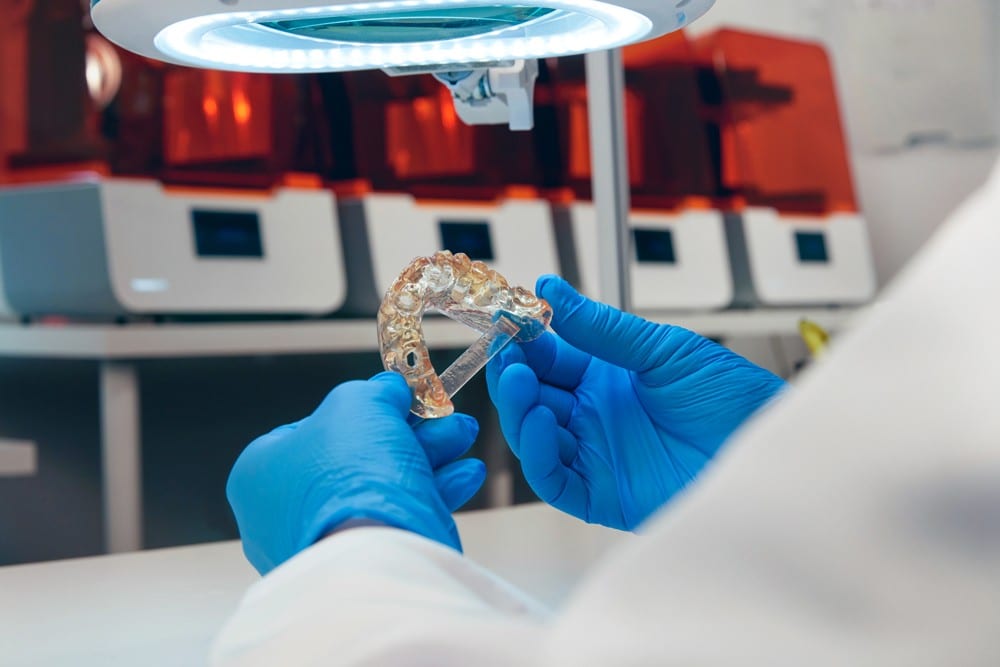
Dentist 3d printing
Resin Library and 3D Printing Materials
Resin Library and 3D Printing MaterialsSkip to Main Content
Dental Resins
Bring production in-house or improve existing workflows with industry-leading Formlabs 3D printers. Our Dental Resins empower dental labs and practices to rapidly manufacture biocompatible surgical guides, splints, fixed patterns and models, clear aligner models, and full dentures.
Visit the Formlabs Store
See and feel Formlabs quality firsthand. We’ll ship a free sample part to your lab or practice.
Request a Free Sample Part
The Form 3B+ and Form 3BL are compatible with the complete Formlabs resin library of more than 20 general purpose and speciality materials.
Explore All Formlabs Materials
Data Sheets
Download safety and technical data sheets for all Formlabs materials.
Handling & Safety
Handling & Safety
Resin should be handled with care. Proper handling will ensure safe printing and efficient use. Our resins have been designed to be similar or safer to handle as other household chemicals or adhesives. Formlabs materials do not contain volatile solvents so special ventilation is not required. Skin contact should be avoided.
The Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are up to date for every resin product and follow the latest government guidelines. Always consult the SDS as the primary source of information to understand safety and handling of Formlabs materials. For more information about handling resin, learn more tips for resin maintenance in our Help Center.
