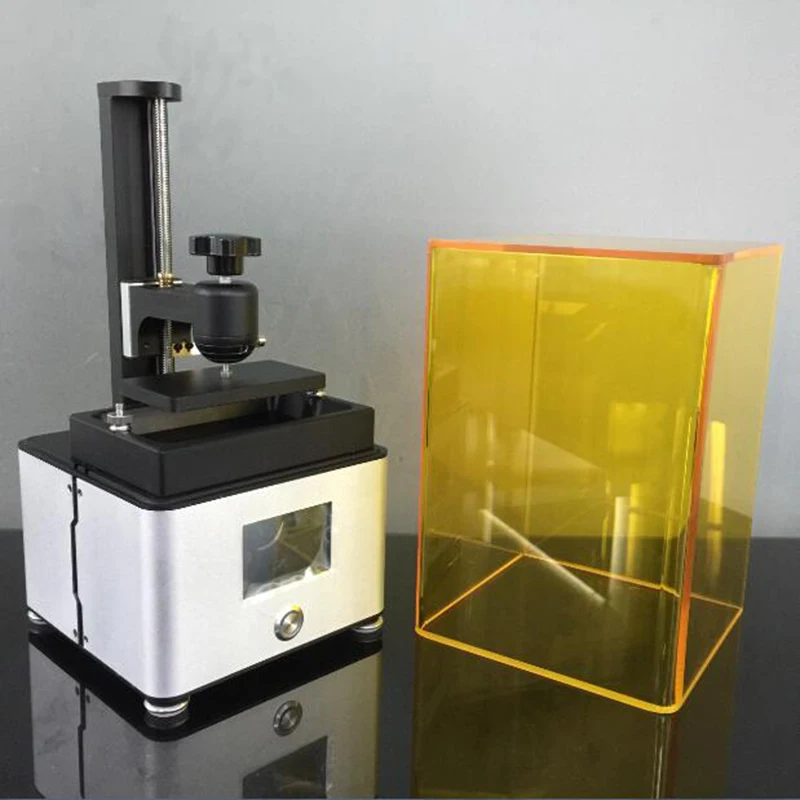
Dlp 3d printer for sale
Large selection of DLP, LCD & SLA printers
Sort byRelevanceBestsellersCustomer ReviewsPrice, Low to HighPrice, High to LowNew arrivalsHighest Discount
-
Elegoo Mars 3 Pro- 6.6 inch 4K monochrome display
- Large build volume (143 x 89.6 x 175 mm)
- High resolution - precise details
-
Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K- 4K resolution
- 35 micron precision
- 6.
1 inch monochrome LCD
-
Anycubic Photon Mono X 6K- For vivid 6K detail
- Impressive print speeds
- Powerful light matrix
-
Phrozen Sonic Mini 8K- Ultra-high resolution of 22 µm (1152 ppi)
- Extremely realistic textures
- 7.1 inch mono LCD screen
-
Elegoo Saturn S- Build volume: 196 x 122 x 210 mm
- Matrix light source
- Fast printing
-
Elegoo Saturn 2- Build volume: 219 x 123 x 250 mm
- 8K monochrome LCD
- 7680x4320 resolution
-
Phrozen Sonic Mighty 4K- 4K resolution
- 52-micron precision
- 9.
 3-inch monochrome LCD
3-inch monochrome LCD
-
Anycubic Photon M3- Large build volume (163.9 x 102.4 x 180mm)
- 7.6 inch 4K monochrome display
- LighTurbo Matrix light source
-
Phrozen Sonic Mighty 8K- 10" mono LCD screen
- Laser cut build plate
- Linear projection LED module
-
Elegoo Saturn 8K- For stable & precise prints
- Exquisite adhesion by sandblasting process
- Contains PFA film
-
Anycubic Photon Mono X2- 4K+ monochrome LCD display
- Anycubic LighTurbo Matrix light source system
- Dual linear rails for stability
-
Anycubic Photon M3 Max- 13" 7K monochrome display
- Large build volume (298 x 164 x 300 mm)
- High resolution - ultra-precise details
-
Anycubic Photon M3 Plus- 9.
 25" 6K monochrome display
25" 6K monochrome display
- Large build volume (197 x 122 x 245 mm)
- Smart resin filling
- 9.
-
Elegoo Jupiter- 12.8" 6K LCD display
- All-Metal Structure
- Automatic resin feed
-
Creality Halot-One CL-60- ARM Cortex-A53 M4 CPU
- WIFI / WLAN
- Monochrome LCD
-
Anycubic Photon Mono 4K- 4K monochrome LCD
- Large build volume
- Fast print speeds
-
Creality LD-006- 4K monochrome LCD display
- Large installation space of 192 x 120 x 250 mm
- High printing speed
-
Anycubic Photon D2- Larger build volume
- Longer lifetime
- Energy saving
-
Phrozen Sonic Mega 8K- 8K resolution
- 43-micron precision
- 15-inch monochrome LCD
-
Creality Halot-Lite- 8.
 9" monochrome LCD display
9" monochrome LCD display
- Large print size
- High precision & uniformity
- 8.
-
Zortrax Inkspire 2- Immediately ready to go
- Protective UV coverage
- With a resin tank
-
Zortrax Inkspire- Highest precision
- Easy operation
- External resins are supported
-
Anycubic Photon M3 Premium- 10-inch monochrome LCD display
- 8K resolution
- LightTurbo 2.
 0 light source system
0 light source system
-
Zortrax Inkspire & Ultrasonic Cleaner 1 set- Highest precision
- Easy operation
- External resins are supported
All prices incl. VAT.
Best resin 3D printers in 2022
What is the best resin 3D printer on the market?
Resin 3D printers are able to offer a very high level of detail and smooth surfaces. They are most commonly seen in dental labs and clinics as well as in jewelry workshops but are also increasingly popular with hobbyists and makers.
