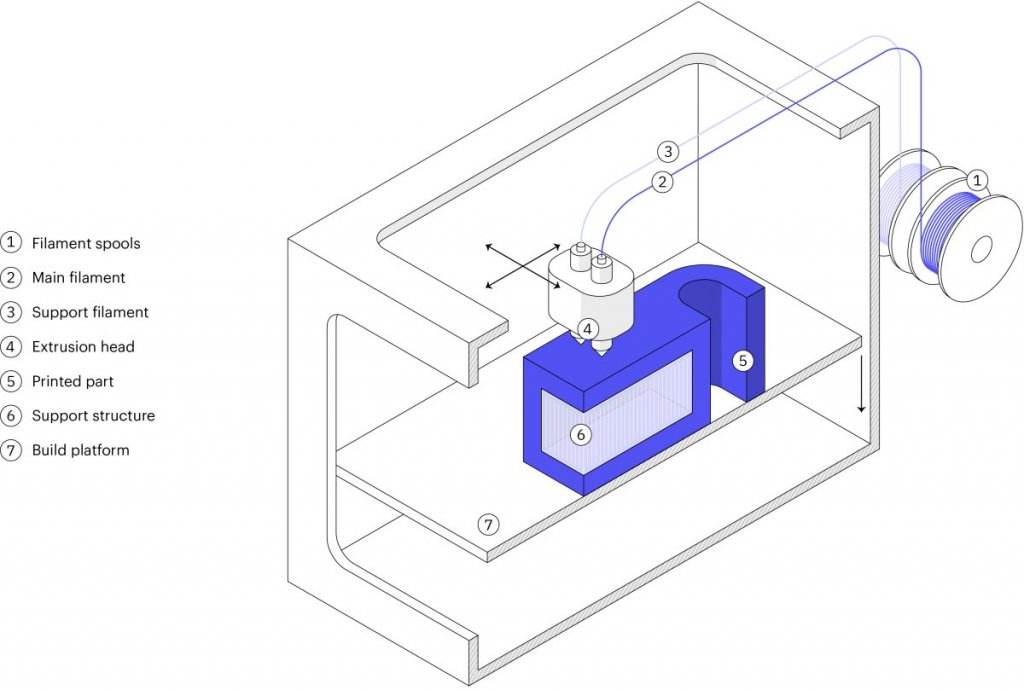
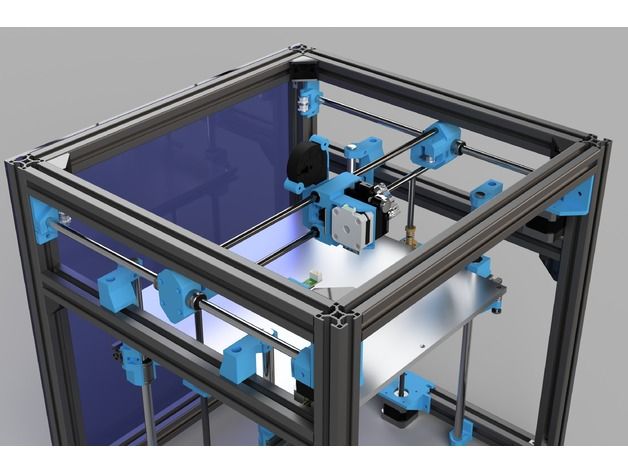
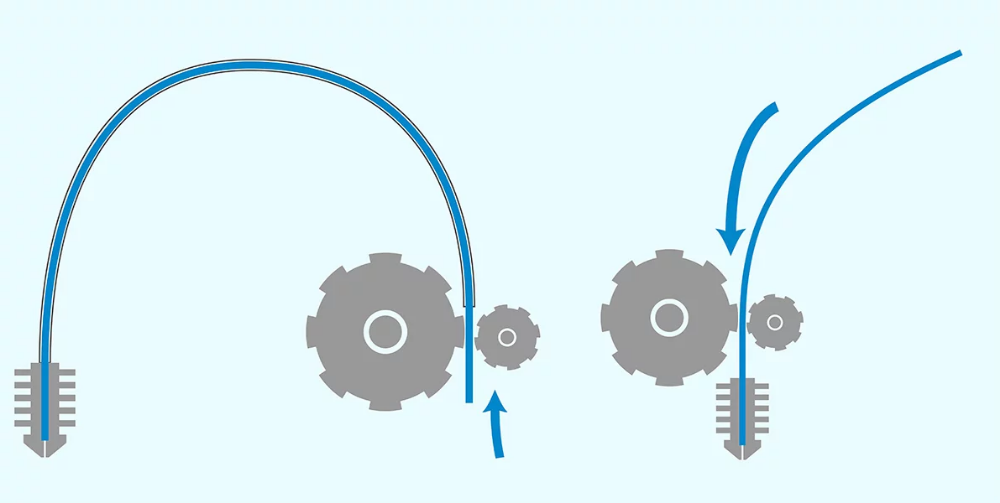
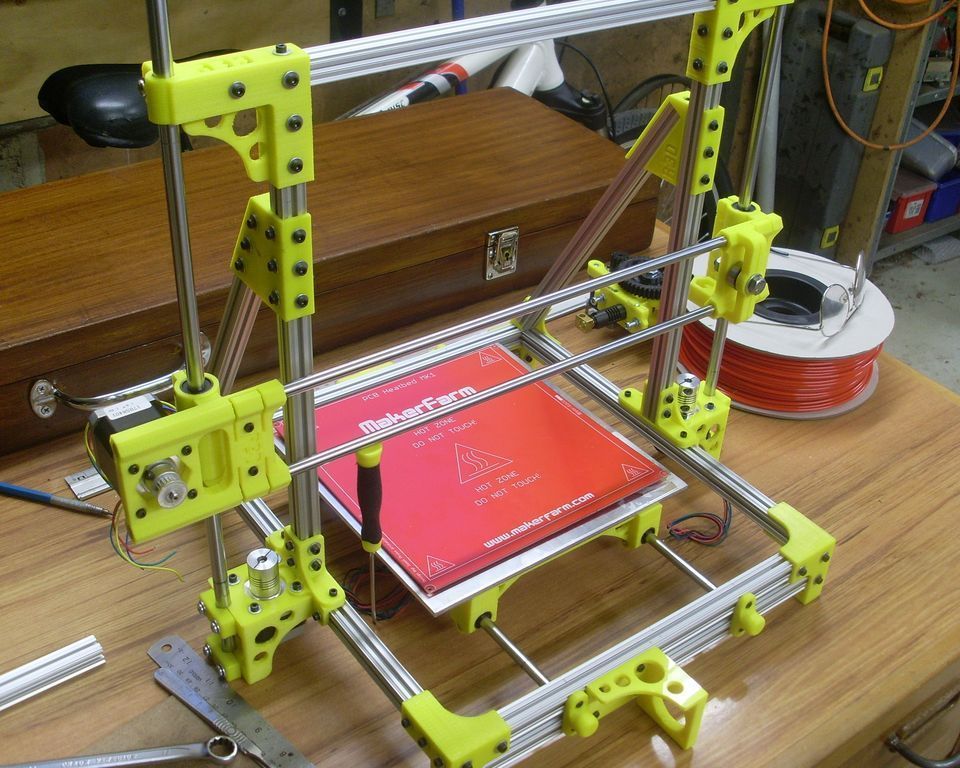
Build reprap 3d printer
Build a reprap - RepRap
This page has been flagged as containing duplicate material that PartsSupplies also attempts to cover.
These pages should be merged such that both pages do not attempt to cover the duplicate topics.
This page has been flagged as containing duplicate material that Darwin/Buyers Guide also attempts to cover.
These pages should be merged such that both pages do not attempt to cover the duplicate topics.
This page has been flagged as containing duplicate material that What Tooling Do You Have also attempts to cover.
These pages should be merged such that both pages do not attempt to cover the duplicate topics.