Technical Data
Technical Data
Plastics are complex materials, and finding the right one for your specific application requires balancing multiple attributes. Our library of resins is ideal for product development, rapid prototyping, and a variety of specialized applications. Download our Technical Data Sheets to explore the mechanical properties of each material.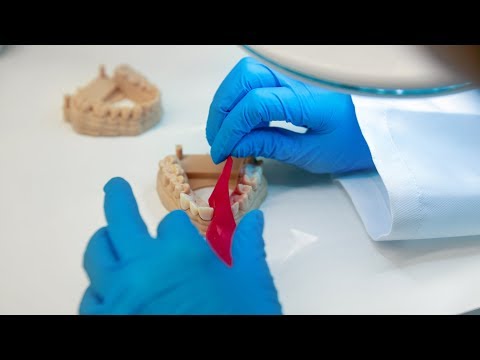
Material
– Select –BioMed AmberBioMed BlackBioMed ClearBioMed WhiteBlackCastableCastable WaxCeramicClearColor BaseColor PigmentsCustom TrayDental LT ClearDental LT Clear V2Dental SGDigital DenturesDraftDurableESDElasticElastic 50AFlexibleFlexible 80AFull Materials LibraryGreyGrey ProHigh TempIBTModelModel V3Nylon 11Nylon 12Permanent CrownRigid 10KRigid 4000Soft TissueSurgical GuideTemporary CBToughTough 2000White
Language
– Select –BulgarianChineseCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEstonianFinnishFrenchGermanGreekHungarianIrishItalianJapaneseKoreanLatvianLithuanianMalteseNorwegianPolishPortugueseRomanianRussianSlovakSlovenianSpanishSwedishTurkish
Technical Data Sheets
There is no technical data sheet available for the chosen material.
Safety Data Sheets
There is no safety data sheet available for the chosen material.
For more information, help choosing a material, or bulk orders, we're here to help.
3D Printing for Dental Practices
Simple print preparation
Import digital impressions directly and prepare models for printing in just a few clicks.
Download PreForm
Rigorously tested materials
Fully validated workflows with our proprietary resins give you peace of mind.
Browse Materials
The easiest 3D printer to use
The intuitively designed Form 3B makes in-office printing clean and hassle-free.
Meet Form 3B
Hands-off post-processing
Automated washing and curing units take the guesswork out of finishing printed parts for clinical use.
Automate Your Post-Processing
“The printers from Formlabs are simply the best, simplest printers on the market. Best in class user experience. Fast change of material. The biggest choice of certified and tested resins on the market. Every print was a success in the last 5 years. No failure at all.”
Every print was a success in the last 5 years. No failure at all.”
Dr. Antonino Cacioppo, DDS, PhD, Prosthodontist, Studio Dentistico Associato Cacioppo
Diagnostic models
Up to 9 models per print in ~3.5 hr or 1 model in 20 min for $2-3 a model.
Get started with diagnostic models
Clear aligner models
Up to 9 models per print in ~3.5 hr or 1 model in ~20 min for $2-3 a model.
Scale production and ROI with aligner models
Surgical guides
Up to 29 quadrant surgical guides per print in ~5 h for $2-$4 a part.
Secure safer, faster operations
Occlusal guards
Up to 8 guards per print in ~2.5 h for $4-$6 a part.
Protect your patients and their oral health
See How Much You Can Save
Try our interactive ROI tool to see how much time and cost you can save when 3D printing on Formlabs dental 3D printers.
Calculate Your Savings
Direct printed full dentures and try-ins
Meet Digital Denture Resins
Temporary crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays, and veneers
Meet Temporary CB Resin
Permanent crowns, inlays, onlays, and veneers
Meet Permanent Crown Resin
From CE-certified courses to quick videos that can quickly teach you a new skill, learn with Formlabs Dental Academy.
Browse Educational Content
With 75+ support and service staff and 150+ engineers, Formlabs backs its products with the strongest team in 3D printing.
Don’t want to learn one more software program?
Ask if your lab will do appliance design for you. Otherwise, fully digital services can take this off your plate.
Our Dental Service Plan (DSP) includes personalized onboarding training, proactive check-ins, and the best phone and email support in the industry.
Learn More About Dental Service Plan
Learn how digital dentistry is transforming dental workflows and how you can integrate 3D printing into your practice with our free resources.
Explore Dental Resources
The Form 3B Complete Package includes all of the tools required to bring high-precision 3D printing into your office.
Order NowRequest a Sample Part
All about a 3D printer in dentistry: features, applications, technologies
The first attempts to use 3D printing in dentistry were made by specialists from Align Technology in the 1990s. Using a 3D printer, mouth guards were made, which served as a start for the development of this technology in the dental industry. The process of making teeth was looked at from a radically new point of view.
