Features of a 3d printer
What to Look for When Buying a 3D Printer
3D printing, and accordingly 3D printers, have exploded in popularity. While once these awesome gadgets were relegated to the most hardcore makers, increasingly affordable 3D printers and a slew of resources, from downloadable 3D printable files to 3D printing software, now the masses can enjoy 3D printing at home. However, as with virtually any purchase, and especially in the technology arena, you’ll want to focus on the right features. Learn what to look for in this 3D printer buying guide!
What to Look for When Buying a 3D Printer - Why Purchase a 3D Printer?
Though the price tag for even a budget 3D printer can be pretty steep, buying a 3D printer is worth it. Owning a 3D printer provides nearly limitless opportunity to create your household objects, from Raspberry Pi cases to napkin holders. You can create replacement parts for furniture, and extend the life of objects around your home.
Whereas normally you’ll need to either visit a maker space or order a print off of a website such as Thingiverse, now you can simply make your creations at home. You might even be able to make a bit of income by processing print jobs. Moreover, it’s simply fun. I have a blast with my Elegoo Neptune and Elegoo Mars printers, whipping up anything from chess pieces to a T-800 endoskeleton bust to sit under my computer monitor. Finally, it’s a fantastic learning opportunity. You’ll get hands-on with hardware and software, a better understanding of how.
Reasons to buy a 3D printer:
3D Printer Buying Guide - What to Look for When Buying a 3D Printer
If you’re buying a 3D printer, there are tons of considerations. From resin vs. filament printers to self-levelling beds, these are the features you should look for when purchasing a 3D printer!
Resin vs.
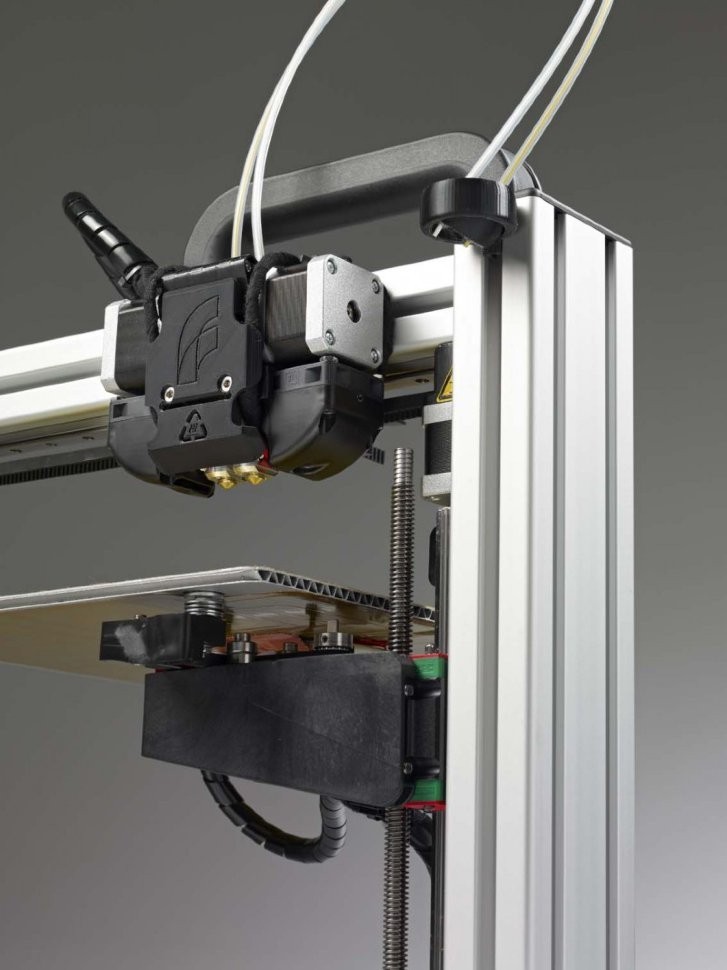 Filament 3D Printers
Filament 3D PrintersThe first debate you’ll have is whether to opt for a resin or filament 3D printer. Both are excellent and should satisfy basic users. Generally, filament 3D printers are more common. FDM or fused deposition modelling printing melts down a string of plastic, known as filament. This filament gets melted and deposited through a HotEnd onto a bed. Then, the filament is added layer by layer until the final print is produced. When using an FDM printer, the material is deposited beginning with the bottom layer and builds up from there.
