3D printer hotend
6 Best 3D Printer Hot Ends In 2023
- Last Updated: January 19, 2023
- Jackson O'Connell
The hot end is perhaps the most essential part of a 3D printer. Without it, an FDM 3D printer wouldn’t be able to melt filament, which is basically the most important step in the 3D printing process.
If you’re unfamiliar with the term, a “hot end” is the assembly on a 3D printer that gets very, very hot and melts your plastic filament so it can come out of the nozzle. The hot end is usually behind a fan shroud, and the nozzle is screwed into the bottom of this assembly.
Today, there are hundreds of different 3D printer hot ends out there, each with different features, temperature capabilities, and compatible hardware. It’s important to get a good hot end because the hot end controls what filament materials you can use and the reliability of your printer’s extrusion.
If you’re in the market for a new 3D printer hot end, I strongly suggest getting the E3D V6 or E3D Revo Six. Both hot ends have very high-temperature capabilities, are compatible with many different printers and filaments, and are reliable options. The Slicer Engineering Mosquito is another great option too, with an even high-temperature limit!
Want to hear about more of the best 3D printer hot-end options? Just keep reading!
E3D V6
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
E3D RapidChange Revo Six
Check Latest Price
Slice Engineering Mosquito
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
Table of Contents
- Best 3D Printer Hot End At A Glance
- 1. E3D V6 (Best Value)
- 2. E3D RapidChange Revo Six (Premium Choice)
- 3. MicroSwiss All-Metal Hot End (Best Choice)
- 4.
 Slice Engineering Mosquito
Slice Engineering Mosquito - 5. BIQU Dragon Fly
- 6. E3D Hemera
- What Is a Hot End?
- Considerations When Picking a Hot End
- Maximum Temperature
- 3D Printer Compatibility
- Nozzle Compatibility
- Reliability
- Value
- When to Replace the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
- How to Replace the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
- How to Clean the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
- Difference Between the Hot End and Extruder
- Conclusion
Best 3D Printer Hot End At A Glance
1. E3D V6 (Best Value)
2. E3D RapidChange Revo Six (Best Choice)
3. MicroSwiss All-Metal Hot End
4. Slice Engineering Mosquito(Premium Choice)
5. BIQU Dragon Fly
6. E3D Hemera
The E3D V6 is one of the most classic hot-end options for 3D printers. Developed by E3D, a very reputable manufacturer of 3D printer hot ends, the V6 has been around for close to ten years, and its performance is still very high-end today!
The E3D V6 is an all metal hot end, meaning it doesn’t have a PTFE liner. As such, it can reach 300 °C without any internal damage.
As such, it can reach 300 °C without any internal damage.
This is insane, considering the relatively low cost of the E3D V6. Additionally, this high maximum temperature means you can print a wide variety of filament materials from PLA to polycarbonate.
And, even while printing at 300 °C, you shouldn’t have to worry about heat creep, which is when the hot jams due to heat reaching filament too early. That’s because of the intuitively-designed cylindrical heat sink on the E3D V6 that provides exceptional heat dissipation for the assembly.
But what I love most about the E3D V6 isn’t its temperature capabilities but instead its wide compatibility. On top of working with basically any filament material, the E3D V6 can fit on basically any 3D printer through the many available user-designed 3D printable mounts for different machines.
The E3D V6 is one of the best hot ends ever made, and due to its budget-friendliness, wide compatibility, and high-temperature range, it will make an excellent upgrade for your 3D printer.
- Great community support; just check Reddit!
- Many 3D printable mounts to expand its compatibility
- Available in 12V and 24V
- Maximum temperature of 300 °C; works with any filament material
- Very reliable
- Well-designed heat sink for preventing heat creep
- Replaced by later versions (e.g. E3D Revo Six)
- Pretty weak hot-end fan
- No PTFE liner means more friction for the filament extrusion process
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
2. E3D RapidChange Revo Six (Premium Choice)
E3D RapidChange Revo Six (Premium Choice) Next, we have another product from E3D: the RapidChange Revo Six. The Revo Six is supposed to be the replacement for the E3D V6, though the E3D V6 is still being made.
The Revo Six came out in 2021 and is one of the most innovative hot-end products out there. That’s because of the integration of E3D’s new RapidChange technology, a system that makes swapping nozzles a breeze.
Moreover, each nozzle for the Revo Six has an integrated heat break (throat), and there’s a spring at the end of the actual hot-end assembly. As such, if you want to swap nozzles on the Revo Six, all you have to do is loosen the thumbscrew on the nozzle, pop out the old nozzle, and stick the new nozzle right in!
Source: Jackson O’ConnellOn top of making the process a lot less physical work, you also are able to make nozzle swaps without heating up the hot end due to the integration of a heat break. It’s a total lifesaver!
Besides the RapidChange system, the features on the E3D Revo Six are similar to those of the original E3D V6, with a maximum nozzle temp of 300 °C and a cylindrical heat sink. But E3D stepped it up with the heater, using a 40W heater, which can heat up the nozzle much faster than the V6’s 30W heater cartridge.
But E3D stepped it up with the heater, using a 40W heater, which can heat up the nozzle much faster than the V6’s 30W heater cartridge.
So, if you hate changing out the nozzle or just want a cutting-edge hot end that’s powerful and reliable, the E3D Revo Six is a terrific choice!
- RapidChange technology for easy nozzle swaps
- High maximum temperature
- Powerful and fast 40W heater
- Cylindrical heat sink; provides great heat dissipation
- Very reliable
- A good bang for your buck
- Fairly new; relatively not as much community support available
- You can only use E3D nozzles
Check Latest Price
3. MicroSwiss All-Metal Hot End (Best Choice)
MicroSwiss All-Metal Hot End (Best Choice) MicroSwiss makes all sorts of 3D printer hardware, including nozzles, extruder assemblies, and even a hot end. The MicroSwiss All Metal Hot End is a very reliable option that fits perfectly for the Creality Ender 3 (Pro/V2), CR-10, and many other printers.
Source: Jackson O’ConnellHence the name of the product, the MicroSwiss hot end is all-metal, with no PTFE liner. As such, you can print with the maximum temperature of 285 °C without any damage to the hot end components. While 285 °C isn’t as high as other products, it’s still enough to print most materials, like PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and Nylon.
But the best part of this hot end is its wide compatibility. Moreover, MicroSwiss mentions that this hot end is the same size (and voltage) as the stock hot ends on many Creality printers, as well as some by TronXY, Elegoo, Tevo, and other brands. Because of this, you can install the hot end super easily on these printers!
So, if you want a hot end that’s both easy to install and more powerful than the stock one on your 3D printer, then I suggest going with the MicroSwiss All-Metal Hot End!