The way a resin 3D printer works depends on its technology: laser SLA (stereolithography), DLP (Digital Light Processing), or LCD-based (using an LCD screen to mask projected light).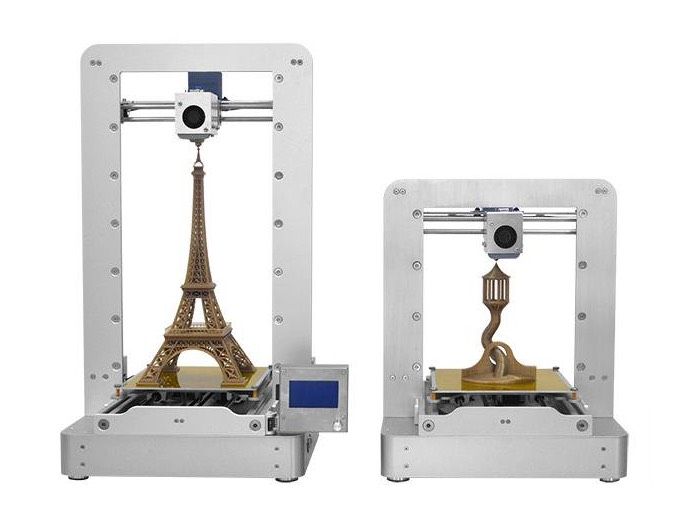
All resin 3D printers involve the same workflows, however, requiring several post-processing steps such as resin removal and post-curing.
In this guide, we take a look at some of the best resin 3D printers available in each category (SLA, DLP, and LCD) and provide you with key concepts linked to resin 3D printing.
The best resin 3D printers (SLA/DLP/LCD)
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | Original Prusa SL1 | 120 × 68 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.68 × 5.91 in | Czech Republic | $ 1,6991 727 €1,507 £253,246 ¥ | Buy |
| Peopoly | Phenom | 276 × 155 × 400 mm10. 87 × 6.1 × 15.75 in 87 × 6.1 × 15.75 in | China | $ 1,9991 899 €1,773 £297,963 ¥ | Contact |
| Formlabs | Form 3 | 146 × 145 × 185 mm5.75 × 5.71 × 7.28 in | United States | $ 3,4993 557 €3,104 £521,547 ¥ | Quote |
| UNIZ | SLASH 2 | 190 × 120 × 200 mm7.48 × 4.72 × 7.87 in | – | $ 3,5003 558 €3,105 £521,696 ¥ | Quote |
| FlashForge | Hunter DLP | 120 × 67 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.64 × 5.91 in | China | $ 3,9994 065 €3,547 £596,075 ¥ | Quote |
| DWS | XFAB | 180 × 180 × 180 mm7.09 × 7.09 × 7.09 in | – | $ 6,6006 000 €5,854 £983,770 ¥ | Quote |
| B9Creations | B9 Core 550 | 96 × 54 × 127 mm3.78 × 2.13 × 5 in | – | $ 9,95510 119 €8,830 £1,483,852 ¥ | Quote |
| Asiga | MAX | 119 × 67 × 75 mm4.69 × 2.64 × 2.95 in | – | $ 10,99011 171 €9,749 £1,638,125 ¥ | Quote |
| ETEC | Envision One | 180 × 101 × 175 mm7. 09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in 09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in | Germany | upon request | Quote |
Expand to see more specs
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).
| Brand | Product | Technology | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | Original Prusa SL1 | LCD | 120 × 68 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.68 × 5.91 in | Czech Republic | $ 1,6991 727 €1,507 £253,246 ¥ | Buy on Prusa |
| Peopoly | Phenom | LCD | 276 × 155 × 400 mm10.87 × 6.1 × 15.75 in | China | $ 1,9991 899 €1,773 £297,963 ¥ | Contact manufacturer |
| Formlabs | Form 3 | SLA | 146 × 145 × 185 mm5.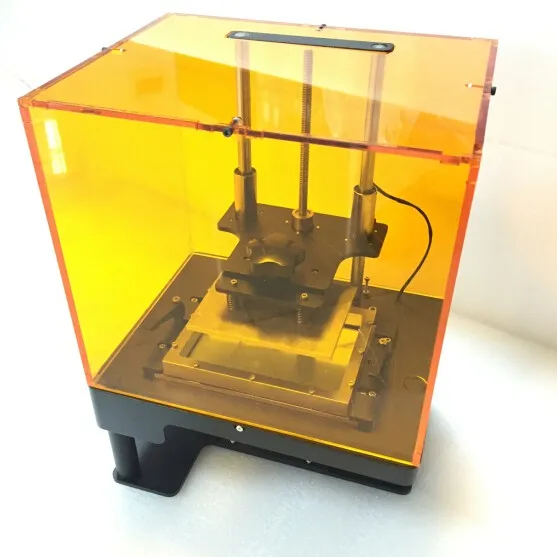 75 × 5.71 × 7.28 in 75 × 5.71 × 7.28 in | United States | $ 3,4993 557 €3,104 £521,547 ¥ | Get a quote |
| UNIZ | SLASH 2 | LCD | 190 × 120 × 200 mm7.48 × 4.72 × 7.87 in | – | $ 3,5003 558 €3,105 £521,696 ¥ | Get a quote |
| FlashForge | Hunter DLP | DLP | 120 × 67 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.64 × 5.91 in | China | $ 3,9994 065 €3,547 £596,075 ¥ | Get a quote |
| DWS | XFAB | SLA | 180 × 180 × 180 mm7.09 × 7.09 × 7.09 in | – | $ 6,6006 000 €5,854 £983,770 ¥ | Get a quote |
| B9Creations | B9 Core 550 | DLP | 96 × 54 × 127 mm3.78 × 2.13 × 5 in | – | $ 9,95510 119 €8,830 £1,483,852 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Asiga | MAX | DLP | 119 × 67 × 75 mm4.69 × 2.64 × 2.95 in | – | $ 10,99011 171 €9,749 £1,638,125 ¥ | Get a quote |
| ETEC | Envision One | CDLP | 180 × 101 × 175 mm7. 09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in 09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in | Germany | upon request | Get a quote |
Overview of the best resin 3D printers (SLA/DLP/LCD)
This overview is divided into three sections according to the resin 3D printers’ technology (SLA, DLP, or LCD).
