3D food printer youtube
Top 10 3D Printing Youtube Channels You Should Know About
There are many Youtubers out there that have great content dedicated to 3D printing. Here we have compiled some of our favorites for you to check out.
- Creator name: Devin Montes
- Country: United States
Make Anything is one of the largest YouTube channels specializing in 3D printing. In each video, Devin shares his experience working on 3D printing projects that range from useful practical projects to fun and unique creations.
- Creator name: Uncle Jessy
- Country: United States
Uncle Jessy specializes in creating 3D printed props and replicas for cosplay. The videos he makes are very informative and detailed showing the process he takes from 3D printing to post processing. He also occasionally does reviews of 3D printers and over all just makes high quality fun videos.
- Creator name: Naomi Wu
- Country: China
Naomi is first and foremost a maker at heart. She is based in Shenzhen, China and showcases her unique creations creations many of which utilizes 3D printing technology. Being in the heart of tech manufacturing in Shenzhen, she also visits many very interesting tech related companies and faires. She is one of very few females in the industry and is a great perspective in the field.
- Creator name: Joel Telling
- Country: United States
Over the past few years, Joel has skyrocketed to popularity within the 3D printing community. Due to his upbeat videos and great social media presence he has won the hearts of many. He makes a wide range of videos from product reviews to factory tours. He makes great videos that appeal to both 3D printing enthusiasts and beginners a like.
- Country: Germany
Tom is among the most famous 3D printing YouTube makers. The videos on his channel covers many subjects from tutorials to product reviews. They are well produced and educational for people from all levels of 3D printing knowledge.
- Creator name: Angus Deveson
- Country: Australia
Maker’s Muse is one of the early channels that feature 3D printing. The channel started in 2013 and has since garnered nearly half a million subscribers. Angus offers videos on 3D design and printing tutorials, reviews and projects. He is a great resource for testing the performance of printers as well because has created many models that showcase the capabilities of 3D printers.
- Country: Sweden
- Creator name: Simon Sörensen
Although the channel name may seem like the focus is on RC content, this really is not the case. Simon does have a love for all things RC but also for 3D printing. Most of his videos focus on 3D printed projects and covers many different categories from the obvious 3D printed RC car to 3D printed food.
- Creator name: Garrett
- Country: United States
Garret is a full time programmer, who is passionate about making things.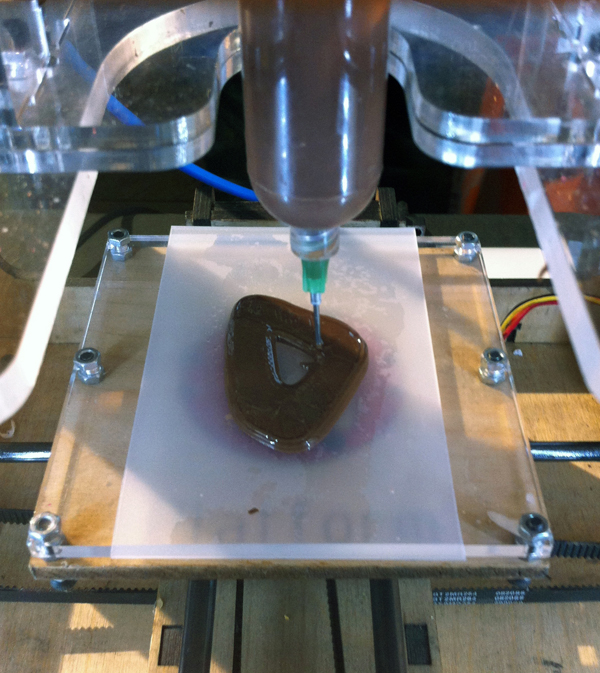 He uses 3D printing to create much of his projects. The 3D printed parts are then given a fresh coat of paint by his wife Chelsey. This duo creates some pretty awesome projects and the best part is that he shares the files for his work!
He uses 3D printing to create much of his projects. The 3D printed parts are then given a fresh coat of paint by his wife Chelsey. This duo creates some pretty awesome projects and the best part is that he shares the files for his work!
- Creator name: Chuck Hellebuyck
- Country: United States
Chuck is a well established maker in the 3D printing community and is focused on helping new users get started. He shows tips and tricks in his videos to help newcomers get the most success with their 3D printer.
- Creator name: Travis
- Country: United States
Travis brings logos to life! He shows you the process of taking a 2D logo design turning it into a 3D print. You’ll learn how he uses 3ds Max, Photoshop, Cura, Zbrush, and simplify 3d programs to make his creations. He also collaborates with many others in the 3D printing community so you’ll probably see some familiar faces.
- Country: Sweden
Daniel Norée is an award-winning Swedish 3D designer and 3D printing evangelist. He also is the author of The OpenR/C Project and The OpenRailway Project, and the creator of the famous Benchy model. Daniel’s videos showcase builds of RC cars, boats, drones and much more.
He also is the author of The OpenR/C Project and The OpenRailway Project, and the creator of the famous Benchy model. Daniel’s videos showcase builds of RC cars, boats, drones and much more.
