Practical 3d printers brian evans
Practical 3D Printers By Brian Evans | Used | 9781430243922
- Home
- Non-Fiction Books
- Computing and I.T.
- Computer hardware
Reviews:
Trustpilot
Condition - Good
Only 1 left
Good
Summary
Desktop or DIY 3D printers are devices you can either buy preassembled as a kit, or build from a collection of parts to design and print physical objects including replacement household parts, custom toys, and even art, science, or engineering projects.
Practical 3D Printers Summary
Practical 3D Printers: The Science and Art of 3D Printing by Brian Evans
Desktop or DIY 3D printers are devices you can either buy preassembled as a kit, or build from a collection of parts to design and print physical objects including replacement household parts, custom toys, and even art, science, or engineering projects. Maybe you have one, or maybe you're thinking about buying or building one.
Practical 3D Printers takes you beyond how to build a 3D printer, to calibrating, customizing, and creating amazing models, including 3D printed text, a warship model, a robot platform, windup toys, and arcade-inspired alien invaders. You'll learn about the different types of personal 3D printers and how they work; from the MakerBot to the RepRap printers like the Huxley and Mendel, as well as the whiteAnt CNC featured in the Apress book Printing in Plastic.
You'll discover how easy it is to find and design 3D models using web-based 3D modeling, and even how to create a 3D model from a 2D image. After learning the basics, this book will walk you through building multi-part models with a steampunk warship project, working with meshes to build your own action heroes, and creating an autonomous robot chassis. Finally, you'll find even more bonus projects to build, including wind-up walkers, faceted vases for the home, and a handful of useful upgrades to modify and improve your 3D printer.
About Brian Evans
A bio is not available for this author.
Table of Contents
Ch. 1: A World of 3D Printers
Ch. 2: 3D Printer Toolchain
Ch. 3: Calibrating Your Printer
Ch. 4: 3D Models From The Cloud
Ch. 5: 3D Haiku
Ch. 6: Steampunk Warship
Ch. 7: Action Hero Mashups
Ch. 8: Mini Sumo Projetcs
Ch. 9: Bonus Round 1: More Projects
Ch. 10: Bonus Round 2: Upgrades
Appendix A: Printing Tips
Appendix B: Resources
Additional information
Sku
GOR007612397
ISBN 13
9781430243922
ISBN 10
1430243929
Title
Practical 3D Printers: The Science and Art of 3D Printing by Brian Evans
Author
Brian Evans
Condition
Used - Good
Binding type
Paperback
Publisher
Springer-Verlag Berlin and Heidelberg GmbH & Co. KG
KG
Year published
20120828
Number of pages
332
Prizes
N/A
Cover note
Book picture is for illustrative purposes only, actual binding, cover or edition may vary.
Note
This is a used book - there is no escaping the fact it has been read by someone else and it will show signs of wear and previous use. Overall we expect it to be in good condition, but if you are not entirely satisfied please get in touch with us
Customer Reviews - Practical 3D Printers
Trustpilot
Wob sells used books online to over 190 countries worldwide.
You can connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or through our Blog.
Trustpilot
Practical 3D Printers by Brian Evans (ebook)
This title will be released on .

This eBook is no longer available for sale.
This eBook is not available in your country.
About the eBook
Desktop or DIY 3D printers are devices you can either buy preassembled as a kit, or build from a collection of parts to design and print physical objects including replacement household parts, custom toys, and even art, science, or engineering projects. Maybe you have one, or maybe you're thinking about buying or building one.
Practical 3D Printers takes you beyond how to build a 3D printer, to calibrating, customizing, and creating amazing models, including 3D printed text, a warship model, a robot platform, windup toys, and arcade-inspired alien invaders. You'll learn about the different types of personal 3D printers and how they work; from the MakerBot to the RepRap printers like the Huxley and Mendel, as well as the whiteAnt CNC featured in the Apress book Printing in Plastic.
