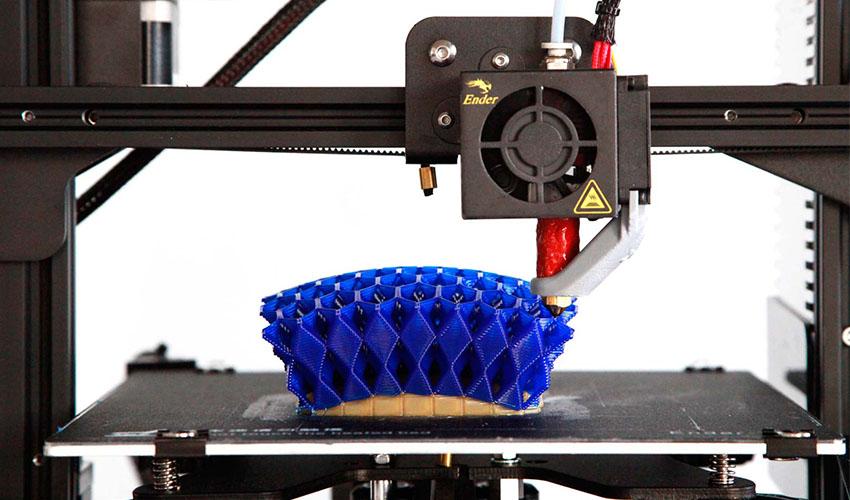
Black 3d printer filament
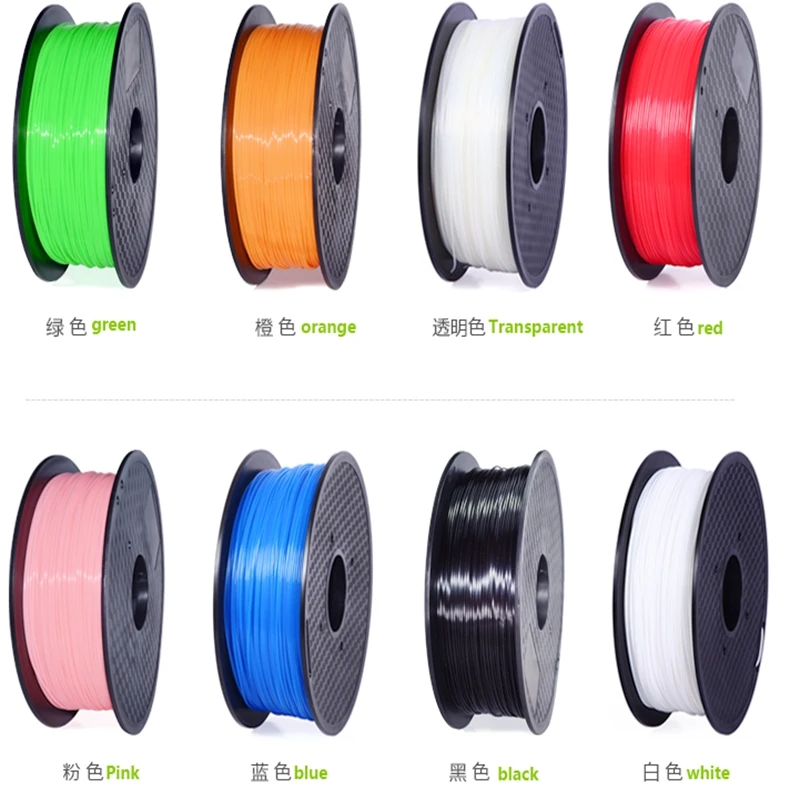
Flashforge Black PLA 3D Printer Filament, 1.75mm, 1kg Spool, compatible with most FDM 3D printers.
2023 New Year Sale: up to 60% off. Enjoy your holiday with Flashforge.
- Home
loading
Share the product to
Worry-free warranty
Dedicated support
Fast shipping.Free shipping for items available at USA/UK/AU/EU warehouses.
