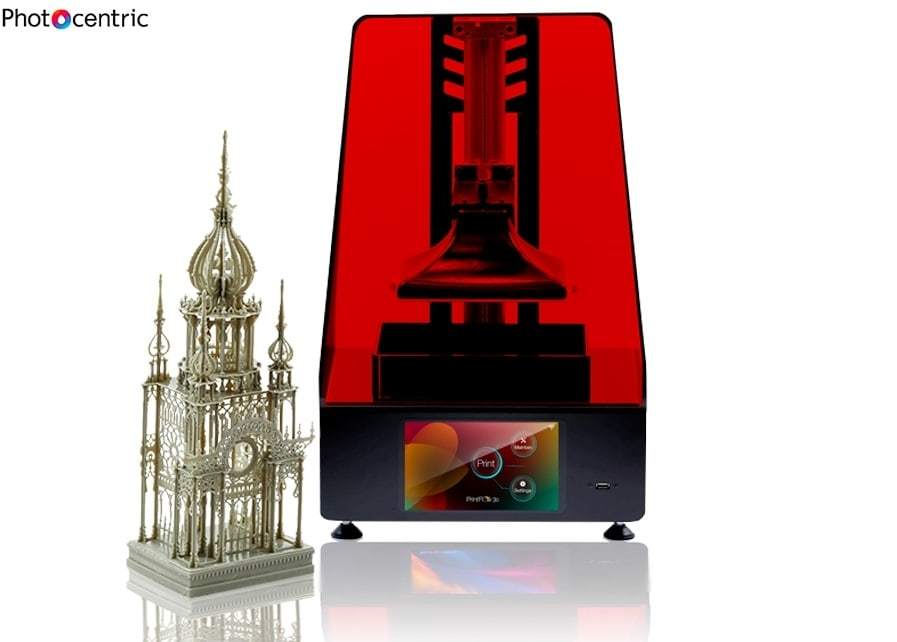
Liquid printer 3d
9 Best Liquid 3D Printers In 2022
3D printing has become more than just a hobby for a lot of users now. Before, you would only find such machines in mass production companies and professional workplaces as 3D printers used to be very expensive, and so were the materials used for printing. But nowadays, you can easily find a 3D printer around the price point of a premium photo printer, if not cheaper.
And with the advancement in 3D printing technology, you can now install a small unit right on your desk and use it for creative applications. One such option for 3D printers is a liquid 3D printer which is preferred by a lot of users for basic applications. Here are some things that matter the most for a liquid 3D printer.
- Printing Size: The supported printing size of a 3D printer is one of its most crucial properties since it directly affects its application and compatibility with the user’s request. When you are looking for a liquid 3D printer, you should make sure that you go with an option that can generate prints of the size that you need.
While some machines are designed for basic miniature models, some can generate larger options with better details.
- Screen: The monochrome screen present below the vat of resin liquid is the most important part of a liquid 3D printer. In fact, it is the only part of a 3D printer that is responsible for the accuracy and quality of the print. Therefore, you have to thoroughly check the parameters of the display before buying the liquid printer. It includes factors like size, resolution, contrast ratio, and other similar features of the display.
- Printing Duration: One of the main reasons that people are preferring liquid 3D printers over other types of rapid prototyping machines is their faster output speed. Unlike a filament 3D printer that melts the filament to generate the printer layer by layer, a liquid 3D printer offers a continuous printing pace for faster prints. Still, different models for a liquid 3D printer differ in terms of printing speed and you should check that out before finalizing your choice.

Today, we are bringing you the best liquid 3D printers available on the market. These are the best options that offer a satisfying 3D printing experience, high production quality, and highly affordable running costs. These options are selected based on the features specified above and a few more that can affect the performance as well as the compatibility of the liquid 3D printer according to your requirements. We will also talk about a few more important factors about the best liquid 3D printer in our “Buying Guide”. But before that, let’s take a look at the best options that we have for a liquid 3D printer.
Outline
Best Liquid 3D Printers 2022
| Best Liquid 3D Printer | Monochrome Screen Size | Printing Size | Compatible Material | Buy Now |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANYCUBIC Photon Mono Resin 3D Printer | 6.23 Inches | 5.19 x 3.14 x 6.49 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| ELEGOO Resin 3D Printer | 6. 6 Inches 6 Inches | 5.647 × 3.52 × 6.8 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| Comgrow Resin 3D Printer | 5.96 inches | 5 x 3.1 x 6.3 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| PHROZEN Sonic Resin 3D Printer | 5.5 Inches | 4.7 x 2.6 x 5.1 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| LONGER Orange 30 3D Printer | -- | 4.72 x 2.68 x 6.69 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| Voxelab Resin 3D Printer | 6.08 Inches | 5.11 x 3.70 x 6.10 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| Creality 3D Resin Printer | 5 Inches | 5 x 3.14 x 6.29 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| LeeCHee Resin 3D Printer | 8.9 Inches | 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 Inches | Resin | Check On Amazon |
| Uniformation 3D Resin Printer | Build Plate 10. | Tool Size 9 x 5.9 x 10.2 Inches | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Resin | Check On Amazon |
Best Liquid 3D Printer Reviews
1. ANYCUBIC Photon Mono Resin 3D Printer
If you don’t have any prior experience with 3D printers and this is your first time buying one, we will strongly suggest going with a tried and tested option like the one made by ANYCUBIC.
The ANYCUBIC Photon Mono Resin 3D Printer is our first choice for this list of the best liquid 3D printers and it also happens to be the most popular option on the market right now. The ANYCUBIC Photon Mono Resin 3D Printer is a 4K printer and it has a 6.23 inches monochrome display, allowing compatible printing sizes of up to 5.19 x 3.14 x 6.49 inches, making a lot of complicated designs possible.
The LCD display on the ANYCUBIC Photon Mono Resin 3D Printer is almost 29% larger than many other options available around this price point. As for the printing speed, ANYCUBIC is promising a printing speed of merely 1. 5 seconds per layer which is quite difficult to find with such high resolution. And since the display is not an RGB one, you can expect up to 4 times better longevity.
5 seconds per layer which is quite difficult to find with such high resolution. And since the display is not an RGB one, you can expect up to 4 times better longevity.
Best Features
- Comes with a 6.23 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 5.19 x 3.14 x 6.49 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Capable of printing one layer within 1.5 seconds
Pros
- One of the budget options for a liquid 3D printer
- Most popular choice on the market
- Capable of generating minute details
Cons
- Maximum supported print height is only 12 cm
Buy Now From Amazon
2. ELEGOO Resin 3D Printer
ELEGOO also has a highly popular option for a liquid 3D printer which you must check out before moving forward. This is also one of the great options that are capable of printing larger designs.
In 2nd place, we have the ELEGOO Resin 3D Printer. The Mars 3 Pro MSLA 3D Printer from ELEGOO is also one of the budget options on this list with support for up to 5.647 × 3.52 × 6.8 inches printing size. On top of that, you will get the accuracy of a 4K liquid printer thanks to the 6.6 inches 4K LCD display. The display also features an anti-scratch replaceable tempered glass so that you can always get the best results by replacing the glass.
The lens of the Mars 3 Pro MSLA 3D Printer is quite a special one. Unlike its previous versions, the Mars 3 Pro MSLA 3D Printer features the upgraded COB lens with 36 UV LED light to offer a strong and powerful light source and reduce the curing time. This light source delivers a 405 nm wavelength light beam so that you will get a smoother surface finish on the prints without compromising on the printing speed.
Best Features
- Comes with a 6.6 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 5.647 × 3.
 52 × 6.8 inches printing size
52 × 6.8 inches printing size - Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Light source delivers a 405 nm wavelength light beam
Pros
- Overall printing quality is very good
- Large display with 4K resolution
- Powerful light source with COB lens
Cons
- Overall printing size could have been better
Buy Now From Amazon
3. Comgrow Resin 3D Printer
Moving on to the affordable range of options for a liquid 3D printer, we have a great option coming from Comgrow. Since standard liquid 3D printers are quite expensive, this option can be perfect for hobbyists.