You'll discover how easy it is to find and design 3D models using web-based 3D modeling, and even how to create a 3D model from a 2D image. After learning the basics, this book will walk you through building multi-part models with a steampunk warship project, working with meshes to build your own action heroes, and creating an autonomous robot chassis. Finally, you'll find even more bonus projects to build, including wind-up walkers, faceted vases for the home, and a handful of useful upgrades to modify and improve your 3D printer.
Show more
Show more
In The Press
About the Author
- ;
- ISBN:
- Edition:
- Title:
- Series:
- Author:
- Imprint:
- Language:
- Number of Pages: [disclaimer] Page count shown is an approximation provided by the publisher. The actual page count will vary based on various factors such your device's screen size and font-size.
Download file formats
This ebook is available in file types:
This ebook is available in:
After you've bought this ebook, you can choose to download either the PDF version or the ePub, or both.
DRM Free
The publisher has supplied this book in DRM Free form with digital watermarking.
Required software
You can read this eBook on any device that supports DRM-free EPUB or DRM-free PDF format.
Digital Rights Management (DRM)
The publisher has supplied this book in encrypted form, which means that you need to install free software in order to unlock and read it.
Required software
To read this ebook on a mobile device (phone or tablet) you'll need to install one of these free apps:
- Ebook Reader (recommended)
- PocketBook (iOS / Android)
- Aldiko Reader (iOS / Android)
- Bluefire Reader (paid app)
To download and read this eBook on a PC or Mac:
- Adobe Digital Editions (This is a free app specially developed for eBooks. It's not the same as Adobe Reader, which you probably already have on your computer.)
Limits on printing and copying
The publisher has set limits on how much of this ebook you may print or copy. See details.
- {{ format_drm_information.format_name }} unrestricted {{ format_drm_information.format_name }} {{format_drm_information.page_percent}}% pages every day{{format_drm_information.interval}} days {{ format_drm_information.format_name }} off
Read Aloud
- {{ read_aloud_information.format_name }} on {{ read_aloud_information.format_name }} off
3D printer - technology of the future
References:
Mikhailova, A. E. 3D printer is the technology of the future / A. E. Mikhailova, A. D. Doshina. - Text: direct // Young scientist. - 2015. - No. 20 (100). - S. 40-44. — URL: https://moluch.ru/archive/100/22467/ (date of access: 12/23/2022).
This article will focus on new technology for creating objects and objects - 3 D printer. The history of occurrence is described, the basic principles and device operation technologies are indicated. 3 D printer application in Rostov-on-Don, and highlights the problems and prospects for using this technology in 0014 different areas of life.
The history of occurrence is described, the basic principles and device operation technologies are indicated. 3 D printer application in Rostov-on-Don, and highlights the problems and prospects for using this technology in 0014 different areas of life.
Keywords: 3 D printer, 3 D printing, stereolithography, SLA technology, SLS technology, DLP technology, EBM technology.
3D entered our everyday life at the beginning of the new millennium. Naturally, we associate this definition with film art or animation. But this technology covers much more spectrums of our life. So, what is a 3D printer, and what is printing on such a device? nine0009
A 3D printer is a device that creates an image in three dimensions. But first, let's take a look at the history.
History of
3D printing technology has been around since 1984. CharlesHull has developed 3D printing technology to create objects using digital data. In 1986, this technique was patented and given the name stereolithography.
The same company, CharlesHull, developed the first industrial 3D printer. And at 19In 1988, 3DSystem developed a 3D printer for printing at home - SLA-250.
Solidscape was founded in 1993. It starts mass production of inkjet-based 3D printers at low cost.
And finally, in 2005, the first color 3D printer appears - the Spectrum Z510. The credit for this advancement in the development of 3D printers belongs to ZCorporation (ZCorp).
nine0080 Working principle 3 D printing
The principle of forming a figure from three-dimensional printing is called additive (from the word Add (English) - to add). To begin with, a computer model of the future object is created. This can be done either with the help of a three-dimensional graphic editor of a CAD system (3D StudioMax, SolidWorks, AutoCAD), or by scanning the entire object in 3D. Then, with the help of a special software product, it splits the scanned object into layers and generates a set of commands that will determine the sequence in which layers of material will be applied during printing. nine0009
This can be done either with the help of a three-dimensional graphic editor of a CAD system (3D StudioMax, SolidWorks, AutoCAD), or by scanning the entire object in 3D. Then, with the help of a special software product, it splits the scanned object into layers and generates a set of commands that will determine the sequence in which layers of material will be applied during printing. nine0009
Further, the 3D printer forms the object in layers, gradually applying portions of the material (Fig. 1). By positioning the print head on an X and Y coordinate system, the printer deposits material layer by layer according to a simulated electronic circuit. When the platform is moved one step along the Z axis, the construction of a new level of the object begins.
