Glass for 3d printer bed
Borosilicate Glass VS Tempered Glass for 3D Printing – 3D Printerly
The conditions for a good print start, quite literally, from the ground up. A good build plate is fundamental to ensuring your 3D model comes out looking great.
It serves several functions like making sure there’s a level surface for printing and enhancing print adhesion.
There are many materials for fabricating build plates, depending on the print requirements.
A popular option among 3D printing enthusiasts is glass. Its high resistance to warping, thermal stability, and conductivity make it a prime choice for printing.
The two main types of glass that people use for 3D printing are borosilicate glass and tempered glass, but many people don’t know which to buy.
This article is going to aim to help you identify the differences and key comparisons to help you move forward and get the right type.
Let’s quickly look at both options before we compare them.
What Is Borosilicate Glass in 3D Printing?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass made with silica and at least 13% Boron trioxide. This combination gives it some properties that make it useful in 3D printing applications.
Let’s examine these properties.
Thermal Stability
Borosilicate glass has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. That is, it expands very little with changing temperatures. This means that it will not crack or shatter under extreme temperatures.
Its thermals stability is one of its most important properties, as this makes it possible to use it with a heated bed. It also makes printing with high-temperature materials like ABS very easy.
Durability
Borosilicate glass is strong. It is shatter-proof, which means when it’s dropped, it won’t break. Also, its durability means it lasts longer and is less susceptible to surface degradation from scratches and nicks.
Chemical Resistant
Borosilicate glass has a very stable chemical structure that doesn’t degrade when attacked by outside elements. This is very helpful when printing with reactive filaments.
It’s nice to know your build plate won’t leak dangerous chemicals into the print or the air.
Thermal Shock Resistant
Thermal shock resistance is a property of borosilicate glass that makes it resistant to rapid changes in temperatures. Most materials exposed to rapid changes in temperature lose their strength and may even fail. But, Borosilicate glass stands up well to these thermal shocks.
Some people wonder whether borosilicate glass warps, and most people’s experience show that it doesn’t warp over time due to its physical characteristics.
What Is Tempered Glass in 3D Printing?Tempered glass is any form of glass that has gone through thermal and mechanical processes (tempering) to increase its strength. Tempered glass finds applications in car windshields and things like screen protectors.
All these are made possible due to the properties given to it by tempering. Let’s take a look at some of those properties below:
Strength
Tempered glass is strong and durable by nature. It can withstand impact shocks far better than regular glass. Its strength comes from tempering, which pre-stresses the glass’s structure to make it stronger.
It can withstand impact shocks far better than regular glass. Its strength comes from tempering, which pre-stresses the glass’s structure to make it stronger.
Thermal Stability
Tempered glass is also heat-resistant. The thermal tempering treatment makes it able to withstand temperatures up to 300℃ without failure. Tempered glass can also withstand thermal shock, just not as well as Borosilicate glass.
Scratch Resistant
Tempering gives the surface of the glass a scratch-resistant finish.
It hardens the surface making it more resistant to penetration from an external object. This quality makes tempered glass retain its surface quality for a long time.
The video below shows how easy installation is, and gives a nice review on a tempered glass bed.
Borosilicate Glass Vs Tempered Glass: Which One is Best for You?
When buying a glass build plate, the odds are you are going to get either one made from borosilicate glass or tempered glass. So, how do you decide between them? Let’s take you through some things that can influence your decisions.
So, how do you decide between them? Let’s take you through some things that can influence your decisions.
Quality
Both borosilicate glass and tempered glass have excellent qualities that set them apart from regular glass. Let’s go through those qualities one by one and see how they stack against each other:
- Thermal Stability: Both tempered and borosilicate glass perform well at high temperatures. You can print high-temperature filaments on them with no problem. However, when it comes to thermal shock resistance, Borosilicate glass is the better option.
Due to the pre-stressed nature of tempered glass, it cannot withstand large temperature variations. Prolonged exposure to these temperatures can cause warping, or in extreme cases, total failure.