- Overview
- Parameter
- In the Box
About Black PLA Filament
Black PLA (Polylactic Acid) filament is a hot selling 3d printer material on almost all filament stores. It has easy accessibility, greater heat resistance, a simple post-production process, and fits almost all 3d designs. Flashforge black PLA filament is odor and bubbles-free, compatible with 99% FDM 3D Printers in the market. Properties are as following:
- RoHS certified;
- Nozzle temperature requirement: 190-220°C;
- Build plate temperature requirement: non-essential;
- Printing speed: 60-90mm/s;
- Layer height: 0.1~0.2mm;
- Density: 1.25±0.05g/cm3;
- Outstanding diameter accuracy +/- 0.02mm;
- Smoothen filament extrusion;
- Ultra-pure grade material & strict quality control standards to guarantee print quality;
- Minimal filament warping, curling, shrinkage, and bubbles during 3d printing process;
- Compatible with most FDM 3D Printers, perfect for Flashforge Adventurer 3, Finder, and Dreamer series 3D printers.
- Permits longer storage time without any compromise on filament quality;
| Shipping Notice | ||
|---|---|---|
| Warehouse | Destination | Delivery Time |
| United States | United States | 3-8 biz days |
| United Kingdom | The United Kingdom and most European countries | 3-8 biz days |
| Australia | Australia | 8-15 biz days |
Accessories and some filaments will be shipped separately from the China warehouse. | 10-22 biz days | |
Tech Specifications
| Spool Diameter | 200 mm [7.9 in] |
| Spool Hub Hole | 52 mm [2.1 in] |
| Spool Width | 76 mm [3.0 in] |
| Filament Diameter | 1.75 mm |
| Shipping Weight | 1.5 KG (3.3lbs) |
| Net Weight | 1.0 KG (2.2lbs) |
\
Comparison between Flashforge PLA, PLA Pro, PLA-CF, ABS, ABS Pro, PETG, PETG Pro, PETG-CF.
| Spec & Print Setting | PLA | PLA Pro | PLA-CF10 | ABS | ABS Pro | PETG | PETG PRO | PETG-CF10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 45-49 | 45.5-49 | 40-45 | ≥43 | ≥53 | 40-45 | 35-40 | 40-43 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | 69-75 | 73-76 | 85-95 | 50-55 | 45-50 | 75-85 | ||
| Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | 1000-1100 | 950-1050 | 1100-1300 | 1000-1100 | 1100-1200 | 2100-2400 | ||
| Elongation @ Break (%) | 13. 5-15.5 5-15.5 | 14.5-16.5 | 11.5-13.5 | ≥10 | ≥20 | 6.0-8.0 | 6.0-8.0 | 7.5-8.5 |
| Heat Deflection Temp (oC) | 53 | 53 | 60 | 88℃ | 88℃ | 74 | 68 | 70 |
| Nozzle Temp (℃) | 200-220 | 190-210 | 200-230 | 230-250 | 230-250 | 240-250 | 220-240 | 230-250 |
| Bed Temp (℃) | 50-55 | 50-55 | 40-50 | 100-110 | 100-110 | 80-90 | 70-80 | 60-80 |
| Printable with Glass Plate | YES | YES | ! (with glue stick) | ! (with glue stick) | ! (with glue stick) | YES | YES | ! (with glue stick) |
| Printable with PEI Sheet | YES | YES | / | ! (with glue stick) | ! (with glue stick) | YES | YES | / |
| Print in Enclosed Chamber | / | / | / | YES (recommend) | YES (recommend) | / | / | / |
| Print with Hardened Nozzle | / | / | YES | / | / | / | / | YES |
| Dryer Box | / | / | YES | / | / | / | / | YES |
Flashforge Filaments Key Features
| Key Features | PLA | PLA Pro | PLA-CF10 | ABS | ABS Pro | PETG | PETG PRO | PETG-CF10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filament Type | Standard | Standard | Carbon fiber filament | Standard | Standard | Standard | Standard | Carbon fiber filament |
| Food Safe | YES | YES | / | / | / | YES | YES | / |
| Low Warping | YES | YES | YES | / | / | YES | YES | YES |
| High Tenacity | YES | YES | YES | / | / | YES | YES | YES |
| Dissolvable | / | / | / | YES | YES | / | / | / |
| Chemical Resistance | / | / | / | / | / | YES | YES | / |
Your questions will be answered by the users who have purchased this product
May not be greater than 255 characters.
