Why 3d printing is good
Advantages of 3D printing (and disadvantages) Complete guide
Back
(and disadvantages)
TL;DR : The main advantages of 3D printing are: reducing costs, less waste, reduce time, get an competitive advantage, reduce errors, confidentiality, production on demand. Disadvantages …
As far as recent inventions go, the advantages of 3D printing make it one of the most promising technologies. The additive technology is one of the biggest advantages of 3D printing, it opens a whole new way in which product are created and it offers a lot of advantages compared to the traditional manufacturing methods.
There are many different types of 3D printing technologies available, but the benefits of 3D printing discussed here are applicable to the whole industry. Through fast design, high levels of accuracy and the ability to make informed decisions, the following 3D printing advantages make this technology a real prospect for businesses but also highlight its importance in future production techniques.
Our 7 advantages of 3D printing:
- Cost reduction
- Less waste
- Reduce production time
- An enhanced competitive advantage
- Reduce errors
- Confidentiality
- Production on demand
1. Cost reduction
Less machine, material and labor costs
For any business, costs reduction is important and one of the advantages of 3D printing is that it will help to bring those costs down. Manufacturing costs are split into three different categories known as: machine operation costs, labor costs and material costs.
Machine costs
Machine operation costs play a very small part in the overall cost of the manufacturing process. While the energy required to create parts in an industrial environment can be high, the ability to develop and create complex parts and products in one step creates an increased level of efficiency and saves on time. Therefore, the cost of running the machines is offset by the savings made during the manufacturing process.
Labor costs
One of the good points of 3D printing is the fact that labor costs are kept low. Unlike traditional manufacturing where different people may be required to operate a number of different machines or a production line is required to put the product together. Each 3D printer will require an operator to start the machine and start the automated process of creating the uploaded design. Therefore, the labor costs are significantly lower as traditional manufacturing.
Material costs
The range of 3d printer filaments used for 3D printing is growing and this makes it possible for the price to decrease over the last years. But, in the same way as the machine operation costs, in comparison to traditional methods, the overall cost are a lot lower.
Less travel costs
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is that it can also help to reduce the amount of distance that a product will travel. As 3D printers can create a product from start to finish, it enables designers to design the product in one country, email it to another country in preparation for production. There is no requirement to create prototypes that have to be moved around from factory to factory in order to complete the process. This makes 3D printing an industry that can be created around the world without leaving a footprint. Therefore, there is a reduction in shipping, air travel and road travel.
There is no requirement to create prototypes that have to be moved around from factory to factory in order to complete the process. This makes 3D printing an industry that can be created around the world without leaving a footprint. Therefore, there is a reduction in shipping, air travel and road travel.
Next to the design and production of prototypes, it’s also possible for spare parts to be produced on site and that can help to significantly reduce the carbon footprint.
2. Less waste, more sustainable
The traditional manufacturing process is mostly a subtractive process, where the raw material gets wasted and reused over and over again, this results in high costs and waste. An advantage of 3D printing is the unique way it builds the product with very little waste, this is called additive manufacturing. While the more traditional methods will have waste that can be re-used or recycled it still takes time and effort to determine just how and when the waste will be used. This even makes large volume 3D printer a very sustainable option.
This even makes large volume 3D printer a very sustainable option.
Thermoplastic materials, for instance, can be melted, cured (cooled down such that they become solid), melted again, cured again, and so forth. Therefore manufacturing ‘waste’ can be reused (thus preventing it from becoming “waste” in the first place).
