Cocojet 3d printer price
3D Systems Unveils CocoJet Chocolate 3D Printer At 2015 CES - 3DPrint.com
With their CocoJet and ChefJet Pro series of 3D printers, 3D Systems is intent on delivering a whole new world of edible delights to what’s being called “culinary printing.”
3D Systems’ CocoJet
To that end, 3D Systems announced today that the CocoJet, a chocolate 3D printer developed in collaboration with The Hershey Company, will be prominently featured at the 2015 International CES show.
Calling it “ideal for the baker or chocolatier,” 3DS says the CocoJet prints custom designs in dark, milk or white chocolate, and it’s the latest innovation to arise from the company’s partnership with The Hershey Company.
“Our partnership with Hershey, the largest producer of quality chocolate in North America and a global leader in chocolate and confections, allows us to create unique, exciting and personalized edible experiences,” says Chuck Hull, Chief Technology Officer and Co-Founder of 3DS, of the collaboration.
“Our preview of CocoJet at CES showcases the power – and possibilities – of 3D printing, and it extends our experience and innovation in culinary 3D printing.”
Following the recent debut of the device at the 3D Chocolate Candy printing exhibit at Hershey’s Chocolate World, 3DS calls the machine “the most advanced 3D chocolate printer in operation.”
The work behind the project was meant to incorporate 3D chocolate printing into Hershey’s Chocolate World live experience, and the company says it will provide valuable market research on various consumer applications for chocolate 3D printing in the future.
“We are now using 3D technology to bring Hershey goodness to consumers in unanticipated and exciting ways. 3D printing gives consumers nearly endless possibilities for personalizing their chocolate, and we look forward to continued development of this amazing technology,” says Will Papa, the Chief Research and Development Officer for Hershey.
3D Systems says they intend to share upcoming commercial plans for this class of chocolate 3D printers at a later date.
Also on the agenda for 3DS is a showcase for its ChefJet Pro series, the first professional-grade food 3D printers. According to 3DS, the full-color ChefJet Pro will be food certified and able to produce edible, 3D printed candies and decor. Built atop the company’s ColorJet Printing technology, the ChefJet Pro features intuitive, chef-friendly Digital Cookbook software and creates intricate candies and sweets with a variety of flavor options.
The ChefJet Pro is expected to be commercially available in the second half of 2015, and it will be featured at the 3D Systems CES 2015 booth as well.
Have you ever sampled 3D printed food? What did you think of the texture and taste? If you’ve ever experienced the wonder of 3D printed culinary items, please let us know in the CocoJet forum thread on 3DPB.com. Check out a video of the CocoJet in action below:
Stay up-to-date on all the latest news from the 3D printing industry and receive information and offers from third party vendors.
Tagged with: 2015 international ces • 3d chocolate printing • 3d systems • CES • chefjet • chocolate 3d printer • chuck hull • CocoJet • culinary 3d printing • Culinary Institute of America • Digital Cookbook software • The Hershey Company • Will Papa
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
3ders.org - 3D Systems unveils new CocoJet chocolate 3D printer At CES 2015
Jan 6, 2015
3D Systems unveils the CocoJet, a chocolate 3D printer at 2015 CES in Las Vegas today. Developed in collaboration with The Hershey Company, the CocoJet 3D printer prints custom designs in dark, milk or white chocolate, making it an ideal tool for bakers and chocolatiers craft confections.
Much like traditional 3D printers produce plastic objects, CocoJet heats and squeezes chocolates instead of plastic filaments. As chocolate is temperature dependent, it is very important to control the heating and cooling cycles accurately.
CocoJet debuted at the 3D Chocolate Candy printing exhibit at Hershey's Chocolate World on December 19, 2014. Visitors to Hershey's Chocolate World Attraction can witness live 3D printing, see examples of finished 3D printed chocolate, interact with a library of 3D graphics pre-loaded on iPads and be scanned to see what they would look like as a piece of 3D chocolate.
"Our partnership with Hershey, the largest producer of quality chocolate in North America and a global leader in chocolate and confections, allows us to create unique, exciting and personalized edible experiences," said Chuck Hull, Chief Technology Officer and Co-Founder, 3DS. "Our preview of CocoJet at CES showcases the power and possibilities of 3D printing, and extends our experience and innovation in culinary 3D printing."
The collabration with Hershey was meant to incorporate 3D chocolate printing into Hershey's Chocolate World live experience, and 3D Systems says it provides valuable market research on the consumer applications for chocolate 3D printing.
"We are now using 3D technology to bring Hershey goodness to consumers in unanticipated and exciting ways," said Will Papa, Chief Research and Development Officer, The Hershey Company. "3D printing gives consumers nearly endless possibilities for personalizing their chocolate, and we look forward to continued development of this amazing technology."
3D Systems is also showcasing its ChefJet series, the first professional-grade food 3D printers, in its CES 2015 booth. The full-color ChefJet Pro will be food certified and produce edible 3D printed candies and decor, says the company. Built from 3DS' ColorJet Printing (CJP) technology, the ChefJet Pro features intuitive, chef-friendly Digital Cookbook software and creates intricate candies and sweets with a variety of flavor options. The ChefJet Pro is expected to be commercially available in the second half of 2015.
3D Systems says they intends to share its commercial plans for this class of chocolate 3D printers at a later date. Watch a video of this technology below.
Watch a video of this technology below.
Posted in 3D Printers
Maybe you also like:
- Multi-delta robotic arm design creates large-build 3D prints in small spaces
- Students create large-scale 3d prints with their adaptable Sky Printer
- Students build a 7-foot (213cm) tall 3D printer for weaving ultra-lightweight structures with fibrous materials
- FLUX 3D Printer surpasses $1million on Kickstarter
- New startup raised $2.8 million for developing a reinforced composite 3D printer
- Marvell announces first fully integrated 3D printer system-on-chip solution
- HYPER hydrogel 3D printing pen creates Nanoscale 3D structures in platinum
- 10,000 Euros offered for an open source plastic recycling machine design
- 3D Hubs releases The 2015 3D Printer Guide
Jay wrote at 1/12/2015 1:15:00 AM:
". ..and each pre-filled 8 ounce cartridge is only $16.95..." XD
..and each pre-filled 8 ounce cartridge is only $16.95..." XD
MN wrote at 1/8/2015 8:57:46 PM:
How much does it cost?