We cannot include all the creators out there because there are just so many quality people in the 3D printing community but here are some of other channels you can check out.
| 3D Print Guy |
| Tech3C |
| 3D Maker Noob |
| 3D Printing Professor |
| Mold3D TV |
| The Hot End |
| PRINT THAT THING |
| Hoffman Engineering |
| 3D Print – Tech Design |
| Nerdly |
| 3DprintedLife |
| Joe Mike Terranella |
| FugaTech 3D Printing |
| Jimmy Shaw's Tidbits |
| Make It And Fake It |
| The 3D Print General |
| Desktop Makes |
| Print 3D Channel |
| Novice Expert |
| Think Making |
| 3d Print Creator |
| Practical Printing |
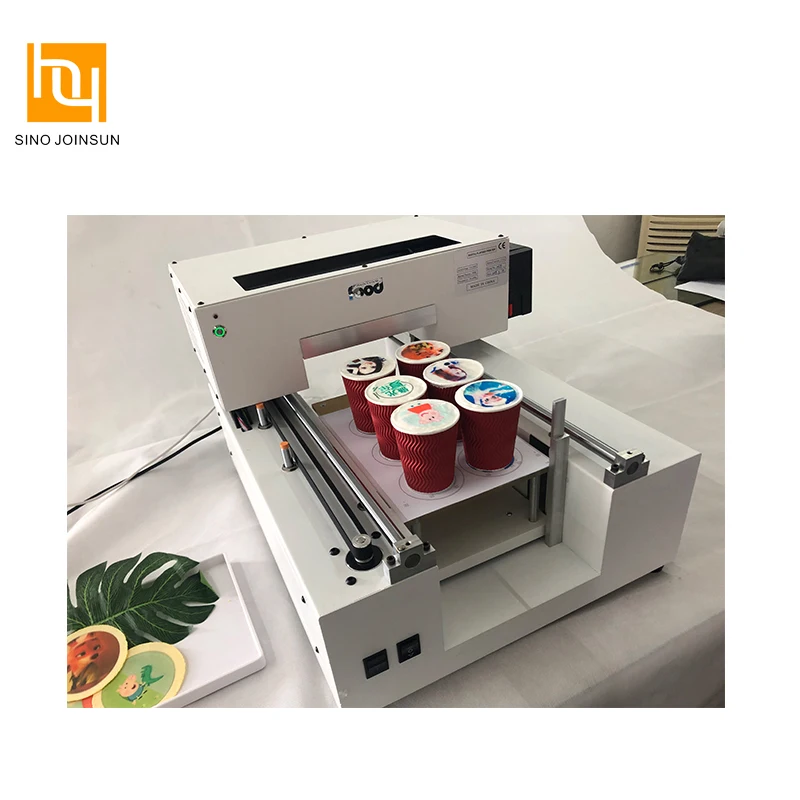
Top food 3D printers available this year
What is food 3D printing?
Although it may sound like something from a sci-fi movie, food 3D printers do actually exist. Edible 3D printing is becoming more and more popular not only for professionals but also for personal use. That said, how does food 3D printing work? To what extent is it similar to standard 3D printing?
Edible 3D printing is becoming more and more popular not only for professionals but also for personal use. That said, how does food 3D printing work? To what extent is it similar to standard 3D printing?
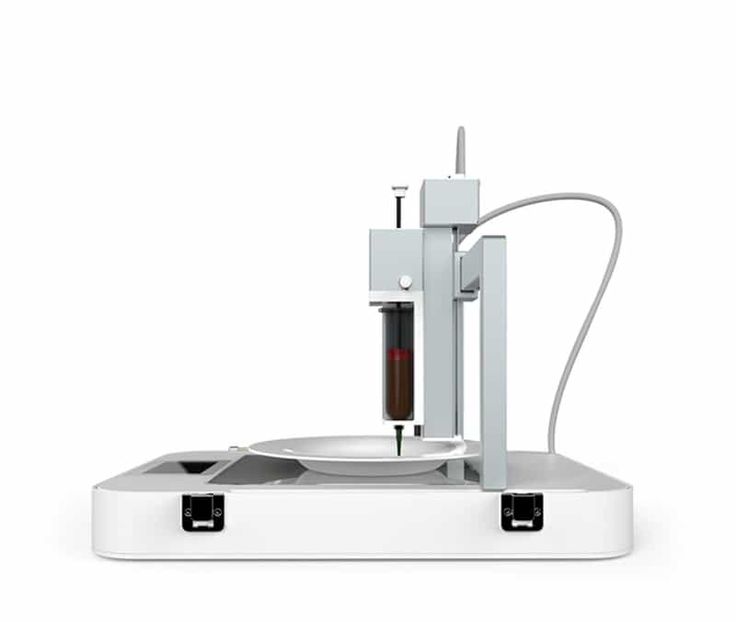
Most food 3D printers use extrusion 3D printing technology, much like regular desktop FFF (FDM) 3D printers. Instead of using plastic material, though, food 3D printers use paste-type ingredients. The most common ingredients are chocolate, pancake batter, and cream, although there are many other possibilities (even pizza!). They are 3D printed layer after layer, generally through a syringe-like extruder.
To get a better overview of this niche, we have put together a comprehensive list of food 3D printers on the market. This selection is based on available food 3D printers under $6,000. We also mention a few other food customization solutions, including coffee 3D printing, food ornament 3D printing, and 3D printing food molds.
Bon appétit!