- Scratch Resistance: The scratch resistance of a material is a function of its hardness and resistance to penetration. Both Borosilicate and tempered glass are harder than regular glass.
 On the Mohs hardness scale, tempered glass is rated slightly higher than borosilicate glass.
On the Mohs hardness scale, tempered glass is rated slightly higher than borosilicate glass.
The higher rating means Tempered glass is a slightly harder material. As such, it will be more resistant to chipping and flaking. This will make it retain its surface quality longer.
Ease Of Use
For ease of use, we’ll be rating both glasses on how user-friendly they are. Both provide good quality bottom finishes, are easy to clean, and are flat. We’ll be using different criteria.
We’ll be comparing them based on safety and ease of print removal.
Let’s look at these criteria:
- Safety: Tempered glass is a safer material. It is highly durable and can resist impact shocks better. Even if it breaks, it breaks into cube-like pieces that aren’t harmful.
- Ease of Print Removal: Print removal generally depends on a lot more things than the build plate, but prints are easier to remove from borosilicate glass. Due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, it won’t expand when heated.
 So as it cools, the stresses from the shrinking model make it easier to remove.
So as it cools, the stresses from the shrinking model make it easier to remove.
For more stubborn prints, you can put the build plate in a freezer to cool it faster. Borosilicate glass can survive this swing in temperature because of its resistance to thermal shocks.
Price
The price difference is not so significant, so you can really choose either and be good on price, but let’s look at which one actually comes up as cheaper.
A standard borosilicate glass bed for an Ender 3 on Amazon comes to around $15, with the Dcreate 235 x 235 x 3.8mm Borosilicate Glass Bed.
A standard tempered glass bed for an Ender 3 on Amazon comes to around $20 on Amazon, with the Creality Authentic Tempered Glass Bed, though these prices can fluctuate depending on the brand and the seller.
The prices of 3D printer beds have been getting cheaper over time, which is great for 3D printer hobbyists out there!
Overall, I’d recommend going with the Dcreate Borosilicate Glass Bed from Amazon.
You can also get yourself some professional 3D printer clamps to add onto your 3D printer to hold the glass bed into place. When I tried using the binder clips that came with my Ender 3, it was just too small for the glass bed addition.
The 4-Pack Ender 3 Stainless Steel Clamps from Amazon are a good product to keep your bed in place. They are fairly pricey but they get the job done very well.
Another option which gives you more bang for your buck is the 40 Pcs Extra Large Binder Clips from Amazon. They have a 2-inch width and has multiple practical uses outside of holding your bed in place.
Custom Glass for 3D Printing Applications
The Role of 3D Printing in the Manufacturing World
3D printing—also known as additive manufacturing—is a manufacturing process that creates physical objects from a digital model. It uses a specialized fabrication unit—i.e., a 3D printer—to add successive layers of plastic or metal material to form a 3D component. Compared to other manufacturing methods, it offers greater versatility, better cost-efficiency, and faster production speeds, especially for prototyping and small volume production runs. For these reasons, more and more manufacturers across a wide range of industries are turning to it for their product development projects.
Compared to other manufacturing methods, it offers greater versatility, better cost-efficiency, and faster production speeds, especially for prototyping and small volume production runs. For these reasons, more and more manufacturers across a wide range of industries are turning to it for their product development projects.
While 3D printing is now the go-to technique for prototyping, it has also found increasing use as a primary production method in recent years. As the technology continues to develop over time, it is likely to rise even more in popularity. As a result, the demand for quality 3D printing supplies—including the printing bed—will increase too.
The Importance of the Printing Bed
The printing bed—also referred to as the build plate or print surface—is one of the most important parts of any 3D printer. It serves as the platform on which objects are 3D printed. While its primary function is providing a flat surface for the bottom layer of the print, its secondary function is providing an adhesive surface or a surface on which adhesive can be applied. Both ensure the print remains stable as it is created.
Both ensure the print remains stable as it is created.
