3D food printers market
Food 3D Printing Market Size, Share
Food 3D Printing Market Research, 2031The global Food 3D Printing Market Size was at $226.2 million in 2021, and is projected to reach $15.1 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 52.8% from 2022 to 2031.
The effects of the pandemic were also reflected in 3D food printing market, owing to closure of hotels and the 3D printing manufacturers, and this is attributed to the labor shortage and the complete description of logistic & supply chain in the world. The halt in the production of 3D food printing had an adverse impact on the overall market growth.
The food 3d printing market is segmented into Ingredient, End User and Technologies.
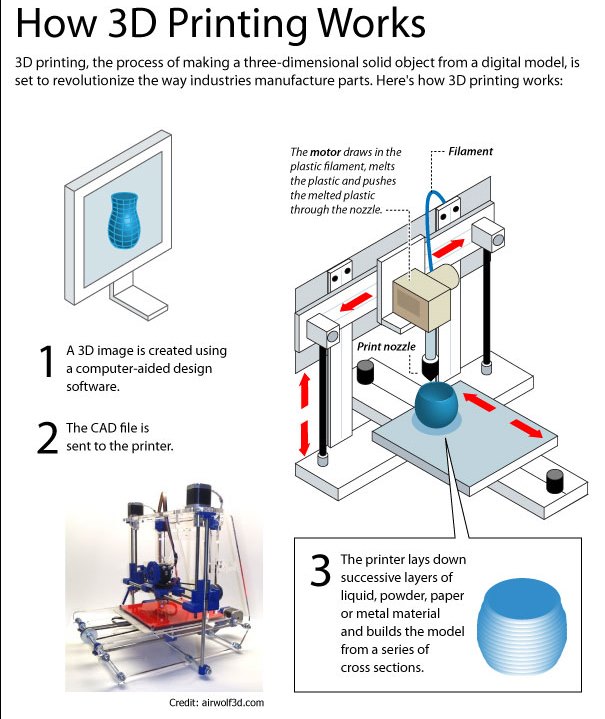
A food manufacturing and modification technique called food 3D printing allow for the creation of three-dimensional food products. An assembly of actuators, software, sensors, and storage containers—typically made of stainless steel or food-grade plastic—are coordinated to function together as a 3D food printer. Incorporating three-dimensional digital designs into delectable real-world foods, 3D food printing not only gives food ingredients three-dimensional shapes however preserves the product's style, framework, and texture. Insect, protozoan, or beet leaf proteins are converted into delectable products by this process, which is regarded to be harmless for the environment.
3D food printing offers the possibility to personalize food to consumers’ individual needs. The growth of the custom food market is the main reason behind the growth of the Food 3D Printing Market. People are often busy with work and are unable to taste their favorite foods due to lack of time hence technology plays a vital role in production of such food products. However, custom foods should be infused with the appropriate preservatives to keep them fresh. Frequent intake of preservatives is not good for health in the long run. Therefore, 3D food printing technology gives users the option of producing such food products at home without the use of preservatives.
The 3D Food Printer can print a variety of complex food designs that are not possible manually. A food-grade 3D printer consists of a food-grade syringe or cartridge containing the material, and the actual food, and deposits the exact sub layer by layer directly onto the plate or other surface through the food-grade nozzle. This food is a healthy source of nutrition for both adults and kids who want to enjoy foods such as pizza, chocolate, and pancakes in unique shapes and designs. Thus 3D food printing technology helps in production of healthy and nutritious food products in large quantity and in small time. Thus all these factors are expected to boost the market growth and increase Food 3D Printing Market technology penetration in restaurants, hotels, and residences. 3D food printing is currently used primarily for preparing foods for those with special nutritional needs e.g., dysphagia and associated eating-related conditions, as well as for snack and novelty products. It has the potential to decrease food waste by recycling foods, such as leftover cuts of meat, seafood scraps, and other vegetable. Thus such recycling food trends are expected to boost the adoption of 3D food printing technology across the globe. In addition, opportunities lie in the growing trend for alternative protein sources, such as insects, algae, duckweed, grass, spirulina, lupin seeds, and beet leaves, to produce foods that satisfy consumer taste and nutritional requirements. New forms and figures that were previously impossible to manufacture can now be produced, ranging from chocolates and other desserts to pasta shapes and protein patties. By adding hydrocolloids (examples are xanthan gum and gelatin) to maintain the form, fruits and vegetables in purée form can be extrusion printed. The fact that they can be easily extruded from a syringe supports their positive printability qualities. Using techniques such as these, 3D printing provides the opportunity to print one dish that contains all necessary daily nutrients.
Thus such recycling food trends are expected to boost the adoption of 3D food printing technology across the globe. In addition, opportunities lie in the growing trend for alternative protein sources, such as insects, algae, duckweed, grass, spirulina, lupin seeds, and beet leaves, to produce foods that satisfy consumer taste and nutritional requirements. New forms and figures that were previously impossible to manufacture can now be produced, ranging from chocolates and other desserts to pasta shapes and protein patties. By adding hydrocolloids (examples are xanthan gum and gelatin) to maintain the form, fruits and vegetables in purée form can be extrusion printed. The fact that they can be easily extruded from a syringe supports their positive printability qualities. Using techniques such as these, 3D printing provides the opportunity to print one dish that contains all necessary daily nutrients.
Rise in demand for gourmet food is the major driver for the growth of the Food 3D Printing Market, owing to the expansion of the custom food market.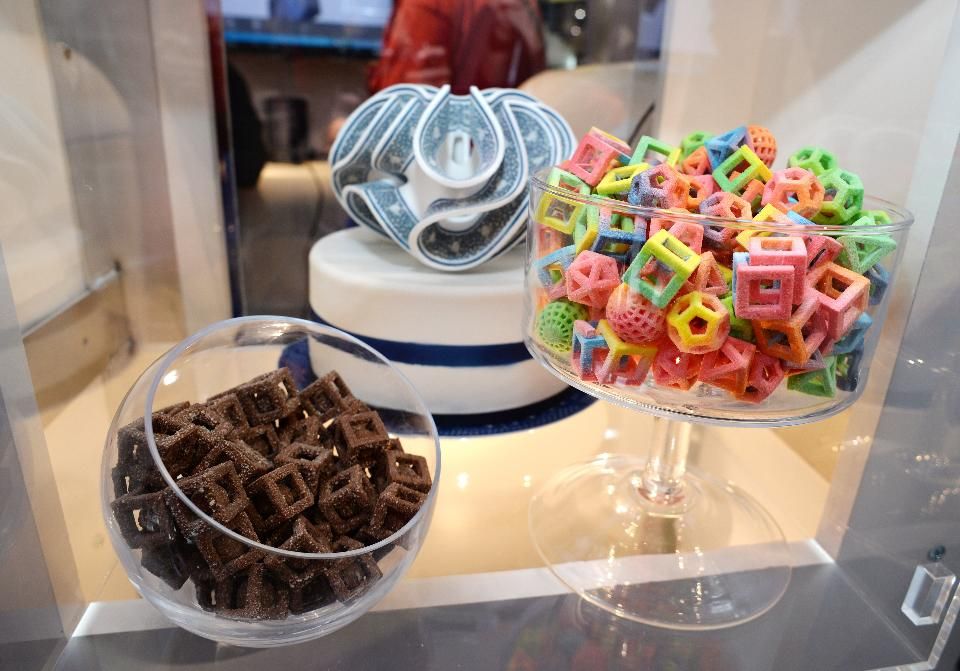 owing to advancements in technology, people are frequently preoccupied with their jobs and unable to enjoy their favorite foods due to lack of time. To keep them fresh, however, proper preservatives need to be added to personalized foods. Preservative consumption on a regular basis is bad for health in the long run. Owingto this, 3D food printing technology allows users to offer fresh and handcrafted food. Thus, the increasing Food 3D Printing Market Demand for gourmet food is driving the market growth. Moreover, a higher focus on the development of nutritionally customized foods for enhanced health benefits is a factor further acting as a key driver of the 3D Food Printing market. In addition, the rise in the use of 3D printers in plant-based meat alternatives is another factor driving the market growth. The scientists developed a new sequence of plant-based components for 3D-printed meat substitutes in a study published in ACS Food Science & Technology. Their primary recipe for success called for the addition of a strange-sounding cocoa butter derived from cocoa beans, which are best known for their chocolate.
