly that can be chewed and digested more easily.
In addition, the German company Biozoon is printing food for the elderly that can be chewed and digested more easily.
Advantages and disadvantages of printed food
Benefits
3D printed food is safe to consume, although the taste will sometimes be unusual, to put it mildly. It will have an intricate shape that would be difficult to reproduce by hand. To create it, layers of vegetable puree will stick together, for example, with sugar syrup. Good? Yes. Delicious? Question.
This paves the way for personalization of food. In terms of controlling the variety and amount of nutrients, vitamins and calories per meal, 3D printing ensures accuracy. This can be extremely important in hospitals where therapeutic diets are common and it is important to tailor them individually for each patient.
We can make exotic food attractive. It is possible to create attractive dishes from insects in a semi-liquid state, which are rich in protein. In the future, even synthetic food could be 3D printed. Who knows!
To exchange recipes, just send a file to a friend. It's all!
Disadvantages
With all these interesting benefits of 3D food printing, there are also disadvantages to be mentioned. Although time may vary depending on the printer and product being printed, food printing is a lengthy process. Time is especially important for mass production businesses.
In addition, edible materials require pre-cooking or pre-treatment to achieve the consistency required for extrusion. The expected output and reliability of 3D food printers is highly dependent on the proper preparation of materials.
What models are available?
As of 2021, there are only a few professional food 3D printers, mostly in desktop versions. There is still no industrial equipment. Despite this, some of the following models are already used for catering, events and restaurants.
Despite this, some of the following models are already used for catering, events and restaurants.
byFlow
It may not sound like much, but this little printer is capable of great things. FbyFlow is a 3D printer for the extrusion of materials used by professional chefs around the world. It is controlled via Wi-Fi and uses refillable cartridges (syringes) that can be filled with edible paste. Michelin-starred restaurant Smink in the Netherlands uses this printer to create intricate patterns on desserts.
Now byFlow costs about 4.3 thousand US dollars (3.9thousand euros).
Foodini
This is one of the most hyped food 3D printers of all, and deservedly so. Foodini from Natural Machines can process almost any ingredient, from jellies to delicious burgers, using five different cartridges at the same time. Natural Machines takes a healthy approach by providing recipes for new users to try before they create their own. Foodini costs about four thousand dollars.
Natural Machines takes a healthy approach by providing recipes for new users to try before they create their own. Foodini costs about four thousand dollars.
MMuse
The MMuse chocolate 3D printer is unique in that it processes chocolate chips up to four millimeters in diameter and melts them for extrusion. It's pretty sturdy, weighing in at around 25kg (~55lbs), but still in the desktop range. It is produced in China, it is quite expensive - about 5.7 thousand dollars.
Mycusini
Mycusini is a chocolate 3D printer released by the German startup Print2Taste, originally funded through a Kickstarter project. It has a great design and is compact enough for a kitchen. Stainless steel cartridges are easy to fill and clean, but refills must be purchased directly from Print2Taste. Mikusini costs about 69$0 (~600 euros).
#bit.ua
Follow us at
Telegram
informational article of the Polymernagrev company on the site tvoy-nagrev.
 ru
ru
3D printing , although developed for a long time, is becoming more and more in demand. There are new versions of three-dimensional printers that can produce a wide variety of high-precision products. If earlier it was possible to use only primitive polymers as a material, then over the past few years the list of raw materials for printing on a 3D printer has increased significantly. And not only a wide variety of plastic options with all kinds of colors are used, but also more serious metal materials. There are already whole developments of parts for rockets and aircraft made on a three-dimensional printer.
In the technology of manufacturing products on a 3D printer, probably the most important factor is uniform and correct heating of the workpiece . Therefore, heating elements in this type of production perform one of the most important functions.
Each filament at the exit from the nozzle of a three-dimensional printer is heated by elements such as a finger-type heater or a flat aluminum heater. Many users are often worried about the low speed of printing, and they can not find a way out of this situation. And the main factor affecting the speed is the operation of the installed heating element and its possible characteristics.
Many users are often worried about the low speed of printing, and they can not find a way out of this situation. And the main factor affecting the speed is the operation of the installed heating element and its possible characteristics.
Some time ago, 3D printers were produced only with induction heating, but it was imperfect and had a lot of drawbacks. To date, there is a wide selection of printers with a contact heating type , which has proven itself very well.
When choosing a contact heater for a 3D printer, first of all, pay attention to its power and heating speed . These are the most important criteria in choosing a heater for a 3D printer. Also, the heater must be capable of temperature control and high-precision heat generation within a certain range.
An LED display showing the heating temperature will make it easy to control printing. Contact heater must operate within 0. 5 degrees Celsius . Its temperature production can be controlled by special sensors or an installed thermocouple.
5 degrees Celsius . Its temperature production can be controlled by special sensors or an installed thermocouple.
The work of a three-dimensional printer is based on the layer-by-layer manufacturing of products previously designed by a computer program. During processing, a three-dimensional model is saved in STL format, after which the equipment forms a real product.
Overlay layer-by-layer printing is made on a special desktop. Each layer is applied in stages. This continues until the product is completely printed.
3D printing allows you to create physical objects designed on a computer. New developments show us the versatility of using 3D printers in a wide variety of areas of human life.
Cartridge heater for 3D printing
Cartridge heater for 3D equipment is made to order only. The minimum diameter of the finger heating element can be 3 mm and the length 50 mm. Despite the small geometric dimensions, this type of heater has a fairly high power density.