Best food 3D printers available on the market
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micromake | Food 3D printer | 100 × 100 × 15 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 0.59 in | – | $ 9991 015 €886 £148,907 ¥ | Contact |
| Choc Edge | Choc Creator V2.0 Plus | 180 × 180 × 40 mm7.09 × 7.09 × 1.57 in | – | $ 2,6832 727 €2,380 £399,929 ¥ | Quote |
| ZMorph | VX | 250 × 235 × 165 mm9.84 × 9.25 × 6.5 in | – | $ 2,7992 845 €2,483 £417,208 ¥ | Quote |
| byFlow | Focus | 208 × 228 × 150 mm8.19 × 8.98 × 5.91 in | – | $ 3,6303 300 €3,220 £541,073 ¥ | Quote |
| Natural Machines | Foodini | 250 × 165 × 120 mm9. 84 × 6.5 × 4.72 in 84 × 6.5 × 4.72 in | – | $ 4,0004 066 €3,548 £596,224 ¥ | Quote |
| Mmuse | Chocolate 3D printer | 160 × 120 × 150 mm6.3 × 4.72 × 5.91 in | – | $ 5,4995 590 €4,878 £819,659 ¥ | Quote |
Expand to see more specs
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micromake | Food 3D printer | 100 × 100 × 15 mm3.94 × 3.94 × 0.59 in | – | $ 9991 015 €886 £148,907 ¥ | Contact manufacturer |
| Choc Edge | Choc Creator V2.0 Plus | 180 × 180 × 40 mm7.09 × 7.09 × 1.57 in | – | $ 2,6832 727 €2,380 £399,929 ¥ | Get a quote |
| ZMorph | VX | 250 × 235 × 165 mm9. 84 × 9.25 × 6.5 in 84 × 9.25 × 6.5 in | – | $ 2,7992 845 €2,483 £417,208 ¥ | Get a quote |
| byFlow | Focus | 208 × 228 × 150 mm8.19 × 8.98 × 5.91 in | – | $ 3,6303 300 €3,220 £541,073 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Natural Machines | Foodini | 250 × 165 × 120 mm9.84 × 6.5 × 4.72 in | – | $ 4,0004 066 €3,548 £596,224 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Mmuse | Chocolate 3D printer | 160 × 120 × 150 mm6.3 × 4.72 × 5.91 in | – | $ 5,4995 590 €4,878 £819,659 ¥ | Get a quote |
Pros and cons of food 3D printing
Benefits of 3D printing food
Time-saving
Edible 3D printing can be less time-consuming than traditional cooking. Indeed, users can launch a food 3D print and move on to other activities. Once the food 3D print is launched, there is no more need for manual operation.
Customization
Food 3D printing enables users to customize their food according to special events or simply to their mood. It can vary from writing a name on a birthday cake to 3D printing a heart-shaped pancake, for instance.
It can vary from writing a name on a birthday cake to 3D printing a heart-shaped pancake, for instance.
Creativity
Edible 3D printing enables cooking aficionados to unleash even more creativity in the kitchen. Users can imagine and actually create intricate designs. Amazing 3D-printed food artwork already exists!
3D printed food art by Marijn Roovers. Source: Marijn RooversLimits to food 3D printers
Type of food
Not just any sort of food can be 3D printed. The food must be in the form of a paste, such as cream or mashed potatoes.
Partial cookingThe 3D printing process doesn’t encompass every step of a meal’s preparation. For instance, food 3D printers cannot bake a cake or sprinkle oregano over a pizza.
Price
Food 3D printers are a bit expensive, generally in a price range between $1,000 and $5,000 (although there are exceptions).
Risk of failure
Just like with any other type of 3D printing, food 3D prints can be unsuccessful – too bad if it’s a birthday cake!
Food 3D printers: overview
The byFlow Focus is a compact food 3D printer made by byFlow, a Dutch 3D printing company specialized in edible 3D printing. This food 3D printer targets mostly professionals in the bakery industry.
The Focus works with refillable cartridges containing any kind of paste-type food to create customized meals. Furthermore, users have the possibility to access downloadable recipes.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Choc Edge Choc Creator is a chocolate 3D printer targeting mostly professionals in chocolate and confectionery industries.
In addition, Choc Edge develops three apps, CHOC DRAW, MIX & MATCH and CHOC TEXT, to help users to draw and write on their chocolate 3D prints.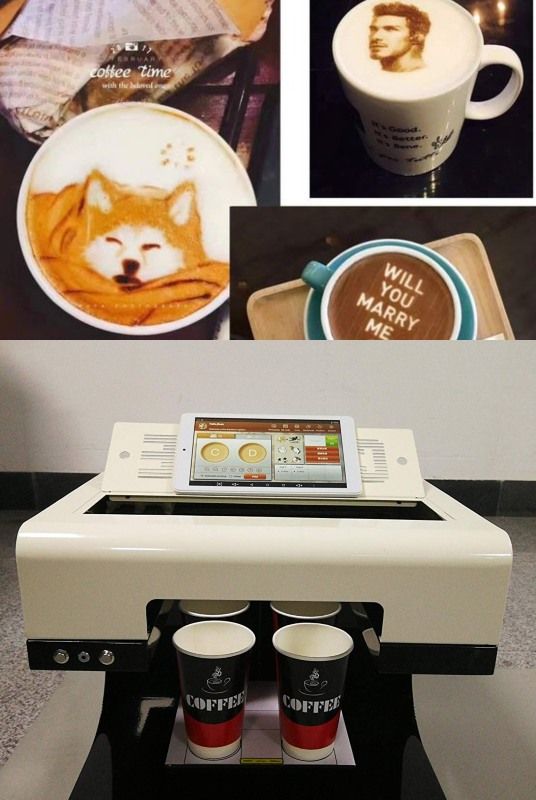 A slicing software, ChocPrint, is also available.
A slicing software, ChocPrint, is also available.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Micromake Food 3D printer can 3D print all kinds of paste-type ingredients, such as tomato sauce, chocolate sauce, and salad sauce. Also, the removable heated build plate is able to bake ingredients such as pancake batter.
Contact manufacturer Add to comparison
The Mmuse Chocolate 3D printer is a closed-framed chocolate 3D printer made by Muse, a manufacturer from China. This 3D printer uses chocolate beans as consumables: they melt in the extruder, just as with regular FFF/FDM 3D printing.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Natural Machines Foodini is a 3D printer able to 3D print all kinds of paste-type food. Users can fill the Foodini’s capsules with any type of paste food they wish.
