3D scanner specifications
EinScan Multifunctional 3D Scanner Specs
Get a quote
Please fill this form to receive a free quote within 24 hours (during working days).
AfghanistanALAND ISLANDSAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntigua And BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBolivia, Plurinational State OfBosnia And HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape VerdeCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongoCook IslandsCosta RicaC?te D'IvoireCroatiaCubaCyprusCzech RepublicDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEthiopiaFalkland Islands (Malvinas)Faroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard Island And Mcdonald IslandsHoly See (Vatican City State)HondurasHong KongHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIran, Islamic Republic OfIraqIrelandIsle Of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, Republic OfKosovoKuwaitKyrgyzstanLao People'S Democratic RepublicLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyan Arab JamahiriyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacaoMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesia, Federated States OfMoldova, Republic OfMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNetherlands AntillesNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayNORTH KOREAOmanPakistanPalauPalestinian Territory, OccupiedPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarReunionRomaniaRussian FederationRwandaSaint BarthélemySaint HelenaSaint Kitts And NevisSaint LuciaSaint MartinSaint Pierre And MiquelonSaint Vincent And The GrenadinesSamoaSan MarinoSao Tome And PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSpainSri LankaSudanSurinameSvalbard And Jan MayenSwazilandSwedenSwitzerlandSyrian Arab RepublicTaiwan, Province Of ChinaTajikistanTanzania, United Republic OftestThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad And TobagoTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks And Caicos IslandsTuvaluUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited StatesUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuela, Bolivarian Republic OfViet NamVirgin Islands, BritishVirgin Islands, U. S.Wallis And FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabweMACEDONIASOUTH GEORGIADemocratic Republic of the Congo
* Which product are you interested in?* Desktop 3d scanner* Hybrid light source handheld 3d scanner* Multifunctional handheld 3d scanner* Multiple scan range 3d scanner* Other Products and Service
submit...
3D Object Scanner Artec Eva
| Scanner type | Handheld | Handheld | Handheld | Handheld | Desktop |
| 3D point accuracy, up to | 0.1 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.05 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.01 mm |
| 3D resolution, up to | 0.2 mm | 0.5 mm | 0.1 mm | 0.2 mm | 0.029 mm |
| 3D accuracy over distance, up to | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.05 mm + 0.3 mm/m | 0.1 mm + 0.3 mm/m | — |
| HD Mode | Yes | No | N/A | Yes | N/A |