owing to advancements in technology, people are frequently preoccupied with their jobs and unable to enjoy their favorite foods due to lack of time. To keep them fresh, however, proper preservatives need to be added to personalized foods. Preservative consumption on a regular basis is bad for health in the long run. Owingto this, 3D food printing technology allows users to offer fresh and handcrafted food. Thus, the increasing Food 3D Printing Market Demand for gourmet food is driving the market growth. Moreover, a higher focus on the development of nutritionally customized foods for enhanced health benefits is a factor further acting as a key driver of the 3D Food Printing market. In addition, the rise in the use of 3D printers in plant-based meat alternatives is another factor driving the market growth. The scientists developed a new sequence of plant-based components for 3D-printed meat substitutes in a study published in ACS Food Science & Technology. Their primary recipe for success called for the addition of a strange-sounding cocoa butter derived from cocoa beans, which are best known for their chocolate. Thus, the rise in the use of 3D printers in plant-based meat alternatives further boosts the 3D food printing market.
Thus, the rise in the use of 3D printers in plant-based meat alternatives further boosts the 3D food printing market.
However, limitations in processing different ingredients hamper the growth of the market. The largest issue facing businesses using food 3D printers is the scarcity of food ingredients. Large-scale commercialization of 3D food printers is not possible since they lack all the necessary ingredients. Major firms in the Food 3D Printing Industry, such as Nestle (Switzerland) and Barilla (Italy), are collaborating with makers of 3D food printers to create ingredients with various nutritional compositions for these printers.
The 3d food printing market is segmented into ingredient, end user, technology, and region. On the basis of ingredient, the market is classified into dough, fruits and vegetables, proteins, sauces, dairy products, carbohydrates, and others. On the basis of end user, the market is classified into government, commercial, and residential. On the basis of technologies, the market is classified into extrusion-based printing, binder jetting, selective laser sintering, and inkjet printing. Region-wise, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-pacific, and LAMEA.
Region-wise, it is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-pacific, and LAMEA.
Food 3D Printing Market
By Ingredient
The carbohydrates segment has the largets market share in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 52% during forecast period.
Get more information on this report : Request Sample Pages
By ingredient, the carbohydrates segment accounted for a major share in the 3D Food Printing market in, and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Carbohydrates or carbs in general are sugar molecules and one of the three main nutrients along with fats and proteins, which are found in foods and drinks. Carbohydrates are one of the major sources of energy to the human’s body cells, organs, and tissues. The global carbohydrate market is growing due to the several factors such as its high usage in the production of nutritious and convenience food products coupled with high usage as ingredients in the production of various energy food products. Moreover, it is easy to customize carbohydrate containing foods according to the consumers’ need, which has a positive impact on the market.
Moreover, it is easy to customize carbohydrate containing foods according to the consumers’ need, which has a positive impact on the market.
Food 3D Printing Market
By End User
The commercial segment has the largets market share in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 52% during forecast period.
Get more information on this report : Request Sample Pages
By end user, the commercial segment accounted for a major share of the market in and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Commercial segment can be classified into restaurants, bakeries, and confectionaries. The global commercial segment is growing due to the high adoption rate of 3D food printers by the confectionaries and the Food 3D Printing Industry to gain the diversity and accuracy in the manufacturing of food products within the least possible time and according to the consumers need and wants.
Food 3D Printing Market
By Technologies
The Extrusion-based printing segment has the largets market share in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 53.
 6% during forecast period.
6% during forecast period.Get more information on this report : Request Sample Pages
By technology, the extrusion-based printing segment accounted for a major Food 3D Printing Market Share, and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period. Extrusion-based printing fused deposition modelling (FDM) which is meant to provide the commercial manufacturers the ability to produce different shapes of food products by using different type of nutrition ingredients for the customization according to the requirements of the consumers. The global extrusion-based printing market is growing due to the several factor such as the manufacturers can make wide range of food products by using a large number of nutrients according to the requirements or the needs of the consumers. In addition, the limited cost of the digital design of an object and its ability to provide range of customizations are the key drivers of the market Food 3D Printing Market Growth. Moreover, it helps to reduce the food wastage, which is going to make positive impact on the market in the upcoming future.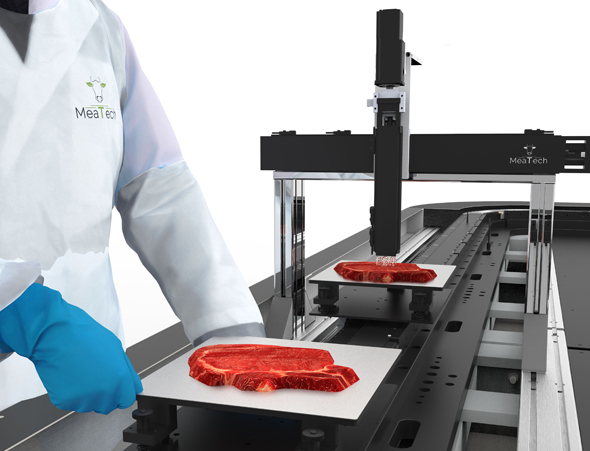
Food 3D Printing Market
By Region
2031
Europe
North America
Asia-pacific
Lamea
The Europe region has the largets market share in 2021 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 55.2% during forecast period.
