Wooden 3d printer filament
Ultimate Materials Guide - 3D Printing with Wood Filament
Overview
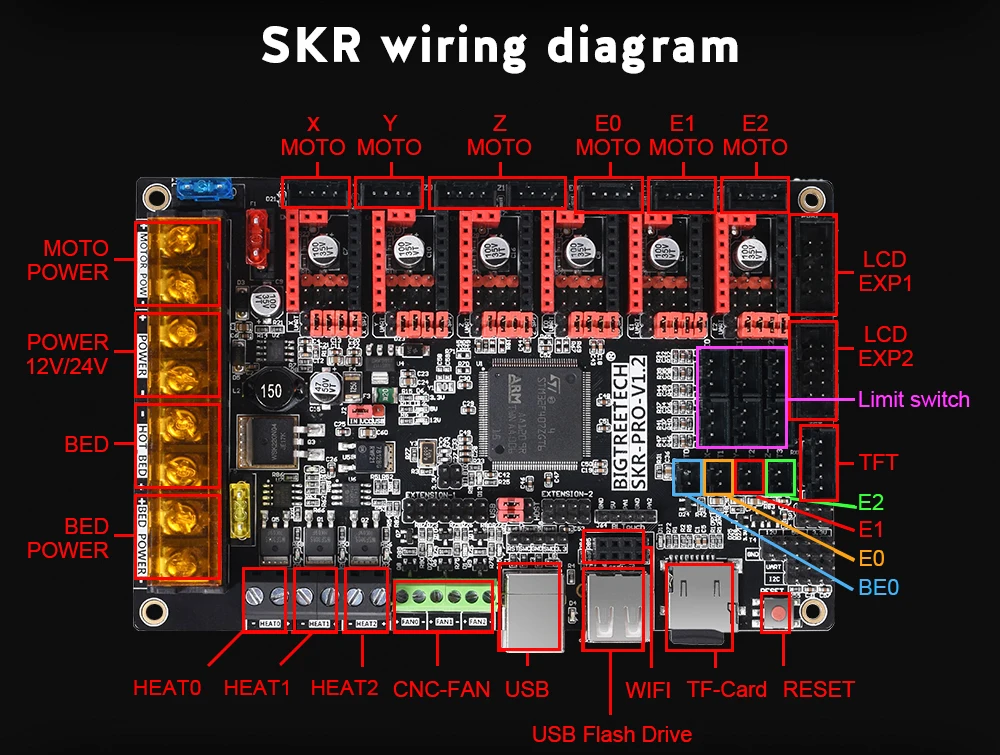
Wood-based filaments are typically a composite that combines a PLA base material with wood dust, cork, and other powdered wood derivatives. Typically, the filament consists of around 30% wood particles, but the exact number may vary depending on the brand. The presence of these particles gives the 3D printed parts the aesthetics of real wood. This filament is also less abrasive compared to other composite filaments such as carbon-fiber filled and metal filled, since wood particles are much softer. There are some wood-like filaments on the market that only contain wood coloring, but no actual wood particles, so these typically have a very different look and feel. This guide will focus on wood infused PLA filaments since these are the most common, but you can use these tips as a starting point for other wood-based filaments as well.
- Wood-textured finish is aesthetically appealing
- Does not need any expensive wear resistant nozzles
- Aromatic and pleasant smelling
- Prone to stringing
- Smaller nozzles can end up with partial clogs over time
- May require a larger size nozzle
Hardware Requirements
Before 3D printing with wood filled filaments make sure your 3D printer meets the hardware requirements listed below to ensure the best print quality.
Bed
Temperature: 45-60 °C
Heated Bed Optional
Enclosure Not Required
Build Surface
Painter’s Tape
Glue Stick
Glass Plate
PEI
Extruder
Temperature: 190-220 °C
No special hotend required
Cooling
Part Cooling Fan Required
Best Practices
These tips will help you reduce the chances of common 3D printing issues associated with wood filaments such as clogging, oozing, and stringing.