This page is out of date --Sebastien Bailard 04:34, 31 October 2010 (UTC)
This page is not only out of date, but contains in part simply nonsense - especially the "Software installation" section. For the lack of editors, this page should be removed. --Traumflug 21:18, 13 April 2011 (UTC)
Contents
- 1 Build a RepRap
- 2 Overview
- 2.
1 Object Creation Software
- 2.2 System control Software
- 2.3 Installing the Software (experimental)
- 2.4 Thermoplast extruder
- 2.5 Positioning system
- 2.6 Shopping list
- 2.
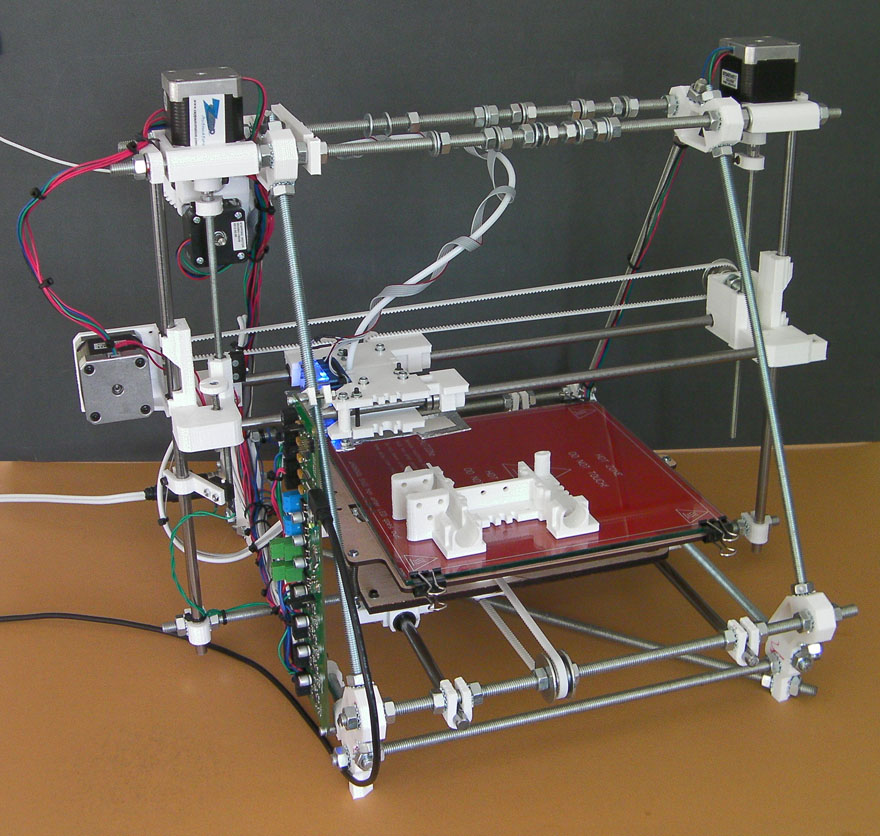
There are multiple ways to build a RepRap or RepStrap; the method selected for these instructions has been chosen to minimize skills and tools needed. If you wish to explore other options click Alternative Build Documentation.
The Classic RepRap Design is "Darwin" pictured on the right. There are very full and accurate building instructions in Make Your Own RepRap.
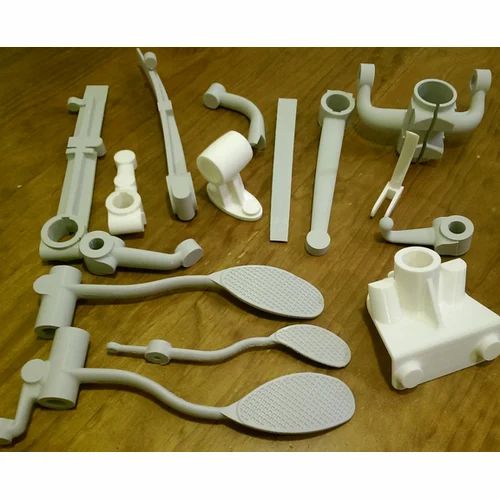
The RepRap was carefully designed to use only parts that can be made on a RepRap and other cheap parts that you can get anywhere. It was also designed to require few skills to assemble. The one snag is you have to find someone to supply you with the parts that must be made on a RepRap.
RepStrap Darwin Clones are RepRap designs which are fairly accurately copies of the Darwin design but the RepRapped parts are replaced by parts created some other way, Perhaps molded plastic or laser cut acrylic or plywood. Generally parts of one of these machines are interchangeable with RepRapped Darwin parts. Here are some Parts Suppliers.
Generally parts of one of these machines are interchangeable with RepRapped Darwin parts. Here are some Parts Suppliers.
Other RepStraps, these are 3D printers capable of making RepRap (Darwin) parts but are not structurally similar to Darwin. These machines may vary a lot but may be separated into two kinds. Those like Darwin in which the extruder (print head) is moved in the x and y directions and the work is slowly lowered as the print progresses and others where the work is moved in the x and y directions under a stationary head which gradually moves upwards as the print progresses. Here are some references to various RepStrap Machines.
If this is your first RepRap that you are building, here is a basic guide of which build option you should choose:
- If you have a friend nearby that can print out the RepRap part on their RepRap or some other 3D printer. Choose the Classic Darwin
- If you don't have access to a 3d printer then you have 3 options.
- You can build a Classic Darwin, but this means you will have to use a commercial service to print out parts for you; it can easily cost over $1000 for just those parts depending on what deals you can get. This option is probably the most expensive option.
- You can build a RepStrap Darwin Clone. This means you can either buy a lasercut acrylic kit from Bits from Bytes or make some part yourself by machining them. This option is becoming the more common option especially because soon you will be able to buy a lasercut kit from Ponoko which has offices in the US. This is also usually cheaper than the first option.
- The third option is to build non-clone RepStrap that does not have the same frame as a Darwin, such as McWire which uses pipes for the frame. This option is usually the cheapest, but each RepStrap has it own weaknesses. The good thing is that when complete they can print out parts so that you can build a Classic Darwin. The electronics are compatible with Darwin so you only have to buy them once.
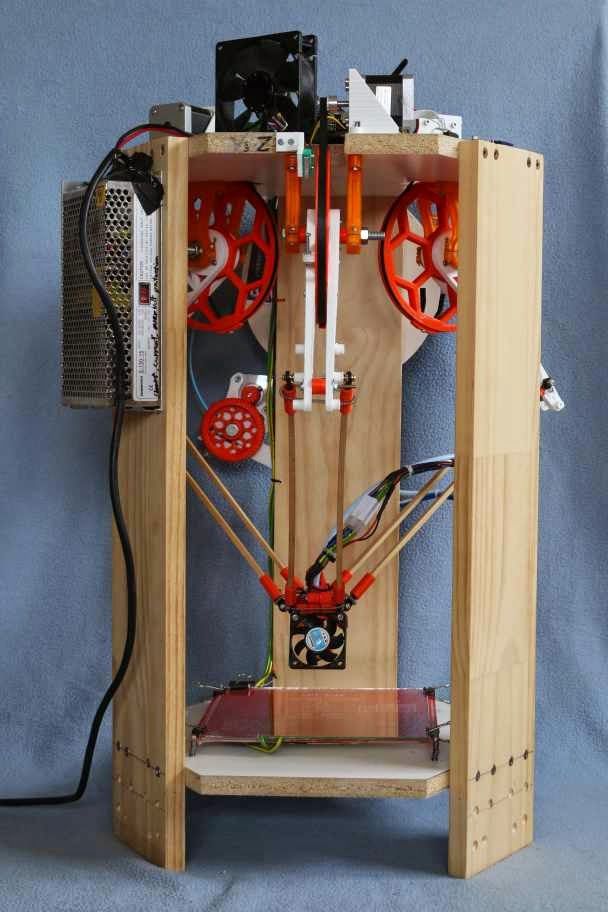
A RepRap or RepStrap (A RepRap can build itself, a RepStrap can build something that can build itself) can be divided into several key areas:
- Object creation Software
- System control Software
- Thermoplastic extruder
- Positioning system (the Cartesian Bot)
- The electronics to control the positioning system
Object Creation Software
Art of Illusion is currently the software most recommended for designing objects to be printed. It's not a CAD package but it is easy to use. The software allows you to create and manipulate 3D shapes. You can store these shapes in STL file format. STL files are object files that are used in Rapid Prototyping. These STL files can be printed off into real 3D objects using your 3D printer (RepRap).
