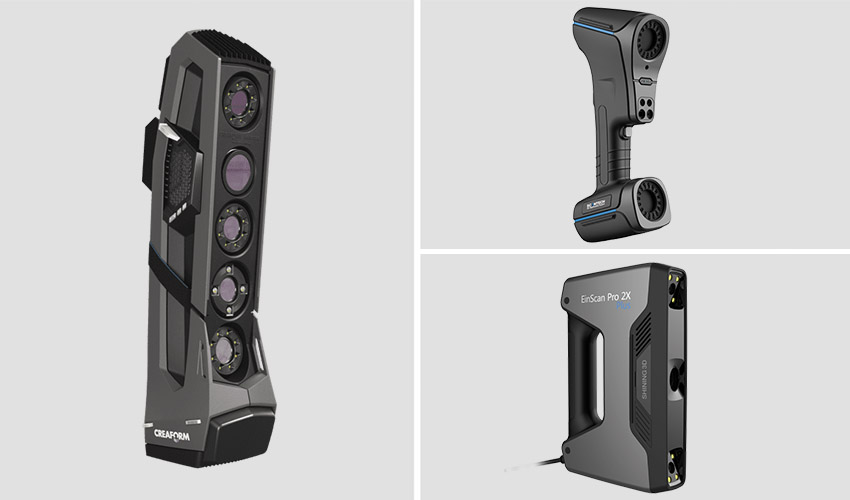
Best 3d scanner for architecture
The Best 3D Scanners in November 2022 (Hobbyist & Commercial)
3D scanners are changing how we make, design, and see the world. By scanning nearby objects, people and almost anything else, these scanners create entire 3D digitized models of physical objects in just seconds.
Buying The Best Radar Detector In 2...
Please enable JavaScript
Buying The Best Radar Detector In 2018
Sometimes called 3D laser scanners, 3D model scanners or 3D object scanners, 3D scanners are integral for custom 3D printing and other fun home 3D scanner uses, for saving historical artifacts as digital models, dentistry – and so much more.
What’s more, you can now pick up powerful low-cost 3D scanners for just a few hundred dollars, and if you’re content with low-quality basic scans, you can even use your phone!
BUDGET PICK
Revopoint POP 2
Versatile and portable with handheld & stationary options and color scanning
Up to 0. 05mm accuracy on a small scanner that costs under $1000
Available at:
Revopoint hereMID-RANGE PICK
Matter & Form V2
Accurate 0.1mm scans
Powerful stationary scanner for 25x18cm objects
Comes with specialized software
Available at:
Amazon hereDynamism herePREMIUM PICK
Shining 3D EinScan H
0.05mm scan accuracy and 0.25mm resolution with 1.2 million points/s
Infrared scan sensors make scanning darker colors easier
Available at:
Dynamism hereTo rank the best 3D scanners, we considered:
- Accuracy and resolution
- Scan area (benefiting handheld scanners that can scan larger areas)
- Scan speed
- Ease of use
- Price-performance ratio
- Versatility
We also separated our 3D scanner reviews into three main price categories:
- 3D scanners under $1000
- Mid-range 3D scanners ($1,000 to $10,000)
- Industrial 3D scanners ($10,000+)
The Best 3D Scanners for All Prices Ranges
| 3D Scanner Brand & Name | Type of 3D Scanner | Price | Where to buy and where has the best price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revopoint 3D POP 2 | Structured Light | $699 | Revopoint 3D here |
| Creality CR-Scan 01 | Structured Light | $700 | Creality Store here |
| SOL 3D scanner by Scan Dimension | Desktop 3D Scanner | $699 | Amazon here |
| BQ Ciclop | Laser Triangulation (DIY) | Depends if pre-assembled or DIY | Amazon here |
| Matter & Form V2 | Desktop 3D Scanner | $749 | Amazon here |
| Shining 3D EinScan SE | Desktop 3D Scanner | $1,399 | Amazon here |
| EinScan H | Handheld | $4,999 | Dynamism Store here |
| Shining 3D EinScan Pro 2X Plus | Handheld 3D Scanner | $6,800-$8,300 | Amazon here |
| Scantech iReal2E | Handheld 3D Scanner | $3,980 | Scantech Site |
| Artec EVA | Industrial 3D Scanner | $19,800 | |
| Scantech SIMSCAN | Portable 3D scanner | Contact for price | Scantech site |
| Scantech KSCAN | Handheld 3D Scanner | Contact for price | Scantech site |
But before we get into the best scanners, here’s a quick intro to how 3D scanners work:
How Does a 3D scanner Work?
3D scanners work by creating point clouds based on images taken of a solid surface or object — basically huge numbers of data points that denote where an object is — to create a 3D model of the scanned part. Millions of individual data points make up the model, which you can then export as an STL, OBJ or other file type and import to CAD software, or 3D print via a slicer.
Millions of individual data points make up the model, which you can then export as an STL, OBJ or other file type and import to CAD software, or 3D print via a slicer.
3D scanning includes several different technologies, such as Structured Light scanning and Laser Triangulation, while some are stationary and some are handheld.
The Best 3D Scanners 2022: Budget Picks
3DSourced is reader-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
Revopoint POP 2
- Price: $699 — Available at Revopoint Official store here
- Precision: 0.05 mm
- Scan Speed: 10 FPS
- Minimum Scan Volume: 20 x 20 x 20 mm
- Single Capture Range: 210 x 130 mm
- Working Distance: 150 – 400 mm
- Point Cloud Distance / Single-Frame Accuracy: 0.15 mm
We were extremely impressed with the Revopoint POP 2 when we tested it recently, and overall we feel it’s the most versatile and powerful 3D scanner under $1,000. While there are some great stationary scanners like the Matter and Form V2, the Revopoint’s usability for turnstile stationary scanning, color scanning, as well as handheld scanning for faces and bodies makes it the ideal multi-use 3D scanner.Scanning a toy with the Revopoint POP 2 using the “fill holes” setting (often leave it off and sort any errors in post).
While there are some great stationary scanners like the Matter and Form V2, the Revopoint’s usability for turnstile stationary scanning, color scanning, as well as handheld scanning for faces and bodies makes it the ideal multi-use 3D scanner.Scanning a toy with the Revopoint POP 2 using the “fill holes” setting (often leave it off and sort any errors in post).
The POP 2 notably upgrades on the original POP, with precision increased from around 0.3mm to up to 0.05mm (our tests found it to be in the 0.07mm range, which is still very impressive), a slightly faster scan speed of 10fps vs 8, and a slightly smaller minimum scan volume of 20mm³ vs the original POP’s 30mm³.
Testing the precision accuracy of the Revopoint POP 2 during calibration.It scanned color images well when we tested it on some kids toys and a multi-color Rubik’s cube, and scanned faces accurately (but you need to change some settings around to prevent any noise distorting your scanned faces). Don’t automatically mesh clouds however when face scanning – it’ll create distorted scans such as this one we tried.
Don’t automatically mesh clouds however when face scanning – it’ll create distorted scans such as this one we tried.
Overall, we highly recommend it as one of the best scanners in its price range – standard scanning, face scanning, color, or entire body scanning, it’s good for all uses.Testing the color 3D scanning and editing the scan in Revo Studio software.
Compare the scanners: Revopoint POP vs POP 2
Creality CR-Scan 01
- Price: $650-$700 — Available at Creality Official store here / Amazon here
- Accuracy: 0.1 mm
- Resolution: 0.5 mm
- Max Scan Volume: 536 x 378 mm
- Technology: Structured light
- Speed/Frame Rate: 10 FPS
With a cemented reputation for offering some of the best budget 3D printers on the market today, Creality aims to do very much the same with the affordable Creality CR-Scan 01 3D scanner. It employs structured light technology to feel out the shape, size, and texture of a 3D object to generate a digital reproduction.
It employs structured light technology to feel out the shape, size, and texture of a 3D object to generate a digital reproduction.
Creality has fitted the CR-Scan 01 with both a handheld mode and a stationary turntable mode, each with their own set of advantages:
- In handheld mode, the scanner quickly works through larger objects, offering flexibility and on-the-fly capture.
- Switch to turntable mode, and the tripod-mounted Creality CR-Scan 01 creates an automated, higher-accuracy 360° scan as the object rotates on the turntable.
Both modes offer accuracy of 0.1 mm, a resolution of 0.5 mm, 24-bit high-fidelity color mapping, and marker-free scanning thanks to a clever alignment algorithm.