Use Larger Nozzle Sizes
Due to the added wood particles in this plastic, standard 0.35 or 0.4mm nozzles can be challenging. The particles have a tendency to clump near the nozzle orifice, causing inconsistent extrusion or partial clogs. We recommend using a 0.5mm or larger diameter nozzle, as this significantly reduces the chances of clogging. It may also be a good idea to clear your nozzle regularly to remove any partial clumps that may have formed within the nozzle.
Fine Tune Your Retraction Settings
Optimizing the retractions for wood filaments can be challenging.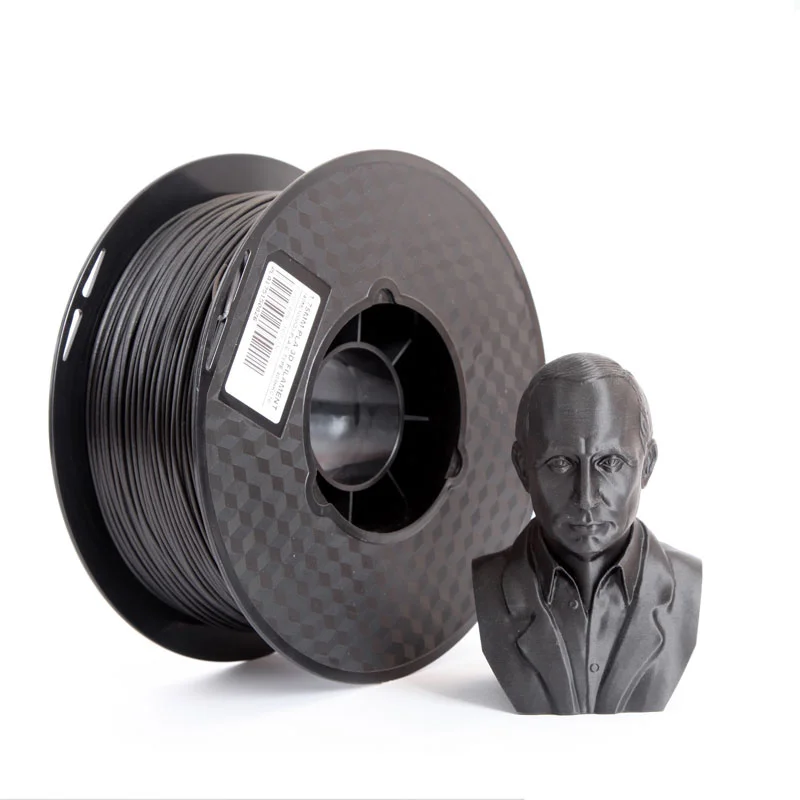 The wood particles in the plastic can interfere with the nozzle’s ability to maintain the suction pressure after a retraction. This means that the nozzle may ooze more than normal at the start and end of each printing segment. Simplify3D includes a unique feature called Coasting, which can be very useful for these situations. Coasting will automatically reduce the pressure in the nozzle as the extruder approaching the end of a printing segment. This way, when it needs to retract and move to the next location, there is far less pressure to deal with. This can significantly improve the surface finish of your models by removing the blobs at the end of a segment. You can also try using a negative value for the “extra restart distance” setting on the Extruders tab of your process settings. For example, a value of -0.1 or -0.2mm can help account for the extra oozing that takes place due to the wood particles. For more tips on how to combat blobs and optimize your retraction settings, please refer to our Print Quality Guide, which contains an entire section devoted to this issue: How to Reduce Blobs and Zits.
The wood particles in the plastic can interfere with the nozzle’s ability to maintain the suction pressure after a retraction. This means that the nozzle may ooze more than normal at the start and end of each printing segment. Simplify3D includes a unique feature called Coasting, which can be very useful for these situations. Coasting will automatically reduce the pressure in the nozzle as the extruder approaching the end of a printing segment. This way, when it needs to retract and move to the next location, there is far less pressure to deal with. This can significantly improve the surface finish of your models by removing the blobs at the end of a segment. You can also try using a negative value for the “extra restart distance” setting on the Extruders tab of your process settings. For example, a value of -0.1 or -0.2mm can help account for the extra oozing that takes place due to the wood particles. For more tips on how to combat blobs and optimize your retraction settings, please refer to our Print Quality Guide, which contains an entire section devoted to this issue: How to Reduce Blobs and Zits.