Materials for 3D Printing Beds
Printing beds are available in many variations, differing in material, surface finish, thermal characteristics, price point, and more. While they are traditionally made from metal or plastic, glass printing beds have become more ubiquitous.
Glass sheets are a simple and effective solution for print surfaces. Compared to other printing beds, they offer the following advantages:
- They are stiff and flat, meaning they will provide a solid and stable print surface for years.
- They have high material density and low thermal conductivity, which results in a longer heat up time but better heat distribution.
- They offer smoother surface finishes, making it easier to remove a finished print creating a nicer finish on the bottom surface.
Glass printing beds with heating capabilities further enhance prints by allowing for better material adhesion, a lower risk of material warping, and easier component removal.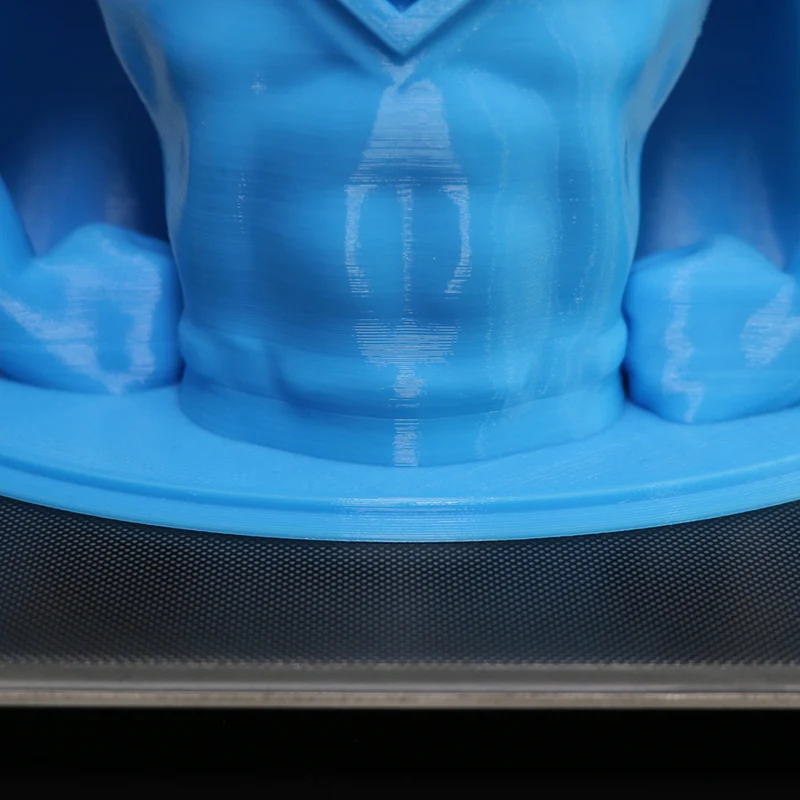
Two of the most common types of glass used for 3D printing beds are:
- Borosilicate Glass. This specialized glass contains a high concentration of boron trioxide and silica. It is characterized by its high durability and low coefficient of thermal expansion. When exposed to high temperatures, it remains clear, strong, and dimensionally stable.
- Clear Float Glass. Clear float glass materials (e.g., soda lime glass) are a low-cost alternative to borosilicate glass. They have lower durability and a higher coefficient of thermal expansion, which make them better suited for 3D printing applications involving lower temperatures and/or more flexible tolerance requirements.
Glass Printing Beds From Swift Glass
Need glass printing beds for your 3D printer? Swift Glass is here to help! We’ve manufactured industry-leading glass components for over 100 years. This experience enables us to provide high-quality glass cutting and edging services for customers who need glass 3D printing beds. Whether you need borosilicate or soda lime printing beds, we’ve got you covered. We can produce them in a variety of shapes, sizes, and quantities to suit virtually any 3D printing need.
Whether you need borosilicate or soda lime printing beds, we’ve got you covered. We can produce them in a variety of shapes, sizes, and quantities to suit virtually any 3D printing need.
