Dissolvable filament 3d printer
PVA Filament Review - Best Soluble, Dissolvable Strand For 3D Printing
PVA filaments are among the most popular materials to use for 3D printing. It can be used independently, and it can also be used as a support material for PLA filaments.
PVA filament is among several types of filaments that can be used for 3D printing. Each of these filaments has their own distinct advantages. As for PVA, its unique characteristic is that it can quickly dissolve in water.
It highly depends on your project as well as your creative pursuits but PVA 3D printer filament can offer a lot when it comes to providing innovative solutions for your 3D printing projects. However, you must first understand how PVA should be stored and how it can be used so you can make the most out of the material. Read more to
Contents
- 1 What is PVA Filament
- 2 Advantages of Using PVA
- 3 Disadvantages of Using PVA
- 4 PVA Filament Settings
- 5 PVA Filament Temperature
- 6 Drying Your PVA Filament Before Using
- 7 How to Dissolve the PVA Filament?
- 8 PVA Support Material Limitations
- 9 3D Filament Storage Tips for PVA
- 10 Best PVA Filament: Top 3 Brands On The Market
- 10.
1 1. eSUN PVA Filament
- 10.2 2. Gizmo Dorks PVA Filament
- 10.3 3. Rigid.Ink PVA Filament
- 10.
- 11 Conclusion
What is PVA Filament
PVA is the acronym for PolyVinyl Alcohol. It can also be shortened to PVAL of PVOH. It is a synthetic polymer. The process first begins with the polymerization of vinyl acetate so that it can form polyvinylacetate. After that, it is hydrolyzed so that the PVA filament can be created. You now have the material that you can use for 3D printing.
PVA is a material that is water soluble and is usually utilized as a support material. But the PVA can still be independently used in 3D printing.
When used as a support material, you can use PVA filaments for printing complex designs. This is because, with such designs, the manual removal of the material supporting it is difficult if not impossible.
But with PVA material, you just need to leave it in a water bath for a night, and it will dissolve the material completely.
📌What you have to keep in mind when using PVA is that it is hygroscopic. This means that it can absorb water from the air easily. You have to be mindful when it comes to storing PVA filaments by using sealed containers. You can even dry it in an oven prior to using it for printing.
Advantages of Using PVAA primary advantage when it comes to using PVA is that it dissolves in water. You may not immediately like the idea that your print is water-soluble. However, there are specific applications where that is exactly what you want to happen.
A good example is when you will need to print a support structure for your other prints and you need to remove that support when it is no longer needed. You can just submerge the print in water overnight and it will dissolve it leaving the main print as it is.
You can just submerge the print in water overnight and it will dissolve it leaving the main print as it is.
Another advantage of using water soluble PVA filament is that it is sustainable and biodegradable. It is also non-toxic as there is no oil needed in the process of its production.
When you just want to print prototypes or test out some prints, this is a great material to use because you can dispose of it and it will just decompose.
Disadvantages of Using PVASince PVA 3D filament easily dissolves in water which is its unique feature as it can be used in many applications, it is also its disadvantage. Again, it depends on your project and the purpose of your print. There may be times that PVA dissolvable filaments won’t be the best material to use.
When the print becomes exposed to weather, moist environments, or water, then the print is at risk of dissolving. Another thing to consider is the manner of storing this material.
Another thing to consider is the manner of storing this material.
It can be quite challenging to not expose it to moisture. Once you do, it will be damaged and it will affect the quality of your print. You will observe bubbles in the print
In addition, you also need to keep PVA filaments away from high temperature and heated elements because it has a low melting point. The melting point of PVA is just at 190°C. When it is exposed to temperature above 200°C, it will undergo pyrolysis.
When this happens, tar jams will be formed and those are hard to remove. You have to be careful about setting the right temperature because applying force or increasing the temperature will not be able to clear up the nozzle. When the nozzle is jammed, it needs to be re-drilled or even replaced.
