3D printers jobs
9 Great 3D Printing Jobs
- 3D printing is a technology that creates a three-dimensional object using a computer-aided design (CAD).
- The 3D printing industry is rapidly growing thanks to its ability to create a wide range of versatile products in a fast, cost-effective way.
- For job seekers, the 3D printing industry offers some cool jobs on the cutting edge of the technology.
- This article is for professionals and entrepreneurs who want to work in the 3D printing industry.
President Barack Obama once said 3D printing has the “potential to revolutionize the way we make almost everything.” For that reason, the 3D printing industry was valued at $13.78 billion in 2020. And market research projections suggest it will continue its meteoric growth through 2028 – when it is expected to reach an estimated $59.65 billion.
As the 3D printing industry booms, what does it mean for job seekers? Here are 9 opportunities that will be created or get a boost from 3D printing.
What is 3D printing?
Rather than using ink and paper, a 3D printer uses materials like plastic, metal or ceramic to create a 3D model. By using computer-aided design (CAD) files as digital instructions to create an object, a 3D printer repeatedly covers a work surface with layers of material in precisely the right spots to create a structure from scratch.
While 3D printing can be used for large-scale structures, 3D printing is most useful in creating smaller, customized parts or prototype components for various uses – including automotive engineering or the medical industry. With the versatility of 3D printing, it’s a field that’s filled with opportunities. Let’s take a look at some of the areas 3D printing is being used today.
3D printing jobs
1. 3D design
3D printing relies heavily on designers who can take a product idea and bring it to life. Thanks to its growth, 3D printing will create jobs for 3D designers at 3D printing firms, in companies as part of creative teams and as freelancers.
3D printers are being used in many design disciplines – such as product design, medical device design, architectural visualization and entertainment design, said Erol Gunduz, a professor at New York University’s School of Continuing and Professional Studies (NYU-SCPS), which offers programs in 3D printing, design and modeling.
To be competitive, job seekers should gain hands-on experience in 3D technologies and stay current on how companies are using 3D printing. For instance, recent graduate student designers and researchers who are familiar with 3D printing methods have the benefit of knowing how to use the technology within their design process, Gunduz explains.
“This gives them a significant advantage when looking for career opportunities within creative fields,” Gunduz said.
Did you know? 3D printers can create replacement parts for the human body, among the many things that 3D printers make.
2. 3D CAD modeling
3D printing would not be possible without CAD experts who have the skills to convert product designs into digital blueprints that the printers need. Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
“I see a lot more demand for CAD and 3D modeling jobs on the horizon because of 3D printing,” said Alex English, owner of ProtoParadigm. ProtoParadigm is a 3D printing business that also performs research and development on 3D printing hardware and new printing materials.
Although 3D CAD professionals are also needed to construct models for mass 3D printing, they are especially important for custom products.
“Bespoke manufacturing and custom prototyping both rely on the user’s ability to conceptualize the object they want and accurately create its digital representation,” English said.
Consequently, 3D CAD modeling jobs will require printing-specific modeling skills, such as feature size, geometrical constraints and knowledge of materials, English added.
3. Research and development
3D printing is all the buzz – and not just in the gadget world. Just as the 3D printing industry will require more product designers and CAD modelers, jobs will open up for forward-thinking research and development professionals who understand the intersection of tech and consumer products.
“While 3D visualization technologies have been used in the past within various fields, such as engineering and scientific agendas, many artistic and consumer product industries – such as fashion design and jewelry design – are beginning to take advantage of 3D printing systems,” Gunduz said.
Companies will need people who can find the best way to utilize 3D printing for consumer products at the lowest cost possible.
“The ability to visualize a line of fashion accessories or jewelry designs before committing to working with expensive materials affords an advantage for companies to reduce costs in development cycles,” Gunduz said.
Tip: Is your business experimenting with 3D printing research and development? Consider these tax credits that are available to companies performing cutting-edge research.
4. Biological and scientific modeling
3D printing is not limited to consumer products; it creates many products that promote medical advancement and save lives. It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
Accordingly, the 3D printing industry will need more engineers, designers and modelers who have a biomedical or scientific background to further innovate and produce highly advanced 3D-printed products.