- Easy to install on many 3D printers
- All-metal; won’t burn
- Reliable
- Relatively low maximum temperature
- Not very different from the stock hot ends on most 3D printers
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
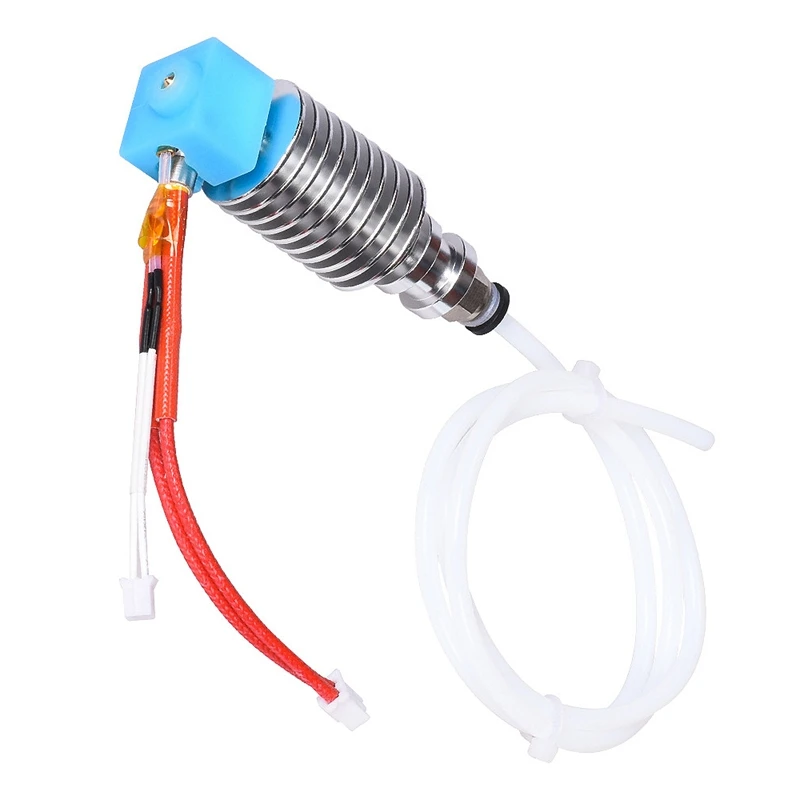
4. Slice Engineering Mosquito
Slice Engineering Mosquito Slice Engineering is a company that specializes in making high-end 3D printer hot ends. The Mosquito is one of Slicer Engineering’s flagship products, and it’s one heck of a hot end.
With a true (and tested) maximum temperature of 500 °C, the Mosquito can handle any filament material you give it, including PETG, PC, nylon, and even PMMA! Additionally, the well-engineered heat break means extrusion flow will be super smooth.
And, if you like to just print PLA, then the Mosquito is still a great hot end, as its high-temperature capabilities mean you can use insanely high print speeds without any issues with extrusion. I’ve seen people use this hot end to print at 100+ mm/s speeds!
The Mosquito also has a very well-designed cooling system. Moreover, the heat sink on the Slice Engineering Mosquito has been designed using heavy research on heat and airflow. So, even when you use high temperatures, you likely won’t have issues like heat creep, where filament melts too early.
The only obvious downside of the Mosquito is its high price. But if money isn’t an issue, the Mosquito is an amazing choice for any printer!
- Insanely high maximum temperature
- Well-designed heat sink
- Well-engineered structure (durable)
- Very reliable
- Very expensive
- The maximum temperature isn’t very practical for most users
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
5. BIQU Dragon Fly
BIQU Dragon Fly BIQU is a popular manufacturer of 3D printing accessories, from motherboards to hot ends. The BIQU Dragon Fly BMO is one of the company’s latest hot ends. Designed after the much-more-pricey Phaetus Dragonfly BMO, the BIQU Dragon Fly is a high-temperature hot end that’s compatible with printers like the Prusa i3 MK3S+, Creality Ender 3, and more!
The Dragon Fly hot end is specifically meant for maximum extrusion capabilities. This means it’s a great hot end if you want to print fast or use a very wide nozzle (e.g. 0.8-1.2 mm), where a high filament flow is required.
Source: Jackson O’ConnellAnd the Dragon Fly has the specs to substantiate high extrusion flow! Moreover, according to the manufacturer, the BIQU Dragon Fly is resistant up to 500 °C, which is insane. While you probably shouldn’t put it to more than 320 °C for safety reasons, it’s still a crazy-high maximum temperature.
With this much heat, you’ll be able to print whatever filament material you want, from PLA to PC, and also use very high print speeds for maximum extrusion flow.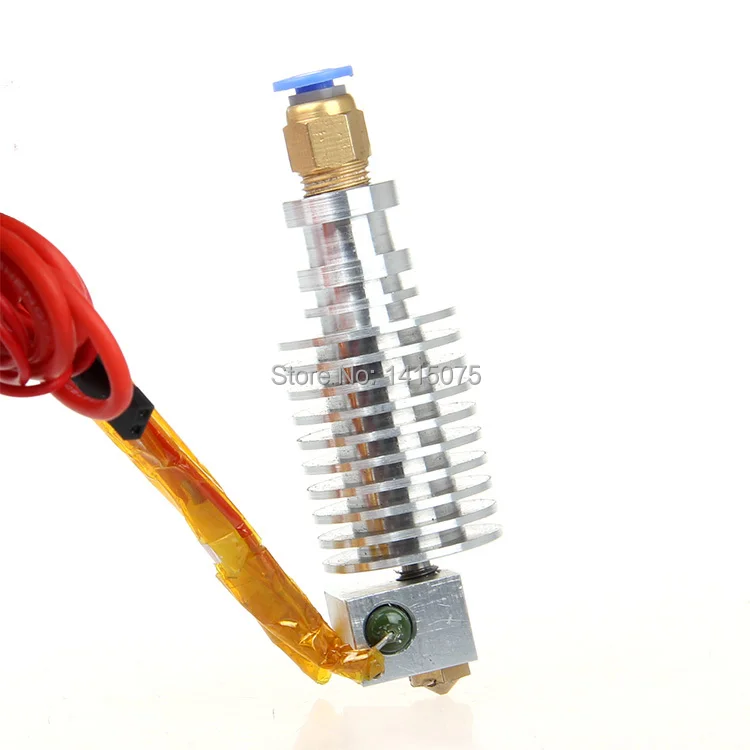
So definitely give the BIQU Dragon Fly hot end a chance if you’re looking for a low-cost hot end that can handle super-fast and high-flow 3D printing.
- Very high maximum temperature
- Not many mounting options available
- High-flow; can handle fast speeds
- It’s not as good as the official Phaetus Dragonfly hot end
- Likely not safe to print at a temperature of 500°C
Check Latest Price
6. E3D HemeraOur last hot end option is the E3D Hemera, yet another product for the famous manufacturer E3D.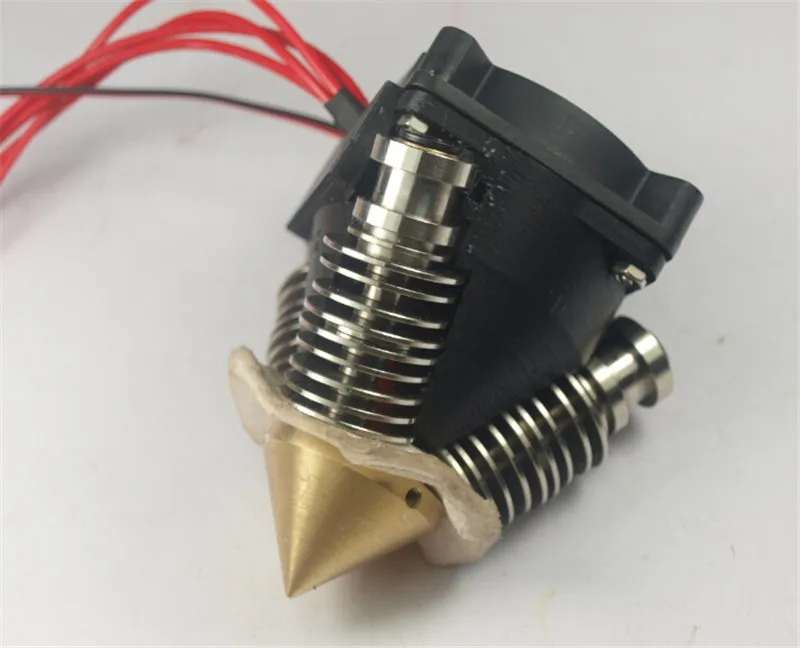 The Hemera, unlike some of the other hot ends on this list, is both an extruder and a hot end combined into one assembly. As such, it’s meant to be used in a direct drive configuration.