3. Reduce time
We live in a fast paced world where everything is required quickly and so, this is where 3D printing can really make a difference. One of the big advantages of 3D printing is that parts and products can be manufactured a lot quicker than they can using traditional methods. Complex designs can be created as a CAD model and then transformed into a reality in just a few hours. This delivers design ideas in a way that enables them to be verified quickly and designed in a short space of time. This is so advantageous over traditional methods as they can take weeks or months to go from the design stage to prototype stage and right through to the production process.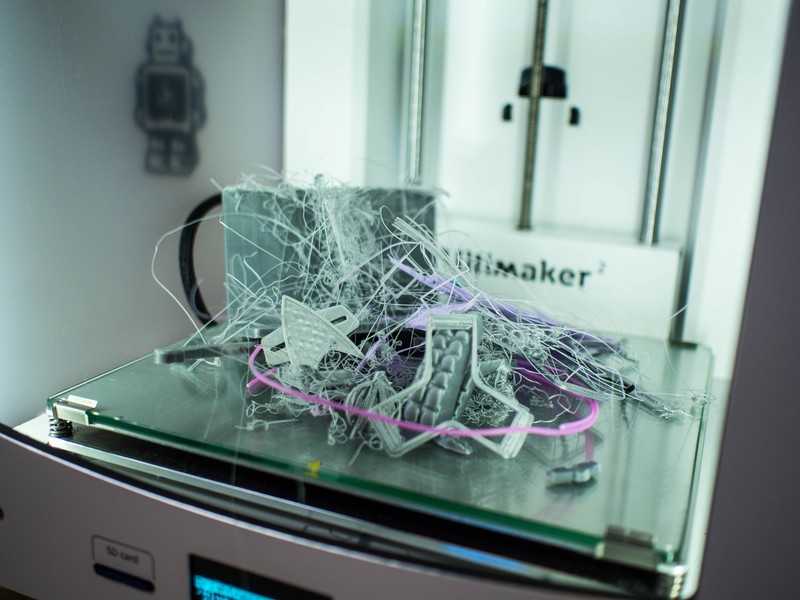
4. Provides an enhanced competitive advantage
The ability to reduce the time of the prototyping phase, businesses can deliver better, improved and enhanced products in a shorter space of time. Giving a competitive advantage over the competition. But it also makes it possible to develop products early, creating prototypes more frequently until the product is perfected and ready for production creating a highly effective product launch.
And the competitive advantage of 3D printing is taken to the next level with our 3D printers. Having the ability to create a life-size prototype makes it possible for designers to think differently about the products that they design.
In business, it is important to show customers or investors the products that you are going to offer. But, to produce a product that they may not even like can prove costly and so, it is often left to the imagination as products have to be described. This increases the risk of information being lost somewhere during communication and that can cause severe problems at some point. One of the advantages of 3D printing is that it makes it possible to create a product quickly that people can physically hold, removing any concerns or miscommunication. While it may be a prototype and open to alterations, it at least provides a small insight into what the product will look like, offering a truer representation than that of a description.
One of the advantages of 3D printing is that it makes it possible to create a product quickly that people can physically hold, removing any concerns or miscommunication. While it may be a prototype and open to alterations, it at least provides a small insight into what the product will look like, offering a truer representation than that of a description.
Test the Market
Understanding whether a product will be a success requires a lot of research, especially where traditional manufacturing methods are concerned. However, creating a prototype through 3D printing will make it possible for businesses to obtain feedback from potential buyers and investors in a way that could never be achieved before. The product can be customized and altered right up to the very last minute which is something that traditional manufacturing methods do not offer. This means that 3D printing offers a unique and valuable way of identifying whether a product has the potential to make it to market and be successful at the same time.
5. Reduce errors
When it comes to designing parts and products, designers have to consider efficiency. Many parts and products require a high number of steps using traditional methods of manufacturing in order to be produced. Therefore every step could result in an error, with the risk of starting over again, leading to problems with the overall manufacturing process. A single step manufacture process is more beneficial.
There are many industries that have a long and drawn out production process. Where some of the steps are to create a CAD model, then developing a prototype that may require adjustments before it is finally sent for final production. This is a process that takes a lot of time and none of the steps can be skipped because they all play a part in the production process. However, one of the advantages of 3D printing is that it creates the product in one single step, with no interaction from operators during this process. Just finalize the design and upload it to the printer. This removes dependence on a number of manufacturing processes and enhances the control over the final product.