Minimize Stringing and Oozing
The wood particles in this material make it very difficult to maintain proper suction in the nozzle when moving between two locations. This frequently leads to oozing or stringing while printing. Thankfully, Simplify3D includes a feature that was designed for this exact purpose. If you go to the Advanced tab of your process settings, you can enable the “avoid crossing outline for travel movements” option. With this option enabled, the software will try to move within the interior of your model as much as possible. So instead of moving in a straight line from point A to B, it will chart an alternate route that keeps the extruder over top of the model to avoid stringing and oozing. This can frequently reduce the exterior movements by over 50% and can greatly improve your print quality.
Pro-Tips
- With certain wood filaments, using different extruder temperatures will produce slightly different colors for the final printed part.

Using this effect, you can setup different temperatures for different layers of your print in Simplify3D to create a realistic grain pattern on the surface of the printed part. - Wood filaments are very good at hiding the layer lines between different layers of your print. For simple shapes, you can likely print with a much larger layer height, since the lines between layers will be less visible.
- Many wood-based filaments can be easily post-processed using standard wood sand paper. This can further smooth and refine the surface finish of your prints.
Get Started with Wood Filled Filaments
Now that you’ve learned the basics for this material, here are some ideas to help you tackle your first project. We’ve included sample applications, a few projects you try, and popular filament brands we see from our customers.
Common Applications
- Household decorations
- Cosplay props
- Toys
Sample Projects
- Tree Stump Pencil Holder
- Frankenstein Switch Plate
- Wand
- Baby Groot
Popular Brands
- ColorFabb WoodFill, BambooFill, CorkFill
- Fillamentum Timberfill
- Hatchbox Woodfill
- FormFutura EasyWood
- Polymaker PolyWood
3D Printer Wood Filament - Gizmo Dorks
Gizmo Dorks
$29. 95
95
Size *
1.75mm 3mm (2.85mm)
Qty:
Share:
Add to Wishlist
Current stock: 0
3D Printing Wood Filament
Wood filament for 3D printing is a new FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) filament that was developed to print wooden-like objects. This filament is comprised of recycled wood combined with PLA filament and some binding polymers. Therefore, printing our wood filament is similar to printing PLA filament. However, our wood filament is slightly less viscous when compared to PLA or ABS filament during printing. Please extrude a little extra wood filament at the beginning of a print to prevent dry extrusion.
Because 3D wood filament has real wood fibers, the print temperature can be adjusted during the print to produce differing shades of color.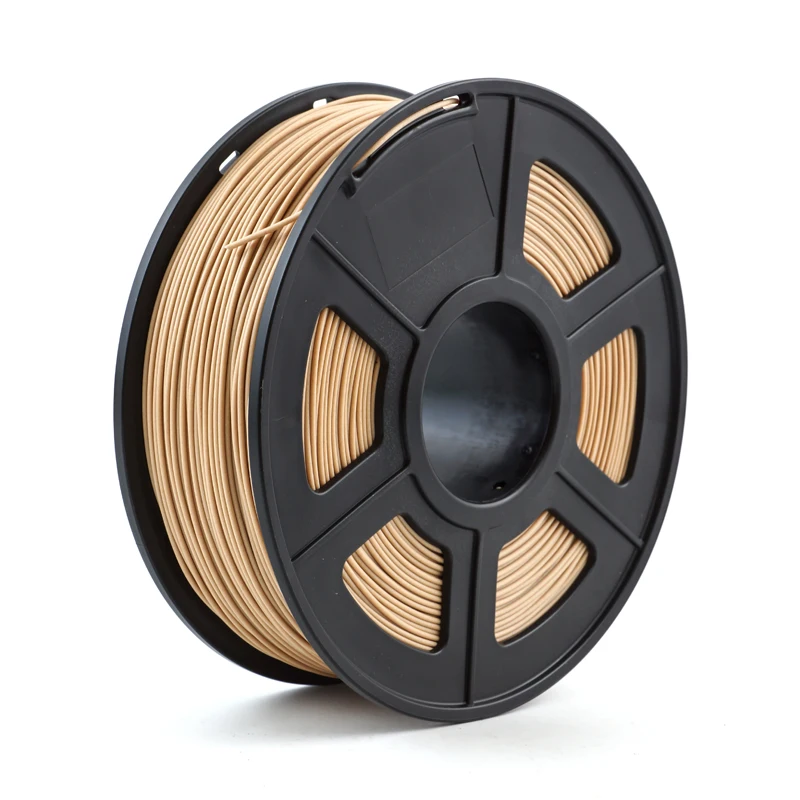 If the print temperature is adjusted by as little as 10 degrees mid-print, the resulting color will have a "grainy" look. Printing at lower temperatures will produce a brighter color, versus a print at higher temps will create a darker print.