The best SLA 3D printers (laser stereolithography)
Formlabs has been one of the main players on the professional resin 3D printer market for years. The Form 3, evolution of the award-winning Form 1 and Form 2, is their latest model, along with the Form 3L (large volume). This professional liquid resin printer boasts an array of practical features that make it a great choice for many businesses.
In the past, users have praised Formlabs’ hardware quality and precision, while criticizing the company’s decision to limit compatible materials to expensive Formlabs proprietary resins only. Today, the Form 3 features an “Open mode” that allows the use of generic materials.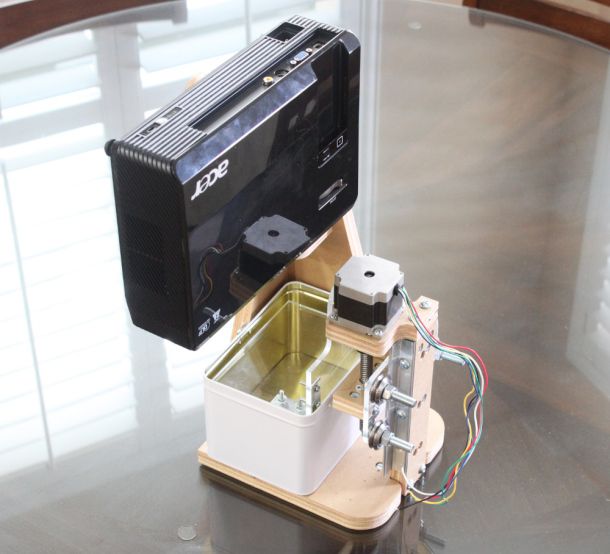
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Phenom is an affordable and large-format LCD (MSLA) 3D printer that is suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike. An advantage of this resin 3D printer is large-format. The Peopoly Phenom 3D printer also exists in larger versions: Phenom L, Phenom Noir, Phenom XXL.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
DWS Systems is specialized in manufacturing professional and industrial-grade resin 3D printers. The XFAB stereolithography 3D printer is their most affordable option, but is capable of delivering high-quality results. One of this SLA 3D printer’s most interesting characteristics is its cartridge resin system.
This makes material handling much easier and cleaner than with non-cartridge systems.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The best DLP 3D printers (Digital Light Processing)
This professional resin 3D printer boasts a number of user-friendly features including a touchscreen, automatic calibration, and Wi-Fi connectivity. FlashForge develops its own resins, but users may also use third-party materials.
FlashForge develops its own resins, but users may also use third-party materials.
With its special jewelry support mode, the Hunter DLP mainly targets jewelers.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
B9Creations’ Core series of 3D printers all provide fine levels of detail for professionals. According to the manufacturer, the B9 Core 550 resin 3D printer offers faster printing speeds (100+ mm/hour) than most DLP 3D printers in the same price range.
This digital light processing 3D printer is available with a smaller build volume (B9 Core 530).
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Envision One is a professional resin 3D printer produced by ETEC. ETEC, a German company known as EnvisionTEC before its acquisition by Desktop Metal in 2021, manufactures professional DLP 3D printers. The ETEC Envision One uses CDLP 3D printing technology. This 3D printer offers a build volume of 180 x 101 x 175 mm.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Asiga MAX is equipped with a resin level sensor, automatic calibration function and touch screen. Asiga also provides free lifetime technical support.
Asiga also provides free lifetime technical support.
This 3D printer is particularly suitable for the medical and dental sectors, being compatible with silicone resins.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The best LCD 3D printers (liquid crystal display)
For many years, Prusa Research has been famous for manufacturing reliable 3D printers. The Original Prusa SL1 is Josef Prusa’s first resin 3D printer, but there is no doubt that it has been endowed with as much quality as the award-winning Prusa MK3 FDM 3D printers.
This LCD 3D printer– which is also available as a DIY kit– is packed with features such as a tilted print bed, auto calibration, vapor extraction, and more.
Buy on Prusa Get a quote Add to comparison
The SLASH 2 is a desktop resin 3D printer produced by UNIZ. UNIZ is a 3D printer manufacturer based in China. The UNIZ SLASH 2 uses resin 3D printing technology. This 3D printer offers a build volume of 190 x 120 x 200 mm.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Resin 3D printers under $1,000
As LCD screens are very affordable, they have been the key to bringing resin 3D printing to the masses. Indeed, more and more manufacturers are launching affordable desktop resin 3D printers with LCD 3D printing technology, and the price drop is radical.
These affordable resin 3D printers obviously can’t be expected to provide the same level of detail and accuracy as the professional 3D printers listed above. However, they are great as an introduction to resin 3D printing and they do produce good quality prints.
Read our full-length budget resin 3D printer article for a list of affordable machines (starting from $149).
Post-processing for resin 3D prints: necessary steps
Resin removal
Since the objects are printed within a tank of resin, resin drips off of the objects as they are lifted up and out of the tank. There’s always a layer of uncured resin left on the object, and it must be removed with IPA (isopropyl alcohol).
There’s always a layer of uncured resin left on the object, and it must be removed with IPA (isopropyl alcohol).
This can be done manually by dipping the part in an IPA bath and gently scrubbing the part with a soft brush, but it is quite time-consuming.
For users that produce resin parts on a regular basis, there are machines called resin washers, or resin cleaners. Ackuretta, for example, markets Cleani, a dual-tank resin cleaner that can wash both the parts and the printer’s platform (yes, that needs to be washed, too.).
Post-curing
When removing a resin 3D printed part from the build plate, it is still soft and slightly malleable. To reach its final physical state the part must go through a post-curing step. This means exposing the object to heat or light. Various SLA post-curing techniques exist:
UV curing chamber / UV cure box
Professional users will definitely want to use a dedicated UV curing chamber for their parts in order to get the most out of the material (strength, for example). Most resin 3D printer manufacturers have UV curing chambers available separately.
Most resin 3D printer manufacturers have UV curing chambers available separately.
UV nail lamp
For small parts, nail UV lamps can do the trick. There are dozens of nail UV lamps available for less than $50.