This removes dependence on a number of manufacturing processes and enhances the control over the final product.
During the traditional manufacturing process, faulty prototypes cost time and money. With every faulty prototype, you need to go back to the drawing board, with no guarantee it would be right the second time around. Even small adjustments have a significant financial and time impact on the whole process. This is where 3D printing can remove risk because designs can be verified through creating a production-ready prototype before going ahead with the final creation. This helps to increase confidence in the design before investments and further money is paid to take it to the next level of production for the mass market.
6. Confidentiality
Continuous prototyping and manufacturing in-house with a 3D printer ensures that designs never leave the company premises, safeguarding your intellectual property. No third parties can ever claim your innovations for themselves. Every innovative design is kept in-house, so there is no need to worry about confidentiality any longer.
Every innovative design is kept in-house, so there is no need to worry about confidentiality any longer.
7. Production on demand
The ability to have full freedom in the design is one huge advantage of 3D printing. It also enables designers to customize designs. As 3D printing is perfect for one-off productions and building single parts in one process, it means that the ability to customize is there to take advantage of. Therefore, many industries such as medical and dental have embraced 3D printing and design because of the ability to create customized implants and aids. In fact, sporting gear can be created to fit athletes and so, custom, person specific parts can be created in a way that has never been seen before.
Traditional methods relied on molds and cutting and this makes customizing a very time-consuming process. In contrast to this, the customization of products created through 3D printing can have enhanced structural integrity improved, complex changes made and parts altered to fit certain requirements. Customization in this way, gives 3D printing an endless amount of possibilities.
Customization in this way, gives 3D printing an endless amount of possibilities.
Conclusion
For any business, their customers are key to their success and so, customer satisfaction becomes an important part of their strategy. Through keeping ahead of the competition and providing customers with what they want, industrial 3D printers have changed the way in which businesses deliver exactly what their customers want. The expectations of customers has changed because they want their items quickly and efficiently.
It is clear to see that there is a wide and varied array of 3D printing advantages. Many different industries are starting to introduce 3D printing into their processes in an attempt to benefit from using the technology in the various different ways. It is a technology that has grown considerably in recent years and it will continue to grow as it continues to fine-tune what it has to offer. When all of the 3D printing advantages are considered, it is obvious that this will soon become a technology that will overtake traditional methods, it is just a matter of time.
It is the ability to print complex shapes and interlocking parts without the need for any form of assembly that makes 3D printing so unique. It is possible to create small, intricate shapes at a very small cost and in a short space of time. The ability to develop and produce different shaped objects without the need for specific tooling offers businesses a higher level of flexibility when it comes to production and it helps to reduce costs. The strong point about 3D printing is that it improve innovation and is perfect for on-demand customisation needs. It gives businesses the power to design and create products in a way that has never been seen before. It is a process that enables the imagination to be free because there are almost no boundaries. It can bring back to life old designs for a number of industries where parts have become obsolete.
Despite 3D printing being a relatively new technology, it has grown in popularity to the point where it is now accessible due to a reduction in costs. The number of printers that are being sold is growing at an incredible rate and what was once a niche technology to only those who could afford and use it, it is not reaching far and wide to many different industries. This ease of access has changed the manufacturing process in a way that has not been seen for decades.
The number of printers that are being sold is growing at an incredible rate and what was once a niche technology to only those who could afford and use it, it is not reaching far and wide to many different industries. This ease of access has changed the manufacturing process in a way that has not been seen for decades.
Disadvantages of 3D printing:
- Initial costs of printer
- Post processing
- Printing time
- Special skill required for 3D models
- Manufacturing Job Losses
1. Initial costs of printer
You need to buy the 3D printer, and even tough the return on investment is quick and high, the initial investment has to be done.
2. Post processing
A 3D printed object, in most cases, needs some post processing to be used.
