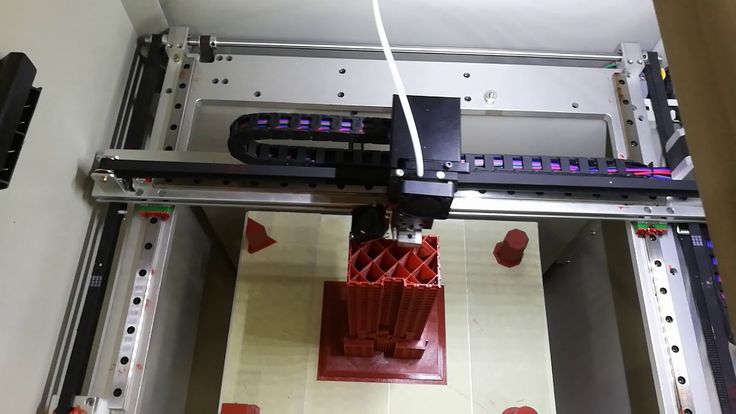
Fdm 3d printing technology in manufacturing composite elements
Advantages of FDM 3D printing technology in manufacturing composite elements
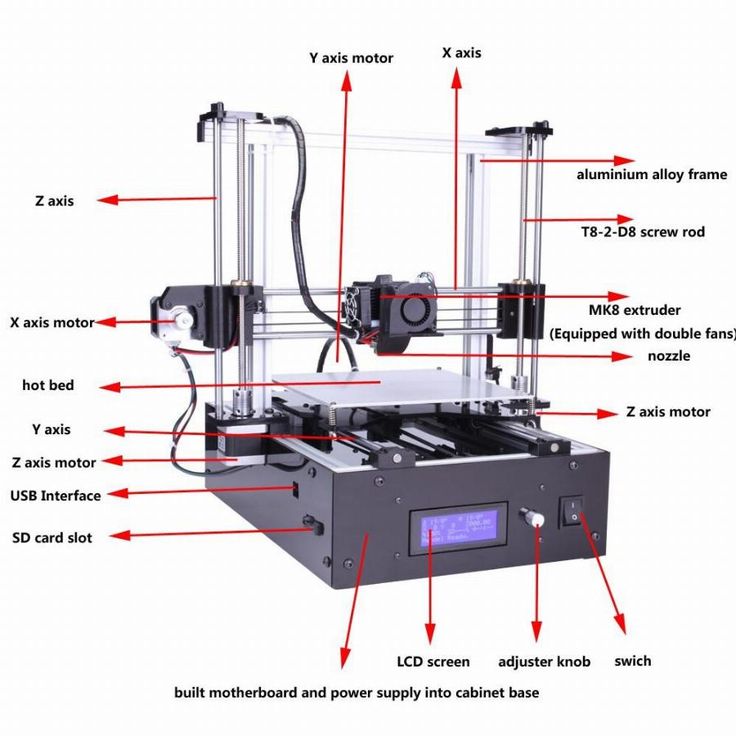
3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of producing physical object directly from CAD file. This is a material addition process and so no or minimal material is wasted during the production of parts. The object is created by laying layer over layer until complete object is printed.
Fusion Deposition Modelling or FDM is the most common 3D printing technique, that forms layer both in horizontal and vertical directions using moving extrusion nozzle over a build platform.
Composite materials have properties combined by materials which are formed together. Composites material consists of a core polymer material and a reinforcing material, like continuous fibre. This offers higher strength and stiffness compared to normal polymers. Fibre Reinforced plastic or FRP is the most common household example of composite materials. Using similar concept for 3D part manufacturing has multiple advantages to the user. 3D printing technology is emerging to take up the use of composite material to make components.
Few of the Advantages of FDM for composite material rapid prototype part manufacturing are as below :
Uniformity of Distribution: Uniform distribution of one material into other material is especially important to get the benefits of composites structure. By using dual head deposition FDM process, where part is manufactured by layering of the materials, uniform distribution of mixture of materials is possible.
Array of Composites: With option of layering material in FDM technique as per need using computer aided controlling, its possible to obtain variety of combinations for composite materials as per applications of the parts.
Speed of Production: With minimal changes into the existing FDM 3D printers, composite material parts can be printed with faster rate than traditional production methods, without investing in moulds or tooling. This readies the prototype parts for verification and assembly checks, with the option of improvement at lower cost and quickness.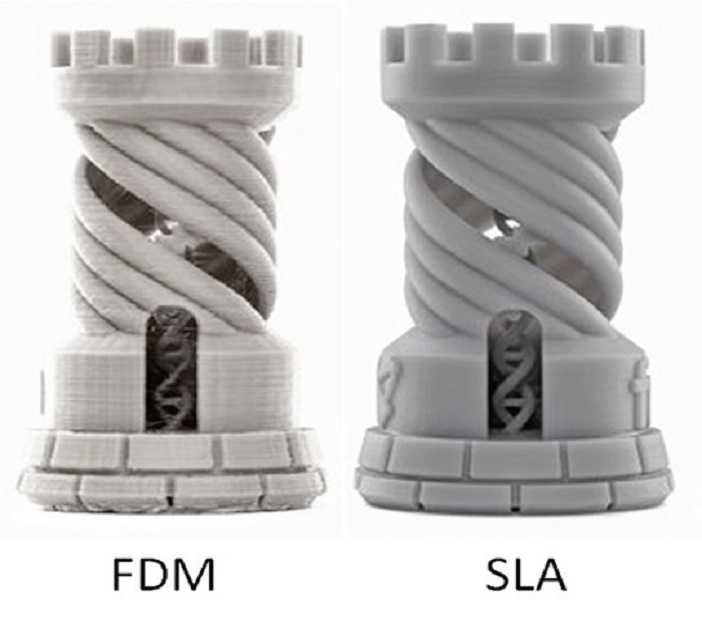
Accuracy of Manufacturing: Thinner wall thickness composite parts can also be produced with greater accuracy than traditional manufacturing techniques. So designer can be rest assured to achieve desired results in terms of weight and assembly.
Easy to adapt Complex designs: Complex designs which are difficult or costly by using traditional methods, can be easily manufactured using 3D printing with Composite or reinforced materials. This gives freedom to design the part.
Possibility of combining metal strength into Polymers: With dual head nozzles, continuous fibre 3D printing uses continuous strands of reinforcement fibre reinforcement to the base material to achieve higher strength to weight ratio. The 3D printer builds the pattern of a thermoplastic with continuous fibres into the part. This process is called Continuous Fibre Fabrication (CFF).
For single head FDM technology, filament with iron or CU powder into ABS material, so it has strength of metal with light weight of plastic.
Minimised wastage of material: The 3D parts only printed using the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. This save on wastages but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
Reduced environmental impact: Glass fibres composites are hazardous to human health as well as have environmental impact. So using lowest and controlled quantity of such composite fibres make this process desirable.
Conclusion:
FDM is the most common and matured 3D printing technology among all known rapid prototyping methods. Using of composite materials in FDM provides more flexibility and cost effectiveness for the customers.
3D Incredible is one of the leading 3D metal printing companies in Pune with shortest lead time. We offer the most effective and reliable 3D printing solutions to help our clients manufacture complex parts at a rapid pace in a cost-effective manner.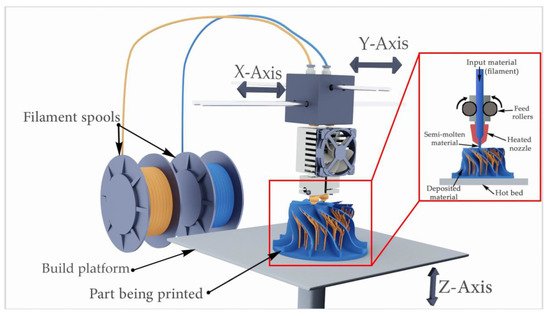 Our team comprises of the best engineers and experts who have a rich understanding of the 3D printing technology.
Our team comprises of the best engineers and experts who have a rich understanding of the 3D printing technology.
SCIRP Open Access
Scientific Research Publishing
Journals A-Z
Journals by Subject
- Biomedical & Life Sci.
- Business & Economics
- Chemistry & Materials Sci.
- Computer Sci. & Commun.
- Earth & Environmental Sci.
- Engineering
- Medicine & Healthcare
- Physics & Mathematics
- Social Sci. & Humanities
Journals by Subject
- Biomedical & Life Sciences
- Business & Economics
- Chemistry & Materials Science
- Computer Science & Communications
- Earth & Environmental Sciences
- Engineering
- Medicine & Healthcare
- Physics & Mathematics
- Social Sciences & Humanities
Publish with us
- Paper Submission
- Information for Authors
- Peer-Review Resources
- Open Special Issues
- Open Access Statement
- Frequently Asked Questions
Publish with us
- Paper Submission
- Information for Authors
- Peer-Review Resources
- Open Special Issues
- Open Access Statement
- Frequently Asked Questions
Follow SCIRP
Contact us
customer@scirp. org org |
|
| +86 18163351462(WhatsApp) | |
| 1655362766 | |
| Paper Publishing WeChat |
| Recently Published Papers |
| Recently Published Papers |
Follow SCIRP
Contact us
customer@scirp. org org |
|
| +86 18163351462(WhatsApp) | |
| 1655362766 | |
| Paper Publishing WeChat |
Free SCIRP Newsletters
Copyright © 2006-2022 Scientific Research Publishing Inc. All Rights Reserved.