Resin printing, on the other hand, uses a liquid resin. The build plate lowers into a vat of resin and uses a light source to cure its liquid resin into layers. Resin printers boast better quality than their FDM printer counterparts, excelling with fine detail. However, this often comes at a price. Namely, monetary cost as well as messiness. Resin is pretty nasty stuff, making set up and clean up a chore. Moreover, resin printers are typically more expensive. Still, certain affordable resin printers are available.
Moreover, resin printers are typically more expensive. Still, certain affordable resin printers are available.
3D Printer Noise
3D printer noise is a huge factor. No 3D printers are completely silent, but some remain quieter than others. Likewise, physical set up can contribute to the noise level. If you’re printing in your bedroom, 3D printer noise level plays a key role, especially since even a moderately-sized print can take the upwards of a few hours. Even if you’ve got a dedicated 3D printing area, 3D printing sounds can be heard around your home or by neighbours. Tricks such as placing your printer on a solid surface, on top of a yoga mat or carpet, and dampening surfaces help for 3D printer noise reduction.
Printing Speed
Speed of 3D printers varies. Typically, resin printers feature slower printing speeds than their FDM counterparts. If you’re merely printing for fun, speed might not matter quite as much.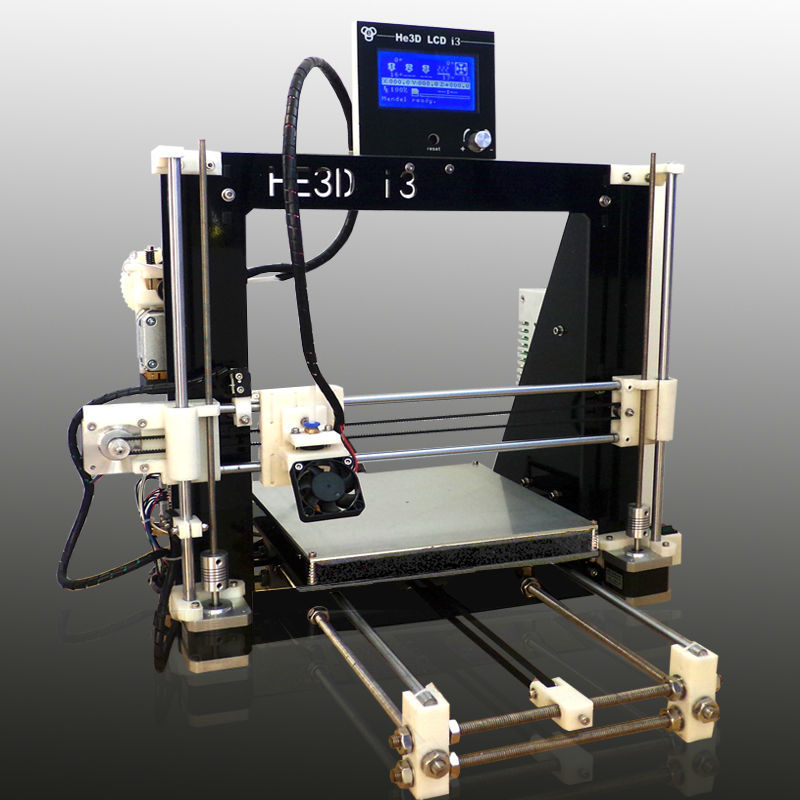 However, for business purposes, 3D printing speed may be more of an issue. For smaller print jobs, faster speeds don’t usually impact quality. But for larger prints, faster might come at the expense of fine details, and may even create problems such as vertical banding, or ringing. At the same time, too slow of a print could lead to stringing. Regardless, you’ll want a printer able to meet your desired printing speed requirements.