3. Printing time
When it comes to manufacturing many objects, the 3D printers are slow in comparison to other manufacturing technologies. Next to the mass production, an other disadvantges is the long printing times for one off prints. Depending on printer size and quality, it can take several hours to days to print, but when the printer makes a fault when it’s almost finished printing, you have to start over again. However, by making sure the 3D model and the print file are designed and sliced well and the printer is setup correctly you can almost guarantee the print will come out perfect.
Depending on printer size and quality, it can take several hours to days to print, but when the printer makes a fault when it’s almost finished printing, you have to start over again. However, by making sure the 3D model and the print file are designed and sliced well and the printer is setup correctly you can almost guarantee the print will come out perfect.
4. Special skill required for 3D models
Once you have obtained a printer you have to learn how to make and alter 3D models. 3D modeling is a skill that requires a lot of time and effort to fully master, it’s a process of trial and error. But once you know how to use the software you will be able to print whatever comes to mind.
5. Manufacturing Job Losses
As we mentioned in the advantages of 3D printing, the technology can make product designs and prototypes in a matter of hours as it uses only one single step. It eliminates a lot of stages that are used in traditional manufacturing. As a result it doesn’t require a lot of labor cost. As such, adopting 3D printing may decrease manufacturing jobs. For countries that rely on a large number of low skill jobs, the decline in manufacturing jobs could dramatically affect the economy. However, it’s likely that robotics will have a much larger impact here.
As such, adopting 3D printing may decrease manufacturing jobs. For countries that rely on a large number of low skill jobs, the decline in manufacturing jobs could dramatically affect the economy. However, it’s likely that robotics will have a much larger impact here.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10 Benefits of a 3D Printer: Save Time and Money
More recently, 3D printing has been viewed as something completely new. The technology was underdeveloped, the hardware was too expensive for widespread use. But only a few years have passed, and the situation has changed radically. Not only did more and more 3D printers begin to appear in stores, but also some enthusiasts began to assemble this equipment themselves.
1.
 Economy
Economy Although large-scale projects with thousands of 3D printed parts are not cheap, they are still much more profitable than other technologies. Many manufacturers use 3D printing for small runs or for prototyping. Plastic can also be used for injection molding, but casting small batches can require expensive equipment. But even in this case, manufacturers can produce cast 3D parts several times cheaper than using aluminum.
Prototype parts printed on Prusa i3 Bizon 3D printer, layer height 0.1mm, PLA material
2. Faster production cycle
Compared to traditional production methods, the entire process can take weeks or days, and most products are printed in hours. Some manufacturers have even begun to make parts to order, which has also allowed them to optimize their warehouse capacity and resource management scheme, making them more flexible. With this new approach, the manufacturer does not need to store every single part or component, they can simply be printed as needed and immediately put into action.
Miniature parts printed by Wanhao Duplicator 7 photopolymer 3D printer, layer height 0.5mm, photopolymer resin material
It not only affects the reputation of the company in its industry, insufficient technical control can lead to injury to employees and customers. Since 3D printing uses a completely different production method than most machine tool operations, the process has significantly fewer weaknesses and flaws overall.
Model printed on Picaso Designer X PRO 3D printer, 0.2 mm layer, ABS materials, HIPS
4. Less waste
The press is gaining more and more support in the form of supporters of the "green" movement. Because 3D printing produces significantly less waste than traditional processing, the technology is more environmentally friendly while reducing costs. 3D printing has even made its way into the textile industry, allowing clothing and prototypes to be printed.
Hercules Strong 3D printed yacht steering parts. Details printed in 15 hours with a 0.5 mm nozzle and a layer height of 0.3 mm at a speed of 60 mm/s.
Details printed in 15 hours with a 0.5 mm nozzle and a layer height of 0.3 mm at a speed of 60 mm/s.
5. Greater customization
3D printed products are also highly customizable. Parts can be printed not only with light plastic, some next-generation models may also have a metal coating. As a result, objects are not only aesthetic, but also functional. In addition, they can acquire thermal and chemical resistance. The existing metallization method can also be used for plastic.