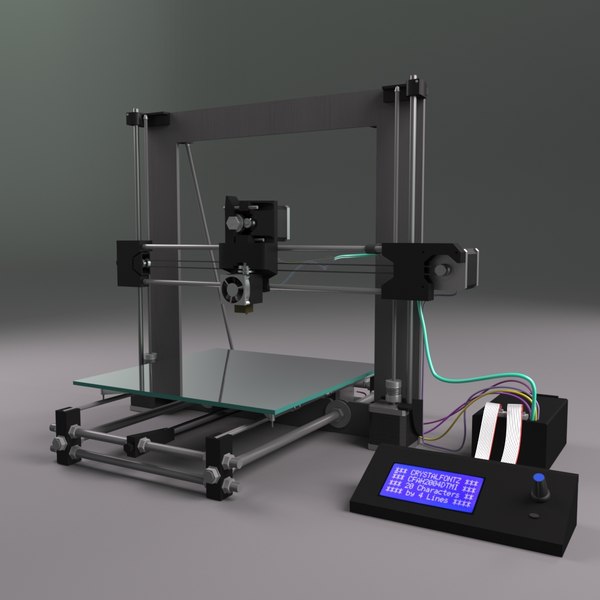
Top3D Printing Technologies - FDM, FFF, SLA, DLP, PolyJet, CJP, SLS, SLM
FUSED DEPOSITION MODELING PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + FDM
One of the most popular, simple and cheap 3D printing technologies is Fused Depsition Modeling.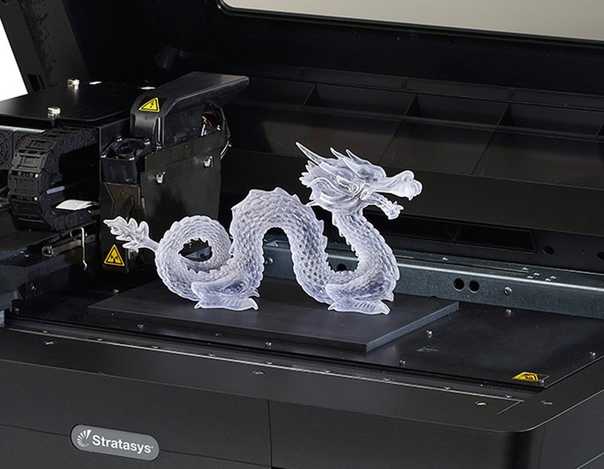 The technology was invented more than 20 years ago and implemented by Stratasys, and still it remains the most popular. The principle of building a prototype using this method is simple and clear. The simulated 3D object in STL format is transferred to the 3D printer software. After placing the model in a virtual working chamber (automatically or manually), cutting the model into horizontal layers, the 3D printing process begins. The extruder print head melts the filament, laying down layer by layer according to the model data. If necessary, before starting printing, auxiliary structures (supports) are automatically or manually placed on a virtual 3D model, which, after printing, can be removed with a special solution or manually.
The technology was invented more than 20 years ago and implemented by Stratasys, and still it remains the most popular. The principle of building a prototype using this method is simple and clear. The simulated 3D object in STL format is transferred to the 3D printer software. After placing the model in a virtual working chamber (automatically or manually), cutting the model into horizontal layers, the 3D printing process begins. The extruder print head melts the filament, laying down layer by layer according to the model data. If necessary, before starting printing, auxiliary structures (supports) are automatically or manually placed on a virtual 3D model, which, after printing, can be removed with a special solution or manually.
There are many types of equipment that print using this technology. They differ in terms of accuracy, the number of print heads, the size of the working platform, the presence or absence of a closed working chamber, consumable options, etc. There are models that support the ability to use different materials when printing.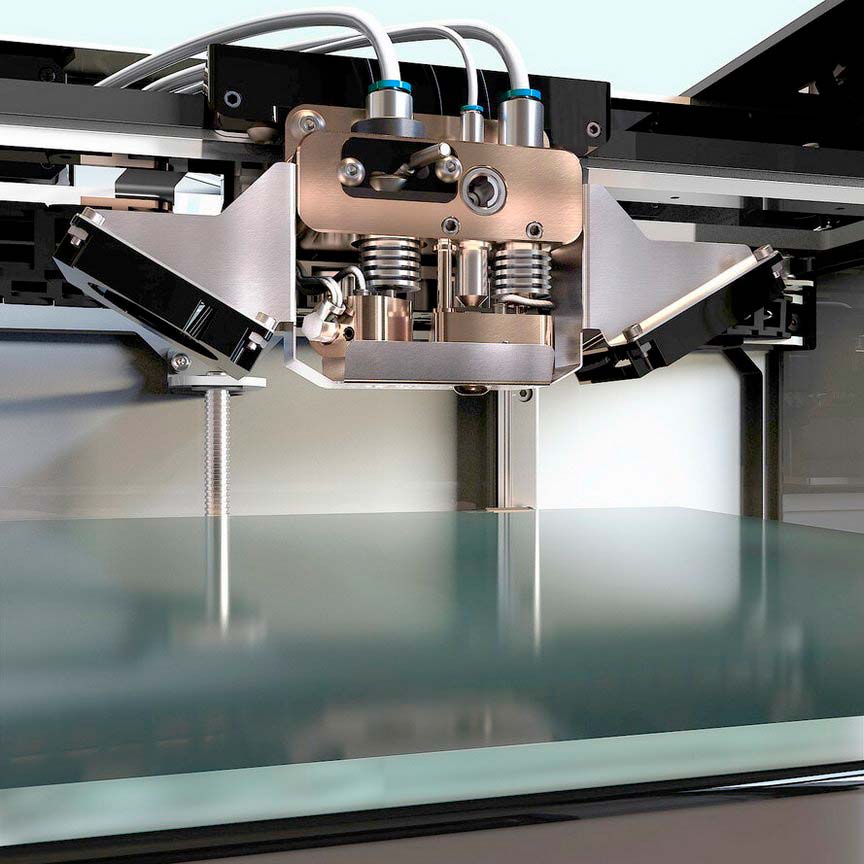 There are also industrial FDM 3D printers and personal ones.
There are also industrial FDM 3D printers and personal ones.
The following materials can be used in FDM 3D printing:
- ABS
- PLA
- SBS plastic
- Nylon
- Polycarbonate
- HIPS support material
- PVA support material
- PETG plastic
- FLEX rubber-like plastic
- RUBBER plastic with rubber properties
The most popular materials are ABS and PLA. Products printed using FDM technology are characterized by elasticity, strength and stable physical characteristics, depending on the selected material. The construction accuracy varies from 0.027mm to 1mm. As a rule, the printed object has a layered (ribbed) surface, the severity of which depends on the thickness of one layer. This effect can be eliminated by post-processing with chemicals or grinding.
The advantages of FDM 3D printing technology include sufficient speed and ease of manufacture of products, safety, high accuracy, a wide choice of materials, as well as ease of use and maintenance of equipment. In addition, consumables for printing in this way are affordable. All this together makes this technology the most highly competitive and affordable in economic terms.
In addition, consumables for printing in this way are affordable. All this together makes this technology the most highly competitive and affordable in economic terms.
FDM 3D printing technology can be used for rapid prototyping and even small series production. Depending on the selected consumable material, this technology can be used to create parts of mechanisms, toys, interior items, jewelry, souvenirs and much more. The use of high-strength engineering thermoplastics makes it possible to apply this 3D printing method to products used in the aerospace industry.
Our company has several 3D printers working on this technology. You can order high-quality 3D printing using FDM technology from us with any of the available materials and in any available color option. We guarantee you the quality and efficiency of order execution of any degree of complexity.
To order 3D printing using FDM technology, you need to send us a file in STL format. Trust our professionalism and take advantage of the most affordable 3D printing.
STEREOLITHOGRAPHY PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + SLA
SLA 3D printing technology or laser stereolithography is based on the layer-by-layer curing of a liquid photopolymer under the action of a laser beam. The technology was invented in 1986 by Charles W. Hull, who founded 3D Systems, which manufactures 3D printers that print using this technique.
Photopolymer, which in this case acts as a consumable, is a resinous substance that changes its properties under the influence of ultraviolet radiation - it polymerizes and hardens. In this case, the wavelength and time of exposure to radiation will depend on the environmental conditions and the specific material.
The principle of building a model using laser stereolithography technology at the initial level is similar to any other - the modeled object in STL format is loaded into the 3D printer software, placed in a virtual working chamber and cut into layers. Photopolymer resin is poured into a special container. It contains a working platform on which the part will be built. Initially, the working platform is set so that it is covered with the thinnest layer of photopolymer (0.05-0.13 mm). This will be the size of the layer when printed. Then the laser is turned on, it irradiates the areas that will later become parts of the finished product. As a result of irradiation, the material hardens and the working platform sinks to the extent of the layer. The algorithm repeats again until all programmed layers are exhausted. Then the finished product is immersed in a special bath, into which a composition is poured to remove excess elements. And at the end, the product is again irradiated so that it gains maximum strength.
Photopolymer resin is poured into a special container. It contains a working platform on which the part will be built. Initially, the working platform is set so that it is covered with the thinnest layer of photopolymer (0.05-0.13 mm). This will be the size of the layer when printed. Then the laser is turned on, it irradiates the areas that will later become parts of the finished product. As a result of irradiation, the material hardens and the working platform sinks to the extent of the layer. The algorithm repeats again until all programmed layers are exhausted. Then the finished product is immersed in a special bath, into which a composition is poured to remove excess elements. And at the end, the product is again irradiated so that it gains maximum strength.
Stereolithography, like most other 3D printing technologies, requires support. After printing is completed, they are removed manually.