PVA Filament SettingsFirstly, when using PVA filament 1.75, you will need a 3D printer that can perform dual extrusion. It is highly advisable that you use PVA alongside PLA filaments as the primary material because of the similar printing temperature of the two, making them a good pair.
It is highly advisable that you use PVA alongside PLA filaments as the primary material because of the similar printing temperature of the two, making them a good pair.
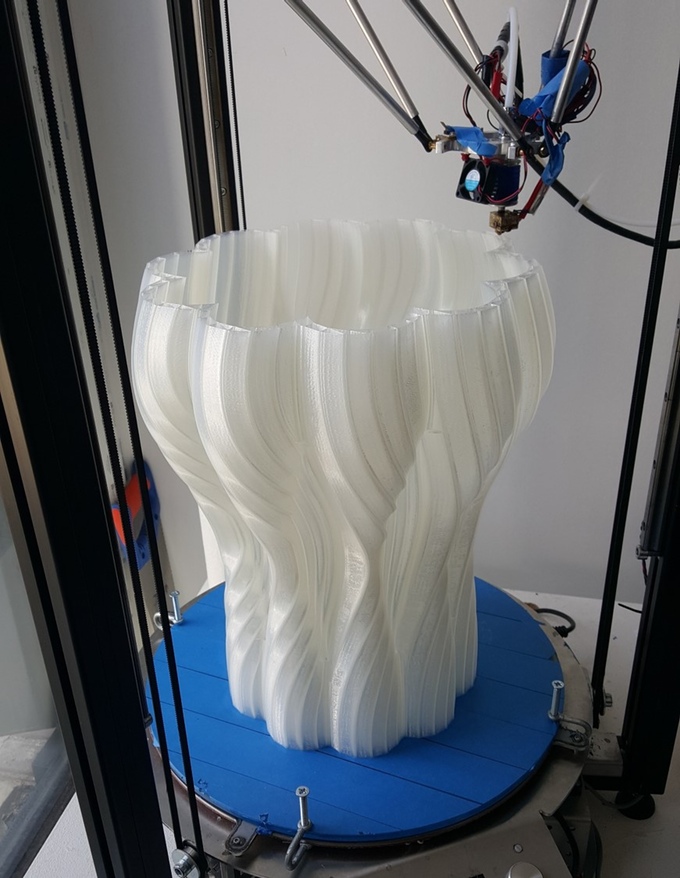
With dissolvable supports, you can print parts that have intricate details, parts with internal cavities that you will have a hard time clearing if you will use the same material for support, or suspended parts that you don’t want to have any scarring when you remove the support.
When you use PVA filament 3mm as support material, you just have to soak the parts, wait overnight, and see your masterpiece in the morning.
PVA Filament TemperatureYou have to be aware that the brand of filament PVA that you will use is also a factor in the temperature setting. The PVA filaments from MatterHackers print at around 185°C. For Ultimaker, the temperature for printing is at around 215°C.
Remember not to set the temperature too high when you are using PVA filaments because it is prone to carbonizing and cooking in your nozzle. In short, it easily clogs. So, be mindful of the temperature setting and also remove the filament from your nozzle when you are not using it.
In short, it easily clogs. So, be mindful of the temperature setting and also remove the filament from your nozzle when you are not using it.
The same with nylon, PVA filaments are hygroscopic, meaning they easily absorb water from the air. When opening your PVA filament roll, keep the desiccant that came along with it so that you can use it when storing the material in a sealed container.
If you do not store your PVA filaments properly, you will observe that the material will hiss and pop while you are printing. This indicates that it has absorbed water. But don’t worry about it. You can still use your material. Simply pop it in the oven for a few hours so that the moisture will evaporate. And then make sure that you store it properly after that.
How to Dissolve the PVA Filament?Dissolving the print from PVA filament is very easy. You just have to submerge it in water. Within just twenty minutes, it will begin to dissolve at room temperature. Within twenty-four hours, the print will be dissolved completely. You can also speed things up by using warm water.
