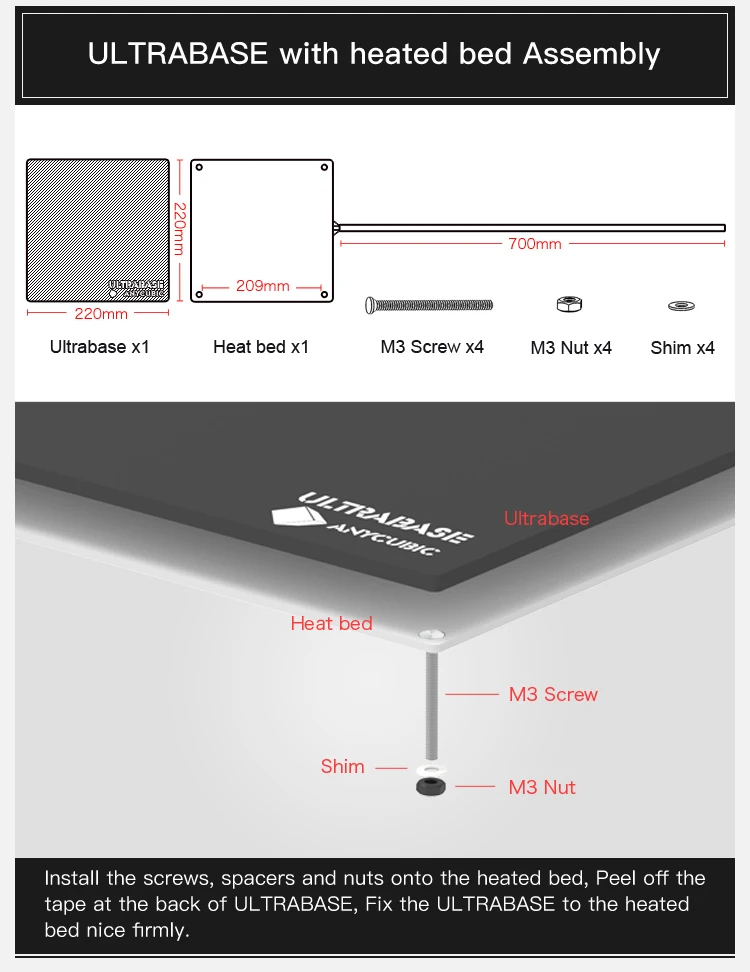
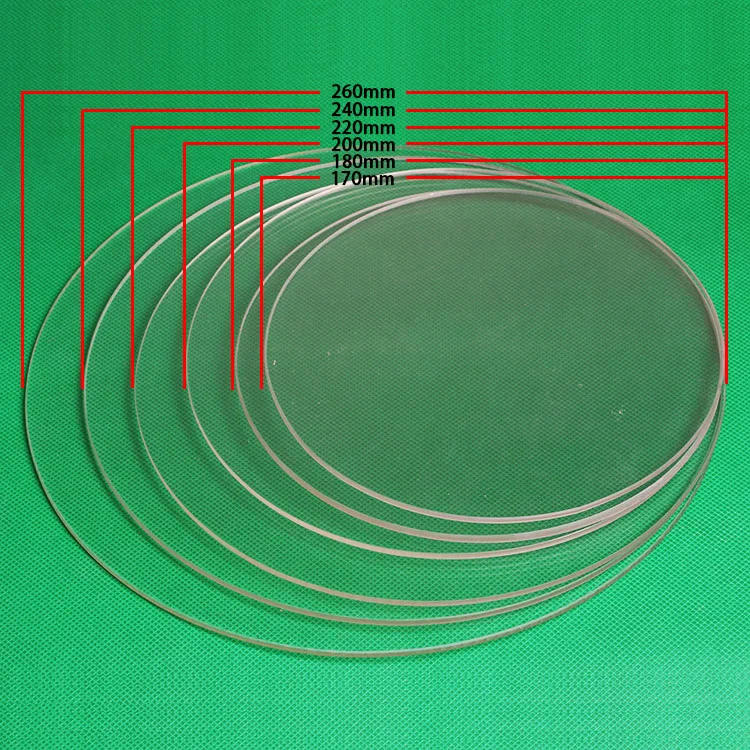
Borosilicate glass for 3d printer
Borosilicate Glass VS Tempered Glass for 3D Printing – 3D Printerly
The conditions for a good print start, quite literally, from the ground up. A good build plate is fundamental to ensuring your 3D model comes out looking great.
It serves several functions like making sure there’s a level surface for printing and enhancing print adhesion.