The Creality CR-Scan 01 also makes smart adjustments based on light levels, making it suitable for low-light environments. These are all excellent features for the asking price and sufficient for most hobbyist scanning needs, although somewhat lacking for high-precision scanning.
However, where the Creality CR-Scan 01 shines is a distance of 400-900 mm, which outclasses most budget 3D scanners, with a scanning area of 536 x 378 mm. In practice, you can scan medium to large objects further away with a larger frame size, which speeds up the scanning process considerably.
Finally, the bundled Creality’s CR Studio is a robust post-processing suite with all manner of editing, repair, color, and smoothing tools to polish off digital scans ready for 3D printing or other applications. It’s a solid competitor to the Revopoint scanners.
SOL 3D Scanner by Scan Dimension — Perfect desktop 3D scanner
- 3D scanner price: $699 — Available on Amazon here
- Accuracy: up to 0.1 mm
- Scan volume: up to 170 x 170 mm
- Scan speed: 10 min in Turbo mode, 20 min normally
SOL is a desktop laser scanner designed for scanning small yet detailed items, with good accuracy for the price.
The actual scanner itself weighs just 7 pounds, and can scan objects that weigh up to 2kg. This light weight makes it a perfect portable 3D scanner if you’re on the move.
It has two different modes depending on what you’re scanning:
- Near mode: for scanning objects of up to 100 mm in diameter and 100 mm in height.
- Far mode: for scanning objects up to 170 mm in diameter and 170 mm in height.
The SOL boasts an accuracy of around 0.1 mm, extremely good for the price range. You scan objects with their included SOL 3D software, and can then easily export your scans as OBJ or STL files and import them into a 3D slicer for 3D printing.
Danish company Scan Dimension promotes this impressive 3D visualizer not only for makers or hobbyists, but also for entrepreneurs. They sell the SOL 3D scanning camera as a way for entrepreneurs to show their products off with a 360-degree view, with easy ways to share these scans on Facebook.
Additionally, Scan Dimension say the scanner is also perfectly suited for education, for teaching students STEM education through scanning and editing structures.
Overall, it’s well suited as both a 3D scanner for businesses, as well as a home 3D scanner for hobbyists.
BQ Ciclop — Home-made 3D scanner for technical makers
- Price: Depends if buying or DIY — Available on Amazon here
- Resolution: 0.5 mm
- Scan time: 2-8 mins
- Maximum scan volume: 200 x 200 x 205 mm
- 3D scanning technology: Laser Triangulation
Unlike many scanners, this DIY 3D scanner is open source, with all the files hosted on Thingiverse for you to download and print. The Ciclop has proven popular, with tens of thousands of downloads on Thingiverse alone.
BQ provides all of the information, software, and electronics for this 3D scanner kit which you can modify for yourself on their website, and other variations have been brought to market offering tweaks and improvements on the opensource design, such as CowTech’s version.
Read more: the other variations of Ciclop feature in our DIY 3D scanners review
The BQ Ciclop 3D scanner uses laser triangulation technology, and can scan objects in a few minutes. Moreover, the simple and well-written instructions allow anyone, no matter their skill level, to build the scanner in under an hour. BQ host downloads for all the drivers for the camera and firmware that you need, and developed a specialized 3D scanner app called Horus for scanning on your Ciclop.
It’s simple but effective. It’s made from ten 3D printed parts (download .STL files from Thingiverse), a threaded rod, a Logitech C270 webcam, two line lasers, and a turntable platform with a stepper motor, though you can edit and modify it as you wish.
The BQ Ciclop scans a volume of 250 x 205 mm and has a resolution of up to 0.5mm. It can be connected via USB or Bluetooth, making it a versatile and affordable low-cost 3D scanner for beginners.
Spanish tech company BQ have released this open-source 3D scanner which you can put together inexpensively.
Matter and Form V2 MFS1V2 — Portable 3D scanners under $1,000
- 3D scanner cost: $749 — Available on Amazon here / Available on Matterhackers here
- Scan volume: 250 x 180 mm
- Accuracy: within 0.1 mm
- Scan speed: up to 65 seconds
The Matter and Form V2 is an updated version of the original desktop 3D scanner made by the Canadian tech startup. This low-cost 3D scanner uses 2 lasers and an HD-CMOS sensor to produce high-resolution, full-color 3D scans.
The scanner has an accuracy of up to around 0.1mm, and is easily connectable to your computer through USB to transfer over your scans.
For editing scans, the Matter and Form scanner comes with specialized Mfstudio, and +Quickscan which boosts scan speed to up to 65 seconds. You can then export the STL file and print them with your 3D printer.
The 3D scanner can scan objects in sizes up to 25 cm tall and 18 cm in diameter. It is compatible with every major OS, so Mac users needn’t worry. What we like most however is that it folds up, making it a perfect portable 3D scanner.The new Matter and Form scanner can generate a full 3D scan in 65 seconds.
It is compatible with every major OS, so Mac users needn’t worry. What we like most however is that it folds up, making it a perfect portable 3D scanner.The new Matter and Form scanner can generate a full 3D scan in 65 seconds.
Medium Priced 3D Scanners: $1,000 to $10,000
Shining 3D EinScan SE — Best 3D scanner under $2000
- Price: $1,199 — Available on Amazon here / Dynamism here
- Scan accuracy: within 0.1 mm for single shots
- Scan range: single scan = 200 x 150 mm, maximum scan range = 700 x 700 mm
- Scan speed: a single shot is under 8 seconds
Shining 3D have made a name for themselves in the medium-range 3D scanning sector, with cheaper options such as the EinScan-SE as well as more expensive scanners like the EinScan Pro 2X Plus.
The EinScan SE is one of the best 3D object scanners in its price range. It scans in around 8 seconds (versus 4 seconds for the EinScan SP) and can complete a whole 360-degree scan in its Automatic Scan mode in around 2 minutes.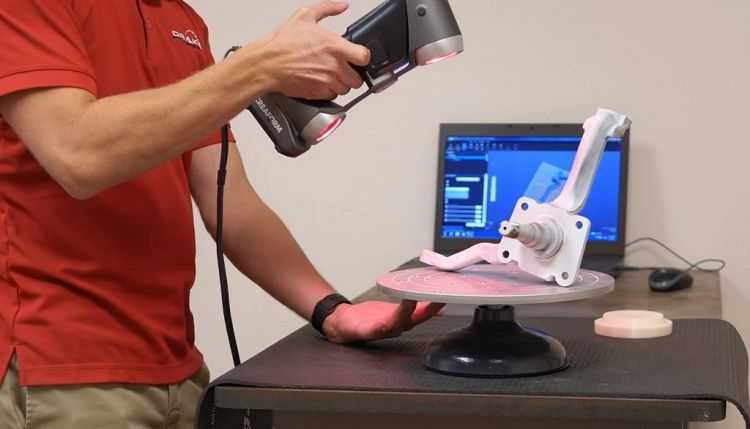
It can scan objects up to around 200 mm wide and 150 mm tall, with a single shot accuracy of within 0.1 mm — making it one of the best 3D scanners under $2000. For a fixed scan without the turntable, max scan volume increases up to 700 x 700 mm.
Overall, this 3D model scanner is accurate, reliable, and makes it easy to quickly scan stationary objects and 3D print them with ease. The EinScan SP — described in more detail further in this guide — is more precise, but costs more. Therefore, it’s a matter of your budget and how important this additional quality is for you personally.
EinScan H
- Price: $5,000 — Available at Dynamism here
- Accuracy: 0.05 mm
- Resolution: 0.25 mm
- Max Scan Volume: 780 x 900 mm
- Technology: Hybrid structured light LED and infrared
- Speed/Frame Rate: 1,200,000 points/s, 20FPS
The EinScan H is a professional-grade handheld 3D scanner that combines speed, accurate reproduction, and ease of use with a particular emphasis on bringing usually tricky 3D objects to digital life.
The EinScan H combines two light sources – structured LED and invisible infrared – to cover a wide range of 3D objects, modes, and applications.
For example, the infrared light excels at capturing the detail and intricacies of darker colors, notably those of human hair and general facial scanning – with dark hair the bane of any experienced face 3D scanner.
An added benefit of the invisible light is more comfortable scanning for the subject and no on-face glare to complicate the scanning process.
Manufacturer Shining 3D has also gone to considerable lengths to merge impressive accuracy and resolution along with fast scanning speeds. The EinScan H pushes a resolution of 0.25 mm with accuracy as low as 0.05 mm, all at roughly 1,200,000 points/s at 20FPS.