| Hybrid geometry and texture tracking | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| Data processing algorithms | Geometry and texture based | Geometry based | Geometry and texture based | Geometry and texture based | Geometry based |
| Working distance | 0.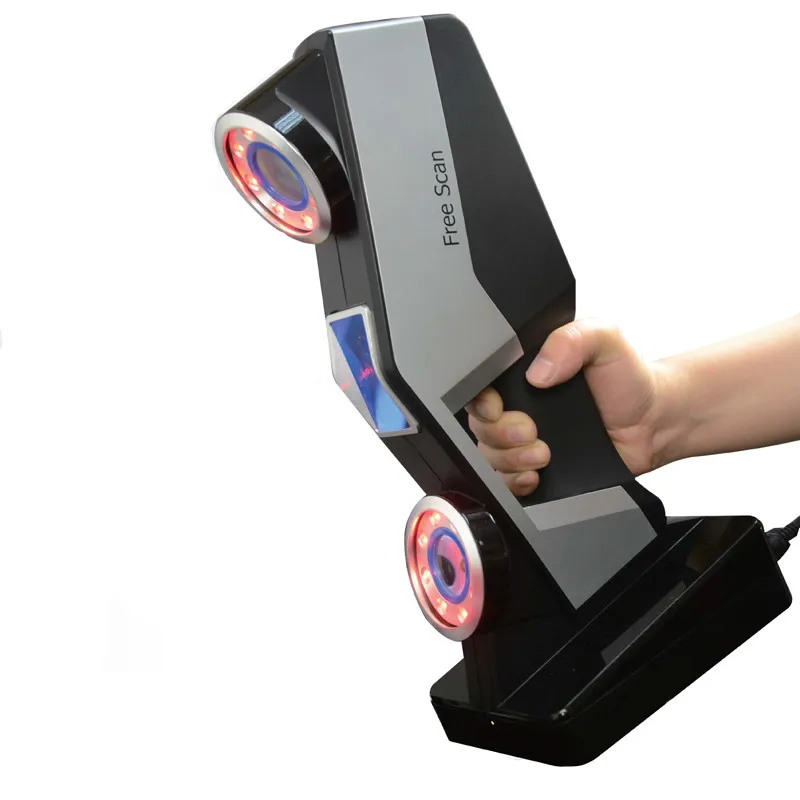 4 – 1 m 4 – 1 m | 0.4 – 1 m | 0.2 – 0.3 m | 0.35 – 1.2 m | — |
| Volume capture zone | 61,000 cm³ | 61,000 cm³ | 2,000 cm³ | 160,000 cm³ | 324 cm³ |
| Linear field of view, H×W @ closest range | 214 × 148 mm | 214 × 148 mm | 90 × 70 mm | 244 × 142 mm | — |
| Linear field of view, H×W @ furthest range | 536 × 371 mm | 536 × 371 mm | 180 × 140 mm | 838 × 488 mm | — |
| Angular field of view, H×W | 30 × 21° | 30 × 21° | 30 × 21° | 38.5 × 23° | — |
| Ability to capture texture | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Texture resolution | 1.3 mp | — | 1.3 mp | 2.3 mp | 6.4 mp |
| Colors | 24 bpp | — | 24 bpp | 24 bpp | 24 bpp |
| 3D reconstruction rate for real-time fusion, up to | 16 fps | 16 fps | 7. 5 fps 5 fps | 22 fps | — |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video recording, up to | 16 fps | 16 fps | 7.5 fps | 44 fps | — |
| 3D reconstruction rate for 3D video streaming, up to | — | — | — | 80 fps | — |
| Data acquisition speed, up to | 18 mln points/s | 2 mln points/s | 1 mln points/s | 35 mln points/s | 1 mln points/s |
| 3D exposure time | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s | Customizable |
| 2D exposure time | 0.00035 s | 0.00035 s | 0.0002 s | 0.0002 s | Customizable |
| 3D light source | Flashbulb | Flashbulb | Blue LED | VCSEL | Blue LED |
| 2D light source | White 12 LED array | White 12 LED array | White 6 LED array | White 12 LED array | RGB LED |
| Position sensors | — | — | — | Built-in 9 DoF inertial system | — |
| Display/touchscreen | USB streaming through external computer | USB streaming through external computer | USB streaming through external computer | Integrated 5. 5" half HD, CTP. Optional Wi-Fi/Ethernet video streaming to external device 5" half HD, CTP. Optional Wi-Fi/Ethernet video streaming to external device | USB streaming through external computer |
| Multi-core processing | On external computer | On external computer | On external computer | Embedded processors: NVIDIA® Jetson™ TX2 Quad-core ARM® Cortex®-A57 MPCore Processor NVIDIA Maxwell™ 1 TFLOPS GPU with 256 NVIDIA® CUDA® Cores | On external computer |
| Interface | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | 1 × USB 2.0, USB 3.0 compatible | Wi-Fi, Ethernet, SD card | USB 3.0 |
| Internal hard drive | — | — | — | 512 GB SSD | — |
| Supported OS | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Windows 7, 8 or 10 x64 | Scanning: No computer required Data processing: Windows 7, 8, 10 x 64 | Windows 10 x64 |
| Recommended computer requirements | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with 8+ GB VRAM, CUDA 6. 0+ 0+ | Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with 8+ GB VRAM, CUDA 6.0+ | Intel Core i7 or i9, 64+ GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with at least 3 GB VRAM, CUDA 3.5+ |