But development did not progress as fast as we would like: it took almost 20 years to achieve satisfactory print quality and optimize performance. The first implant was printed by Layer Wise in 2012. In the same year, for the first time, it was possible to implant a patient with a titanium lower jaw, which was made using a 3D printer. Since then, the technology has evolved and raised the quality bar. nine0003
In the same year, for the first time, it was possible to implant a patient with a titanium lower jaw, which was made using a 3D printer. Since then, the technology has evolved and raised the quality bar. nine0003
The advantages of using a 3D printer in a short time to solve almost any problem. With a dental 3D printer, a significant number of required instances can be modeled in a single session. All projects are saved in files, so in the future you can re-make the same model if necessary. nine0003
It is no longer necessary to send the patient for 2-3 days to wait for the production of plaster models. Now everything happens much faster: the doctor builds a 3D model in a few minutes using an intraoral scanner and instantly transfers the data to the laboratory, where printing also does not take much time. Speed and maximum precision increase the level of treatment and really save resources and time.
What you can print
Let's highlight the most common uses of 3D printing in dentistry. Using the printer, you can create:
Using the printer, you can create:
- demonstration and collapsible models of the jaw, sectoral reproduction of the upper and lower jaws in the occlusion;
- ashless constructions, caps, bases for crowns and bridges, clasp prostheses;
- surgical guides for implantation, individual trays, guides for maxillofacial surgery. nine0034
Such a promising direction as the printing of permanent and temporary orthopedic structures, removable denture bases is actively developing.
About the types of printing
As we have already found out, the main task of a 3D printer for dentistry is to reduce the time of manufacturing restorations and reduce the cost of production without loss of quality and accuracy. We will understand the printing technologies and their features.
Stereolithography (SLA or SL). With this technology, a laser beam selectively impacts a container of liquid resin through the printable area. Thus, the resin hardens in layers in specific places and forms a three-dimensional figure.
Thus, the resin hardens in layers in specific places and forms a three-dimensional figure.
Stereolithography gives the best surface finish on parts and is most commonly used in today's 3D printer models. SLA machines provide a large area of restoration construction and work with a wide range of materials designed for a variety of tasks. nine0003
To switch from one material to another, it is enough to change the cartridge and the resin bottle. Relatively compact dimensions, simple workflow and affordable price make SLA printers the best choice for dental laboratories. An example of SLA models - Form 2 and Form 3 from Formlabs, SLASH PLUS from Uniz Technology, Basic Dental from Omaker, Asiga PICO2.
Digital LED projection (DLP). nine0014 Here, the chemical process is similar to SLA, but a digital projector is used instead of a laser as a light source to cure the resin. DLP printers have a simple interaction process, a fairly modest footprint, and a good selection of material options, but at a higher price compared to SLA.
Due to the nature of the illumination of the LED projector, there is a tendency for voxel lines-layers formed by small rectangular bricks of material. Models made by DLP have inferior surface quality to SLA models. But it is worth noting that DLP printers print much faster than laser ones. Examples of DLP printers include Varseo S by Bego, AccuFab-D1 by Shining 3D, D2-150 by Veltz 3D, Versus by Microlay. nine0003
PolyJet technology. The process is similar to that of a regular inkjet printer, but instead of inkjet drops on paper, the 3D printer blows layers of liquid resin onto the printable area. The layers harden when exposed to light.
Once upon a time PolyJet gained popularity in the dental industry, but its development was slowed down by two factors: the high cost of equipment and the impressive dimensions of the devices. Models made using PolyJet technology require long post-processing and are again inferior to SLA in terms of surface quality. nine0003
nine0003
PolyJet systems produce parts very quickly, but are limited in scope due to expensive proprietary consumables. Therefore, in the context of our industry, it is better to buy a dental 3D printer with SLA technology.
SLS and EBM. Allows titanium printing of ready-made elements for replacement of jaw parts. These technologies work on the principle of laser sintering of metal clay, a special metal powder for dentistry. So, the SLS and EBM systems allow you to work with a biocompatible titanium alloy. Since pure metal powder does not require a binder filler, the finished models do not differ in porosity. To achieve the required mechanical strength, the products do not require additional firing. An example of a printer capable of printing with metals is the EP-M150T from Shining 3D. nine0003
Filament printing. Technology is not relevant in dentistry and now we will explain why.
Printed with filament, a material similar to fine garden trimmer wire. The wound filament is charged directly into the 3D printer head, which moves on three axes.
The wound filament is charged directly into the 3D printer head, which moves on three axes.