The main advantages of stereolithography technology are the highest precision and the ability to create the smallest and thin-walled objects.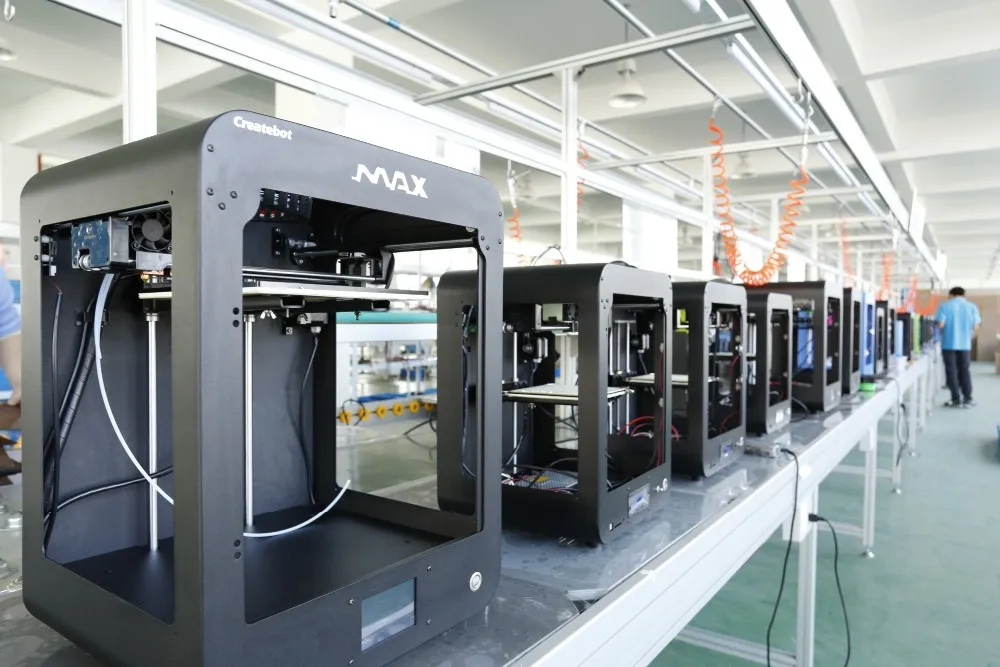 The technique is distinguished by easy post-processing of products and their almost perfect surface. The disadvantage of this technology is the impossibility of using several materials at once. Color printing is also not possible. The properties of the model and its color will determine the initial characteristics of one photopolymer. In addition, the cost of such printing and equipment is not cheap.
The technique is distinguished by easy post-processing of products and their almost perfect surface. The disadvantage of this technology is the impossibility of using several materials at once. Color printing is also not possible. The properties of the model and its color will determine the initial characteristics of one photopolymer. In addition, the cost of such printing and equipment is not cheap.
Due to the fact that stereolithography allows you to get a model of almost any degree of complexity, the main scope of this 3D printing is research. And due to the highest accuracy and detail, this technique is used in medicine, in particular in dentistry. Also, printed models are in demand in art, jewelry, museum work and restoration. There are photopolymers that can be used to print molded models. The model printed on a 3D printer, in this case, is poured with molding sand and placed in an oven for annealing at a temperature of 1000 degrees. As a result, the polymer burns out without leaving a trace, and the resulting form can be used for pouring metal under vacuum. As the metal cools, the mold breaks and the metal part is removed.
As the metal cools, the mold breaks and the metal part is removed.
In our company you can order 3D printing using SLA technology. We have in our arsenal professional 3D printers using this technology and a wide range of photopolymer resins with various characteristics for 3D printing. We guarantee you high quality and prompt execution of the order. To order 3D printing using the laser stereolithography method, you need to provide us with a file in STL format.
Get the most out of high-precision and highly detailed stereolithographic 3D printing.
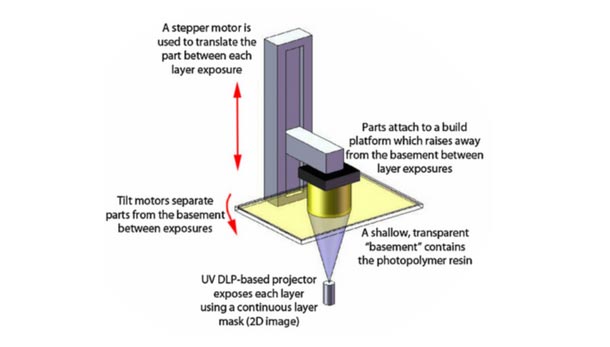
DIGITAL LIGHT PROCESSING PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + DLP
DLP 3D printing is one of the most accurate and fastest 3D printing methods. It is based on the technology that Larry Hornbeck invented for multimedia projectors. The peculiarity lies in the use of a special mirror matrix. Each individual pixel of this matrix is a microscopic mirror.
DLP stands for Digital Light Processing, which means "Digital Light Processing". Thus, this technology is one of the varieties of photopolymer 3D printing and photopolymer resin is used as a consumable. This resin is irradiated with projected light from the LEDs and hardens. The technology is very similar to stereolithography. However, with SLA 3D printing, each layer is, as it were, loomed with laser beams. And in DLP technology, the layer is completely projected onto a photopolymer using the same matrix with micromirrors, that is, this method is more like stamping. Thus, while maintaining the highest accuracy of 3D printing, it was possible to significantly increase its speed. At the moment, the speed of DLP printing is several times higher than FDM, SLM and SLA printing. For this reason, the DLP 3D printing technique is one of the most promising.
Thus, this technology is one of the varieties of photopolymer 3D printing and photopolymer resin is used as a consumable. This resin is irradiated with projected light from the LEDs and hardens. The technology is very similar to stereolithography. However, with SLA 3D printing, each layer is, as it were, loomed with laser beams. And in DLP technology, the layer is completely projected onto a photopolymer using the same matrix with micromirrors, that is, this method is more like stamping. Thus, while maintaining the highest accuracy of 3D printing, it was possible to significantly increase its speed. At the moment, the speed of DLP printing is several times higher than FDM, SLM and SLA printing. For this reason, the DLP 3D printing technique is one of the most promising.
The thickness of one layer when printing using DLP technology is 10-15 microns, which is basically similar to the indicators for SLA 3D printing technology. For comparison, the FDM method implies a minimum thickness of at least 50 microns.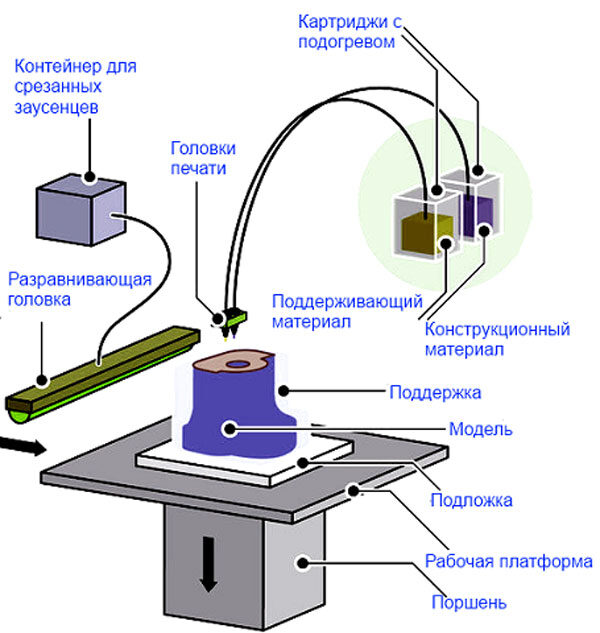
Since DLP printers are the main competitors of SLA printing, their application is about the same. They can print products for dentistry, jewelry, complex designs and even souvenirs. The technology is also in demand in the research area.
Photopolymers used in 3D printing with this method are diverse, and you can choose a material with the desired characteristics. For example, there are materials that mimic the properties of ABS plastic, hard engineering plastics, and even rubber. However, it is important to know that in some cases, under the influence of light, photopolymer products can crack and become brittle. This technology implies the impossibility of using several materials at once. Color printing is also not possible. The properties of the model and its color will determine the initial characteristics of one photopolymer.
However, there is also a drawback to DLP technology - as in the case of SLA 3D printers, the cost of equipment is very high, as in principle the price of photopolymers. Not every, even a large company, can afford such a 3D printer.
Not every, even a large company, can afford such a 3D printer.
But this does not mean at all that you will not be able to take advantage of the speed and advantages of DLP printing, because you have the opportunity to order 3D printing on such a 3D printer in our company. To do this, you just need to provide us with an STL file with the desired model. We guarantee you prompt execution of the order and high quality.
Enjoy high-quality, fast, high-precision DLP printing.
PRINT TECHNOLOGY LED DISPLAY – + LED
One of the varieties of DLP 3D printing technology is LED 3D printing. That is, this method is based on the same digital light processing (as Digital Light Processing stands for). However, in devices for LED 3D printing, instead of a mirror chipped matrix, there is an LED display that immediately highlights a whole layer on the material, like a kind of light stamp. Using an LED display allows you to increase the speed of 3D printing.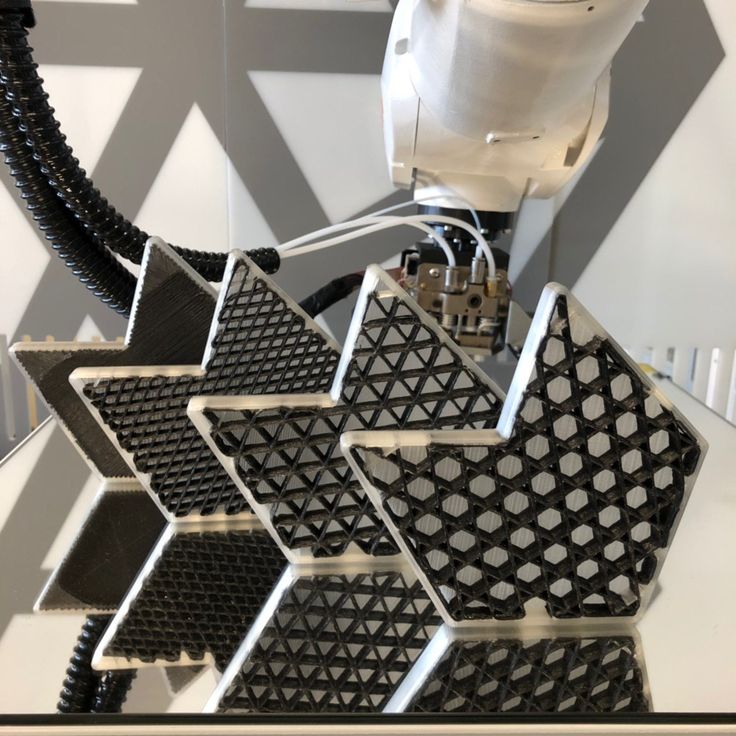 So it takes about 10-15 minutes to 3D print 2.5 cm along the Z-axis, and it's really fast. Although the print speed in any case will directly depend on the thickness of one layer.