Get more information on this report : Request Sample Pages
By region, Europe accounted for a major Food 3D Printing Market Share of the market in and is expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the Food 3D Printing Market Forecast period. In Europe 3D food printing market is increasing as it is the largest region in the term of geographical footprint and also a home to several manufacturing industry players which holds the strong technical expertise in additive manufacturing process. Also, the region is the worldwide leader in international tourism and the continuous Food 3D Printing Market Growthin the sector along with the adaptation of new technology by the leading manufacturers is the key driver to the Food 3D Printing Market Size in the region.
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the food 3d printing market analysis from 2021 to 2031 to identify the prevailing food 3d printing market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the food 3d printing market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global food 3d printing market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.

Food 3D Printing Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Size By 2031 | USD 15.1 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 52.8% |
| Forecast period | 2021 - 2031 |
| Report Pages | 280 |
| Ingredient |
|
| End User |
|
| Technologies |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Natural Machines, Systems and Materials Research Corporation, byFlow B.V., Print4taste GmbH, Barilla G. e R. Fratelli S.p.A, BeeHex, Modern Meadow, Dovetailed, 3Desserts Graphiques, 3D Systems, Inc., Redefine Meat Ltd., NOVAMEAT, Aniwaa Pte. Ltd, TNO, Shiyin Technology Co., Ltd. |
3D Food Printing Market by Ingredient ; By Vertical ; and
Product Overview 3D printing is a cutting-edge method of layer-by-layer structuring and development. The computer is programmed with the product design, and the software is also programmed with the same method.
| Source: ReportLinker ReportLinker
New York, June 16, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Reportlinker. com announces the release of the report "3D Food Printing Market by Ingredient ; By Vertical ; and Region – Global Analysis of Market Size, Share & Trends for 2019–2020 and Forecasts to 2030" - https://www.reportlinker.com/p06191892/?utm_source=GNW
com announces the release of the report "3D Food Printing Market by Ingredient ; By Vertical ; and Region – Global Analysis of Market Size, Share & Trends for 2019–2020 and Forecasts to 2030" - https://www.reportlinker.com/p06191892/?utm_source=GNW
The raw materials are fed into the machines in small granules, which are then released by the robot arm to form the 3D shape. Food goods are produced using a similar technology. 3D printers not only assist in the creation of 3D shapes, but also produce food with an appealing appearance and, most importantly, taste. With many companies around the world trying their hand at 3D printing food, technology has brought about enormous change in the food industry. The process of 3D printing technology is known as additive manufacturing, in which 3D deposition printers slowly deposit layers of materials, one on top of the other until a product is formed. 3D printers, which use lasers, powdery materials, and nozzles to manufacture and create food, are opening new doors for the customization of food products by delivering a powerful mix of the right nutrients.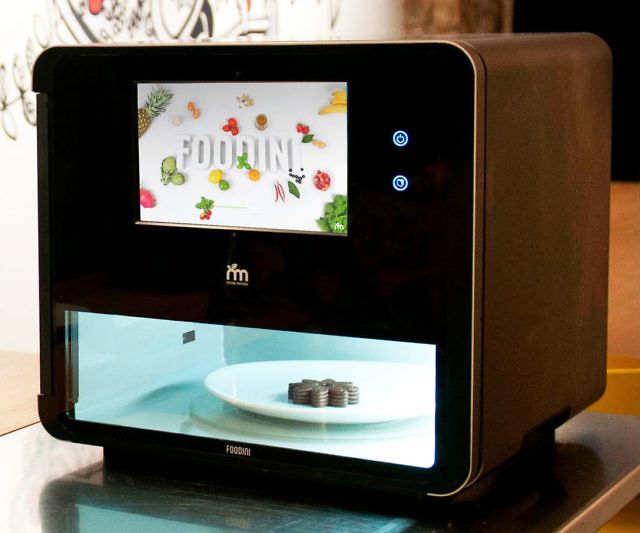
Market Highlights
Global 3D Food Printing Market is expected to project a notable CAGR of 16.54% in 2030.
Global 3D Food Printing Market to surpass USD 1617.99 million by 2030 from USD 350.24 million in 2020 at a CAGR of 16.54% in the coming years, i.e., 2021-30. This growth is anticipated due to increasing mergers and acquisitions across various sectors which will create a worldwide demand for 3D Food Printing Market. Increased consumer demand for mass customization, the ability of 3D printers to prepare food that is suitable and time-saving, customization of nutrients needed by distinct in their food products, gaining the benefit of substitute ingredients, and others are expected to drive the global 3D Food Printing Market. As the world becomes more self-centered, people are seeking more customization in their products, including their food. The demand for mass customization is growing, with different shapes, colors, flavors, nutrition, and textures becoming more common. Food items such as coffee, hamburgers, ice cream, cake, cookies, confectionery, and others are commonly customized.
Food items such as coffee, hamburgers, ice cream, cake, cookies, confectionery, and others are commonly customized.
Global 3D Food Printing Market: Segments
Carbohydrates segment to grow with the highest CAGR during 2020-30
Global 3D Food Printing Market is divided by ingredients into Dough, Fruits & Vegetables, Dairy Products, Carbohydrates, and Others. Over the forecast period, the carbohydrates segment is projected to expand at the fastest pace. The factors that can be attributed to the preferable use of 3D food printers for the development of personalized chocolates and other sweet food products containing carbohydrates as the main constituent, such as donuts, candies, and pancakes, are accelerating the demand for carbohydrates segment.
Commercial segment to grow with the highest CAGR during 2020-30
Global 3D Food Printing Market is segmented by vertical into Government, Commercial and Residential. The commercial segment held the largest market share in the year 2020.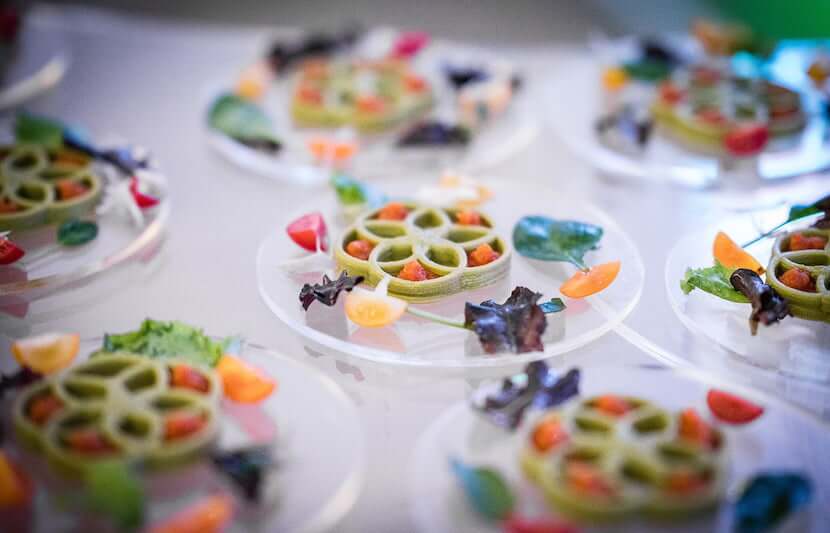 Since it is simple to offer training and maintenance services to consumers from the commercial vertical, the majority of key 3D food printer manufacturing companies target them as their most likely clients.