Compared to other materials for 3D printing, this filament is quite inexpensive, but gives low accuracy compared to powders. The most popular types of filament are ABS and PLA plastic. nine0003
Comparison of the main 3D printing technologies used in dentistry
To clearly show the main pros and cons of each technology, we compare them in a table format.
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Digital Light Processing (DLP) | PolyJet Technology | SLS and EBM technologies | |
| Precision | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Surface finish | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Print speed | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Availability of materials | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| Metal printing | ||||
| Benefits |
|
|
|
|
| Drawbacks | Slow single print speed |
|
|
|
nine0003
Our CV
PolyJet technology is becoming a thing of the past due to high cost and imperfect print results. SLS and EBM are more relevant for large laboratories than ordinary clinics. Therefore, it is worth considering SLA and DLP printers for everyday tasks. For example, take a closer look at Bego Varseo S, Formlabs Form 2. These devices have already proven themselves in the dental market and provide guaranteed high-quality results. You can see all 3D printers presented in StomShop.pro here. nine0003
SLS and EBM are more relevant for large laboratories than ordinary clinics. Therefore, it is worth considering SLA and DLP printers for everyday tasks. For example, take a closer look at Bego Varseo S, Formlabs Form 2. These devices have already proven themselves in the dental market and provide guaranteed high-quality results. You can see all 3D printers presented in StomShop.pro here. nine0003
← General requirements for the placement of portable X-ray machines | TOP-5 illuminated physiodispensers →
3D printing dentist - the future of dentistry and prosthetics
3D printing dentist
We have already written a lot about where and how you can use 3D printers and 3D technologies. Another area where 3D printers are becoming indispensable is dentistry and prosthetics. 3D printers are used by dentists to create prostheses, models, braces and implants. nine0003
3D printing dentist
3D printers are increasingly used in dental clinics, dental laboratories, research centers. With their help, the quality of implants, prostheses and services has improved, as well as significant time and cost savings. But most importantly, 3D printers guarantee the highest precision of finished products.
With their help, the quality of implants, prostheses and services has improved, as well as significant time and cost savings. But most importantly, 3D printers guarantee the highest precision of finished products.
3D printing dentist
The unique shape of each tooth of each patient is very difficult to reproduce using manual fabrication or a milling machine. The work of dental technicians is very laborious and takes a lot of time to get a good result. nine0003
3D printing dentist
Implants, prostheses, enameling, etc. must be made individually, because. each has its own structure of teeth and jaw. Therefore, technicians create separate models. To do this, the plates are filled with sodium alginate, silicone or polyester. Patients bite into the plate and leave impressions of the teeth. After that, based on the shape, the dentist adjusts the tooth and the prosthesis so that they are suitable. 3D printing guarantees high precision and quality. nine0003
nine0003
3D printing dentist
3D printers allow you to remove a rather complicated and time-consuming stage - manual modeling of prostheses, crowns and other products. This ensures a reduction in waiting times, the number of fittings and fittings, from the first visit of the patient to the installation of the final design.
Thanks to 3D technologies and 3D printers, the process is reduced to:
- scanning the patient's mouth using a scanner, MRI or CT. nine0034
3D printing dentist
- data processing with special software,
- print the required model or shape on a 3D printer,
- fabrication of a finished prosthesis using an electronic model,
3D printing dentist
- installing an implant for a patient.
The patient receives a perfectly fitting crown or prosthesis in the shortest possible time. nine0003
nine0003
The latest 3D technology and the most advanced materials provide the finished product much faster than ever before. And models, prostheses and implants made on a 3D printer exactly repeat the individual characteristics of each patient.
Due to the high manufacturing precision and mechanical properties of the ceramic, the lifetime of the 3D restored tooth is significantly increased.
To summarize, there are several main advantages of using 3D printers in dentistry and prosthetics:
- the ability to store all anatomical data of patients in digital form, instead of impressions and samples;
- significant acceleration of the production of the necessary prototypes and models;
- fully automatic printing process that eliminates possible errors and inconsistencies;
- increase in production without increasing staff;
- the highest manufacturing precision, which eliminates the possibility of errors;
- The use of the latest 3D technologies will make it possible to improve the company's image, which means it will increase the number of customers.