Furthermore, if users choose a specific Foodini recipe, the 3D printer gives instructions on which ingredients to insert into the capsules.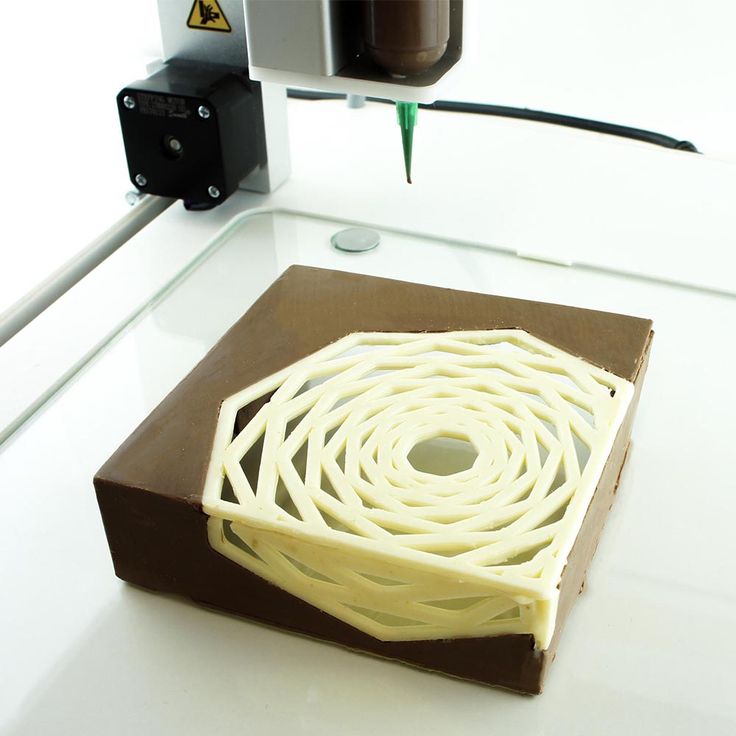
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Thanks to its thick-paste extruder, the ZMorph VX can 3D print ceramics as well as food!
This multifunctional 3D printer is indeed able 3D print with chocolate, cookie dough, cream cheese, frosting and more.
In addition to paste extrusion, the VX is features CNC milling and laser engraving capabilities.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Special mention: Cakewalk
- Materials: chocolate, meringue, royal icing, ketchup, guacamole, cream cheese, butter, mashed vegetables, Swiss butter cream
- Price:
- During KS campaign: €49 to €89
- After KS = €119
Cakewalk 3D is a precise and practical extruder that converts your desktop 3D printer into a food printer. The screw-in extruder is designed to be easily installed on any type of Cartesian 3D printer. All parts are food-safe and easily washable in your dishwasher.
To adapt Cakewalk 3D to your printer, you just need to 3D print 3 or 4 pieces of support in plastic. Disassembling your plastic extruder, screwing in the support parts, and connecting the motor to your card takes less than 30 min. The extruder then works with your usual slicer.
Cakewalk3D Kickstarter campaign
Edible 3D printing: who is it for?
Restaurants and bakeries
Edible 3D printing is indeed very useful for professionals in the food industry. 3D printed food can be attractive to new customers seeking different food experiences. A restaurant serving 3D-printed food, the Food Ink. pop-up store already exists.
Industrial food production
In the industrial food production sector, edible 3D printing allows manufacturers to vary their product ranges with new creations. Furthermore, food 3D printers can achieve a high level of precision. Barilla, an Italian food company, 3D prints some of its pasta products.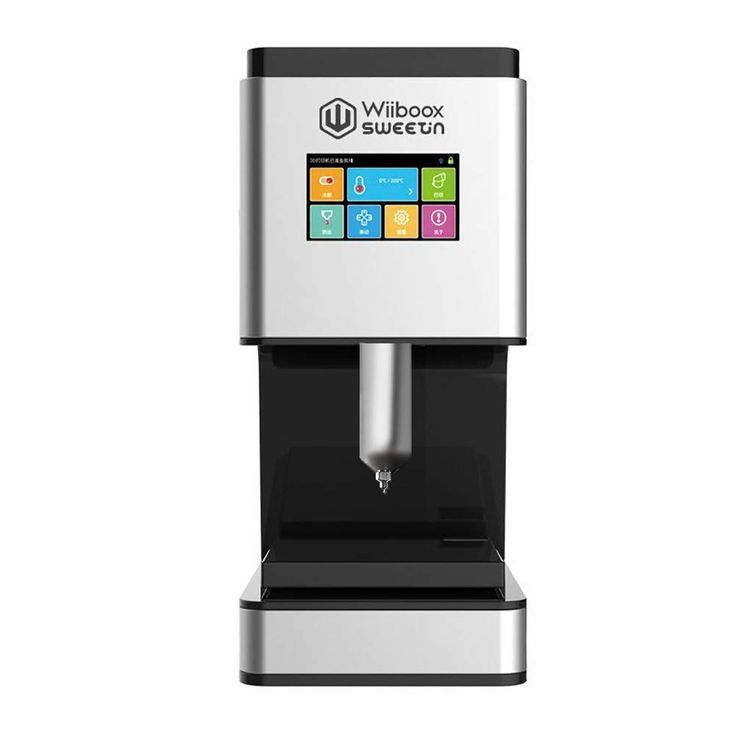
Food 3D printing at home
Food 3D printers are also adapted for personal use. They allow for more creativity in the kitchen with food customization.
What food can be 3D printed?
Ingredients
Virtually any type of fresh food can be 3D printed as long as it’s a paste, or “purée”. For instance, ingredients could be:
- Chocolate, candy and sugars
- Pancake batter or cookie dough
- Dairy products
- Pasta, wheats and grains
- Fruits and vegetables
Even pizza can be partly 3D printed! However, users will have to sprinkle their favorite toppings manually.