The scanner also features authentic, full-color reproduction with solid texture mapping that translates to systematically excellent scan quality.
According to Shining 3D, it’s possible to scan an entire human body in fine detail in a matter of minutes. A generous 420 x 440 mm single capture range helps keep things speedy even when scanning large objects aided by an optimized alignment algorithm to keep scans crisp and precise.
A generous 420 x 440 mm single capture range helps keep things speedy even when scanning large objects aided by an optimized alignment algorithm to keep scans crisp and precise.
Although priced at $5000, the EinScan H falls roughly in the affordable range and is a versatile tool suited for healthcare, art, forensic science, and other professional 3D modeling applications.
Scantech iReal 2E Color 3D Scanner — A complete 3D scanning solution
- Price: $3,980
- Scanning area: Up to 850 mm x 800 mm
- Accuracy: Up to 0.100 mm
iReal 2E is a professional handheld color 3D scanner manufactured by Scantech. The company specializes in developing, manufacturing, and selling intelligent visual inspection equipment and sells an entire range of 3D scanners for various applications and sectors.
The iReal 2E uses red VCSEL structured light technology to offer you a simple and safe 3D scanning experience, eliminating the issues of dazzling lights and difficulties in hair 3D scanning.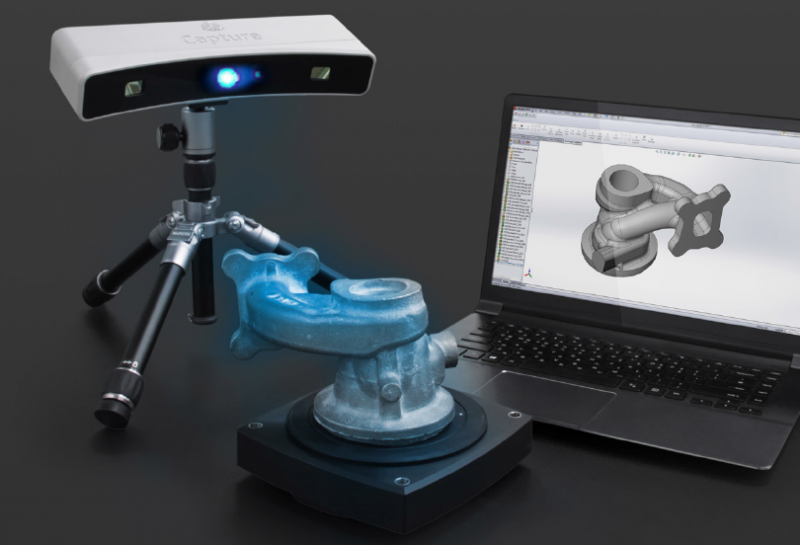
Without attaching markers, a quick and accurate texture and geometry scan can be achieved with a wide scanning area of 850 mm x 800 mm, 750 mm depth of field, 1.5 million measurements per second, and at 0.100 mm accuracy. Mixed alignment modes meet various scanning situations.
Shining 3D EinScan SP
- Price: $2,599 — Available on Amazon here / Dynamism here
- Scan range: single scan = 200 x 150 mm, max scan range = 1200mm³
- Accuracy: within 0.05 mm for single shots
- Speed: single shot speed of under 4 seconds
The second Shining 3D medium-range 3D scanner in our ranking, the EinScan SP is more accurate than the EinScan SE, with accuracy up to 0.05 mm rather than 0.1 mm, and scans single shots in half the time (4s vs 8s).
To save you time: double the price, double the accuracy — and half the scanning time.
The scanner uses white light scanning technologies to make very accurate scans of objects as small as 30 x 30 x 30 mm.
Full objects are typically scanned in less than a minute, and images in less than four seconds.
What’s more, despite its cheaper price, many buyers have reported that it can compete with scanners costing ten times as much for scan quality. It also comes with a tripod for stationary object 3D scanning.
Shining 3D EinScan-Pro 2X Plus — One of the best 3D scanners around
- Price: $5,999 (full industrial pack costs extra) — Available on Amazon here / Dynamism here
- Accuracy: up to 0.04mm in fixed scan turntable mode
- Volumetric accuracy: 0.3mm/m
- Speed: fixed scan single shot in under 0.5 seconds / up to 30fps with handheld use
The EinScan-Pro 2X Plus costs more than the EinScan SP and H, and can be used as a fixed or handheld 3D scanner to capture various-sized objects.
It uses white light 3D scanning technologies to increase accuracy and scan faster (sub 0. 5-second single shot scans), creating high-quality scans in record time.
5-second single shot scans), creating high-quality scans in record time.
You can simply hold the scanner and point it towards the object or room you want to 3D scan, and instantly record crisp scans of your surroundings. Whereas lower-cost scanners limit you to desktop sizes, the Pro 2X Plus frees you to capture entire rooms.
You may want to 3D scan a car, your friend, or even turn it into a baby 3D scanner for a 3D memory of your child before it grows up!
You retain the accuracy however with the scan volume freedom, with accuracy up to 0.03mm for objects less than 4m away.
Industrial & Professional 3D Scanners: $10,000+
Artec EVA — Powerful handheld 3D scanner
- Price: $19,800
- Accuracy: up to 0.1 mm + 0.3mm/m
- Resolution: up to 0.2 mm
- Speed: captures up to 16fps in HD and full-color
- Working distance: 0.4m – 1m
Creating new innovative solutions in 3D technology since 2007, Artec 3D is a global leader in handheld 3D scanners. Their most popular scanner, the Eva, is a handheld, industrial 3D object scanner, and an excellent solution for medium-sized objects ranging from motorcycle wheels to car exhaust systems, human busts and facial close-ups.
Their most popular scanner, the Eva, is a handheld, industrial 3D object scanner, and an excellent solution for medium-sized objects ranging from motorcycle wheels to car exhaust systems, human busts and facial close-ups.
Light, quick, and versatile, Artec Eva captures precise measurements in high resolution, while structured light scanning technology makes the scanner safe to use in any situation – even difficult to scan surfaces such as black or shiny surfaces are effectively captured by Eva.
Ideal for use in industries including product design, heritage preservation, healthcare, and reverse engineering, this market leader can accurately scan full-color objects at a range of up to 100cm with color and texture, making it a great solution for fast and accurate 3D models.
Scantech SIMSCAN — hand-sized portable 3D scanner
- Accuracy: up to 0.020 mm
- Resolution: up to 0.025 mm
- Scanning area: up to 410 x 400 mm
Scantech’s SIMSCAN consists of two sets of industrial black & white cameras, a laser projector with 30 laser lines, and a set of multifunctional buttons. Its high-quality components ensure fast and stable 3D scanning.
Its high-quality components ensure fast and stable 3D scanning.
It features three scanning modes: ultra-fast scanning, hyperfine scanning, and deep hole scanning optimized for different scanning situations. With its intelligent auxiliary lights, it can even scan darkly lit objects.
Powered by a robust algorithm, SIMSCAN’s measurement rate can be up to 2.02 million measurements/s with an accuracy of up to 0.020 mm. It has a field of view of up to 410 x 400 mm.
With a net weight of 570g, SIMSCAN can be among the top list of the most lightweight and portable 3D scanners in the market. It is designed for both beginners and professionals to conduct 3D scanning regardless of ambient conditions. Thanks to its compact size and portability, SIMSCAN enables on-site and efficient 3D scanning, and it suits well for scanning hard-to-reach areas.
Made from aerospace-grade aluminum-alloy, Scantech’s SIMSCAN scanner is sturdy and durable and performs well in heat dissipation. Its material ensures a prolonged use of the 3D scanner. With an anti-slip shell and a hand strap, you can orient this scanner in any way you choose to suit your 3D scanning needs.
With an anti-slip shell and a hand strap, you can orient this scanner in any way you choose to suit your 3D scanning needs.
Scantech KSCAN-Magic — industrial handheld 3D scanner
- Resolution: 0.010 mm
- Scanning rate: 1,350,000 measurements/second
- Scanning area: 1440 x 860 mm
Esteemed 3D scanner company Scantech have announced the launch of their latest KSCAN 3D scanner, with 5 five different modes for all types of scanning. These include a large area scanning mode, fast scanning mode, photogrammetry, as well as a fine scanning mode. Featuring both infrared lasers and blue laser technologies allows the KSCAN-Magic to accomplish a wide range of scanning functions effectively.The KSCAN-Magic 3D scanner can handle large, industrial objects like plane parts, as well as intricate, smaller objects.