The Comgrow Creality HALOT ONE Resin 3D Printer is our 3rd choice for the best liquid 3D printer since it offers many attractive features without an overly expensive price tag. Thus, it is also one of the popular choices amongst hobbyists and beginners. The Comgrow Creality HALOT ONE Resin 3D Printer comes with a 5. 96 inches 2K display with support for up to 5 x 3.1 x 6.3 inches printing size.
96 inches 2K display with support for up to 5 x 3.1 x 6.3 inches printing size.
This is also a smart option as you will get WiFi compatibility on the unit to offer remote access. For the light source, the Comgrow Creality HALOT ONE Resin 3D Printer uses a new generation optical system that takes advantage of reflection as well as refraction principle to generate an intense and consistent light source. The uniformity of this liquid 3D printer is nearly 80%, offering you a perfect replica of your 3D designs.
Best Features
- Comes with a 5.96 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 5 x 3.1 x 6.3 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Takes about 1 to 4 seconds to print a layer
Pros
- Printing speed is pretty good
- Advanced light source
- Highly precise z-axis module
Cons
- Printing resolution could have been better
Buy Now From Amazon
4.
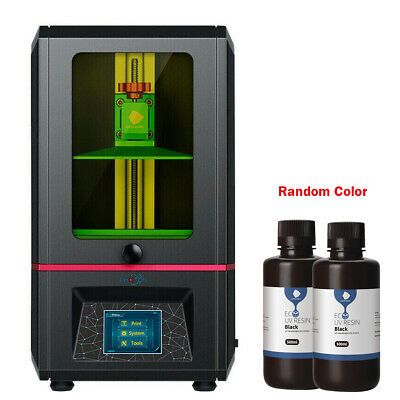 PHROZEN Sonic Resin 3D Printer
PHROZEN Sonic Resin 3D PrinterSince we are discussing budget options for a liquid 3D printer, let us introduce you to the cheapest option available out there for one from PHROZEN. This is a mini 3D printer that is perfect for checking out your designs.
If you need a liquid 3D printer for prototype testing or just to create a 3D replica of your designs for fun, the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer will be perfect for you. Costing almost as much as a standard photo printer, the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer is the cheapest option you can find on the market right now. Still, you will get a 5.5 inches monochrome display on the printer with a maximum supported printing size of 4.7 x 2.6 x 5.1inches which is not too bad.
Another benefit of the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer is its high printing speed. PHROZEN is promising to cure a layer of resin within just a second, making it a perfect option for smaller jobs. The light source used inside the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer is the ParaLED UV LED system which offers 95% optical uniformity, making it more accurate than many other premium options. You will also get a 3-month warranty period on the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer.
You will also get a 3-month warranty period on the PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer.
Best Features
- Comes with a 5.5 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 4.7 x 2.6 x 5.1 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Comes with 3 months of warranty
Pros
- Best option for beginners and hobbyists
- Offers up to 50 mm per hour printing speed
- Mini liquid 3D printer
Cons
- Not suitable for larger and complicated designs
Buy Now From Amazon
5. LONGER Orange 30 3D Printer
Nowadays, you will come across a lot of options for a standard 3D printer, even if you are looking for a liquid 3D printer. But, not all options are as reliable as the following one from LONGER.
The LONGER Orange 30 3D Printer is yet another standard 2K liquid printer that we found for this list of the best liquid 3D printers. It is also a mini option considering the machine only measures about 20.75 x 10.75 x 10 inches in size. But, you will still get a printing size support for up to 4.72 x 2.68 x 6.69 inches which is quite good. It means that you are basically getting up to 13% larger printing volume than other options of similar size.
It is also a mini option considering the machine only measures about 20.75 x 10.75 x 10 inches in size. But, you will still get a printing size support for up to 4.72 x 2.68 x 6.69 inches which is quite good. It means that you are basically getting up to 13% larger printing volume than other options of similar size.
The LONGER Orange 30 3D Printer also offers high precision printing performance despite being a mini version as you get a 47.25 µm pixel size on its display. This machine is backed by the LONGER small angle UV LED light source which ensures better light uniformity as well as illumination. The LONGER Orange 30 3D Printer is capable of printing 100 mm under just a minute, making it nearly 3x faster than other options.
Best Features
- One of the mini liquid 3D printers
- Supports up to 4.72 x 2.68 x 6.69 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- It can print 100 mm layer within a minute
Pros
- Fast cooling system
- Nearly 3 times faster than other options
- 25 µm pixel size
Cons
- Not the best option for large and complicated designs
Buy Now From Amazon
6.
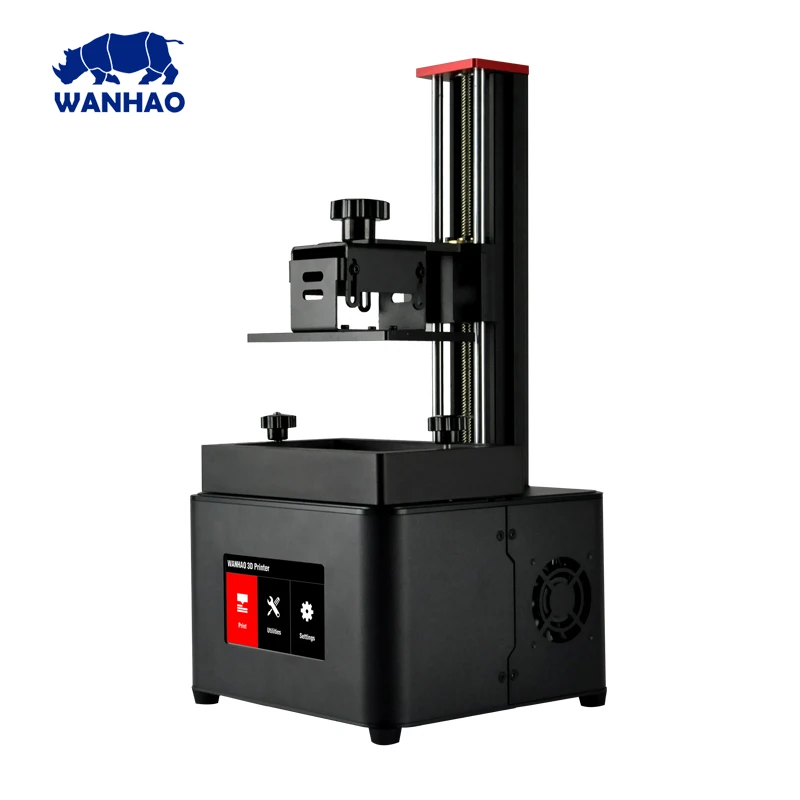 Voxelab Resin 3D Printer
Voxelab Resin 3D PrinterVoxelab is also bringing a 4K resolution liquid 3D printer to our list. This option from Voxelab is also one of the budget options on this list. In fact, it is cheaper than many other 4K 3D printers on the market.
The Voxelab Proxima 6.0 Resin 3D Printer has received an upgrade in the model recently and secured a slot on our list of the best liquid 3D printers on the market. The Voxelab Proxima 6.0 Resin 3D Printer is also a 4K liquid 3D printer with 6.08 inches wide monochrome display. Keep in mind that the display size offered with the Voxelab Proxima 6.0 Resin 3D Printer is larger than many of its competitors. So, you will get a supported printing size of 5.11 x 3.70 x 6.10 inches which is pretty good for all types of applications.
The Voxelab Proxima 6.0 Resin 3D Printer also features an upgraded parallel matrix LED design to offer a 4.5 nm LED light beam. With that, the machine can easily cure the precise points on the layers and offer you a sharp and accurate print. Voxelab is promising up to 2000 hours of lifespan with the machine which is very good for this price point. This machine also does not require any prep time. You can start printing your designs within just 5 minutes after connecting the device.