DIY UV curing chamber
Crafty people also have the possibility to make their own UV curing station!
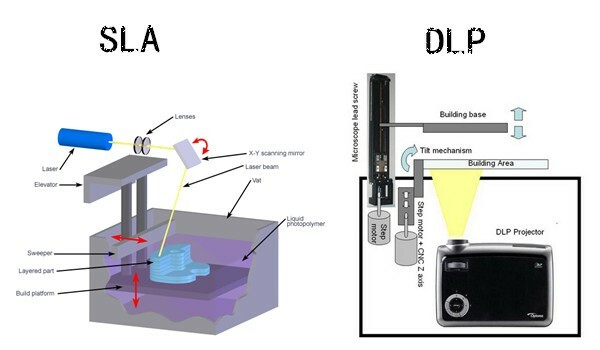
How do resin 3D printers work and what are the differences between LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printing?
SLA 3D printers, LCD 3D printers, and DLP 3D printers all use liquid resin as a 3D printing material. The resin, a photopolymer, becomes solid when cured (activated) by a specific light source.
That light source cures the liquid resin, which is stored in a tank or vat, to form the object layer after layer.
The resin solidification process (photopolymerization) is at the core of three main 3D printing technologies:
- Laser-based Stereolithography (SLA): a UV laser cures the resin in the tank to form the object point by point.

- Digital Light Processing (DLP): the resin is cured by a light projector one whole layer at a time. The light shines in a specific shape depending on the layer.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) or Masked SLA (MSLA): An array of LED lights shine through an LCD screen. The LCD screen acts as a mask or stencil between the LED and the bottom of the resin tank, only letting light through in specific shapes.
All of these resin-based 3D printing technologies form part of the same family: stereolithography. That’s why some manufacturers include “SLA” in the name of their 3D printers, while they actually use DLP or LCD-based technology.
SLA, DLP, and LCD 3D printing technologies.Laser-based SLA 3D printing technology
An SLA 3D printer cures the liquid resin spot by spot with a laser, so it is potentially more precise than DLP 3D printing.
Contrary to DLP 3D printing, the build volume is completely independent of the resolution of the 3D print.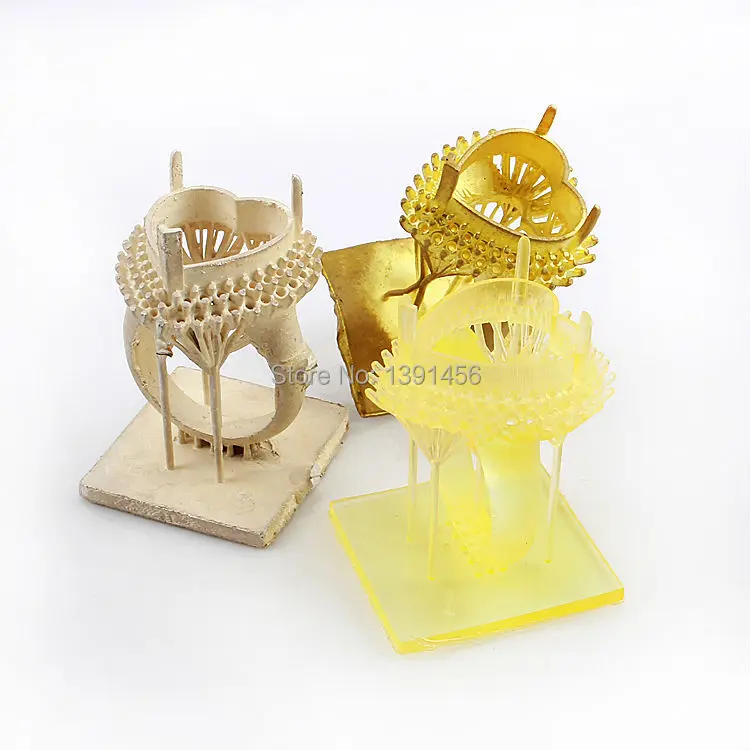 A 3D print with a laser stereolithography 3D printer can be of any size and resolution.
A 3D print with a laser stereolithography 3D printer can be of any size and resolution.
DLP 3D printing technology (digital light processing)
DLP 3D printers use a light projector. The layer’s shape is defined by reflecting or deflecting light with mirrors. With DLP, the 3D printer is able to cure a whole layer of resin at once. Therefore, a DLP 3D printer can potentially 3D print faster than an SLA 3D printer, as an entire layer is exposed all at once instead of one spot at a time with a laser.
However, a DLP 3D printer’s resolution depends on its projector and how many pixels/voxels are available (a full HD projector usually offers 1080p). A 3D printer with a large build volume has a fixed number of pixels, making it impossible to 3D print small details when building at full scale.
The projector used by the DLP 3D printer is less expensive and easier to change than the laser used by SLA 3D printers.
LCD-based resin 3D printing technology
Most LCD resin 3D printers use an LCD screen as a photomask– like a stencil– above another light source (LED, UV…). This is where LCD resin 3D printing is different than DLP 3D printing, which makes use of mirrors or other complex systems to direct the light into a certain shape. The technology is also called Masked Stereolithography (MSLA).
This is where LCD resin 3D printing is different than DLP 3D printing, which makes use of mirrors or other complex systems to direct the light into a certain shape. The technology is also called Masked Stereolithography (MSLA).
Since LCD screens are inexpensive, this technology has made resin 3D printing much more affordable than before and there are now dozens of low-cost, budget resin 3D printers available for a couple of hundred dollars.
In some cases, the light emitted by an LCD screen is used to directly cure the daylight-sensitive resin.
What is best between LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printers?
The answer depends on the user’s needs in precision, speed, and budget. We can highlight that:
- Laser SLA 3D printers are best for 3D printing highly detailed and intricate 3D prints, big or small.
- LCD and DLP 3D printers are best for 3D printing batches of small parts, or quickly 3D printing large parts without too many details.
- LCD-based 3D printers are generally much more affordable than SLA and DLP 3D printers.