You just have to submerge it in water. Within just twenty minutes, it will begin to dissolve at room temperature. Within twenty-four hours, the print will be dissolved completely. You can also speed things up by using warm water.
One of the best ways that you can clean off the PVA material that you have used as support is to try and break of as much as you can before you soak it. Remember to be careful as you may damage the smaller parts that are in the PVA material.
After you have removed as much material as possible, you can now submerge the parts in warm water. Don’t use boiling water or very hot water because you might damage the parts. Just keep in mind that warm water will allow the PVA material to dissolve faster.
PVA Support Material LimitationsThe best material to be used with PVA is PLA because they have similar printing temperature.
If you will use other types of filaments for 3D printing such as TPE, Nylon, PETG, or ABS, you will need to set the temperature higher as compared to PVA.
In this case, you have to consider using another support material. As mentioned, PVA filaments have low melting point and should not be exposed to temperature above 200°C.
For example, when printing with ABS, the perfect support will be HIPS. Get to know which of these materials match well with others so that you get the right support that you need for your 3D printing projects.
3D Filament Storage Tips for PVAMake sure that you store your PVA filaments inside an airtight container. Place silica in it so that it remains dry.
Store the container at room temperature and make sure that it stays dry. If you store your PVA filaments properly, it will greatly increase its shelf life.
Best PVA Filament: Top 3 Brands On The MarketNow that we have covered the basics that you need to know about this 3D printing material, we’ll share with you some of the best brands that manufacture PVA filaments.
Check Price at Amazon
This brand produces good PVA material that lets you print great parts.
However, it does cost a bit compared to other types of filaments from the same manufacturer. eSUN is arguably the most preferred brand when it comes to PVA filaments today.
Pros
- Excellent adhesion
- Great support material
- Dissolves nicely
Cons
- May clog nozzles at high temperatures
- May sometimes bubble when printing
- May ooze out of control at high temperatures
Check Price at Amazon
Go to top
2. Gizmo Dorks PVA FilamentCheck Price at Amazon
This is another brand that manufactures reliable PVA filaments. Just like PVA filaments from other brands, you may find that it can be somewhat stringy.
Do take some time to adjust the temperature settings so that you get just the right temperature so that you won’t have any problems with it being stringy.
Pros
- Works great when printed slowly
- Sticks well with PLA
- Reliable printing material for support
Cons
- Some find that it does not dissolve as easily as expected
- May be a bit costly compared to other brands
- Only sticks to PLA not to ABS
Check Price at Amazon
Go to top
3. Rigid.Ink PVA FilamentCheck Price at Amazon
With this brand, you can expect a good quality PVA material that is almost identical with other top brands.
You may observe though that compared to other brands, this one will stick better to ABS and PLA. So it’s a good point to consider.
Pros
- Bonds well with PLA
- Easy to clean up after printing
- High quality material
Cons
- Some users experienced that it doesn’t stick to the print bed
| Brand | Star Rating | Print Temp. | Diameter | Weight | Prices |
| eSUN | 3.8 | 190-200°C | 1.75 mm | 1.1 lbs | $39.99 |
| Gizmo Dorks | 3.7 | 170-190°C | 1.75mm | 1.79 lbs | $38.95 |
| Rigid.Ink | 4.4 | 190°C | 1.75 mm/ 2.85mm/ 3mm | 1 kg/ 300g/ 10m | $44.63 |
Check Price at Amazon
Go to top
ConclusionPVA is a great filament and as a supporting material. However, storage and handling are quite critical as it has a low melting point and should be kept from moisture. But there are certain applications when this is the best option to get the job done.
What do you think about the brands we have listed above? What are your experiences in using PVA filaments for 3D printing? Do share your thoughts with us. We would love to know.
We would love to know.