Axlotl wrote at 1/6/2015 4:52:52 PM:
at least print failures will be yummy
Wonders of computer technology - fiction and reality. 3 D technologies
State budgetary educational institution
GBOU Gymnasium No. 11
Informatics project
“Miracles of computer technology – fantasy and reality.
3-D technologies"
Podtorzhnova Karina
Mihu Vadim
8 "A" class
Supervisor Gailit I.V., computer science teacher
St. Petersburg, 2018 fantasy and reality. 3D technologies»
3D is short for three-dimensional. Objects in the real world do indeed have 3 dimensions.
The development of 3D technologies lasts only about 20 years, but they have already managed to find application in many areas of human activity and continue to develop rapidly. And one can only try to imagine what level of development they will reach and what opportunities they will give to humanity in the foreseeable future.
According to some industry experts, the impact of 3D printing on manufacturing will be as significant as the industrial revolution. nine0003
Today there are many applications for 3D printed models in a wide variety of fields.
3D printing and 3D scanning are becoming more and more integral to our lives, turning from a narrowly focused and expensive service into an indispensable assistant for professionals in various fields of activity.
Hypothesis: modern 3D printers, scanners, pens are one of the most promising areas of technological progress in the 21st century.
Purpose: To study the variety of 3D devices (printers, scanners, pens) and their application in various areas of human life
Objectives:
- To study the directions and applications of 3D devices
- To study the development prospects of 3D devices
- To find the most interesting projects using 3D technologies
- To identify possible problems of their implementation
- To analyze the negative consequences of their use 4D92
Working methods:
- search for information in various sources;
- analysis and systematization of the received information; nine0042
- processing the received information
Work plan:
- Search for sources of information on the project topic
- Collection of information on the project topic, its analysis and structuring.
- Selection of graphic design (photos, illustrations, diagrams).
- Presentation of project results in the selected form (presentation, bulletin, booklet, Web-article)
- Preparation for project defense
- Protection of research results. Summing up the results of the project. nine0042
Project product: presentation, abstract, information booklet
Introduction 4
History of development 3D print 4,0003
∙ Technology for the formation of volumetric models from layered sheet material (LOM) 5
∙ Selective laser sinter 5
∙ Layered sealing (SGC) 6
Most typical applications for 3D printers 7
∙ 3-D printing in medicine 7
∙ Architecture and construction 9
∙ Clothing sewn on a printer 10
∙ Production of shoes 10
∙ Geoinformation systems. 11
∙ Industrial products and mechanical engineering. 11
∙ Print toys and souvenirs 12
∙ Flying 3D printer that prints nests and fights radiation 12
∙ Education. 12
12
∙ Artistic and theatrical fields 13
∙ Printing and related fields 13
∙ Small batch production. 13
∙ Cooking and confectionery production 13,
∙ Printing jewelry on a 3D printer 14
∙ 3D printer as a sewing machine 14
∙ Weapons 14,
Caution, 3D will bend! 15
What is a 3D pen? 15
What types of 3D pens are there? 15
How does a 3d pen work? 16
A 3D pen is the best gift for a child 16
Benefits of a 3D pen 16
3D printing: what's next? 16
3D printing, 3D scanning, 3D copying: ALL IN ONE 17
Do you know… ? 17
Sources: 17
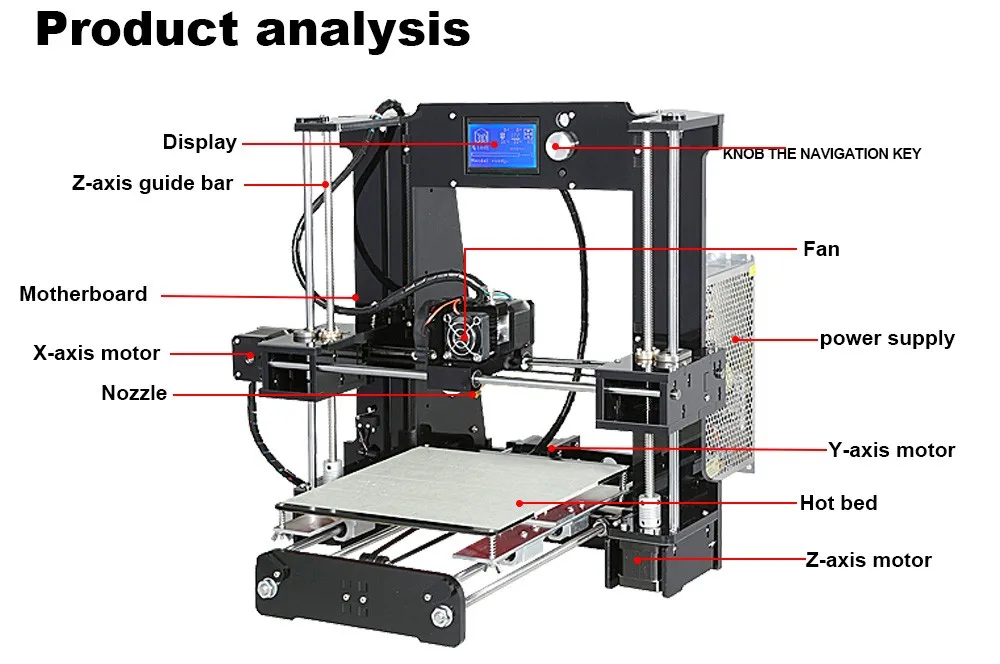
A 3D printer is a special device for outputting three-dimensional data. Unlike a conventional printer that prints two-dimensional information onto a sheet of paper, a 3D printer allows you to output three-dimensional information, i.e. create certain physical objects. 3D printing technology is based on the principle of layer-by-layer creation (growing) of a solid model.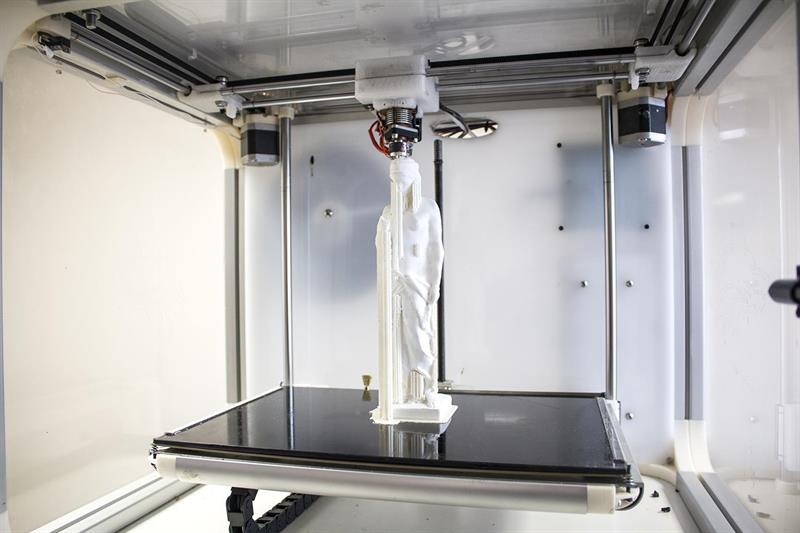 nine0003
nine0003
The advantages of such devices over conventional methods of creating models are high speed, simplicity and low cost. For example, in order to create a model manually, it may take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of the product. As a result, development costs are significantly increased, and the time for the release of finished products is increased. 3D printers allow you to completely get rid of manual labor and create a model of a future product in just a few hours, while eliminating the possibility of errors inherent in the "human factor". nine0003