Main resin 3D printing applications
Samples by La Bête à Pois, SprintRay, and Photocentric (top to bottom). Source: AniwaaResin 3D printers mostly target professional users. Indeed, they are suited for specific applications requiring high levels of detail and top-quality finishes. These applications include:
Resin 3D printers for jewelry
Jewelers use high-precision 3D printers to create molds with the lost wax technique and create incredible jewels.
SLA, DLP, and LCD 3D printers in dentistry
Dentists and dental labs are starting to use resin 3D printing to build dental crowns, mouth guards, surgical guides, and much more.
Resin 3D printing in medical and healthcare fields
SLA and DLP 3D printing can be used to create medical appliances such as hearing aids.
Hobbies: resin 3D printer for miniatures
Some tinkerers, DIYers, and cosplayers love 3D printing miniatures and figurines.
Key benefits and limitations of resin 3D printing
Benefits of LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printing technologies
These are some of the advantages of 3D printing with resin:
- Ability to build small and very detailed parts or objects with fine, complex geometries
- Diversity of 3D printable resin materials (ceramic, metal, biocompatible, flexible, rigid, etc.)
- Smooth finish of the parts produced (no easily visible layers like with FFF 3D printers)
Limits of resin 3D printing
As with any technology, resin 3D printing has its limits:
- Post-processing is mandatory (removing delicate support structures, post-curing, resin removal, etc.) and requires a UV curing chamber for good results
- Requires time-consuming cleaning time (for the vat and for the 3D printed part)
- Very smelly and toxic fumes
- Safety precautions required when handling the material
Resin 3D printer price
Laser SLA resin 3D printer price
SLA 3D printer prices depend on many factors. The price for a basic SLA 3D printer kit like the Peopoly Moai usually starts at about $1,200. Industrial resin 3D printers, on the other hand, can reach several hundred thousand dollars.
The price for a basic SLA 3D printer kit like the Peopoly Moai usually starts at about $1,200. Industrial resin 3D printers, on the other hand, can reach several hundred thousand dollars.
DLP resin 3D printer price
The price of a DLP 3D printer generally starts around $2,000 or $3,000. DLP 3D printers with higher precision and more features cost around $10K to $20K. More expensive digital light processing 3D printers also exist.
LCD resin 3D printer price
LCD-based resin 3D printers are the most affordable resin 3D printer type. There are many LCD resin 3D printers available for under $1,000, and even under $300. Higher-quality LCD 3D printers may cost a few thousand dollars.
UV curing chamber price
Most resin 3D printer brands sell UV curing chambers separately, with prices starting around $300 to $500.
FAQ
What does SLA stand for in 3D printing?
In 3D printing, SLA stands for stereolithography.
What does DLP stand for in 3D printing?
In 3D printing, DLP stands for Digital Light Processing.
What does LCD stand for in 3D printing?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, which is a type of screen used in electronic devices (smartphone, TV, etc.). A growing number of resin 3D printers use an LCD screen’s light to cure light-sensitive resin and form objects in 3D.
What is SLA resin made of?
SLA resin is a photopolymer material, which is mainly composed of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators. Depending on the “recipe”, the stereolithography resin can be plastic, ceramic, or even metal-based.
How much does a resin 3D printer cost?
A resin 3D printer can cost anywhere from $500 to over $250,000. However, there are many resin 3D printers available for under $10,000.
What is a resin 3D printer?
A resin 3D printer (stereolithography) is a machine that solidifies liquid resin layer by layer to form an object in 3D.
Where are resin 3D printers for sale?
There are resin 3D printers for sale on major e-commerce sites like Amazon, AliExpress, GearBest, and Banggood. Online retailers specialized in 3D printing also exist, such as MatterHackers.
90,000 differences SLA/DLP/LCD Printers, Printing examples, ApplicationContent
-
- SLA
- Principle of operation
- PLASUS
- Printing
- Printers 9009 9000 9000) work
- Pros
- Cons
- Printing example
- Best DLP printers
- SLA
- LCD
- How it works
- Pros
- Cons
- Printing example
- Best LCD printers
- Scope
- Summary
Photopolymer printing is usually associated with delicate, miniature products. After all, it is photopolymer printers that come to the rescue if you need to make a small but detailed model.
After all, it is photopolymer printers that come to the rescue if you need to make a small but detailed model.
Currently, photopolymer printers can work on one of three technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. Each of the technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages. nine0003
In order not to make a mistake with the choice of model, you need to understand which technology is suitable for printing specific products. For example, for a jeweler and a dentist, the main criterion will be accuracy, and for a person who plans to print figurines for his hobby, the quality of the surface and the not very expensive cost of consumables.
SLA
SLA is one of the first patented 3D printing technologies. It was patented in 1986 by Charles Hull. DLP and LCD are similar in basic principles to SLA, but appeared much later. nine0003
How it works
As a material for printing, SLA printers use photopolymer resins - light-sensitive polymers that harden under the influence of a certain spectrum of UV radiation.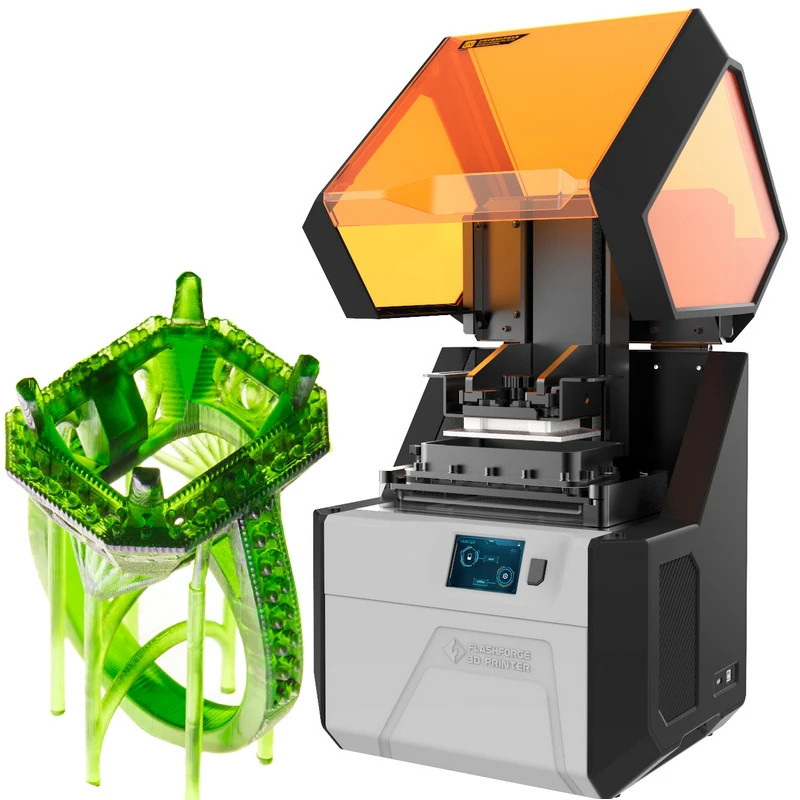
A laser beam is used as a “hardener”, which is focused on the desired point with the help of mirrors. The beam sequentially “draws” a slice of the model. So gradually, layer by layer, the model is “grown” on the desktop.