If the print temperature is adjusted by as little as 10 degrees mid-print, the resulting color will have a "grainy" look. Printing at lower temperatures will produce a brighter color, versus a print at higher temps will create a darker print.
The finished wood print will appear rough and similar to MDF, Medium Density Fiberboard. Also, increasing the retraction setting during slicing will reduce "leakage." After printing please allow thirty to sixty minutes for the print to sit and settle. The 3D wood print will appear delicate and time will allow the print to settle properly.
3D Wood Filament Sizes
The 3D wood filament comes in 2 different sizes:
- 1.75mm Wood Filament
- 3mm (2.85mm) Wood Filament
3D Wood Filament Specifications
- Net weight: 1 kg
- Color: Natural
- Diameter: +/- 0.05mm
- Roundness: +/- 0.07mm
3D Wood Print Settings
- Hotend Temperature: 210 C - 230 C
- Heated Bed Temperature: 110 C - 120 C
- Nozzle Size: 0.
 5 mm or bigger (The larger nozzles help prevent clogs)
5 mm or bigger (The larger nozzles help prevent clogs) - Print Surface: Kapton tape or blue tape with glue stick
Your shopping cart
Account
Log in
Email Address *
Password *
Forgot password?
New Customer
Create an account with us and you'll be able to:
- Check out faster
- Save multiple shipping addresses
- Access your order history
- Track new orders
- Save items to your wish list
Create Account
Forgot Password
Fill in your email below to request a new password. An email will be sent to the address below containing a link to verify your email address.
An email will be sent to the address below containing a link to verify your email address.
Email Address *
Creative materials for 3D printing. The most incredible materials for 3D printer
Today, the main materials for printing on a 3D printer are PLA and ABS plastic. Both materials have long established themselves on the market and are used for printing on a 3D printer using layer-by-layer material build-up technology.
ABS plastic is a plastic formed by the polymerization of substances , such as acrylonitrile (A) with butadiene (B) and styrene (S).
PLA plastic , or as it is also called - biodegradable plastic is an aliphatic polyester with a monomer in the form of lactic acid. The materials for the production of such plastic are rapidly renewable resources - corn or sugar cane, that is, starch or cellulose.
Recently PVA-plastic has appeared on the market. The well-known PVA glue is transferred from a dry state to a liquid of the desired consistency, then melted using special equipment and formed into PVA threads or special granules that are used for 3D printing. Even newer material - Nylon - Resistant to a wide range of chemicals and solvents.
The materials discussed above are known to everyone involved in the 3D technology market. But this is not all materials. Manufacturers have taken a step forward, and are already using a wide variety of materials for printing on a 3D printer - clay, resin, seaweed, and more. other
Formlabs White Resin :
3D printing equipment manufacturer Formlabs introduces a new material - White Resin ("White Resin") . A year ago, the company already launched two new 3D printing materials, Clear Resin and Gray Resin.
The main feature of White Resin is the striking white and opaque color of and the exceptional smoothness of the printed object . In addition, new material is ideal for subsequent coloring.