| Minimum computer requirements | HD: Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with CUDA 6.0+ and at least 2 GB VRAM SD: Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 12 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 12 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 18 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM | HD: Intel Core i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, NVIDIA GPU with CUDA 6.0+ and at least 4 GB VRAM SD: Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 32 GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAMA computer is needed only for data processing. Scanning does not require a computer. | Intel Core i5, i7 or i9, 32GB RAM, GPU with 2 GB VRAM |
| 3D mesh | OBJ, PLY, WRL, STL, AOP, ASC, PTX, E57, XYZRGB |
| CAD | STEP, IGES, X_T |
| Measurements | CSV, DXF, XML |
| Power source | AC power or external battery pack | AC power or external battery pack | AC power or external battery pack | Built-in exchangeable battery, optional AC power | AC power |
| Dimensions, H×D×W | 262 × 158 × 63 mm | 262 × 158 × 63 mm | 190 × 140 × 130 mm | 231 × 162 × 230 mm | 290 × 290 × 340 mm |
| Weight | 0.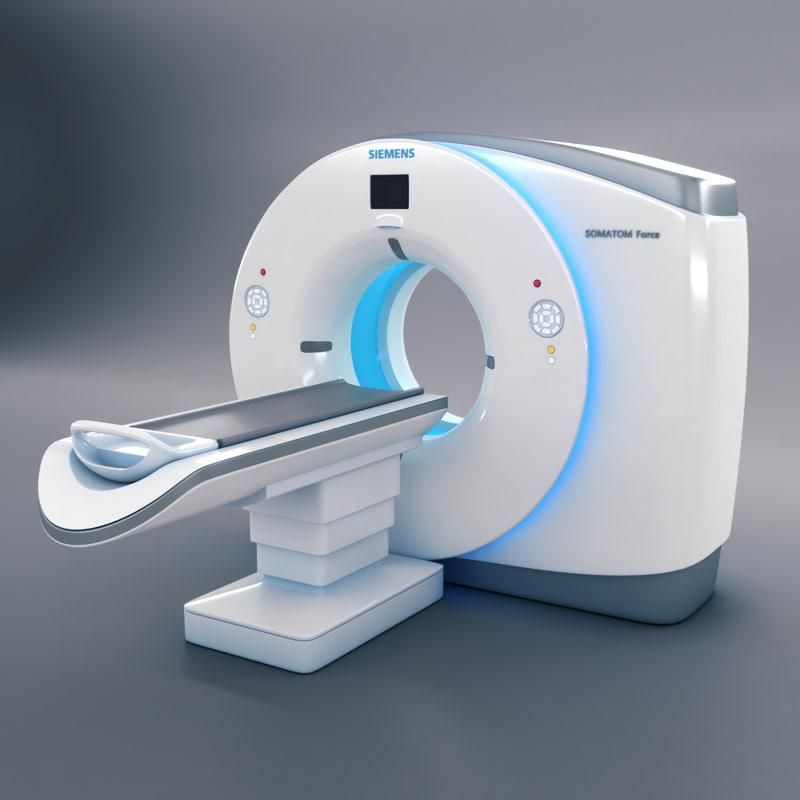 9 kg / 2 lb 9 kg / 2 lb | 0.9 kg / 2 lb | 0.8 kg / 1.8 lb | 2.6 kg / 5.7 lb | 12 kg / 26.7 lb |
04/16/2021
Content
-
- What is 3D scan and why it is used by
- How 3D scanner
- 3D scan technologies
- Methods 3D
- Contact 3D scanners
- Non-contact 3D scanners
- Types of 3D scanners according to the principle of use
- Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
- Things to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
- Applications
Currently, few people are not familiar with such a concept as 3D printing. Many companies are using modern 3D printers with might and main, recreating layouts of various shapes and sizes with their help. There are also those that recreate whole objects - not only small ones (for example, phone cases, souvenirs, sneakers), but also large ones (houses, engine parts, etc. ). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
). But all this would not be possible without 3D scanners. It is they who allow you to accurately copy almost anything - from huge buildings and structures to humans, animals, small objects and much more.
What is 3D scanning and what is it used for
Three-dimensional scanning is a technology that appeared in the 60s of the 20th century. It was created in order to transfer the physical parameters of the object into a digital format in the form of a three-dimensional model. The need for this naturally arose when people around the world increasingly began to use computers both in everyday life and in production.
The first samples of 3D scanners were quite simple and did not have wide functionality. Gradually, they became more complex and improved, making it possible to achieve an ever clearer image of the object. This has become especially relevant with the advent of lasers.