Rice. 1. Printing with a 3D printer
For printing, metal alloys, plastic, paper, photopolymers, mineral mixtures can be used as a material in additive manufacturing. Some types of 3D printers are able to work simultaneously with different materials, both in terms of properties and color. nine0009
nine0009
There are a lot of 3D printing technologies. They differ in the principle of formation of layers and their connections. Consider the main production technologies.
Core Technologies (SLA, SLS, DLP, EBM, HPM)
Printing on 3D printers can be done in different ways, depending on the material used.
SLA technology. This technology allows the fastest construction of objects. The technology uses a photopolymer, on which a laser beam is directed, after which the material hardens. After hardening, the product can be easily processed (glued, painted, etc.). nine0120 SLS technology. Represents the sintering of powder reagents under the influence of a laser beam. This is one of the technologies that allows the production of molds for metal and plastic casting.
DLP technology. This is a relatively new technology that uses stereolithographic printing machines. Printers of this type use digital light processing. To create three-dimensional figures, this technology uses photopolymer resins and a DLP projector. nine0009
To create three-dimensional figures, this technology uses photopolymer resins and a DLP projector. nine0009
EBM technology. This technology uses electron beam melting to create three-dimensional objects. For the layer-by-layer deposition of high-precision parts, a special material was developed - metal clay. This material is made from a mixture of organic glue, metal shavings and water.
HPM technologies. Enables the production of final models from structural and high performance thermoplastics. This is the only technology that provides mechanical, thermal and chemical strength of parts. nine0009
Nowadays, another interesting device has appeared that is used for manual printing - pens for drawing 3D objects. Pens are made in the same way as printers. The plastic thread is fed into the pen, where it melts to the right temperature and is squeezed out through a small nozzle.
Applications 3 D printing
- Building.
 There is an assumption that in the future the process of erecting buildings will be much faster thanks to 3D printing. nine0146
There is an assumption that in the future the process of erecting buildings will be much faster thanks to 3D printing. nine0146 - The medicine. Thanks to 3D printing, doctors have been able to create replicas of the human skeleton. 3D printers are widely used in dental prosthetics.
- Architecture and design. Creating layouts of interior elements, buildings and districts allows you to evaluate the ergonomics, functionality and appearance of the prototype.
- Marketing and advertising allow you to demonstrate the benefits of a new product. nine0146
- Education. 3D models are excellent visual materials for teaching at all levels of education.
- Automotive. Such a method as 3D modeling allows you to test the car at the development stage.
- Modeling. Production of packaging materials, toys and souvenirs.
- Light industry. Manufacture of various elements of consumer goods. nine0146
- Manufacture of clothes and shoes.
 Such clothes and shoes are used only at shows. The material here is polyurethane, rubber and plastic.
Such clothes and shoes are used only at shows. The material here is polyurethane, rubber and plastic. - Jewelry business. 3D modeling technologies allow you to create full-fledged products from metal powder.
- History and anthropology. Models are created on the basis of archaeological finds and allow assessing the reliability of scientists' guesses. nine0146
In all other areas not mentioned above, 3D modeling is gradually finding its way. Slowly but surely, it is crowding out other ways of representing an object.
Study of using 3 D printer in city of Rostov-on-Don
We conducted a market research for 3D printing services in the city of Rostov-on-Don.