📌For any questions about PVA filaments and other types of filaments or brands, simply leave a comment, and we will get back to you.
References:
www.matterhackers.com/news/how-to-succeed-when-3d-printing-with-pva-support-material
www.allthat3d.com/pla-vs-abs/
www.allthat3d.com/pla-filament/
www.printermaterials.com/best-pva-filament/
www.amazon.com/eSUN-1-75mm-filament-natural-0-5kg/dp/B00MVIQASU
www.amazon.com/Gizmo-Dorks-Filament-Printers-Natural/dp/B00ITZQT8U
www.rigid.ink/products/pva-soluble-support-material-1-75-mm-2-85-mm-0-03-mm-tolerance
www.gizmodorks.com/blog/all-about-pva-filament/
Water Soluble Filament: Properties, How to Use, and Best Brands
3D Insider is ad supported and earns money from clicks, commissions from sales, and other ways.
Anyone who has ever been interested in 3D printing knows about ABS and PLA. After all, they are the stars of the show, so to speak. However, as in any movie or TV show, there are also some supporting characters who are less famous but are no less vital to the bigger picture. Water-soluble filaments fulfill this role in 3D printing. In this article, we go over what water-soluble filaments are, how they work, how to use them, and which brands you should buy.
However, as in any movie or TV show, there are also some supporting characters who are less famous but are no less vital to the bigger picture. Water-soluble filaments fulfill this role in 3D printing. In this article, we go over what water-soluble filaments are, how they work, how to use them, and which brands you should buy.
What are water-soluble filaments?
As the name implies, water-soluble filaments produce prints that dissolve when soaked or submerged in water. If you have never used them before, you might ask – what will a print that degrades so easily be good for? Water-soluble filaments are primarily used to create support structures. You may be eyeing a design that has several overhanging features or have parts that are more complex than usual. If you do not want your print to fall apart before you are even done printing, then it would be a good idea to incorporate support structures into your design.
The most common compound used for water-soluble filaments is polyvinyl alcohol, or PVA. Being a polar compound, PVA completely dissolves in water, although the process may take a couple of hours. It is non-toxic and biodegradable, making it the material of choice for many industrial applications, such as textile glazing, paper coating, and contact lens solutions.
Being a polar compound, PVA completely dissolves in water, although the process may take a couple of hours. It is non-toxic and biodegradable, making it the material of choice for many industrial applications, such as textile glazing, paper coating, and contact lens solutions.
The best part about using PVA is that it breaks down into harmless and non-toxic alcohols after it dissolves in water. This means that you can safely dispose of the dissolved solution down your drain after using, although we still recommend flushing it down with liberal amounts of water to remove the alcohol-saturated solution from your drain pipes.
How do they work?
Prints with support structures made with PVA only need to be soaked in water to dissolve the support material. It can take up to 24 hours for PVA to fully dissolve. This process can be accelerated by using warm water, or by agitating the solution every now and then. You can even use a sonicator to really quicken up the dissolving process.
It is essential to use sufficient water to allow for the complete dissolution of PVA. PVA tends to become water-starved quickly and will form solid and viscous clumps under these conditions. Should this happen, mixing the solution or manually removing the support material using pliers are easy remedies. You might have to experiment a little to get the perfect ratio of water to PVA material.
How do you use water-soluble filaments?
PVA in particular works really well as a support material in tandem with PLA since they print at practically the same temperature range. If you are printing with PLA and will need to provide support structures, then PVA is by far your best choice. It is also possible to use PVA in tandem with other filaments, such as Nylon or TPU, but this may not be as easily done as with PLA. In such cases, you may want to consider other materials for support structures such as HIPS.
Since PVA will be printed simultaneously with PLA, you will need to use a printer that is capable of dual extrusion. If this is something that you do not have right now, then we recommend that you get an upgrade. Dual extrusion printers not only allow you to print designs with support structures, but you can also make prints using two filaments with different colors. The upgrade will definitely be worth it as it opens up a whole new dimension of 3D printing.