3D printed pizza by Beehex. Source: BeehexFood 3D models
To 3D print food, we can let our imagination take over. Users indeed have the opportunity to create their own food 3D models with special CAD software. However, it is also possible to directly download any 3D model on dedicated STL file websites.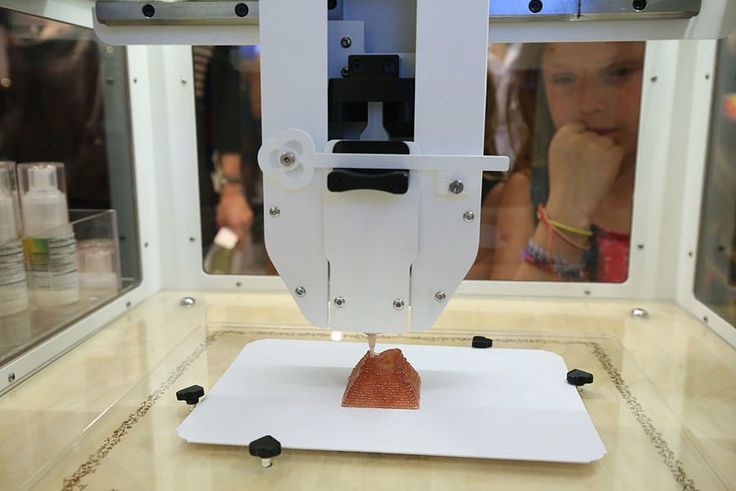
How much does a food 3D printer cost?
Food 3D printer price
There are various price points for food 3D printers. Prices can depend on the food 3D printer’s build volume and/or on the variety of 3D printable ingredients it is compatible with.
In general, the minimum price for a food 3D printer is around $1,000 (although the PancakeBot is available for under $400). However, prices may decrease in the future, just as they have for regular extrusion (FFF/FDM) 3D printers.
Other promising food 3D printing applications
Here are a few industries where food 3D printing is already beneficial.
Sustainable food
Food 3D printing could be a part of the answer to the world hunger crisis. Indeed, some food 3D printers use hydrocolloids as a consumable.
This chemical, gel-like substance can mimic food. 3D printed meals with hydrocolloids could also include sustainable ingredients, such as algae.
Medical
As explained above, certain food 3D printers use hydrocolloids to create different shapes and textures for meals. Also, like the EU’s PERFORMANCE program is proving, it can be very useful to make softer meals for people with chewing or digestion problems, especially elders.
In addition, medicine can be presented in the shape of yummy food, instead of pills or powder.
Army
The US Army is carrying out scientific research to provide personalized food for their soldiers.
According to Lauren Oleksyk, a food technologist leading the team at the Army’s Natick research center, a sensor installed in soldiers’ bodies could detect their specific dietary needs. This sensor would be interfaced with a food 3D printer, to produce customized meals.
This sensor would be interfaced with a food 3D printer, to produce customized meals.
Aerospace: NASA food 3D printer
Beehex, an American startup, has received a grant from NASA to develop a food 3D printer.
Indeed, the aerospace agency aims to allow astronauts to produce their own food during long-term space missions to go to Mars!
3D printed food ecosystem
Food ornament 3D printers
Coffee 3D printers: 3D printing on coffee
There seems to be no connection between the portrait of the Mona Lisa and coffee. However, thanks to coffee 3D printers, it is possible to see the beautiful smiling lady in a cup of coffee. Indeed, a combination between 3D printing and inkjet printing technologies allows these machines to draw images on top of any foam-covered beverage.
As such, the Ripple Maker, a coffee 3D printer made by Ripples, can help users print “their own selfies, favorite quotes, or special messages and images on their drinks”. Another existing coffee printer is the Lixian 3D CafeMaker.
Another existing coffee printer is the Lixian 3D CafeMaker.
Cake ornament 3D printers
Bakery industry professionals also use 3D printers to adorn cakes or pastries. Thanks to edible sheets of paper and ink, any kind of image (including photos) can be 3D printed to decorate cakes.
Food extruders
If users already have an FFF 3D printer at home, another solution exists to 3D print food: food extruders. These tools generally feature universal compatibilities with regular extrusion 3D printers. Some of them, such as the Structur3D Discov3ry, allow 3D print with non-only edible food and clay, silicone, etc. An open-source extruder, the BotBQ Extruder, can 3D print raw meat – a good fit for your future barbecue!
3D printed food molds
3D printers can also 3D print very useful tools for food production: this is the case of 3D printed food molds. Users can create their own molds and print them in 3D to customize cakes, for example.
Users can create their own molds and print them in 3D to customize cakes, for example.
Conclusion
Food 3D printers are suitable for professional, industrial, and personal use-cases. Only paste-type ingredients are printable, but a wide range of food – from pizzas to cakes – can be created. As 3D-printed food can be customized according to users’ needs, it can be helpful in many fields, such as medicine.
3D printed food may also represent a hope for the world hunger crisis in the future. What food 3D printers are still missing is the ability to actually cook or bake. That is why cooking robots could be more and more popular in the future.
90,000 characteristics, pros and cons of each model07.04.2021
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Field of use
- used raw materials
- 9000 9000 9000 9000
- Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
- 1.
 PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 - 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus Food 3D Printer with Cooling Chamber
- 5. byFlow Focus
- 6. Chefjet Pro
- 7. Foodini
- 8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer Commercial ArtcakesOT7 .90BOT Printer F5
- 1.
- 10. ZMorph VX
- What is a food 3D printer
- Selection guide
- Output
A food printer is a high-tech device that is used to create culinary masterpieces. The decorative design of food products has reached a new level thanks to the use of modern technologies: high-quality and large-format printing is carried out on cakes, waffles, pancakes and even coffee. Here are the top best 3D food printers in different price categories for people who are fond of cooking.