So it takes about 10-15 minutes to 3D print 2.5 cm along the Z-axis, and it's really fast. Although the print speed in any case will directly depend on the thickness of one layer.
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin is used, which polymerizes under the action of ultraviolet light, that is, it changes its qualities, passing from a semi-liquid state to a solid one. There are many options for photopolymers, among which there are materials that, after the polymerization process, imitate the characteristics of solid, including engineering plastics. There are also those that are very similar to classic rubber after hardening, that is, they have the same strength and elasticity indicators. You can also choose biocompatible photopolymers. When choosing a material for printing, you should be guided by the technical characteristics and scope of a particular photopolymer.
Like any other photopolymer 3D printing, LED technology is characterized by the highest precision and detail. The thickness of one layer is only 10-15 microns. With its help, you can print thin-walled products, objects with complex geometry. Photopolymers practically do not shrink and do not change their geometry after hardening, and this is also an advantage, especially when it is necessary to print anatomically accurate models. The DLP LED 3D printing technology itself, although it provides for a layer-by-layer method for creating a model, still does not differ in pronounced layering of the finished model. The surface is almost perfectly smooth, requiring no additional processing.
The thickness of one layer is only 10-15 microns. With its help, you can print thin-walled products, objects with complex geometry. Photopolymers practically do not shrink and do not change their geometry after hardening, and this is also an advantage, especially when it is necessary to print anatomically accurate models. The DLP LED 3D printing technology itself, although it provides for a layer-by-layer method for creating a model, still does not differ in pronounced layering of the finished model. The surface is almost perfectly smooth, requiring no additional processing.
If complex objects are printed, support must be used. They can be set in automatic or manual mode immediately before printing during the positioning of the model in the virtual working chamber. These supports are subsequently removed manually.
LED technology implies the impossibility of using several materials at once. Color 3D printing is also not possible. The properties of the finished prototype and its color will determine the initial characteristics of the photopolymer used.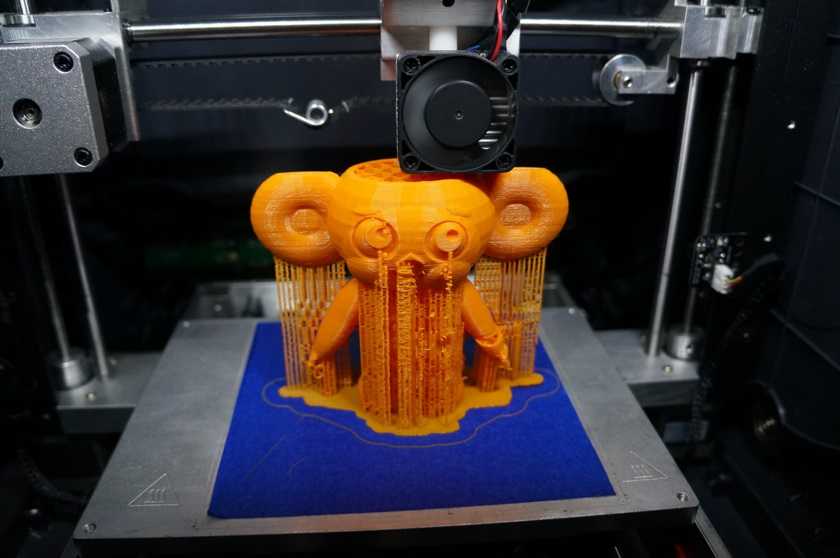
The field of application of LED 3D printing is basically the same as the field of use of DLP printing, since this technology is, in fact, its improvement. The technology is in demand in the production of hearing aids and earmolds, in dentistry and orthodontics, as well as in jewelry. Due to the high accuracy and detail of 3D objects printed using this technology, products will also be in demand in the field of research and engineering activities.
LED 3D printer is very expensive. However, this does not mean that its benefits are not available to you. You can order 3D printing using LED technology in our company. We offer you a large selection of photopolymer resins for printing and guarantee the high quality of models, in full compliance with the provided STL-file, and the prompt execution of the order.
Take full advantage of LED technology with our help.
POLYJET PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + PJ
PolyJet is a revolutionary 3D printing technology that is a powerful tool for high performance additive manufacturing. The technique was invented and patented by Stratasys. The operation of a PolyJet 3D printer is very similar to a conventional, well-known inkjet printer, but printing is carried out not on paper and not with simple ink, but on a special substrate in the chamber, and an acrylic-based liquid photopolymer acts as a material.
The technique was invented and patented by Stratasys. The operation of a PolyJet 3D printer is very similar to a conventional, well-known inkjet printer, but printing is carried out not on paper and not with simple ink, but on a special substrate in the chamber, and an acrylic-based liquid photopolymer acts as a material.
The PolyJet-enabled 3D printer is equipped with a special print head with nozzles. There can be several printheads, which allows you to print faster and even prototyping several objects at once. The printing process is carried out by dosed deposition of a photopolymer. One layer of 16 microns is sprayed at a time. Then this layer is exposed to an ultraviolet lamp and the photopolymer turns into a hard plastic. After that, the working platform with the substrate is lowered, and the algorithm is repeated again. When printing complex geometric shapes, a support material is used. For this technology, a special gel-like material has been created, which is easily removed with plain water or hands.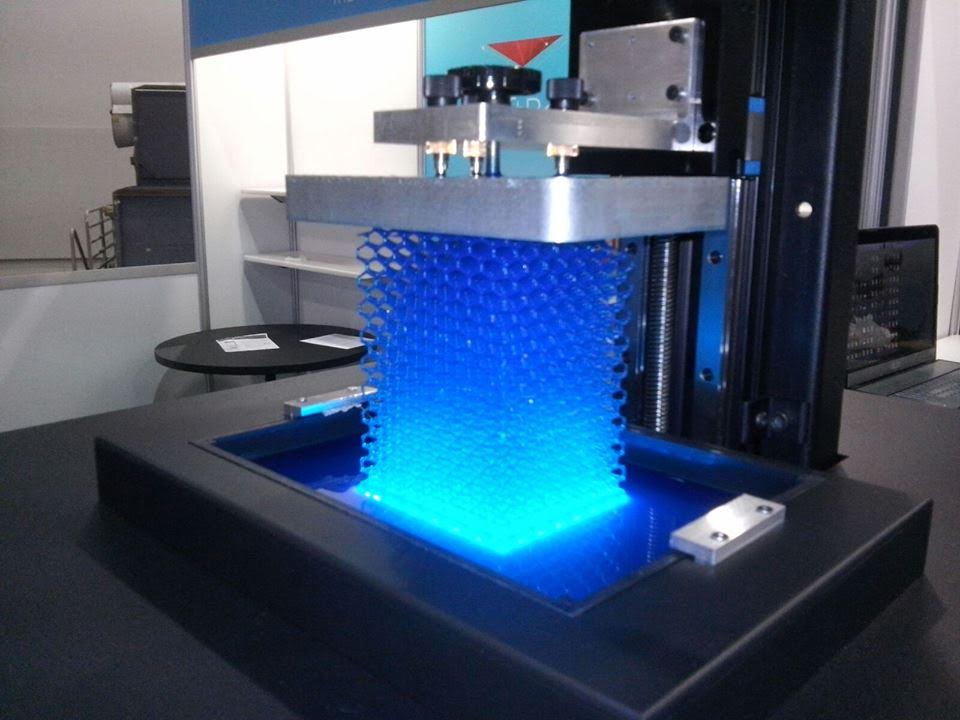
A key feature of PolyJet 3D printing technology is the ability to use multiple materials in one print run. At the same time, there are models of 3D printers that can mix photopolymers in various proportions, obtaining a variety of composite materials with certain characteristics. Also, this technology is characterized by the possibility of complex color reproduction. That is, it is possible to use color printing, the palette of which includes about 1000 colors and shades. In fact, it is the only additive manufacturing technology that supports these capabilities.
Other advantages of the method include: high printing speed, high accuracy and detail, perfect surface and generally excellent quality of printed objects. In addition, a wide range of materials allows you to create objects of almost any kind. More than 100 different photopolymer resins can be used as a base, mixing of which allows obtaining materials from transparent to completely opaque, from hard to elastic and rubbery.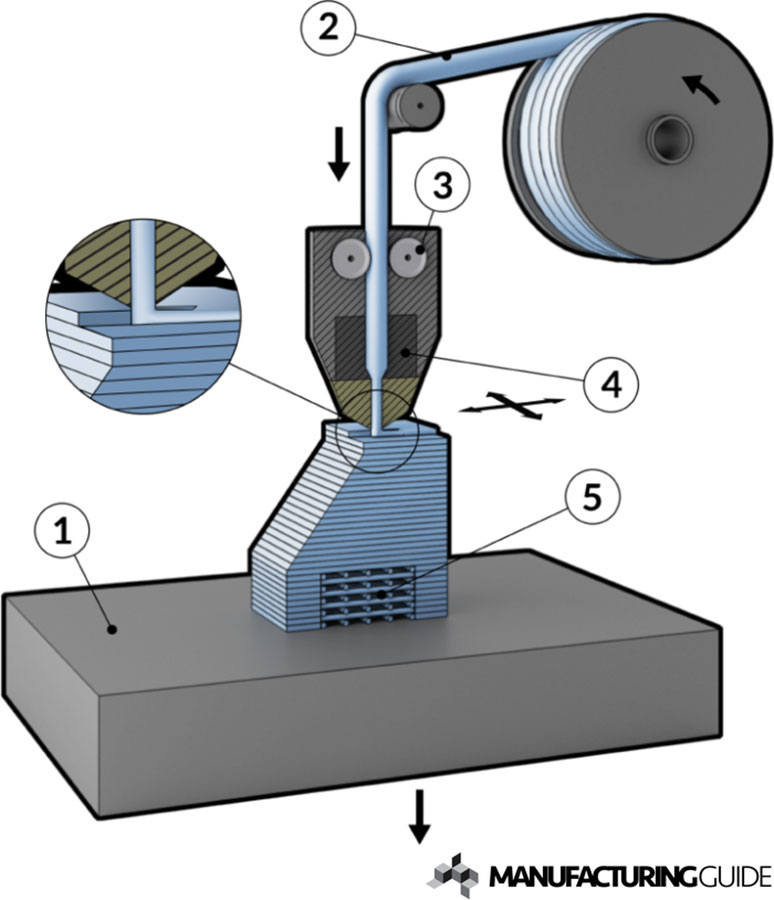 This is truly a new standard for realism in the most complex prints. PolyJet technology allows you to achieve perfect surface smoothness and imitate any even the most subtle texture. The camera of the PolyJet 3D printer is quite large, but if you need to print a large object, then it can be broken into parts, which are then simply glued together.