Here are the results: There are about 10 3D printing service points in this city, as well as several 3D scanning points. About 80% of customers deal with the tasks of manufacturing accessories, parts for personal projects. 8% try this technology by heart, the remaining 7% use 3D printing directly for work. Also, there is another group that uses 3D printing to create global personal projects. This group is only 5%. This percentage includes such a project as a “touching museum”. A group of students from Rostov-on-Don plans to create a network of museums in Russia using 3D printing and crowdfunding (crowd funding). The idea is to print on a 3D printer the world's works of art that can be touched not only by ordinary people, but also by those who have visual impairments. nine0009
8% try this technology by heart, the remaining 7% use 3D printing directly for work. Also, there is another group that uses 3D printing to create global personal projects. This group is only 5%. This percentage includes such a project as a “touching museum”. A group of students from Rostov-on-Don plans to create a network of museums in Russia using 3D printing and crowdfunding (crowd funding). The idea is to print on a 3D printer the world's works of art that can be touched not only by ordinary people, but also by those who have visual impairments. nine0009
To find out people's awareness of 3D printing, a survey was conducted among residents of Rostov-on-Don.
A different age contingent and different social groups were interviewed. As a result, according to a survey of 348 people, data was obtained: many residents (92%) are aware of the existence of 3D printing. Young people under the age of 30-35 are more aware in this area. Older residents of the city, if they know about such technology, do not dare to try it. Only 19% of the population knows that 3D printing exists not only from plastic, but also from metal. 45% of respondents are aware of the capabilities of a 3D printer and printing materials. But at the same time, only 15% of respondents used this service at least once in their lives, of which 3% used it often. Which suggests that 3D printing is not yet in great demand. But 80% of those respondents who had not heard of 3D printing became interested in this technology and expressed their desire to learn more about this technology. About 51% of respondents had heard of a 3D pen, but the majority had not used it. But quite a lot of people are ready to entrust their lives to new technologies. 50% of those surveyed would trust their lives to such technology. nine0009
Only 19% of the population knows that 3D printing exists not only from plastic, but also from metal. 45% of respondents are aware of the capabilities of a 3D printer and printing materials. But at the same time, only 15% of respondents used this service at least once in their lives, of which 3% used it often. Which suggests that 3D printing is not yet in great demand. But 80% of those respondents who had not heard of 3D printing became interested in this technology and expressed their desire to learn more about this technology. About 51% of respondents had heard of a 3D pen, but the majority had not used it. But quite a lot of people are ready to entrust their lives to new technologies. 50% of those surveyed would trust their lives to such technology. nine0009
Details are shown below.
Problems and prospects for using this technology in different areas of life
3D printing technology is not yet perfect.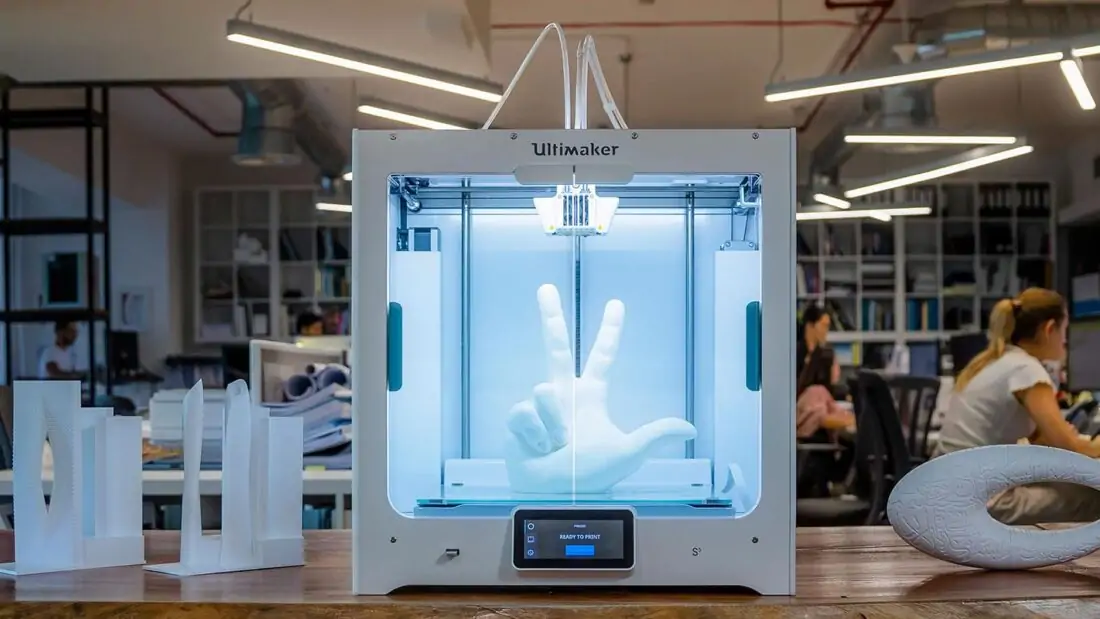 There are several problems that can lead to some rather unexpected results. For example, a printer printing several parts at the same time can print them linked together. Another problem is that due to the layered construction of the part, the lower layer may not withstand the weight of the upper layers, and then the part is destroyed. Before printing, it is necessary to carefully work out a computer model so that the result is the way it is expected to be. nine0009