The first applications of 3D printing technology date back to the 1980s. Then three-dimensional printers were bulky and extremely expensive, and their scope was very limited, and the term itself - 3D printing - did not exist yet.
The founder of modern installations for the formation of 3D objects can be considered the American Charles Hull. presented to the public a year later, at 1987 year. Since the term "3D printer" had not yet been introduced into circulation, Charles Hull's apparatus was called the "setup for stereolithography". Stereolithography is a technology for the layer-by-layer manufacturing of parts from liquid photopolymerizable compositions. The device grew a computer-simulated three-dimensional object from a liquid photopolymerizable composition, applying it layer by layer on a moving platform immersed in a FPA bath. The thickness of each layer was about 0.1-0.2 mm.
Since the term "3D printer" had not yet been introduced into circulation, Charles Hull's apparatus was called the "setup for stereolithography". Stereolithography is a technology for the layer-by-layer manufacturing of parts from liquid photopolymerizable compositions. The device grew a computer-simulated three-dimensional object from a liquid photopolymerizable composition, applying it layer by layer on a moving platform immersed in a FPA bath. The thickness of each layer was about 0.1-0.2 mm.
Stereolithograph - this is the name of the device patented by Charles Hull in 1986 year. Thanks to his appearance, the first 3D printers were created.
Of course, it was far from being called a 3D printer, but the main ideas of layer-by-layer creation of three-dimensional figures were laid down in it.
The modern history of 3D printers began in 1993 when Solidscape was formed to manufacture inkjet printers, the forerunners of 3D printers.
The expression "3D printing" originated at the famous Massachusetts Institute of Technology only 1995, when two students - Jim Bredt and Tim Anderson modified a "flat" inkjet printer so that it outputs images not to paper, but to a special container and makes them voluminous.
Charles Hull was not the only inventor who experimented with 3D printing technologies. Along with stereolithography, other 3D printing technologies also developed.
This technology appeared in 1985, a year before Charles Hull received a patent for stereolithography. Its author is Mikhailo Feigen, who proposed layer-by-layer formation of three-dimensional models from sheet material: films, polyester, composite, plastic, paper, etc., fastening the layers together using a heated roller. nine0003
Making a model by hand would take days or even weeks of work, but with a LOM printer such a model can be recreated in a few hours. Models made using the M. Feigen technology turn out to be rough, it is difficult to remove excess material from their surface due to the risk of delamination.
In 1986 Carl Descartes invented the method of selective laser sintering. The essence of the method lies in the layer-by-layer sintering of the powder material by a laser beam.
In the working chamber, the powder is heated to a temperature bordering on the melting point. After that, the material is leveled and the laser beam draws the necessary contour on its surface. When the beam touches the powder, it is heated to the melting point and sintered. After that, a new layer of powder is poured into the chamber, and the sintering process is repeated. The cycles of adding material, its leveling and sintering are repeated according to a predetermined scheme until a finished model with a rough porous structure is formed on the working table of the chamber. The finished product is removed from the printer and excess powder is removed. nine0003
After that, the material is leveled and the laser beam draws the necessary contour on its surface. When the beam touches the powder, it is heated to the melting point and sintered. After that, a new layer of powder is poured into the chamber, and the sintering process is repeated. The cycles of adding material, its leveling and sintering are repeated according to a predetermined scheme until a finished model with a rough porous structure is formed on the working table of the chamber. The finished product is removed from the printer and excess powder is removed. nine0003
The device is capable of working with powdered polymers, foundry wax, nylon, ceramics, metal powders, while moving from one material to another, the chamber must be thoroughly cleaned of the remnants of the previous material. Several models can be grown in one chamber at once.