“While all manner of designers will be able to print the things they design, there will be a high end to the market – particularly in medical, aerospace, military, and other high-precision or mission-critical applications – for those that better understand the printing technologies and how to design for their strengths and limitations,” English said.
5. Architecture and construction modeling
3D printing will disrupt various industries, particularly those that rely heavily on blueprinting or prototyping. For the construction industry, this paradigm shift will boost the need for 3D modelers that may replace current 2D construction planning solutions.
“In the architecture, engineering and construction industries, 3D printing will redefine the production of construction documents,” said Lira Luis, chief collaboration architect at Atelier Lira Luis LLC, a Chicago-based architecture and design firm.![]()
Instead of 2D CAD modeling on paper, 3D printing can produce true-to-life models to better represent what structures will look like.
“As the 3D printing process becomes more streamlined, it could potentially eliminate the need for construction documents and move directly to printing full-scale mock-ups prior to construction of structures,” Luis said.
6. Education
What good are these jobs if no one has the qualifications to fill them? To help fill the skills gap, schools are developing – and some have already launched – 3D printing programs at all grade levels. This will open up jobs for educators who can teach the technical and business aspects of 3D printing.
“From an educational perspective, many K-12 schools are looking to 3D printing as a point of exposure for students within the arts as well as scientific areas of study,” Gunduz said. Colleges and universities are also launching 3D printing courses and certificate programs, such as NYU-SCPS’ certificate in 3D printing rapid prototyping.
Teachers will need to have a background in the 3D printing industry. They will also need specific skill sets to teach specialized courses and stay current on the latest trends.
“For educators, having an understanding of 3D modeling and 3D printing techniques will be invaluable, as the culture of fab labs is starting to gain support as an important aspect of education,” Gunduz said. “Teachers with 3D modeling and fabrication experience have a range of opportunities open to them within educational programs looking to incorporate this new technology.”
7. Legal professionals
3D printing is not confined to the tech world. As a creative field, the industry is wide open to legal issues, prompting a need for more lawyers and legal professionals who specialize in intellectual property (IP) rights.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become more widely accessible, it will be easier for infringers to create, market, and sell products that infringe patents, copyrights, and valuable brands,” said Julie Matthews, partner at Edwards Wildman – an Am Law 100 firm with offices in the U. S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
As a result, there will be an increased need for IP enforcement actions and lawsuits, as well as expanded services to monitor for infringements, Matthews explained.
Growth areas include IP ownership, scope of rights, licensing, fair use and international rights.
8. Startup companies
Thinking of starting a new business? 3D printing offers opportunities for innovation – not only in creating products, but also for entrepreneurship. 3D printing spans across various technical and design roles, many of which make great business ideas to support companies’ 3D printing needs.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become readily accessible to home users, undoubtedly, this will lead to new business opportunities for individuals and companies offering onsite and remote 3D printing services, new product and industrial designers, and computer-aided design specialists,” Matthews said.
With 3D printing costing between $1,999 and $3,500, anyone with 3D printing knowledge can start their business.
Tip: Consider a 3D-printing-as-a-service franchise for your new business venture.
9. Administrative roles
3D printing companies don’t run on engineers and technicians alone. As the industry grows, new and established 3D printing companies will need employees to keep their business running smoothly. This includes operations and administrative staff, analysts, finance and sales professionals, and retail employees.
“The businesses that will spring up with new business models centered on 3D printing will also have a need for more common jobs that other businesses need, like marketing, clerical, shipping, etc.,” English said.
These jobs will open up in all types of 3D printing companies, including vendors, manufacturers and retail stores.
Business News Daily editorial staff contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
3D Printing Jobs of the Future
3D printing is one of the hottest STEM fields today. From airplane parts to cars, 3D printing is redefining the manufacturing industry.
“Multiple industries are reaping the benefits of utilizing 3D printing,” said Kforce Strategic Account Executive Tyler Brown. “Efficiencies are built, money is saved and new technologies constantly emerge.”
Also, nearly 41% are considering 3D printing adoption by 2022. As 3D printing continues to expand, so does the need for qualified professionals to break the mold. Organizations are searching for specialized individuals to understand the technology, operate and innovate.