There are several problems that can lead to some rather unexpected results. For example, a printer printing several parts at the same time can print them linked together. Another problem is that due to the layered construction of the part, the lower layer may not withstand the weight of the upper layers, and then the part is destroyed. Before printing, it is necessary to carefully work out a computer model so that the result is the way it is expected to be. nine0009
3D printing is the technology of the future. Every day this printing technology finds itself in new areas. Such a service is interesting in the field of entertainment: anyone can make a scan of their body and get their own miniature copy. In the field of medicine, the manufacture of shoes, insoles, and headphones is gradually coming into use, ideally repeating the shape of certain parts of the body or detailed parts for the functioning of the body, for example, a section of the human cranial cortex. The size of parts is gradually increasing, and the choice of materials for printing is also expanding. nine0009
nine0009
Conclusion
Summing up, it is worth noting that the use of 3D printers allows you to completely eliminate manual labor and the need to make drawings and calculations on paper, and eliminate the identified shortcomings not in the process of creation, but directly during development. In creating models using a 3D printer, there is no restriction on design and complexity of the form, which allows you to fully use your imagination and make an individual and original product. Products are very light, and at the same time their production time is minimal. nine0009
This technology is only gaining momentum in its development and distribution. This can be seen in the city that was chosen for the study - Rostov-on-Don. Most of the orders belong to the group of personal interest in the new technology and nothing more. But it is also impossible not to notice that the process of using 3D printing technology in large and useful projects for society is already underway.
Undoubtedly, this technology is the technology of the future.
List of literary sources nine0009
Literature:
- Brian Evans, Practical 3D Printers: The Science and Art of 3D Printing. Press, 2012.
- I. Canesa, S. Fonda, M. Zenaro, Accessible 3D Printing for Science, Education and Sustainability. The Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical Physics, 2013.
- Christopher Barnat. 3D printing: the third industrial revolution. 2013. nine0146
- 3D printer. [Electronic resource]. Access mode - www.printbox3d.ru.
- 3D printers. [Electronic resource]. Access mode — www.magnum3d.ru
Basic terms (automatically generated) : printing, printer, Rostov-on-Don, DLP, EBM, SLA, SLS, 3D printing, HPM, history of occurrence.
3D printers and 3D pens
HOW DO 3D pens AND 3D PRINTERS WORK AND WHAT DO YOU NEED? nine0081
Devise. discovery.
discovery.
“Maybe you guys are not mature yet. But your kids will love it.”
“Wow!” - you will say when you find out that 3D printers are actively used in medicine. At the moment, scientists are already able to make some organs. The simplest ones (ears, nose, face) can be printed, while the complex ones (heart, liver, kidneys) are still in development. Is this not the future?
Technologies in the 21st century are developing rapidly, you will not have time to get up from the couch, as something new will come out. Now you won’t surprise anyone with the abbreviation “3D”, but not everyone knows that the First Department of Computer Graphics was opened back in 1960s Ivan Sutherland and David Evans at the University of Utah. Sutherland created the program that was the prototype of all modern 3D editors and CAD systems - Sketchpad.