Layered compaction technology was developed by the Israeli company Cubital in 1987. At its core, it resembles photocopying. On a selectively charged plate made of glass, a pattern of the base of the model is formed. This template is placed over a thin layer of photopolymer evenly distributed over the work surface, after which it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The photopolymer layer corresponding to this template layer becomes solid, liquid residues are removed, and the voids are filled with liquid wax, which quickly hardens. The described sequence of actions is repeated many times until the finished model is formed. The operation of the machine can be paused to remove defective layers, and later resumed. nine0003
This template is placed over a thin layer of photopolymer evenly distributed over the work surface, after which it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The photopolymer layer corresponding to this template layer becomes solid, liquid residues are removed, and the voids are filled with liquid wax, which quickly hardens. The described sequence of actions is repeated many times until the finished model is formed. The operation of the machine can be paused to remove defective layers, and later resumed. nine0003
The machine, based on SGC printing technology, uses expensive, toxic and rare polymers. It works quite noisily and requires constant monitoring by the operator. The estimated cost of the 3D printer is $470,000.
3D printing technologies are currently developing very rapidly, and 3D printers are emerging that are already quite affordable for use in a small office and even at home. These include 3D printers that print by layer-by-layer polymer deposition. Of course, it will be difficult to obtain large models on such devices, but they can be successfully used to develop models of souvenirs or jewelry, as well as to solve various design problems. nine0003
nine0003
3D printing can be done in many ways and using various materials, but any of them is based on the principle of layer-by-layer creation (growing) of a solid object. Various materials can be used to make items, such as high-strength heat-resistant plastics.
Theoretically, with the help of a 3D printer, you can print any item that is in the house: from a tablespoon to a floor rug with a complex texture.
3D printing is good for industry: it can be used to “cast” body parts that are difficult or time consuming to obtain by other methods, such as milling. nine0003
In addition, 3D printing can be used to create products that are basically impossible to obtain by other methods, for example, to print a sphere inside another sphere. There are no geometric restrictions for 3D printing.
Today there is no doubt that the rapid production of robotic prostheses, glasses, assistive devices for people with disabilities, not to mention artificial organs - all this means a revolution in medicine and the discovery of new approaches to treatment. 3D printing is widely used in medicine to create models of human internal organs, prostheses and implants. nine0003
3D printing is widely used in medicine to create models of human internal organs, prostheses and implants. nine0003
The use of 3D printers in medicine can save lives. Such printers can recreate an exact replica of the human skeleton to practice techniques to ensure a successful operation.
Increasingly, 3D printers are being used in prosthetics and dentistry, as 3D printing makes it possible to obtain prostheses and crowns much faster than conventional production technology.
At the end of the first decade of the 21st century, a group of scientists from the Institute of Regenerative Medicine at Wick Forest University came to the conclusion that human tissues can be printed using inkjet printers, filling them with living cells. From that moment, painstaking work began on the creation of a bioprinter for growing human organs. Such a device was demonstrated in September 2011 at the TED-2011 conference on new technologies and design. The device functions just like an ordinary inkjet printer, but instead of ink, it uses human and animal stem cells. nine0003
nine0003
The 3D printer is capable of printing pieces of tissue, skin, spinal discs, knee cartilage and complete organs. Before printing, the patient's organ is scanned from different angles and the information obtained is loaded into a three-dimensional printer, along with a tissue sample of the organ. For several hours of operation, the device recreates an exact copy of the organ, including blood vessels.
Using 3D printing, American scientists have grown the human bladder and genital organs of rabbits, which, after implanting them in amputated rabbits, allowed the animals to mate again. The scientists also recreated the heart of a rat, which worked successfully after being implanted in an experimental animal. nine0003
This unique device can heal wounds directly on the patient, as well as eliminate mechanical damage to organs resulting from gunshot and stab wounds, accidents, etc. To do this, he scans the wound (organ) and fills it with the appropriate type of freshly grown tissue.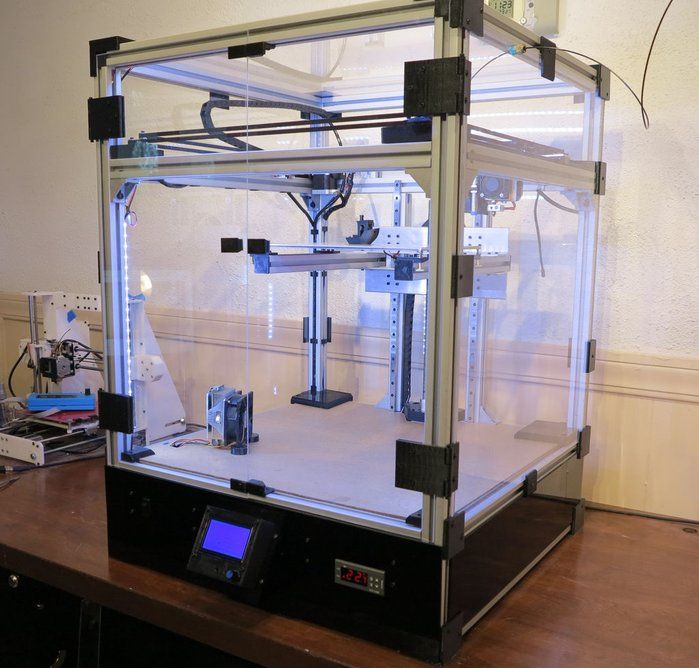
3D printing has proven itself in the production of mechanical prosthetic hands that perform simple functions. Such a lightweight bionic arm was designed and 3D printed by a team from the University of Saarland led by Professor Stefan Seeleke. nine0003
Unfortunately, this prosthesis is still in the prototype stage, but the team is very excited about their results and imagines that in the near future these prostheses that look and function like a real hand will become a reality.
3D printing can also be used to produce prosthesis elements required for use in orthopedics or dentistry. So, in early 2012, an 83-year-old woman from the Netherlands, instead of a jaw destroyed by cancer, was implanted with a titanium jaw, printed entirely on a 3D printer. nine0003
Emma Lavelle, an American girl from Philadelphia, suffered from congenital arthrogryposis, which left her completely unable to move her arms, her shoulder joints were turned inward, and she could only move her thumb. The 3D-printed outer skeletal elements, which Emma called "my magic hands," gave her the ability to play, draw, and hug her parents.
The 3D-printed outer skeletal elements, which Emma called "my magic hands," gave her the ability to play, draw, and hug her parents.