Companies are looking for people who can quickly understand what 3D technology is capable of and start applying that to business problems.
— Tyler Brown
3D printing technology is still young. There is much exploration to be done to realize the breadth of capabilities within 3D printing. With any emerging domain, new 3D printing jobs are on the horizon. The future talent landscape of 3D printing will create new occupations as industries capitalize on this burgeoning technology’s potential.
There is much exploration to be done to realize the breadth of capabilities within 3D printing. With any emerging domain, new 3D printing jobs are on the horizon. The future talent landscape of 3D printing will create new occupations as industries capitalize on this burgeoning technology’s potential.
Check out these pioneering 3D printing jobs of the future below:
Biomedical Science: 3D organ and prosthetic designers
Perhaps one of the most significant spaces in the future of 3D printing is biomedical science.
Undeniably, exciting things are happening. In less than a decade, scientists report that 3D bio-printed tissues will be available for use. Yes, you read that right! Researchers are currently developing 3D printing technology to print skin, build hearts and other vital organs.
3D printed organs, once approved for human use, will revolutionize the medical space. The possibilities are endless, and they will change lives. Long wait times for organ donations will cease to exist as doctors will have the ability to print organs when patients need it. Car accident and burn victims can have functional bio-printed skin grafts to heal wounds.
Long wait times for organ donations will cease to exist as doctors will have the ability to print organs when patients need it. Car accident and burn victims can have functional bio-printed skin grafts to heal wounds.
Search Jobs
Alongside printed tissues, 3D printing technologies are allowing for the custom design of prosthetics, making prosthetic limbs and other physical aids more accessible to people. Prosthetic wearers will soon enjoy tailored devices, improving their quality of life through the ability to do the activities they love.
Since 3D printed prosthetics are projected to cut cost and manufacturing time, more devices will also be available for consumption. In the U.S., advanced prosthetic limbs can range from $5,000 to $50,000. However, a 3D printed limb could be made for the price of an oil change—for as little as $50.
This application of 3D printing in the biomedical field will help change the way we treat patients and provide medical care. For this revolution to happen, new professionals such as 3D organ and prosthetic designers who understand biology, anatomy, technology and manufacturing will emerge.
For this revolution to happen, new professionals such as 3D organ and prosthetic designers who understand biology, anatomy, technology and manufacturing will emerge.
Job responsibilities:
- Using biomaterials and 3D printing technology to create bioengineered products
- Creating prototypes and fitting newly created organs and limbs for human use
- Executing end-to-end design and product implementation
- Designing algorithms to perform body functions
- Employing software to tackle bio-engineering solutions
Computer Science: 3D printing software developers
Another growing STEM career alongside the onset of 3D printing technology is the high demand for software developers. This career is vital to discover the full potential of 3D printers and how to use the technology. In the years to come, experts forecast 3D printers to become universal household items like the desktop printer.
The current state of 3D printing doesn’t have a seamless interface for users with a non-technical background. Computer programmers are needed to create user-friendly software, features and functions to improve the accessibility of 3D printers.
As cloud-based 3D printing alternatives become more available, web developers will also rise in demand. Programmers with backgrounds in user experience, software testing and API integration will be an additional asset to the additive manufacturing industry.
Perfect candidates for this career field will be familiar with 3D printers or other manufacturing processes. Prospective employees for 3D printing jobs will also possess the ability to work along scrum teams to write efficient, testable code to solve challenging technical problems.
Job responsibilities:
- Integrating and testing software modules to debug interface issues
- Combining 3D CAS model geometry with programming knowledge
- Building new capabilities and optimizing existing code alongside evolving technology
- Designing cross-platform software based on specifications and required functionality
- Collaborating with scientists, engineers and technicians in the development of control software
Law: 3D printing IP and copyright lawyers
While 3D printing continues to unlock possibilities for manufacturing, it’s becoming increasingly easier to reproduce products.
Today, users can simply download computer-aided design (CAD) files to 3D printers for production. Greater access to 3D printing technology will create a new domain of law careers to prevent intellectual infringement, protect patents and provide legal services.