Read All Reviews
FAQ
No questions.
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA High Strength 3D Printer Filament Black - 1.75mm / 4kg Spool
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA was developed to be the strongest, easiest to print, most accurate, and most reliable PLA filament on the market today. Many PLA filaments tend to be brittle, but IMPACT PLA is a true high strength 3D printer filament. I-BEAM IMPACT PLA is based on a custom blend of Natureworks brand high temperature PLA using proprietary impact modifiers.
- Strong filament for making functional parts
- Near perfect overhangs and supported layers
- Annealable for even stronger parts and higher heat deflection temps
- 100% consistent and accurate results
- Very easy to print on any printer
- Bio-based using genuine NatureWorks PLA polymer
- Made in USA
$159.99
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA High Strength 3D Printer Filament Black - 1. 75mm / 4kg Spool quantity
75mm / 4kg Spool quantity
SKU: 90-175-600-4 Categories: 1.75mm, Filaments, I-BEAM IMPACT PLA 1.75mm Tags: 3d printer filaments, 3d printers, 3d printing, black pla, filament, I-BAEM, pla, stacker
- Description
Material: I-BEAM IMPACT PLA
Actual Weight on Spool: 4000g
Approximate Length on Spool: 1320m
Diameter Tolerance: ± 0.05 mm
Density: 1.24 g/cm3
Glass Transition Temperature: 55°C to 60°C
Suggested printing temperature: 210°C – 240°C‡
Suggested print speed: 35 – 100 mm/s
Cooling Fan: yes
Suggested heated bed temperature: 50°C – 60°C
Build platform
I-BEAM IMPACT PLA filament adheres well to both heated and non-heated build platforms. We recommend printing on BuildTak.
If printing on a glass bed, apply glue-stick. A very thin layer of glue will be sufficient to keep your print nicely in place. Another gluing method is dissolving PVA glue in water. The consistency of the mixture can be quite thin, like skim milk. By applying just a few drops and smearing the mixture out before you start printing will create a very thin layer which will hold the filament down.
The consistency of the mixture can be quite thin, like skim milk. By applying just a few drops and smearing the mixture out before you start printing will create a very thin layer which will hold the filament down.
‡3D printers use a variety of hot-end designs which makes it difficult for us to provide a universal temperature. Please refer to your printer’s operating manual for safety and temperature specifics.
In-house testing
All I-BEAM filaments have been rigorously tested at STACKER to ensure the best results possible. We not only test I-BEAM filament on our STACKER 3D printers, but we have also test I-BEAM on a variety of other 3D printers in our print lab to ensure quality and functionality of I-BEAM filaments. If you’re not sure how to print with I-BEAM, please contact us at [email protected].
Low Carbon Footprint Bio Filament
IMPACT PLA filament uses bio-plastic from NatureWorks. Because I-BEAM IMPACT PLA is made from plants, it is essentially made from greenhouse gasses. As a result, PLA has a much lower carbon footprint than any other 3D printer filament. I-BEAM proudly uses a specialized formula of NatureWorks. Click here to learn more about Ingeo and greenhouse gasses.
As a result, PLA has a much lower carbon footprint than any other 3D printer filament. I-BEAM proudly uses a specialized formula of NatureWorks. Click here to learn more about Ingeo and greenhouse gasses.
Excellent diameter tolerance
I-BEAM uses sophisticated and highly precise laser measuring systems to check the diameter of the filament in real time during the actual production process. It’s measured over 1000 times per second and this helps guarantee that each spool of filament is produced within tolerance. We can guarantee +/- 0.05mm for our 1.75mm diameter filament, which means you can be rest assured that your printer is extruding the exact amount of material called for.
Climate Controlled Warehouse
STACKER warehouses all of its filaments in a climate controlled warehouse to protect the filament from heat and moisture which can degrade the life and performance of some filaments.
Annealing I-BEAM IMPACT PLA
We recommend using a lab oven (although any oven will work). Set the temperature at approximately 120°C (250°F). Place your part on a baking sheet and place in the preheated oven. The annealing process takes approximately 20 minuets for smaller parts (larger parts may take up to an hour to fully anneal). Note, the part will shrink during the annealing process. After baking the part, remove from oven and allow to cool before handing the part.