The software is free (GNU GPL version 2) and it is available for Mac OS X, Windows and Linux. If you want to try it out without installing it's available bundled in the Linux distribution liveCD with the rest of the hosted software for the RepRap project.
System control Software
RepRap is controlled via USB or an RS232 interface. You may find a description or download from RepRap Host Software.
There is a RepRap variant which allows you to print an object from a file saved onto a SD card.
Installing the Software (experimental)
This set of instructions tells you how to set up all the software you need for a Reprap in one big blow under Linux Debian.
It involves 5 steps that anyone should be able to complete in a few hours of his/her spare time.
It's easy.
Really.
Warning: Proceed at your own risk. The instructions are not double checked yet.
Prerequisites
You'll need
- a PC (not too old)
- broadband internet access
- some time
Step 1: If you have Windows, go to [Here], get your copy of the Debian installer with one click and start it.
If you already have Linux: Install Debian Lenny some way or the other (you know how to do that ;-)) and continue with Step 3.
Step 2: Follow the instructions. I suggest installing on a 4GB USB stick - but you can also install it all on your hard disk. Be careful to select "testing" instead of stable - this installs Lenny instead of etch. Otherwise the standard settings should be ok in most cases. Don't say "yes" to things you might regret. After a while, a standard system should be installed. Don't forget to install the GRUB boot loader.
Step 3: Log in and say
sudo apt-get install firefox
on the command line.
Step 4: Start firefox and download this Media:Reprap_setup.sh script.
Step 5: Run the script from the shell with
sudo ./Reprap_setup.sh"
Now all the software specific to Reprap is retrieved and installed.
This includes the AVR-Tools, Subversion, Java3d, the Reprap-source tree etc. Installing all that will take some time.
Having successfully reached this point you should try to start the software in reprap-host with:
ant run
If you now see the main window of the host software, you're done.
Congrats! You have made it!
You still have to learn how to use it - but that is another story and another tutorial.
Thermoplast extruder
There are three different extruders all of which, in the end, perform the same function. There is the "official" extruder that can be made by another RepRap. Then there are the kits which are mass produced so it is easier to start printing your first parts. Both kits are designed to be interchangeable with the official extruder.
- RepRapable Thermoplast Extuder
Can be made by another RepRap or commercial rapid prototyper. These are not the only ways the parts can be made but are the easiest. Some builders have made them from machining aluminum or plastic. Others by making molds and casting from resin. This is only for the main pieces of the extruder. The drive screw and other mechanics must be bought or machined. - Kit from Bits from Bytes (laser cut acrylic)
There is an extruder kit currently available from Bits from Bytes who are based in the UK. The kit is part of the silver or gold kits and doesn't need ordering separately unless you want a spare. Assembly instructions are available on the Bits from Bytes website in the 'Assembly Instructions' area:
The kit is part of the silver or gold kits and doesn't need ordering separately unless you want a spare. Assembly instructions are available on the Bits from Bytes website in the 'Assembly Instructions' area:
Bits from Bytes Extruder Assembly instructions
Bits from Bytes Extruder 3d Model - the model requires a recent copy of Adobe Acrobat.
There are videos of the construction process, in the 'Tutorials' section of the website.
Bits from Bytes Heater Barrel Assembly
Bits from Bytes Extruder Drive Assembly
- Kit from Ponoko (laser cut plywood)
A kit will soon be available via Ponoko which has offices in the US.
Positioning system
The positioning system is the greatest part of the size of a RepRap. It is what moves the extruder head from place to place. Kits are available from Bits from Bytes, either the FULL Mechanical Kit - Silver or Gold contain all the components necessary to build a positioning system and extruder. Assembly instructions are available on the bits from bytes website in the 'Assembly Instructions' area:
Bits from Bytes Assembly Instructions
Shopping list
The following list contains all the components necessary to build a RepStrap and enough plastic to print a RepRap.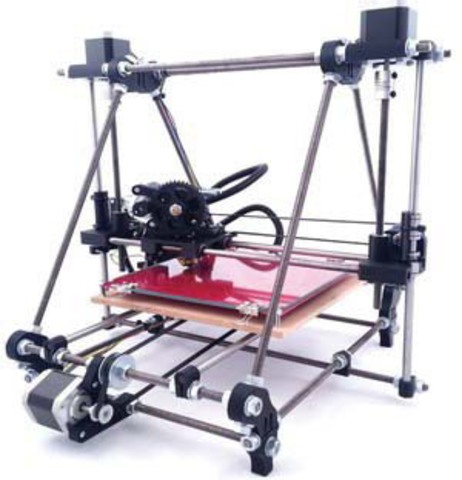 Some handtools are required for assembly, but the only power tool used is a soldering iron.
Some handtools are required for assembly, but the only power tool used is a soldering iron.
Extruder and Positioning System
Bits from Bytes - FULL Mechanical Kit - Silver or Gold
Ponoko - coming soon
(only one required)
Electronics
Plastic
The extruders all use 3mm diameter plastic filament/wire. ABS is the recommended plastic for its combination of strength, availability and dimensional stability. Suitable plastic is available from RRRF in 5lb reels. It is also available by request from plasticweldingrod.com.
Total
Shipping and tax vary by country of order but $1000 total is a reasonable approximation.
MendelMax - RepRap
MendelMax
Release status: working
| Description | A true reprap; printed brackets, with the rigidity of aluminium extrusions. |
| License | GPL |
| Author | User:Kludgineer |
| Contributors | |
| Based-on | Prusa |
| Categories | |
| CAD Models | GitHub |
| External Link | mendelmax. |
This article is about the MendelMax 1.x, see MendelMax 2 for its successor.
PLEASE NOTE: This is the current home for community generated documentation (Please Contribute!). The official MendelMax documentation is maintained at MendelMax.com. Please refer to that site as well.