To learn more about our custom glass 3D printing beds or discuss how we can help with your next project, contact us today.
- I'm looking for...
- Data Sheets
- Tools
- eBooks
- Certifications & Standards
- Videos
or
Request a Quote Today
Cleaning the 3D printer table. Tips and Tricks.
3D printing is a very unstable process, I think everyone who is at least slightly familiar with plastic filament printing technology will agree with this. Unpleasant crashes in the 3D printer can occur for various reasons, and one of the most common reasons is the detachment of the model being grown from the desktop surface. And as a rule, this happens in the middle of printing, when you are already convinced of the stability of the press and are distracted by another activity. It is precisely for this reason that ensuring good adhesion of the first layer to the platform is very important for the successful completion of 3D printing.
Unpleasant crashes in the 3D printer can occur for various reasons, and one of the most common reasons is the detachment of the model being grown from the desktop surface. And as a rule, this happens in the middle of printing, when you are already convinced of the stability of the press and are distracted by another activity. It is precisely for this reason that ensuring good adhesion of the first layer to the platform is very important for the successful completion of 3D printing.
Today there are many ways to improve the adhesion of the first layer to the bed. A lot of articles and recommendations have been written about this, so we will not talk about them. It is worth noting one of the simplest methods - is keeping the desktop of a 3D printer clean . Regular and thorough cleaning of the platform will not only improve adhesion, but will make printed models more beautiful and smooth.
In this article we will look at the best way to clean the 3D printer table, using the example of popular coatings:
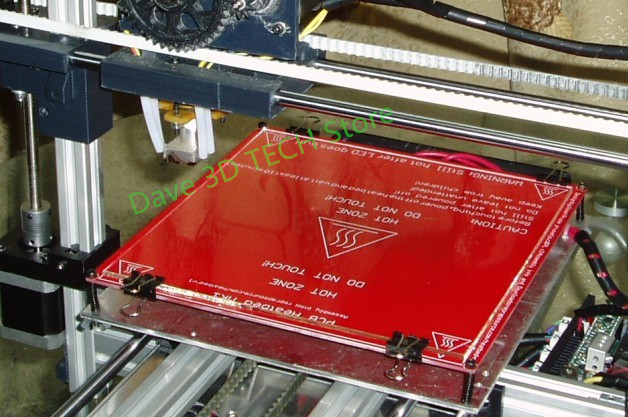
Remember to be careful when using the methods below, as spilled liquid may damage the 3D printer. We recommend removing the bed from the printer before cleaning (if possible).
We recommend removing the bed from the printer before cleaning (if possible).
PEI sheet surface cleaning
Recently, PEI sheet has become a very popular material for improving adhesion in 3D printers. It provides excellent adhesion to various materials, and when it cools down, the printed model lags behind it very easily. The sheets are very simple and not fussy to use, and most often it does not require additional application of glue or adhesive tape.
Unfortunately, in order to achieve maximum efficiency, the PEI surface also requires regular and high-quality cleaning. If PEI is touched frequently, it can develop greasy spots that reduce adhesion to the material. Rough cleaning can also damage the surface and reduce sticking. Regular cleaning and maintenance of PEI will ensure that your models do not come off.
How to clean the surface of PEI
To clean this surface, we recommend using isopropyl alcohol (Chemical pure, odorless) with a concentration of more than 70%. You can use it with a smell, but it is very caustic and unpleasant, the room will need to be ventilated.
You can use it with a smell, but it is very caustic and unpleasant, the room will need to be ventilated.
Wait for the platform to cool, then liberally soak a dry cloth or paper towel with alcohol and wipe the surface. This will remove a significant portion of the fats and oils from the bed.
Acetone is also good at dissolving plastic residues on the surface. In the same way, liberally moisten the cloth with liquid, then gently wipe the surface of the 3D printer desktop. We strongly recommend doing this work in a well-ventilated area, as acetone is highly flammable and its vapors can penetrate the electronics of the device
If you have been using PEI sheet for quite a long time, and visually its resource has been significantly used up, then we recommend using fine grit sandpaper (1500+). With gentle, circular motions, sand the surface until light scratches and depressions are removed.