Voxelab is promising up to 2000 hours of lifespan with the machine which is very good for this price point. This machine also does not require any prep time. You can start printing your designs within just 5 minutes after connecting the device.
Best Features
- Comes with a 6.08 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 5.11 x 3.70 x 6.10 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Ready to print within 5 minutes
Pros
- It has a printing speed of 25 mm per hour
- 405 nm printing beam
- 4K resolution printing display
Cons
- Printing size should have been larger
Buy Now From Amazon
7. Creality 3D Resin Printer
Creality is also bringing a great option within an affordable price range for a liquid 3D printer. This is also a smart option that is highly beneficial for beginners.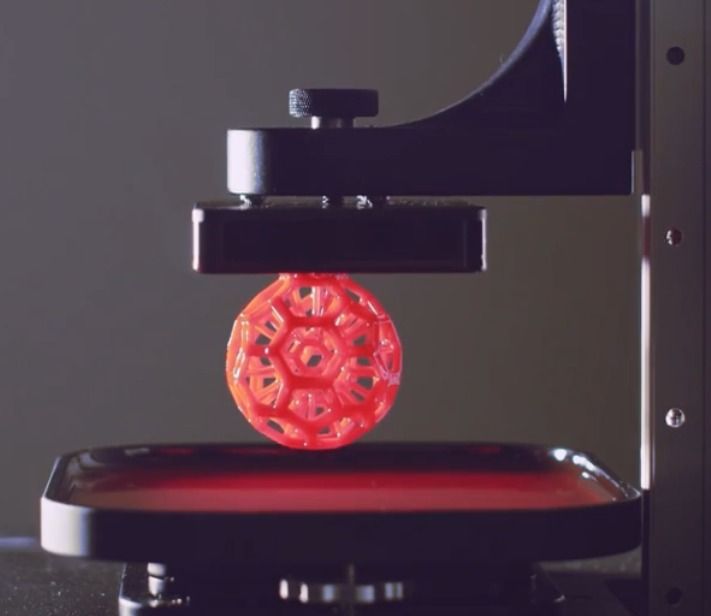
The Creality HALOT-ONE (CL-60) 3D printer is one of the updated models for a liquid 3D printer from Creality. With that, Creality is offering its self-developed light source to offer 20% higher precision, 30% better light uniformity, and nearly 99% saturation to maintain the perfect contrast ratio. Therefore, the prints developed by the Creality HALOT-ONE (CL-60) 3D printer are pretty similar to that of a premium 3D printer.
The Creality HALOT-ONE (CL-60) 3D printer also features the new and powerful cortex-A53 64-bit processor so that the machine can easily maneuver the Z-axis module for complicated designs. And with the 6.08 inches monochrome display, you will also find support for up to 5 x 3.14 x 6.29 inches printing size. The Creality HALOT-ONE (CL-60) 3D printer also houses dual cooling systems so that the curing time is significantly reduced.
Best Features
- Comes with a 5 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 5 x 3.14 x 6.
 29 inches printing size
29 inches printing size - Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- Comes with a year of warranty
Pros
- One of the most reliable options
- Perfect choice for complicated design
- Features a powerful cortex-A53 64-bit processor
Cons
- It does not have a 4K display
Buy Now From Amazon
8. LeeCHee Resin 3D Printer
Lastly, we are featuring one more option from Creality for this list of the best liquid 3D printers. While this is one of the latest additions from Creality, it offers the best specifications in terms of printing size.
There are a lot of inspired 3D designs for which standard 3D printers just aren’t enough. If you also work with such designs, you will need the Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer for your designs. This is the most premium option we have for this list. But, the display size on the Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer is 8.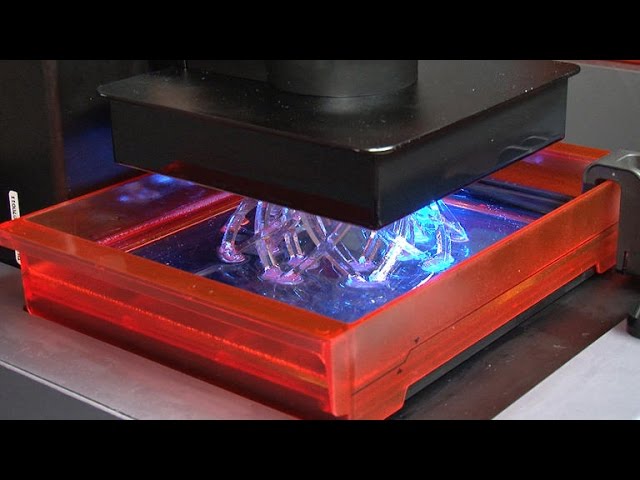 9 inches, making it the largest on this list. And, you will also get 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 inches printing size support which is unmatched by any other option.
9 inches, making it the largest on this list. And, you will also get 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 inches printing size support which is unmatched by any other option.
Apart from that, there is much more to check out on the Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer. For starters, this machine is backed by the 2nd Gen ILS integral light source that ensures the best printing performance out of all. So, you can expect up to 90% light uniformity and a 95% printing success rate with this machine. As for precision, the Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer is capable of maintaining up to 0.05 mm of precision while printing your designs. You can also remotely control the Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer thanks to its WiFi compatibility.
Best Features
- Comes with an 8.9 inches monochrome display
- Supports up to 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 inches printing size
- Compatible with standard liquid resin material
- 2nd Gen ILS integral light source
Pros
- Offers the best printing results out of all
- 4K display with 8.
 9 inches size
9 inches size - 05 mm accuracy level
Cons
- Very expensive choice for a liquid 3D printer
Buy Now From Amazon
9. Uniformation 3D Resin Printer
You will also need a handful of tools and accessories along with a liquid 3d printer. While a lot of the options come with the accessories included in the package, it is better to get a decent removal tool to take proper care of your prints.
The Uniformation 3D Resin Printer GKone Removal Tool is one of the best 3D print removal tools on the market and is compatible with all of the options mentioned on this list. This 3D print removal tool has a 10.1 inches build plate so that you can easily fit even some of your largest creations on this tool.
As for the maximum printing size support, the Uniformation 3D Resin Printer GKone Removal Tool offers the removal of up to 9 x 5.9 x 10.2 inches large prints without any problem. The tool itself is made up of aluminum pins whereas its handle is made up of stainless steel. Since this tool is highly durable as well as portable, it should not take you more than 10 seconds to safely remove your designs.
Since this tool is highly durable as well as portable, it should not take you more than 10 seconds to safely remove your designs.
Best Features
- Comes with a 10.1 inches build plate
- Tool size is 9 x 5.9 x 10.2 inches
- Made up of Stainless Steel and Aluminum
- Best option for most liquid 3D printers
Pros
- Highly durable print remover
- Comparatively cheaper than many other options
- Easy to assemble
Cons
- Assembly is required for the tool
Buy Now From Amazon
Buying Guide For The Best Liquid 3D Printer
The manufacturing and product development industry has advanced a lot now and there is not a single design that you could come up with which cannot be converted into a 3D prototype. Unlike before, there are now advanced manufacturing options available such as 3D printing that can directly generate the model based on its 3D STL design that you can create on your desktop computer or laptop. Even with the 3D printing technology, there are many different options to choose from and liquid 3D printing is right now the best choice for a lot of buyers. This is quite unique and surprising printing technology for 3D printing.
Even with the 3D printing technology, there are many different options to choose from and liquid 3D printing is right now the best choice for a lot of buyers. This is quite unique and surprising printing technology for 3D printing.
First of all, it offers continuous printing speed, making it a much faster alternative to other options. Plus, it can work with intricate details and reach an accuracy of microns whereas filament printers are only accurate up to a couple of millimeters. Therefore, a lot of users are switching to a liquid 3D printer for DIY hobby projects or some for mass production of intricate objects. If you are also looking for a decent liquid 3D printer, make sure you check the following factors before finalizing your choice.