Effective management of intellectual property (IP) ownership will be pivotal for brand reputation to avoid similar catastrophes like digital sharing and piracy that ran rampant from the 90s through the early 2000s.
New arenas of 3D application in courtrooms might also emerge in liability cases to determine whether a product has faulty design during litigations. Firms could use 3D printers to prototype evidence, demonstrate findings in real-time and illustrate a product’s bad design before a courtroom’s eyes.
STEM careers in this field will demand legal practitioners who understand the concept of 3D printing, industry developments and the reaches of law for intellectual protection. If you have a passion for 3D printing and an affinity for intellectual law, a 3D printing lawyer might be the job for you.
Job responsibilities:
- Applying knowledge of the patent, copyright, intellectual property and licensing laws
- Protecting and defending the client’s intellectual property in court
- Understanding 3D printing techniques and additive materials for patent applications
- Using algorithms to design and replicate existing products for reproduction
Automotive: 3D printing auto mechanics and engineers
The automotive industry has already begun to create and develop 3D printed cars in the hopes of innovative products, an accelerated development process, efficient part replacement and further personalization.
Organizations are increasingly leveraging 3D printing to manufacture car parts independent from third parties. To date, companies have used 3D printing for prototyping as a cost-effective method for designing and testing new concepts with speed to market.
In the natural evolution of supply and demand, there will be a push to harness 3D technology for customization. Futurists foresee automobile customization for individual needs and specific driver experiences as a new market.
3D printed cars won’t be mainstream for some time, but when commercialization is finally scalable, who will design and repair the vehicles of the future? The answer—3D printing mechanics and engineers.
The automotive industry will need qualified talent who understand 3D printing concepts to create replacement parts and custom vehicles quickly per consumer demand.
Job responsibilities:
- Preparing schematics and drawings to construct prototypes
- Understanding consumer needs to achieve customer satisfaction
- Improving iteration cycles for product design and manufacturing
- Using technical knowledge of mechanics, materials and design to create components
Without a doubt, 3D printing is changing our world and will lead to one of the most groundbreaking STEM careers in the years to come. The future workforce of 3D printing will need talent interested in transcending traditional manufacturing techniques. This transportive technology will redefine how we engineer products and experiences to better our everyday lives.
The future workforce of 3D printing will need talent interested in transcending traditional manufacturing techniques. This transportive technology will redefine how we engineer products and experiences to better our everyday lives.
Those proficient in this rapidly evolving space will be pioneers who are determined to push the boundaries of 3D printing, curious to discover new applications and passionate about revolutionizing our future.
Are you a STEM professional looking to break into the 3D printing sector? Click here to learn how to highlight your experience on your resume to land a career in this ever-growing field.
Search Jobs
×
Our STEM Webinar Series is Now Available On Demand
No Thanks
Vacancies
Home
Vacancies
Your work in the largest integrator of digital production
Send resume
By clicking the button, you agree to the processing of personal data.
Find out more about us
www.top3dshop.ru
How our
works inside the company
www.habr.com
How the company was created - an unusual story
www.rbc.ru
Millions in 3D: Who and how makes money on 3D printing
Video about us
Our certificates and references
We sell
Why you will like it here
The Top 3D Shop team brought together people with experience in large international companies who understand how to make a quality product. A feature of our corporate culture is a high degree of openness and trust within the team, the ability to value ideas based on their usefulness, and not the age and status of the person who proposes them.
The company grows because the team solves the most ambitious tasks and is not afraid to take on difficult challenges. For its part, Top 3D Shop offers the best conditions on the market, including opportunities for rapid career growth and decent wages.
Our conditions
Best training programs
High level corporate training: online and offline trainings on leadership, corporate culture, products and business processes.
Close-knit team
No random people - only professionals. Plus - a community where you can always get support.
Participation in conferences
Russian and international exhibitions, conferences and seminars are open to you. Extensive opportunities for the exchange of experience and access to technological innovations and up-to-date knowledge of the industry.
The widest product portfolio
We work with customers from such areas as automotive, medicine, design and advertising, dentistry, construction, aerospace, military and food industries.