However, for business purposes, 3D printing speed may be more of an issue. For smaller print jobs, faster speeds don’t usually impact quality. But for larger prints, faster might come at the expense of fine details, and may even create problems such as vertical banding, or ringing. At the same time, too slow of a print could lead to stringing. Regardless, you’ll want a printer able to meet your desired printing speed requirements.
Self-levelling Bed
Among the most sought-after 3D printer features is a self-levelling bed. Manual bed levelling can be a right pain, a lengthy, frustrating process. An unlevel bed botches prints. Thankfully, many prints come with auto bed levelling features where a sensor tests various points on the print bed to best calculate the distance between the nozzle and print bed. Then, software adjustments ensure that the nozzle maintains the correct distance from the bed while printing. Although some users may prefer manual bed levelling, an auto-levelling 3D printer bed offers a fairly plug-and-print experience which massively streamlines the printing process.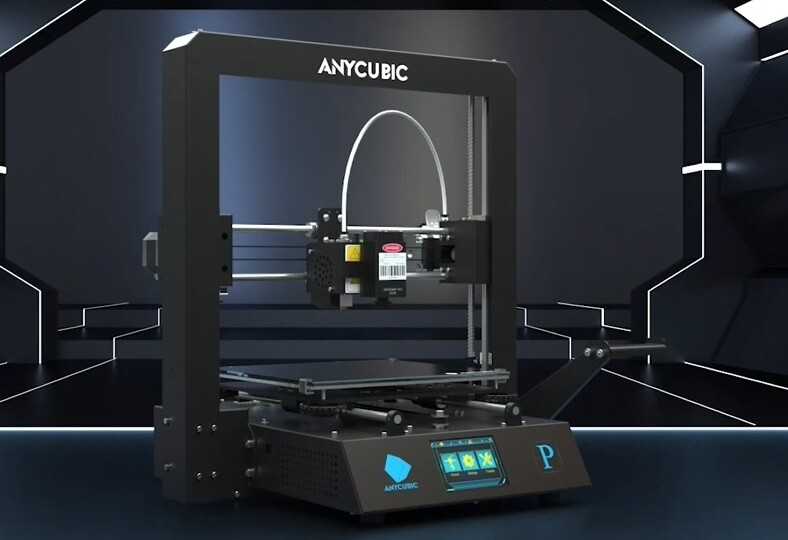 An auto-levelling bed is a great pick for 3D printing beginners.
An auto-levelling bed is a great pick for 3D printing beginners.
3D Printer Connectivity Options
Before you print anything, you’ll need to send a 3D printable file to your printer. This can be accomplished through several methods. Most 3D printers feature a means of connecting via USB cable. Additionally, 3D printers commonly feature an SD card slot or USB port for plugging in a flash drive or SD card. My Elegoo Neptune comes with a USB bus as well as SD card slot whereas my Elegoo Mars resin 3D printer touts a USB port for printing straight from a flash drive.
Device Footprint and Build Size
While resin, filament, bed levelling, and print speed are all essential, you’ll want to think about how much physical space you’ve got. 3D printers come in all shapes and sizes, from mini 3D printers to industrial-sized behemoths. Tied pretty directly with device footprint, there’s build size. The 3D printing volume is the total maximum size of a print. Most resin printers carry a smaller build size than comparable filament-based 3D printers. For the average user, a moderate to smaller build platform should suffice. But for later prints, you’ll need to snag a 3D printer with a larger print volume, and even then you might have to print multiple pieces, then put everything together into a larger whole.
Most resin printers carry a smaller build size than comparable filament-based 3D printers. For the average user, a moderate to smaller build platform should suffice. But for later prints, you’ll need to snag a 3D printer with a larger print volume, and even then you might have to print multiple pieces, then put everything together into a larger whole.