1. Printing Size
The printing size possible with a 3D printer is one of its most essential features. It directly affects the compatibility of the printer with your application. For example, if you are willing to print an object between 5 to 6 inches in length, you should go with a liquid printer that comes with a large enough vat so that your object can be printed with ease. The printing size is also dependent upon the display present below the vat of liquid resin.
The printing size is also dependent upon the display present below the vat of liquid resin.
If the size of the design is larger than that of the display, it is not possible to print the object with the given liquid 3D printer. To make the selection process easier for you, we have specified the possible printing size with each of our choices for the best liquid 3D printer. So now, you can simply check the maximum dimensions of the product that can be printed with the liquid 3D printer and see if your preferred designs are compatible with the size limitations or not. We will suggest going with a compact option in case your designs include miniature designs for desk props.
2. Display Parameters
The digital display present on a liquid 3D printer is the most important part of the machine. You can also consider it as the tool that has a direct effect on the production quality and accuracy available on the prints. One of the best display options available for liquid 3D printers is a monochrome LCD screen. It offers many advantages over traditional RGB displays like energy efficiency, faster printing time, and lesser maintenance to name a few. The most prominent benefit of a monochrome display is the reduced printing time.
It offers many advantages over traditional RGB displays like energy efficiency, faster printing time, and lesser maintenance to name a few. The most prominent benefit of a monochrome display is the reduced printing time.
When it comes to printing large 3D designs, monochrome displays offer the best results without compromising accuracy. Apart from the display type, you should also consider some other important display parameters such as the display resolution and size. As we mentioned before, the size of the display should always be larger than the model that you are willing to print with the machine. As for the resolution, it works quite similarly to that of a digital image.
The higher the resolution, the more accuracy you will get on your prints. There is one more factor called contrast ratio that deals with the accuracy around edges and sharp corners which is also equally important.
3. Printing Speed
No one likes to wait for hours and hours at a time while the printer is developing the print of their custom designs. With filament printers, you would simply have to keep the machine running all night and wait till the printer would finish printing a complicated object within 7 to 8 hours at a time. On the other hand, liquid printers have managed to cut that time pretty short thanks to their continuous printing technology. Unlike filament printing where the printing material is first melted and then solidified again, the printing material for a liquid 3D printer is already in liquid form, which is liquid resins.
With filament printers, you would simply have to keep the machine running all night and wait till the printer would finish printing a complicated object within 7 to 8 hours at a time. On the other hand, liquid printers have managed to cut that time pretty short thanks to their continuous printing technology. Unlike filament printing where the printing material is first melted and then solidified again, the printing material for a liquid 3D printer is already in liquid form, which is liquid resins.
This liquid is poured into a vat where it is solidified or cured with the help of UV light. Once one layer is solidified, the printer instantly starts working with the next layer. And since the solidification process of a liquid resin is quite fast, you would almost feel like the process is happening continuously and not layer by layer. Even though the speed of a liquid 3D printer is quite faster than that of a filament printer, you should still consider the speed for every individual option before you make a choice. The speed also varies based on the capacity of the printer as well as the type of liquid resin you are using for your prints.
The speed also varies based on the capacity of the printer as well as the type of liquid resin you are using for your prints.
4. Safety Features
Safety features are of paramount importance when it comes to manufacturing machines and technologies. Even if you are working with a rather safer option like 3D printing where you won’t have to make direct contact with the workpiece or the tool while it’s operational. But, since it is an electrical device at its core and the liquid resins are also harmful and toxic, you need to be very careful while working with a liquid 3D printer.
And it is always an advantage if the liquid 3D printer comes with some built-in safety measures to ensure all safety protocols are properly followed. For example, some liquid 3D printers will not start printing until the UV light cover is not properly placed or unless the vat of liquid is not properly fitted on the bed. Other than that, the only remaining important safety protocols are related to the electrical connection.
You need to get a liquid 3D printer that comes with built-in overloading and overcurrent protection. Since these matches aren’t exactly cheap, you would definitely want something that lasts for a long time. And to ensure that, you can also go with one that comes with a long warranty period.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What should be the resolution of the monochrome display?
Ans: The resolution of a liquid 3D printer represents the sharpness of the image and the total number of pixels available on the monochrome display that is responsible for controlling the UV light and solidifying the liquid resins. As you may already know, a liquid 3D printer can get as accurate as the size of a pixel since the printing technology works with UV light. Therefore, the accuracy can be directly affected by the resolution of the display. If you are going with a 2K option, you will not get as many details as a 4K option. But again, 4K liquid printers are quite expensive and a bit much for basic designs.
But again, 4K liquid printers are quite expensive and a bit much for basic designs.
2. What type of resin should I use with the liquid 3D printer?
Ans: Most liquid 3D printers these days use photopolymer resin. However, there are many different options available on the market for liquid resins that differ in colors, viscosity, and even curing time. While color is merely subjective to preference, the viscosity and approximate curing time are the main factors that can affect your experience with the liquid 3D printer. Therefore, you should carefully pick the right option based on your designs. Also, check if the resins you are buying are compatible with your printer or not.
3. How long does it take to solidify resins?
Ans: The curing time required for liquid resins is automatically determined by the software which is used for slicing the designs. Therefore, you would not have to think about the curing time at all. However, if you are not finding satisfying results, the software allows you to change the curing time and increase the exposure for better solidification. The best way is to offer longer exposure to the bottom layer so that the machine can create a strong base. Typically, each layer would need about 10 to 15 seconds for proper curing.
Therefore, you would not have to think about the curing time at all. However, if you are not finding satisfying results, the software allows you to change the curing time and increase the exposure for better solidification. The best way is to offer longer exposure to the bottom layer so that the machine can create a strong base. Typically, each layer would need about 10 to 15 seconds for proper curing.
Conclusion
As you can tell by the name, a liquid 3D printer works with liquid resins instead of solid filaments like other printing technologies. In this printing method, the liquid resins are particularly solidified so that they can be separated from the vat to form a layer of the final product. The process is then repeated for each individual layer until the product is completely printed. Since this printing method has numerous advantages over other options, it is a highly preferred option for DIY projects as well as intricate jobs since it can offer the best accuracy.
Today, we have introduced you to the best options you can find right now for a liquid 3D printer on the market. These options are carefully chosen by considering some very important factors and comparing them with hundreds of options on the market. You can read more about the essential features of a liquid 3D printer in our buying guide. Lastly, we will offer some recommendations that we personally liked from this list.
These options are carefully chosen by considering some very important factors and comparing them with hundreds of options on the market. You can read more about the essential features of a liquid 3D printer in our buying guide. Lastly, we will offer some recommendations that we personally liked from this list.
- As you may already know, liquid 3D printers aren’t exactly cheap. But, there are still a few brands like the PHROZEN that are offering a liquid 3D printer at quite an affordable price tag. The PHROZEN Sonic Mini LCD Resin 3D Printer is the cheapest option that we have for you today. But still, this unit holds up against its competition with a 5.5 inches monochrome display and a supported printing size of 4.7 x 2.6 x 5.1 Inches. You will also get a 2.8 inches smart touchscreen display at the front to control the machine.
- On the other hand, if you are looking for a professional-grade liquid 3D printer to generate larger 3D objects, then you should consider going with the LeeCHee liquid 3D printer.
 The LeeCHee Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer is the most premium option available on the market right now that offers an 8.9 inches wide display to support wider 3D projects. The overall supported 3D dimensions for a project are about 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 Inches which is pretty good. The display on the other hand features a 4K resolution to achieve high levels of accuracy.