It scans accurately, quickly, can handle small and large objects, and is designed to accelerate time-to-market. The 41 equipped laser lines can handle an incredible 1. 35 million measurements per second, creating detailed scans in record time.
35 million measurements per second, creating detailed scans in record time.
If you are looking for leading-edge 3D solutions for your business, KSCAN definitely surpasses expectations with its resourcefulness and precision.
Are 3D Scanners Worth It?
3D scanners are almost always worth the investment, but to decide which is best for you, you’ll need to consider your budget, needs, and priorities. Keep an eye on scan resolution quality and accuracy, scan speed, and price to find a 3D scanner that’s worth it for you.
Buyer’s Guide – Things To Consider When Buying A 3D Scanner
Budget
Expect to pay anywhere from $400 to $200,000 for a 3D scanner. There are numerous options suited to all budgets dotted between those two extremes.
Entry-level hobby scanners suitable for 3D printing are available for less than $1,000, while more robust machines suited for light-professional scanning sell for around $5,000.
Should you want the cream of the crop scanners designed for the most-demanding industrial-level applications such as engineering, expect to pay more than $10,000.
Speed
When applied to 3D scanners, speed refers to the rate at which a machine captures or scans a 3D object. Consumers and most professional 3D scanners record speed in points per second or frames per second. The higher the count, the faster the scanner.
If you’re buying for a professional setting where productivity is critical, we recommend eyeing faster printers, which generally push points per second into the millions and frame rates around 20 FPS.
Resolution and Accuracy
Accuracy refers to how well the finished digital object matches its real-world counterpart. Accuracy pops up in specification sheets expressed in mm, which indicates to what degree the 3D scan sticks to the shape, size, features, etc., of the real-world object.
For a budget 3D scanner, 0.1-0.2 mm is a solid reference point, while much more expensive industry scanners can jump to as low as 0.009 mm on the most powerful devices.
Though similar to accuracy, the resolution refers to the smallest possible distance between points on a 3D scan. In layman’s terms, a higher resolution delivers finer details and more intricate, faithful features. You’ll find manufacturers refer to resolution in mm, a measure that balloons and shrinks based on the price of the 3D scanner.
In layman’s terms, a higher resolution delivers finer details and more intricate, faithful features. You’ll find manufacturers refer to resolution in mm, a measure that balloons and shrinks based on the price of the 3D scanner.
Budget printers waver around 0.3-0.5 mm, while professional scanners can push resolutions as high as 0.1 mm.
Software and Connectivity
Connectivity refers to how a 3D scanner allows you to scan, export work, and interface with a PC or other device as well as the source of power. In most cases, USB is the standard, with some outliers offering Bluetooth.
If you’re looking for portability, consider handheld scanners that pair with Smartphones and power banks so you can quickly scan on the move.
Software tied to 3D scanners come in all shapes and sizes, from barebones scanning tools to advanced suites with all manner of post-processing touch-up options.
It goes without saying that software capabilities match the target audience of each scanner. Pay more for a professional scanner, and the software generally features a more robust set of tools.
Pay more for a professional scanner, and the software generally features a more robust set of tools.
Use Case
Entry-level 3D scanners are a good option for hobbyists looking to scan objects with 3D printing in mind. They are just about affordable and work well, although they lack the detail and speed of pricier models.
We recommend handheld 3D scanners for larger models. These grant a degree of freedom and movement to capture all the detail and breadth of bigger objects. A large scan area helps speed up scanning large objects, too.
For small fixed object scanning, where capturing all the rich details and texture of a model tops your list of requirements, look to stationary scanners, ideally with a turntable, tripod, and an optimized alignment algorithm.
3D Scanning to 3D Print
3D scanners are often used to create 3D printable models, with 3D scanner and 3D printer setups allowing you to replicate almost anything in front of you. Simply use the 3D scanning camera to create a digital model of your object, and then 3D print the scan.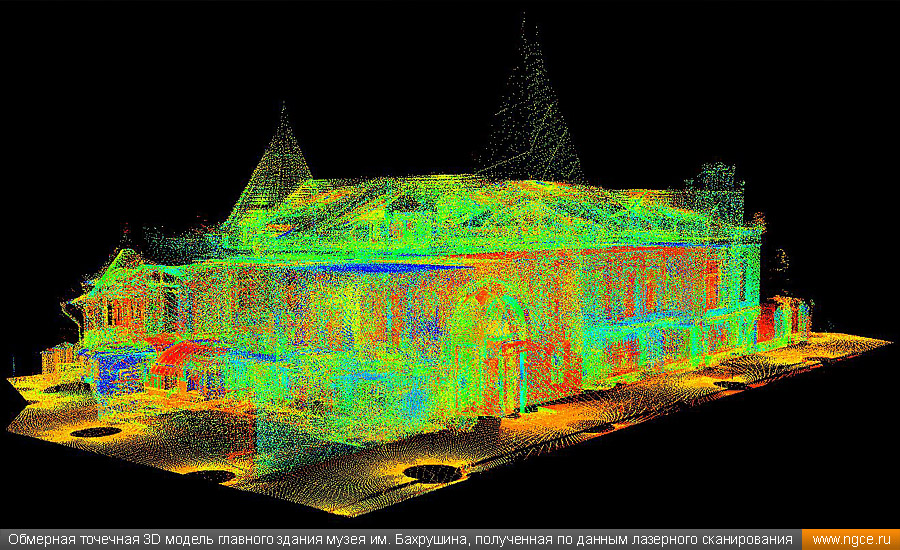
Large objects can be scanned using handheld 3D scanners and moved around the object’s dimensions, and then sized down and 3D printed as a scale model. These 3D printer scanner combos offer almost limitless versatility.
3D Scanner Cost
Budget/entry-level
Thanks to efforts from companies like Creality and Revopoint, there’s a concerted effort to lower the cost of entry and boost accessibility to 3D scanners.
It’s now possible to buy a decent entry-level scanner for under $1,000, with ultra-budget options like the Phiz 3D scanner dropping as low as $400.
Even though the experience and features measure up to the price paid, budget 3D scanners offer everything needed to create decent quality scans suitable for hobbyist applications.
Read more: the top low-cost 3D scanners
Mid-range
Jumping up to the mid-range category, you’ll find 3D scanners priced anywhere from $1,000 to $10,000. These are generally professional-grade machines with a range of tech, modes, and excellent scan quality, striking a balance between functionality and price.
Top-range/Industrial
The top-shelf 3D scanners. Expect to pay upwards of $10,000 for industrial-grade devices. These are very much no-compromise options boasting the peak in accuracy, resolution, and scan speeds for industry applications such as scientific measurements, reverse engineering, demanding 3D visualization, architecture, and rapid prototyping.
3D Scanner Uses
Medical: custom orthopedics, wheelchair and mobility aids, prosthetics, plastic surgery implants, protective equipment, realistic dummies for training.
Dental: bespoke implant and crown design suited to specific patients.
Jewelry: bespoke designs, repairs, and easy duplication/replication of damaged family heirlooms or discontinued jewelry with sentimental value.
Hobbyist 3D Printing: scanning real-world objects for reproduction using a 3D printer. Miniatures, cosplay, household items and repairs, toys, and other functional parts.
Virtual Reality and Game Design: real-world object/landmark scanning for use in VR environments, and body scans to create realistic animations and in-game models.
Engineering: tolerance testing, quality control, data analysis, fully textured models, infrastructure building and monitoring.
Reverse Engineering and Repairs: automotive, aviation, naval repairs, and restoration of antique or discontinued vehicles.
Archeology and Conservation: heritage conservation of objects, artifacts, and skeletal remains.
Architecture: building scanning for surveying, design, and reverse engineering degraded exteriors for repair.
Forensics: digital replicas of crime scenes to capture evidence such as shoe prints, blood stains, bullet holes, and so on.
Types of 3D Scanners
The main types of 3D scanners include:
- Laser triangulation 3D scanners
- Structured light 3D scanning
- Photogrammetry
- LIDAR (time-of-flight)
- Metrology 3D scanners
- Intraoral 3D scanners for dentistry
- 3D body scanners
The two most-used technologies are structured light scanning and laser triangulation.
Structured Light Scanning
Structured light scanning is commonly used in handheld 3D scanners and involves projecting patterns of light at an object, with two cameras usually placed on either side of the projector to measure the light pattern from each side and calculate precise differences at every point in their field of view.