This is truly a new standard for realism in the most complex prints. PolyJet technology allows you to achieve perfect surface smoothness and imitate any even the most subtle texture. The camera of the PolyJet 3D printer is quite large, but if you need to print a large object, then it can be broken into parts, which are then simply glued together.
The only disadvantage of the technology is its high cost. The equipment is very expensive, and photopolymer resins are not cheap. But this does not mean that you cannot use this technology, because you have the opportunity to order 3D printing using PolyJet technology in our company. In a short time, we will implement your project on our own 3D printer. All you need is to provide us with the STL file.
PolyJet 3D printing technology is truly limitless.
COLOR JET PRINTING TECHNOLOGY – + CJP
Color inkjet 3D printing - CJP (ColorJet Printing) technology - a patented technique invented by 3D Systems. It consists in layer-by-layer gluing and coloring of the powder gypsum composite. 3D printing of this type is based on a technique called 3DP, which is its improvement.
It consists in layer-by-layer gluing and coloring of the powder gypsum composite. 3D printing of this type is based on a technique called 3DP, which is its improvement.
3D printing by this method is based on the use of two materials: base and binder. To create the base layer, a consumable of the main type is used. It consists of gypsum mixed with a polymer. And the binder is used for gluing and staining the layers.
ColorJet Printing 3D printer has two cameras. A gypsum composite is poured into one of them, and the second chamber is used to remove excess material. The model is "grown" in layers. A special roller distributes a thin layer of material on the working platform. The print head applies the adhesive and colors the main consumable particles. All this is carried out in accordance with the loaded mathematical 3D model. The working surface is lowered by the amount of the layer (0.1016 mm), and the roller again applies a layer of gypsum composite powder, and so on until the model is printed to the end.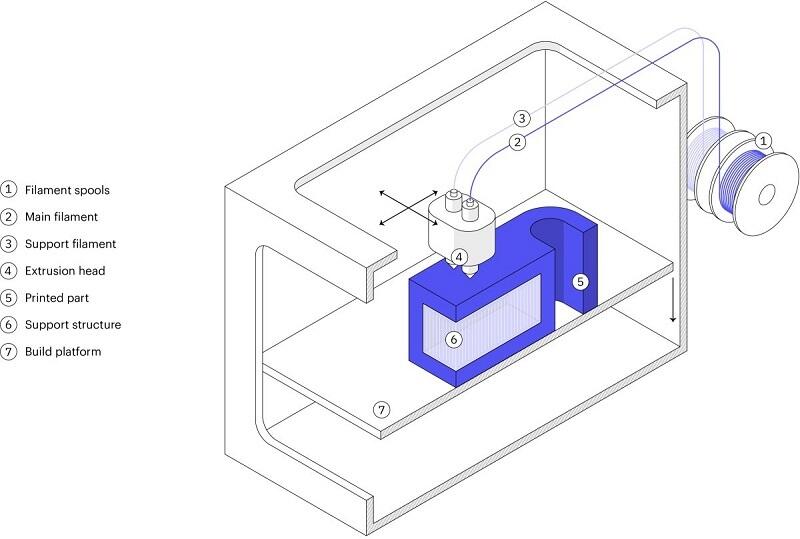
ColorJet Printing technology has a relatively low cost of printed models. Its advantage is the absence of the need for supports, since the non-glued material will act as supporting structures. In addition, the material that was not used during printing can be reused. It turns out that this method of additive manufacturing is waste-free.
The CJP technology is the only one that uses the CMYK printing color palette. This palette includes 390 thousand colors and shades. The material is dyed during the gluing of the layer, resulting in details with excellent color reproduction.
The accuracy of building a model by this method is very high, the minimum printed element has dimensions of 0.1-0.4 mm. The thickness of the walls of the prototype, which will not collapse under their own weight, is 0.102-0.089 mm.
Models printed using ColorJet Printing technology have a typical gypsum rough surface, characterized by a high degree of hygroscopicity. The strength of the models is average. However, finished models are easy to sand, paint and glue. To improve the characteristics of the model and protect them from moisture, you can cover the surface with varnishes, waxes, resins, as well as all kinds of fixatives.
However, finished models are easy to sand, paint and glue. To improve the characteristics of the model and protect them from moisture, you can cover the surface with varnishes, waxes, resins, as well as all kinds of fixatives.
The technology can be used for 3D printing of architectural models, product presentations, souvenirs, miniatures, etc. Despite the fact that the products are of low strength, they allow you to visually evaluate the prototypes.
CJP 3D printer has impressive dimensions and is quite expensive, despite the fact that the cost of printed prototypes is low, not everyone can afford such pleasure. In our company, you can order 3D printing using ColorJet Printing technology. We guarantee you prompt execution of the order and full compliance of the prototype with the modeled object. All you need is to provide us with an STL file with a 3D model.
Take advantage of CJP 3D printing technology with our help and appreciate all its advantages in practice.
SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + SLS
Selective, that is, selective, laser sintering is a 3D printing technology that was created back in 1979.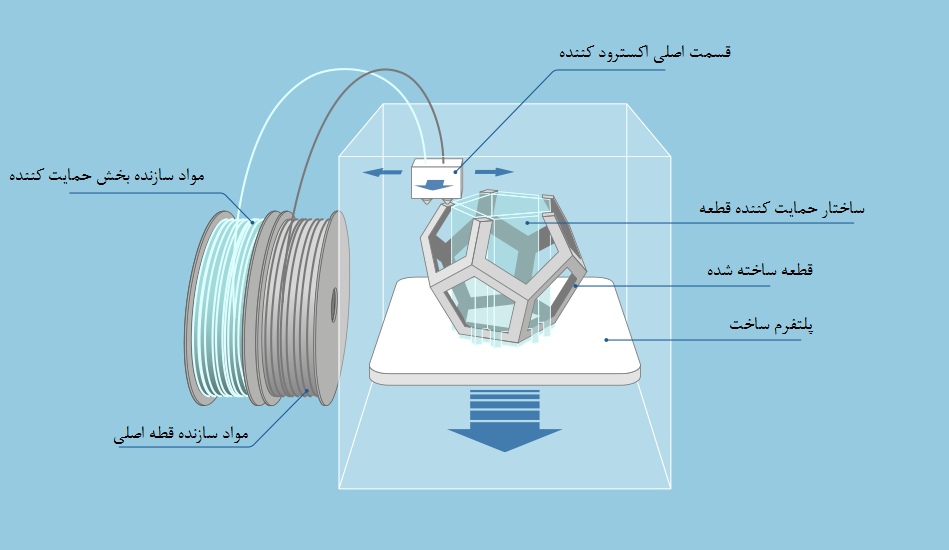 However, for a long time it was not available to the market until DTM was created in 1996. In 2001, 3D Systems bought this company, and in 2014 the patent expired, and now this technology is available to a wide range of consumers.
However, for a long time it was not available to the market until DTM was created in 1996. In 2001, 3D Systems bought this company, and in 2014 the patent expired, and now this technology is available to a wide range of consumers.
The SLS 3D printing technique consists in the fact that the material is heated by a laser beam until the particles are sintered, that is, not completely. As a result, the model turns out not to be solid, but as if “sintered” from individual tiny particles. If we consider the structure under magnification, then individual particles of the material will be visible, as if glued to each other.
The operation of a 3D printer that prints using SLS technology is as follows. Powder material is poured into the chamber. A 3D model in STL format is loaded into the software. The working platform is exposed and a thin layer of material (thickness about 120 microns) is applied to it, leveled with a roller. The laser sinters the powder particles according to the loaded model.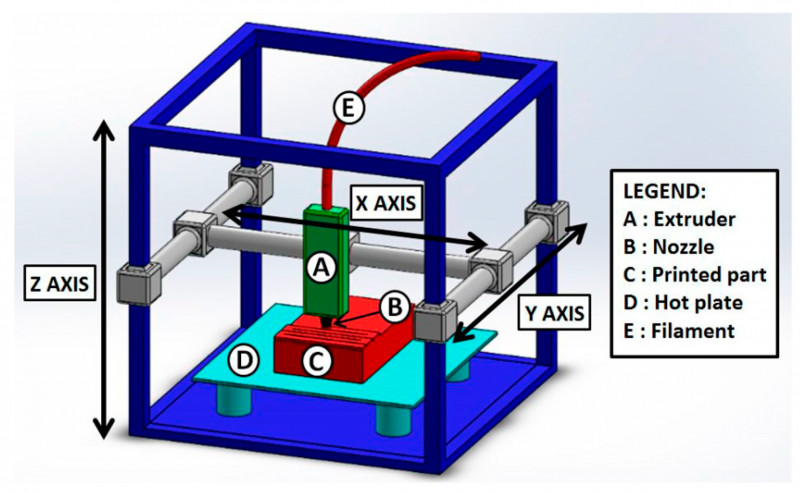 After the layer is completed, the platform is lowered and a new layer of material is applied. The procedure will be repeated until the very last layer is completed.
After the layer is completed, the platform is lowered and a new layer of material is applied. The procedure will be repeated until the very last layer is completed.