Since it is simple to offer training and maintenance services to consumers from the commercial vertical, the majority of key 3D food printer manufacturing companies target them as their most likely clients.
Market Dynamics
Drivers
Demand for customization and nutritious food innovation
The demand for customization is driving the global market for 3D printers, as 3D printing saves both time and effort. The nutrients themselves can be personalized, allowing consumers to benefit from food that is specifically tailored to their nutritional needs. 3D printing enables the development of easy-to-chew food with a formulation tailored to the patients’ nutritional needs. This is likely to aid in the feeding of elderly patients with unique nutrient-rich foods based on their needs. In addition, nutritious food innovation has widened the sector to a global scale. The 3D food printers are used to produce yeast structures that look like crackers and contain spores and seeds that sprout over time.
Ability to revolutionalize nutrition and growing demand in the healthcare sector
As opposed to conventional food processing systems, 3D printing has the potential to supply an ever-growing global population. 3D food printers have the ability to revolutionize nutrition by determining the exact amount of vitamins and carbohydrates needed without the need for tedious calculations. It also enables customers to print food with personalized nutritional content that is optimized using biometric and genomic data. Personalization of nutritionally based food has thus resulted in market growth, as it assists consumers in producing nutritionally based food that meets their needs. The demand has also developed as a result of applications in the healthcare industry. Patients with illnesses and allergies will benefit from 3D printers because they can use technology that purees vegetables like carrots and broccoli into nutritional, easy-to-chew soft-molds of their original form. WASP, an Italian 3D printing company, is experimenting with a printer that can create gluten-free versions of common foods.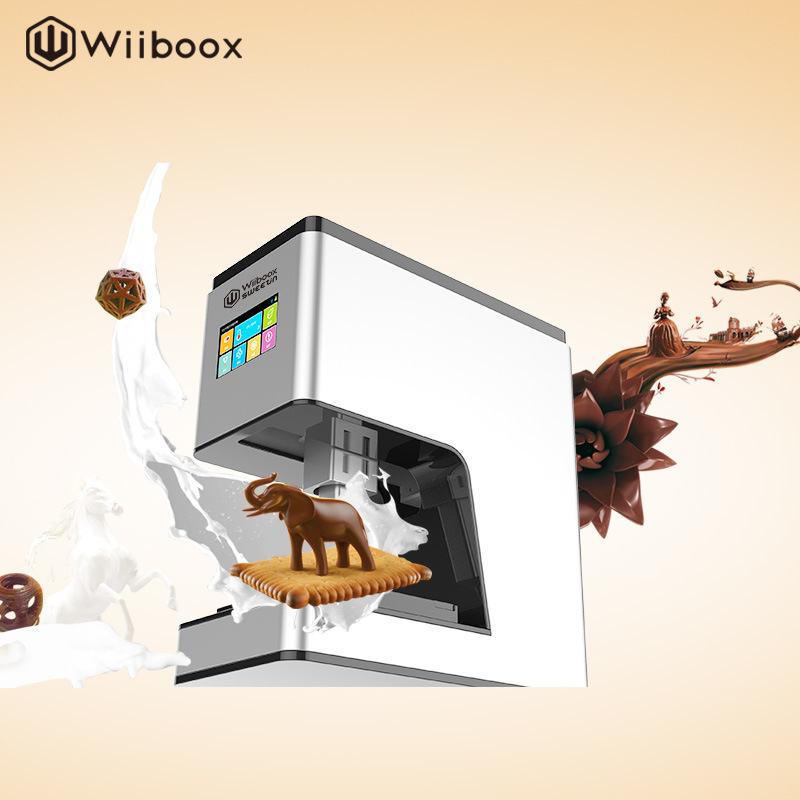
Restraint
Time-consuming method and high costs associated with market
Many of the materials used in 3D printing, on the other hand, are converted to paste. There are only a few foods that can be turned into paste. 3D Food Printing Market is also a time-consuming method that necessitates several cooling cycles before the food can be eaten. The requirement for 3D Food Printing Market is that it can solve the current trend of less efficient food customization techniques while not having a high manufacturing cost.
Global 3D Food Printing Market: Key Players
TNO
Company Overview, Business Strategy, Key Product Offerings, Financial Performance, Key Performance Indicators, Risk Analysis, Recent Development, Regional Presence, SWOT Analysis
3D Systems
Natural Machines
Systems and Materials Research Corporation
byFlow
Print2taste GmbH
Barilla
CandyFab
Beehex
Other Prominent Players
Global 3D Food Printing Market: Regions
Global 3D Food Printing Market is segmented based on regional analysis into five major regions. These include North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa. Global 3D Food Printing Market in Europe held the largest market share in the year 2020. Because of the rapid acceptance of the technology by customers and its incorporation into everyday food preparation procedures, Europe dominates the global 3D Food Printing Market industry. The United States is expected to grow rapidly as a result of rapid technological advancements and the introduction of advanced machines that can produce food using 3D printing technology.
These include North America, Latin America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa. Global 3D Food Printing Market in Europe held the largest market share in the year 2020. Because of the rapid acceptance of the technology by customers and its incorporation into everyday food preparation procedures, Europe dominates the global 3D Food Printing Market industry. The United States is expected to grow rapidly as a result of rapid technological advancements and the introduction of advanced machines that can produce food using 3D printing technology.
Global 3D Food Printing Market is further segmented by region into:
North America Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities, Y-o-Y Growth, CAGR – the United States and Canada
Latin America Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities, Y-o-Y Growth, CAGR – Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, and Rest of Latin America
Europe Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities, Y-o-Y Growth, CAGR – United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Belgium, Hungary, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Poland, NORDIC, Russia, Turkey, and Rest of Europe
Asia Pacific Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities, Y-o-Y Growth, CAGR – India, China, South Korea, Japan, Malaysia, Indonesia, New Zealand, Australia, and Rest of APAC
Middle East and Africa Market Size, Share, Trends, Opportunities, Y-o-Y Growth, CAGR – North Africa, Israel, GCC, South Africa, and Rest of MENA
3D Food Printing Market Segments:
By Ingredient
Dough
Fruits & Vegetables
Dairy Products
Carbohydrates
Others
By Vertical
Government
Commercial
Residential
3D Food Printing Market Dynamics
3D Food Printing Market Size
Supply & Demand
Current Trends/Issues/Challenges
Competition & Companies Involved in the Market
Value Chain of the Market
Market Drivers and Restraints
3D Food Printing Market Report Scope and Segmentation
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the 3D Food Printing Market?
What is the 3D Food Printing Market growth?
Which segment accounted for the largest 3D Food Printing Market share?
