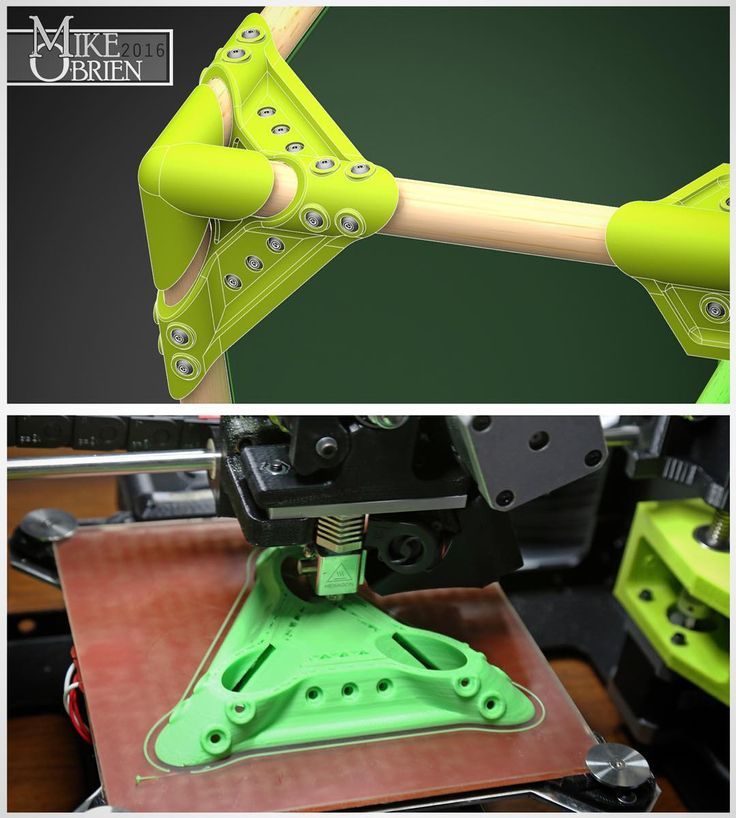
3D printing tutorials free
How To 3D Print? Basic 3D Printing Tutorials For Beginners
This page covers a number of tips and tricks on how to print 3D models. We also recommend some sites where you can get ready to print 3D designs.
📌If you want to learn 3D printing, the job is quite challenging, but if you are interested to learn the craft, you will eventually understand the procedure. The difficult part is actually setting up your printer and adjusting it accordingly to deliver the results you desire because the machine does the majority of the job.
So, for those who wish to learn the craft, here is a 3d printing for beginners tutorial to help the novice get started with 3D printing.
Contents
- 1 3D Printing Basics
- 1.
1 Step 1: Select a design
- 1.2 Step 2: Choose Your Materials
- 1.3 Step 3: Find a 3D Printer
- 1.
- 2 How to Use a 3D Printer?
- 3 How to Print a 3D Printer?
- 4 Conclusion
Before I go into details, I’ll give you an overview of the entire procedure. First, let’s identify the things that you need to get the job done. Here’s what you need:
- 3D printer
- 3D models
- Filaments
For the 3D model, you can design your own 3D object or use the existing models available online. It’s more fun if you do your own design.
Doing your own 3D model will be easy if you are already familiar with the 3D printing software for modeling. Otherwise, designing your own 3D model alone might take time as you have to get yourself familiar with the tool.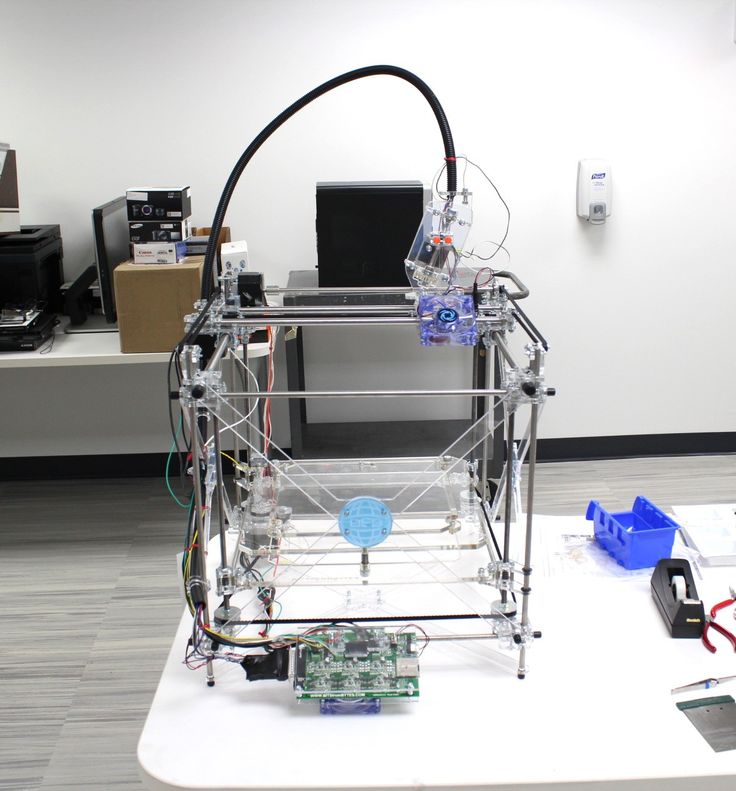
For this reason, I suggest that you use the readily available 3D models online, for the sole purpose of getting your first 3D printed object done.