How SLA technology works
There are two options for the location of the printed table - top and bottom.
Top table
Visually it looks like an inverted FDM machine, the model is printed upside down on such a machine. The table moves during printing from the bottom up, the laser module is located at the bottom of the machine, under the polymer bath. The bottom of the bath is usually made of silicone - it transmits UV radiation well and practically nothing sticks to it. nine0003
Top position printer model
This is the most popular desktop SLA printer solution.
Table down
The laser module is located at the top of the printer above the resin bath, and the printing table, during printing, gradually lowers down, plunging into the resin.
Industrial SLA with table bottom
This arrangement is traditionally used in industrial machines with a large print area. The only inconvenience is that the bath must always be filled with a photopolymer. And when changing the type of resin, you will have to completely drain the entire photopolymer and thoroughly wash the bath.
Pros
-
Large selection of consumables. Due to the growing popularity of photopolymer printing, many specific resins have appeared - from soft flexes to photopolymers with increased strength characteristics (for example, there is a very strong, biocompatible photopolymer for making temporary dental crowns). nine0003
Cons
-
Expensive consumables.
Printing example
Cardiac muscle printed on Formlabs Form 3
SLA printed rings
Prototype Spoon
Butterfly figurine printed on Formlabs Form 3
Technical model
Snow shovel prototype.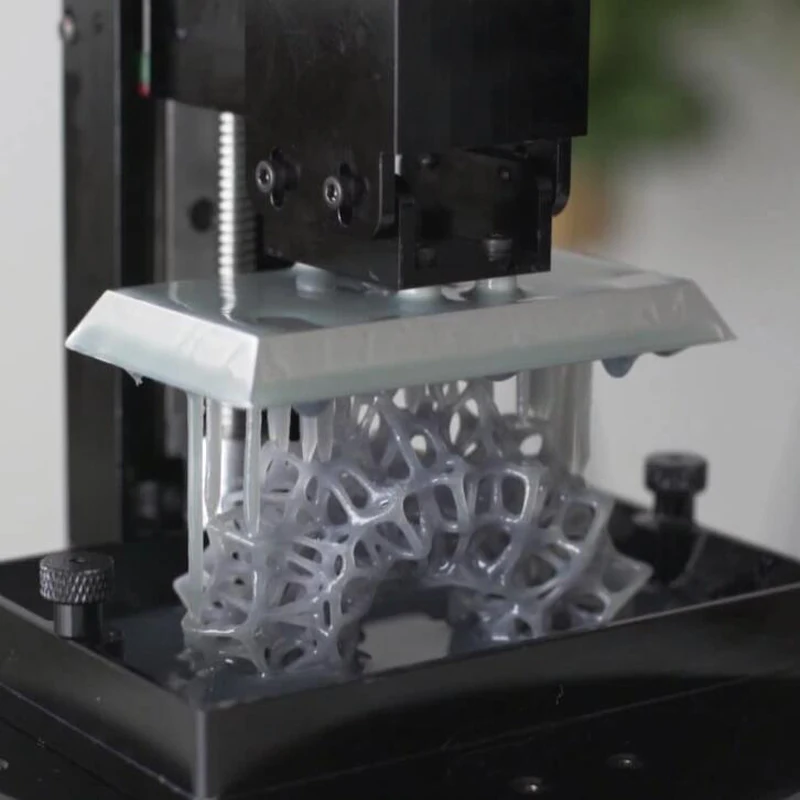 Made on Formlabs Form 3L
Made on Formlabs Form 3L
Top SLA printers
The leader in the production of SLA printers is Formlabs. In the Formlabs lineup, you can find both small desktop models and professional machines with a large print area. nine0003
Form 3
Formlabs Form 3
Specifications:
-
XY resolution: 25 µm
-
Laser spot size: 85 µm
-
Laser power: One 250mW laser
nine0010 -
Working area size: 14.5×14.5×18.5cm
-
Layer thickness: 25 – 300 µm
This printer can be compared to a small professional machine. Despite its small dimensions, it can easily cope with the most complex models.
Formlabs Form 3L
Formlabs Form 3L Versus Form 3
-
XY resolution: 25 µm
-
Laser spot size: 85 µm
-
Laser power: One 250mW laser
-
Working area size: 33.
 5×20×30cm
5×20×30cm -
Layer thickness: 25 – 300 µm nine0003
This printer allows you to print large format models or quickly produce small batches of products.
With the advent of faster and cheaper technologies, SLA printers have become less popular. They are mainly used in industries with high requirements for quality and print stability.
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go nine0003
| Manufacturer | Formlabs |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Formlabs |
DLP
DLP technology is based on the principles of SLA, but instead of a laser, a projector is used as a source of UV radiation. nine0003
How it works
The material used is photopolymer resin, but unlike SLA, the light source is not a beam, but a DLP projector. This significantly speeded up printing, because the projector, unlike the beam, illuminates the entire layer at once.
This significantly speeded up printing, because the projector, unlike the beam, illuminates the entire layer at once.