The Hemera, unlike some of the other hot ends on this list, is both an extruder and a hot end combined into one assembly. As such, it’s meant to be used in a direct drive configuration.
The Hemera is easily one of my top-10 favorite 3D printing products out there. That’s because the product not only performs well when it comes to the hot end side of things but also with the extruder.
Moreover, the E3D Hemera has a maximum temperature of 300 °C, so it can print basically any filament material you throw at it, from PLA and ABS to nylon and polycarbonate. And, because it’s a direct drive extruder, flexible materials, like TPU and TPE, will print very nicely.
As for the extruder, the Hemera features an E3D-custom-built stepper motor that’s geared at 3:1 for maximum pushing power. Additionally, the actual extruder assembly is dual-drive, meaning there are two drive gears rather than one drive gear and one idle bearing. As such, the Hemera provides very accurate and reliable filament extrusion.
Lastly, it’s worth mentioning that the E3D Hemera has a specialized heat sink designed using airflow research to provide maximum cooling to the hot end. This means issues like heat creep aren’t likely.
So, if you need a do-it-all hot end product that gives you high-temperature heating capabilities with an integrated extruder, then the E3D Hemera is definitely the one for you!
- Integrated extruder; direct drive
- Very powerful extruder
- Easy mounting options
- A lot of community support
- High-temperature capabilities
- Well-designed heat sink
- Heavier than a standalone hot end
- No part cooling fan included
Check MatterHackers
Check Latest Price
What Is a Hot End?
A hot end is perhaps the most essential part of a 3D printer, responsible for melting filament and giving it a clear path to the nozzle.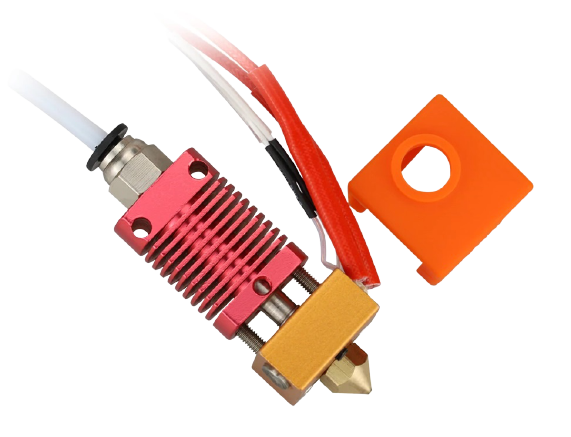
Hot ends are only on FDM 3D printers, and they typically consist of a heat sink, heat break (throat), heater block, heater cartridge, thermistor wire, nozzle, and PTFE coupler. Below you can see a diagram of a hot end with each part labeled:
Source: Jackson O’ConnellWithout a hot end, an FDM 3D printer simply could not function. And a low-quality one will yield very inconsistent extrusion, leading to ugly and inaccurate prints. As such, make sure you get a good one, like one of the options we went over previously!
Considerations When Picking a Hot End
Source: Youtube NERO 3DWhen choosing what hot end to use on your 3D printer, there are a few important factors to keep in mind. I’ve gone over these considerations in the mini sections below:
Maximum Temperature
Source: Youtube CHEPThe most important element of a 3D printer’s hot end is the maximum temperature it can reach. This is usually dependent on the type of metal used for the heater block and the quality of the heater cartridge and thermistor cables.
The higher the maximum temperature, the more filament materials a hot end can handle. For example, a hot end that can only reach 250 °C can print PLA and ABS. But one that can get up to 300 °C can print PLA, ABS, PETG, carbon fiber composites, TPU, TPE, and so many other options.
3D Printer Compatibility
Source: Youtube Thomas SanladererNot all hot ends are compatible with all 3D printers. The compatibility of a hot end with a 3D printer depends on the voltage of the hot end’s electronics, the mounting screws, and the size/shape of the assembly.
You can check the compatibility of a hot end with a certain 3D printer by looking up the following “<name of hot end> on <name of 3D printer>” and checking Reddit and other forums.
Nozzle Compatibility
Source: Youtube Thomas SanladererOn top of looking at the compatibility of a hot end on a 3D printer’s frame, you should also look at what nozzles work with the assembly. Depending on the nozzle thread of a 3D printer hot end, only certain nozzles will work.
The two most common hot end nozzle threads are M6 and M7. You also might see hot ends listed as either MK6, MK8, and MK10. The first two types have M6 threads, so nozzles are interchangeable between them. On the other hand, an MK10 hot end has an M7 thread.
Reliability
Source: Youtube Thomas SanladererReliability is another very important consideration for a hot end that outlines how consistent and dependable a hot end is. While there’s no easy metric for determining the reliability of a hot end, you can check the reviews to see what users have to say.
Value
Source: Youtube Thomas SanladererLastly, you should consider the value of the hot end you’re using. I like to think of “value” as the bang for your buck. I suggest keeping the value, or features-for-dollar, in mind, so you don’t overpay for only a slightly-better hot end.
When to Replace the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
Source: Youtube CHEPUnlike the nozzle, replacing the hot end on a 3D printer isn’t something you should try to do every few months.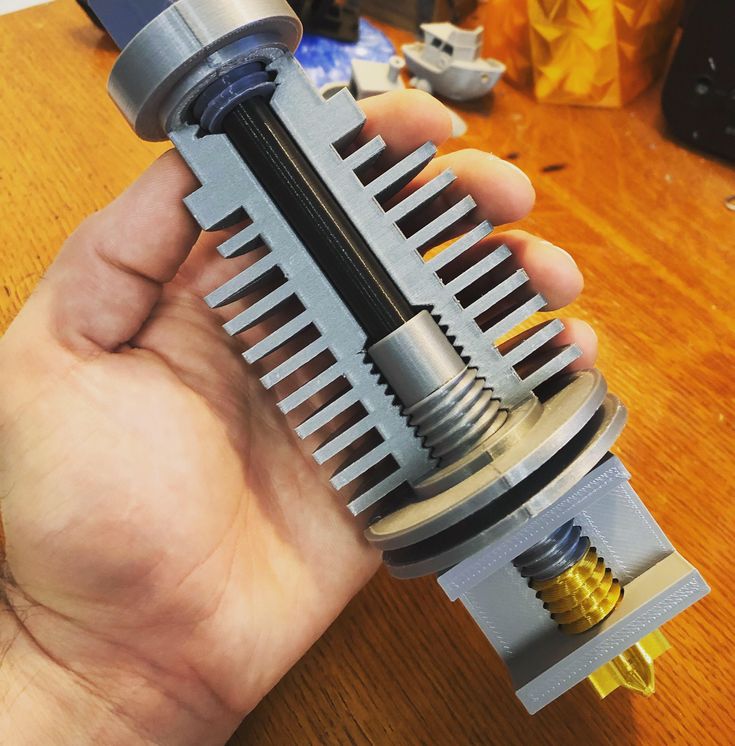 Instead, you should only replace the hot end when it’s actually broken or failing you.