You can look for free 3D models in the following sites:
- Turbo Squid
- Exchange 3D
- TheFree3DModels
- DMI 3D
- Oyonale
- 3Delicious
- NASA Space Models
- Thingverse
The first 3D printers only use plastic parts. But, the new models of the machine can now handle a growing variety of materials.
The most popular materials are plastic filaments like ABS and PLA, but there are more materials to choose from. If you want a tough and flexible material, plastics like ABS or nylon works great especially for functional parts like gears and integral hinges.
If you want to produce 3D objects that can handle the heat, the best material would be ceramics. Ceramics can withstand a temperature of 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
Ceramics can withstand a temperature of 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
📌Meanwhile, if you want to create a detailed model, then resin would be a smart choice. Resin’s smooth surface and ability to show details make it perfect for prototypes and models.
If you are looking for the real thing, there are already plastic filament embedded with wood shavings or chalk that produces a final product that resembles a wooden or concrete product.
Step 3: Find a 3D PrinterFor the 3D printer, you can borrow your friend’s machine or purchase a low-cost machine. You do not need an expensive machine, an entry-level low-cost 3D printer will be a good start.
How to Use a 3D Printer?This is an overview on how to use your 3D printer for the first time.
- Visit a site and download a 3D printer model. For instance, you can visit Thingiverse and select a 3D object that you want to 3D print.
 You will get a zip folder. Extract it.
You will get a zip folder. Extract it. - Download a 3D printing software. For this example, you can download Cura Software, this is free. You will use this software to set your printing parameters and slice your model. Once Cura is ready, open it and click on the machine. Then, click add new machine.
Click next. Select Other and choose your 3D printer. Cura is now ready to be used. Please remember that you might need to tweak the setting if your printer is not in the list. You can also use another program like Craftware, KISSlicer, MatterControl or Astroprint to get the job done.
- Set the parameters. You have to open the basic and advanced tap to adjust the parameters accordingly
Basic
- Layer height: 0.1mm or 0.2mm
- Print Speed: 50mm/sec
- Printing temp: 190 C
- Bed temp: 45C
- Filament diameter: 1.75mm
- Flow: 100%
- Nozzle Size: 0.
 4mm
4mm
Advanced
- Travel speed: 100mm/sec
- Infill speed: 60mm/sec
- Save your file. Click on toolpath to SD to save the file to your USB. The process will convert the file into .gcode.
- 3d print your design. Insert the SD card to your printer. Turn on the printer and adjust the setting of your machine. Once the set up is done, the 3D printer will start printing your 3D model.
If you wish to learn more, you can find more 3D printer videos online.
How to Print a 3D Printer?I understand that you have reached this part because you are interested in producing your own 3D printer. The good news is – that’s possible. However, do not expect a ready-to-use 3D printing machine because the process requires you to assemble the output.
Dr. Adrian Bowyer invented the first self-replicating 3D printer through the RepRap project. His first functional machine called the RepRap “Darwin” with 50% self-replicated parts was unveiled in 2008.
His first functional machine called the RepRap “Darwin” with 50% self-replicated parts was unveiled in 2008.
The 3D printed 3D printers are made using the FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printing technology with plastic materials. They are desktop 3D printers and has limited applications compared to industrial machines.
📌These printers cannot totally print themselves, they can only print some parts of themselves just like they could totally build other 3D printed objects. You then need to assemble the part yourself and add the components that can’t be 3D printed like the electronics or metal parts.
RepRap project is open source and you can find 3D models available online. In fact, the Prusa i3 is one of its improved versions.