Print Quality, Accuracy, Precision, and More
Quality and accuracy of 3D prints are hugely variable. However, accuracy doesn’t necessarily translate to precision. You might find some printers are precise but inaccurate. While accuracy is a measure of hitting a target metric, precision focuses on determining repeated actions. So a printer may be accurate insofar as it hits close to the desired spot on a print bed, but imprecise insofar as it fails to consistently deposit in the same spot repeatedly.
Price
Finally, there’s the price. 3D printers, even budget devices, usually retail for hundreds of dollars.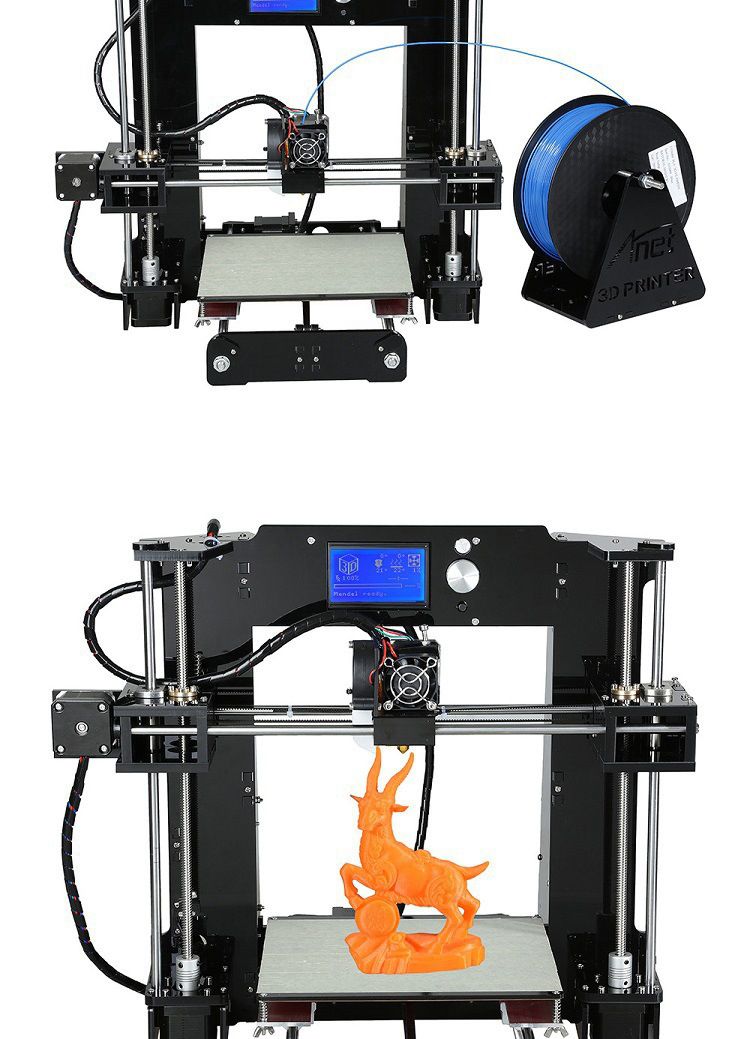 Nevertheless, there are loads of 3D printers under $500 which don’t compromise on quality. If you’re starting a 3D printer-centric business, such as selling 3D printed miniature figurines, consider upping your budget. But if you’re just getting a 3D printer for kicks, you might instead pick an affordable 3D printer.
Nevertheless, there are loads of 3D printers under $500 which don’t compromise on quality. If you’re starting a 3D printer-centric business, such as selling 3D printed miniature figurines, consider upping your budget. But if you’re just getting a 3D printer for kicks, you might instead pick an affordable 3D printer.
3D Printer Buying Guide - Final Thoughts
Purchasing a 3D printer requires thinking about your specific use cases, preferences, and needs. Resin printers are often pricier than competing filament 3D printers but boasts better fine detail quality. However, they’re much slower than filament printers. Print volume, noise level, printing speed, and bed levelling mechanism rank among the most essential considerations. I prefer resin printers despite the messiness, smell, and slower speed. Quality of budget resin printers often surpasses that of mid-range to high-end filament printers. I’d recommend for filament printers snagging a unit with a self-levelling bed if possible, though many budget 3D printers come with a manual levelling print bed.