Since there is unused material in the working chamber, the need for supports simply disappears, because complex and overhanging parts will be supported by unused material. This allows you to get models of any, even very complex geometry.
Powder polymers, metals and their alloys, ceramics, glass, composite materials can be used as consumables. But in any case, the material must be in powder form. Due to the fact that the power of laser radiation can be adjusted, the degree of melting of the material can change, and, accordingly, the strength and uniformity of the structure of the resulting model. Currently, the most popular material for 3D printing using SLS technology is polyamide. This is a versatile powder material that can be used in almost any field. If powdered metal is used for printing, it is preheated to make printing faster and easier.
As a result of 3D printing, models are obtained with a surface that requires processing, in particular grinding. Models made of polyamide are sensitive to moisture, so they must be coated with a protective compound, such as moisture-resistant paint, if outdoor use is planned.
Selective laser sintering shows excellent results when used in small-scale production, as well as for the manufacture of master models. This 3D printing technology is in demand in the aerospace industry, in manufacturing, etc.
The disadvantages of SLS 3D printing technology are the high cost of equipment. In addition, the powder material is potentially harmful to the human body, so a separate room with air conditioning and an air filter is equipped for such 3D printers. All this imposes difficulties for additive manufacturing using this technique. But this does not mean that you cannot take advantage of the possibilities of selective laser sintering technology, because our company provides professional 3D printing services on such equipment.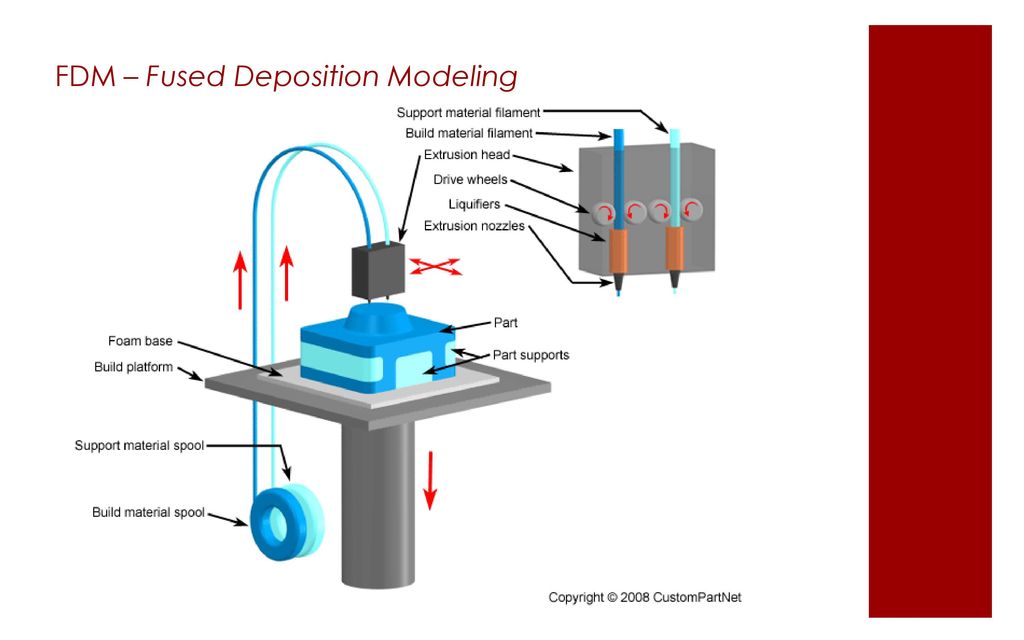 You can order 3D printing using SLS technology from us. All you need is to provide us with a file with a 3D model in STL format. We guarantee you high quality printing in full accordance with the provided 3D model.
You can order 3D printing using SLS technology from us. All you need is to provide us with a file with a 3D model in STL format. We guarantee you high quality printing in full accordance with the provided 3D model.
SELECTIVE LASER MELTING PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + SLM
Selective (selective) laser melting - SLM is a 3D printing method from a mathematical CAD model, which is used to create 3D objects by melting metal powders. For this, high-power lasers are used.
Using this technology, it is possible to create precise metal parts that will later be used in various units and assemblies, including non-separable structures that change their geometry during use. This type of printing is becoming more and more widespread, because the parts created by this method are in many ways superior in their mechanical and physical characteristics to products produced by traditional methods.
The advantages of 3D printing using SLM technology are: the ability to solve the most complex production problems, including in the aerospace industry, where parts and assemblies have a hard load and serious requirements are imposed. Also, SLM printing is used in experimental and scientific and technical activities, where it is possible to significantly reduce the R&D cycle, because the most complex mechanisms and products can be created without serious equipment.
Also, SLM printing is used in experimental and scientific and technical activities, where it is possible to significantly reduce the R&D cycle, because the most complex mechanisms and products can be created without serious equipment.
The technology also allows you to print objects with internal cavities, which can significantly reduce the weight of products.
The essence of the method lies in the layer-by-layer application of metal powder on a special heated platform and its subsequent processing with a high-power laser, in accordance with the CAD model. The working chamber of the 3D printer, where the melting process itself takes place, is filled with argon or nitrogen. The choice of gas will depend on which consumable is selected for printing. Inert gas will be mainly consumed in preparation for printing, when the chamber is purged, because it is necessary to achieve conditions so that the percentage of oxygen in the chamber is no more than 0.15%. This is a necessary condition in order to avoid the oxidation of metals. Consumables can be: powdered metals and alloys. It can be tool or stainless steel, titanium and its alloys, aluminum, platinum, gold, as well as cobalt-chromium alloys.
Consumables can be: powdered metals and alloys. It can be tool or stainless steel, titanium and its alloys, aluminum, platinum, gold, as well as cobalt-chromium alloys.
The model is fused layer by layer. After the printing of the prototype is completed, it is removed from the chamber with the working platform and separated from it mechanically. In the future, it may require processing, because the surface of the product may not be ideal. However, the product will be very strong and uniform in structure, similar to cast.
One of the advantages of the technology is its economy and non-waste. After all, unsintered material can be reused. The thickness of one layer is 20-100 microns. Thus, SLM 3D printing is a very precise and highly detailed additive manufacturing technique.
The cost of 3D printers using this method is very high. And in general, their operation is by no means a simple matter, requiring special conditions. But you have a great opportunity to use 3D printing using selective laser fusion technology with the help of our company. All you need is just to order 3D printing using this technique in our company. To do this, you need to provide us with an STL file with a CAD model for printing.
All you need is just to order 3D printing using this technique in our company. To do this, you need to provide us with an STL file with a CAD model for printing.
Take advantage of the innovative method of creating high-precision metal products - SLM printing.
ELECTRON BEAM MELTING PRINT TECHNOLOGY – + EBM
One of the most reliable metal 3D printing methods is EBM printing or electron beam melting. This is an additive manufacturing technology that is used to create high-strength, comparable to cast, metal products. Pure (without impurities) metal powder acts as a consumable. Printing is carried out in a vacuum chamber, which minimizes the oxidation of the material, such as pure titanium.
Electron beam melting is very similar to SLS 3D printing technology, that is, selective laser melting. However, it does not use powerful lasers, but electron emitters, which serve as sources of powerful energy used to melt metal.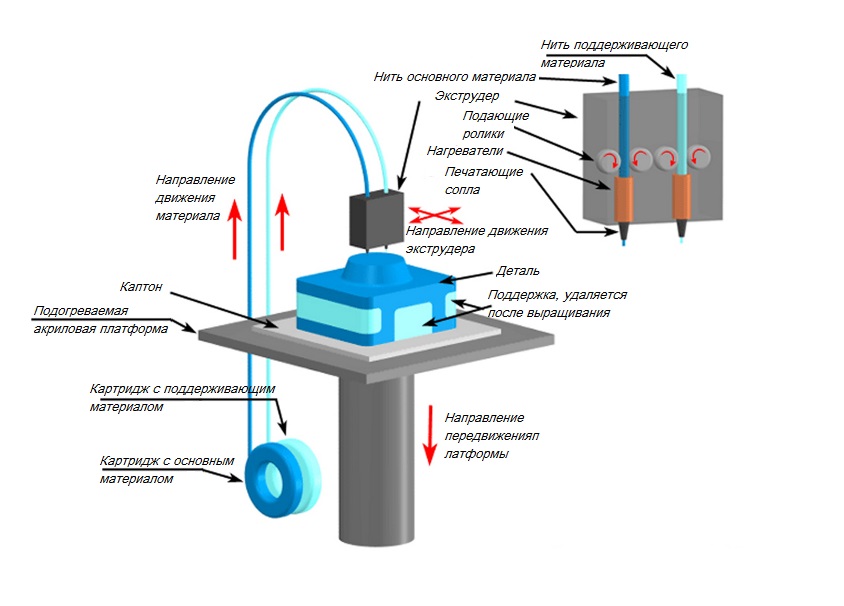 So-called electron guns fire high power electron beams that fuse metal powder. The method is similar to other 3D printing methods - the layering of consumables. A layer of metal powder is applied, and electron beams, following the contour of the model, fuse the material. Then the algorithm is repeated again until all layers are created and a finished three-dimensional object is obtained in accordance with the mathematical 3D model.
So-called electron guns fire high power electron beams that fuse metal powder. The method is similar to other 3D printing methods - the layering of consumables. A layer of metal powder is applied, and electron beams, following the contour of the model, fuse the material. Then the algorithm is repeated again until all layers are created and a finished three-dimensional object is obtained in accordance with the mathematical 3D model.
As a result of such 3D printing, a high-density metal model is obtained, and the porosity of the structure is absent. This means that additional processing by the method of firing for a strong fusion of the material in the model is not required. And the model itself will have high strength characteristics initially, that is, it will not differ in any way from cast products.
Electron beam melting is printed at high background temperatures of 700-1000 degrees Celsius. This avoids a strong temperature difference between the already cooled printed layer and the fresh hot layer. Therefore, printed parts will not suffer from residual mechanical stress. This is how the highest possible strength of EBM-printed products is achieved.