Comfortable office
Cozy offices in Moscow (5 minutes from Alekseevskaya metro station) and St. Petersburg (5 minutes from Frunzenskaya metro station).
Comfortable workplace
Modern technology and everything you need for successful work is already waiting for you in Top 3D Shop.
Food and recreation
You can have a bite to eat in a separate kitchen, where there is always tea and fruit, and dine in an inexpensive canteen on the territory of the office.
Free English
For experienced employees.
Corporate events and sports
We communicate informally and have fun at boring corporate parties, we hold team competitions in football, volleyball and basketball.
Decent pay
Everyone answers the question where he wants to be in a year and goes to this goal together with the team. Payments without delay. Interesting bonuses.
Rapid professional growth
Gaining new knowledge and competencies opens up opportunities for rapid career growth for any team member.
VHI after probation
Including dental services and sick pay.
Social responsibility
Financial assistance, gift certificate for the birth of a child, travel allowance.
Loan from the company
On favorable terms for employees with experience
Don't take our word for it, look at the company through the eyes of the team
Vyacheslav Nigamedzyanov
Dealer manager
Nice, clean office. Friendly colleagues, good management. The pay system is clear.
Malakhovsky Evgeny
Sales manager prof. equipment
Interesting work in a friendly team. Continuous development of your skills and knowledge. Decent pay.
Alexander Larionov
Service engineer of the service department
Young and close-knit team, excellent communication between departments. Completely satisfied!
Be part of a great story
Custom projects
Professionals
Outstanding results
Vacancies
If you are close to responsibility, diligence, adequacy and thirst for new knowledge - we will be happy to consider your candidacy for one of the open vacancies below.
- Service engineer (3D printers, CNC)
- Account Manager
- Warehouse picker
- Public Procurement/Tender Manager (3D printers, 3D scanners, Machine tools)
- Online store manager
- CNC Machine Sales Manager
- CNC Sales Manager
- Sales manager for robotics and automation projects
How to become our employee
- Contact our HR department.
- Submit a test assignment for the position.
- Interview in the office and tell us about yourself.
Or respond via the feedback form:
Reply
How to find us
Our address: Saint-Petersburg , BC Kyiv, st. Kyiv 6, room 300 (m. Frunzenskaya)
Our address: Moscow , Technopark "Caliber", Godovikova, 9, building 16, office 1.2
How to work with a 3D printer: explaining the basic principle
How to work with a 3D printer: features
When buying a new functional device, the first thing that arises is a completely logical question - “How to work with it?”.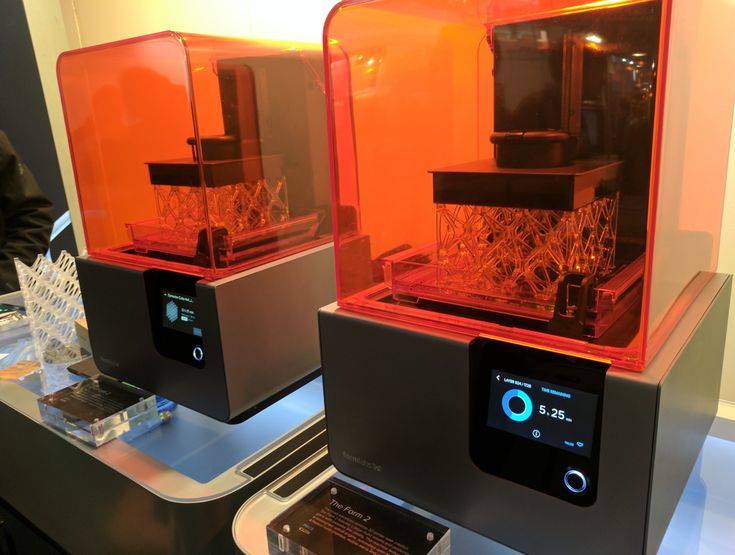 3D printers are no exception in this case, especially if the user has not previously had to deal with 3D printing devices. Of course, no one has canceled the instruction manual, and you should definitely read it. But in today's article, we want to briefly talk about how to work with a 3D printer and highlight the main points of operation, without going into the specifics of specific models. These rules apply to desktop FDM 3D printers and apply to all standard printers in this class.