Why is 3D printer iterations successful? This type of printers is low-cost. In addition, it’s easy to construct and modify. In fact, this is a must-have for hobbyists. It’s also popular in the education field.
We keep our tips and tricks simplified so it’s easy to understand. We hope that the aforementioned hacks will help you create your first 3D printed objects with ease.
Please keep in mind that you might need to make some tweaks in the settings we provided above to make it work for your 3D printer. Also, you might need to make additional changes if you are using another 3D printing software. But, overall, this is how to 3d print something.
If you need to learn more about 3D printers and 3D printing, feel free to check our homepage.
References
www.popularmechanics.com/technology/gadgets/a19698/get-started-3d-printing
www.lifehacker.com/how-to-get-started-with-3d-printing-without-spending-a-1340345210
www.youtube.com/watch?v=FOxZcpyKmzM
www.allthat3d.com/3d-printing-pen
www.sculpteo.com/blog/2017/10/24/3d-print-3d-printer
3D Printing Software | Coursera
About this Course
11,565 recent views
This course will demonstrate how to use 3D printing software to create digital designs that can be turned into physical objects. It will also demonstrate how 3D scanners work to turn physical objects into digital designs. This course is hands-on in nature and will provide step-by-step instructions to guide you through two popular 3D modeling programs, Tinkercad and Fusion 360. Learners who complete this course will be able to use 3D software to design a wide variety of objects for both personal and professional use. In addition, learners who enroll in the course certificate will receive extended free access to Fusion 360 (provided by Autodesk).
It will also demonstrate how 3D scanners work to turn physical objects into digital designs. This course is hands-on in nature and will provide step-by-step instructions to guide you through two popular 3D modeling programs, Tinkercad and Fusion 360. Learners who complete this course will be able to use 3D software to design a wide variety of objects for both personal and professional use. In addition, learners who enroll in the course certificate will receive extended free access to Fusion 360 (provided by Autodesk).
Flexible deadlines
Reset deadlines in accordance to your schedule.
Shareable CertificateShareable Certificate
Earn a Certificate upon completion
100% online100% online
Start instantly and learn at your own schedule.
SpecializationCourse 3 of 5 in the
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing Specialization
Beginner LevelBeginner Level
Hours to completeApprox. 15 hours to complete
Available languagesEnglish
Subtitles: Arabic, French, Portuguese (European), Italian, Vietnamese, German, Russian, English, Spanish
Flexible deadlinesFlexible deadlines
Reset deadlines in accordance to your schedule.
Shareable CertificateShareable Certificate
Earn a Certificate upon completion
100% online100% online
Start instantly and learn at your own schedule.
SpecializationCourse 3 of 5 in the
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing Specialization
Beginner LevelBeginner Level
Hours to completeApprox. 15 hours to complete
15 hours to complete
English
Subtitles: Arabic, French, Portuguese (European), Italian, Vietnamese, German, Russian, English, Spanish
Instructor
Jeffrey Smith
Education Manager
Autodesk
41,029 Learners
1 Course
Offered by
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign is a world leader in research, teaching and public engagement, distinguished by the breadth of its programs, broad academic excellence, and internationally renowned faculty and alumni. Illinois serves the world by creating knowledge, preparing students for lives of impact, and finding solutions to critical societal needs.
Reviews
4.7
Filled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled StarHalf Filled Star120 reviews
5 stars
75.
 68%
68%4 stars
17.70%
3 stars
3.50%
2 stars
2.33%
1 star
0.77%
TOP REVIEWS FROM 3D PRINTING SOFTWARE
Filled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled Starby HANov 14, 2020
This course has really amazing given me in-depth of the software which I don't know like a sketchbook, 3D scanning. Highly recommended for the 3D printing enthusiastics.
Filled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled Starby AVMay 22, 2020
Avery good and useful course. Recommended for all those who have an interest in 3D modelling and 3D printing
Filled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled Starby KAMay 10, 2019
good course for learning how to design a model for 3D printing. the teacher is teaching very clearly and good sort of knowledge is provided.
Filled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled StarFilled Starby PIMay 9, 2017
The 3D Printing Software class was challenging and Fun. It took a lot more time for me than estimated: Great Class!
It took a lot more time for me than estimated: Great Class!