3D printers have also been used to create a bone augmentation platform for treating hospital patients. Professor Dietmar Hatmacher of the University of Queensland in Australia used 3D printing to help heal a hole in the skull of a nine-year-old girl. nine0003
After South African carpenter Richard Van Az lost his fingers in an accident, he set out to create an inexpensive prosthetic hand for people without fingers. Called the Robohand, the hand was designed by Richard with a designer on the other side of the world in Seattle.
At the same time, another unique operation was performed at the Utrecht University Medical Center: a young girl had almost her entire skull replaced with a printed plastic copy. This was extremely necessary, since the thickness of the girl’s own skull was constantly increasing due to illness, which created a real threat to life. At the time of surgery, the girl had loss of vision and severe headaches. The operation lasted 23 hours, and the result exceeded all expectations. After only a few months, the girl has already gone to work and feels much better than before the operation. Her sight has returned, and nothing reminds her that her life hung in the balance. nine0003
At the time of surgery, the girl had loss of vision and severe headaches. The operation lasted 23 hours, and the result exceeded all expectations. After only a few months, the girl has already gone to work and feels much better than before the operation. Her sight has returned, and nothing reminds her that her life hung in the balance. nine0003
But even this is not as impressive as the prototypes of bionic implants that biologists constantly demonstrate. For example, McAlpine, assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Princeton, last year showed a printed artificial ear that allows you to hear radio waves.
In 2011, scientists were able to reproduce a living human kidney. It took the 3D printer only 3 hours to do this.
Medical 3D models can be made from a variety of materials, including living organic cells. The choice of one or another material for medical prototyping depends on the goals and objectives facing physicians and the problems associated with the patient's health. nine0003
nine0003
More recently, the power and power of 3D printing has been demonstrated on the example of an ordinary eagle, which lost its beak due to the fault of poachers. 3D printing has made it possible to make an exact copy of the eagle's beak.
3D printing is widely used in the manufacture of architectural models of buildings, structures, entire neighborhoods, cottage villages with all the infrastructure: roads, trees, street lighting.
Using a 3D printer, you can make a model of an individual building or its various important elements, or immediately a model of an entire microdistrict or cottage village with roads and trees. nine0003
Cheap gypsum composite is used to print 3D architectural models, which provides a low cost of finished models One of the hot topics of discussion right now in the world of 3D printing is the possibility of its application by architects and in the construction industry. Every day, the reality is getting closer when buildings will be created thanks to additive technologies.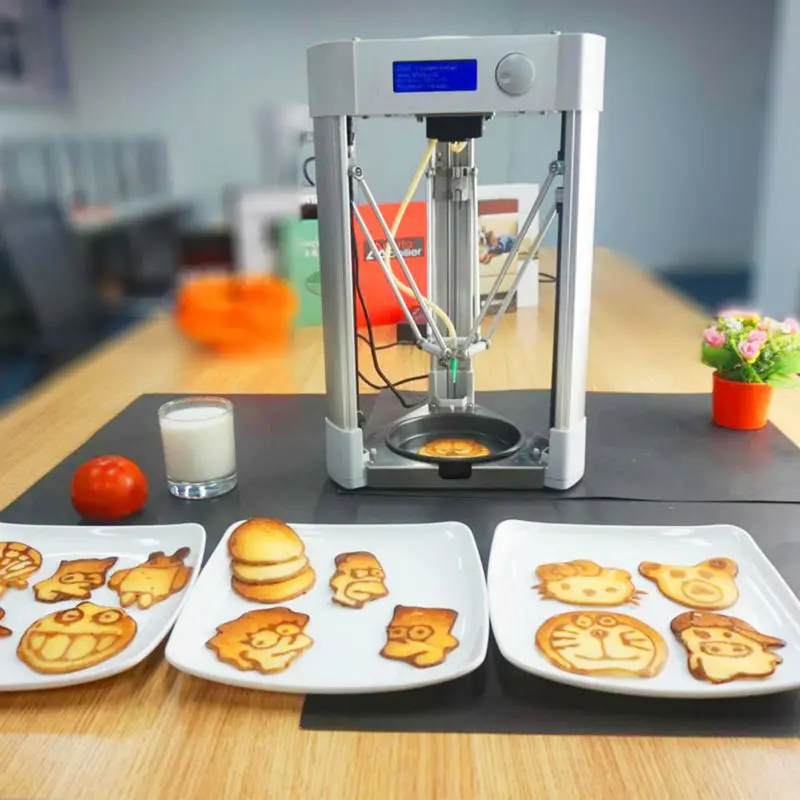
Winsun New Materials, a little-known Chinese firm in Suzhou County, Jiangsu Province, has developed a new approach to building simple one-story buildings. With the help of a huge 3D printer, Chinese builders promise an unprecedented speed of building houses - up to ten buildings in 24 hours! To design such a super-useful construction tool, Chinese businessmen invested $3.2 million. The printer itself for building houses was developed by engineers for 12 years. nine0003
No less interesting is the material used in the construction of new houses. Winsun New Materials uses unclaimed construction waste to make homes that are environmentally friendly and incredibly cheap—only $4,800 to build. China bribed everyone with cheapness, proving that 3D printing in modern construction is no longer expensive pampering and exotic.
The only detail that the Chinese have not yet learned how to print on a printer is the roof. The builders explain that at this stage it is impossible to erect this part of the building for technical reasons. nine0003
nine0003
University of Southern California engineers have created a 3D printing system for large objects. The system works on the principle of a construction crane, which erects walls from layers of concrete. Such a 3D printer can build a two-story house in just 20 hours. Workers will only have to install windows, doors and carry out interior decoration of the premises.