3D printers are no exception in this case, especially if the user has not previously had to deal with 3D printing devices. Of course, no one has canceled the instruction manual, and you should definitely read it. But in today's article, we want to briefly talk about how to work with a 3D printer and highlight the main points of operation, without going into the specifics of specific models. These rules apply to desktop FDM 3D printers and apply to all standard printers in this class.
Our advice will be useful for both novice users of 3D printers and those wishing to purchase this device in the future. For general development, the article will be useful to everyone who is interested in three-dimensional technologies and the principle of operation of hardware for 3D printing. And for those who have just purchased their own rapid prototyping device, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the rules for faster mastering of a new device and in order to avoid problems when launching an object for printing.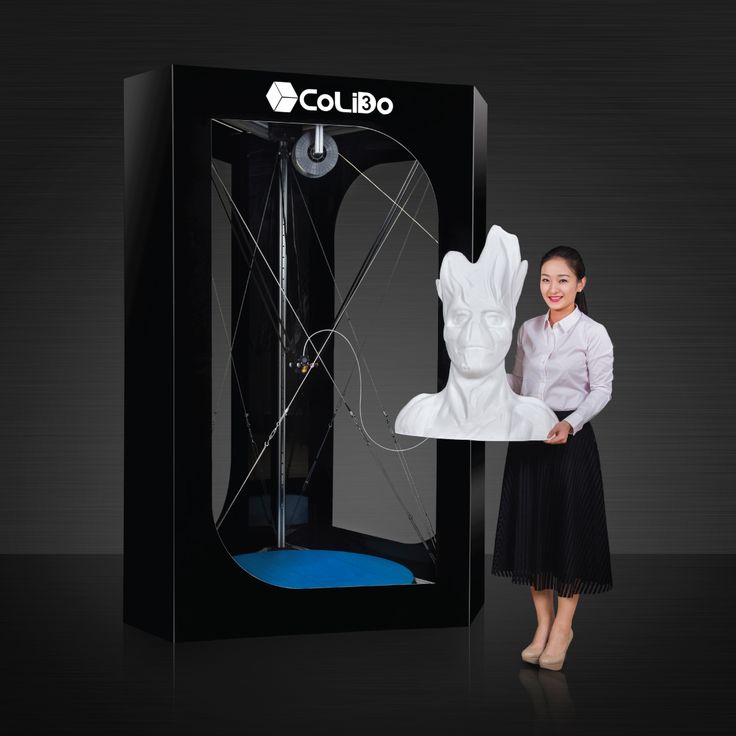 So, let's get down to business.
So, let's get down to business.
Preparing the 3D printer for operation
First of all, you should make sure that the 3D printer is working. What to check:
- Whether the printing backing has been applied. Care must be taken to cover the table with a material that improves the adhesion of products and facilitates their removal from the platform. It can be masking tape, kapton, or specialized coatings such as BuildTak. The table needs to be cleaned first.
- Is the table installed at all :) Sometimes it happens that the working platform is not connected, or is missing. In this case, it is necessary to install the table according to the user's instructions.
- Extruder patency. Residual cured plastic in the printer nozzle can block the passage of new resin. Therefore, before starting printing, it is better to make sure that the extruder is clean and clean it if necessary.
- Is the filament loaded. Although this point is obvious, it should not be ignored.
 Make sure that the 3D plastic you need is loaded into the printer in accordance with all the rules, otherwise what kind of printing can we talk about 🙂
Make sure that the 3D plastic you need is loaded into the printer in accordance with all the rules, otherwise what kind of printing can we talk about 🙂
And, of course, check the power supply. If desired, at this stage, you can put the device on preheating. This is not required, but will speed up the print launch process.
Preparing the 3D Model
Now that the 3D printer is exactly ready for the printing process, it's time to prepare the 3D model. If you are interested in how to work with a 3D printer, this point cannot be ignored. The model in STL format must be uploaded to the slicer program that generates the control code for the printer. There are different versions of slicers (Cura, slic3r, KISSlicer), and some printers support certain programs by default.