The LeeCHee Creality Halot Lite Resin 3D Printer is the most premium option available on the market right now that offers an 8.9 inches wide display to support wider 3D projects. The overall supported 3D dimensions for a project are about 7.55 x 4.72 x 7.87 Inches which is pretty good. The display on the other hand features a 4K resolution to achieve high levels of accuracy.
- Lastly, we will suggest the ANYCUBIC Photon Mono 4K since this machine maintains the perfect balance between budget options and high-accuracy models. Despite being a budget option, the ANYCUBIC Photon Mono offers a 4K resolution monochrome screen which is about 6.23 inches in size. And to offer faster and more precise output, the display of the ANYCUBIC Photon Mono 4K has been upgraded to UV LCD. It is also a pretty fast device since it has a printing speed of about 50 mm/hour.
Types of 3D Printers, 3D Printing Materials, and Applications
Skip to Main Content
3D printing or additive manufacturing (AM) technologies create three-dimensional parts from computer-aided design (CAD) models by successively adding material layer by layer until physical part is created.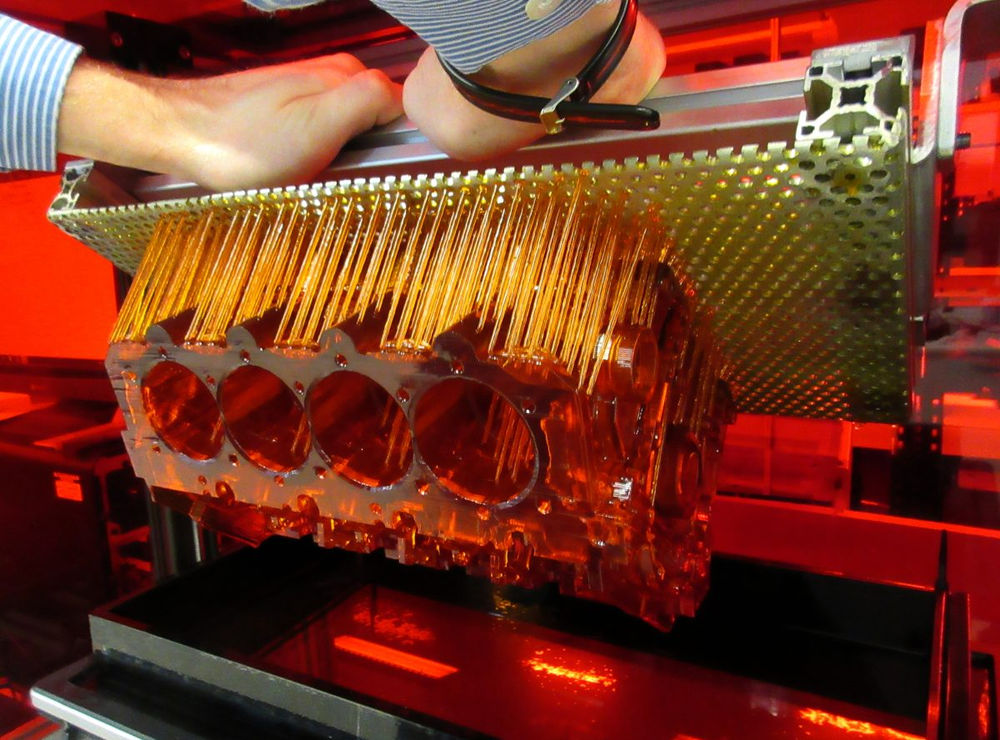
While 3D printing technologies have been around since the 1980s, recent advances in machinery, materials, and software have made 3D printing accessible to a wider range of businesses, enabling more and more companies to use tools previously limited to a few high-tech industries.
Today, professional, low-cost desktop and benchtop 3D printers accelerate innovation and support businesses in various industries including engineering, manufacturing, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, jewelry, and audiology.
All 3D printing processes start with a CAD model that is sent to software to prepare the design. Depending on the technology, the 3D printer might produce the part layer by layer by solidifying resin or sintering powder. The parts are then removed from the printer and post-processed for the specific application.
See how to go from design to 3D print with the Form 3 SLA 3D printer. This 5-minute video covers the basics of how to use the Form 3, from the software and materials to printing and post-processing.
3D printers create parts from three-dimensional models, the mathematical representations of any three-dimensional surface created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or developed from 3D scan data. The design is then exported as an STL or OBJ file readable by print preparation software.
3D printers include software to specify print settings and slice the digital model into layers that represent horizontal cross-sections of the part. Adjustable printing settings include orientation, support structures (if needed), layer height, and material. Once setup is complete, the software sends the instructions to the printer via a wireless or cable connection.
Some 3D printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic, others fuse small particles of polymer powder at high temperatures to build parts. Most 3D printers can run unattended until the print is complete, and modern systems automatically refill the material required for the parts from cartridges.
With Formlabs 3D printers, an online Dashboard allows you to remotely manage printers, materials, and teams.
Depending on the technology and the material, the printed parts may require rinsing in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) to remove any uncured resin from their surface, post-curing to stabilize mechanical properties, manual work to remove support structures, or cleaning with compressed air or a media blaster to remove excess powder. Some of these processes can be automated with accessories.
3D printed parts can be used directly or post-processed for specific applications and the required finish by machining, priming, painting, fastening or joining. Often, 3D printing also serves as an intermediate step alongside conventional manufacturing methods, such as positives for investment casting jewelry and dental appliances, or molds for custom parts.
The three most established types of 3D printers for plastics parts are stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and fused deposition modeling (FDM).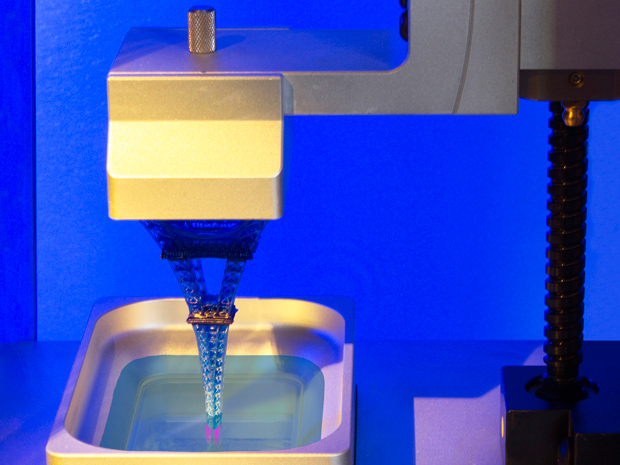 Formlabs offers two professional 3D printing technologies, SLA and SLS, bringing these powerful and accessible industrial fabrication tools into the creative hands of professionals around the world.
Formlabs offers two professional 3D printing technologies, SLA and SLS, bringing these powerful and accessible industrial fabrication tools into the creative hands of professionals around the world.
Stereolithography was the world’s first 3D printing technology, invented in the 1980s, and is still one of the most popular technologies for professionals. SLA 3D printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization.
SLA resin 3D printers have become vastly popular for their ability to produce high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and parts in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface finish. SLA resin formulations offer a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties to match those of standard, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
Resin 3D printing a great option for highly detailed prototypes requiring tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, such as molds, patterns, and functional parts. SLA 3D printers are widely used in a range of industries from engineering and product design to manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model making, and education.
SLA 3D printers are widely used in a range of industries from engineering and product design to manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model making, and education.
- Rapid prototyping
- Functional prototyping
- Concept modeling
- Short-run production
- Dental applications
- Jewelry prototyping and casting
Learn More About SLA 3D Printers
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing uses a laser to cure liquid photopolymer resin into solid isotropic parts.
SLA parts have sharp edges, a smooth surface finish, and minimal visible layer lines.
Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-power laser to sinter small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure. The unfused powder supports the part during printing and eliminates the need for dedicated support structures. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including interior features, undercuts, thin walls, and negative features. Parts produced with SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
Parts produced with SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
The most common material for selective laser sintering is nylon, a popular engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties. Nylon is lightweight, strong, and flexible, as well as stable against impact, chemicals, heat, UV light, water, and dirt.