Therefore, printed parts will not suffer from residual mechanical stress. This is how the highest possible strength of EBM-printed products is achieved.
This 3D printing technology is used to create high-precision titanium prostheses and implants, such as hip and knee implants, skull parts, etc. Titanium combines strength and biocompatibility.
EBM printing is also used in the aerospace industry. With the help of this technology, load-bearing structural elements of various devices (aircraft, rockets), as well as parts of their engines, are printed. For this purpose, strong and light powder metals are used.
EBM printing equipment is very expensive. However, you can order 3D printing using the technology of electron beam melting of powder metal. We are ready to fulfill your order in the shortest possible time, and we guarantee the high quality of printed products, in full accordance with the provided STL file.
Take advantage of high-precision and high-strength metal 3D printing - electron beam melting (EBM).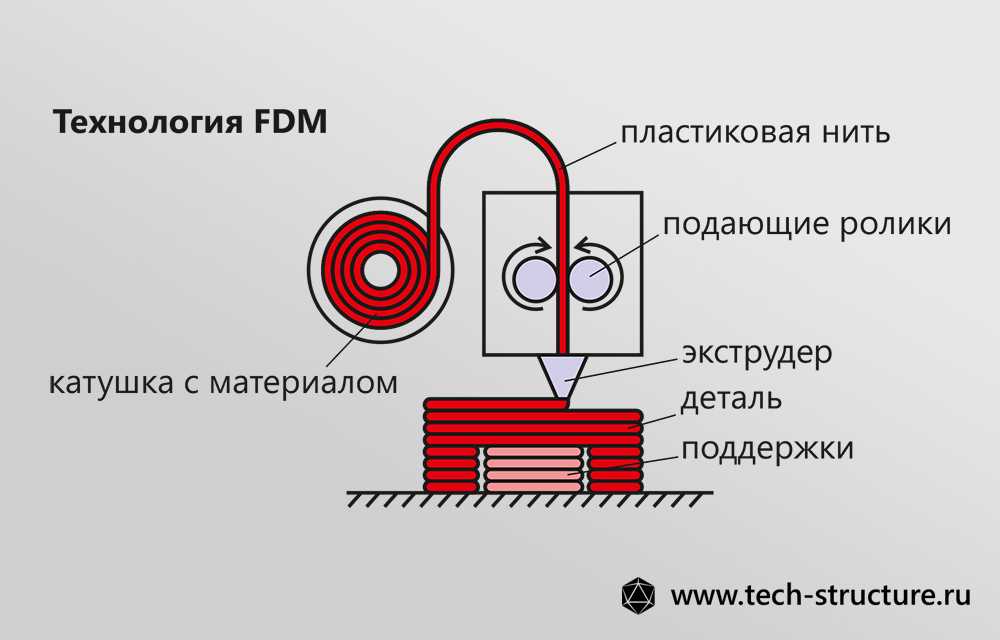
FDM technology. How it works.
Hello everyone, 3DTool is with you!
In this article on 3D printing, we will look at the basic principles of FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) technology. Let's deal with the basic mechanics of this process. Its advantages and limitations.
FDM technology
Overlay printing (FDM) is an additive manufacturing process that is realized through the extrusion of materials. In FDM, an object is built by applying molten material according to a predetermined algorithm, layer by layer. The materials used are thermoplastic polymers and are filament-shaped.
FDM is the most widely used 3D printing technology. FDM printers are on the market in a wide variety. It's basically the first technology people come across when they start working with 3D. The following will introduce the basic principles and key aspects of this printing method.
An engineer who designs a 3D model should take into account the possibilities of technology when manufacturing a part with FDM, this knowledge will help him achieve the best result.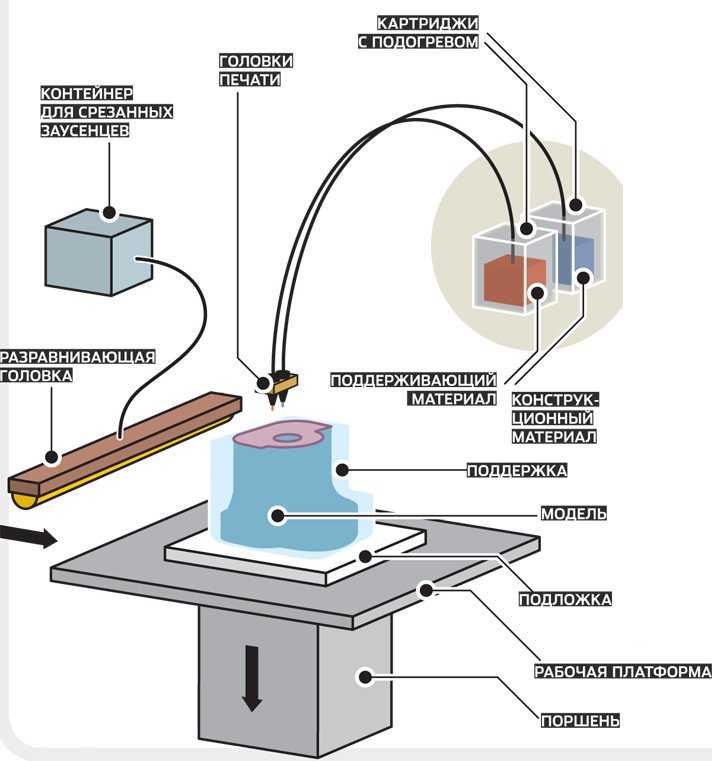
Process FDM printing
Here is how the FDM process works:
A spool of thermoplastic filament is loaded into the printer. Once the nozzle reaches the required temperature, the filament is fed into the extruder and into the nozzle where it is melted.
The extruder is attached to a 3-axis system that allows it to move in the X, Y and Z directions. The molten material is extruded in thin filaments and melted in layers at predetermined locations where it then cools and solidifies. Sometimes the cooling of the material is accelerated by the use of fans attached to the extruder.
The extruder requires several passes to fill the printable area. When the layer is finished, the platform moves down (or, as in some printer models, the extruder moves up), and a new layer is welded onto the already set one. This process is repeated until the entire model is printed.
FDM printer specifications
Most FDM systems allow you to adjust several parameters of the printing process. Such as nozzle temperature, platforms, print speed, layer height and cooling fan speed. These are usually set by the printer operator and do not bother the modeler.
Such as nozzle temperature, platforms, print speed, layer height and cooling fan speed. These are usually set by the printer operator and do not bother the modeler.
What is important from a modeling standpoint is to consider the size of the table and the layer height of the part itself:
The standard printable area of a desktop 3D printer is usually 200 x 200 x 200 mm, while for industrial machines it can be up to 1000 x 1000 x 1000 mm. If a desktop 3D printer is preferable (e.g. for cost reasons), the large model can be broken down into smaller pieces and then reassembled/glued together.
The typical layer height used in FDM varies from 50 to 400 microns and can be determined during the software slicing step. A lower layer height will provide a smoother detail and more accurately represent complex geometry, while a higher layer height will print the part faster and at a lower cost. The layer height of 150-200 microns is optimal in terms of the ratio of printing time and its quality.
Part deformation
Warp is one of the most common defects in the FDM printing process. Some plastics shrink during cooling after extrusion. Since different regions cool at different rates, their dimensions can also change at different rates. Differential cooling causes an accumulation of internal stresses that pull the layer, the one from the bottom - up, deforming it, as shown in the figure below. From a technical point of view, deformation can be prevented by more careful control of the temperature of the platform and the chamber as a whole. By increasing the adhesion between the part and the platform.
The modeler can also reduce the chance of peeling and other warp-related defects:
Large flat areas (such as a rectangular box) are more prone to deformation and should be avoided if possible.
Thin protruding elements (for example, battlements, spiers) are also prone to deformation.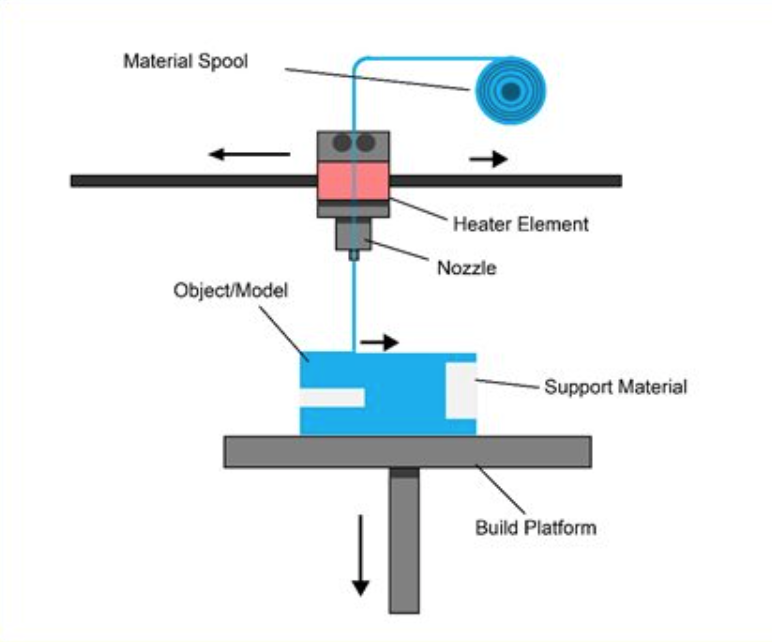 In this case, it can be avoided by adding some support material around the edge of the thin element (for example, a 200 micron thick rectangle) to increase the contact area.
In this case, it can be avoided by adding some support material around the edge of the thin element (for example, a 200 micron thick rectangle) to increase the contact area.
Sharp corners deform more often than rounded shapes, so smoothing the corners slightly can achieve a good result.
Different plastics are more susceptible to deformation: ABS is generally more sensitive to this factor than PLA or PETG due to its higher glass transition temperature and relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion.