3D scanners allow you to transfer object data into digital format
3D scanning has opened up new opportunities in various areas of human activity - from the automotive industry and the military industry to design, medicine and cinema.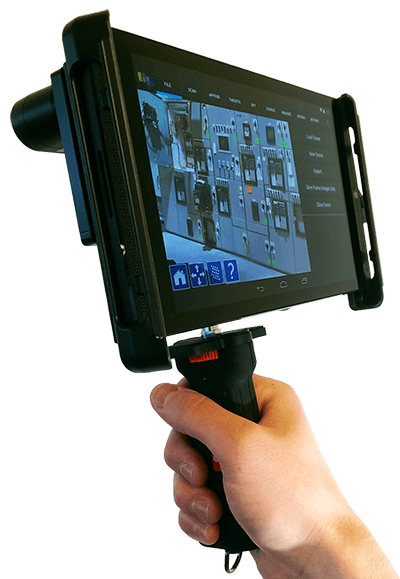
How a 3D scanner works
A 3D scanner is a device that examines an object by digitizing it using sensors and using the information received to create a three-dimensional model. In fact, a 3D scanner creates a digital copy of a physical object of any configuration and complexity. In this, it fundamentally differs from its predecessors - conventional scanners that can only read information from documents and photos.
The scanning process itself can take place in different ways - depending on the type of 3D device and the technology used, as well as on what object you want to process with it - moving or static.
3D Scanning Technologies
There are 2 main types of 3D scanners - laser and optical. Their fundamental difference lies in how and with the help of what the “removal” of data takes place. Let's take a closer look at both.
Laser 3D scanning, as the name implies, uses a laser and can be carried out both at short and long distances from the object.
Laser Scanner
For the most part, 3D laser scanners work on the principle of triangulation, when the camera finds a beam on the surface of an object and measures the distance to it, after which a cloud of points is created, each of which has its own coordinates in space, and a 3D model is built. Their "advantages" are affordable price and ease of use combined with high scanning accuracy. Of the "minuses" - there are restrictions on the remoteness and size of the object.
Another type of laser scanner works by measuring the response time of a beam from the surface of an object - the so-called laser range finder. They are widely used where it is necessary to create 3D models of various buildings and structures. It is not advisable to use them at short distances, since in such cases the response time is very short and the accuracy of the data is reduced. Otherwise, this type of scanner is characterized by high scanning speed and the ability to read all the details.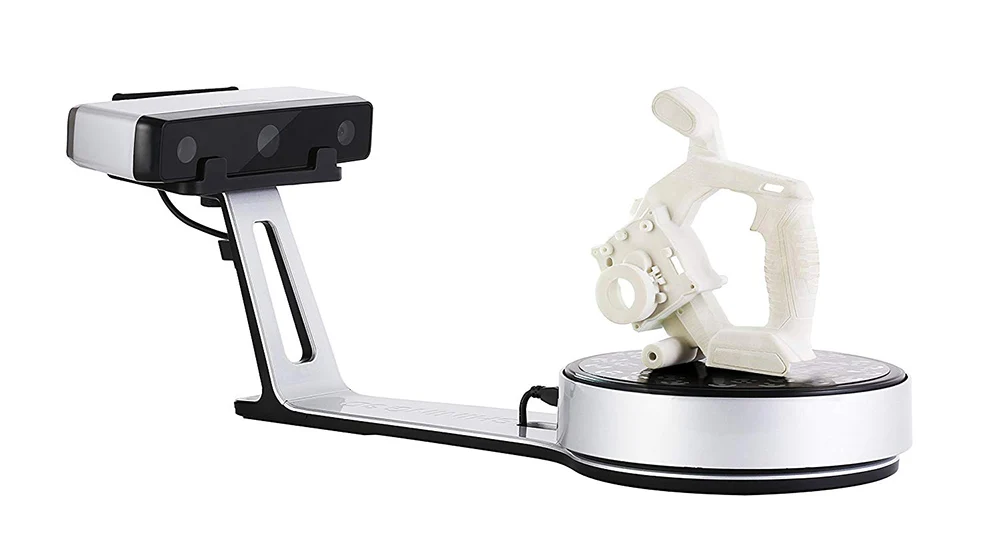
The disadvantage of laser scanners is the impossibility of their use on moving objects. Then optical 3D scanners come to the rescue, which shoot with one or more cameras from different angles an object illuminated by a special projector. Based on the received image, a three-dimensional image is built.
Optical scanner
A "contraindication" for the use of this technology are reflective and translucent surfaces - shiny, mirror or transparent. But when scanning a person, they are simply irreplaceable.