When should I clean?
Most manufacturers recommend cleaning the surface with isopropyl alcohol every 2 to 3 prints. After a few months of use, sand the surface and wipe thoroughly with acetone. If it is no longer possible to restore the surface by the listed methods, then replace it with a new sheet from PEI. The lifespan of such material varies depending on the brand and frequency of use of the 3D printer.
After a few months of use, sand the surface and wipe thoroughly with acetone. If it is no longer possible to restore the surface by the listed methods, then replace it with a new sheet from PEI. The lifespan of such material varies depending on the brand and frequency of use of the 3D printer.
Glass Surface Cleaning
Glass is another very common 3D printer desktop material. Much more durable than PEI and similar surfaces. The glass plates provide a smooth and level surface at the bottom of the model.
This surface is usually used in combination with other aids (eg glue stick or hairspray) to improve the adhesion of the first coat. Such products are especially popular on tables that are not equipped with heating. Therefore, regular cleaning of the glass is necessary to prevent adhesive or varnish from sticking.
How to clean the glass platform
The easiest way to clean a glass plate is to use a scraper or a non-metal spatula. If the table is heated, then heat it until the material remains soft, after which they should be easily removed with a scraper.
If the table is heated, then heat it until the material remains soft, after which they should be easily removed with a scraper.
Be careful when scraping. Depending on the scraper, the blade can be very sharp, so be careful not to scratch the surface. We recommend that you put your hand on the handle of the scraper, and with the other hand press down on its middle, so that the greatest force is directed downwards.
If this does not work, try wiping the glass with warm soapy water. Although simple, this method is very effective for removing hairspray, glue, and other adhesives. Keep in mind that this method is only recommended if the 3D printer allows you to remove the platform. Spilled water can seriously damage the heating element, power supply or other electronics of the device.
Dirt can also be removed with specialized cleaning products. For example, wet alcohol wipes, window cleaner, isopropyl alcohol will also effectively wash away adhesive residue and restore the glass surface. However, do not take too strong cleaners. Such substances can severely damage the surface or even the 3D printer. In order to be sure to select a cleaning agent for your particular 3D printer, it is best to contact its manufacturer. Most often, they willingly make contact with users and willingly give advice.
However, do not take too strong cleaners. Such substances can severely damage the surface or even the 3D printer. In order to be sure to select a cleaning agent for your particular 3D printer, it is best to contact its manufacturer. Most often, they willingly make contact with users and willingly give advice.
When to clean the glass surface
Again, this will depend on how often you use the printer. We recommend cleaning the surface after each print to prevent buildup of glue or varnish. Such a procedure will not take much time, but the print will be more stable, and the resulting prints will have a beautiful and even surface. Once the models stop sticking (usually after a month), try washing the surface with soap and water. After about two to four months, you will have to resort to isopropyl alcohol or other specialty drugs. substances.
Cleaning adhesive tapes
Adhesive tape is another proven way to increase adhesion to the print platform. Today, this method is more common on 3D printers without the function of heating the desktop. Masking tape is the most common remedy, but so are Kapton and others.
Today, this method is more common on 3D printers without the function of heating the desktop. Masking tape is the most common remedy, but so are Kapton and others.
One of the reasons for the popularity of such linens is their ease of use and relatively inexpensive cost. They are easy to stick to the surface and are available at almost any hardware store. However, there are also disadvantages: the tape quite often peels off when the printed model is removed, so it must be reapplied regularly.
How to clean?
Unfortunately masking tape is one of the most difficult to clean due to its fragility. however, we have found that gentle scraping is one of the most effective ways to clean it. With light pressure, evenly scrape off the remaining plastic thread from the surface, being careful not to tear it.