Adhesion between layers
Good adhesion between layers is very important for an FDM printed part. As the molten plastic is extruded through the nozzle, it is pressed against the previous layer. High temperature and pressure remelt the surface of the previous layer and allow the new layer to bond with the old one.
The strength of the bond between different layers is always lower than the basic strength of the material.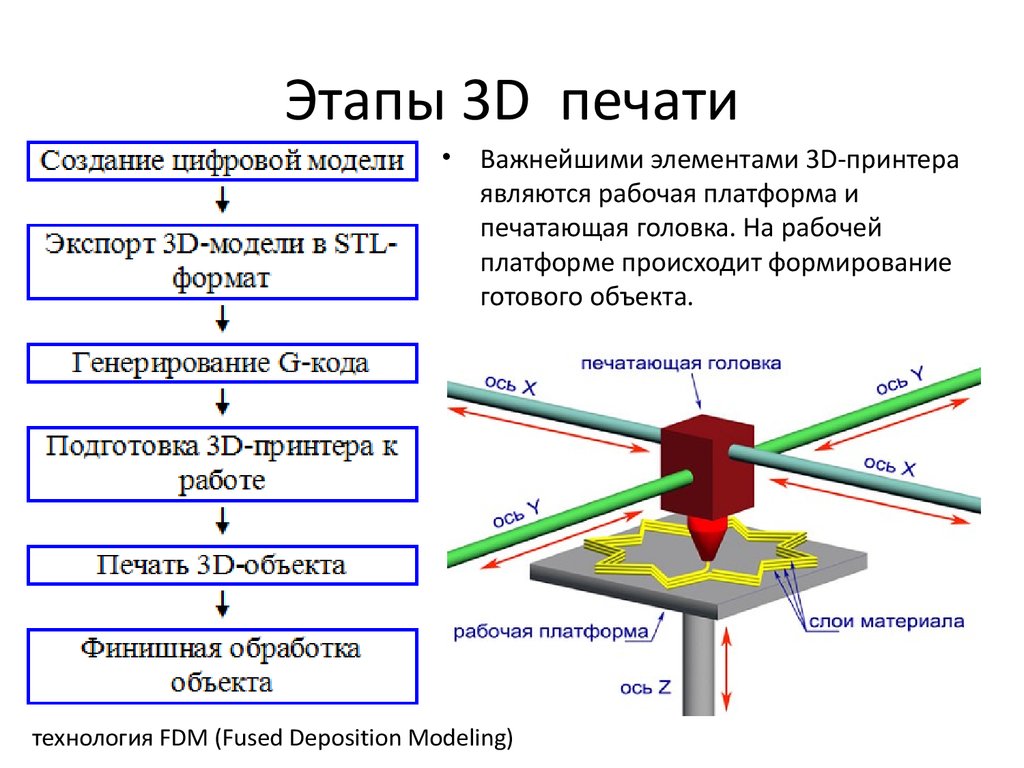
This means that FDM parts are inherently anisotropic: their Z strength is always less than their X/Y strength. For this reason, it is important to keep the orientation of parts in mind when designing.
For example, tensile test specimens printed horizontally with ABS at 50% infill were compared with test specimens printed vertically and found to have nearly 4 times higher tensile strength in the X, Y axis compared to the Z axis ( 17.0 MPa compared to 4.4 MPa). Such a part is stretched to failure, almost 10 times more (4.8% compared to 0.5%).
Moreover, since the molten material is pressed against the previous layer, its shape is deformed to an oval. This means that parts will always have a wavy surface, even at low layer heights, and that small features, such as small holes, may need post-printing post-processing.
Supports
The support structure is essential for creating tab geometries. Because plastic cannot be applied to air, some geometries require a support structure.
Because plastic cannot be applied to air, some geometries require a support structure.
Surfaces printed with supports are usually of lower quality than the rest of the part. For this reason, it is recommended that the part be modeled in such a way as to minimize the need for support.
Supports are usually printed from the same material as the part. There are also special materials that dissolve in a liquid, but they are mostly used in high-end desktop or industrial 3D printers. Printing on soluble supports greatly improves the surface quality of the part, but increases the overall cost of printing because a special printer with two print heads is required and because the cost of soluble material is relatively high.
Filling and shell thickness
FDM parts are usually not printed full in order to reduce printing time and save material. Instead, the outer perimeter is made with several passes, it is called a shell, and the inner part is filled with a low density structure called infill.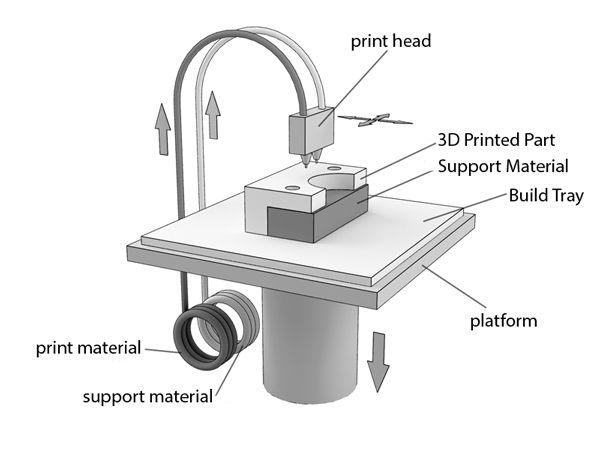
The filling and thickness of the body greatly affect the strength of the part. For desktop FDM printers, 25% infill density and 1mm body thickness are mostly suitable. Usually, these are the standard settings for fast printing and a good compromise between strength and speed.
Above you see the internal geometry of parts with different degrees of filling
FDM Essential Consumables
One of the strengths of FDM printing is the wide range of materials available. They can range from conventional plastics (such as PLA and ABS) to engineering plastics (such as TPU and PETG) and high strength materials (such as PEEK).
Below is a pyramid of materials most available in FDM printing.
The material used directly affects the mechanical properties and accuracy of printing, as well as its price. The most common FDM printing materials are listed below.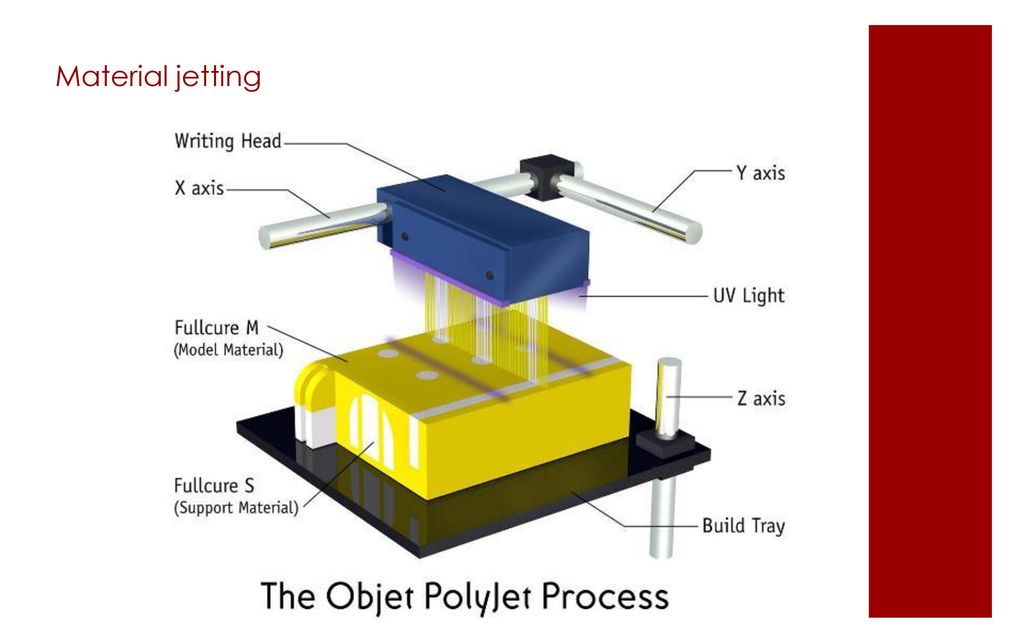 We will also consider the pros and cons of certain plastics. An overview of the main differences between PLA and ABS, and a detailed comparison of all common types of filament is a very extensive topic and can be found in special articles on the Internet and on thematic forums.
We will also consider the pros and cons of certain plastics. An overview of the main differences between PLA and ABS, and a detailed comparison of all common types of filament is a very extensive topic and can be found in special articles on the Internet and on thematic forums.
ABS
pros
· Durability
Good temperature resistance
Minuses
Shrinks when printed
PLA
pros
Excellent visual quality
Easy to print
· Unharmful. May come into contact with food
Minuses
· Low impact strength
· Longevity
Nylon
pros
· Very high strength
Excellent wear and chemical resistance
Minuses
· Actively absorbs water
PET-G
pros
· Unharmful. May come into contact with food
Sufficiently strong
Minuses
Capable of precise temperature print settings
TPU
pros
· Very flexible
Minuses
Printing accuracy is very difficult to achieve
pros
· Extremely durable and lightweight
Excellent flame retardant and chemical resistance
Minus
· High price
Need a specialized 3D printer whose extruder is capable of reaching temperatures above 300C
Postprocessing
FDM parts can be processed to high standards. When using various methods such as: sanding, polishing, priming, painting, cold welding, acetone bath (to smooth the surface and create a glossy surface), epoxy coating and plating.
When using various methods such as: sanding, polishing, priming, painting, cold welding, acetone bath (to smooth the surface and create a glossy surface), epoxy coating and plating.
Advantages and disadvantages of FDM printing
+
· FDM printing is the most economical way to produce custom thermoplastic parts and prototypes.
· FDM printing lead time is acceptable. The technology is quite affordable these days.
Wide range of materials suitable for both prototyping and some non-commercial functional applications.
-
FDM printing has the lowest dimensional accuracy and resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies, so it is not suitable for models with complex geometry and fine details
The final product will have visible layer lines, so post-processing is required for a better look
Layer adhesion mechanism makes FDM printed parts anisotropic
Highlights
· With FDM printing, prototypes and functional parts can be produced quickly and at a low cost.