View all reviews
About the 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing Specialization
This Specialization will introduce you to the magic of 3D printing. Through a series of four cohesive courses and a hands-on capstone experience, you will acquire the knowledge and skills to turn your ideas into objects and your objects into ideas. This course brings together a unique mix of academics and industry through partnerships with Ultimaker, a leading desktop 3D Printer manufacturer, and Autodesk, the leader in 3D modeling software.
Frequently Asked Questions
When will I have access to the lectures and assignments?
What will I get if I subscribe to this Specialization?
Is financial aid available?
What are the technical requirements for the course?
More questions? Visit the Learner Help Center.
Free 3D modeling software
Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Vkontakte
There are many programs for 3D modeling : paid, free, simple, complex. In a word, it is rather difficult to understand their diversity, so we have prepared for you a brief overview of free programs for 3D modeling . Choose, try and create in 3D! And if you know more free software that should be included in the article, write to us and we will add it.
Autodesk 123D
According to Christian Pramuk, manager of Autodesk, Autodesk 123 Design's hallmark is a clear and intuitive design that will allow even users with basic (or even zero) modeling skills to work with the program. In Autodesk 123 D you can create 3D objects using a set of basic shapes and their modifications. It is also worth noting that the program has a number of ready-made objects for editing.
Autodesk 123 Design is compatible with 123D Sculpt, 123D Catch, 123D Make, supported on Windows, Mac and iOS (iPad).
Blender
Probably one of the most popular open source 3D modeling software available for most operating systems. Blender has all the basic 3D modeling tools that are used in professional 3D editors. Basic objects are also available - rings, cubes, cylinders and so on. It is also possible to expand the functionality by connecting various plugins. The program is updated regularly.
BRL-CAD
This open source, cross-platform 3D modeling system for includes an interactive geometry editor, parallel ray tracing, rendering, and geometric analysis. The program runs on BSD, Irix, Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, and Windows platforms.
K-3D
This is an editor for working with three-dimensional images: both for editing them and for creating them from scratch using basic geometric shapes. Supports file formats such as OBJ, GTS, RAW, JPEG, PNG and TIFF. Various plugins are also provided to expand the range of possibilities.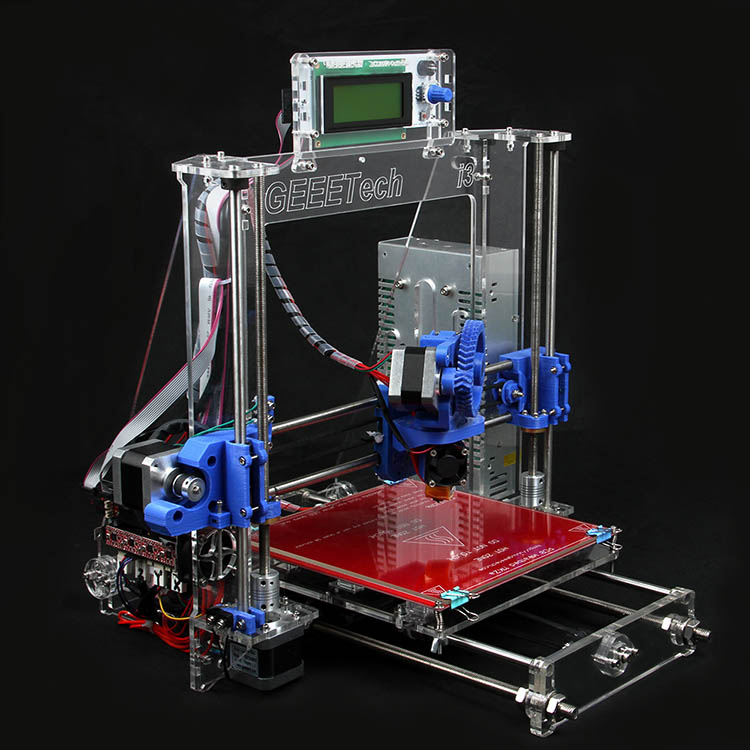
MakeHuman
As the name suggests, this open source 3D Modeling software specializes in quickly creating 3D models of people. It is constantly updated and improved. Work in it begins with a template model of a person in virtual space, on the basis of which you then create your character. You can export the finished model in one of the proposed formats: OBJ, MHX, BVH, DAE.
MeshLab
This program is more popular in the technical fields of 3D design and data processing. Its main purpose is to help process typical (not small) unstructured 3D models resulting from 3D scans . The program copes well with the following tasks: editing, cleaning, restoring, checking, visualizing and converting similar models.