These cameras measure how the light deforms the light pattern, and by triangulating these multiple different reference points across different images of the scan from each camera view, you can accurately calculate the dimensions of the object.
As a result of its portability and accuracy, dental 3D scanners typically use structured light scanning to scan patients’ mouths and create dental implants and models. Beyond this however, architects and historians are using these types of 3D scanning to keep digital records of priceless historical monuments, and NASA even use it to map interplanetary terrains.
However, the use of projected light makes it very sensitive to the lighting conditions in the scanning environment, so working outside or in other similar environments can be difficult.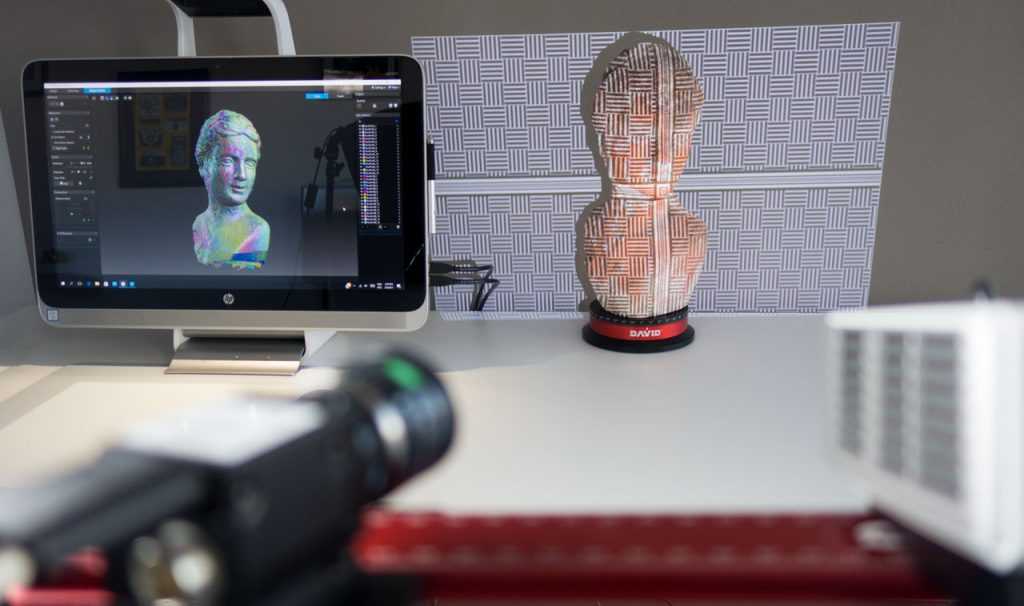
Laser triangulation
Laser scanning involves projecting a laser point on an object and then using sensors to capture the reflections to gather data on the object’s size. Based on the reflection angle from the laser’s sensors, the 3D scanner can create accurate textures and surfaces using trigonometric functions.
However, because it works off reflections it can be ineffective if scanning shiny or reflective surfaces, and won’t work well with anything transparent.
Structured light scanning is generally considered more accurate than laser scanning, with less noise in scans.
LiDAR 3D scanning and Time of Flight 3D scanning
Another form of 3D scanning, and the technology used in the latest iPhone 12 Pro, is LiDAR. Light Detection and Ranging involves shooting out light beams and calculating the object’s area — based on the speed of light — on the time taken to reflect back to the Lidar 3D scanner.
These are very similar to time-of-flight 3D scanners. These scanners shoot light pulses, calculating the time of flight for each pulse to create a 3D visualization — or point cloud. They’re commonly used to map terrains, measure real estate, and in architecture and construction.
These scanners shoot light pulses, calculating the time of flight for each pulse to create a 3D visualization — or point cloud. They’re commonly used to map terrains, measure real estate, and in architecture and construction.
Handheld 3D Scanners
Portable and versatile by design, handheld scanners allow you to efficiently and freely scan large objects, narrow spaces, or all the details of a human subject, for example.
Stationary 3D Scanners
Fixed scanners are a solid option if you plan to scan small objects and want the device to do most of the heavy lifting. They generally come with a stand or tripod and turntable. Automated scanning is also typically part of the deal here, with different modes of alignment to choose from.
3D Body Scanners
As the name implies, 3D body scanners are specifically designed to capture a full 3D scan of human bodies.
Towering machines, usually priced in the tens of thousands of dollars, 3D body scanners provide a fast and accurate 3D body scan for various applications, including health, fitness, animation, and more.
Read more: our feature story on 3D body scanners.
3D Scanner FAQs
Which is the Best 3D Scanner?
For those on a budget, our top pick is the Revopoint POP. It’s versatile, portable, affordable, and offers a solid level of accuracy for the price.
The EinScan H is a solid mid-range option for businesses and professionals looking for fast, highly-accurate printing.
Finally, if you want the best on the market today and have the budget to spare, Scantech’s SIMSCAN and KSCAN or the Artec EVA are all top-shelf options for the most demanding applications.
Who Makes the Best 3D Scanner?
Revopoint with their POP 3D scanner range, along with Creality’s low-cost scanners, make some of the best 3D scanners for hobbyists at home.
Companies like Artec, Shining 3D with their Einscan range, Scantech, and Creaform are known for high-quality commercial scanners.
What Is The Best 3D Scanner For Small Objects?
We recommend a stationary 3D scanner like the BQ Ciclop for affordable home scanning, and the Shining 3D EinScan SP for professional small object scanning.
What Is The Best 3D Scanner For 3D Printing?
We recommend the Creality CR-Scan 01. Creality has made the most of its 3D printing know-how to design a scanner that blends seamlessly into the 3D printing workflow. It’s compact, versatile, and reasonably accurate, perfect for most 3D printing hobby applications.
What Is The Best 3D Scanner For Reverse Engineering?
Scantech’s SIMSCAN rises above the rest as our top choice for reverse engineering. It’s particularly adept at capturing highly-detailed and accurate scans of objects in hard-to-reach spaces, perfect if you’re looking to reverse engineer a part from an aging piece of machinery or antique car, for example.
Best 3D Scanner - The Top 10 3D Scanners for 2022 [Reviews]
Much like a regular scanner, laser scanning 3D uses various methods to analyze a physical object and then relay that data to a computer to create digital 3D models.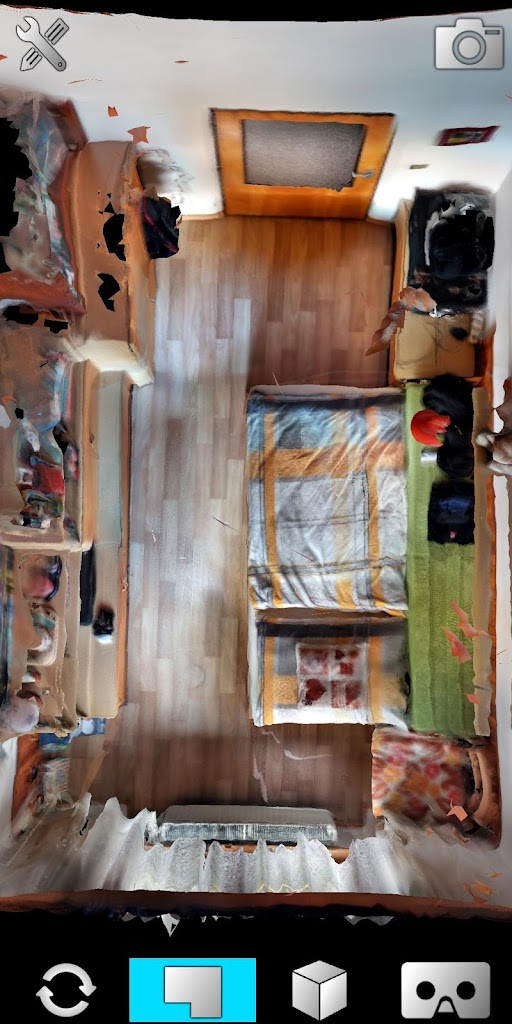 The 3D digitizer process might be automatic or users might need to complete the model to their requirements by using software. The aim is usually to get an accurate model to the right standard and format, ready for 3D printing, for virtual reality applications or other purposes.
The 3D digitizer process might be automatic or users might need to complete the model to their requirements by using software. The aim is usually to get an accurate model to the right standard and format, ready for 3D printing, for virtual reality applications or other purposes.
Such scanners are used in many professional industries, but with advances in home 3D printing, there are now also a good variety of home options. They are sometimes called portable 3D scanners or handheld scanners if they’re designed as such. These allow you to easily scan small to medium-sized objects for 3D printing.