3D scanning methods
Any object can be digitized both by contact and non-contact methods. In the first case, active interaction with the subject is necessary, in the second, accordingly, no. Both of these methods have their advantages and disadvantages.
Contact 3D scanners
They have a mechanical probe with a special sensor that measures parameters and transmits the collected information to the device.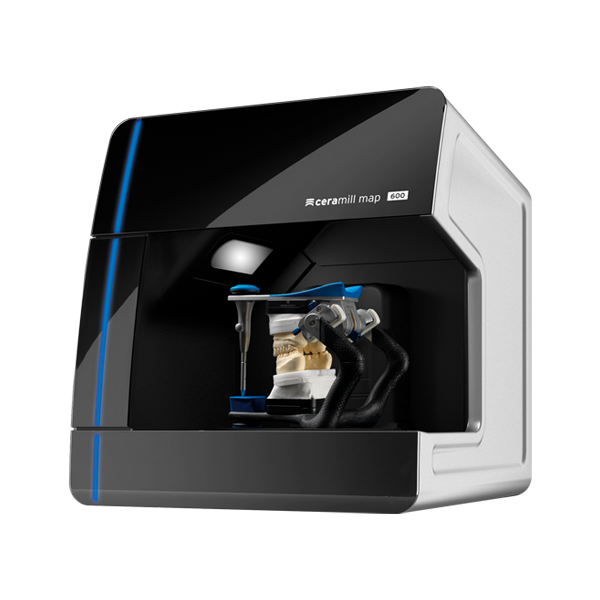 To do this, the object under study is placed on a special surface and fixed (if necessary). Such tight physical contact makes it possible to determine and then build a 3D image as accurately as possible, however, there is a small risk of damage to the prototype.
To do this, the object under study is placed on a special surface and fixed (if necessary). Such tight physical contact makes it possible to determine and then build a 3D image as accurately as possible, however, there is a small risk of damage to the prototype.
Non-contact 3D scanners
This category includes all devices capable of scanning at a distance. This is especially true for objects located in hard-to-reach places.
Non-contact 3D scanner
A stream of radiation (it can be ultrasound, light, X-rays or a laser) is directed to the object and reflected from it, it is recognized by the 3D scanner. They are similar in principle to a video camera and may require the use of additional devices for better lighting.
Non-contact 3D scanners come in 2 types:
-
Active - work with the help of a laser beam or structured light directed at an object, which, when reflected, give information about the location of the object in the form of coordinates.

-
Passive - use time-of-flight rangefinders that read the time and distance that the laser beam travels to the object, and so - for each point in space, which ultimately allows you to accurately recreate its three-dimensional image.
Desktop 3D scanners are very popular and widespread, since they are mostly simple and safe to use, do not require any special technical skills and are quite cheap. The EinScan-SE 3D scanner is one such example. It can be used both at home and in the office. It has access to the API of many popular 3D printers, which makes it possible to immediately print the created three-dimensional model.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Thor3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Shining 3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Range Vision |
Types of 3D scanners according to the principle of use
There is also a variety of species here.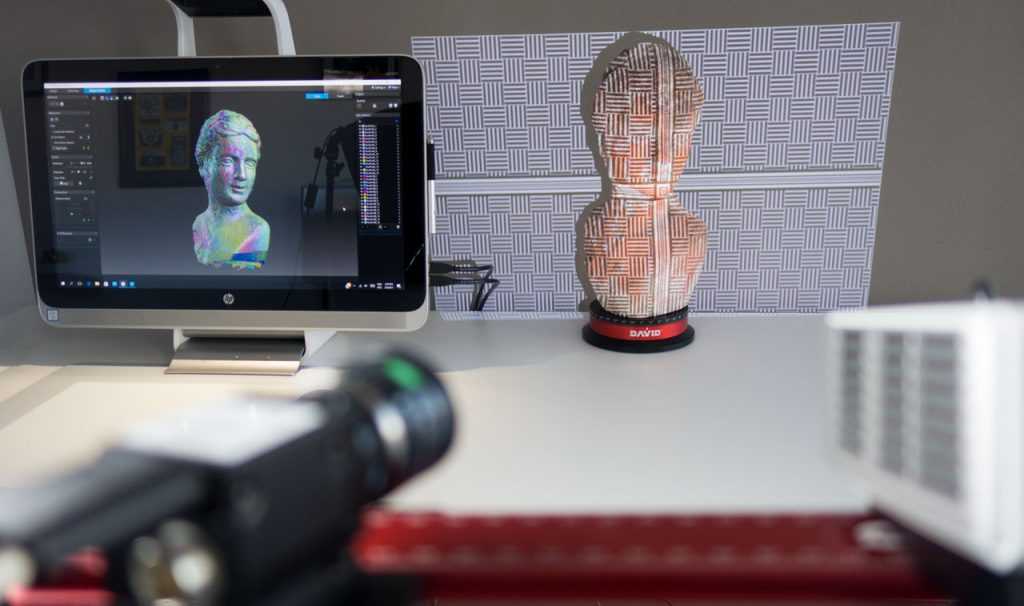 Let's highlight the main ones:
Let's highlight the main ones:
-
Manual: The are handy and simple models that are easy to use as they are quite compact and do not require special skills. True, their technical capabilities may be somewhat limited.