The combination of low cost per part, high productivity, and established materials make SLS a popular choice among engineers for functional prototyping, and a cost-effective alternative to injection molding for limited-run or bridge manufacturing.
- Functional prototyping
- End-use parts
- Short-run, bridge, or custom manufacturing
Learn More About SLS 3D Printers
SLS 3D printers use a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of polymer powder.
SLS parts have a slightly rough surface finish, but almost no visible layer lines.
Fused deposition modeling (FDM), also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), is the most widely used type of 3D printing at the consumer level. FDM 3D printers work by extruding thermoplastic filaments, such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), PLA (Polylactic Acid), through a heated nozzle, melting the material and applying the plastic layer by layer to a build platform. Each layer is laid down one at a time until the part is complete.
FDM 3D printers are well-suited for basic proof-of-concept models, as well as quick and low-cost prototyping of simple parts, such as parts that might typically be machined. However, FDM has the lowest resolution and accuracy when compared to SLA or SLS and is not the best option for printing complex designs or parts with intricate features. Higher-quality finishes may be obtained through chemical and mechanical polishing processes. Industrial FDM 3D printers use soluble supports to mitigate some of these issues and offer a wider range of engineering thermoplastics, but they also come at a steep price.
- Basic proof-of-concept models
- Simple prototyping
Learn More About FDM 3D Printers
FDM 3D printers build parts by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament, which a printer nozzle deposits layer by layer in the build area.
FDM parts tend to have visible layer lines and might show inaccuracies around complex features.
Having trouble finding the best 3D printing process for your needs? In this video guide, we compare FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies, the most popular types of 3D printers, across the most important buying considerations.
Each 3D printing process has its own benefits and limitations that make them more suitable for certain applications. This video compares the functional and visual characteristics of FDM, SLA, and SLS printers 3D printers to help you identify the solution that best matches your requirements.
Do you need custom parts or prototypes fast? Compared to outsourcing to service providers or using traditional tools like machining, having a 3D printer in-house can save weeks of lead time. In this video, we compare the speed of FDM, SLA, and SLS 3D printing processes.
Comparing the cost of different 3D printers goes beyond sticker prices—these won’t tell you the full story of how much a 3D printed part will cost. Learn the three factors you need to consider for cost and how they compare across FDM, SLA, and SLS 3D printing technologies.
As additive manufacturing processes build objects by adding material layer by layer, they offer a unique set of advantages over traditional subtractive and formative manufacturing processes.
With traditional manufacturing processes, it can take weeks or months to receive a part. 3D printing turns CAD models into physical parts within a few hours, producing parts and assemblies from one-off concept models to functional prototypes and even small production runs for testing. This allows designers and engineers to develop ideas faster, and helps companies to bring products more quickly to the market.
Engineers at the AMRC turned to 3D printing to rapidly produce 500 high-precision drilling caps used in drilling trials for Airbus, cutting the lead time from weeks to only three days.
With 3D printing, there’s no need for the costly tooling and setup associated with injection molding or machining; the same equipment can be used from prototyping to production to create parts with different geometries. As 3D printing becomes increasingly capable of producing functional end-use parts, it can complement or replace traditional manufacturing methods for a growing range of applications in low- to mid-volumes.
Pankl Racing Systems substituted machined jigs and fixtures with 3D printed parts, decreasing costs by 80-90 percent that resulted in $150,000 in savings.
From shoes to clothes and bicycles, we’re surrounded by products made in limited, uniform sizes as businesses strive to standardize products to make them economical to manufacture. With 3D printing, only the digital design needs to be changed to tailor each product to the customer without additional tooling costs. This transformation first started to gain a foothold in industries where custom fit is essential, such medicine and dentistry, but as 3D printing becomes more affordable, it’s increasingly being used to mass customize consumer products.
Gillette's Razor Maker™ gives consumers the power to create and order customized 3D printed razor handles, with the choice of 48 different designs (and counting), a variety of colors, and the option to add custom text.
3D printing can create complex shapes and parts, such as overhangs, microchannels, and organic shapes, that would be costly or even impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. This provides the opportunity to consolidate assemblies into less individual parts to reduce weight, alleviate weak joints, and cut down on assembly time, unleashing new possibilities for design and engineering.
Nervous System launched the first-ever 3D printed ceramic jewelry line, consisting of intricate designs that would be impossible to manufacture using any other ceramic technique.
Product development is an iterative process that requires multiple rounds of testing, evaluation, and refinement. Finding and fixing design flaws early can help companies avoid costly revisions and tooling changes down the road. With 3D printing, engineers can thoroughly test prototypes that look and perform like final products, reducing the risks of usability and manufacturability issues before moving into production.
The developers of Plaato, an optically clear airlock for homebrewing, 3D printed 1,000 prototypes to fine tune their design before investing in expensive tooling.
3D printing accelerates innovation and supports businesses across a wide range of industries, including engineering, manufacturing, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, jewelry, audiology, and more.
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing empowers engineers and product designers to turn ideas into realistic proofs of concept, advance these concepts to high-fidelity prototypes that look and work like final products, and guide products through a series of validation stages toward mass production.
Applications:
- Rapid prototyping
- Communication models
- Manufacturing validation
Learn More
Manufacturers automate production processes and streamline workflows by prototyping tooling and directly 3D printing custom tools, molds, and manufacturing aids at far lower costs and lead times than with traditional manufacturing. This reduces manufacturing costs and defects, increases quality, speeds up assembly, and maximizes labor effectiveness.
Applications:
- Jig and fixtures
- Tooling
- Molding (injection molding, thermoforming, silicone molding, overmolding)
- Metal casting
- Short run production
- Mass customization
Learn More
3D printers are multifunctional tools for immersive learning and advanced research. They can encourage creativity and expose students to professional-level technology while supporting STEAM curricula across science, engineering, art, and design.
Applications:
- Models for STEAM curricula
- Fab labs and makerspaces
- Custom research setups
Learn More
Affordable, professional-grade desktop 3D printing helps doctors deliver treatments and devices customized to better serve each unique individual, opening the door to high-impact medical applications while saving organizations significant time and costs from the lab to the operating room.
Applications:
- Anatomical models for surgical planning
- Medical devices and surgical instruments
- Insoles and orthotics
Learn More
High definition physical models are widely used in sculpting, character modeling, and prop making. 3D printed parts have starred in stop-motion films, video games, bespoke costumes, and even special effects for blockbuster movies.
Applications:
- Hyper-realistic sculptures
- Character models
- Props
Learn More
Jewelry professionals use CAD and 3D printing to rapidly prototype designs, fit clients, and produce large batches of ready-to-cast pieces. Digital tools allow for the creation of consistent, sharply detailed pieces without the tediousness and variability of wax carving.
Applications:
- Lost-wax casting (investment casting)
- Fitting pieces
- Master patterns for rubber molding
Learn More
Hearing specialists and ear mold labs use digital workflows and 3D printing to manufacture higher quality custom ear products more consistently, and at higher volumes for applications like behind-the-ear hearing aids, hearing protection, and custom earplugs and earbuds.
Applications:
- Soft silicone ear molds
- Custom earbuds
Learn More
The market for 3D printing materials is wide and ever-growing, with printers for everything from plastics to metals, and even food and live tissue in development. Formlabs offers the following range of photopolymer materials for the desktop.
Standard 3D printing materials provide high resolution, fine features, and a smooth surface finish ideal for rapid prototyping, product development, and general modeling applications.
These materials are available in Black, White, and Grey with a matte finish and opaque appearance, Clear for any parts requiring translucency, and as a Color Kit to match almost any custom color.
Explore Standard Materials
3D printing materials for engineering, manufacturing, and product design are formulated to provide advanced functionality, withstand extensive testing, perform under stress, and remain stable over time.