Functional parts printed on Hercules. Material ABS, nozzle diameter 0.5 mm, layer height 150 µm, filling 100%. The model consists of 3 parts: the body and 2 halves of the latch, after printing and processing, the parts were glued together with acetone.
6. Customer Accessibility
If some craftsmen set up small mechanical workshops, for example, in garages, then most of us cannot afford such a luxury. 3D printing allows you to bring a significant part of the manufacturing process directly into the home, made possible by the availability of user-grade 3D technology. While it turns out to be quite expensive for one-off projects, the price of 3D printers and consumables is dropping rapidly.
3D printing allows you to bring a significant part of the manufacturing process directly into the home, made possible by the availability of user-grade 3D technology. While it turns out to be quite expensive for one-off projects, the price of 3D printers and consumables is dropping rapidly.
Technical wing caps in REC RUBBER or REC FLEX. The models are printed on a Prusa i3 Steel 3D printer.
7. High complexity
In most cases, when it comes to complex parts and elements, the manufacturing process imposes certain limitations. Techniques used in casting and finishing objects may not be subtle enough for sophisticated design details. 3D manufacturing processes make it possible to realize almost any design solution, regardless of its complexity, and in a reasonable time. This not only eliminates the extra assembly steps required by traditional methods, but also provides more freedom to create future-proof designs.
Zenit 3D Printing Big Details From Engine 3D Printer
8.
 Less risk
Less risk While there are inherent risks associated with these new technologies, in terms of day-to-day business, 3D printing risks are significantly lower than with traditional manufacturing methods. Not only is 3D printing much cheaper when it comes to testing a new design or product, the printed prototypes themselves can stir up investor and customer interest and get them to decide whether to proceed with mass production of a product, whether it is worth the time and effort required.
Wanhao Duplicator i3 3D Printer Miniature Printing
9. Variety of materials
The materials used in today's 3D printers are much more diverse than most raw materials in traditional production methods. 3D printing also provides the ability to mix different substances, a luxury that is not always available with conventional methods. Although many 3D printer manufacturers offer their own, very limited set of sources, 3D printers can work not only with original materials, allowing you to simulate ceramics, metal, glass and more.
Wanhao D6 3D Printer PEGT, ABS-PC, PLA, SBS
The manufacturer not only needs to clearly understand what the customer wants, the manufacturer must also be able to explain what he himself can. Drawings, diagrams, diagrams are all good, of course, but there is nothing better than a real prototype that you can hold, look at and study. The fact that the materials are inexpensive, coupled with the short prototyping time on today's 3D printers, helps a lot during the prototyping phase, keeping all stakeholders connected.
THE PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE OF 3D PRINTING
Despite a relatively slow start, the concept of 3D printing is finally gaining momentum and popularity among manufacturers and customers. We already see a lot of benefits of 3D printing, including shorter production cycles, more complex designs and improved quality, and the peak of the popularity and functionality of this technology is yet to come.
What is 3D printing in 2021
3D printing technology has changed the manufacturing process of everything that surrounds us. From children's toys and clothes to prostheses, implants, etc.
From children's toys and clothes to prostheses, implants, etc.
The 3D printing process is also known as additive manufacturing. In simple terms, a computer program tells the printer where to lay thin layers of material that gradually turn into a solid object.
Types and processes of 3D printing technologies
The first mention of 3D printing technology appeared in the late 1980s. They were called rapid prototyping technologies. The name refers to a process that was conceived as a faster and more cost-effective method of prototyping in product development. The very first patent application for this technology was filed by Dr. Hideo Kodama on May 1980 years. But, unfortunately for the inventor, the full patent specification was not submitted until one year after the application was filed. Kodama used ultraviolet light to cure plastic and create an AM object.