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 1.1 Versions
- 1.2 Specifications
- 2 Links
- 3 Community
- 4 Files and Documentation
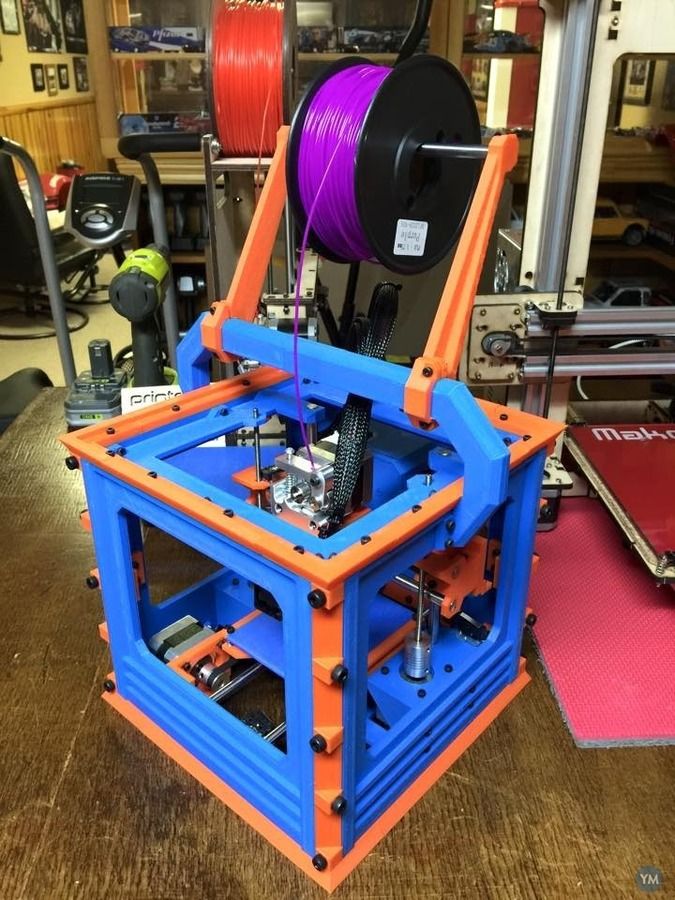
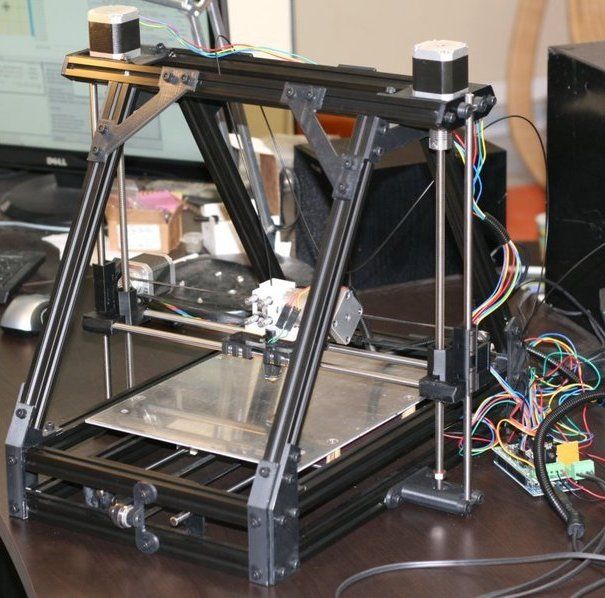
MendelMax (MM) is an Open Source RepRap 3D printer designed by Maxbots in December 2011. It is a true reprap, using printed brackets, but instead of using threaded rod for the structural elements it uses inexpensive aluminum extrusions. This gives a huge increase in rigidity for a minimal extra cost (Self sourcing will cost about $80 more than a standard Prusa when purchased from the recommended suppliers). The required extrusions are available world wide from a variety of suppliers.
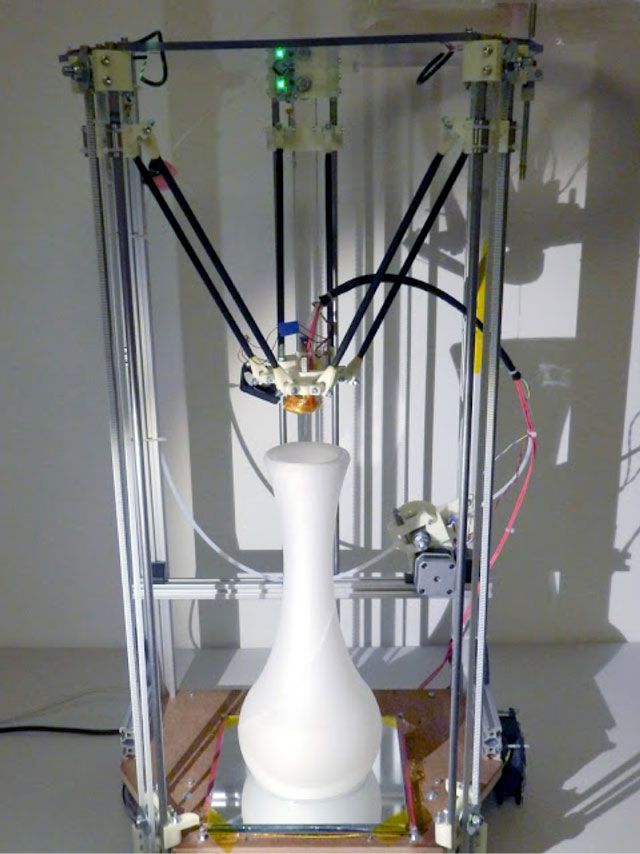
A prototype of the MendelMax RepRap 3d Printer
MendelMax is based on the Prusa Mendel, and keeps its best parts. The Prusa Mendel kept the frame of the Sells Mendel, but fixed the problems in the X,Y and Z axes. MendelMax 1.0 builds on that by largely keeping the current XYZ axes, but completely redesigning the frame.
In addition to the increased rigidity, the printer is much easier to assemble than a standard Prusa. Even an inexperienced builder should have no trouble building the whole frame in an evening, two at most. And along with the easy assembly comes easy hackability. Almost any part on the bot can be removed with just a few screws, so swapping out literally any part on the bot is now a trivial operation.
The X axis is taken stock from the Prusa Mendel, in fact we don't even specify a specific X axis design, there are several good ones available, including the various vertically-oriented X axis designs that many people are exploring lately.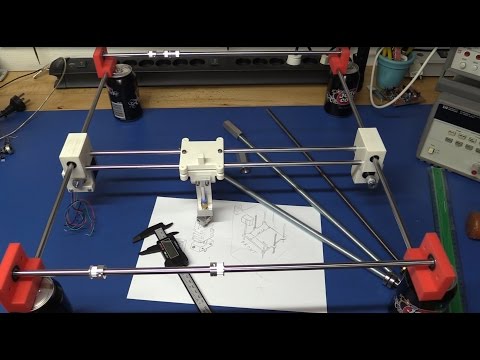 As long as it sticks to the defined standard spacing between the Z rod and the Z leadscrew, it will work fine with MendelMax. We also use the standard Prusa Y design (For version 1.0), though we simplify it just a bit by making it easier to get everything aligned right. Z adds optional thrust bearings to support the weight of the axis (greatly reducing the problems with printed couplers), but this is a purely optional upgrade, and you can easily use the old design if you prefer.
As long as it sticks to the defined standard spacing between the Z rod and the Z leadscrew, it will work fine with MendelMax. We also use the standard Prusa Y design (For version 1.0), though we simplify it just a bit by making it easier to get everything aligned right. Z adds optional thrust bearings to support the weight of the axis (greatly reducing the problems with printed couplers), but this is a purely optional upgrade, and you can easily use the old design if you prefer.
Because MendelMax is primarily defining a new frame design, it is linear-bearing agnostic. I have used both LM8UU's and PTFE bushings and both work just fine. Brass or even printed bushings could be used, though I recommend avoiding the latter for highest reliability.
The current revision as of July 17 2012 shipping as kits from the official MM store is considered the MM 1.5+. It uses a linear slide for a Y axis rather than polished rods to give the heaviest axis a smoother motion and seems to have cleaned things up greatly.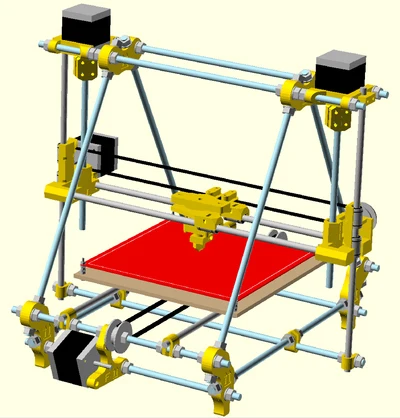 Also different from earlier models the steppers controlling the Z axis have been moved from the top of the printer to the base.
Also different from earlier models the steppers controlling the Z axis have been moved from the top of the printer to the base.
Versions
| Version number | Source links | Bill of Materials | Assembly instructions | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Main frame | BoM | TechPaladin's guide (Archived) | Top mounted Z-motors. Rod based Y-table |
| 1.5 | Main frame Lasercut Y-table | BoM | Instructions by Theo Deyle (Note: The Y table described is for 1.5+) | Bottom mounted Z-motors. Rod based Y-table with laser-cut parts |
| 1.5+ | Same as 1.5. | Similar to 1.5, except for Y parts. Kit packing list | Instructions by Theo Deyle | Bottom mounted Z-motors. Rail & car based Y-table |
| 2.0 | See the MendelMax 2 article for information about that version. |
Specifications
These specifications are for the MendelMax 1. 5+:
5+:
- Printed Parts: very few (around 25 different parts)
- Non-Printed Parts: ???