Who are the key players in the 3D Food Printing Market?
What are the factors driving the 3D Food Printing Market?
Read the full report: https://www.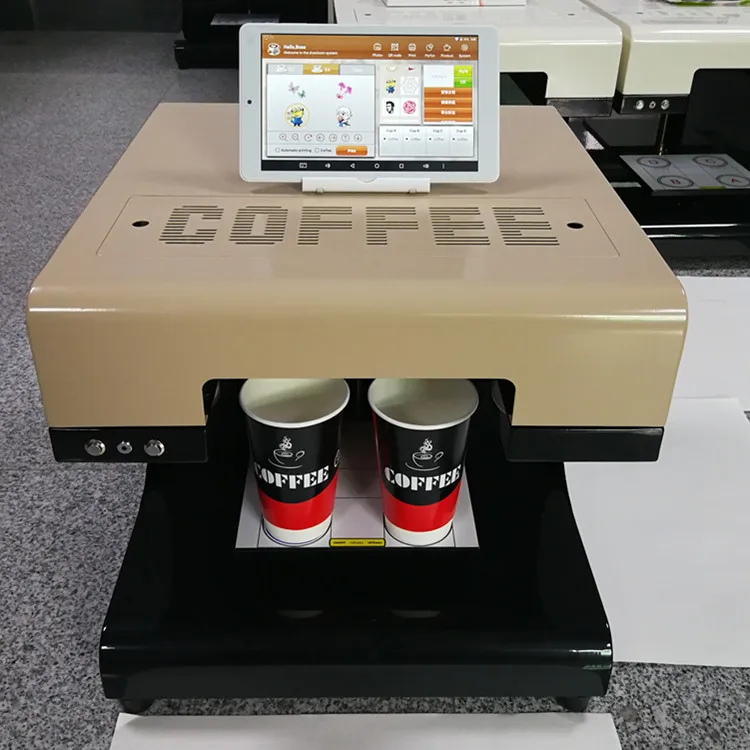 reportlinker.com/p06191892/?utm_source=GNW
reportlinker.com/p06191892/?utm_source=GNW
About Reportlinker
ReportLinker is an award-winning market research solution. Reportlinker finds and organizes the latest industry data so you get all the market research you need - instantly, in one place.
__________________________
Contact Data
Clare: [email protected] US: (339)-368-6001 Intl: +1 339-368-6001
Contact
90,000 characteristics, pros and cons of each model07.04.2021
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Field of use
- used raw materials
- 9000 9000 9000 9000
- Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
- 1. PancakeBot 2.0
- 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus Food 3D Printer with Cooling Chamber
- 5.
 byFlow Focus
byFlow Focus - 6. Chefjet Pro
- 7. Foodini
- 8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer Commercial ArtcakesOT7 .90BOT Printer F5
- 10. ZMorph VX
- What is a food 3D printer
- Selection guide
- Output
A food printer is a high-tech device that is used to create culinary masterpieces. The decorative design of food products has reached a new level thanks to the use of modern technologies: high-quality and large-format printing is carried out on cakes, waffles, pancakes and even coffee. Here are the top best 3D food printers in different price categories for people who are fond of cooking.
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients. The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer.
The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer.
Application
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops. The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products.
Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes;
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.
The confectionery pattern is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear. The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used.
Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
Food 3D printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database.
 The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges;
The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; -
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies. Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
-
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake.
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe;
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
 The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular brands
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. Quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products.
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making.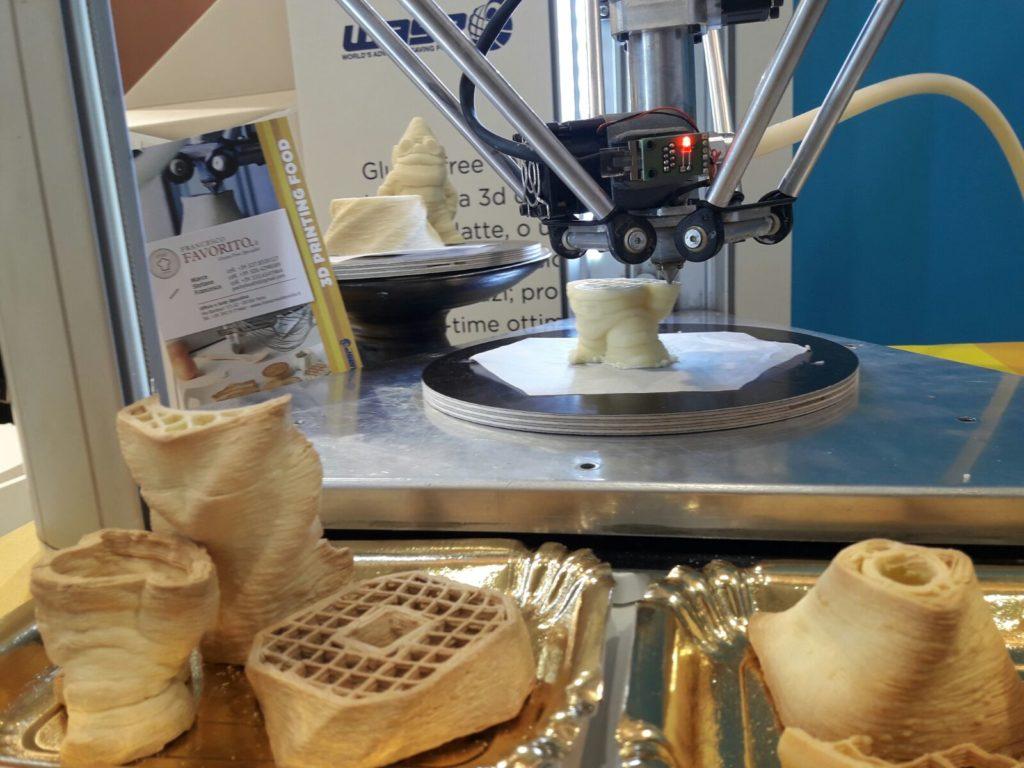 Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
Free shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Choc Edge |
Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the cart and follow the instructions Go
| Manufacturer | Wiiboox |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Choc Edge |
Top 10 Best Food Printers: List of the Most Current Models
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market. The top is based on ratings and customer reviews.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews.
1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
A wide range of proposed projects;
-
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment.
Pros:
-
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
High build quality;
-
Convenient control by touch panel.

Cons:
-
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, thanks to which it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate.