Years later, American Scott Crumb developed the most common type of 3D printing today - FDM (Fused deposition modeling).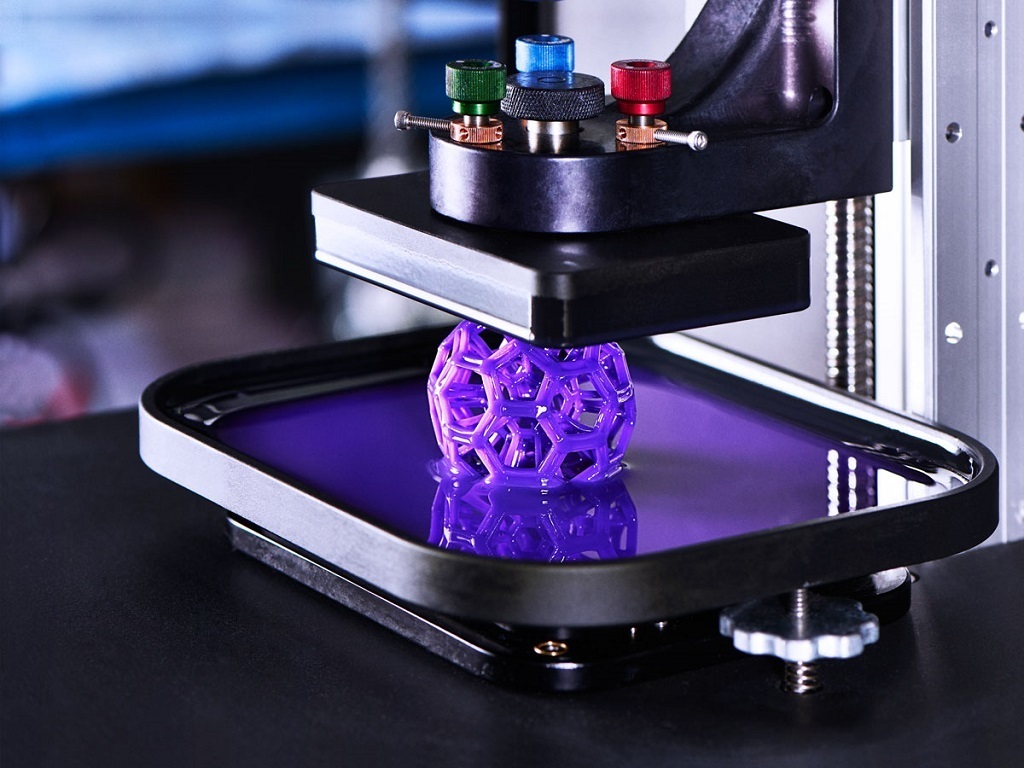 This technology stands for deposition modeling. This type is characterized by the fact that the thermoplastic material is heated to a liquid state and extruded through the nozzle layer by layer.
This technology stands for deposition modeling. This type is characterized by the fact that the thermoplastic material is heated to a liquid state and extruded through the nozzle layer by layer.
Charles Hull, co-founder of 3D Systems, was one of the inventors of the 3D printing technology known as stereolithography. The technology is based on photochemical processes.
But Kodama, Crump, and Hull weren't the only developers of 3D printing techniques.
WINBO 3D printer at Art-Up Design Studio
Here are some other types of 3D printing that are in use today:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is by far the most common method for producing thermoplastic parts and prototypes today. Based on the melting of the filament in the nozzle with its subsequent laying in layers. It is also the most economical way of 3D printing due to the availability of a wide range of thermoplastic materials with different technical characteristics, which allow generating both functional parts of mechanism prototypes and volumetric cases, as well as any free spatial decorative forms.

- SLA (Stereo Lithography Apparatus) is based on the layer-by-layer curing of a liquid photopolymer material under the influence of UV study. Can print objects in multiple colors and materials with different physical properties, including rubber-like parts. The high printing accuracy of this method makes it more expensive and not optimal for simple plastic structures.
- DLP (Digital Light Processing) cures polymers using a light projector rather than an ultraviolet laser. This allows you to create a whole layer in one exposure, thus increasing the speed of production.