If the tape does break during cleaning, replace this area with a new strip. The main thing is not to overdo it and do not apply a thick layer, this can adversely affect the quality of the print. If the tape is full of holes and looks like Swiss cheese, then it needs to be completely replaced. Strip and scrape the old tape from the surface. Then wash the platform with warm soapy water to remove adhesive residue.
If the tape is full of holes and looks like Swiss cheese, then it needs to be completely replaced. Strip and scrape the old tape from the surface. Then wash the platform with warm soapy water to remove adhesive residue.
Once the old tape has been removed and the surface has been thoroughly washed, apply a new layer of masking tape or Kapton. Squeeze out any air bubbles if necessary.
When should I clean?
Masking tape wears out quickly and needs to be replaced much more frequently than PEi for example. We recommend lightly scraping off any plastic that has stuck to it after each print. Depending on the frequency of printing, you will need to change such a surface daily, weekly or once a month.
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented.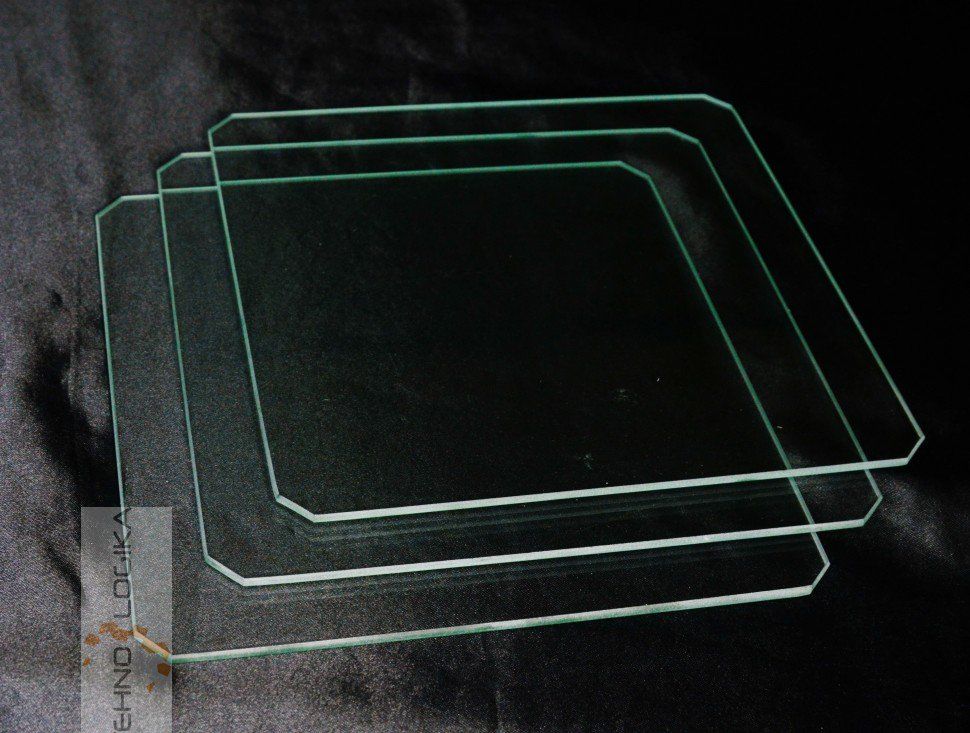 This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
We all know that precise calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them. Many will say that it is wrong to compare them or Read more→
XYZprinting, best known for its daVinci line of desktop 3D printers, is bringing five new devices to the professional and industrial environment. One will use laser sintering technology, the second full color inkjet printing and three DLP machines. First of all, the novelties will be of interest to dentists and jewelers. Read more→
Cleaning the nozzle of a 3D printer is a fairly common process that any user of such a device has to deal with. This is not at all a complicated procedure that anyone can handle. You can complete this task in 15 minutes, using only handy tools and accessories. Read more→
Acetone steam polishing of ABS plastic is a process for smoothing the surface of 3D printed models. The result of this treatment makes your printed products look as if they were made by a professional mold casting method.