Engineering materials are ideal for 3D printing strong, precise concept models and prototypes to rapidly iterating through designs, assess form and fit, and optimize manufacturing processes.
Explore Engineering Materials
Medical resins empower hospitals to create patient-specific parts in a day at the point of care and support R&D for medical devices. These resins are formulated for 3D printing anatomical models, medical device and device components, and surgical planning and implant sizing tools.
Explore Jewelry Materials
Jewelry resins are formulated to capture breathtaking detail and create custom jewelry cost-effectively. These resins are ideal for jewelry prototyping and casting jewelry, as well as vulcanized rubber and RTV molding.
Explore Jewelry Materials
Specialty Resins push the limits of 3D printing, featuring advanced materials with unique mechanical properties that expand what’s possible with in-house fabrication on our stereolithography 3D printers.
Explore Specialty Materials
In recent years, high-resolution industrial 3D printers have become more affordable, intuitive, and reliable. As a result, the technology is now accessible to more businesses. Read our in-depth guide about 3D printer costs, or try our interactive tool to see if this technology makes economic sense your business.
Calculate Your Savings
New to 3D printing? Explore our guides to learn about the key terms and specific characteristics of 3D printing to find the best solution for your business.
For further questions,
Explore 3D Printing Resources
Photopolymer 3D printer
3D printers can be sorted not only by the printing technologies used, but also by the consumables used. In this section, we will look at devices that use photopolymer resins to build models.
- 1 Consumables
- 2 Laser stereolithography (SLA)
- 3 Projector stereolithography (DLP)
- 4 Multi-jet (MJM and PolyJet)
- 5 3D pens
- 6 Additional illumination
Consumables
Photopolymer resins are liquid polymers that harden when exposed to light. As a rule, such materials are sensitive to the ultraviolet range, which determines the design of photopolymer printers. One of the common design elements is a transparent colored cap or housing made of a material that filters ultraviolet radiation. This is done both to protect the user's eyes and to protect the supplies inside the printer from exposure to sunlight and background lighting.
Photopolymer resin loaded into Form 1 3D printer
The physical properties of resins after polymerization vary widely. Both rigid and flexible options are available, transparent and matte. A wide selection of colors is also available. Resin consistency and exposure times also vary, so a range of compatible media should be considered when choosing a printer.
The last aspect to consider when choosing a material is its toxicity. There are both quite toxic options and biologically safe ones.
The cost of consumables can be considered the Achilles' heel of photopolymer printing. The plants themselves are already reaching quite acceptable price levels, but it is still quite difficult to find inexpensive photopolymer resins. It is hoped that the proliferation of inexpensive photopolymer printers will lead to an increase in the production of consumables and lower prices.
Laser Stereolithography (SLA)
SLA Model
The firstborn of photopolymer printing and modern 3D printing in general. The technology was developed in 1984 by Charles Hall, who later founded 3D Systems.
SLA printers use laser emitters to cure the photopolymer supply.
A typical SLA printer consists of a consumable tray sitting under a build platform driven vertically by a raise/lower mechanism.
Alternatively, the cuvette itself can be driven - what matters is the relative movement of the platform and the container. Above the cuvette is a laser emitter and a mirror system for deflecting the laser beam.
During the printing process, the platform is immersed in the consumable for the thickness of one layer of the digital model.
Since photopolymer resins can be quite thick, a leveling mechanism is often used to speed up the process.
SLA printer operation scheme
After leveling, the process of illumination of the material begins. Illumination is produced by laser irradiation. Most photopolymer resins are designed to cure (polymerize) when exposed to ultraviolet light, which determines the choice of laser frequency. The movement of the beam along the X and Y axes is determined by the operation of the deflecting mirrors.
After the drawing of the layer is completed, the platform is immersed in the material for the thickness of one more layer, and the process is repeated with the drawing of the next layer of the digital model.
Model building animation
SLA printing takes quite a long time, and printers using this method tend to have relatively small build areas.
This is mainly due to the high cost of laser emitters: printing large objects with a single laser will take too much time, and installing additional emitters and mirrors will complicate the design, increase the dimensions of the installation and raise the price to an unacceptable level for most users.
Despite the success of this technology, projected stereolithography is considered to be a more promising, although very similar method.
Projector Stereolithography (DLP)
Formlabs Form 1 Desktop DLP Printer
A close relative of laser stereolithography, this method uses digital LED projectors instead of laser machines with mirror deflection systems. The method became popular due to the development of technology for the production of low-cost high-resolution digital projectors by Texas Instruments.
Layers are illuminated using a digital projector that highlights patterns of the entire layer, which distinguishes this method from SLA, where the "picture" emerges progressively using an ultraviolet laser.
A similar approach has previously been used on SGC-type plants, but this technology used physical photomasks, making the process costly, time consuming, slow and noisy.
At the moment, the FTI technology continues to exist - the development of SGC, almost indistinguishable from DLP printing, since it also uses digital LED projectors.
DLP printer design
Simultaneous illumination of an entire layer using projectors can significantly speed up the printing process even compared to SLA printers that have a high scanning speed (ie beam movement).
In addition, these printers are less sensitive to rough physical impact due to the absence of delicate mirror systems.
The absence of mechanical mirror systems improves accuracy. Finally, the cost of projectors sets them apart from laser systems.
Projection size can be quite significant, reaching the average of popular FDM printers.
An interesting feature of DLP printers is the ability to "reverse" or "reverse" printing.
In this case, the projector is installed under a transparent (material choice for transparency in relation to ultraviolet light) cuvette, and the platform does not sink into the material, but gradually rises, pulling out the layers of exposed polymer.
This approach eliminates the alignment mechanism and achieves even higher Z resolution than SLA printers.
In addition, the size of models in height is not limited by the depth of the cuvette, which favorably affects the dimensions of the printer and the possibility of increasing the build area.
Multi-jet printing (MJM and PolyJet)
3D Systems ProJet 3500HDMax MJM printer
MJM and PolyJet technologies are practically indistinguishable from each other. The name difference comes from the respective patents: Multi Jet Modeling is owned by 3D Systems, while PolyJet is owned by rival Stratasys.
The very principle of multi-jet polymer printing was developed by the Israeli company Objet, which eventually became a division of Stratasys.
Multi-jet printing technology combines features of 3D inkjet printing (3DP) and projection stereolithography (DLP).
How the MJM PolyJet printer works
Models are built by spraying photopolymer using linear arrays consisting of multiple nozzles.
The applied layer is immediately exposed to ultraviolet lamps - as a rule, two processes occur simultaneously.
By the time the array reaches the end of the build chamber, the previously deposited material is hard enough to print a new layer.
Composite models created on the ProJet 3500 DP dental printer
This approach allows to achieve very high printing speed, but is characterized by high design complexity, which negatively affects the cost of such installations and limits their distribution to professional use.
One of the advantages of MJM and PolyJet technologies is the ability to create composite structures from photopolymer resins with different physical characteristics.
It is therefore possible to create models with easily removable supports, use multiple colors and use flexible and rigid materials in parallel within the same model.
3D Pens
CreoPop 3D Pen
Recently, there has been a craze for hand-held printing devices called 3D pens. At the moment, there are three main options for such devices: drip-jet pens (DOD), called BioPen and used in the development of new methods for treating damaged tissues, FDM 3D pens, which are manual extruders (essentially similar to the usual hot glue guns, but using thermoplastics) and developments in 3D-drawing with photopolymer resins.
CreoPop 3D pen was the first "handheld resin printer". The design of this device is quite simple, because the most complex function, positioning, is performed by the user himself. The pen only extrudes resin through the tip surrounded by LED emitters.
CreoPop 3D pen in action
This way the resin hardens immediately after application, allowing you to literally draw on air.
The advantage of such handles over FDM-analogues is the low operating temperature - there are no heating elements in the device. As a result, with such pens you can even draw on the skin.