Metals too have their own 3D printing techniques. The type of technology is selected depending on the features of the object.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is based on layer-by-layer sintering of polymer powder particles using laser radiation. The nylon powder melts into a strong, hard plastic. Due to the peculiarity of the technology, the surface of the part is not ideal, but very functional for use in prototypes with hinges and latches.

- SLM (Selective Laser Melting) is based on layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder under the action of a laser beam. Used in the manufacture of decorative items. Therefore, it is useful for applications in medicine and lightweight structures. Often this method is used in conjunction with traditional metal casting technology to create prototypes or final products.
- EBM (Electron Beam Melting) is based on layer-by-layer melting using an electron beam. The printing uses electromagnetic coils to superheat the metal powder in a vacuum.
How 3D printing works
3D printing is the process of layering one on top of another. Every 3D printed object starts life as a 3D model in a computer program.
You can create your own design in programs such as Maya, Blender, ZBrush, CATIA, Solidworks. In addition, ready-made 3D models of parts can be downloaded from sites such as Thingiverse or CGTrader.
When you have a 3D model obtained in one way or another, you “run” it through the “slicer” program (from the English word “to slice”), which converts the original 3D model in STL format into print layers. The information received is eventually converted into a special data format called G-code for further printing on a 3D printer.
The information received is eventually converted into a special data format called G-code for further printing on a 3D printer.
Such programs usually come with the 3D printer, or they can be freely downloaded, such as the Cura program. What these softwares have in common is that they create thousands of lines of code for layers. This code tells the printer how to print.
Next, you need to set up your 3D printer, select the print quality and the correct settings for the material. To start printing, you load your "sliced" part into the printer via a USB stick, SD card, or send directly from your computer. And the printer starts a slow additive layering process.
Photograph of Christian Reil from Pixabay
Materials used in 3D printing
The materials available for 3D printing have come a long way. Currently, there is a wide range of materials that differ both in properties, types, and in the states supplied (powder, threads, granules, resins, etc. ).
).
Some materials are developed for specific applications to perform special tasks. For example, the medical sector, where special photopolymer resins (SLA 3D printing technology) are used, the properties of which make it possible to print implants, casts, and so on.
Some of the most commonly used materials:
- Plastics. Sintering (SLS) typically uses polyamides or nylon supplied in powder form. It is a strong, flexible and durable material. It is white in color, so it needs to be tinted before or after printing. The most common 3D printing technology today is FDM, which uses ABS or PLA plastic filaments. These plastics are available in a wide range of colors. Compared to PLA, ABS plastic has higher strength characteristics. But PLA is biodegradable, so it's as widespread as ABS.
- Metals. More and more metals and metal composites are finding their way into industrial 3D printing. The most common of them are derivatives of aluminum and cobalt.
 Due to its strength characteristics, stainless steel is often used in powder form in 3D printing technologies such as sintering, melting, EBM. In the last couple of years, silver and gold have been added to the list of metals suitable for printing. This made it possible to significantly expand the possibilities of jewelry production.
Due to its strength characteristics, stainless steel is often used in powder form in 3D printing technologies such as sintering, melting, EBM. In the last couple of years, silver and gold have been added to the list of metals suitable for printing. This made it possible to significantly expand the possibilities of jewelry production. - Ceramics. A relatively new group of materials used in 3D printing. The peculiarity of printing with these materials is that the printed ceramic parts must go through the same processes as ceramic products made by traditional methods - firing and glazing.
- Biomaterials. Currently, a large number of studies are being conducted aimed at exploring the possibility of 3D printing from biomaterials for the needs of medicine. This includes the printing of human organs for transplantation, external tissues for replacement of body parts. To do this, leading institutions research living tissues.
- Food. Over the past few years, there has been an increase in experimentation with food 3D printing extruders.
 Chocolate printing is the most widely used. There are 3D printers that use sugar, pasta, meat, dough.