In our case, the Cura slicer is used. After loading the model, we check its readiness for 3D printing. The presence of any errors and inaccuracies will immediately be reflected in the program, which will require correction of the 3D model in accordance with the rules of 3D modeling for printing.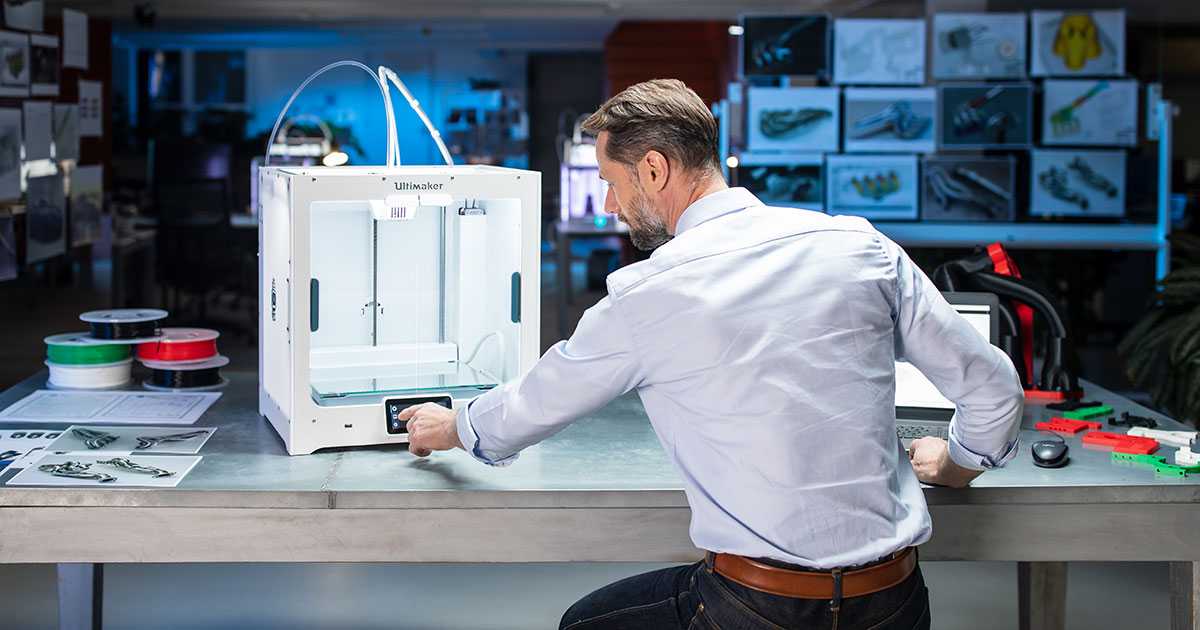
If everything is in order with the digital version of the created product, set the print settings. Remember that competent actions at this stage will affect the quality of the 3D printed sample. The following settings should be checked:
- Table and extruder temperature. These values depend on the type of plastic used, different types of polymers correspond to different temperature conditions.
- Print speed. It should also be adjusted depending on the filament, not forgetting that a high print speed can be detrimental to the quality of the product.
- Availability of support. It is advisable to print complex structures with overhanging elements with a supporting structure, this will ensure accurate reproduction of the model and prevent possible deformations of the object during cooling.
- Type of sticking to the table. For better adhesion of the product to the platform and protection against detachment of corners, there are several options for setting this parameter.
 Depending on the type of element being created and the type of plastic, they may differ.
Depending on the type of element being created and the type of plastic, they may differ.
- Printing accuracy. Everything is very clear here - the higher the accuracy, the better the detail of the finished sample. The layer height should be chosen depending on the requirements for the product.
Having done these simple steps, the 3D model can be sliced and written to a USB flash drive. Then everything is quite simple: we connect the USB flash drive to the printer, and we start the product for printing.
It is important to control the reproduction of the first layer, because the entire subsequent printing process often depends on it.
How to work with a 3D printer: final
If you can't avoid problems, you can try restarting the printing of the object. Often this helps. If the restart did not work, you will need to rewrite the model, possibly by changing the settings.
This completes the list of the main stages of launching a product for printing.