-
Portable: are mainly used for field work, they are convenient to take with you.
-
Desktop: have extended functionality and are used to create high-quality 3D models. Most often used in offices.
-
Stationary: are used, as a rule, in production, various enterprises, as they can scan a large number of objects of the same type at once. Mounted on special turntables.
Handheld 3D Scanner Calibry
Such a choice of products allows you to select the right model for a specific task. In some cases, scanners independently measure objects, in others - with the help of a person who sequentially moves the device until all the necessary information is collected.
Such options for hand-held 3D scanners as Calibry are in high demand among buyers. Despite the apparent simplicity of execution, it has a high resolution and scanning accuracy, due to which it is able to digitize objects with a length of 0.2 to 10 meters. Objects that have a non-standard surface - dark or shiny, with a large number of corners and small details will not become a problem either. Among other things, its undoubted advantage is its low weight, only 900 grams.
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D scanners
Surely, many of the potential buyers are wondering: do you really need a 3D scanner to invest a lot of money in it? What can this acquisition give and will such an investment be justified?
3D scanning has become an integral part of any modern manufacturing process
In order to understand how much you need this equipment, we will list its advantages and disadvantages.
Benefits:
-
They make it possible to scan objects located at a remote distance and in places inaccessible to the presence.

-
They have the ability to "read" not only colors and images, but also to convey the texture of the surface.
-
Significantly speed up the process of "taking" data from any object, even a very complex one with a large number of planes.
-
A variety of models allows you to choose the most convenient version of the scanner, including manual or portable, which can be easily taken with you.
Weaknesses:
-
Some scanners are unable to recognize transparent or black and white objects. In this case, their preliminary preparation (treatment with a special composition) is required.
-
I do not always display complex objects correctly, with a large number of inserts and partitions.
-
To obtain a high-quality result, they require skills and abilities to work with certain computer programs for creating 3D models.
-
If the rules of operation are constantly violated, it may become necessary for expensive repairs to the equipment.

If you need high-precision and high-quality three-dimensional copies of objects, then you cannot do without a 3D scanner. It makes it possible to work in almost any conditions - indoors and outdoors, and with any objects by type and size. It is not surprising that now these devices are in great demand, which gives rise to the annual release of a large number of models, from which you can always choose the one that suits you in terms of quality and price.
What to consider when choosing a 3D scanner
The computer equipment market offers a huge amount of all kinds of equipment, including devices for three-dimensional scanning. Navigating that variety is sometimes not at all easy: some buyers are only concerned about the cost, others are interested in the number of options (sometimes completely useless), but the most far-sighted look at the ratio of the first and second.
Choosing the right 3D scanner is a big deal
It is not always easy to take into account all the technical points that can significantly affect what result will be ultimately achieved. We will tell you what you should pay attention to if you are thinking about buying a 3D scanner.
We will tell you what you should pay attention to if you are thinking about buying a 3D scanner.
Focus on the following parameters:
-
How high is the accuracy of the 3D scanner. This is one of the most important features. It needs to be targeted first.
-
Resolution also plays an important role. It follows from the first, since the accuracy of measurements and the quality of copying depend on the resolution.