Set the temperature at approximately 120°C (250°F). Place your part on a baking sheet and place in the preheated oven. The annealing process takes approximately 20 minuets for smaller parts (larger parts may take up to an hour to fully anneal). Note, the part will shrink during the annealing process. After baking the part, remove from oven and allow to cool before handing the part.
Spool Size:
Outer Diameter: 300mm
Thickness: 100mm
Inner Diameter: 53mm
Tech Downloads: Technical data and MSDS sheets are available at http://i-beamfilament.com/Materials
Best 3D Printer Filaments (Review 2021)
Once you've chosen your 3D printer, you need to choose the type of filament intended for your project. Filament is a raw material used in 3D printers that will be heated to a high temperature to turn it into a semi-solid state. At this point, the printer can easily create the appropriate design layers and print the entire 3D CAD model onto the plate.
However, as you research the various 3D printer filaments, you will hear of numerous materials that can only make it harder to choose the right one for you. This is especially true for people who are just starting to explore the world of the 3D printing process. nine0003
While most of us are not new to PLA and ABS, there are other fiber materials you should be aware of such as HIPS, PET, PETG, TPE, TPU, TPC and a few others. And to get a better idea of them, here are some of the more typical types of 3D printer filaments available on the market.
3D Printer Filament Types
PLA Filament
Polylactic acid (PLA) reigns supreme in the industrial 3D printing world. 3D printing with PLA is so easy. It has a lower plate temperature, so it doesn't need a heating bed and therefore has fewer warping issues. nine0003
It is widely used in prototyping, such as printing low-wear toys, prototype parts and containers. Please note that it cannot be used for anything that has a temperature rating of 60°C or higher as it warps at 60°C. For all other purposes, PLA is suitable for a general 3D printer.
Please note that it cannot be used for anything that has a temperature rating of 60°C or higher as it warps at 60°C. For all other purposes, PLA is suitable for a general 3D printer.
ABS Filament
ABS (also known as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is the second most popular 3D printing filament. In general, ABS withstands high loads and high temperatures. Thus, it is suitable for most applications. It is great for items that are frequently handled, dropped or heated. For example, mobile phone cases, high-wear items, automotive trim parts, and electronic houses. nine0003
Nylon filament
Nylon is the preferred family of synthetic polymers for many industries, professional 3D printing being one of them. As for other forms of filament, they have better performance, efficiency, versatility and durability. Given the strength and versatility of nylon, this type of 3D printer filament can be used to make loops, buckles or gears, as well as working prototypes.
PET (G) thread
The most widely used plastic in the world is polyethylene terephthalate (PET). It is best known as water bottle thread, but it is also used in clothing fibers as well as food containers. Although PET is commonly used in 3D printing, its modified version PETG is becoming more common.
The G in PET stands for glycol, resulting in a more transparent filament that is less prone to cracking and easier to use. PETG is versatile but surpasses many forms of 3D printer filament in its strength and inability to reach high temperatures or withstand strong impacts. The fulfillment of the following conditions makes it an excellent choice for 3D printing filament for practical parts such as mechanical parts, printer parts, and protective materials. nine0003
TPE, TPU, TPC filament
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPE) is a flexible and durable plastic similar to rubber. In addition, TPE is mainly used for the production of auto parts and household appliances.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyester E) is a special form of TPE that is very common among high end 3D printers. Compared to conventional TPE, TPU is significantly more flexible, hence allowing more control during printing.