Instead, you should only replace the hot end when it’s actually broken or failing you.
That’s because 3D printer hot ends can get somewhat expensive, costing anywhere from $20-200, so replacements shouldn’t be too frequent. Additionally, hot ends aren’t meant to be consumables like nozzles, so they should last you a very long time.
You’ll know when it’s time to replace your 3D printer’s hot end if the melted filament is oozing from the heater block or if any part of the assembly physically breaks. Additionally, if the threading for the nozzle is damaged, you’ll need to replace the hot end.
How to Replace the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
Source: Youtube 3D Printing CanadaThe process for replacing your 3D printer’s hot end will vary depending on what printer you have. However, the general process goes something like this:
- Turn on the printer.
- Heat up the hot end to your regular printing temperature.
- Remove the filament.
- Unscrew the nozzle.
- Unscrew the fan shroud and move it to the side.
- Wait for the hot end to cool down, and then unscrew the mounting bolts that hold the hot end assembly to the printhead carriage.
- Unscrew the PTFE tube coupler from the hot end assembly.
- Remove the PTFE tube.
- Open up the motherboard housing.
- Turn off your printer.
- Locate the hot end heater and thermistor cables on the motherboard and unplug them.
- Pull out the heater and thermistor wires and place your old hot end to the side.
- Wire the heater and thermistor wires of your new hot end to the motherboard. Plug them in securely.
- Screw the mounting bolts of the hot end into the printhead carriage. Make sure they’re very tight.
- Reattach the nozzle.
- Move the fan shroud back over the hot end assembly and screw it in.

And that’s it!
Of course, this process might not work for all printers, especially if your hot end isn’t natively compatible with your 3D printer. For example, if you’re installing an E3D hot end on a stock Creality Ender 3, you’ll need to change the firmware settings to account for the different thermistor wires.
But, for specific upgrades, you can check out the other articles on our site or the many video tutorials available online!
How to Clean the 3D Printer’s Hot End?
Source: Youtube Ricky ImpeyTo clean your 3D printer’s hot end, start by turning on your printer and heating the nozzle up to your normal printing temperature. For PLA, this would be around 220 °C.
Once the hot end is actually hot, remove the filament from the printer. Make sure you pull it out of both the hot end and extruder assembly.
Next, remove the fan shroud from your printhead. You can usually do this by taking the right-size Allen Key and unscrewing the fan shroud mounting bolts.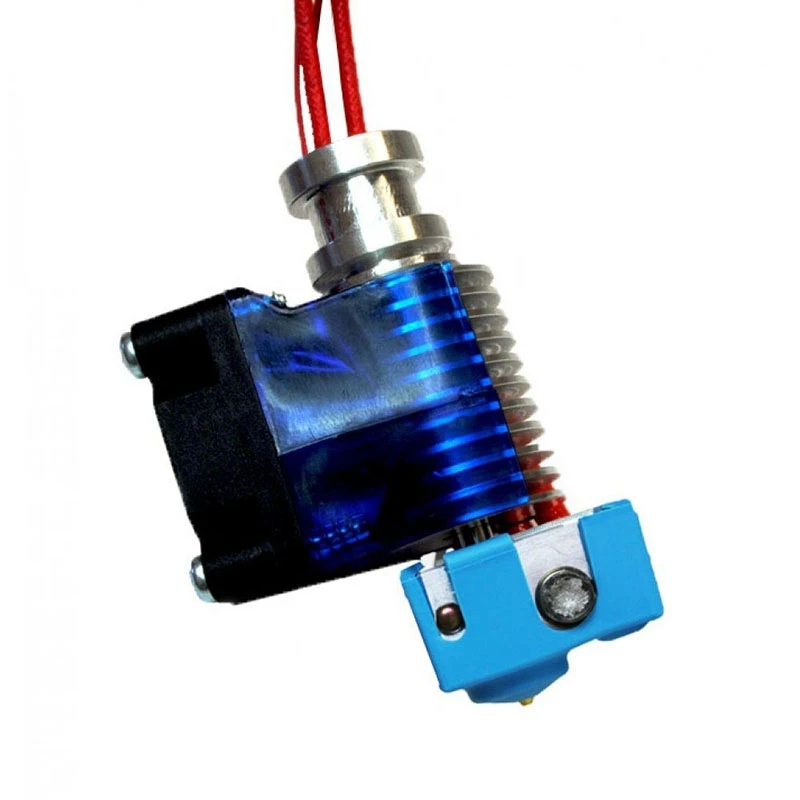
Move the fan shroud to the side and then, with the right size spanner wrench, unscrew the nozzle. With the nozzle removed, take a peek at the inside of the hot end to see if it’s damaged at all. Damage will look like any obvious deformations to the metal.
If there’s no damage, you can start cleaning the hot end assembly. To do this, I like to get a small metal pic and tweezers and then go ham at pulling out guck from the inside of the hot end.
Once you remove all the large chunks, you can get an alcohol or acetone wipe (e.g. nail polish remover wipe), and, using the tweezers for safety, rub it around inside the hot end. If you do this while the hot end is still hot, it will be most effective. Just make sure you don’t leave the wipe there too long as it will burn if heated for too long.
And that’s it!
Difference Between the Hot End and Extruder
Source: Youtube Thomas SanladererThe difference between the hot end and the extruder is that one stays hot (the hot end, obviously), and one stays cold.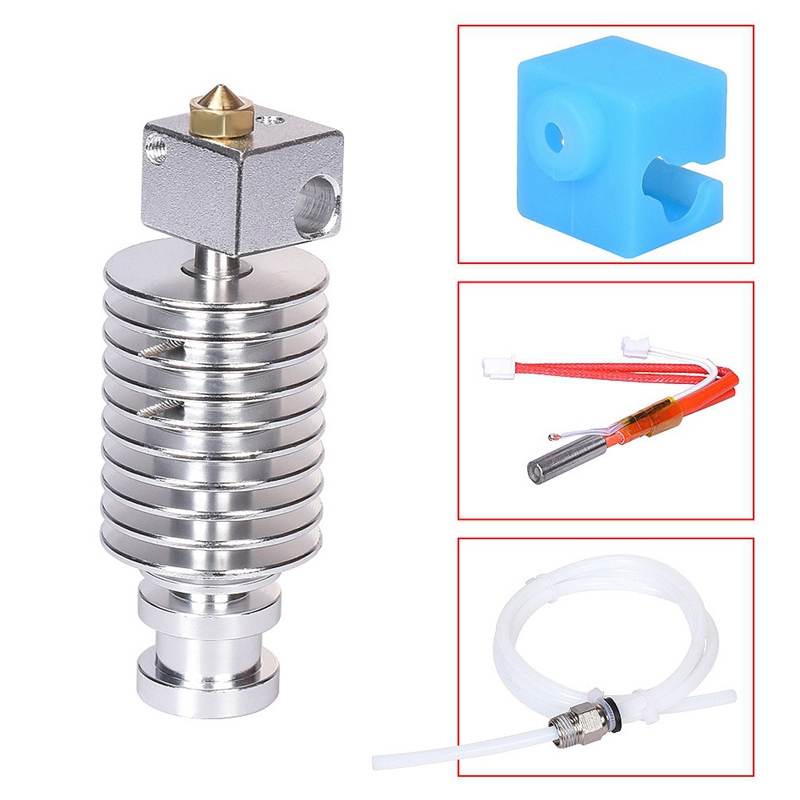
Moreover, the hot end, as we went over, is responsible for melting the incoming filament so that it can flow out of the attached nozzle.