Some come completely assembled while others, like 3D printers themselves, you’ll have to put them together by yourself. The benefit for those that are good with that type of thing is it reduces the price and allows for easier upgrades and modifications.
Scanning is typically done using laser triangulation or various forms of structured light to surround the object and measure its 3D dimensions or ‘geometry’. High-quality 3D scanner camera lenses also capture the color and surface texture of the object. Using accompanying or third-party software, the model can then be scaled up or down, or completely modified.
High-quality 3D scanner camera lenses also capture the color and surface texture of the object. Using accompanying or third-party software, the model can then be scaled up or down, or completely modified.
It’s never been easier to scan 3D objects!
How Do 3D Scanners Work?So, how do you scan 3D objects into a computer? Whether it’s on an industrial scale, at a small business, or on a desk at home, 3D scanners all share similar characteristics in the way they work.
The majority use laser and/or white light technology and cameras. The physical object is placed in a bed, tray, or suitable location. Electromagnetic light bounces off the object, measuring its circumference, full dimensions, and all its finer details.
Depending on the scanner it may use multiple light sources, cameras, and other tech to aid this process. The collected data is called a point cloud, which refers to the number of points captured by the laser.
The more points collected the more accurate the scan. A high-resolution scanner can capture hundreds of thousands of points in seconds and reach millions overall. The whole process only takes a few minutes.
While the light tends to be a measure of the object’s geometry, HD cameras tend to capture the surface detail and color.
The data recorded can then be fed into a computer-aided design program or similar software for inspection and manipulation. E.g. if you’re planning to use it for 3D printing, the model might need scaling up or down, hollowing, have added support structures, be re-colored or have brightness/contrast changes, etc.
There are, of course, different types of 3D scanner and scanning technology. So, let’s take a closer look at each one:
Types of 3D ScannersThere are several 3D scanner types. Before making your decision check out the section below:
Handheld vs StationaryHandheld and stationary 3D scanners often use the same technology and can overlap in their functions. The difference lies mainly in the design.
The difference lies mainly in the design.
A handheld scanner has a grip and lets the user move around the object themselves to capture it at every angle.
A stationary scanner has to be positioned in front of the object, which is typically placed on a rotating plate and captures it as it spins 360 degrees. The user may have to reposition the object several times to capture every angle.
Newer designs are becoming smaller and more easily portable.
Laser TriangulationThe most common technology used in 3D scanning is laser trigonometric triangulation. It records millions of different points on the surface of the object to build an accurate overall polygon mesh. These are common in handheld options and industrial-grade scanner machines. They can also work long-range and for laser-tracking objects.
Structured-Light 3D ScannersSimilar and often used interchangeably with laser triangulation, structured light or ‘white light’ projects itself in a grid-like pattern over an object. It can then measure the structure of that grid as it applies to the object by using sensors/3D scanner cameras and triangulation.
It can then measure the structure of that grid as it applies to the object by using sensors/3D scanner cameras and triangulation.
Longer range scanners use phase shift or pulse technology that can capture millions of points while rotating 360 degrees with the aid of mirrors. This is more commonly used to scan large objects like cars or buildings.
They might also use ‘time of flight’ technology that measures the distance of an object in relation to the speed of light and the time it takes for it to return to a sensor.
This is less relevant for everyday 3D scanning and printing.
3D Scanning ApplicationsThere are many different applications for 3D laser scanning - from those for 3D printing at home, to prototyping, industrial scale medical supply production and even architecture.
Hobbyist 3D printingCheaper 3D scanners are typically used by home users for scanning simple objects and 3D printing them for fun.
The medical field and dentistry commonly use 3D scanning to create implants and aids to serve their patients’ needs. For example, scanning people’s feet with a high-quality 3D scanner allows for the creation of orthotics (shoe inserts). It is also used in the creation of prosthetics.
Virtual EngineeringIndustrial 3D scanners are used both in the creation and quality control of cars, planes, and even aerospace. It ensures existing parts are as accurate as their original models and that new viable parts are made.
Reverse Engineering and RepairsFrom the home computer desk to the manufacturing floor, 3D scanning allows users to reverse engineer or copy existing objects. Saved models also allow for the reconstruction of damaged objects.
Virtual RealityFrom creating realistic 3D worlds to the people that occupy them, 3D scanning devices are integral to the growing virtual reality industry.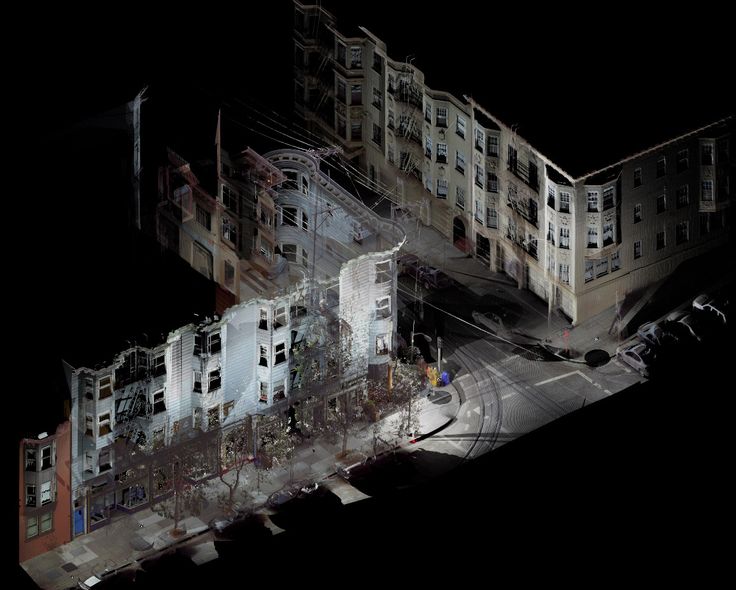 This ranges from AAA video games, virtual cinematography, and computer-generated imagery (CGI), to virtual tours and office meetings. It is also a side industry to motion capture.
This ranges from AAA video games, virtual cinematography, and computer-generated imagery (CGI), to virtual tours and office meetings. It is also a side industry to motion capture.
CSI has come a long way. Forensic experts nowadays don’t just have to rely on memory, photos, and evidence of a crime scene. They can capture the entire location in a full 3D model for closer inspection and for running through different scenarios.
Archeology and ArchivingFrom museums to libraries, 3D scanning is being used to log and preserve everything from artifacts to digitizing books. This also gives experts and the public remote access.
Architecture3D scanning can also help architects map the areas they will be designing their buildings in, take inspiration from existing architecture, and aid in building miniatures/prototypes.
What Should I Know Before Buying a 3D Scanner?Before you buy a 3D scanner, there are several things to consider:
- your budget
- what you’ll actually be using it for
- it’s speed and accuracy
- the device’s other features.
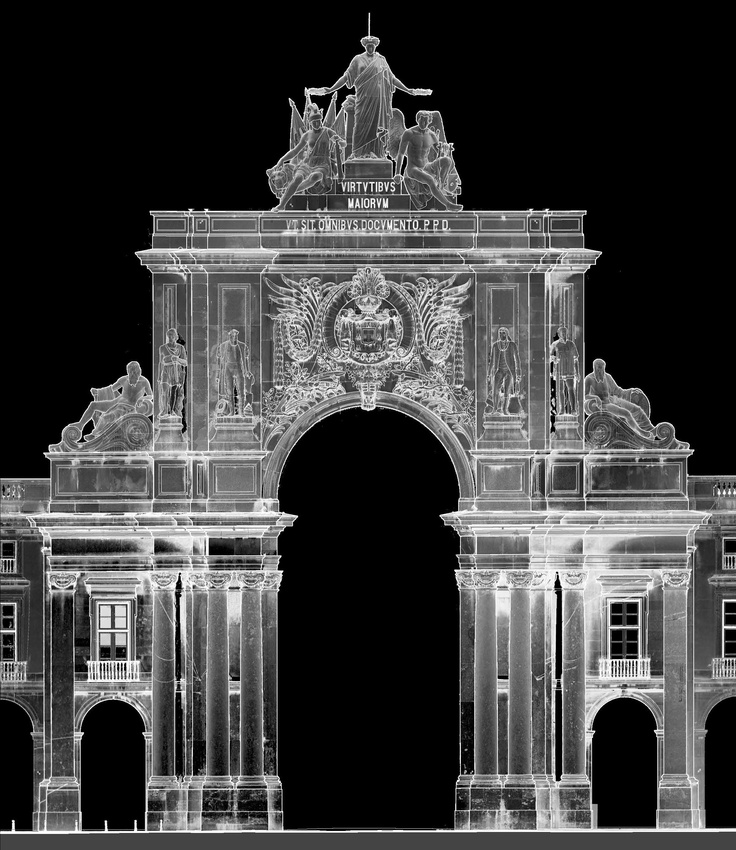

3D laser scanner price ranges vary greatly. On the cheaper end, you may be able to pick one up for home for just shy of $300, like the XYZprinting 3D Scanner 1.0 A. However, if you want the highest overall quality and the ability to scan small and large objects. Or, if you’re a professional and need a 3D part scanner in a field like medical implants or automotive parts, you’re looking at anywhere between $3,000 and $35,000.