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients.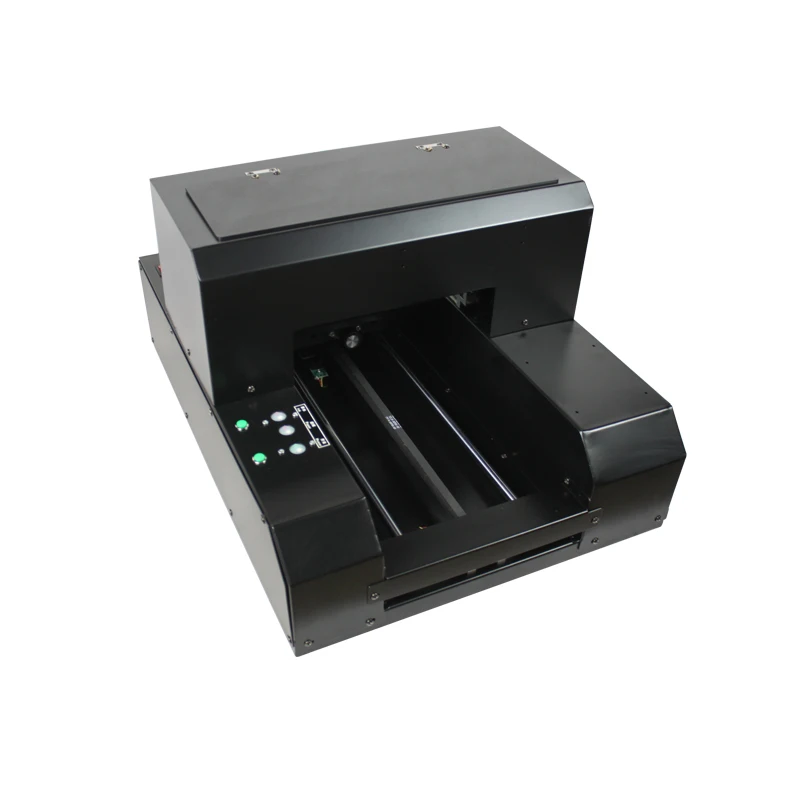 The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer.
The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer.
Application
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops. The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products.
Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes;
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.

The confectionery pattern is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear. The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used.
Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
Food 3D printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database.
 The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges;
The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; -
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies. Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
-
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake.
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe;
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
 The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular brands
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. Quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products.
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making.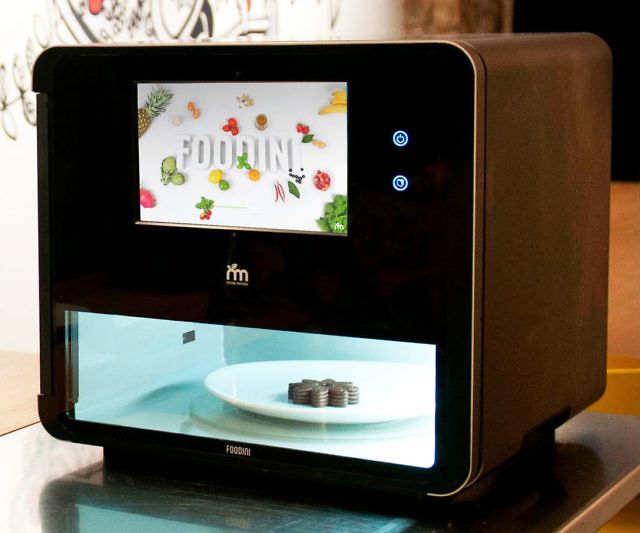 Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
Free shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Choc Edge |
Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the cart and follow the instructions Go
| Manufacturer | Wiiboox |
Free Shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Choc Edge |
Top 10 Best Food Printers: List of the Most Current Models
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market.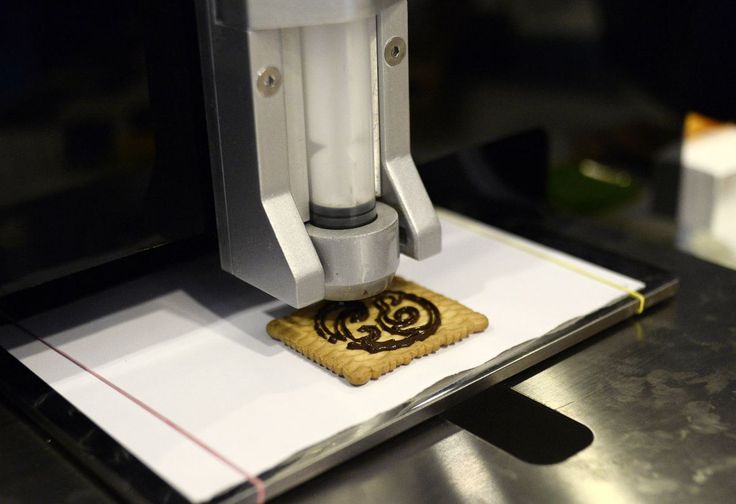 The top is based on ratings and customer reviews.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews.
1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
A wide range of proposed projects;
-
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment.
Pros:
-
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
High build quality;
-
Convenient control by touch panel.

Cons:
-
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, thanks to which it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate.
Pros of :
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Uninterrupted work;
-
Durability;
-
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
 Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs.
Pros of :
-
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
-
High printing precision;
-
Long service life;
-
Ease of use: You can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
-
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
5. byFlow Focus
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients.
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients.
Pros:
-
The ability to create unique flavors;
-
Neat and bright printing;
-
Aesthetic appearance of the device.

Cons:
-
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
-
Practicality;
-
High build quality;
-
Attractive appearance;
-
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.
Pros:
Cons:
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision.
Pros:
-
Ease of operation;
-
High build quality;
-
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling.
Pros:
Cons:
-
High price.

Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing:
-
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
-
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
-
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
-
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.

Output
In the catalog of our online store, you can choose the best food printers from famous brands to create culinary masterpieces. Explore our range, learn about the characteristics of each printer and make great purchases.