OpenSCAD
This is a program for creating solid 3D CAD models available for Linux / UNIX, Windows and Mac OS X. OpenSCAD is a kind of compiler that gives the designer complete control over the modeling process by changing and customizing the available parameters. Two modeling methods are available in the program: constructive stereometry (CSG) and object formation by a 2D contour. OpenSCAD works with DXF, STL and OFF format files.
Two modeling methods are available in the program: constructive stereometry (CSG) and object formation by a 2D contour. OpenSCAD works with DXF, STL and OFF format files.
Sculptris
This is a relatively simple 3D modeling program based on the sculpting principle. The role of the sculptor is performed by virtual brushes with different profiles and different strengths, the nature of the impact for each brush is customizable, which provides ample opportunities for the designer. The program supports export and import of OBJ files.
SketchUp
Google SketchUp is a free and intuitive 3D modeling software , which can be used quite effectively by both advanced users and beginners. There are two versions of Google SketchUp: free and paid. One of the disadvantages of the free version is the lack of advanced functionality available in other similar programs and the inability to export to CAD formats.
TinkerCAD
This 3D modeling tool is interesting in that you don't need to install anything to work with it, just a browser with WebGL support (Chrome, Firefox) will be enough. With TinkerCAD you can create 3D models directly in the browser window, save your projects both on the server and by downloading them to your computer as files with the STL extension. The service is free for non-commercial use only.
With TinkerCAD you can create 3D models directly in the browser window, save your projects both on the server and by downloading them to your computer as files with the STL extension. The service is free for non-commercial use only.
Wings3D
This is also free and open source software. It helps to create and texture models with low to medium poly counts. The nice thing about it is that it imports and exports to various formats: 3DS, STL, OBJ and others. Also, the context menu can be attributed to the distinguishing features. Also, you can be pleased with the customizable interface and the presence of hot keys.
If you have a 3D model of , please send it to us for a quote. Or just ask all your questions by phone 8 (800) 550 40 45, write to [email protected] or use the feedback form:
Attach a picture
I agree to the terms of the user agreement and privacy policy*
Privacy Policy and User Agreement
Free 3D Printing Education Course at Brooklyn Public Library
Today, computers and the Internet are no longer a delightful novelty, but part of everyday life. In this regard, libraries that keep up with the times can also introduce modern technologies into their work and diversify their routine by organizing various presentations and master classes. Once 3D printing hardware and software is installed, libraries will be lined up to take advantage of it, of all ages and technical levels.
In this regard, libraries that keep up with the times can also introduce modern technologies into their work and diversify their routine by organizing various presentations and master classes. Once 3D printing hardware and software is installed, libraries will be lined up to take advantage of it, of all ages and technical levels.
One of the library renaissance programs is hosting free workshops and lectures on 3D printing at the Brooklyn Public Library. The project was initiated by Ultimaker and 3DPrinterOS. Among other things, this is a great way to educate the general public, promote greater interest in technology, and provide an opportunity to gain practical skills from experts in a structured program. The lessons are designed to answer basic questions about what this technology is, what it can be used for, and how it works. The program includes the following aspects:
- introduction to the technical device and principle of operation of a 3D printer;
- discussion of how to use 3D printed models and prototypes;
- discussion of traditional 3D printing plastics as well as alternative materials such as chocolate, sand, metal;
- lectures on various 3D printing technologies, history and terms;
- individual practical training;
- free access to 3DPrinterOS, a cloud-based 3D printing operating system;
- the ability to make your own model using 3D printing, including the use of alternative materials.
The educational initiative is based on the interests of all its participants. For example, the values traditionally promoted by libraries are learning, creativity, and inspiration. In addition, the program pays special attention to education in the technical field. Ultimaker, in turn, is known for using the concept of free access to projects and encourages everyone to participate in the 3D printing revolution. Already award-winning, Ultimaker aims to encourage people to share knowledge and experience, actively participate in community life, make a difference and be committed.
3DPrinterOS, which received an award in the Positive Change category at last year's 3D Printshow Global Awards, is primarily responsible for the learning process in this project. They collaborate not only with the library itself, but also with Shapeways and Foxsmart Filament. As part of the educational project, students will also learn about the cloud-based production system 3DPrinterOS, which is compatible with almost all models of personal 3D printers.

 html Sketchfab: https://help.sketchfab.com/hc/en-us/articles/203059088-Compatibility 123D Catch: Same as Tinkercad
html Sketchfab: https://help.sketchfab.com/hc/en-us/articles/203059088-Compatibility 123D Catch: Same as Tinkercad