Typically, it’s best to look for 3D scanners for sale online where you can find the best selection and prices.
3D PrintingWhile a dual 3D printer scanner combo is rare, if you want to scan models for 3D printing, you will need to make sure it has good accuracy and resolution. The software also must be able to export to a usable format. You will need to check your 3D printer and its own software to see what file types it accepts and then choose your scanner accordingly.
Fortunately, almost all of our 3D scanner reviews include devices that can export in common file types like OBJ and STL.
It’s typically only the more expensive scanners that are good for other applications, like VR, full-body scanning, architecture, and engineering.
Handheld vs StationaryWe already explained the difference, but basically, a handheld scanner is mobile, while the stationary one will require you to move and adjust the object. Neither is necessarily better than the other, it’s all down to your needs.
SpeedHow fast is the scanner? Do you have a lot of spare time or require the job to be done as fast as possible? All 3D scanners will take a few minutes to complete, while many scanning complex objects in high resolution can talk half an hour or longer.
Accuracy and ResolutionAccuracy refers to how close to the object being scanned your digitized model will be, measured in millimeters.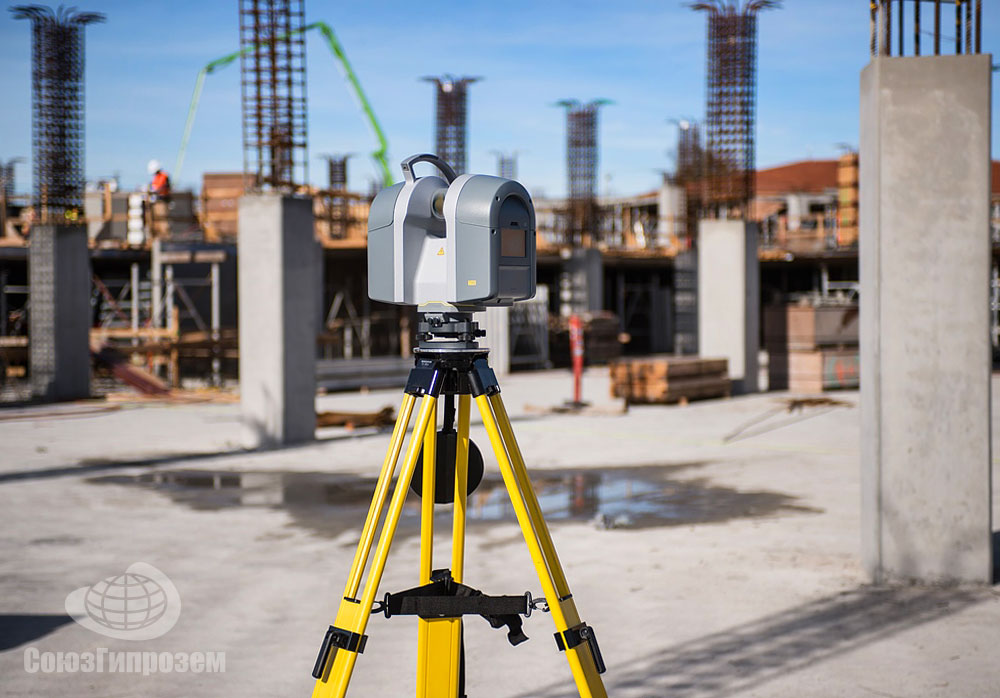 Therefore, the smaller the better. The term resolution may be used interchangeably with accuracy or refer to the resolution of any cameras being used as part of the scanning process.
Therefore, the smaller the better. The term resolution may be used interchangeably with accuracy or refer to the resolution of any cameras being used as part of the scanning process.
Generally, the lower the millimeter, the better. Other factors also play a role in overall quality, such as lighting conditions, color, and depth.
Object Size and SpaceSome types of 3D scanners excel at scanning small objects while others are better at medium to large. Others are all-rounders. Before buying a scanner, you should decide the general size of the items you will be scanning.
You will also need to make room for the scanner. Although all the products on our list are small and relatively portable, stationary scanners at least need a table to work from. Likewise, there will be a minimum and maximum distance the scanner must be in relation to the object being scanned.
You’ll need more room when scanning larger objects in full.
All 3D scanners need to be connected to a computer or device to help monitor the process and for saving the digital model. This is usually done via a USB or HDMI cable. You will need to check that your computer or laptop meets the minimum requirements for the scanning and modeling software. Also, make sure that you have a tablet to make real-time monitoring easier.
SoftwareYour device will either come with its own software or a popular third-party program to aid the process and to help touch-up the model once it’s scanned. Different 3D printing software is better suited to different skill levels. Some programs have a lot of features for experienced users and others do most of the basic tasks automatically. Check our 3D scanner reviews to see the software each device comes with and how advanced and easy to use it is.
Wrap UpWhether you’re looking for a tool for your home or something more on an industrial scale for your business, our 3D scanner reviews have something for everyone. From handheld devices to structured lightboxes with turntables, you’ll be creating 3D models or reverse engineering parts in no time. Perhaps you’ll even do a 3D selfie or two!
From handheld devices to structured lightboxes with turntables, you’ll be creating 3D models or reverse engineering parts in no time. Perhaps you’ll even do a 3D selfie or two!
If you’re still unsure about 3D printing after reading our reviews and guides, check out our answers to your most commonly asked questions below.
Top 13 3D scanners on the market!・Cults
In the past, 3D scanners were mainly used for industrial and professional applications. For example, scanning architectural objects or creating digital models for films. As technology advances, the price continues to drop. Now, 3D scanning gives the average person the ability to custom-make just about anything they want. With more affordable prices, 3D scanning is becoming more accessible to consumers for personal use.
But first, a basic overview of 3D scanning:
A 3D scanner scans real objects and passes the image data to a 3D modeling program. The object can then be manipulated in the software and - if desired - exported and created on a 3D printer.
1. Select any object (or person!) you want to scan
Why is 3D scanning useful?
Imagine if you could scan your body and see how clothes fit and look online before you order them? 3D scanning technology can do just that. For example, bodylabs uses 3D scanning to understand how products will work for customers based on their body shape and posture.
2. Scan it and customize it in 3D modeling software
After scanning the object, you can reduce the size or edit it with free 3D design software. You can then choose to 3D print the edited file.
3. Export your model and print it in 3D!
After scanning the model and editing it to your liking, you can export it to .stl format and send it to a printer to bring it to life.
We have listed the 3D scanners below in ascending order of price (from cheapest to most expensive). Their rating does not necessarily reflect our judgment of the quality of the product. We've included some handy YouTube videos that go into more detail about each product.
1. XBox Kinect 3D Scanner - $95 USD
If you want to get by on the cheap, there are ways to use your old Xbox 360 or Xbox One Kinect device to get great results! If you have a Kinect.
2. iSense 3D Scanner for iPhone/iPad - $99
This scanner was developed by 3D Systems as part of the Cubify family. Although they don't sell 3D printers anymore, they keep their 3D scanner in the market. Like a structure sensor, iSense attaches to an iPad or iPhone. Its range of motion is 0.5m more than the Sense.
3. XYZprinting 3D Scanner - $139
XYZprinting 3D Scanner is the cheapest portable 3D scanner on the market. At under $200, it's perfect for anyone looking to get into 3D scanning on a budget.
The size of the scanner is 60 cm x 60 cm x 30 cm, so it is best used for small items. It also uses the new Intel RealSense image capture software, which means it can connect to any Windows device with a 4th generation Intel processor.
4. BQ Ciclop 3D Scanner Kit - $199
This open source hardware project has been released under an open source license so that all mechanical design, electronics and software information is available to the community for further development . The full package costs about 199 USD. You can even download the design and print it in 3D!