What's more, TPC (Thermoplastic Copolyester) is also another form of TPE that is not as widely used as TPU. The key advantage of TPC over TPE is its greater resistance to chemical and UV attack, as well as heat (up to 150°C). nine0003
If you need to create items that require a lot of wear, use TPE or TPU because these filaments use 3D printed filaments that are vulnerable to deformation. Products such as toys, mobile phone cases, or wearable items such as wristbands can be some examples of its application. On the other hand, TPC performs well for comparable applications, but outperforms it in harsher environments, including outdoors. nine0003
Wood filament
Technically not wood because it contains wood fiber in enhanced PLA. Generally speaking, wood products are valued for their natural beauty rather than their practical utility. When printing items for tables, tables or shelves, it is recommended to use wood 3D printing media. Any of the application examples include chalices, figurines, and trophies. What's more, it's a truly innovative application for 3D printers, which are often used to model real buildings, structures, or trees. nine0003
Generally speaking, wood products are valued for their natural beauty rather than their practical utility. When printing items for tables, tables or shelves, it is recommended to use wood 3D printing media. Any of the application examples include chalices, figurines, and trophies. What's more, it's a truly innovative application for 3D printers, which are often used to model real buildings, structures, or trees. nine0003
Metal thread
Like wood thread, it is not 100% metal. Specifically, it is composed of metal powder, and one of the following materials is PLA or ABS. However, the effects also have a metal-like aesthetic appeal. Metal Infused can be printed for both decorative and practical purposes. Figures, prototypes, toys, including tokens, can be 3D printed from metal and give them a great look. You can also use metallic 3D printer filament to make parts such as tools or finishing components in light applications. nine0003
Biodegradable (biophila) filament
This biodegradable 3D printer filament aims to reduce the impact of all plastic waste into the atmosphere. Although biodegradable 3D filament was originally environmentally friendly, it can still produce quality printed products. Choose this biophile if you don't have special requirements for strength, versatility or endurance. For projects that require prototyping, you can also benefit from these flawless fiber prints that can be biodegraded responsibly. nine0003
Although biodegradable 3D filament was originally environmentally friendly, it can still produce quality printed products. Choose this biophile if you don't have special requirements for strength, versatility or endurance. For projects that require prototyping, you can also benefit from these flawless fiber prints that can be biodegraded responsibly. nine0003
Conductive thread
This is a kind of three-dimensional material with conductive carbon particles in it. It is ideal for Arduino-based open source businesses. You'll want to look into this filament if you want to make circuits, LEDs, sensors, and other low voltage projects.
Magnetic filament
PLA magnetic iron filament is as magnetic as the name suggests. This one-of-a-kind filament is made from PLA material impregnated with powdered iron. It is ideal for making fridge magnets and other custom-made decorative items. Also, it can be used to create multiple DIY structures, sensors, educational resources, etc. 0003
0003
Top Five 3D Printer Filaments
Access to a 3D printer creates a whole new world of creative printing. There are several purposes and hobbies that 3D printing serves, but they all rely on the same raw material - 3D printer filament.
While unique materials are recommended for durable and impressive models, you need to select the right material for your 3D image. need printer. You also need to consider the quality and attributes of the thread. That being said, finding the right 3D filament is no picnic. nine0003
As such, we sought the advice of tech experts and 3D printer enthusiasts to find the most popular 3D printing filaments on the market. And to give you a clearer idea of their main features and specifications, we have done a detailed analysis to better understand which filament you should pair with your 3D printer. Also, don't forget to click on the buttons below to get the best deals on Amazon!
3D Printer Filament Buyer's Guide
6 - Nylon (Nylon), PA (Polyamide)
WHAT IS NYLON?
Nylon or polyamide, a popular family of synthetic resins used in many industrial applications, is the champion in the world of professional 3D printing. Compared to most other types of 3D printer filament, it takes first place in the competition for strength, flexibility and durability.
Compared to most other types of 3D printer filament, it takes first place in the competition for strength, flexibility and durability.
USER NOTE
Another unique feature of this 3D printing filament is that it can be dyed both before and after the printing process. Nylon also has a drawback - it, like PETG, is hygroscopic, strongly absorbs moisture. Remember to store both materials in a cool, dry place, keep these filaments in perfect condition, and this will ensure the best quality prints. Better yet, dry it before printing. nine0003
in general, there are many varieties of nylon, but among the most common for use as a thread for a 3D printer-618 and 645.
Thread properties for 3D printer: nylon (polyamide)
- 9000 very high | Flexibility: high | Durability: High
-
Difficulty of Use: Medium
-
Print Temperature: 240 ° C - 260 ° C
-
Table temperature: 70 ° C - 100 ° C
-
Sensation: Significant
- 9000 Soluble: NOT 9011 safety: refer to manufacturer's instructions
WHEN SHOULD NYLON (POLYAMIDE) FILAMENT BE USED?