- Printing Size: build area of about 9"x10"x7" or 23cm x 25cm x 17.5cm
- Material Cost: ???
- Cost: US$ 1,300 (complete kit)
- Precision: ??? (position), ??? (printing)
- Speed: ??? (position), ??? (printing)
- [1] MendelMax 1.5 STL Files
- [2] Maker's Tool Works MendelMax 1.5+ Build Instructions
- [3] Lots of pictures, including the assembled printer and several finished prints
- [4] 3D-PDF (View with Adobe Acrobat, most 3rd party viewers do not support 3d PDFs. Click on the image to view in full 3D, pan, zoom, rotate, etc.)
- [5] Packing list for a MendelMax 1.5 kit
- [6] MendelMax 1.5 with SCV8UU Y-Carriage
- [7] RepRapWorld - Mendelmax 1.5 Complete Kit starting at 549.99€ and parts
- [8] Blomker Industries - MendelMax 1.5 Complete Kit at $699
- [9] Ultibots - MendelMax 1.
 5+ Complete Kit starting at $1199
5+ Complete Kit starting at $1199 - [10] ReprapUniverse (NL) - MendelMax 1.5 : Printed Parts €79 - Frame Kit €299 - Complete Kit €699
- 220v.biz Parts for MendelMax and other 3d printers in Ukraine
- [11] MendelMax 3D view and complete files (Spanish)
- [12] 3DMarkt.at in Austria, MendelMax 1.5 Printer Kit 659,99 EUR
- For more information, visit our FreeNode IRC channel at #MendelMax (or ask in #reprap). Please be patient, this is presently a low-volume channel so it may take a while to get responses but someone will help you as soon as possible.
- Please join our Google Group.
For 1.x:
- STL Files can be downloaded from thingiverse. RAScomRAS
- FreeCAD SCAD source files are available at the MendelMax GitHub repository.
- A full Bill of Materials (BOM) is available on Google Docs, although this is the BOM for Version 1. Vendors are typically selling parts for MM 1.5, so you will need to make some substitutions.

- Assembly instructions and lots more information are available on the MendelMax homepage.
- User submitted calibration information and tips at the Mendel Max Calibration page
For 2.0:
- See MendelMax2: Files & Documentation
Build a home 3D printer with your own hands: recommendations from personal experience
3D printing and assembly of 3D printers is my hobby and passion. Here I will not share detailed diagrams and drawings, there are more than enough of them on specialized resources. The main goal of this material is to tell you where to start, where to dig and how to avoid mistakes in the process of assembling a home 3D printer. Perhaps one of the readers will be inspired by applied engineering achievements.
Why do you need a 3D printer? Use cases
I first came across the idea of 3D printing back in the 90s when I was watching the Star Trek series. I remember how impressed I was by the moment when the heroes of the cult series printed the things they needed during their journey right on board their starship. They printed anything: from shoes to tools. I thought it would be great someday to have such a thing too. Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few. nine0003
They printed anything: from shoes to tools. I thought it would be great someday to have such a thing too. Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few. nine0003
Years passed, everything changed. Around 2010, the first working models of 3D printers began to appear on sale. Yesterday's fantasy has become a reality. However, the cost of such solutions, to put it mildly, discouraged. But the IT industry would not be itself without an inquisitive community, where there is an active exchange of knowledge and experience and who just let them dig into the brains and giblets of new hardware and software. So, drawings and diagrams of printers began to surface more and more often on the Web. Today, the most informative and voluminous resource on the topic of assembling 3D printers is RepRap - this is a huge knowledge base that contains detailed guides for creating a wide variety of models of these machines. nine0003
nine0003
I assembled the first printer about five years ago. My personal motivation to build my own device is quite prosaic and based on several factors. Firstly, there was an opportunity to try to realize the old dream of having your own device, inspired by a fantasy series. The second factor is that sometimes it was necessary to repair some household items (for example, a baby stroller, car elements, household appliances and other small things), but the necessary parts could not be found. Well, the third aspect of the application is "near-working". On the printer, I make cases for various IoT devices that I assemble at home. nine0003
Agree, it is better to place your device based on Raspberry Pi or Arduino in an aesthetically pleasing "body", which is not a shame to put in an apartment or take to the office, than to organize components, for example, in a plastic bowl for food. And yes, you can print parts to build other printers :)
There are a lot of scenarios for using 3D printers. I think everyone can find something of their own.
I think everyone can find something of their own.
A complex part in terms of drawing that I printed on my printer. Yes, it's just a figurine, but it has many small elements
Ready solution vs custom assembly
When a technology has been tested, its value in the market decreases markedly. The same thing happened in the world of 3D printers. If earlier a ready-made solution cost simply sky-high money, then today acquiring such a machine is more humane for the wallet, but nevertheless not the most affordable for an enthusiast. There are a number of solutions already assembled and ready for home use on the market, their price range ranges from $500-700 (not the best options) to infinity (adequate solutions start from a price tag of about $1000). Yes, there are options for $150, but we, for understandable, I hope, reasons, will not dwell on them. nine0003
nine0003
In short, there are three cases to consider a finished assembly:
- when you plan to print not much and rarely;
- when print accuracy is critical;
- you need to print molds for mass production of parts.
There are several obvious advantages to self-assembly. The first and most important is cost. Buying all the necessary components will cost you a maximum of a couple of hundred dollars. In return, you will receive a complete 3D printing solution with the quality of manufactured products acceptable for domestic needs. The second advantage is that by assembling the printer yourself, you will understand the principles of its design and operation. Believe me, this knowledge will be useful to you during the operation of even an expensive ready-made solution - any 3D printer needs to be serviced regularly, and it can be difficult to do this without understanding the basics. nine0003
The main disadvantage of assembly is the need for a large amount of time. I spent about 150 hours on my first build.
I spent about 150 hours on my first build.
What you need to assemble the printer yourself
The most important thing here is the presence of desire. As for any special skills, then, by and large, in order to assemble your first printer, the ability to solder or write code is not critical. Of course, understanding the basics of radio electronics and basic skills in the field of mechanics (that is, "straight hands") will greatly simplify the task and reduce the amount of time that needs to be spent on assembly. nine0003
Also, to start we need a mandatory set of parts:
- Extruder is the element that is directly responsible for printing, the print head. There are many options on the market, but for a budget build, I recommend the MK8. Of the minuses: it will not be possible to print with plastics that require high temperatures, there is noticeable overheating during intensive work, which can damage the element. If the budget allows, then you can look at MK10 - all the minuses are taken into account there.
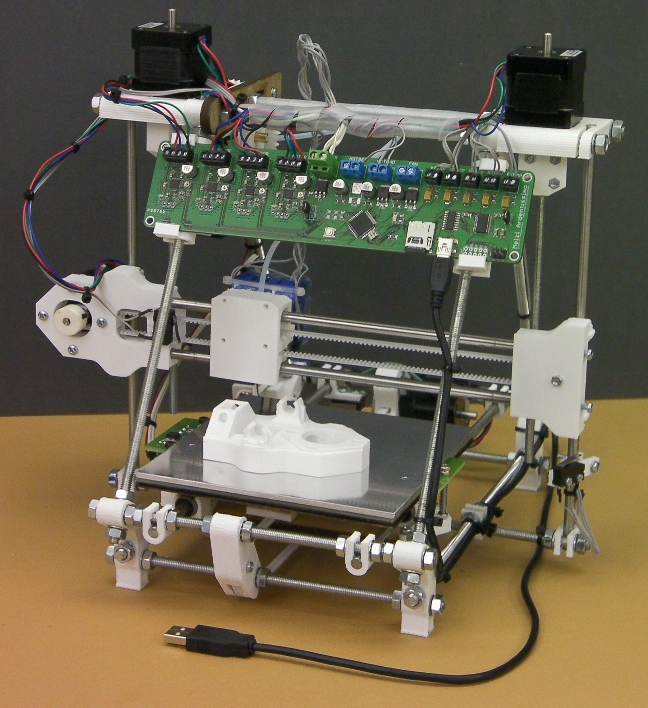 nine0032
nine0032 - Processor board. The familiar Arduino Mega is well suited. I didn't notice any downsides to this solution, but you can spend a couple of dollars more and get something more powerful, with a reserve for the future.