Dutch architects proposed to print a unique house in the form of a Mobius strip using a 3D construction printer. "Printing" at home is scheduled for 2014. The house is planned to be printed from a mixture of sand and binders. nine0003
Designers of all stripes, regardless of occupation, are showing an increased interest in the new 3D printing technology. Are no exception and those who are engaged in the development of clothing. At a fashion show, the most famous fashion designers do not consider it shameful to demonstrate clothes made from non-standard materials. Often on the podium you can see amazing robes made of wood, metal, plastic - beautiful and completely impractical clothes that are rather symbolic. But if you approach the issue of creating dresses, trousers and shirts in this way, then why not use a 3D printer? Especially since 3D printing can do what a fashion designer can only dream of - almost instantly provide a result. nine0003
But if you approach the issue of creating dresses, trousers and shirts in this way, then why not use a 3D printer? Especially since 3D printing can do what a fashion designer can only dream of - almost instantly provide a result. nine0003
One of the first who set out to print clothes on a printer was designer Michael Schmidt. His first creation is a unique dress.
For an unusual dress, an unusual way of designing it was also used. The dress was literally programmed and calculated.
The print out looks really good. It contains more than three thousand fastened movable elements that give the dress some elasticity.
Not so long ago, Dutch fashion designer Iris Van Herpen presented the Tension collection, all models of which were created using 3D printing. The collection was presented at the Fashion Week in Paris. nine0003
3D printed clothes can only be seen at fashion shows. But there is no doubt that the introduction of such products into mass production is only a matter of time. Perhaps in the near future we will be able to print a new shirt, evening dress or even a fur coat of the required color and size without leaving home.
Perhaps in the near future we will be able to print a new shirt, evening dress or even a fur coat of the required color and size without leaving home.
-
Shoe manufacturing
Among the exotic use cases for 3D printing is shoe manufacturing. nine0003
The first pair of 3D printed shoes came out in 2011 thanks to the efforts of Swedish students. Today, 3D printed shoes are on the world's leading catwalks. A significant advantage of such shoes is the exact consideration of the individual characteristics of its owner, including the size and shape of the foot.
The appearance of 3D shoes is significantly different from the traditional one, so it will be in demand among creative young people who want to emphasize their individuality. nine0003
3D printers have learned to print not only women's shoes, but also men's shoes. London College of Fashion student Ross Berber presented five pairs of printed shoes in his debut collection.
Polyurethane, rubber and plastic are used to make 3D shoes. The cost of such shoes is still too high to mass-produce them.
The cost of such shoes is still too high to mass-produce them.
So far, this service is intended for professional athletes. The leg of the future owner is scanned by a laser to create a digital model. Based on this information, shoes are "grown" by layer-by-layer laser sintering. nine0003
A well-known manufacturer of sportswear and footwear, Nike has applied 3D printing on an industrial scale. This brand has announced a new technology for the production of sports boots, which will allow the company to abandon the long process of creating template molds.
The most important thing in sports shoes is maximum grip on the ground. If we consider shoes as a construction, then the main part responsible for the sporting characteristics of the model is the sole. The results demonstrated by the athlete directly depend on the shape of the spikes, their number and the variant of their location on the shoe. Nike has developed a new outsole shaping principle based on selective laser sintering technology. nine0003
nine0003
Using 3D printers, you can create color 3D maps that accurately replicate the landscape of the area or show the level of occurrence of various rocks.
In this area, a 3D printer can be used to create prototypes and concept models of future consumer products or their individual parts. Such models can be used both for experimental purposes, for example, to determine the aerodynamic characteristics of a car body or aircraft fuselage, and for presentations of the appearance of a new product at meetings or in front of customers. nine0003
The use of 3D printers to create unique toys and souvenirs is no longer surprising. Now it's easy to get a ready-made full-color prototype before launching a product into mass production. Analysis of the prototype allows you to study the texture of the future product, its shape, size and color.
Most often, souvenir products are printed from gypsum materials, additionally processed to increase the strength of the finished product. 3D printers print souvenirs with different colors, up to a full-color texture in 3
3D printers print souvenirs with different colors, up to a full-color texture in 3
shades.
The Air Robotics Laboratory at Imperial College London also demonstrated an unusual project. Through the efforts of engineers, a flying 3D printer was created. The main goal of roboticists was to create a device that can be used to clear the area of radioactive debris, for example, in an accident at a nuclear power plant.
Scientists have combined a printer with a quadcopter and developed a special program that determines the behavior of this quadcopter. With the help of sensors, the first flying quadcopter identifies the source of radioactive contamination, after which it flies up and starts printing on the surface of the object with a sticky substance. Next, the robot sends a signal to its partner, which flies up and lands on a sticky "nest". After a while, the substance solidifies, and the second porter robot flies away, carrying away the cargo contaminated with radiation. The prototype is capable of lifting a weight of up to two and a half kilograms, but British specialists intend to build an enlarged copy of these robots in the near future, which will be able to pick up loads of up to forty kilograms. nine0003
The prototype is capable of lifting a weight of up to two and a half kilograms, but British specialists intend to build an enlarged copy of these robots in the near future, which will be able to pick up loads of up to forty kilograms. nine0003
-
Education.
The use of 3D printing technology in education allows you to get visual aids that are great for classrooms of any educational institutions, from kindergartens to universities, because they have increased reliability, do not emit products harmful to health during printing, do not present special disposal requirements, do not contain cutting and shaving materials, do not have lasers, have increased reliability due to improved technology. nine0003
Equipping educational institutions with design or design specialties with 3D printers will help increase the efficiency of the educational process and the rapid assimilation of knowledge by students.
Here there is a need to make exact copies of various objects, for example, as decorations for films or performances, dummies of rare museum exhibits.
For use in printing and related fields, 3D printers make it possible to produce trial models of packaging, bottles and bottles of the original form. Prototypes can be colored, with the inclusion of all design elements, incl. labels, barcodes, brand names. Finished packaging models can be demonstrated to the customer before launching into mass production. The advantage of 3D prototypes is obvious: the customer can hold the package in his hands, evaluate its texture, texture, color scheme and some other characteristics. nine0003
It enhances customer experience by demonstrating full product prototypes. This technology is also used in three-dimensional advertising.