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
7 amazing things that can be printed on a 3D printer
August 16Technologies
Real food, living heart, rice eco-house and other useful "printouts" that can solve the world's problems.
Share
01. Human organs
Scientists can now print skin, kidneys, liver tissue, heart and a number of other organs. True, while they are usually smaller than real ones, and therefore suitable only for clinical trials or surgical practice. But in the future, they should seriously help in the fight against various diseases. For example, they want to use 3D skin as a means for healing wounds. And full-fledged printed hearts or kidneys can shorten the queue for donor organs and save more lives: hundreds of thousands of people need transplants every year.
For example, they want to use 3D skin as a means for healing wounds. And full-fledged printed hearts or kidneys can shorten the queue for donor organs and save more lives: hundreds of thousands of people need transplants every year.
3D organs are created from real living cells, either from adult stem cells or from a sample taken directly from a person. They play the role of ink, which the printer heads put on an organic or synthetic base. The correct shape, texture and tissue layers are programmed based on the results of the scan - this ensures maximum copy accuracy. The main challenge facing scientists now is to find an opportunity to create organs that can function inside the body: to contact the nervous and circulatory systems and perform their tasks correctly.
2. Bones and cartilage
Illustration: Phonlamai Photo / Shutterstock But they are already used by surgeons in real life. For example, 3D implants are used to replace femurs. There are also successful examples of transplantation of printed bones of the skull and cartilage of the auricle. The next step in the application of this technology may be the replacement of small damaged areas right inside the person. Such a 3D printing method, according to the researchers, will speed up the process and save in cases where speed of reaction is critical, for example, in the treatment of bone cancer.
The next step in the application of this technology may be the replacement of small damaged areas right inside the person. Such a 3D printing method, according to the researchers, will speed up the process and save in cases where speed of reaction is critical, for example, in the treatment of bone cancer.
3D printers also come in handy in dentistry. They simplify the process of creating crowns, bridges and prostheses: the specialist does not need to select sizes manually - the model is formed and printed on the basis of images of the oral cavity. They can also be used as temporary implants to help patients get used to their new teeth and make sure they fit well in their mouths. The technology is safe: special photopolymer resins are used for printing. They are strong, retain an aesthetic shade for a long time and do not irritate the mucous membrane.
3. Prostheses
Arms, legs and other parts of the body. Due to the simplified manufacturing process, 3D prostheses cost less and are created faster. In the standard scheme, you first need to make a cast of the remaining part of the patient's limb, then cast a trial version from plaster, then try it on, correct inaccuracies, and only then proceed to create the finished product. In the 3D version, it is enough to collect measurements, correct the model on the screen and print it.
In the standard scheme, you first need to make a cast of the remaining part of the patient's limb, then cast a trial version from plaster, then try it on, correct inaccuracies, and only then proceed to create the finished product. In the 3D version, it is enough to collect measurements, correct the model on the screen and print it.
However, these prostheses do not necessarily have a purely cosmetic function. 3D hands with touch control, that is, a reaction to body signals, or with a vibrational response to touching objects already exist. In addition, it is easier to replace a printed artificial limb after wear with a similar one by re-creating it according to the saved layout.
3D prostheses can be used for more than just humans. For example, in Australia, an artificial leg for a dog was created on a printer.
The speed and cost of producing 3D prostheses is a chance for many children: conventional options are too quickly rendered useless due to the active growth of the child.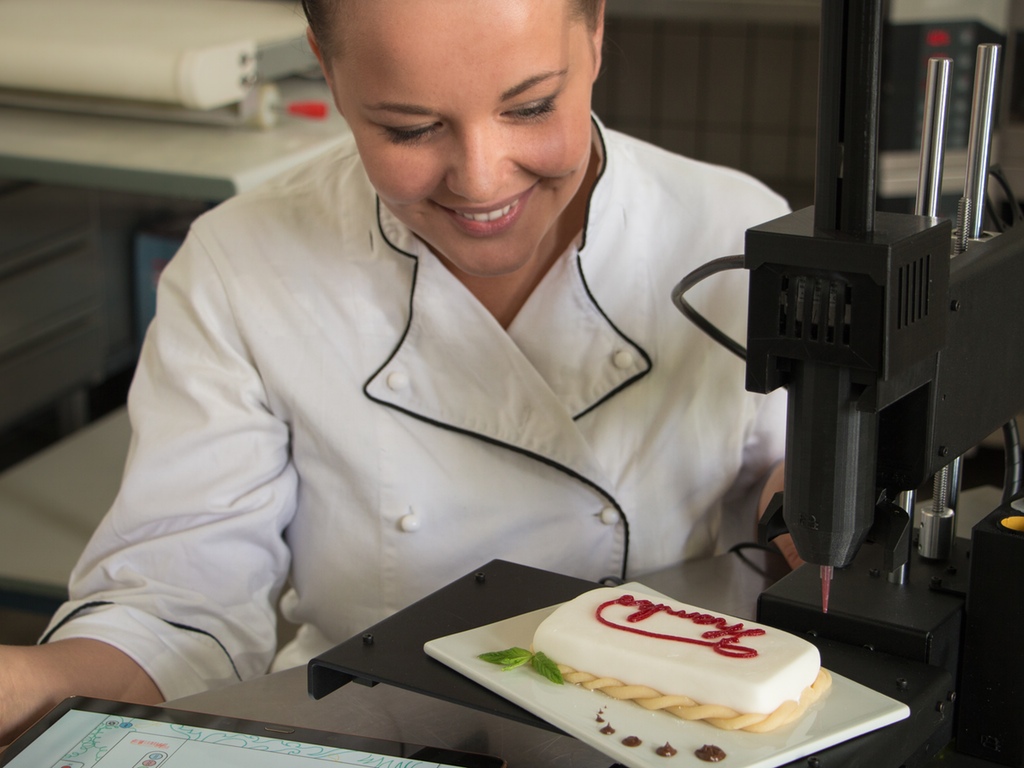 And a printed model can be created even for a one-year-old patient who is just learning to move: scientists from Lincoln University have already presented such a development.