(Ivan Sutherland and David Evans)
Today you can watch movies in 3D at home on your 8K TV, although until recently 3D was only available in theaters.
3D technologies have taken over the world and penetrated into the most diverse areas: 3D image, 3D model, 3D printer and even 3D pens. We will dwell on the last two points in more detail. What do you know about 3D printers and pens? Nothing? We didn’t know anything either, but we figured it out and are ready to share it with you. ISI Media Center is online! Go! nine0009
3D pens - SIMPLE AND COMPLEX
3D pen is something you never dreamed of as a child. This is what modern children beg from their parents in the same way as you once begged for an ordinary kinder.
Where did it come from? In 2012, inventors Peter Dilworth, Daniel Cowen and Maxwell Baugh invented a prototype 3D pen. The 3d pen they created in one day was tested, and it took about 14 hours to create the first 3d object. Realizing that 14 hours is long enough, they improved their prototype and brought 3Doodler to the market. nine0009
nine0009
(photo by Peter Dilworth and Maxwell Baugh)
What is it for? For creativity, for developing activities with children, for correcting models printed on a 3D printer, and even for small household repairs of plastic items.
How does it work? The main material is PLA and ABS plastic: the first is made from natural products, the second is made from petroleum.
What are 3D pens? Cold and hot. The first ones are painted with photopolymers, fast-hardening resins. The latter use a coil with polymer alloys, which, when melted, acquire the desired shape. nine0009
Designation 3 D -handle
Let's start with the fact that 3D pens are not as powerful as you might think. You won't be able to print organs or build houses with them, although the prospect is good. 3D pens are designed to create various shapes of all sizes and colors. They can be used to make small figurines for games, small decorations, and even parts of cosplay costumes!
They can be used to make small figurines for games, small decorations, and even parts of cosplay costumes!
Large selection of 3D pens for every taste:
1. 3D MyRiwell Pen without display is one of the most inexpensive pens that can be a great tool for a creative person or a great gift for a child.
The pen allows you to draw separate parts of the figure on a plane with ABS plastic, and then combine them into three-dimensional objects. Also, any 3D pen can be used as a glue gun to hold together small parts in various miniature hand-made assemblies.
2. MyRiwell RP100B 3D pen with LCD display is the next step in the development of Myriwell Pen.
This pen differs from the younger model by the presence of a display showing the mode and the ability to draw not only ABS, but also PLA. Working with PLA provides a wide field for creativity in decorating various objects with three-dimensional patterns; this plastic adheres especially well to fabric.
Working with PLA provides a wide field for creativity in decorating various objects with three-dimensional patterns; this plastic adheres especially well to fabric.
3. Creopop Pen Creopop is the first 3D pen to feature photopolymerization technology. nine0009
There are no heating elements and the material coming out of it does not have a high temperature, which eliminates the possibility of burns and inhalation of evaporating plastic. Plastic polymerizes under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. A cartridge with a liquid polymer is inserted into the pen - no more filament threads sticking out of the 3D pen will hinder your movements in a fit of creativity. This model does not have any wires at all. Due to the absence of heat in the working process of this 3D pen, its power consumption is low enough to operate from the built-in battery. The properties of the materials used allow you to get an impressive result. nine0264
3D pens are not as simple as they seem at first glance. This is not a tool for entertainment, but is a way to express 's creativity and create amazing new things. If you have never tried to create something with a 3D pen, be sure to correct yourself! We are sure you will like it!
This is not a tool for entertainment, but is a way to express 's creativity and create amazing new things. If you have never tried to create something with a 3D pen, be sure to correct yourself! We are sure you will like it!
It's time to move on to
3D PRINTERS
New generations of 3D printers come out every year, specialists use them to create everything that is enough for imagination, for example, various parts for cars, medical devices, build residential buildings printed on printer, and even recreate human organs! nine0009
What is this miracle machine? 3D printer - external computer device, which is nothing more than a machine tool with numerical control (CNC), designed to quickly produce prototypes of products designed on a PC by layer-by-layer printing.