- Control board. I'm using RAMPS 1.4 which works great with the Arduino Mega. A more expensive but more reliable board is Shield, which already combines a processor board and a control board. In modern realities, I recommend paying attention to it. In addition to it, you need to purchase at least 5 microstep stepper motor controllers, for example - A4988. And it's better to have a couple of these in stock for replacement.
- Heated table. This is the part where the printed element will be located. Heating is necessary due to the fact that most plastics will not adhere to a cold surface. For example, for printing with PLA plastic, the required surface temperature of the table is 60-80°C, for ABS - 110-130°C, and for polycarbonate it will be even higher
There are also two options for choosing a table - cheaper and more expensive. Cheaper options are essentially printed circuit boards with preheated wiring. To operate on this type of table, you will need to put borosilicate glass, which will scratch and crack during operation. Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table. nine0032
Cheaper options are essentially printed circuit boards with preheated wiring. To operate on this type of table, you will need to put borosilicate glass, which will scratch and crack during operation. Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table. nine0032 - Stepper motors. Most models, including the i2 and i3, use NEMA 17 size motors, two for the Z axis and one each for the X and Y axes. Finished extruders usually come with their own stepper motor. It is better to take powerful motors with a current in the motor winding of 1A or more, so that there is enough power to lift the extruder and print without skipping steps at high speed.
- Basic set of plastic fasteners.
- Belt and gears to drive it. nine0051
Examples of elements appearance: 1) MK8 extruder; 2) Arduino processor board; 3) RAMPS control board; 4) motor controllers; 5) aluminum heated table; 6) NEMA 17 stepper motor; 7) a set of plastic fasteners; 8) drive gears; 9) drive belt
This is a list of items to be purchased.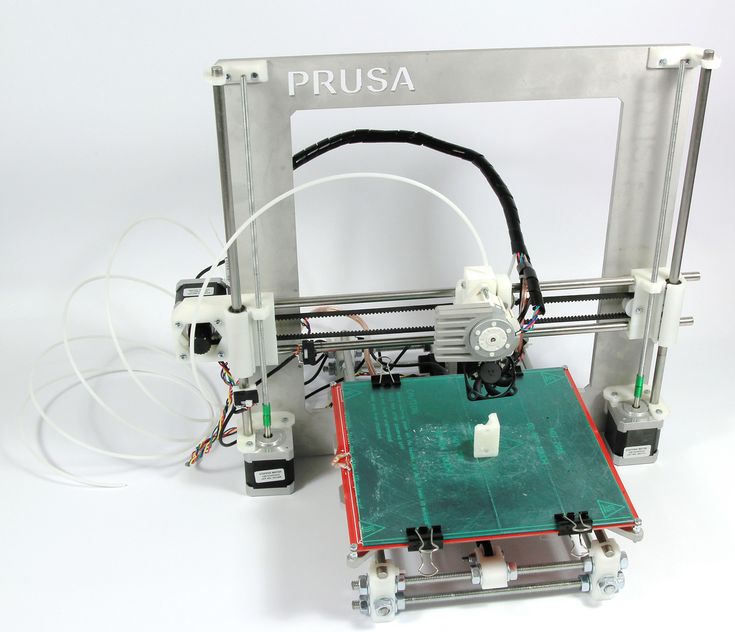 Hardcore users can assemble some of them themselves, but for beginners, I strongly recommend purchasing ready-made solutions. nine0003
Hardcore users can assemble some of them themselves, but for beginners, I strongly recommend purchasing ready-made solutions. nine0003
Yes, you will also need various small things (studs, bearings, nuts, bolts, washers ...) to assemble the case. In practice, it turned out that using a standard m8 stud leads to low printing accuracy on the Z axis. I would recommend immediately replacing it with a trapezoid of the same size.
M8 trapezoid stud for Z axis, which will save you a lot of time and nerves. Available for order on all major online platforms
nine0002 You also need to purchase customized plastic parts for the X axis, such as these from the MendelMax retrofit kit.Most parts available at your local hardware store. On RepRap you can find a complete list of necessary little things with all sizes and patterns. The kit you need will depend on the choice of platform (we'll talk about platforms later).
What's the price
Before delving into some aspects of the assembly, let's figure out how much such entertainment will cost for your wallet. Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price. nine0003
Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price. nine0003
Platform selection
The community has already developed a number of different platforms for assembling printers - the most optimal case designs and the location of the main elements, so you do not have to reinvent the wheel.
i2 and i3 are key platforms for self-assembly printer enclosures. There are also many modifications of them with various improvements, but for beginners, these two classic platforms should be considered, since they do not require special skills and fine-tuning. nine0003
Actually, illustration of platforms: 1) i2 platform; 2) i3 platform
On the plus side of i2: it has a more reliable and stable design, although it is a little more difficult to assemble; more opportunities for further customization.
The i3 variant requires more special plastic parts to be purchased separately and has a slow print speed. However, it is easier to assemble and maintain, and has a more aesthetically pleasing appearance.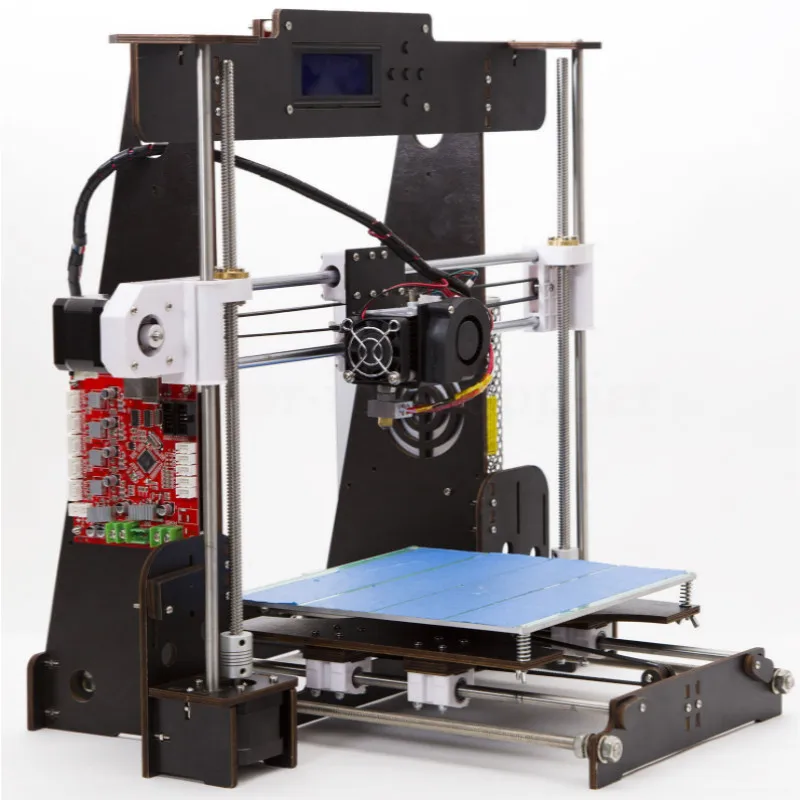 You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy. nine0003
You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy. nine0003
Personally, I started my experiments in assembling printers from the i2 platform. She will be discussed further.
Assembly steps, challenges and improvements
In this block, I will only touch on the key assembly steps using the i2 platform as an example. Full step by step instructions can be found here.