How DLP technology works
The projector is located at the bottom of the printer, under the resin tank. The bottom of the container is usually made of a transparent, wear-resistant film. Such a film transmits UV radiation well, practically nothing sticks to it, and if it breaks, it can be easily replaced. nine0003
Pros
Cons
-
Parasitic light is possible. Exposure of the entire layer at a time can cause parasitic illumination of the resin.
-
projector resource. The projector is the heart of a DLP printer. Be sure to pay attention to the resource of the projector. For example, FlashForge Hunter claims a minimum projector life of 50,000 hours. This is a lot.
nine0020 -
XY Resolution: 0.
 0625mm
0625mm -
Print speed: 10mm/h
-
Light source: 405nm LED
-
Working area size: 120x67.5x150 mm nine0003
-
Layer thickness: 0.025-0.05mm
-
Less accurate. Budget models are good for printing miniatures or figurines, but their accuracy may not be enough for, for example, jewelry. nine0003
-
The print quality may not be the same over the entire printable area. Since an array of LEDs is used as the UV source rather than a single light source, the work area may be illuminated unevenly. This problem can be solved programmatically or physically.

-
LCD display resolution: 854x480 px nine0003
-
XY Positioning Accuracy: 0.1155mm
-
UV wavelength: 405 nm
-
Working area size: 97x54x150 mm
-
Layer thickness: 0.
 01-0.2mm
01-0.2mm -
LCD display resolution: 2560x1620 (2K)
-
XY Positioning Accuracy: 0.051mm
-
UV wavelength: 405 nm
-
Working area size: 130x80x165 mm nine0003
-
Layer thickness: 0.01-0.15mm
-
LCD resolution: 6.1" 4K Mono LCD
-
XY positioning accuracy: 35 microns
-
UV wavelength: 405 nm
-
Working area size: 134x75x130 mm
-
Layer thickness: 0.
nine0010 01-0.30mm
01-0.30mm -
LCD resolution: 6.3" 2K HD
-
XY Positioning Accuracy: 0.055mm nine0003
-
UV wavelength: 405-410nm
-
Working area size: 140x78x200 mm
-
Layer thickness: 35-100 microns
Printing example
A batch of rings printed with DLP technology
Ring patterns printed on FlashForge Hunter
Props for miniatures 28 mm
Jaw model made on FlashForge Hunter
Best DLP Printers
FlashForge Hunter
Specifications:
FlashForge is renowned for the quality of its printers. Hunter is no exception. It turned out to be a good “workhorse” capable of solving a variety of tasks.
DLP technology is used less and less. It is being stubbornly replaced by more affordable 3D printers based on LCD technology.
LCD
LCD technology is the youngest among photopolymer printers. Initially, LCD appeared as a more affordable analogue of DLP technology, suitable for home use. nine0003
The first LCD printers had a number of unpleasant children's sores (uneven illumination of the working area, etc.), which over time were resolved or compensated. With the development of technology, in addition to models for home use, devices have appeared that are not inferior in accuracy to DLP and can be used for production tasks.
How it works
The technology almost completely copies DLP, only LEDs are used instead of a projector. Under the bath is an LCD display (similar to the display of a smartphone or tablet), which dims in some places, allowing light to pass through only in the right places. nine0003
How LCD technology works
Since the module with the screen and LEDs is located at the bottom of the printer, the bottom of the resin tank is transparent. As with DLP, transparent film is usually used.
Pros
Cons
Print example
Small miniature made with Anycubic Photon Mono
Troll printed on LCD machine
Model switchgear busbars made of soft polymer
Castle model made on Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K
nine0077 Figurine made with Anycubic Photon Zero
Troll printed on LCD printer
Best LCD Printers
Anycubic Photon Zero
Anycubic Photon Zero
Specifications:
Budget model focused on home use. Good for home use. nine0003
Anycubic Photon Mono
Specifications:
Anycubic Photon Mono is already a more serious device. Thanks to the LCD display of higher resolution, it was possible to increase the accuracy and quality of the finished models.
Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K
Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K
Specifications:
Mono LCD matrix, with high resolution, allows you to print very quickly and accurately.
Wanhao GR1
Specifications:
The larger working area allows you to make more models at once, and a special UV-LED matrix ensures uniform illumination.
LCD printers are successfully capturing the market by displacing more expensive DLP and SLA printers. This of course contributes to their availability and a wide variety of models. nine0003
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Anycubic |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Phrozen |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Anycubic |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | nine0284 Wanhao
Application
Dentistry
Precision is very important in dentistry. A slight distortion of even 0.1 mm can make the painstaking work of making a crown or prosthesis useless.
A slight distortion of even 0.1 mm can make the painstaking work of making a crown or prosthesis useless.
Jaw Model
3D printed aligner
In addition to the accuracy of the printer, the material chosen also plays an important role. It is necessary to use special resins with a small percentage of shrinkage. nine0003
Jewelry production
The full potential of photopolymer printers is revealed in the jewelry industry. In addition to precision, detail and perfect surface quality are very important.
Ring made of burn-out photopolymer
From model to finished product
Previously, such products had to be very painstakingly cut by hand or made from wax on high-precision CNC machines. Now it is enough to make a digital model and, with the help of a printer and burnt resin, quickly produce the required number of products ready for casting. nine0003
nine0003
Prototyping
Printing prototypes, making master models, etc.
Helmet and other photopolymer prototypes
Prototype housings
FDM technology is not suitable for everything. Sometimes you need to quickly make a model of a future product with a smooth surface, professional photopolymer printers can easily cope with this task. nine0003
Hobby
Affordable photopolymer printers have become a great help for miniature lovers. It is much easier to model and print a 28 mm action figure of your favorite hero than to make it by hand for a long time and painstakingly.
Soviet motorcyclist in 28mm scale
“Spare parts” for miniature 28mm
nine0003
And large decorative figurines are more accurate compared to FDM printing. After the LCD printer, you do not have to sand the model for a long time to smooth out the layers.
bust of a girl
Modeling
For large and sketchy layouts, FDM printers can be used, but their accuracy is not enough for making small parts. Having a 3D model, you can quickly make a very accurate and detailed layout of a building or an entire block. nine0003
Model of the statue of V.I. Lenina
Printed and painted building layout
Summary
Despite all the advantages of photopolymer printers, there are small nuances that are common to all technologies.