What features do you suggest looking for when selecting a 3D printer?
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.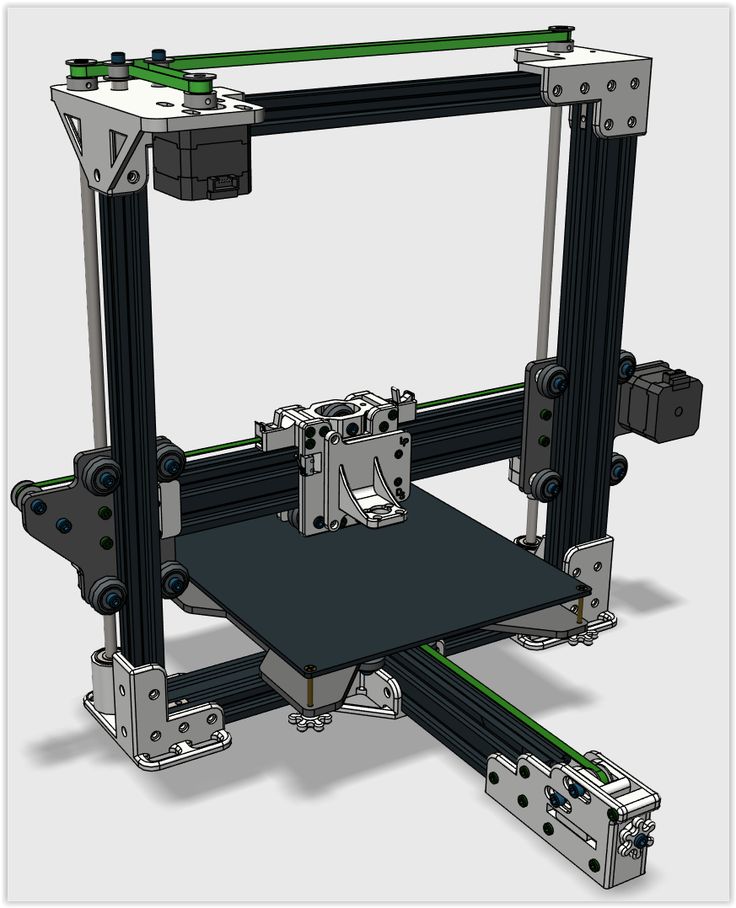
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Features of printing products on a 3D printer
Before you start printing using a 3D printer, you need to understand the proposed process options, find out what features they have, and what consumables you need to choose. Of course, it is quite difficult to deal with this issue on your own, so it will not be superfluous to get expert advice.