Pros of :
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Uninterrupted work;
-
Durability;
-
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
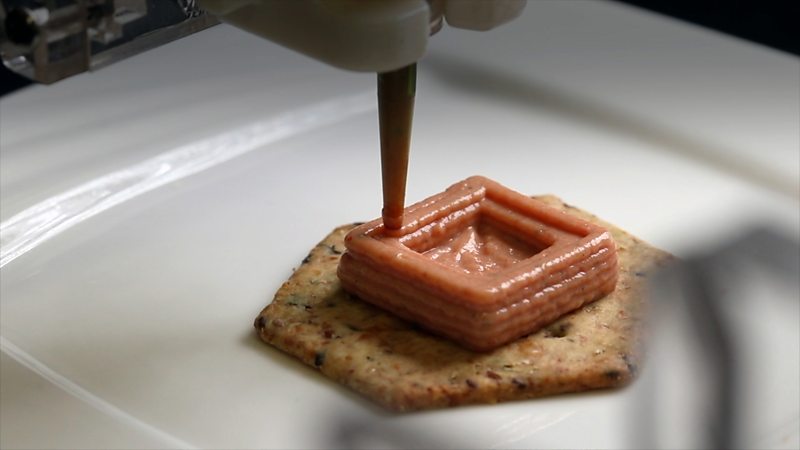 Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs.
Pros of :
-
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
-
High printing precision;
-
Long service life;
-
Ease of use: You can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
-
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
5. byFlow Focus
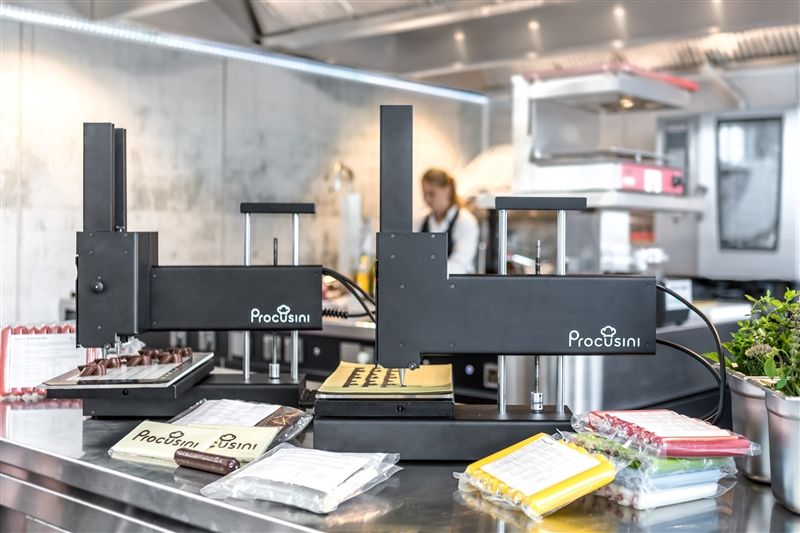
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients.
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients.
Pros:
-
The ability to create unique flavors;
-
Neat and bright printing;
-
Aesthetic appearance of the device.

Cons:
-
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
-
Practicality;
-
High build quality;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.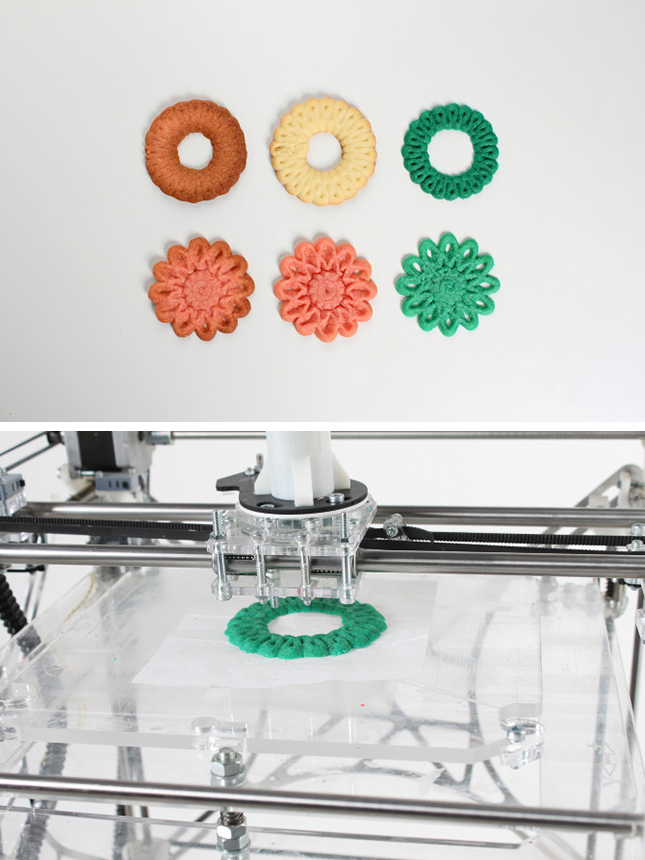
Pros:
Cons:
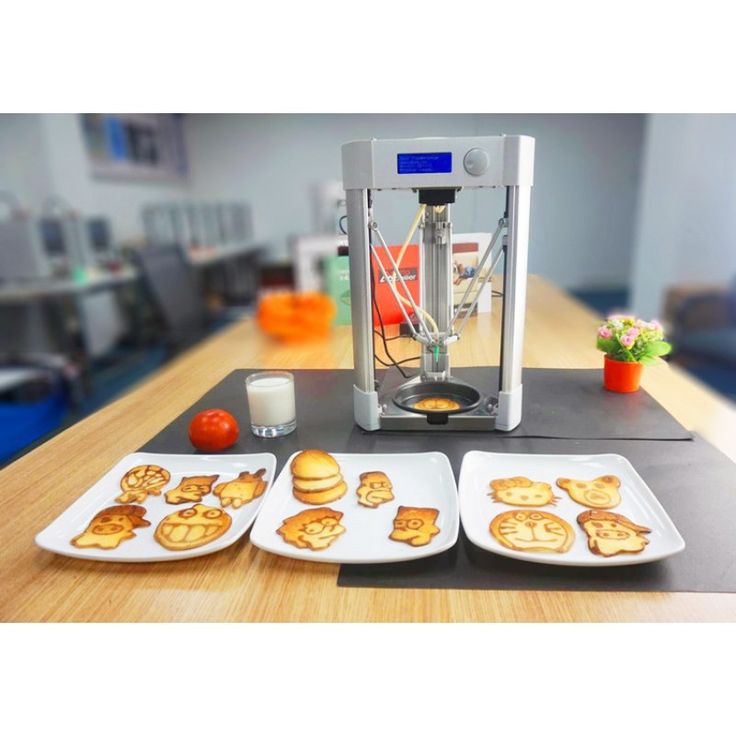
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
High build quality;
-
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling.
Pros:
Cons:
-
High price.

Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing:
-
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
-
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
-
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
-
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.

Output
In the catalog of our online store, you can choose the best food printers from famous brands to create culinary masterpieces. Explore our range, learn about the characteristics of each printer and make great purchases.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
3D food printing
3D food printing
Who needs it and why?