Worth mentioning is also the possibility of using 3D printers to produce not just models and prototypes, but piece goods, such as art objects, for commercial purposes. The most popular and interesting type of such application was the production of character figurines for participants in Internet role-playing games. nine0003
nine0003
Professional 3D printers are gradually gaining ground in the small-scale production industry. Most often, this printing technology is used to produce exclusive products, such as art, action figures for players in Internet role-playing games, prototypes and concepts of future consumer products or their structural parts. Such models are used both for experimental purposes and for presentations of new products.
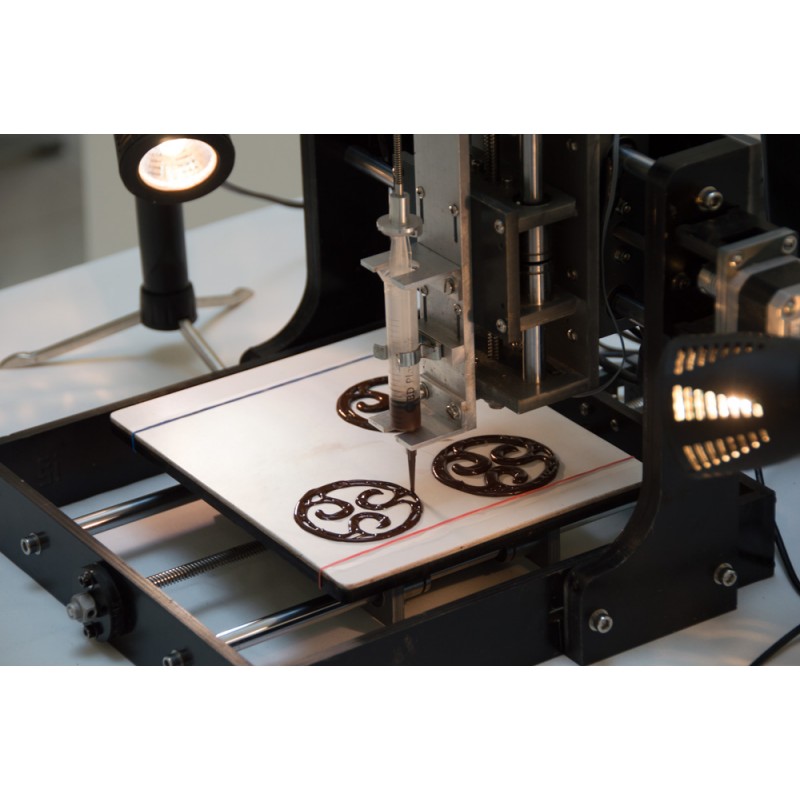
One of the first prototypes of devices for three-dimensional printing can be considered ... a confectionery syringe. Long before the advent of computer technology, confectioners deftly “printed” delicious patterns from cream and dough. But then a lot depended on the individual skill and skill of a person in the kitchen. And with the advent of 3D printers, the task has become easier. It was enough to equip the printer with edible material, correct the printing principle, and the result was a tool for edible masterpieces. nine0003
Modern 3D printers can print all sorts of delicious things. For example, one of the major chocolate corporations, The Hershey Company, uses 3D printing to produce confectionery.
For example, one of the major chocolate corporations, The Hershey Company, uses 3D printing to produce confectionery.
The first chocolate 3D printer is released in the USA. A 3D chocolate printer was unveiled at CES 2015 in Las Vegas. The device was named CocoJet.
The main material for CocoJet is white, milk and dark chocolate. The printer is able to create very complex designs "for tea". For example, using a 3D scanner, you can ask the printer to print a chocolate copy of your own face. Thanks to this device, you can always enjoy your chocolate dog or your favorite car. nine0003
3D printer allows you to create bright and original jewelry (bijouterie).
As you know, the most time-consuming procedure in the manufacture of jewelry is the creation of wax prototypes, which requires an enormous amount of time. With the advent of 3D printers, jewelers have the opportunity to quickly grow wax models of jewelry, previously developed in a special program, with which they can later work visually, improve them or create real jewelry from expensive metals in their image. nine0003
nine0003
A 3D printer developed by Carnegie Mellon University and a team of scientists at Disney Research in Pittsburgh is capable of creating 3D models from... soft yarn. The operation of such a 3D printer is somewhat reminiscent of a sewing machine. Along the base moves the needle combined with the print head, which forms the geometry of the printed model by felting. The first thought that comes to mind when you see such a device is that you can easily make soft children's toys with it. And in this sense, the fact that specialists from the ubiquitous Disney company had a hand in creating the printer seems very symbolic to us. nine0003
-
Weapons
3D printing has many advantages, however, in addition to the benefits it promises, this technology can bring harm to humanity. It all depends on the purpose for which a person will use it. You can print cases for gadgets, you can design prostheses, or you can use 3D printing to make jewelry. And you can set a goal to create a weapon aimed at the destruction of other people. Unfortunately, this thought quickly crossed the man's mind. And as soon as 3D printers became available to the average user, there were enthusiasts who immediately offered their designs of plastic weapons. nine0003
Unfortunately, this thought quickly crossed the man's mind. And as soon as 3D printers became available to the average user, there were enthusiasts who immediately offered their designs of plastic weapons. nine0003
The first pistol that could be easily 3D printed was the Liberator. It was invented by a Texas student named Cody Wilson. Interestingly, at the time of the appearance of the first printed pistol, Cody had a license to develop firearms.
The Liberator model was completely made of standard consumables, with the exception of one small detail - the pistol's firing pin still had to be metal. However, this is not a problem at all, since this part of the gun can simply be made from an ordinary nail. nine0003
As soon as Cody demonstrated his development, it was immediately subjected to a flurry of criticism from officials. Less than a week later, the US government passed a law restricting free access to blueprints for such devices.
Nevertheless, it is almost impossible to control the 3D printing of weapons today. Anyone with a 3D printing device can make firearms at home.
Anyone with a 3D printing device can make firearms at home.