We speak simply about the complex - features of the equipment
So, it should immediately be noted that a 3D printer is a technologically sophisticated equipment that creates objects in a three-dimensional projection using layer-by-layer printing. As for consumables, today their choice is quite extensive, moreover, it is constantly updated with new solutions.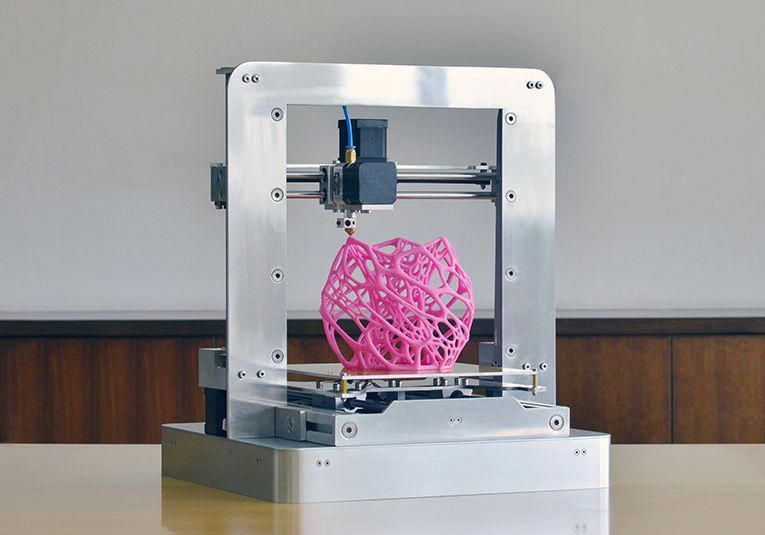
This makes it easy to find consumables that not only meet individual requirements to the maximum, but are also clearly suited to specific tasks. Today, photopolymer resins and thermoplastics continue to be in the greatest demand. The principle of operation of this type of equipment is as follows:
- In a special program, a product/object model is created, indicating the exact geometric dimensions;
- Processing of the prepared model using software. As part of the work, the model is divided into horizontal layers, sequentially converted into a digital code. It is he who will continue to give commands to the printer based on what, the technique will apply consumables;
- Printing in progress. At this stage, an object is formed by layer-by-layer application of the selected material. Note that printing features may differ slightly, which is determined primarily by the features of the equipment used in the work. Please note that the working body of the printer (print head) will move only in the horizontal direction.
 The material is fed and applied strictly in the parameters specified by the program. After applying one layer, the working platform is lowered down to a thickness equal to the layer, after which the next layer is applied. The process is performed until the object 9 is fully formed0006
The material is fed and applied strictly in the parameters specified by the program. After applying one layer, the working platform is lowered down to a thickness equal to the layer, after which the next layer is applied. The process is performed until the object 9 is fully formed0006
Features of printing on a 3D printer may differ slightly, which is determined by the printer model, as well as the technologies chosen for work. Therefore, it is important to study in detail the options used for printing technologies, compare them with each other, paying special attention to the advantages and disadvantages.
Choosing equipment, what to pay attention to
So, we note right away that 3D printing equipment will be expensive, so the choice of equipment should be taken with special responsibility. It is important to take into account the features of the intended use, as well as pay attention to the following characteristics of the equipment:
- Print resolution.
 The indicator indicates the minimum print height limit. The indicator is indicated in microns, the lower the height, the less noticeable the transition between layers will be. In addition, the final quality in terms of the smoothness of the surface of the completed object will depend on this indicator. However, the smaller the height of the print layer, the more time it will take to form the object. You should choose equipment in terms of resolution, focusing on the printing technologies that will be most often used in your work, as well as depending on the accuracy of the printheads, the selected consumables, and software settings.
The indicator indicates the minimum print height limit. The indicator is indicated in microns, the lower the height, the less noticeable the transition between layers will be. In addition, the final quality in terms of the smoothness of the surface of the completed object will depend on this indicator. However, the smaller the height of the print layer, the more time it will take to form the object. You should choose equipment in terms of resolution, focusing on the printing technologies that will be most often used in your work, as well as depending on the accuracy of the printheads, the selected consumables, and software settings. - Printing speed. How quickly the equipment can form an object depends on the accuracy. Therefore, it should be borne in mind that the higher the printing accuracy, the slower the speed of work will be, and vice versa.
- Printable areas. In this case, the size of the object that can be performed using the equipment will depend. Modern equipment provides for the digital designation of parameters.
 In this case, everything is individual and can be determined by the characteristics of the work, namely what exactly is planned to be done.
In this case, everything is individual and can be determined by the characteristics of the work, namely what exactly is planned to be done.
In any case, if you plan to purchase a printer for forming products in three-dimensional projection, then you should not save. It is important to opt for the equipment of well-known and trusted companies that provide warranties for their equipment.