If this is something that you do not have right now, then we recommend that you get an upgrade. Dual extrusion printers not only allow you to print designs with support structures, but you can also make prints using two filaments with different colors. The upgrade will definitely be worth it as it opens up a whole new dimension of 3D printing.
A temperature of 185 °C to 200 °C works best when printing PVA in tandem with PLA. PVA tends to break down rapidly at too high temperatures, so make sure that you do not go over 200 °C. At extremely high temperatures, PVA undergoes pyrolysis, the products of which cannot be removed by high temperature treatment. Removing burned PVA may require some heavy drilling, or you might have to replace your extruder altogether, so you will have to be extra careful.
A heated bed is not necessary when printing with PVA, but it will help in ensuring better adhesion for both PVA and PLA. We recommend using a heated bed at a temperature of 45 °C to 60 °C. If you are not using a glass heated bed, then a layer of blue painters’ tape or glue stick applied to the surface should significantly aid adhesion. To reduce warping, you may set the bed temperature a little on the high side during the first few layers and gradually decrease as the print progresses.
If you are not using a glass heated bed, then a layer of blue painters’ tape or glue stick applied to the surface should significantly aid adhesion. To reduce warping, you may set the bed temperature a little on the high side during the first few layers and gradually decrease as the print progresses.
PVA is quite soft and fragile at high temperatures, so we recommend printing at low speeds. You may start at a very low setting of 30 mm/sec and try to work your way up. To quicken up the cooling of the print, you may use a cooling fan at 50% setting.
What are the best brands of water-soluble filaments?
Being fairly common, there are currently a lot of choice of water-soluble filaments in the market. We highlight the best ones in terms of price and performance below so you will not need to spend unnecessary time choosing.
The PVA filament from the reliable GizmoDorks brands is a good place to start. Coming from a well-known filament manufacturer, this PVA filament will likely have good quality and consistency. The GizmoDorks PVA filament is available in standard 1.75mm and 2.85mm diameters, and are sold in 0.5kg spools.
The GizmoDorks PVA filament is available in standard 1.75mm and 2.85mm diameters, and are sold in 0.5kg spools.
The PVA filament from eSun is also another popular choice amongst 3D printers. The filament is pretty much within the price range of other brands, and many users have reported great performance and ease of use with it. It is available in 1.75mm diameter and in 0.5kg spools.
SainSmart also sells its own version of a no-frills PVA filament. It has all the usual benefits of PVA as a support material and has good compatibility with a wide range of standard 3D printers. Users of this filament have said that it detaches very easily from the PLA, making it easier and quicker to do post-processing dissolution. The SainSmart PVA filament is available in 1.75mm diameter and in 0.5kg spools.
Finally, the Hydrofill Water Soluble Filament from AirWolf 3D is probably the fanciest entry in this selection. This filament was designed to withstand higher temperatures, so it may be used in tandem with either ABS or PLA.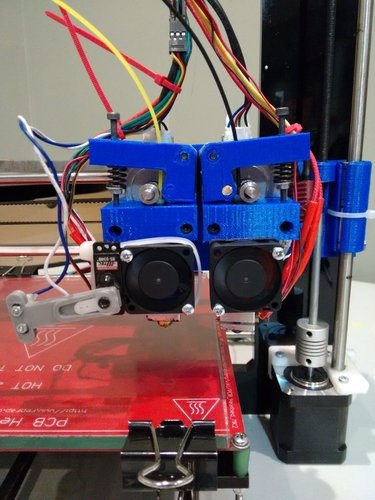 It still readily dissolves in water, so you will not need to buy any other solvent (unlike HIPS). Given its wide printing temperature range, we imagine that you can even use this filament to make support material for other filaments, such as Nylon. It is a little more expensive than the standard PVA filaments, but it opens up a world of possibilities in terms of material compatibility.