On the other hand, the extruder, also known as the “cold end”, is the motor assembly that’s responsible for pushing filament into the hot end.
A Bowden extruder 3D printer, like the Ender 3 (Pro/V2), has the extruder on the left-hand side and the hot end on the printhead assembly. Direct drive 3D printers, like the Ender 3 S1, have the extruder right on top of the hot end assembly.
Conclusion
A hot end is super important for the 3D printing process, and because its impact on the printing process is so significant, you should make sure you’re using a high-quality hot end.
As we went over, a good hot end can reach high temperatures, fits on many printers, has good value, and is very reliable.
The best 3D printer hot end is easily either the E3D V6 or E3D RevoSix. Both products are affordable and can reach a temperature of 300 °C, which is crazy high and more than enough to print any filament material.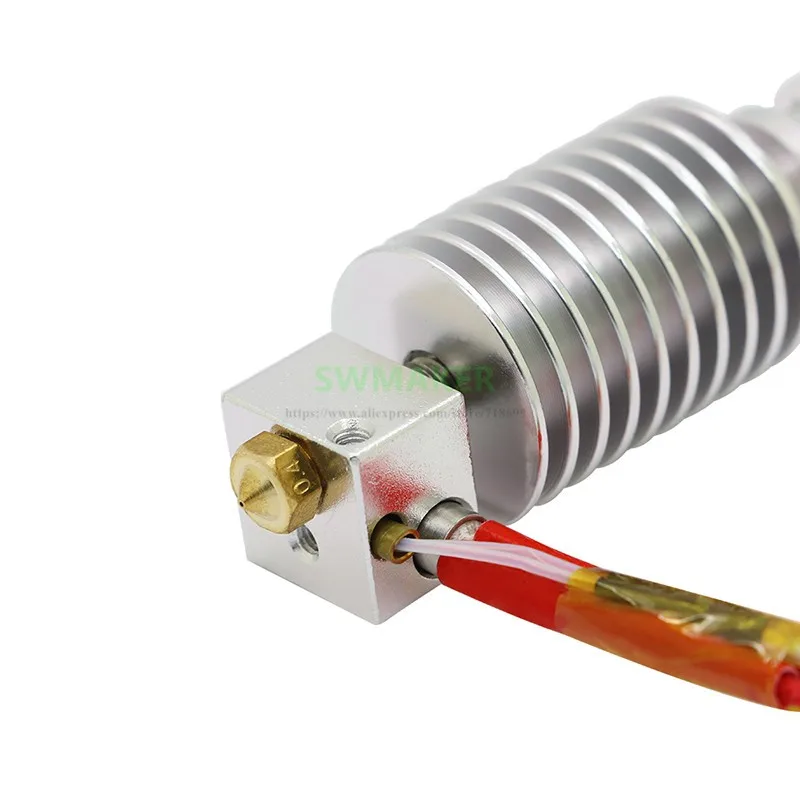 Additionally, reliability and community support are spectacular for these products!
Additionally, reliability and community support are spectacular for these products!
But, if you want the ultimate 3D printing hot end, then I’d go with the Slice Engineering Mosquito, the creme-de-la-creme of 3D printer hot ends. With an insanely high maximum temperature of 500 °C and a super effective heat sink, you’ll be unstoppable with this hot end by your side!
Enjoy!
3D Printer Hot-Ends - 3DJake International
Sort byRelevanceBestsellersCustomer ReviewsPrice, Low to HighPrice, High to LowNew arrivalsHighest Discount
-
Creality Hotend 20 Model types- Original spare part
- From Creality
-
Micro-Swiss All Metal Hotend Kit for CR-10- All metal
- Better heat dissipation
- No adjustments required
-
Micro-Swiss Silicone Socks Set for MK7 / MK8 / MK9 1 set- High-temperature resistant
- Set of 3
- Non-stick
-
BROZZL All Metal Hot-End Upgrade Kit for Ender & CR-10- Easy to use
- Fast assembly
- Precise manufacturing
-
Phaetus Dragonfly Hotend BMS- Temperature resistance up to 500 ° C
- All-metal design
- Good heat dissipation
-
E3D V6 Silicone Socks 1 set- Non-stick surface
- For V6 heating blocks
- Keeps your heating block clean
-
E3D V6 Plated Copper Heater Block- Good high-temperature performance
- Softening point well over 500 ° C
- Less sticking
-
Micro-Swiss All Metal Hotend Kit for CR-10S Pro- All Metal Hotend
- Better heat dissipation
- Can be used without any modifications
-
Phaetus Dragonfly Hotend BMO- Temperature resistance up to 500 ° C
- All-metal design
- Good heat dissipation
-
Slice engineering Mosquito- Perfect heat transfer
- Temperatures up to 450 ° C possible
- Flexible installation
-
Micro-Swiss All Metal Hotend Kit for the CR-6 SE- Titanium alloy heat break
- Well defined melting zone
- Aluminium heating block
-
Anycubic Hotend 10 Model types- Original spare part
- By Anycubic
-
Micro-Swiss High Temperature MK8 Heating Block Upgrade- M6 thread size
- Special alloy
- High printer compatibility
-
E3D Revo Micro Full Kit 2 Model types- Complete set including 4 nozzles
- Compatible with Bowden or Direct Drive setup
- Small & light heat sink
-
Creality Heatsink 5 Model types- Original spare part
- From Creality 3D
-
E3D V6 All-Metal Hotend Bowden - 1.75 mm 4 Model types- High temperature performance
- All-Metal
- Compact design
-
E3D Revo Six 2 Model types- Direct replacement for E3D V6 Hotend
- Including a 0.4 mm nozzle
- All-metal hotend
-
E3D Prusa V6 Hotend 3 Model types- Replacement hotend
- With V6 parts
- Improved version
-
E3D Volcano Silicone Socks- Non-stick surface
- For Volcano heating blocks
- Keeps your heating block clean
-
FLSUN Hotend Thermistor 3 Model types- Original spare part
-
BondTech BMG-M & Mosquito Magnum Set 2 Model types- Perfect upgrade
- Complete set
- Safe 3D printing process
-
E3D Revo Six Full Kit 2 Model types- Direct replacement for E3D V6 Hotend
- Complete set
- Incl.