The general scheme of all the main components looks something like this. There is nothing particularly complicated here:
I also recommend adding a display to your design. Yes, you can easily do without this element when performing operations on a PC, but it will be much more convenient to work with the printer this way. nine0003
Understanding how all components will be connected, let's move on to the mechanical part, where we have two main elements - a frame and a coordinate machine.
Assembling the frame
Detailed frame assembly instructions are available on RepRap. Of the important nuances - you will need a set of plastic parts (I already talked about this above, but I'd better repeat it), which you can either purchase separately or ask your comrades who already have a 3D printer to print.
The frame of the i2 is quite stable thanks to its trapezoid shape.
This is how the frame looks like with parts already partially installed. For greater rigidity, I reinforced the structure with plywood sheets
Coordinate machine
An extruder is attached to this part. The stepper motors shown in the diagram above are responsible for its movement. After installation, calibration is required along all major axes.
Important - you will need to purchase (or make your own) a carriage for moving the extruder and a mount for the drive belt. Drive belt I recommend GT2. nine0003
The carriage printed by the printer from the previous picture after it has been assembled. The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
Calibration and adjustment
So, we completed the assembly process (as I said, it took me 150 hours) - the frame was assembled, the machine was installed. Now another important step is the calibration of this very machine and extruder. Here, too, there are small subtleties.
Setting up the machine
I recommend calibrating the machine with an electronic caliper. Do not be stingy with its purchase - you will save a lot of time and nerves in the process.
The screenshot below shows the correct constants for the Marlin firmware, which must be selected in order to set the correct number of steps per unit of measure. We calculate the coefficient, multiply it, substitute it into the firmware, and then upload it to the board.
Marlin 9 firmware constants0022
For high-quality calibration, I recommend relying on larger numbers in measurements - take not 1-1. 5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
Calibrating the extruder
When the frame is assembled, the machine is calibrated, we start setting up the extruder. Here, too, everything is not so simple. The main task of this operation is to correctly adjust the supply of plastic.
If underfeeding, the printed test item will have noticeable gaps, like test die 1. Conversely, the result will look bloated if plastic is overfed (dice 2)
Getting Started Printing
It remains for us to run some CAD or download ready-made .stl, which describe the structure of the printed material. Next, this structure needs to be converted into a set of commands understandable to our printer. For this I use the Slicer program. It also needs to be set up correctly - specify the temperature, the size of the extruder nozzle. After that, the data can be sent to the printer.
Slicer interface
As a raw material for printing, I recommend starting with regular ABS plastic - it is quite strong, products made from it are durable, and it does not require high temperatures to work with.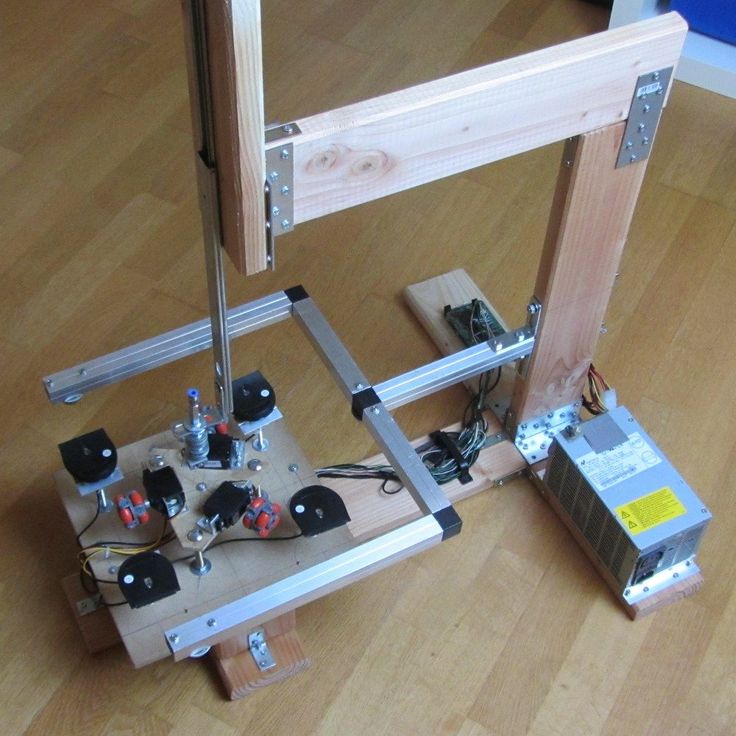 For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
Some important details. Before printing, calibrate the machine along the Z axis. The extruder nozzle should be approximately half a millimeter from the table and ride along it without distortion. For this calibration, a regular sheet of A4 paper inserted between the nozzle and the surface of the heated table is best suited. If the sheet can be moved with little effort, the calibration is correct. nine0003
Another thing to keep in mind is the surface treatment of the heated table. Usually, before printing, the surface of the table is covered with something that hot plastic sticks to well. For ABS plastic, this can be, for example, Kapton tape. The disadvantage of adhesive tape is the need to re-glue it after several printing cycles. In addition, you will have to literally tear off the adhering part from it. All this, believe me, takes a lot of time. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it. nine0003
Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it. nine0003
An alternative option that I use instead of scotch tape is to apply several layers of ordinary light beer, followed by heating the table to 80-100 ° C until the surface is completely dry and re-applying 7-12 layers. It is necessary to apply the liquid with a cloth moistened with a drink. Among the advantages of this solution: ABS plastic separates from the table on its own when it cools down to about 50 ° C and is removed without effort, the table does not have to be peeled off, and one bottle of beer will last you for several months (if you use the drink only for technical purposes :)). nine0003
After we have collected and configured everything, we can start printing. If you have an LCD screen, then the file can be transferred for printing using a regular SD card.
The first results may have bumps and other artifacts - do not worry, this is a normal process of "grinding" the printer elements, which will end after a few print cycles.
Tips to make life easier (and sometimes save money)
In addition to the small recommendations given in the text above, in this section I will also give a short list of tips that will greatly simplify the operation of a 3D printer and the life of its owner. nine0003
- Do not experiment with nozzles. If you plan to immediately print from materials that require high temperatures, then it is better to immediately take the MK10 extruder. On MK8, you can "hang" special nozzles that support high-temperature conditions. But such modifications often cause difficulties and require special experience. It is better to avoid this fuss on the shore by simply installing the right extruder for you.
- Add starter relay for heated table. nine0051 Improving the power supply system for this important printing part with a starter relay will help solve the known problem of RAMP 1.4 - overheating of the transistors that control the power of the table, which can lead to failure of the board.
 I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s.
I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s. - Select the correct filament diameter for printing. I recommend using 1.75mm plastic for MK8 and MK10. If we take plastic, for example, 3 mm, then the extruder simply does not have enough strength to push it at an acceptable speed - everything will be printed much longer, and the quality will drop. ABS plastic is ideal for MK8, MK10 will be able to produce products from polycarbonate. nine0032
- Use only new and precise X and Y guides. Print quality will be affected. It is difficult to count on good quality with bent or deformed guides along the axes.
- Take care of cooling. During my experiments with various extruders, the MK10 showed the best results - it prints quite accurately and quickly. The MK10 can also print plastics that require a higher print temperature than ABS, such as polycarbonate. Although it is not as prone to overheating as its younger brother MK8, I still recommend taking care of its cooling by adding a cooler to your design.
 It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling. nine0032
It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling. nine0032 - Consider heat retention. Yes, on the one hand, we are struggling with overheating of the elements. On the other hand, a uniform temperature around the printer will contribute to high-quality printing (the plastic will be more pliable). To achieve a uniform temperature, you can put our printer, for example, in a cardboard box. The main thing is to connect and configure the coolers before that, as described above.
- Consider insulating your desk. Heated table heats up to high temperatures. And if part of this heat leaves properly, heating the printed part, then the second part (from below) just goes down. To concentrate the heat from the table onto the part, you can perform an operation to insulate it.