Washing the model. After printing, the model must be washed from resin residues. The best way is an ultrasonic bath with alcohol, sometimes you can get by with a glass of isopropyl alcohol and a brush. nine0003
“Illumination” in the UV chamber. After rinsing, the model must be “additionally illuminated” in a UV chamber, otherwise the polymer will not gain the strength declared by the manufacturer.
To illuminate the model, you can use a regular UV lamp or a manicure machine. They will cost less than professional dryers, although it may take more time to “light up”. Before buying, make sure that the lamps shine in the desired UV spectrum.
strength of polymers. Despite the huge variety of resins, they are still inferior in strength to the plastic filaments used by FDM printers. The exception is some highly specialized resins. nine0003
For some, these nuances can be significant disadvantages, but despite this, photopolymer printers are used both as home printers and as work machines in various fields.
DLP and SLA technologies and what is print quality
Colleagues, today we will talk about sore!
Namely, how some 3D printer sellers try to sell you their product by hook or by crook....
First, let's talk about the two most common 3D printing technologies: DLP and SLA, these are the most common 3D printers in dentistry.
In the dental market today, DLP and SLA printers are the most popular, what is the difference between these two technologies?
Both DLP and SLA use "liquid plastic" as their printing stock, in other words a photopolymer that cures and solidifies when exposed to UV radiation. nine0003
A bit of history:
Pioneers in the development of dental 3D printing and the creation of a wide range of biocompatible polymers is the Dutch company Nextdent, formerly known to everyone as Vertex.
This winter, seeing the great potential of these biocompatible materials, Nextdent was bought by the father of 3D printing, 3D giant American company 3D Systems.
Getting certified for biocompatible materials is not easy, so Nextdent photopolymers are purchased by other companies and sold under their different brands: Formlabs, Novux and others. nine0003
Now back to 3D printing technologies.
DLP. Printing principle:
The program that comes with the printer splits the printed object into layers with a given thickness.
Pour photopolymer (print material) into the transparent bottom tray of the printer.
A working table sinks to the very bottom of the bath, retreating from the bottom to one (first) layer of our object (in this "indentation" there is a liquid photopolymer).
The projector located under the bathtub projects the image of the first layer onto the bottom of the bathtub, and thanks to UV radiation, only the plastic material on which the image from the projector hits hardens. nine0003
Next, the worktable rises one more layer and again a new layer is highlighted, which is attached to the previous one.
This is how our printed object grows layer by layer, be it a jaw model or a temporary crown.
SLA. Printing principle: The printing principle is similar, but with the difference that it is not the entire layer that is projected, but a laser beam quickly passes through each point of the object, which polymerizes the liquid photopolymer (material)
printer and its materials, but there is one clear indicator that almost everyone is guided by. And of course, this indicator is mainly played by sellers of 3D printers. nine0003
And of course, this indicator is mainly played by sellers of 3D printers. nine0003
Have you guessed what their main argument is when they sell you their printer?
That's right!
Precision printing!
Let's then deal with this popular parameter, which is twisted in one direction or another intentionally or due to incompetence.
Printing precision .
This parameter depends on many factors, moreover, not only on the printer, but also on the material and environment.
How does it depend on the material? nine0003
The more opaque the material (filled with pigments and light blockers), the more accurate the prints will be. This is due to the absence of light scattering during printing and polymerization of the material adjacent to the model.
How does it depend on the environment?
When printing with photopolymer, it is important to control its temperature during printing.
DLP printers generate a lot of heat during curing.
How does high temperature affect printing?
Very simple, the chemical reaction is accelerated and there is too much current light to polymerize the material.
Increases the risk of polymerization of the boundary layer of the model (exposure of excess plastic), respectively, an increase in its size, in other words, loss of accuracy.
In SLA printers, this is not so scary, since the laser has less power (generates less heat), the volume of the bath for the material is usually much larger (than in DLP printers), which leads to the fact that the photopolymer in the bath heats up more slowly and there is no risk of overheating. nine0003
This is why SLA printing takes a little longer, but it does not have the risk of overheating and loss of accuracy, as in DLP printers.
So, to get the most accurate printed product, and it's hot in your room - control the temperature of the polymer used.
Cold is also not the best option, because the material may not have enough light, it will not fix on the print table and you will have to warm up the material and start the entire printing process from the beginning.
Of course, fiddling with heating the material is not very convenient! nine0003
But if your printer has an automatic media warming feature, you won't have to do this manually.
We use a Formlabs Form 2 3D printer and love it for having a built-in heater that prepares the plastic before printing by heating it up to operating temperature.
So, we come to the most mysterious parameter - the accuracy of the printer itself.
Two concepts are often confused here - print accuracy and print resolution. nine0003
In a DLP system, we are limited by the resolution of the projector.
For example, if the projector built into the printer has a full HD resolution, then the printable area, in which the size of each projected pixel will be relatively small, will be about 115x70 mm. This field is not enough for printing dental work.
And by increasing the printable area, pixels will increase in size and print accuracy will be lost.
There are no pixels in the SLA system. Here, polymerization occurs due to the smooth movement of the laser beam. Therefore, the print field may be larger than in DLP systems. nine0003
Here, polymerization occurs due to the smooth movement of the laser beam. Therefore, the print field may be larger than in DLP systems. nine0003
For example, in the Formlabs Form 2 printer, the print field is 145x145 mm, almost 3 times larger.
For printing dental models, a large field is very convenient, as they can be placed on the table a lot and printed in one go, saving time.
It's no secret that this printer is the most popular among dentists and laboratories around the world.
It has clear, obvious advantages and low cost.
And of course they try to compete with him! nine0003
Many manufacturers and vendors match their 3D printers with the Formlabs leader, giving false information about it.
There are legends and myths about the accuracy of the Form 2 printer (from Formlabs), not only in the Russian, Ukrainian markets, but also in international forums.
Who says that the accuracy of the Form 2 printer is 150 microns, who says 200 .