In addition, a wide range of photopolymer resins with different physical properties can be used with such devices, which greatly expands the range of possible applications. At a minimum, this is a relatively inexpensive, but entertaining toy.
The only drawback is the relatively high cost of consumables, but such devices are unlikely to require large volumes of photopolymer resin when used in everyday life.
Additional Lighting
Final Lighting of Resin Models in a Homemade Camera
Full curing of models can take quite a long time, so models during SLA and DLP printing are only partially polymerized, sufficient to maintain the physical shape of the part.
After production, the models are usually placed in chambers equipped with ultraviolet lamps until fully cured. Of course, if possible, you can simply lay out the models in the sun - the effect will be the same.
Just keep in mind that ordinary glass practically does not transmit ultraviolet light, so exposure to sunlight must be direct.
If desired, a UV-transparent quartz glass container can be used.
Go to the main page of the Encyclopedia of 3D Printing
Choosing a liquid photopolymer for a 3D printer. Classification of materials for SLA/DLP 3D printing.
Contents:
- Introduction
- SLA Overview
- SLA Standard Resins
- Standard photopolymer resin - Standard
- Clear Photopolymer Resin - Clear
- Engineering photopolymer resins
- Rigid photopolymer resin - Tough (like ABS)
- Durable photopolymer resin - Durable (PP-like)
- Heat resistant photopolymer resin - Heat resistant
- Rubber-like photopolymer resin - Rubber-like (Elastic)
- Ceramic photopolymer resin - Ceramic filled (Hard)
- How to choose the right resin for your application
- Dental and medical SLA resins
- Medical Device Photopolymer Resin - Custom Medical Appliances (Class I Biocompatibility)
- Dental Long Term Biocompatible Resin (Class IIa Biocompatible)
- Biocompatibility class I vs biocompatibility class IIa
- Cast SLA resins
- Cast resin for jewelry making
- Generalized rules
Hello everyone, Friends! With you 3DTool!
This article compares photopolymer resins using the Formlabs example for 3D printing by SLA - Standard ( Standard ) , hard ( Toug ) , Durable ( Durable ) heat resistant heat resistant 0025 flexible ) , dental ( dental ) and castable ( castable ) . The information from the article will help you choose a photopolymer resin for your needs.
Catalog of photopolymer 3D printers
Photopolymers from FormLabs
Detailed review of the Formlabs Form 3 3D printer
Introduction
Stereolithography allows you to print plastic parts with high resolution, good fine detail and smooth surface. Due to the variety of photopolymer resins available for SLA, this technology is used in many different industries:
-
"Standard" photopolymers are used for prototyping
-
Engineering photopolymers have certain mechanical and thermal properties
-
Dental and medical photopolymers have biocompatibility certificates.
-
Cast photopolymers have a zero ash content after burning.
SLA 3D Printing Resin Overview
SLA uses a laser to cure a liquid photopolymer resin. This process is called photopolymerization. Various combinations of polymers and other additives that are part of the resin allow you to get different material properties.
The main advantages and limitations that are common to all resins in SLA 3D printing are:
Benefits:
Weaknesses:
Base Resins for SLA
Post-Processing SLA/DLP 3D Printing Article
Standard photopolymer resin - Standard
Standard resins produce parts with high stiffness, detail and a smooth surface. The low cost of resins, from $250 per liter, makes them ideal for prototypes.
The color of the resin also affects its properties. For example, in FormLabs products, gray resin is suitable for models with fine details, and white resin for parts that require the smoothest possible surface.
Benefits of using Standard grade resins:
Cons Standard:
Also included in the class of "Standard" photopolymer resins from FormLabs is the Color KIT - a set of special dyes and "Color Base" photopolymer resin for mixing and obtaining a variety of color solutions. This eliminates the need for painting parts after 3D printing.
FormLabs Engineering Photopolymer Resins
Engineering resins have a range of properties for injection molded plastics.
All engineering resins require additional UV curing, such as using the Form Cure, to achieve their maximum properties.
Tough photopolymer resin - Tough (ABS equivalent)
Tough resin was developed for models that need to withstand high loads and be durable.
This material produces strong, shatter-resistant parts and functional prototypes such as snap-on housings.
Pros:
Cons:
Ideal for: functional prototypes, mechanical parts
Durable photopolymer resin - Durable
Durable resin is a wear-resistant and flexible material with mechanical properties similar to polypropylene.
Durable photopolymer produces models with a smooth glossy surface and high resistance to deformation.
Durable Resin is ideal for:
- Bushings and bearings;
- Various functional compounds
Pros:
Cons:
-
Not suitable for thin wall parts (recommended minimum wall thickness 1mm)
-
Low heat distortion temperature
-
Low flexural strength (lower than hard resin)
Ideal for: functional prototypes.
Refractory Photopolymer Resin - Formlabs High Temp Resin
The heat resistant resin is ideal for parts that require high temperature resistance and operate at high temperatures.
Formlabs High Temp Resin provides the highest melting point (HDT): 238°C at 0.45 MPa.
The resin should be used to print detailed, accurate prototypes with high heat resistance.
Pros:
Cons:
Flexible Resin
Rubber-like resin allows flexible parts to be made. This material has a low tensile strength and high elongation at break and is well suited for parts that will be bent or compressed.
It can also be used to add ergonomic features to multi-material assemblies such as: dies, wearable prototypes, handles, pads and grips.
Pros:
-
High flexibility (high elongation at break)
-
Low hardness (simulates 80A durometer rubber)
-
High impact resistance
Cons:
-
Doesn't have all the properties of real rubber
-
Requires extensive support structures
-
Material properties deteriorate over time as the part is exposed to ultraviolet radiation (sunlight)
-
Not suitable for thin wall parts (recommended minimum wall thickness 1mm)
Ideal for flexible prototyping.
Ceramic Photopolymer Resin - Rigid Resin
This resin is reinforced with glass, which provides very high rigidity and a polished surface. The polymer is very resistant to deformation and is excellent for 3D printing thin elements.
Ideal for: molds and tooling, jigs, manifolds, retainers, electrical and automotive fixture housings
Thermal management components printed with SLA ceramic (hard) resin. Image credit: Formlabs
How to choose the right resin for your application
The table below shows the main mechanical properties of photopolymers for SLA:
Source: Formlabs
Standard resin ( standart ) has high tensile strength but is very brittle (very low elongation at break) so it is not suitable for functional parts. The ability to create a good part surface makes it ideal for visual prototypes and art models.
durable ( durable ) resin has the highest impact strength and elongation at break of any other SLA material. Best suited for prototyping parts with moving parts and latches. It lacks, however, the strength of thermoplastic 3D printing materials such as SLA nylon.
tough ( tough ) resin is a compromise between the material properties of tough and standard resin. It has a high tensile strength, so it is best suited for rigid parts that require high hardness.
heat resistant resin ( heat resistant ) can withstand temperatures above 200 o C, but has poor toughness and is even more brittle than standard resin.
ceramic ( ceramic reinforce ) resin has the highest tensile strength and flexural modulus, but is brittle (poor elongation at break and toughness). This resin is preferred for thin wall parts that require increased rigidity.
The graphs below compare the mechanical properties of the most common SLA materials visually:
Comparison chart for elongation at break and toughness for common SLA printing specifications and standard media. Image courtesy of Formlabs.
Stress-strain curves for conventional SLA technologies and standard materials. Image credit: Formlabs
Comparative chart of material properties of various technical resins. Image credit: Formlabs.
Dental and medical resins
Photopolymer resin for medical devices - Custom Medical Appliances 9028 (Bios Class 1 biocompatible resins can be used to make medical equipment such as surgical guides. Parts printed on this resin can be steam sterilized in an autoclave for direct use in the operating room.
Pros:
Cons:
- Moderate wear and tear resistance
Ideal for: Surgical aids and appliances

 1 Inches
1 Inches