It still readily dissolves in water, so you will not need to buy any other solvent (unlike HIPS). Given its wide printing temperature range, we imagine that you can even use this filament to make support material for other filaments, such as Nylon. It is a little more expensive than the standard PVA filaments, but it opens up a world of possibilities in terms of material compatibility.
The final word
Water-soluble filaments may not be the star of the show, but there is no doubt that they are an essential ingredient when printing highly complicated 3D designs. We consider them specialist filaments, in that they only serve one purpose but perform its objective really well. If you are planning to print complicated designs or designs with long overhangs, then you might have to start learning how to use water-soluble filaments.
It might take some tweaking and some experimentation before you get the hang of working with water-soluble filaments, but they are well worth the effort given the number of designs that you will suddenly be able to make. To top it all off, using water-soluble filaments makes the task of removing support material practically effort-free, on top of being environment friendly. If your goal is to up your 3D printing game, then we suggest buying your first spool of water-soluble filaments and going to town with it.
To top it all off, using water-soluble filaments makes the task of removing support material practically effort-free, on top of being environment friendly. If your goal is to up your 3D printing game, then we suggest buying your first spool of water-soluble filaments and going to town with it.
Warning; 3D printers should never be left unattended. They can pose a firesafety hazard.
Using Dissolvable Filament to Create Supports
Using Dissolvable 3D Printing Filament is an easy and effective way to create support structures for your 3D printed part. In this article, we'll take a look at the different types of dissolvable filaments on offer, the benefits of using them over insoluble filaments, and tips and tricks for the smoothest possible printing process.
FDM 3D printing is a manufacturing technology that allows you to create parts with complex geometries that are usually impossible to obtain using traditional methods. However, when using this technology, each layer of the part requires supports, either on the structure of the part itself or on an additional supporting structure.
With a single extruder 3D printer, you are limited to using the base material of the printed part to create the support structure. Things are different with dual-extruder printers, since dissolvable filaments can be used to create support structures.
Soluble 3D Printing Filament Types
Water Soluble 3D Printing Filaments
Such materials are known for their solubility in ordinary water without any aggregates. This makes them an excellent option, as their dissolution does not pose any danger, and also does not cause any reaction to the base material of the product.
One of these materials is PVA, which is the most commonly used support material in 3D printing. BVOH is another widely used material with better material compatibility than PVA as well as faster dissolution time.
Water Soluble Chemical 3D Printer Filaments
Some industrial grade materials are not compatible with filaments such as PVA or BVO due to their chemical properties and/or heat resistance. For this reason, materials like BVOH or PVA have been designed with additional properties to make them compatible with high temperature materials such as PEEK, PEKK, PPSU, PP and others.
For this reason, materials like BVOH or PVA have been designed with additional properties to make them compatible with high temperature materials such as PEEK, PEKK, PPSU, PP and others.
In order to dissolve these supports, the pH of the water must be acidic in order to break down the sugar that this type of material normally contains, as this is less dangerous than the use of solvents.
Soluble 3D Printer Filaments with Organic Solvents
These are the least used materials due to the difficulty of using organic solvents with polymers most used in 3D printing as the solvent can react with the print material and damage it.
The advantage of using these materials is their high compatibility with the construction material. The most common example is HIPS as a support material for ABS.
Insoluble and dissolvable filaments for 3D printers
Soluble filaments for support structures have advantages and disadvantages compared to using insoluble filaments:
- Easy to remove supports
- Since the supports are soluble, simply dip the model in the appropriate solvent and wait until the supports are gone.
 This is very useful for parts with a very complex structure.
This is very useful for parts with a very complex structure. - Improved contact surface quality
- This advantage is related to the first point; since the material is easily removed, a strong base can be created in the area where supports are required, resulting in a smooth surface without filament residue.