 4 nozzles (0.25 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, 0.8 mm)
4 nozzles (0.25 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, 0.8 mm)
-
E3D Revo CR Full Kit 2 Model types- Simple and quick nozzle change by hand
- Incl. 4 Revo nozzles
- Increased efficiency & safety
-
Slice engineering Mosquito Magnum- High printing speed
- Temperatures up to 450 ° C possible
- Flexible installation
All prices incl.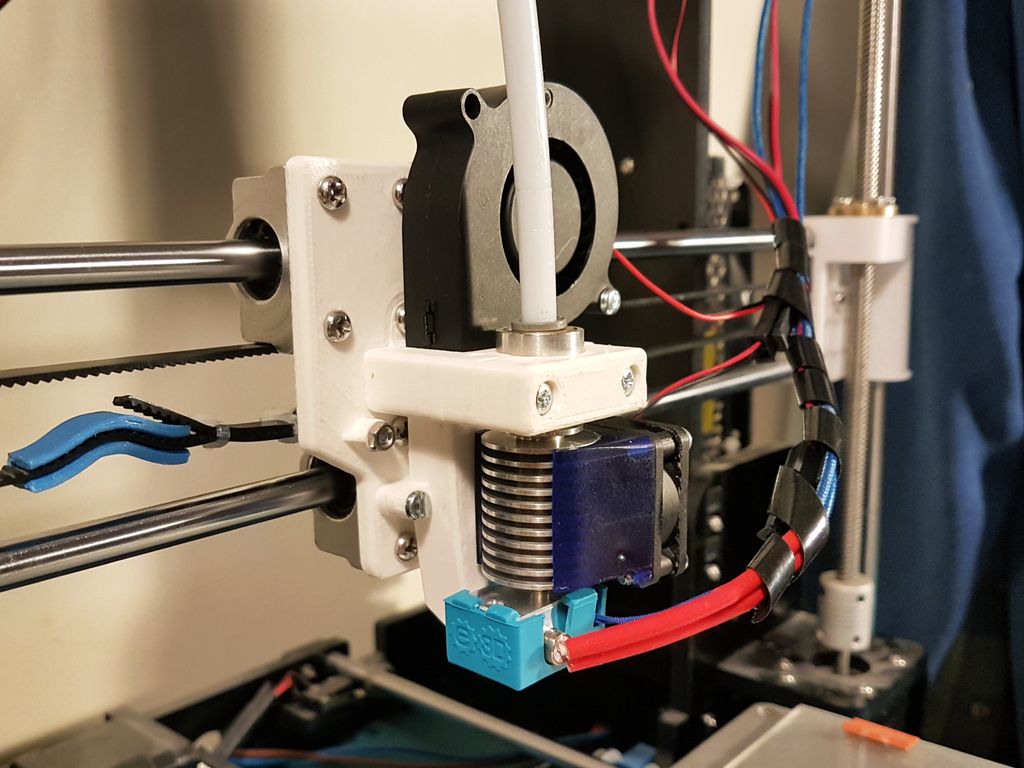 VAT.
VAT.
3D Printer Extruder - Complete Manual Heatle
Learn the basics of direct drive and Bowden extruders, hot and cold ends, nozzle sizes and materials, and find the best 3D printer cartridge for your needs.
The 3D printing process can be briefly described as follows: a filament of plastic material is fed into a heated metal block with a nozzle, where it is melted and extruded in a given form. This path is repeated, gradually building up until a solid three-dimensional object is formed. nine0003
The entire business task of handling the material, melting it and exiting for printing takes place in a block called 3D printer extruder .
In this article, we will look at the main sections of the 3D printer extruder, the options and advantages of different styles of extruders, popular models on the market, as well as cartridge heaters for 3D printers and other items.
What is an extruder
The 3D Printer Extruder is a set of parts that together process and move plastic filament. nine0003
nine0003
Some consider the extruder to be just the motor and associated parts that push and pull the filament, others the entire assembly including the heated part that melts and deposits the filament.
For simplicity, this article treats the entire assembly as an extruder. To begin with, while explaining the key components of a 3D printer extruder, we will divide it into two elements: a cold zone and a hot zone.
Cold zone
As the name implies, the cold zone is exactly that - cold. It's The top of the 3D printer's extruder system, into which the filament is fed and then passed into the hot zone to be melted and extruded onto the print bed.
The appearance and location of the cold zone on your 3D printer depends on whether it is a direct drive or Bowden drive extruder (both of which are detailed below).
There is no filament heating here. The cold zone consists of the extruder motor and gear train, which are usually mounted either on the printer frame or on the print head itself, depending on the type of extruder, and a PTFE tube to smoothly guide the filament into the hot end.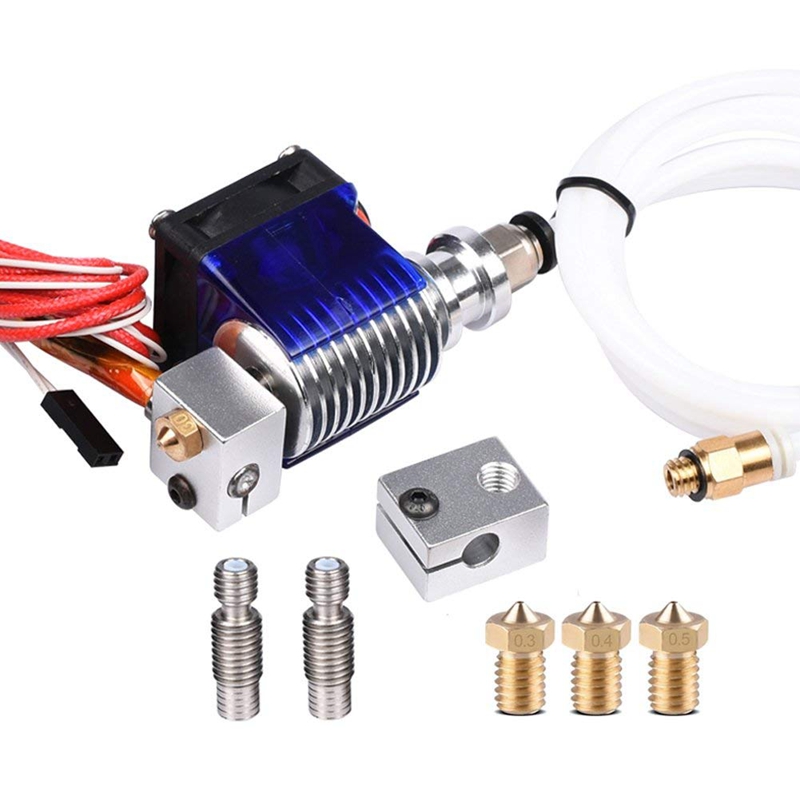 nine0003
nine0003
What happens in the cold zone?
With the heatsink removed on this e3D Titan Aero, we can see the inner workings of the 3D printer's extruder.
Essentially, the cold zone consists of a stepper motor, some form of gear, a toothed bolt or gear, a spring-loaded idler (usually a bearing of some kind) to hold the filament, and then a PTFE tube to guide the filament.
A humble stepper motor with a metal gear required for a 3D printer's extruder drives the filament extrusion in most if not all modern desktop 3D printers.