Taking advantage of nylon's flexibility and durability, this filament can be used to create tools, functional prototypes or mechanical parts (such as hinges, buckles or durable gears), pattern rigging. nine0003
nine0003
resume
-
Plus: High flexibility, high flexibility, durability, self -smuggled material
-
disadvantages: As a rule, expensive moisture, requires high temperature of the nozzle and table
9000 9000 9000 The performance of objects printed from nylon can be significantly improved by using nylon filament made with additional fillers: fiberglass or carbon fiber. nine0003 -
Pros : Can be used as both a support material and a strong base filament for a 3D printer
-
Cons : Requires dilution with relatively expensive D-limonene to remove supports, only compatible with ABS
-
The “cleaning” temperature depends on what types of 3D printer filament you have used before, and which filament you plan to use next (cleaning filament operating temperature: from 150 to 300°C).
-
It is generally not necessary to use more than 10 cm of cleaning thread at a time.
-
There are other cleaning methods, such as cold removal of used filament residue with a solvent, followed by mechanical cleaning. nine0003
-
Pros: The is an easy way to achieve a smooth surface for your print on a less complex 3D printer.
-
Cons: higher price compared to ABS or PLA, inability to process objects with fine surface details.

-
The main condition is that your printer must be able to print at an extruder temperature of 130 o C.
-
The extruder must be built according to the “Direct” scheme (not Bowden!).
-
Preferably Teflon tube up to nozzle for good filament glide.
-
Adjustable push wheel pressure in a wide range of settings.
-
It is also desirable that the feed gear should not be on the motor shaft, but through the gearbox. The motor heats up and can additionally soften the thread on the broach.
-
Other measures may require modifying the extruder and applying print adhesive to your printer table.
-
Pros: Creation of melted forms using a 3D printer
-
Lessine: requires a certain type of extruder design and printed platform, limited use
PA-GF (glass filled nylon)
Glass fiber reinforced nylon. Compared with pure nylon filaments, the mechanical strength, stiffness, heat resistance and fatigue strength of glass-filled nylon are greatly improved, and shrinkage during 3D printing is reduced. Moreover, the hygroscopicity is reduced.
The "trouble" of pure nylon is the relatively low temperature of the onset of softening and thermal deformation under load - total 50 °С. Filling the thread with carbon fiber helps to defeat this effect.
PA-CF (Carbon Filled Nylon)
Environmentally friendly material based on nylon and 20% carbon fiber . Lightweight, odorless print with a matte finish. High hardness, high rigidity, good toughness, wear resistant material, suitable for printing industrial parts. Deformation temperature 120°C, therefore suitable for high temperature use. Compared to nylon, it has lower shrinkage and distortion. Fire rating: UL94-V2.
The positive experience gained with carbon-filled nylon led major filament manufacturers to make the logical decision to launch other grades of thermoplastic filaments enhanced with carbon fiber content. An overview of the various proposed options for such composite threads is the subject of the next paragraph of this Guide.
7 - Carbon-filled filaments
When 3D printer filaments such as PLA, ABS, PETG and nylon are reinforced with carbon fiber, the result is an extremely strong and stiff material with relatively low weight. Such compounds are particularly advantageous in structural applications that must withstand a wide variety of end uses. nine0003
Such compounds are particularly advantageous in structural applications that must withstand a wide variety of end uses. nine0003
NOTE TO THE USER
The downside of this material's outstanding properties is increased wear on your printer's extruder nozzle, especially if it's made of a soft metal such as brass. Just 500 grams of this exotic 3D printer filament will noticeably increase the diameter of a brass nozzle, so if you don't like frequent nozzle changes, consider using nozzles made of a more durable material - steel or even ruby.
WHEN SHOULD CARBON FILAMENT BE USED?
Due to its structural strength and low density, carbon fiber is the best choice for mechanical components. Do you want to replace a part in your car or aircraft model? Try this filament.