Today, progress is progressing by leaps and bounds: robots are being invented, medicines for previously incurable diseases, people's lives are getting easier every year more and more. One of the young inventions with broad development prospects is 3D printing. Machine parts are printed that are difficult to make by hand, prostheses and even food
In March, the world was cheered by the news of a breakthrough in the field of cooking: in Sweden (in hospitals and nursing homes) they began to cook food using 3D printing for those who can no longer chew food on their own. For such people who have difficulty chewing and swallowing food, there used to be only one way out - to switch to a "children's" diet, mashed potatoes, cereals, and so on. But if, for example, you want normal food, you still need to grind it. And in the end, no matter how tasty it is, aesthetically it will still be disgusting.
For such people who have difficulty chewing and swallowing food, there used to be only one way out - to switch to a "children's" diet, mashed potatoes, cereals, and so on. But if, for example, you want normal food, you still need to grind it. And in the end, no matter how tasty it is, aesthetically it will still be disgusting.
“When you have trouble swallowing, you have to settle for food that isn't particularly appetizing. The idea is to make special dishes more attractive by recreating the original shape of the product. That is, the food will look, for example, like a chicken leg, but the consistency will resemble a cream pudding, ”explains Richard Asplund, head of the municipal catering department of the Halmstad district.
The program is currently being implemented on an experimental basis. The project involves researchers from Lund University and the University of Kristianstad, the equipment is offered by Cellink, and 3D printing services are provided by the service bureau Addema.
Residents of nursing homes in Halmstad and Helsingborg will serve as the jury for the pilot project.
So, it's worth understanding how 3D printing appeared, how printing devices work and what prospects await this technology in the future.
How did it all start?
History
1948
1948
The history of 3D printers dates back to 1948, when the American engineer Charles Hull developed a technology for layer-by-layer growth of physical three-dimensional objects. She got the name Stereolithography (stereolithography).
1985
1985
Mikhailo Feigen proposed to form three-dimensional models in layers from film, polyester, plastic, paper, fastening the layers together using a heated roller.
1986
1986
Carl Descartes invented layer-by-layer sintering of powder material (powder polymers, metals, foundry wax, nylon) with a laser beam.
1987
1987
The world saw the first 3D printer in history.
True, at that time the apparatus was called a "installation for stereolithography".
In 1987, the Israeli company Cubital developed a layered sealing technology. However, it requires the use of expensive, toxic, and fairly rare polymers.
1988
1988
Scott Crump described the FDM method.
Printers using this technology print objects with a molten thread of a substance (plastic, metal, etc.), which was later used to print food.
1995
1995
Prior to 1995, 3D printing was only used in industry, until MIT students Jim Bredt and Tim Anderson introduced the technology of layer-by-layer synthesis into the body of a conventional desktop printer.
Early
2000s
Early
2000s
3D Systems also launched its first "home" 3D printer. After that, these devices began to actively penetrate into everyday life.
After that, these devices began to actively penetrate into everyday life.
How does it work?
Technology Analysis
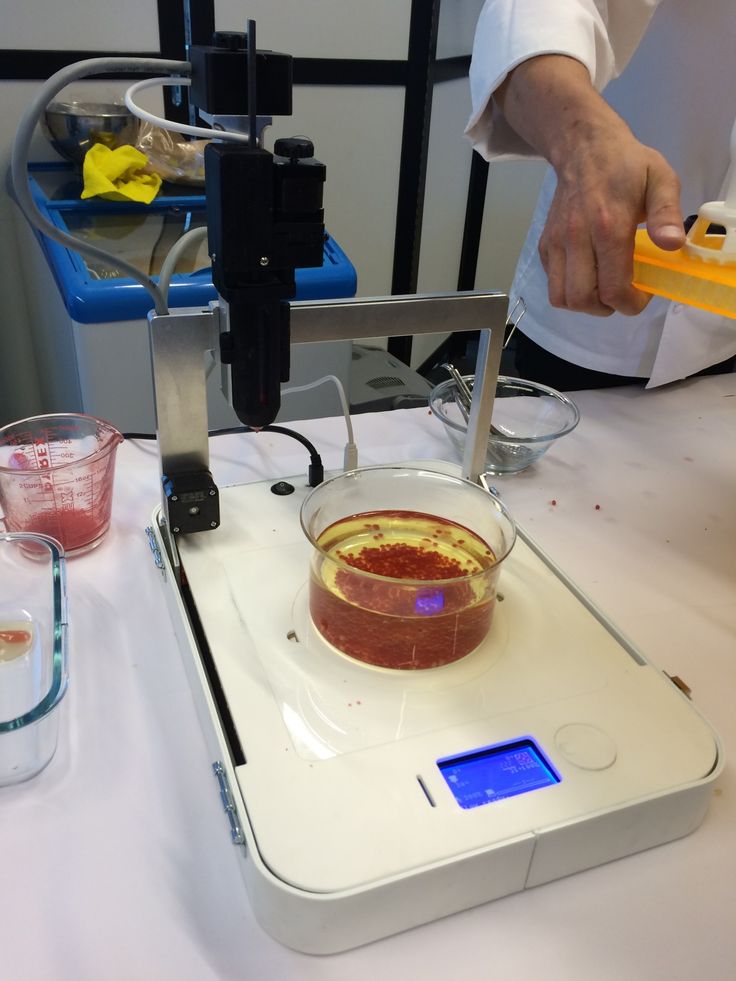
The first food from a 3D printer was obtained several years ago using the Fab@Home printer. The heart of the machine is a syringe that works on the same principle as inkjet printers. Layer by layer, he lays down a viscous liquid, forming an object of a given shape.
The university made the drawings of this printer publicly available, to the delight of many enthusiasts. People began their own experiments with epoxies and silicones. At the same time, gourmets appeared who began to put cheeses, glazes, etc. into the printer. It can use anything that is forced through the head of the syringe.
Instead of repeating already existing organic objects, it is much more important to learn how to create new products with individualized nutritional value.
Let's say a person needs more calcium or omega-3 fatty acids in their diet, why not print out the appropriate foods for them. Van Bomel's team is addressing just such a problem, it is they who are developing food printing technology for people with impaired chewing and swallowing functions. Printed products can use cheaper protein sources. It is more convenient, and besides, the cost of such products will be less. But a significant obstacle is the slow speed of 3D printing from edible components, after each layer is applied, one or another time is required for it to solidify.
Van Bomel's team is addressing just such a problem, it is they who are developing food printing technology for people with impaired chewing and swallowing functions. Printed products can use cheaper protein sources. It is more convenient, and besides, the cost of such products will be less. But a significant obstacle is the slow speed of 3D printing from edible components, after each layer is applied, one or another time is required for it to solidify.
What are printers?