However, one stepper motor is not enough to feed the filament to the hot end. The parts attached to and operating the stepper motor drive shaft must physically grab the filament and push it on its way to the hot end.
In this cutaway view of a 3D printer extruder, we see a metal gear and a plastic gear with a toothed shaft. nine0038
This usually uses a combination of toothed gears and toothed bolts or shafts (in the image above we see a metal gear and a plastic gear with a toothed shaft) serving as a pressure wheel along with a bearing or other rigid frictionless material.
Here we see a plastic lever with an integrated bearing, an extension spring and a plastic gear with a toothed shaft. Together they apply pressure to the filament and force it through the extruder. nine0038
Alternatively, there are versions of the cold end of the 3D printer extruder that use a slightly different arrangement of parts to feed the filament. Such deviations are often claimed to provide increased traction and yarn delivery.
Here we see both sides of the Prusa i3 Mk3 cold end, including the Bondtech extruder gear train.
As mentioned, there are varieties of 3D printer extruder that use these parts in slightly different layouts. Each has its pros and cons. Next, we will look at what is the difference between a direct drive 3D printer extruder and a Bowden 3D printer. nine0003
Direct drive extruders
The Direct Drive 3D Printer Extruder is different in that it places the extruder motor directly above the heating unit.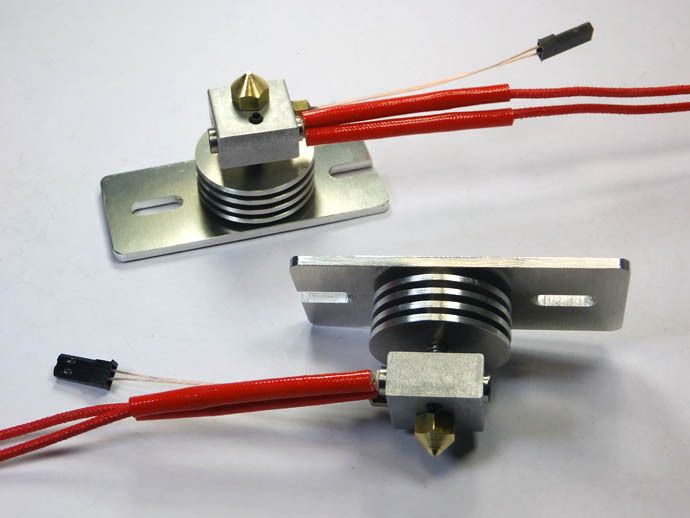 This arrangement minimizes the travel distance of the filament to the hot end and can enable more reliable 3D printing of flexible filaments.
This arrangement minimizes the travel distance of the filament to the hot end and can enable more reliable 3D printing of flexible filaments.
The advantage of using direct drive is more precise retraction control. Due to the location directly above the hot end, there is less distance between the clamp and the thread passing through the thermal barrier into the heating block. Consequently, the filament has less room to bend and deform under pressure. nine0003
Bowden extruders
Bowden Style 3D Printer Extruder The does not mount directly on the top of the hot end like a direct drive 3D printer extruder, but the motor and gear assembly mounts on the frame of the printer. This gives this type of extruder an advantage over its head-mounted direct drive brother: speed.
By placing the mass of the 3D printer's extruder on the frame instead, the printhead is freed up to print at higher speeds without sacrificing print quality. nine0003
A side effect of placing the 3D printer's extruder this way is that the filament now has to travel a long way in a tube that's a fraction wider than it is.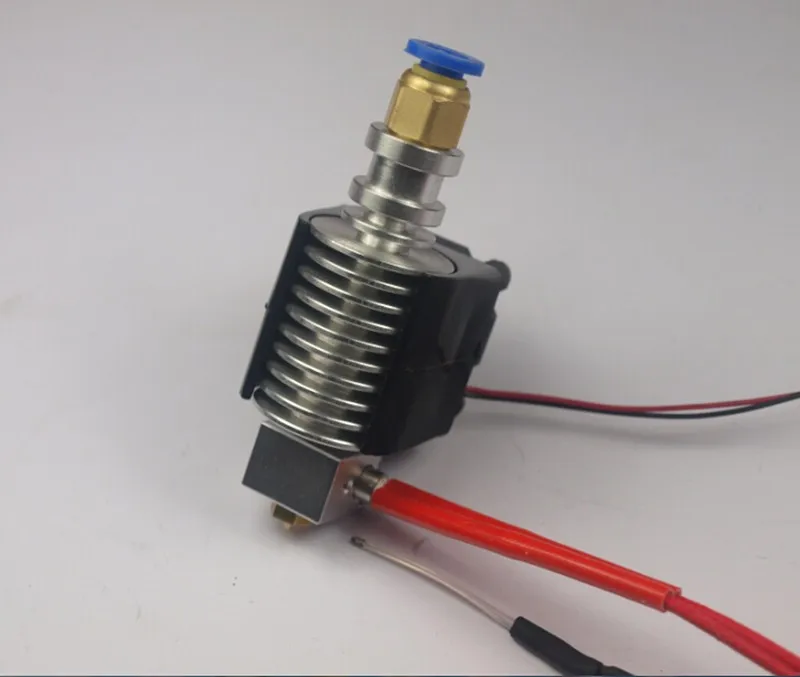 There should be enough room along the entire length of the tube for a slight bend in the thread. When pulling in the thread between strokes, this slack in the thread shortens the pull-in distance. Without correction (i.e., an increase in retraction), this results in a delay in relieving the pressure exerted on the hot end. In short, you can get confused if you don't change your retract settings. nine0003
There should be enough room along the entire length of the tube for a slight bend in the thread. When pulling in the thread between strokes, this slack in the thread shortens the pull-in distance. Without correction (i.e., an increase in retraction), this results in a delay in relieving the pressure exerted on the hot end. In short, you can get confused if you don't change your retract settings. nine0003
Heating block (Hotend)
Inside the knot, known as the hot end, the filament passes into a heated chamber where it changes from solid to liquid. Sounds simple, and mostly it is. Although there is a lot more to make the filament silky extrude onto the build plate.
What happens in the heating zone?
The E3D Titan Aero combines a heating unit and an extruder in one compact unit. The hot end usually only has the central parts of this image: the heatsink (and fan), the heating element (micro cartridge heater), the heater block, the thermistor, and the nozzle. nine0038
nine0038
A typical 3D printer hot end consists of a specific sequence of parts. There is a slight difference depending on whether you are using PTFE/PEEK or a full metal hot end. Here we explain the all-metal hot block.
First, it is a filament supply tube. In both a Bowden 3D printer extruder and a direct drive extruder, it will just be a PTFE tube coming from your cold filament feeder. nine0003
You can sometimes find direct drive 3D printer extruders where the filament runs straight into the print head.
On a Bowden 3D printer's extruder, this feed tube inserts the filament directly into the thermal barrier via a heatsink. The thermal barrier that is screwed into the heatsink is often a threaded stainless steel (or other non-conductive metal such as titanium) tube.