SUMMARY
8 - HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene)
Commercially available High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) for CDs. nine0003 In the world of 3D printing, HIPS usually plays a different role. Using HIPS as a support material is quite simple. Print support structures on these materials where they are needed, and then carefully break them out with tweezers or other suitable tool. If it is difficult or impossible to get to the support printed with HIPS thread, it can be dissolved with D-limonene. It is also useful to squirt D-limonene at the contact points of the main model and the HIPS support before breaking it out. nine0003 Unfortunately, using HIPS as a backing material limits you to printing the main part in ABS only. Other 3D printing materials may be damaged by D-limonene. But HIPS and ABS print well together because they have the same strength, rigidity and close printing temperature. In fact, despite the fact that HIPS was originally used as a support material, it is a worthy filament for basic printing as well. It is stronger than PLA and ABS, warps less than ABS, and is easy to glue, sand, and paint. nine0003 With many characteristics similar to ABS, HIPS 3D Printing Filament is a good all-round solution for parts that must endure wear or for projects that require post-processing material to achieve the final look. 9 - PVA advantage is fully used for commercial purposes. Common uses include packing dishwasher tablets or fishing lure bags (throw one into the water and watch it dissolve, releasing the bait). The same principle is applied in 3D printing, making PVA an excellent support material when combined with another filament in a dual extruder 3D printer. The advantage of using PVA over HIPS is that it can be used to support more materials than just ABS. The downside of this filament is that it is a bit more difficult to handle. Care should also be taken during storage - moisture in the atmosphere can damage the filament before printing. Silica gel dry boxes and pouches are a must if you plan to store your PVA coil for a long time. nine0003 PVA filament is an excellent choice as a backing material for complex raised prints. 10 — Cleaning This filament is unique in its kind because it is the only one designed not to print objects. It is intended solely for cleaning the nozzle of a 3D printer from the remnants of any working material after printing. The usual procedure for using a cleaning filament is as follows: heat the extruder tip to a temperature slightly above the operating temperature for the filament used before. To determine it, before starting the procedure, carefully read the information from the manufacturer of the filament used for printing. First, push the cleaning filament by hand (if your printer is designed to allow this) through the extruder to be cleaned. You should definitely clean your 3D printer's extruder between using two materials with completely different temperatures or colors. Generally speaking, it is very useful to regularly run a little cleaning filament through the heating tip of your 3D printer, for example, after a long (more than a day) printing even without a planned filament type change. 11 - Smooth Many 3D printed objects require a glossy finish. These are molds for casting in silicone, finishing elements of furniture prototypes or other details that are sensitive to a smooth look. In such cases, the main disadvantage of filament printing (layer-by-layer deposition) plays a very unpleasant role. How to get rid of the characteristic layered structure without applying laborious and expensive mechanical post-processing? Printed ABS objects can be processed in an acetone bath, but this operation is not the most pleasant for the printer user. How to be? The answer is: use an easily smoothed plastic, for example, eSmooth from the Chinese manufacturer eSUN. nine0003 Smooth filament printing is no more difficult than PLA, temperature characteristics are close, a closed chamber of a 3D printer is not required. It is enough to treat the constructed object with ordinary ethyl or isopropyl alcohol and leave it for some time, preferably for 8-9 hours. This interesting filament is recommended for applications where a very smooth printed surface is required and mechanical post-processing is difficult or impossible. It is desirable that there are no small significant elements of construction or design on the surface - they can be melted with alcohol. But details with a rounded surface and smooth transitions will turn out very well! 12 - Wax3D (Wax thread) Do you want to get a product made of real brass, pewter or other metal? It's possible! First, you'll print your investment casting pattern using 3D printer wax filament, and after a few extra steps, your idea will be embodied in metal. nine0003 This process is called "lost wax casting" and it works like this: Create a direct wax mold, i.e. a wax copy of the intended final metal product. Dip the mold in plaster or other special compound and allow it to dry and harden. Place an item with a lost shape into the furnace. At a sufficiently high temperature, the wax will melt, leaving a "negative" space inside the shell into which the metal work is to be cast. nine0003 The 3D printer wax filament made the first step much easier. According to traditional technology, first it was necessary to prepare a metal mold on a CNC machine, and then pour wax into it to obtain an investment mold for metal casting. When using this or similar waxy materials, be aware that they are much softer than most types of 3D printer filament. Basic conditions for printing with wax filament: If you are casting metal parts, wax-like filaments such as Filamentarno WAX3D can give you more options, allowing you to print complex 3D objects directly, integrating into your investment casting workflow. 