- Less need for post-processing of the model
- The ability to print complex 3D models with high surface quality using dissolvable filaments also reduces the need for post-processing tasks such as polishing, sanding, gluing, etc.
- Longer print times in increasing the time of 3D printing, since materials need to be changed in the process. However, there are techniques for optimizing the support structure to reduce this problem.
Tips for creating support structures with dissolvable filaments
By changing some settings in your slicer, you can get solid supports to improve the quality of your 3D model.
Strengthening the Supports
It is quite common to create thin supports for very thin parts of a model, however they are not strong and tend to break during the printing process. To increase their durability, you can adjust the following support configuration options:
To increase their durability, you can adjust the following support configuration options:
Horizontal Support Extension: Increases the overall thickness of the support, allowing the tower to be thicker and stronger.
Avoid breakage of supports during printing
The thickness of supports is equal to the diameter of the hot end, so they are usually quite fragile and can break during printing. By changing the pattern and other parameters, the strength can be increased:
- Support pattern: Patterns such as grid and triangle are quite resistant to tearing during printing. It is recommended to print such patterns only on soluble material, as they are quite difficult to remove.
- Supports printing speed: If the supports are printed too fast, there is a risk of breaking the structure. Reducing the speed avoids vibration or damage to the structure as the head passes.
Improving the quality of the surface of the model
The quality of the contact surface depends on the distance Z from the support pattern, the direction of the upper and lower perimeter lines and the amount of material holding the base of the model. Changing these parameters can improve the quality of the surface, but will complicate the process of extracting supports.
Changing these parameters can improve the quality of the surface, but will complicate the process of extracting supports.
- Density of supports: The higher the density, the better the model will hold and therefore the surface finish will improve.
- Top/Bottom Line Direction: Changing the direction of the perimeter pattern helps hold the bottom layer of the model, as it allows the support and the perimeter pattern to intersect better.
- Support Pattern and Top/Bottom Pattern: The support and perimeter patterns affect how the support model attaches, ideally the patterns should overlap as often as possible to better secure the first layer.
Always remember that it is important to keep filaments in a dry environment, as soluble materials readily absorb moisture and can cause printing problems. Materials such as PVA and BVOH can be dissolved in ordinary water. This water can also be heated to shorten the removal time of supports.
We hope you follow our advice and recommendations to improve the surface quality of your 3D printed parts and make the process faster and more efficient.
We will keep you updated with the latest news!
Your team IGO3D Russia
Our groups on social networks:
Vkontakte
Telegram
Youtube
90,000 as a 3D printer imitates the human organsundoubtedly, 3D-pacifier-one of the most epoch and, probably, in a few decades, these years will be remembered as the period of its formation. This is one of the most promising and revolutionary technologies that is used in various fields, in particular, in healthcare. Therefore, it is worth clarifying a few questions. For example, how can 3D printers contribute to the development of medicine and healthcare in general?
A good example is the unique project of the Department of General Surgery of the Sacra Famiglia Fatebenefratelli hospital in Erba (Lombardy, Italy), where, using a Sharebot 3D printer, it was possible to recreate real anatomical organs and structures to simulate basic surgical interventions, such as video laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Sharebot 43 FDM Printed Liver and Gallbladder Segment Models
An experimental liver and gallbladder segment model was created in collaboration with Sharebot using a special material (LAY-FOMM) available as a plastic filament. After immersion in water, this material, thanks to its two-component composition (rubber and PVA-based soluble part), becomes similar to organic tissues, which also allows surgical sutures to be applied. It was found that the degree of extensibility in combination with residual moisture after immersion in water is similar to organic counterparts.
High-precision models for teaching surgeons
In this way, hospital surgeons were able to reproduce video-laparoscopic cholecystectomy directly on printed models. In practice, this involves removing the gallbladder without damaging the liver tissue. Performing surgery on a model pelvis (laparoscopic simulator) allows surgeons to master the correct technique, as well as experiment with new non-invasive methods of removal.