Great variety of food printers
- Pancakebot. Structurally, it is similar to any food 3D printer, but it only prints pancakes of any given shape and immediately fries them;
- Choc Creator 2.0 Plus, Chocola3D, etc. - specialized printers for printing chocolate;
The above examples were taken from the sales site, that is, these printers can already be bought, they have entered the general sales market. But there are also more complex devices that exist almost in a single copy.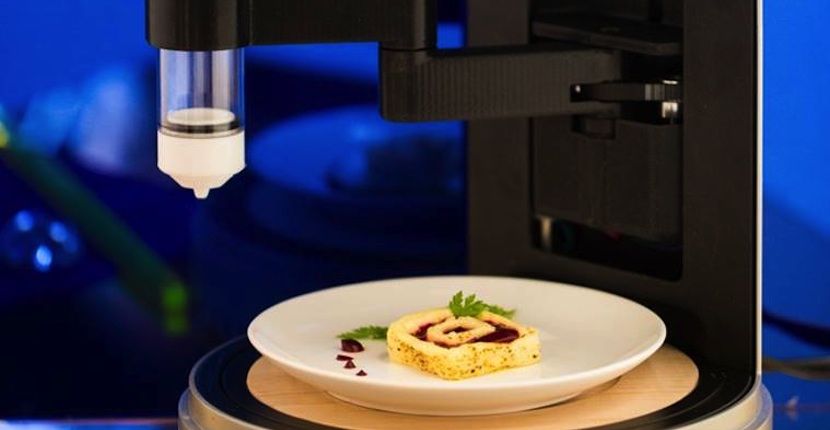
- Foodini by Natural Machines is the answer to the eternal question of healthy eating. Foodini users can cook with fresh ingredients, create a variety of pastas, and place them in reusable capsules, which are then printed in any 3D shape;
- Food printer for NASA from SMRC. Using raw ingredients packaged in capsules, SMRC's food printer can combine different individual ingredients to print a wider variety of foods;
Future Prospects
What's in store for this relatively new but rapidly evolving technology? Will it develop in highly specialized areas or will it go to a wide market, or will it succeed everywhere?
3D food printing is not justified these days. But in space it can be a real salvation. Michel Terfansky of the University of Southern California explored this concept in his thesis project. He learned about the occasional annoyance of astronauts on the International Space Station with poor diets. With the help of 3D printers, friends and family could send recipes to Earth messengers.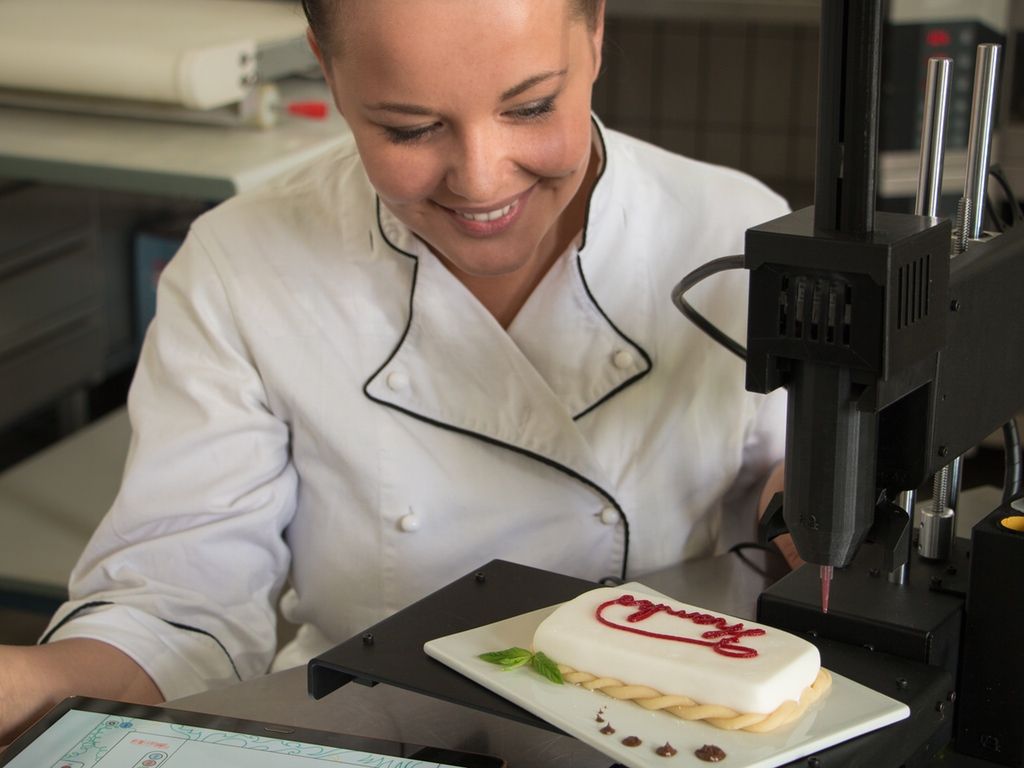 3D printers will help save space and rid the ship of warehouses of meat and vegetables. Terfansky believes that this technology will make people happier.
3D printers will help save space and rid the ship of warehouses of meat and vegetables. Terfansky believes that this technology will make people happier.
Also, 3D printed food can be used to create foods with a specific nutritional value and texture for the elderly that are easy to chew and swallow.
Other applications include home cooking as well as personalized candies and sweets.
One way or another, 3D printing will one day, if not completely replace the product market, then at least displace a significant part of it. It will become more convenient, less expensive, more environmentally friendly. It will give more opportunities and more problems associated, for example, with device maintenance. Whether this is good or bad is your food for thought.
Text: Koryakina Anastasia, Krylova Lyubov, 2nd year student of the Faculty of Journalism, Lomonosov Moscow State University
Photo: site https://make-3d.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/CELLINK -BIO-X-Main-1-768x538.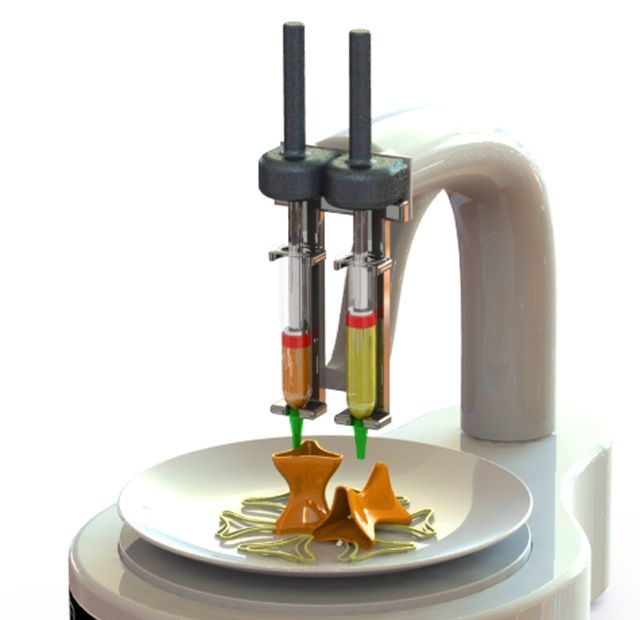

 S., Canada, Mexico)
S., Canada, Mexico)