-
In what range the device operates, how close / far it can be from the scanned object.
-
The scanning field is the parameters of that object, thing that it is able to process in 1 session.
-
Does the scanner capture various atypical types of surfaces with complex terrain - channels, partitions, holes, etc.).
-
Portability, mobility of the device - how easy it can be moved if desired, taken with you, its size.
-
The time it takes to prepare for work, as well as the duration of the digitization process itself.

-
The range of possibilities in terms of copying: are there any restrictions on shapes, textures, material, as well as operating conditions - temperature, light, etc.
Of course, the better the quality of the 3D scanner, the more expensive it is. However, you should focus primarily on the tasks that you face, and only then take into account everything else.
Applications
Three-dimensional scanners are in demand in many areas of human life. They are irreplaceable both in the industry, and for household needs. The range of their application is so wide that it is possible to list for a very long time. It's easier to say where they are not needed.
The most common areas of use are, of course, medicine, industry, architecture, construction, film industry and design.
For example, in dentistry, these devices allow you to create ultra-precise three-dimensional models of dentures. One type of such a scanner is Shining 3D's AutoScan DS-EX PRO, which does a great job with a variety of tasks while being quite affordable and reliable.
Medical 3D Scanner
In engineering, such technologies are also indispensable. Digital building prototypes are now much easier and faster to obtain than in the past, when it required multiple manual measurements and then entered into a database. Any physical object can now be recreated in three-dimensional form, moreover, in the shortest possible time and with a minimum error.
In cinemas, we can see with our own eyes "revived" fantastic characters, which were created using motion capture technology, which made them as realistic and impressive as possible. This would not have been possible without 3D scanners.
A few decades ago, it was even difficult to imagine all the things that we use all the time today. And in many ways this has become achievable thanks to three-dimensional digitization. This approach provides huge advantages in work (especially for technical specialists - engineers, designers, designers), however, in order to use them to the maximum, it is also necessary to understand computer programs for 3D scanning.
We will talk more about this topic in one of our next articles. And if you want to know more about it, stay tuned.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
3D scanners - prices, photos, specifications
Application of 3D scanners
Widely used in industries such as:
- industry,
- aircraft and machinery,
- medicine,
- education,
- consumer goods industry,
- architecture and design10.
Such equipment allows: to carry out engineering developments using CAD (computer-aided design systems), to check the compliance of the physical characteristics of parts with the specified parameters, to detect defects at an early stage of the production process.
3D scans
Single shots. The scanner measures the distance to an object at various points and records all measurements taken as separate images. After comparing the obtained images, a digital model of the object is displayed on the monitor.
After comparing the obtained images, a digital model of the object is displayed on the monitor.
Continuous scan. Inspection of the object is carried out using wave radiation (optical-acoustic or laser beams). A special camera registers the position of the beam at each moment of time and captures all distortions in the shape of the scanned object. The obtained data can be visualized into a three-dimensional model directly during the scanning process or after it.
OfiTrade offers 3D scanners from world famous manufacturers - Creaform, Solutionix, Basis Software, DAVID. Creaform and Solutionix brands produce the most advanced scanners, which are characterized by high accuracy and speed, excellent resolution and detail of digital models. Our range includes several types of 3D scanners. You can choose the best option for your specific task.
| What do you need? | Our solution | Your benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Measuring the linear dimensions of complex body parts, determining deviations in their shape and surface arrangement. | Coordinate measuring machines (CMM): Advantages:
Limits:
| High-precision measurement of small parts, templates and assemblies will help you avoid defective products. |
| Non-contact scanning of objects from any distance. | 3D laser scanners: Advantages:
Restrictions:
| With laser scanners, you can make the most realistic 3D visualization of small parts and large objects. A wide scope of equipment will give your company a tangible competitive advantage. |
| Correction of three-dimensional models of objects right in the process of scanning. | Tracked 3D Scanners: Advantages:
Limitations:
| You will be able to measure objects in real time, carry out timely quality control of parts and products. This will reduce waste and increase profits. |
| High speed detailed scan. | 3D structured light scanners: Advantages:
Restrictions:
| Thanks to its high speed, even large objects can be scanned in minutes. This saves time for employees and improves overall productivity. |
| Fast scanning of small objects. |