White Resin will soon be available in the Formlabs online store at a price of $149 per liter, while (as of the end of summer 2014) it can only be bought in a kit with the company's 3D printer (the relevance of the offer and prices, just in case, check the manufacturer's website).
Titanium powder for 3D printing of auto parts0003 release of new cheap titanium powder , suitable for 3D printing of automotive parts and parts .
Until now, the most popular materials for 3D printing have been plastics, due to the high cost of the titanium powder production process. But recently company Metalysis has found a new cheap way to produce titanium powder , which can become the most demanded in the manufacture of equipment and machinery for the aerospace , defense and automotive industries.
To produce titanium powder, Metalysis uses rutile, which is electrolyzed directly into titanium powder. This method of obtaining a powder makes it possible to change, if necessary, the size of the powder granules, its purity, morphology and the proportion of the content of alloying elements in the composition.
The most amazing material of our time is graphene :
Graphene is a 3D printable material with incredible potential for applications in various fields (molecular programming, solar energy, etc.), a material that can change the lives of many people. In this regard, the Canadian research company Lomiko Metals Inc. announced the opening of a new special laboratory Graphene 3D Labs Inc., which will focus on the development of high-performance materials based on graphene.
Material reference: graphite or graphene is composed entirely of carbon atoms, but 1 mm of graphite contains about 3 million layers of graphene.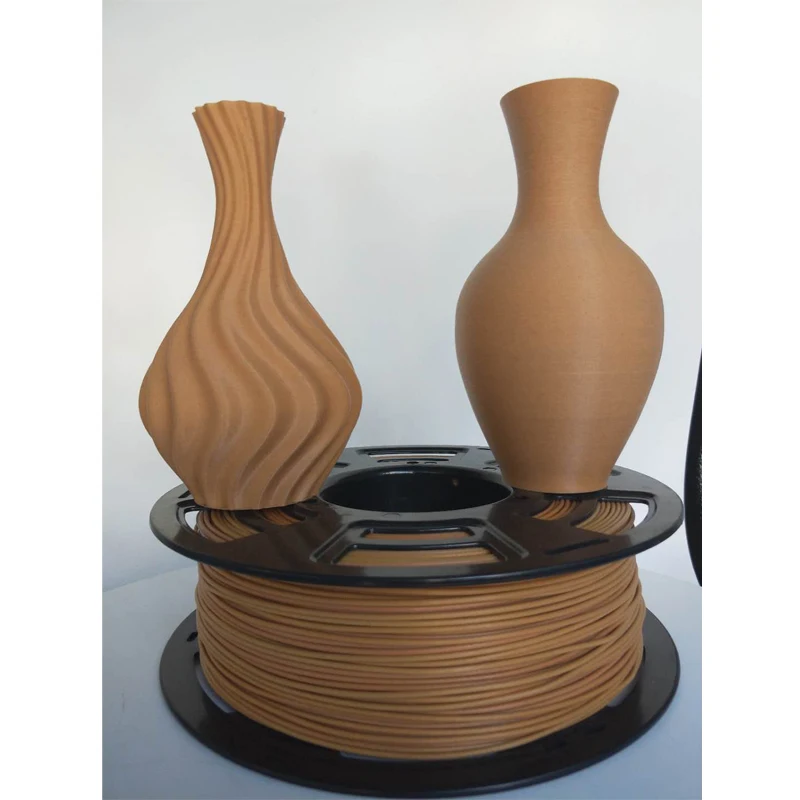 Graphite has a three-dimensional crystal structure, while graphene is a two-dimensional crystal 1 atom thick.
Graphite has a three-dimensional crystal structure, while graphene is a two-dimensional crystal 1 atom thick.
Wood filament for 3D printer :
Dutch 3D printing materials company colorFabb has released a new material - WoodFill wood filament.
WoodFill wood threads are available in two types - Fine (Delicate) and Coarse (Coarse). The main difference between these threads is the quality of the processing of wood fibers. WoodFill Fine uses finely ground wood particles, WoodFill Coarse is thicker - based on coarsely ground wood particles.