13-ASA (acrylonitril-stool) Of course, ABS is good, but it has its drawbacks: ABS prints tend to denature and yellow if left outdoors in direct sunlight. That's why plastics manufacturers have found an alternative - acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), a weather-resistant analogue of ABS plastic that was originally developed for outdoor "street" use. Hence its main application is in the automotive industry. nine0003 ASA has high rigidity, resistance to dilute acids, mineral lubricating oils, diesel fuel. Unlike ABS, ASA plastic is resistant to UV radiation. The material does not turn yellow in the open air, it is easy to process. The ASA range includes high and low gloss grades. The main application of ASA plastic is the production of lampshades, car exterior parts (rear-view mirrors), lighting products. In addition to being strong and relatively easy to print, this 3D printer filament is also extremely resistant to reheating and, most importantly, shape and color changes. Another small benefit of using ASA over ABS is that it warps less during printing. But be careful how you set up your cooling fan - the ASA can easily burst if the fan is set too high during printing. nine0003 For a variety of outdoor applications, from replacement electrical outlet covers and architectural trim to custom garden gnomes and birdhouses. 14 - PP (Polypropylene) Polypropylene (PP) is strong, flexible, lightweight, chemical resistant and food safe, which may explain its wide range of applications including engineering plastics, food packaging , textiles and banknotes. nine0003 Unfortunately, as a type of 3D printer filament, PP is difficult to print, often exhibiting severe deformation and poor adhesion to the table. 3D printers can't print "over the air" - that's where support structures come in. The protruding elements require some support structure, and this is where HIPS really excels. Together with ABS in a dual extruder printer, HIPS acts as an excellent support material.
3D printers can't print "over the air" - that's where support structures come in. The protruding elements require some support structure, and this is where HIPS really excels. Together with ABS in a dual extruder printer, HIPS acts as an excellent support material.
USER NOTES

WHEN SHOULD HIPS BE USED?
SUMMARY
 nine0003
nine0003
NOTE TO THE USER
WHEN SHOULD PVA BE USED?
SUMMARY
 Please note that cleaning the extruder is required not only when it is already clogged. It is especially useful to clean the nozzle when changing to a build with a different color or from one material to another, especially if they are incompatible due to very different extrusion operating temperatures. How can you continue to work with a filament with a relatively low melting point after printing is refractory without completely removing its residue from the nozzle? It is also helpful to keep the extruder clean to prolong its life. Make regular use of the cleaning floss a healthy habit. nine0003
Please note that cleaning the extruder is required not only when it is already clogged. It is especially useful to clean the nozzle when changing to a build with a different color or from one material to another, especially if they are incompatible due to very different extrusion operating temperatures. How can you continue to work with a filament with a relatively low melting point after printing is refractory without completely removing its residue from the nozzle? It is also helpful to keep the extruder clean to prolong its life. Make regular use of the cleaning floss a healthy habit. nine0003
NOTE TO THE USER
 This is necessary to remove the "burned" material residues. Then lower the temperature to operating temperature and feed approximately 10cm of cleaning floss as normal. nine0003
This is necessary to remove the "burned" material residues. Then lower the temperature to operating temperature and feed approximately 10cm of cleaning floss as normal. nine0003 A few additional points to note:

SUMMARY
NOTE TO THE USER
 Alcohol, as it were, melts the outer layer, making the surface glossy. However, during processing, small external parts can “float” or dissolve completely. Therefore, not any geometric shape of a product or tooling can withstand such a smoothing method. This should be taken into account when choosing an object for printing with the Smooth filament. nine0003
Alcohol, as it were, melts the outer layer, making the surface glossy. However, during processing, small external parts can “float” or dissolve completely. Therefore, not any geometric shape of a product or tooling can withstand such a smoothing method. This should be taken into account when choosing an object for printing with the Smooth filament. nine0003
WHEN SHOULD I USE Smooth?
SUMMARY
NOTE TO THE USER

WHEN SHOULD WAX THREAD BE USED?

SUMMARY

NOTE TO THE USER
WHEN SHOULD ASA THREADS BE USED?
SUMMARY
USER NOTE

Learn more