According to researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology, as well as scientists at the National Institute of Applied Sciences in Lyon, 3D printers may pose health risks when used at home. In 2013, a team of scientists conducted a series of studies, and it was found that when plastic is heated during the printing process, it emits up to 20-200 billion ultra-small particles into the air per minute. Their entry into the lungs and blood poses a threat to human health, especially for those who suffer from asthma. nine0003
Also during the heating of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS plastic) by-products are released that are toxic to mammals. Of course, the degree of negative health impact largely depends on the 3D printing technology used, the design of the device, the presence of a hood, and other factors. However, in any case, it is best to print in a well-ventilated area, and the machine itself should ideally be hermetically isolated from the user during operation. At the moment, there are many artisanal designs of printers that are sold under the do-it-yourself scheme. Often these are Chinese assembly kits, where elementary security measures are not provided at all. nine0003
At the moment, there are many artisanal designs of printers that are sold under the do-it-yourself scheme. Often these are Chinese assembly kits, where elementary security measures are not provided at all. nine0003
The 3D pen is a tool that can draw in the air. Magic, you might think, but no, just another technological breakthrough in the field of 3D modeling. A gadget that is destined to forever change the idea of what “drawing” is, because now you can draw not on paper, but in space!
Today there are two types of handles: cold and hot.
The first to be printed with fast curing resins - photopolymers. "Hot" pens use various polymer alloys in the form of spools of plastic filament. nine0003
Unlike conventional writing and drawing devices, the pen is filled with plastic thread instead of ink. In the back of the case there is a special hole into which it is inserted. The built-in mechanism automatically brings the ink to the nozzle, where the thread is melted and squeezed out in the molten form.
The metal tip of the print head heats up to 240°C, so basic safety rules must be followed when working with the device. nine0003
Despite the fact that the handles are equipped with a built-in fan to speed up the plastic hardening process, careless handling of the device is directly related to the risk of burns.
Until recently, children used to draw with pens, pencils and felt-tip pens. Today, there is a 3D pen for this, thanks to which you can create three-dimensional figures in real time just in the air!
If you study the advantages of this gadget in more detail, it becomes clear that it is much more useful than a game console. nine0003
By regularly using a 3D printing pen, your child will noticeably improve finger motor skills. In his hands will be a powerful tool that develops fantasy and abstract thinking.
Of course, a 3D printer is able to create complex shapes, exactly repeating the elements of the programmed model. But the 3D printing pen has a number of exclusive advantages.
First of all, it is the weight. Modern gadgets weigh from 40 grams. Even a child can easily hold them in his hand. nine0003
Small dimensions allow you to take the device on business trips or on vacation. Some devices are equipped with rechargeable batteries, which makes it possible to use them away from power access points. In addition, the small size of the pen allows you to draw with it even in hard-to-reach places.
Today we can safely say that 3D pens are not a seasonal gadget. Multifunctionality, convenient dimensions and affordable price make them not just an addition to a desktop 3D printer, but its alternative. Having such a device at hand, you can realize many of your ideas, as well as solve most household problems in a matter of minutes. nine0003
It is easy to predict the near future. Devices for three-dimensional printing will master more and more new types of materials. The development of technology can be strongly influenced by some new discovery, which we simply cannot predict. The only thing that can be said with certainty is that the scope of three-dimensional graphics will become wider.
The only thing that can be said with certainty is that the scope of three-dimensional graphics will become wider.
The day is not far off when the owner of a 3D printer at home will be able to print not only plastic parts, but also complex electronic devices. One of the most requested features is support for printing with multiple materials at the same time. In the future, the possibility of combining different materials opens up simply fantastic opportunities for the production of objects for various purposes. nine0003
It is likely that the process will become more sophisticated and the functionality of 3D printers will expand. Already now we see the first hint of the evolution of these devices. In the same way that conventional printers have become MFPs with the ability to scan and copy, 3D printers will also learn to digitize the geometry of objects on the fly. This idea has already begun to be implemented by the engineers of the American company AIO Robotics.
Experts predict a stellar future for 3D printers. The times are coming when everyone will be able to print a new pair of shoes, a coffee set, toys for a child, a gourmet meal or heal a wound without leaving home. And such times are not far off. nine0003
The times are coming when everyone will be able to print a new pair of shoes, a coffee set, toys for a child, a gourmet meal or heal a wound without leaving home. And such times are not far off. nine0003
- Every designer's dream is a 3d monitor. These are special expensive monitors that allow you to see a 3D picture.
- University of Southern California scientists have developed a Contour Crafting system that can print a two-story residential building in 20 hours!
- Do you remember the proverb: "What does it cost us to build a house: let's draw - we will live?" Today it is already a reality.
- Peter Jackson's "The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey" features a lion's share of props created by 3D printing. nine0042
- Among the items that came into being in this way are pads that give volume to the hands, feet and ears of the actors, elven swords, helmets and axes.
- In 2000, a Minolta VI-700 3D scanner was used to restore Spain's famous prehistoric cave, Altamira.

Sources:
https://3dnews.ru/820667/page-2.html - Most interesting 3D printing projects
http://www.orgprint.com/wiki/3d-pechat/ -All about 3D printing
http://www.ituniverce.com/articles/nauka/3d-pechat-istoriya-vozniknoveniya/ - 3D printing: history of origin
http://www.invalirus.ru/3501-perevorot-v-medicine-3d-printery-dlya-organov.html - 3D ORGAN PRINTERS
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs? nine0003
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong. In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA). nine0003
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc. nine0003
On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details. nine0003
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
nine0042 -
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy. They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more. nine0003
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
nine0425 CreatBot F160-PEEK for use with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model. nine0003
Prismlab Large Area Industrial Resin Printer Family
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored. nine0003
Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored. nine0003
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support. nine0003
You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support. nine0003
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc. nine0003
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model. Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.). nine0003
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder).
 The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype. nine0003
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale. You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model. nine0003
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.
 5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin. nine0003
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles. nine0419
nine0419
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products). nine0003
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
nine0003
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burnout Resin Rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product. nine0003
Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product. nine0003
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different. nine0003
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.
Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling.
 Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make. nine0003
Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make. nine0003
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
nine0571What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer. For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D Printed Layout
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
If the item is only sold as an assembly.

Learn more