Split in two (note the two separate threads in the image below - longer for the heatsink, shorter for the heater block) and machined on the inside, the thermal break allows the filament to pass freely into the extrusion nozzle.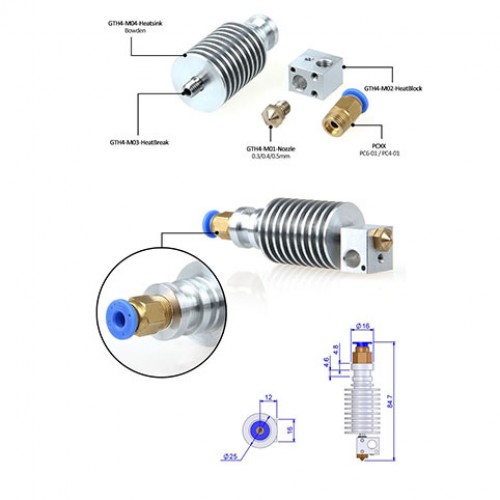 nine0003
nine0003
Clockwise from bottom left: steel thermal barrier, aluminum heating block and brass nozzle.
But since we're dealing with precision and a material that liquefies for rapid recooling, the 's temperature management is critical. The thermal barrier, in combination with the heat sink, maintains a certain limit at which the filament is exposed to high temperatures. nine0003
The top, which is actively cooled by a heatsink and dedicated fan, prevents heat from escaping from the hot end and weakening the filament before it is where it needs to be for extrusion. This unwanted phenomenon is known as thermal creep.
The lower part of the thermal barrier is located inside the heater block together with the cartridge heater, the temperature switch thermistor and the nozzle.
The heater block, usually made of aluminum, ensures a smooth transition of the filament from the open end of the thermal break tube to the nozzle.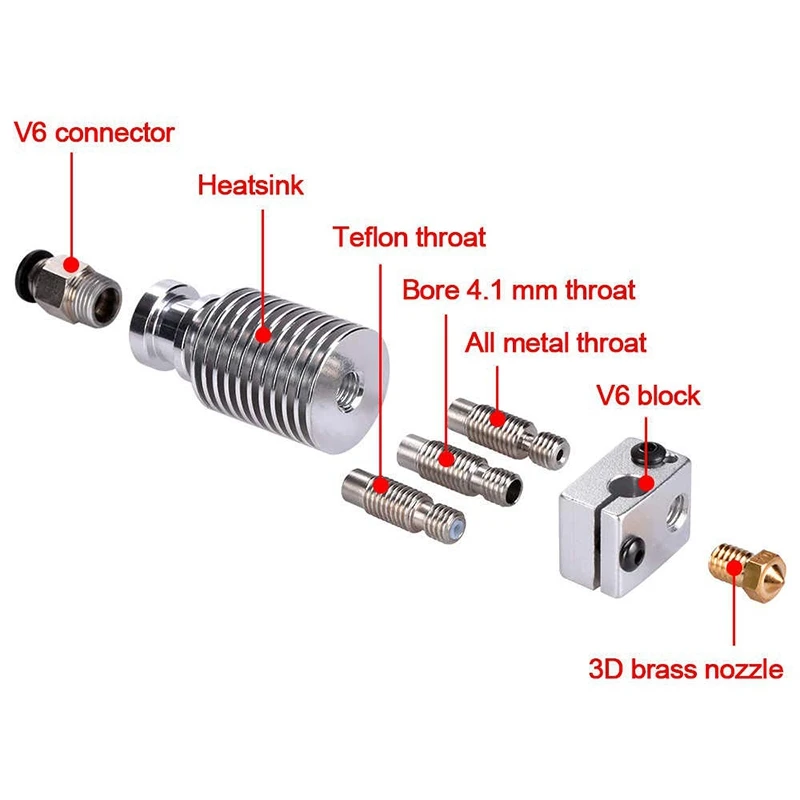 nine0003
nine0003
The temperature to melt the filament has to come from somewhere, and this is where the cartridge heater comes into play. Under the action of an electric current, the cartridge heating element heats up, transferring heat to the nozzle through the heater block, in which they are both enclosed.
Clockwise from top left: heating block, thermistor, cartridge heater, nozzle, thermal break.
Power resistors are an alternative means of heating a hot end block, but they are less common these days. nine0003
Also inside the heater block is a thermistor, a small sensor that transmits the temperature of the block to the 3D printer's motherboard, allowing the correct settings to be made.
And on the uneven edge of the entire system is a nozzle. The nozzle itself is a small piece of machined metal, consisting of a chamber containing molten filament that tapers towards the nozzle opening.
Hotend in the category "Appliances and electronics"
EKSTRUDER QR -M Do Mosquito Hotend - PRAWY - 1. 75 MM (EXTQRM175)
75 MM (EXTQRM175)
On order
Delivery in Ukraine
240 UAH
Buy
BondTech Ekiter -m -msprech Ekiter -mspruder qr -mspruder qr -mspruder qr -mspruder qr -mspruder qr -mspruder qr Hotend LWY - 2.85 MM (Extqrm30lh)
on order
Delivery in Ukraine
240 UAH
11 130 UAH
TEVUP TARANTULA PRO PRO PROINTER, SEMI -AUTOMATIC LEVELELING, 0.4MATOMATIC LEVELELIS Hotend 235x235x250mm
Under order
Delivery in Ukraine
16 010 UAH
1550 UAH
Buy
Bondech LGX Ace Mosquito Hotend (ExtlgxacM)
Delivery according to Ukraine
9000 9000 9,0002 UAHBuy
BondTech EKSTRUDER QR -M Do Mosquito Hotend - PRAWY 2.85 MM (EXTQRM30)
Under order
Delivery in Ukraine
240 UAH
130 GRN
Buy
003
Creality Spider Hotend Kit high temperature nozzle 500C for Ender-3, Ender-3PRO, Ender-6
Delivery across Ukraine
. for Ender 3/3Pro/3V2/Ender-6
for Ender 3/3Pro/3V2/Ender-6
Delivery across Ukraine
1 960 UAH
Buy
Heating element for hotend extruder 3D printer. 12 and 24 volts
Delivery from Lviv 9Ol000 Liquid 1.75mm (850005423416)
On order
Delivery in Ukraine
12 9000 UAH
12 800 UAH
Buy
9000 Hotend E3D Revo Cr Fully Cr Fully EnderUnder order
Copp.0003
Delivery in Ukraine
9 430 UAH
9 340 UAH
Buy
Hotend Raise3d [s] 3.01.1.024.045A01
Under order
Delivery
8 990 GRN
8 900 UAH 900 UAH 900 UAH 900 UAH 900 UA
Buy
See also
Hotend Raise3d [s] 3.01.1.024.043A01
On order
Delivery in Ukraine
9 730 UAH
9 630 UAH
Phaetus Rapido Plus Hotend UHF - Natural A15808B1503) 9Ol000 360 UAH
Buy
BondTech LGX ACE Magnum+ Hotend (Extlgxacempmp)
Cupport
Delivery in Ukraine
20 960 UAH
20 750 UAH
Buy
E3D V6 Gold Hot Hot Hot Hot Hoten - (V6175GOLD12VAS)
Under order
Delivery in Ukraine
8 460 UAH
8 370 UAH
Buy
Slice Engineering Hotend Mosquito Magnum+ Air)
Under the order
Delivery 9000 2 21 800 UAH
Buy
E3D V6 Gold Hotend - 1.