And a printed model can be created even for a one-year-old patient who is just learning to move: scientists from Lincoln University have already presented such a development.
4. Food
Brands use 3D printers to model future products or create unusual shapes for everyday food. Creative serving options are also used in some restaurants. In 2016, an entire restaurant was temporarily opened in London, the menu of which consisted entirely of dishes obtained using 3D technology.
But choosing the look isn't the only benefit of 3D food printing. Due to the possibility of virtual programming of the composition, the dishes created by the printer are easy to adjust to the desired nutritional value: control the calorie content, the amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins. This will make life easier for people who are on a strict diet for medical reasons. Also, the printer will allow you to cook the usual food, but from budget ingredients. For example, to form a fish fillet from seaweed. This, in theory, should help solve the problem of world hunger.
This, in theory, should help solve the problem of world hunger.
In the future, 3D printers could make eating more ethical. For example, they will make it possible to stop killing animals for the production of meat products. One of the alternative options here is the creation of meat entirely based on plant components.
Another way is to form "ink" for a 3D printer from a meat sample taken from an animal by biopsy. A device for printing using this technology was created at the Moscow State University of Food Production (MGUPP). True, for a 3D printer to be able to make a whole steak from a tiny piece of fabric, it takes several months. First, the sample is cultured in a bioreactor. When there are enough cells, they begin to form the base - from ingredients of plant origin. After that, animal and vegetable “ink” are alternately applied to it. As a result, the product retains both taste and texture.
The MGUPP 3D printer is capable of printing not only meat, but also, for example, chocolate or dough.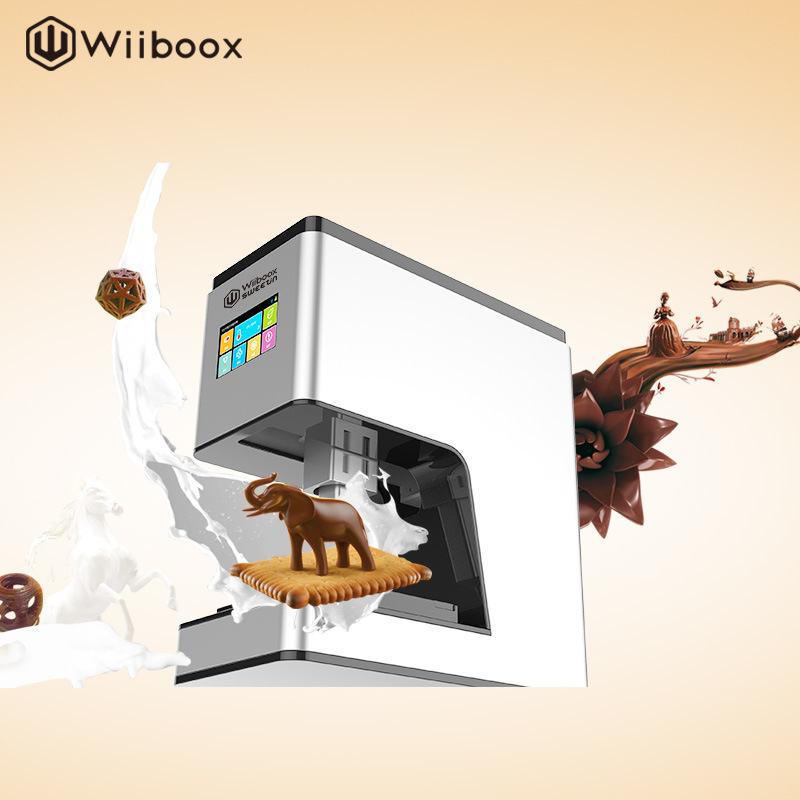 University researchers plan to experiment with the technology further to expand their product range.
University researchers plan to experiment with the technology further to expand their product range.
5. Clothing and footwear
Illustration: asharkyu/ShutterstockMany brands produce 3D printed items. For example, Nike printed the upper part of the sneaker, and Adidas made the midsole. Dresses by Dutch designer Iris van Herpen, sewn using this technology, are regularly worn by celebrities. Austrian Julia Koerner also works with the printer - accessories that she created in collaboration with costume designer Ruth Carter, worn by Angela Bassett in the movie "Black Panther".
Fashion 3D printing expands the creative possibilities of designers, allowing for futuristic shapes that are difficult to achieve with conventional sewing methods. However, this is not the main advantage of the technology. A 3D printer reduces resource consumption: a thing or its element immediately appears in the right size - no extra shreds and threads remain. In addition, 3D fabric requires less water to make than cotton, and it can also be quickly created from recycled or recycled materials. In the future, the printing of things can destroy fast fashion, allowing you to create them piece by piece, ideally suited to the parameters and requests of the client.
In the future, the printing of things can destroy fast fashion, allowing you to create them piece by piece, ideally suited to the parameters and requests of the client.
6. Laboratory instruments
Printed instruments, due to the speed and cost of production, can help in research in poor countries. Now there are several projects that create budget microscopes for diagnosing malaria in Tanzania.
3D technology makes science accessible to amateurs too. For example, Australian researchers have developed a microscope attachment for a smartphone and made the files available to the public: anyone who has a printer can create such a device.
7. Houses
There are buildings with printed walls all over the world, including Russia. 3D printers make it possible to build houses in a few days, while reducing costs and not requiring the participation of an entire construction team. Large special equipment is also not needed - you can work even in hard-to-reach places.