You can choose from our catalog
Wedding Rings 1695
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1191
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 922
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1774
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 802
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1442
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1275
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1048
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1382
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 340
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 466
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Wedding Rings 1422
More info
Quick view
Add to favorites
Features of the operation of 3D printers and their use in practice
Many of the phenomena described in the science fiction works of Asimov, Clark or Verne have found their embodiment in reality. Nowadays, few people can be surprised by a cell phone, electric car or Skype, no matter the distance. However, there is a place for non-standard products today. We are talking about 3D printers.
Nowadays, few people can be surprised by a cell phone, electric car or Skype, no matter the distance. However, there is a place for non-standard products today. We are talking about 3D printers.
History of 3D printers
Chuck Hull is considered the founder of 3D printing. It was he who invented the first printer in 1984. The new technology was called "stereolithography" and was patented in 1986. The first device based on it was created in 1988 by 3D-Systems, founded by Chuck Hull. Already in 1993, Solidscape began mass production of inkjet-based 3D printers that could produce small parts with perfect surface quality. A major breakthrough was the creation of a device that can print three-dimensional objects in color. This happened in 2005 thanks to the efforts of Z Corp. Already in 2006, a printer appeared that could reproduce half of its own components.
What is a 3D printer and how does it work? He builds the final object by layering the material. The main elements of a 3D printer are the print head and the working platform.
 The printhead is needed to apply the layers of material and form the object. It can only move in a horizontal plane. The working platform moves in the vertical direction. It is necessary to place the object.
The printhead is needed to apply the layers of material and form the object. It can only move in a horizontal plane. The working platform moves in the vertical direction. It is necessary to place the object. Scheme of operation of the 3D printer
At the first stage of the device operation, its platform is located in the upper position. Then the print head forms the bottom layer of the future product. After its application, the platform descends exactly to the thickness of the layer and the head applies the next one. This cycle is repeated until the required object is "grown". This is how a 3D printer works. The consumables can be metal clay, ceramic powder, plastic filament or photopolymer resin.
3D Printing Technologies
There are various 3D printing technologies that allow you to understand what can be printed on a 3D printer. One of the earliest and most common is stereolithography or SLA. It is based on the ability of a liquid photopolymer resin to harden under the influence of a laser beam. To build each subsequent layer, the working platform is immersed in a container with liquid resin by a layer size of 0.05-0.15 mm. After leveling the surface, its formation begins. The main advantage of stereolithography is its high precision. Due to this property, it is used to make prototypes of dental prostheses or jewelry.
To build each subsequent layer, the working platform is immersed in a container with liquid resin by a layer size of 0.05-0.15 mm. After leveling the surface, its formation begins. The main advantage of stereolithography is its high precision. Due to this property, it is used to make prototypes of dental prostheses or jewelry.
SLA technology
Digital LED projection or DLP is also based on liquid photopolymer resins. Only in this case, the printer projects the image of the entire layer of the object at the same time until the resin hardens. The technology is highly accurate, allowing it to be used in the manufacture of souvenirs or jewelry, as well as in dentistry.
Another known method is selective laser sintering or SLS. In this case, the formation of the final object occurs as a result of layer-by-layer sintering of particles of powdered material under the influence of a laser beam. This printing technology has become widespread due to the ability to produce parts of complex geometric shapes. These include art and even sports shoes. Sand or composite mixtures, metals and alloys, various polymers can be used as consumables.
These include art and even sports shoes. Sand or composite mixtures, metals and alloys, various polymers can be used as consumables.
SLS technology
Electron beam melting (or EBM) technology is based on the use of electron emitters for layer-by-layer melting of metal powder in an airless chamber. This method allows you to create parts of high strength and density. The final products are indistinguishable in mechanical properties from cast ones. With the help of EBM, medical implants, parts of rocket and jet engines, bearing elements of aircraft are made.
Another technology to note is 3D inkjet printing or 3DP. In this case, three-dimensional objects are created by layer-by-layer application of any powders, including sand mixtures, plastics, and even metals. Color printing is provided by the addition of dyes to the binder. The 3DP method makes it possible to manufacture products of complex geometric shapes that will not be subjected to mechanical stress in the future.