Chocolate printing is the most widely used. There are 3D printers that use sugar, pasta, meat, dough.
Photo of mebner1 from Pixabay
What 3D printing is used for
If you can think of an item, then most likely you can print it. Children's toys, jewelry, phone cases and much more are already being printed by enthusiasts on 3D printers. Some use 3D printing for fun. Fun projects already exist: a printed guitar, a loom, and an intricate sculpture created from a combination of laser-fused glass and nylon. 3D printing has already moved beyond its origins in plastic printing and has moved into the use of metal, rubber, wood, synthetic fabrics, and ceramic resins. Functional 3D-printed human organs have not yet been created, but scientists say that this is a matter of the near future.
Because additive manufacturing of complex objects is faster and cheaper than traditional molding and casting methods, it has found its way into industry and the arts. The possibilities of this technology are almost limitless, but 3D printers are not perfect machines. In addition to all the advantages, there are also reasons for concern.
The possibilities of this technology are almost limitless, but 3D printers are not perfect machines. In addition to all the advantages, there are also reasons for concern.
Ethical issues in 3D printers
3D printers consume a lot of energy and emit ultra-light plastic particles into the air, which are then inhaled by humans. These harmful emissions can be compared to a cigarette lit indoors.
While humanity is trying to reduce the use and consumption of plastic, 3D printers are another technology heavily dependent on it. This presents a problem for all ecosystems, in particular for the already suffering oceans with their floating islands of plastic.
A few years ago, the news of the first 3D printed firearm caused a media frenzy. The creation of untraceable weapons by a private individual remains a modern security problem.
From a legal point of view, there is no clear answer to the question of who is responsible in the event of harm to health caused by a printed object. Indeed, in most cases, the developer of a 3D model, the manufacturer of a 3D printer, and the one who printed it are different people or organizations. Determining liability for potential injury and death is a new challenge.
Indeed, in most cases, the developer of a 3D model, the manufacturer of a 3D printer, and the one who printed it are different people or organizations. Determining liability for potential injury and death is a new challenge.
At the same time, the use of 3D printing technology in the medical field to print tissue raises a number of ethical and moral questions. These issues are similar to the talk of stem cell research and gene editing that has been going on for decades.
On the other hand, we have a powerful tool in our hands that is changing the way we create and produce things. We still don't fully understand what this means for our future.
Potential effect on the global economy
If 3D printing continues to develop at the same pace as it is now, then its use could potentially affect the global economy. The transition of production and distribution from the current model to localized custom manufacturing can reduce the imbalance between exporting and importing countries.
3D printing is creating new industries and new professions. Professions related to the production of 3D printers or, for example, a vacancy for a rapid prototyping technician at the Cartier jewelry house. New professional services are emerging, such as supply of materials, printer operator, legal services in dispute resolution and intellectual property issues. With the development of 3D printing technology, the issue of "piracy" becomes an urgent problem.
The impact of 3D printing on developing countries is a double-edged sword. The positive effect for such countries is the reduction in the cost of production through the use of recycled and other local materials. But the loss of manufacturing jobs could hit these economies hard, and it will take time to find a balance.
Where can I use a 3D printer
Owning a 3D printer with the necessary software and materials can still be expensive for individual needs, so public 3D printers are becoming more common.
There are places like labs and 3D printing shops. You can send your design and pick up the finished part in a couple of days. Some companies, such as ART AP Design Studio, also do 3D printing.
If you are a student or student, 3D printing services may be available at your school.
Art-Up Design Studio
Where can I learn how to use a 3D printer
For those who already have the specialty of an engineer, there are advanced training programs (Additional education) from the Russian Academy of Crafts, designed for 36 or 72 academic hours.
The training course in an accessible lecture form reveals the issues of theoretical and practical foundations of design, three-dimensional modeling, design of plastic products. It provides for the performance of work and tests within the framework of the design tasks of the course and the final exam.
As a result of mastering the program, the trainee receives a certificate "Specialist in Additive Technologies".