Wooden threads allow you to print beautiful and original vases, decorative elements and interior items. Finished objects are highly durable and produced in a short time. WoodFill threads consist of 30% pine wood fibers and 70% PLA plastic. Coils with wooden threads are already on sale at a price of 40 euros for a 750-gram spool.
Seaweed 3D Printer Filament :
Le Fabshop has introduced the world's first SWF filament, a "green" seaweed based filament , , for 3D printing applications.
The manufacturer estimates that the SWF material will be released to the market in the spring of 2014.
Three new materials from Proto-Pasta :
Recently, scientist Aaron Cram and mechanical engineer Dustin Cram launched the Proto-Pasta project, which developed three new materials for use in a desktop 3D printer: Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA (PLA reinforced with carbon fiber), High Temperature PLA (high temperature PLA) and Polycarbonate-ABS (ABS with polycarbonate alloy).
Compared to all known plastics - ABS and PLA, the new materials have improved performance and are affordable.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA is more heat resistant than regular PLA.
Polycarbonate-ABS (PC-ABS) has high elasticity and bending strength.
Stereolithography rubber material , easy to clean, affordable.
Silk based 3D printing material :
The new material was created from raw silk. Raw silk has been sourced from sustainable sources and treated with epoxy resin. Silk based material is flexible and strong, thin and light, ideal for 3D printer applications.
Polished and raw brass as material for 3D printer :
Shapeways has introduced two new materials to the world at once - Polished Brass and Raw Brass.
Polished Brass is a material with a smooth, glossy bright yellow surface. Products printed with its help, then covered with 22 carat gold, are almost indistinguishable from real gold jewelry.
Raw Brass is ideal for 3D printing antique or antique style objects, it is also useful for jewelry prototyping and functional parts.
Soft plastic from Shapeways :
Shapeways has developed a new soft plastic, Elasto Plastics, for use in the production of summer footwear. Elasto Plastics has a milky white color, the material is very flexible, has an uneven grainy surface, and is quite strong.
Elasto Plastics has a milky white color, the material is very flexible, has an uneven grainy surface, and is quite strong.
Clear resin for 3D printer :
Clear resin was developed by specially for stereolithography , based on the technology of layering transparent resin and strengthening the layers with a special laser. This resin is used by to make detailed and fairly complex models.
Clear resin available online for $149 per litre.
3D printing clay covered with chia grass.
"Clay" for 3D printing was obtained by mixing - water, soil and seeds.
Follow our blog posts and you will be aware of all the most significant news in the field of 3D printing!
And, if necessary, KOLORO will help you design, visualize and print any 3D object, regardless of the given complexity! KOLORO is always glad to constructive cooperation! You can contact us by phone: +38-(057)-760-26-05, +38-(099)-618-87-50.
LAYWOOD-D3 allows you to print wood products
Archive
Subscribe author
Subscribe
Don't want
Thanks to this revolutionary fresh material, you can print objects that smell like wood and wood!
LAYWOOD-D3 3D printer consumable is in the form of 1.75mm thick filament. To be precise, this material is a mixture of wood and a binder (polymer). This "polymer-wood" alloy allows the 3D printer to use LAYWOOD-D3 like any other plastic filament - only this time the objects look like they are carved from wood.
The LAYWOOD-D3 consumable was designed for 3D printers based on RepRap technology. The wooden consumable melts at a temperature of 175 ° C, and after printing, the recreated objects will not only smell like wood, but will also feel as unique to the touch as any other product made from sawdust or wood - the only difference is that the user will not be able to drive thorn in the finger. Depending on the temperature level (we do not recommend printing if it exceeds 250 C°), the product will have different shades of brown.
Depending on the temperature level (we do not recommend printing if it exceeds 250 C°), the product will have different shades of brown.
At the moment, the cost of a wooden thread is 20.95 euros per 250 grams. Let's take a look at the specifications:
- 40% recycled wood
- Object does not deform after printing
- Smells like wood
- Flexible material
- Shades of brown change with temperature
The article was prepared exclusively for 3Dtoday.ru
Follow author
Follow
Don't want
Article comments
More interesting articles
6
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
One of the latest developments in 3D printing devices is the advent of extruders.