The full package costs about 199 USD. You can even download the design and print it in 3D!
5. Structure Sensor for iPad - $379
Arguably the best scanner on the market, the Structure Sensor was developed through a Kickstarter campaign that attracted over 3,500 people and raised $1.2 million. Structure Sensor turns your regular iPad into a 3D scanner that captures three streams of data at 30 frames per second.
6. Cubify Sense - $399 USD
Cubify Sense is a portable pen scanner that makes it easy to manually scan 3D objects. This makes it possible to use Sense in quite unique areas, with both advantages and disadvantages. Sense is compatible with Windows and Mac OS.
7. Matter And Form MFS1V1 Desktop 3D Scanner - $467 USD
The first ever crowdfunded 3D scanner, Matter and Form, is a Toronto-based company that has raised nearly half a million dollars to develop this product. It uses a 3D laser scanner with a movable camera head and a 360-degree rotating platform.
MFS1V1 generates a detailed point cloud, which again works very well in some scenarios and less well in others.
8. XYZprinting Da Vinci 1.0 Pro 3-in-1 3D Printer - $810
Da Vinci 1.0 Pro is both a 3D scanner and a 3D printer. It uses a laser diode module with a 2 megapixel camera (higher resolution than 1.2 megapixel iPad scanners). Please note that this machine uses proprietary 3D printing consumables.
9. Einscan-S - $999
Einscan-S has two scanning modes: automatic and free. The first one is the easiest: just place an object on the rotating surface of the Einscan turntable and the machine will scan it in just 3 minutes with an accuracy of .1 mm. For large models, free scan mode works by rotating the scanner on a tripod around the object. Einscan-S generates one STL file that can be sent directly to your 3D printer. Einscan-S produces 3D printable models with greater accuracy (using "Light Structure Phase Shift Technology" instead of lasers) than competitors, providing industrial quality 3D scanning technology within a consumer's budget.
10. IIIDScan PrimeSense 3D Scanner - $1441 USD
Greater accuracy comes at a price. This tripod-mounted 3D scanner is unique in that it uses a short-range image sensor capable of scanning 3D objects in more detail and at a faster rate than other scanners on the market.
11. Fuel3D Scanify - US$1,500
This is a very high speed handheld 3D scanner capable of capturing an object in less than 1/10th of a second. In this regard, it differs significantly from the other 3D scanners on this list. In practice, it's more like taking a 3D photograph than manually scanning an object. Fuel3D Scanify uses a dual HD stereo laser camera combined with photometric data from three xenon flashes to create reasonably realistic 3D scans in the blink of an eye (so to speak). High tech.
12. NextEngine 3D Scanner HD - $2,995 USD
The NextEngine 3D Scanner HD combines portability with very high accuracy - much better than the scanners at the top of this list. Of course, the higher the accuracy, the higher the price! It uses an electro-optical system with a laser array that scans in tandem. The advantage is that the high-precision scanner has no size limits. The scanner comes with its own mesh creation software package, and you can also check out their NURBS and Solid modeling packages as options.
The advantage is that the high-precision scanner has no size limits. The scanner comes with its own mesh creation software package, and you can also check out their NURBS and Solid modeling packages as options.
This is the scanner for those who want to get really serious results from their 3D scanning efforts. If you check out the gallery on their site, you can see how much more detailed NextEngine scans are compared to some of the cheaper scanners on this list. Of course, these are the company's own comparisons for marketing purposes, so feel free to take them with a grain of salt!
13. DAVID SLS-2 Laser Scanner - $3,275
The scanner is expensive, but it has a unique use of "light scanning". The company boasts that you can scan everything from insects to elephants. We are told that the SLS-2 can scan 1.2 million peaks in a few seconds. Blimey!
What if none of these scanners work for you? What if you want the best of the best? What if you have several thousand dollars set aside for a 3D scanning budget? If you happen to be in this position, take a look at some of these bad guys. ..
..
Arctec Eva 3D Scanner - $19,800 (CAD 26,300) dollars)
Creaform HandySCAN 700 - 56 9$00 (CAD 77,700)
This is our list of the best 3D scanners on the market. We hope you find it useful.
via Pinshape
This page has been translated using machine translation. Suggest the best translation
3D scanners in architecture and restoration
Supplier of 3D equipment since 2010
+7 495 646-15-338 800 333-12-82
3D scanners3D printersSoftwareServices
About the CompanyClients and ProjectsDemo HallGovernment ProcurementDeliveryService3D Encyclopedia
BlogContacts
3D scanners are widely used, allowing for rapid digitization of buildings and premises, as well as museum exhibits and architectural values. 3D technologies significantly speed up the preparation of a ready-made design solution. Digitization of ancient monuments or buildings subject to restoration, fixing the circumstances of traffic accidents or crime scenes is far from a complete list of what is possible.
Using 3D scanning technology, you can create an accurate three-dimensional digital model of the surrounding space and objects in a matter of minutes, whether it is the interior decoration of a room or the facade of a building.
Endless possibilities
Making high-precision measurements of a terrain or object and recreating it as a model has always been one of the most pressing engineering challenges. But until recently, it was possible to obtain the most accurate and realistic image only on flat two-dimensional plans and maps. Now this problem is easily solved by a 3D scanner.
Using 3D scanning technology, you can create an accurate three-dimensional digital model of the surrounding space and objects in a matter of minutes, whether it is the interior decoration of a room or the facade of a building.
Architectural scanners easily perform geometric measurements, geodetic support for the design and installation of facade structures, control of deformations when a load is applied to the structure, three-dimensional modeling of buildings, streets and quarters, drawing up detailed plans. Scanners cope with the restoration of project documentation, the creation of working drawings and road mapping.
Scanners cope with the restoration of project documentation, the creation of working drawings and road mapping.
Types of scanners
3D devices used in construction can be divided into two main groups: facade and interior scanners.
Facade scanners are designed to scan the exterior of buildings, open areas and other large objects. As a rule, such a survey is made from several points on the ground.
Interior 3D scanners are designed to digitize tight enclosed spaces: small rooms, engineering channels, caves, tunnels, voids, etc. Such scanners are inferior to facade devices in terms of scanning range, but they capture more details. Both facade and interior 3D scanners consist of a digital video camera and a scanning system. The scanning system simulates the shapes of the measured objects, and the camera provides accurate color reproduction.
Architectural scanners easily perform geometric measurements, geodetic support for the design and installation of facade structures, control of deformations when a load is applied to the structure, three-dimensional modeling of buildings, streets and quarters, drawing up detailed plans. Scanners cope with the restoration of project documentation, the creation of working drawings and road mapping.
Scanners cope with the restoration of project documentation, the creation of working drawings and road mapping.
Types of scanners
3D devices used in construction can be divided into two main groups: facade and interior scanners.
Facade scanners are designed to scan the exterior of buildings, open areas and other large objects. As a rule, such a survey is made from several points on the ground.
Interior 3D scanners are designed to digitize tight enclosed spaces: small rooms, engineering channels, caves, tunnels, voids, etc. Such scanners are inferior to facade devices in terms of scanning range, but they capture more details. Both facade and interior 3D scanners consist of a digital video camera and a scanning system. The scanning system simulates the shapes of the measured objects, and the camera provides accurate color reproduction.
Scanning accident scenes
Architectural scanners have proven themselves in digitizing accident scenes. This work is well illustrated by a case that occurred in the state of Louisiana, USA. The scanner allowed the police to fix all the necessary parameters at the crash site with an accuracy of 2 mm: the relative position of cars with reference to the terrain, braking marks, scree of dirt and broken glass, and physical damage to vehicles. This operation was carried out very quickly, fixing the facts before they were washed away by a hurricane a few minutes later.
This work is well illustrated by a case that occurred in the state of Louisiana, USA. The scanner allowed the police to fix all the necessary parameters at the crash site with an accuracy of 2 mm: the relative position of cars with reference to the terrain, braking marks, scree of dirt and broken glass, and physical damage to vehicles. This operation was carried out very quickly, fixing the facts before they were washed away by a hurricane a few minutes later.
Scanning accident scenes
Architectural scanners have proven themselves in digitizing accident scenes. This work is well illustrated by a case that occurred in the state of Louisiana, USA. The scanner allowed the police to fix all the necessary parameters at the crash site with an accuracy of 2 mm: the relative position of cars with reference to the terrain, braking marks, scree of dirt and broken glass, and physical damage to vehicles. This operation was carried out very quickly, fixing the facts before they were washed away by a hurricane a few minutes later.