The concept of 3D printing was invented in the 1970s, but the first experiments in this field date back to 1981. A patent application for rapid prototyping technology was filed by Dr. Kodama in Japan on May 1980 years. He was the first to describe the method of creating an object using layering, creating an apparatus for stereolithography. Ironically, Dr. Kodama was unable to register the patent because he did not provide a full description of the patent.
A patent application for rapid prototyping technology was filed by Dr. Kodama in Japan on May 1980 years. He was the first to describe the method of creating an object using layering, creating an apparatus for stereolithography. Ironically, Dr. Kodama was unable to register the patent because he did not provide a full description of the patent.
(Dr. Kodam)
In 1986, the first stereolithography device (SLA) patent was issued. This patent belonged to Charles Hull, who invented the SLA machine in 1983.
(Charles Hull)
Do you FDM me? And if "SLA"?
Two old 3D printer technologies.
“Difficult” is what many people think about how 3D printers work. In fact, the printing process is quite simple. There are two main technologies: FDM and SLA. Only threads and resin are needed to work.
In fact, the printing process is quite simple. There are two main technologies: FDM and SLA. Only threads and resin are needed to work.
(filament and resin printers)
The first use of thermoplastic threads is called FDM. The technology lies in the fact that a person inserts a thread into the upper part of the printer (extruder), it becomes soft and flexible. The thread is held on by a structure that moves it in the right direction. It turns out that the user's task is only to drive in the code that must be written in advance, and put the thread. The 3D printer will take care of the rest of the work.
In the second case (SLA), the magic of resin occurs, but not wood, but complex, polymeric. First you need to pour the resin into the container, then enter the code and that's it. The figure will be made by a laser, after which it will be necessary to wash the resulting figure and let it cool with ultraviolet light. Ready! nine0009
Ready! nine0009
(FDM 3D printer, reel of material and a couple of 3D prints)
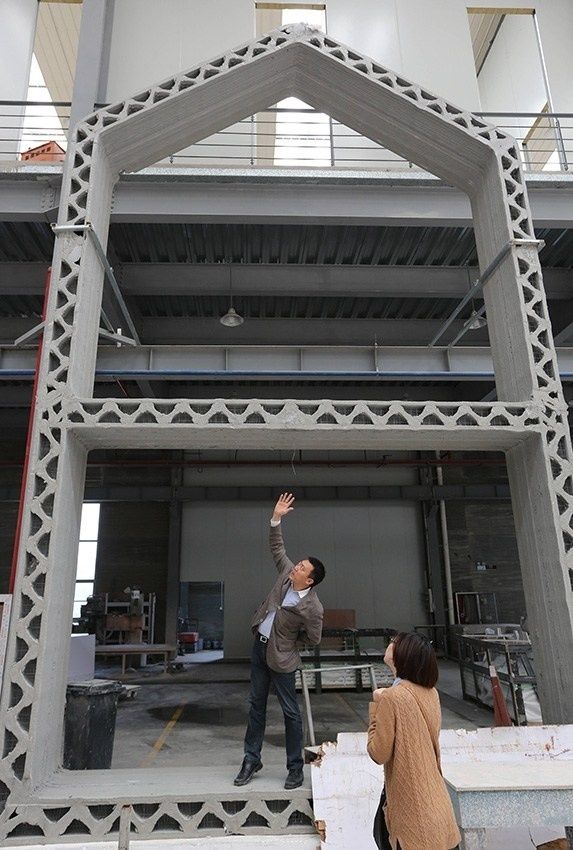
The house that… It's hard to believe, but the house printed on the printer is real. In it you can safely spend time, move, live and work. The site presents 10 real buildings printed on a printer.
Mechanical engineering. The use of 3D printing in the technological process solves many problems. The product can be made cheaper and many times faster. Now creating complex parts is not a problem. You draw the model you need, set the code and the product is ready. The human factor is minimized, all the work is done by the machine. A 3D printer is no longer a luxury, it is a complete tool for any production process. nine0009
Theater and cinema are also on point: a 3D printer can create anything!
How can printers and art be connected? At first we did not understand either, but then we learned that the connection could be the most direct.