Pelvic Surgery Simulator
By simulating important surgeries on high-precision 3D printed anatomical models, we have made a big step in medical technology, which undoubtedly increases the chances of patients recovering with similar interventions .
We are interested in 3D printing in terms of practical training of a new generation of surgeons based on more advanced and accurate models
Specialists of the General Surgery Department of the Sacra Famiglia Fatebenefratelli Hospital
Comments from hospital surgeons
The peculiarity of the model we developed is that there are two holes between the liver and gallbladder, which make it possible to completely empty the gallbladder in order to then fill it with a colored liquid to simulate bile. Due to its elasticity, the liver is also used to develop the technical possibilities of applying laparoscopic and traditional sutures.
In each model, the liver and gallbladder are directly connected by supporting structures. Using a raft (a horizontal mesh of plastic located at the base of the model) and supports, we developed a model of the gallbladder, in which they, simulating the liver bed, allow us to model the plane of the liver section. This model includes only the gallbladder and saves consumables, which speeds up the 3D printing process.
Using a raft (a horizontal mesh of plastic located at the base of the model) and supports, we developed a model of the gallbladder, in which they, simulating the liver bed, allow us to model the plane of the liver section. This model includes only the gallbladder and saves consumables, which speeds up the 3D printing process.
Anatomic base with PLA liver
We also reduced the space between the support and the gallbladder to make the area between them more complex and realistic. For more efficient placement inside the pelvis model (laparoscopic simulator), we created an anatomical base with a liver made of PLA plastic. It contains a soft sponge that mimics a real liver, into which a component of a 3D model of the gallbladder made of LAY-FOMM, an easy-to-use filament, has been inserted through the valve. This rigid model allows quick and easy replacement of LAY-FOMM gallbladder models.
Finally, we have created an ellipsoidal cylindrical model with a vertical hole, which makes it possible to simulate intestinal sutures and anastomoses. 3D printing of this model does not require much time and money.
3D printing of this model does not require much time and money.
Intestinal Suture Models
We believe that this technology opens up a wide range of possibilities. We intend to create models of other organs for high-precision simulation of a number of important surgical interventions. To do this, we need to learn how to perform 3D printing based on DICOM files in particularly complex or atypical cases that sometimes occur in clinical practice. In general, 3D printing with LAY-FOMM interested us in terms of technical perspectives and, most importantly, the practical training of a new generation of surgeons based on more advanced and accurate models.
Specialists of the Department of General Surgery
Sharebot 3D printers – reliable tools for innovation
Fatebfratelli hospital staff uses a compact Sharebot 43 professional 3D printer equipped with two independent extruders. The device allows you to print products of the most complex geometry with soluble supports. In addition, a system of mirroring and duplication is available when printing. The flexible printer platform maintains a temperature of 120°C, and the maximum heating temperature of the extruders reaches 300°C, which allows the use of technical and professional materials that meet a wide variety of physical, chemical and mechanical conditions, including high or low temperatures, the presence of oil and gasoline, as well as impact and friction.
In addition, a system of mirroring and duplication is available when printing. The flexible printer platform maintains a temperature of 120°C, and the maximum heating temperature of the extruders reaches 300°C, which allows the use of technical and professional materials that meet a wide variety of physical, chemical and mechanical conditions, including high or low temperatures, the presence of oil and gasoline, as well as impact and friction.
Printing process on Sharebot 43
The collaboration between Sharebot and the Department of General Surgery at the Fatebenefratelli Hospital in Erba has demonstrated the importance of 3D printing, which opens up new types of models and high-precision surgical simulators. This area is just one of the possible directions for the development of technology. Whether it's recreating organs for experimentation or printing implantable prostheses, 3D technology is becoming a key tool for medical innovation.
Sharebot is a young and innovative company working with four different 3D printing technologies: FDM, LCD, SLS and DMLS.