 To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips. nine0032
To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips. nine0032
Pins
I am sure that during the assembly process you will encounter a number of difficulties specific to your project. Neither this text nor even the most detailed guides will insure against this.
As I wrote in the introductory part, the above does not claim the status of a detailed assembly manual. It is almost impossible to describe all the stages and their subtleties within the framework of one such text. First of all, this is an overview material that will help you prepare for the assembly process (both mentally and financially), understand whether you personally need to bother with self-assembly - or give up on everything and buy a ready-made solution. nine0003
For me, assembling printers has become an exciting hobby that helps me solve some issues in home and work affairs, take my mind off programming and do something interesting with my own hands. For my children - entertainment and the opportunity to get unusual and unique toys. By the way, if you have children whose age allows them to mess around with such things, such an activity can be a good help for entering the world of mechanics and technology.
By the way, if you have children whose age allows them to mess around with such things, such an activity can be a good help for entering the world of mechanics and technology.
For everyone, the vectors of using 3D printers will be very different and very individual. But, if you decide to devote your personal time to such a hobby, believe me, you will definitely find something to print :)
I will be glad to answer comments, remarks and questions.
What to read/see
- what can be printed;
- 3D printer forum;
- RepRap community site with model descriptions and assembly instructions;
- printer that prints electronics.
Subscribe to the Telegram channel "DOU #tech" so you don't miss new technical articles.
Topics: DIY, embedded, tech
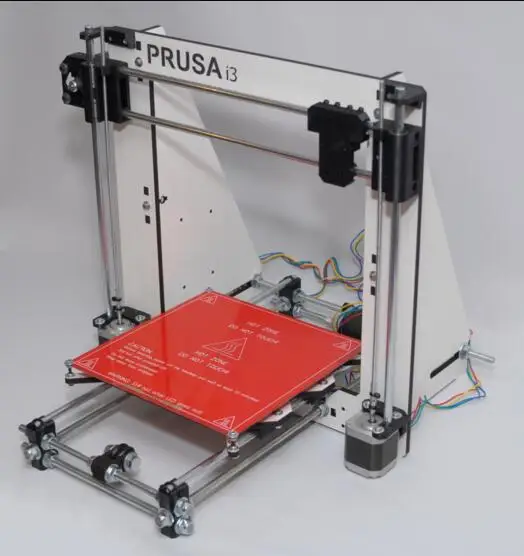
What does it cost us to build a 3D printer / Antonovich.me
So, a fundamental decision was made to build a 3D printer in order to implement some of our own ideas, and, of course, just to keep up with progress.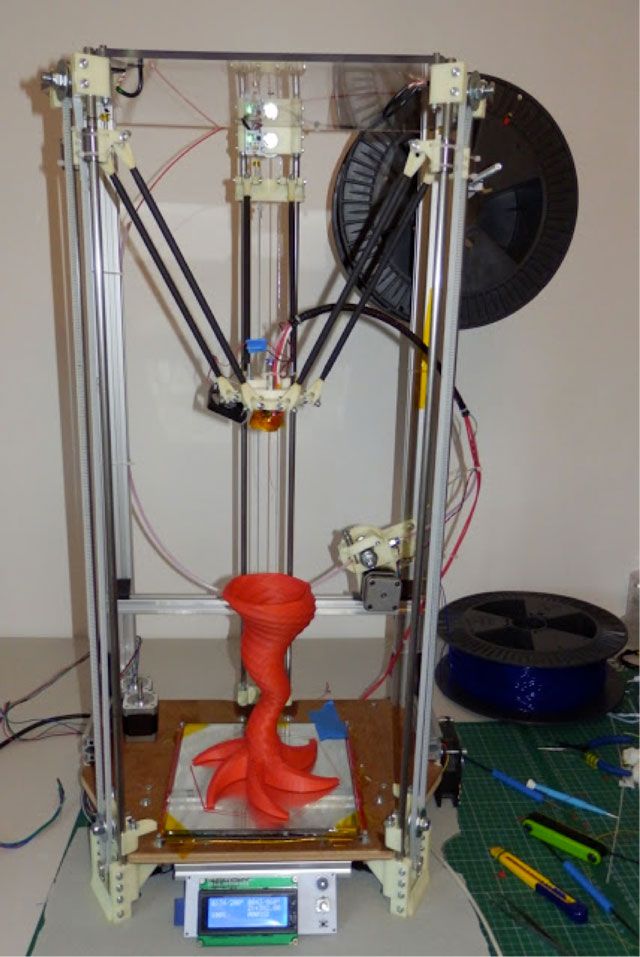 :)
:)
RepRap Prusa i3 selected as base model (aluminum frame version):
Advantages of this model compared to other RepRap models:
- rigid construction
- simple assembly
- reduced number of printed plastic parts nine0037
- movable stage (limits the maximum print speed)
- the frame can only be made on specialized equipment (laser or water cutter)
- Main parts:
- Aluminum frame (6mm sheet) - €100 (delivery included). You can find cheaper ones, but I liked this one more than others from an aesthetic point of view. :) nine0032
- A set of printed plastic parts - thanks to Dmitry (http://minicube.ru/) - 2500r (STL-files).
- E3D v6 HotEnd Full Kit Heated Printhead - 1.75mm Universal - £51.80.
- Heated table MK2 - $10.5.
- Borosilicate heated table glass 213x200x3mm - $26 (for 2 pieces)
- Electronics:
- Power Supply 12V 33.
 3A - AU $33.99.
3A - AU $33.99. - NEMA 17 stepper motor kit, 48mm length, 0.48Nm holding torque 42BYGHW811 (5 pcs) - $75. nine0032
- 3D Printer RAMPS Kit - $51.11
- Arduino mega 2560 controller.
- RAMPS 1.4 controller board.
- Stepper motor drivers (5 pcs)
- Limit switch kit (3 pcs)
- Thermistor 100 kΩ - $6.59 (10 pcs)
- Power Supply 12V 33.
- Axle Shafts - £19.90:
- Z Axis:
- Shafts M8 320mm (2 pcs)
- X-axis:
- Shaft M8 20mm (for extruder). nine0032
- Shafts M8 370mm (2 pcs.)
- Y-axis:
- Shafts M8 350mm (2 pcs.)
- Z Axis:
- Studs:
- Stud M5 300mm (2 pcs)
- Stud M8 205mm (4 pcs.)
- Stud M10 380mm (2 pcs.)
- Bearings:
- Linear bearings LM8UU (10 pcs) - AU $8.
 87.
87. - 608zz deep groove bearings (10 pcs.) - $3.69.
nine0031 Hardware: - Linear bearings LM8UU (10 pcs) - AU $8.
- Washers M10 (8 pcs.)
- Nuts M10 (12 pcs.)
- Washers M8 (22 pcs.)
- Nuts M8 (22 pcs.)
- Washers reinforced M10 (4 pcs.)
- M3x10 screws (23 pcs)
- Screws M3x16 (6 pcs)
- Screws M3x18 (5 pcs.)
- Screw M3x25.
- Screws M3x30 (6 pcs.)
- Screws M3x40 (2 pcs.)
- Bolt M8x60 (for the extruder feeder, with incomplete cutting, look for it in car dealerships). nine0031 Self-locking nut M8.
- Washers M8 - 5 pcs.
- Screws M4x50 - 2 pcs.
- Nuts M4 - 2 pcs.
- Washers reinforced M4 - 4 pcs.
- Self-locking nuts M3 (50 pcs.) - $5.76.
- M5 nuts (2 pcs)
- Self-locking nut M5.
- Washers M5 (2 pcs.)
- Nuts M3 (6 pcs.)
- Washers M3 (2 pcs.)
- Miscellaneous:
- Aluminum bracket for hot end - €6.
- Aluminum bracket for hot end - €6.
Cons:
List of required materials and accessories 1 :


 com Mendel Variations T-Slot
com Mendel Variations T-Slot