There are many materials for fabricating build plates, depending on the print requirements.
A popular option among 3D printing enthusiasts is glass. Its high resistance to warping, thermal stability, and conductivity make it a prime choice for printing.
The two main types of glass that people use for 3D printing are borosilicate glass and tempered glass, but many people don’t know which to buy.
This article is going to aim to help you identify the differences and key comparisons to help you move forward and get the right type.
Let’s quickly look at both options before we compare them.
What Is Borosilicate Glass in 3D Printing?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass made with silica and at least 13% Boron trioxide. This combination gives it some properties that make it useful in 3D printing applications.
Let’s examine these properties.
Thermal Stability
Borosilicate glass has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion. That is, it expands very little with changing temperatures. This means that it will not crack or shatter under extreme temperatures.
Its thermals stability is one of its most important properties, as this makes it possible to use it with a heated bed. It also makes printing with high-temperature materials like ABS very easy.
Durability
Borosilicate glass is strong. It is shatter-proof, which means when it’s dropped, it won’t break. Also, its durability means it lasts longer and is less susceptible to surface degradation from scratches and nicks.
Chemical Resistant
Borosilicate glass has a very stable chemical structure that doesn’t degrade when attacked by outside elements. This is very helpful when printing with reactive filaments.
It’s nice to know your build plate won’t leak dangerous chemicals into the print or the air.
Thermal Shock Resistant
Thermal shock resistance is a property of borosilicate glass that makes it resistant to rapid changes in temperatures. Most materials exposed to rapid changes in temperature lose their strength and may even fail. But, Borosilicate glass stands up well to these thermal shocks.
Some people wonder whether borosilicate glass warps, and most people’s experience show that it doesn’t warp over time due to its physical characteristics.
What Is Tempered Glass in 3D Printing?Tempered glass is any form of glass that has gone through thermal and mechanical processes (tempering) to increase its strength. Tempered glass finds applications in car windshields and things like screen protectors.
All these are made possible due to the properties given to it by tempering. Let’s take a look at some of those properties below:
Strength
Tempered glass is strong and durable by nature. It can withstand impact shocks far better than regular glass. Its strength comes from tempering, which pre-stresses the glass’s structure to make it stronger.
It can withstand impact shocks far better than regular glass. Its strength comes from tempering, which pre-stresses the glass’s structure to make it stronger.
Thermal Stability
Tempered glass is also heat-resistant. The thermal tempering treatment makes it able to withstand temperatures up to 300℃ without failure. Tempered glass can also withstand thermal shock, just not as well as Borosilicate glass.
Scratch Resistant
Tempering gives the surface of the glass a scratch-resistant finish.
It hardens the surface making it more resistant to penetration from an external object. This quality makes tempered glass retain its surface quality for a long time.
The video below shows how easy installation is, and gives a nice review on a tempered glass bed.
Borosilicate Glass Vs Tempered Glass: Which One is Best for You?
When buying a glass build plate, the odds are you are going to get either one made from borosilicate glass or tempered glass. So, how do you decide between them? Let’s take you through some things that can influence your decisions.
So, how do you decide between them? Let’s take you through some things that can influence your decisions.
Quality
Both borosilicate glass and tempered glass have excellent qualities that set them apart from regular glass. Let’s go through those qualities one by one and see how they stack against each other:
- Thermal Stability: Both tempered and borosilicate glass perform well at high temperatures. You can print high-temperature filaments on them with no problem. However, when it comes to thermal shock resistance, Borosilicate glass is the better option.
Due to the pre-stressed nature of tempered glass, it cannot withstand large temperature variations. Prolonged exposure to these temperatures can cause warping, or in extreme cases, total failure.
- Scratch Resistance: The scratch resistance of a material is a function of its hardness and resistance to penetration. Both Borosilicate and tempered glass are harder than regular glass.
 On the Mohs hardness scale, tempered glass is rated slightly higher than borosilicate glass.
On the Mohs hardness scale, tempered glass is rated slightly higher than borosilicate glass.
The higher rating means Tempered glass is a slightly harder material. As such, it will be more resistant to chipping and flaking. This will make it retain its surface quality longer.
Ease Of Use
For ease of use, we’ll be rating both glasses on how user-friendly they are. Both provide good quality bottom finishes, are easy to clean, and are flat. We’ll be using different criteria.
We’ll be comparing them based on safety and ease of print removal.
Let’s look at these criteria:
- Safety: Tempered glass is a safer material. It is highly durable and can resist impact shocks better. Even if it breaks, it breaks into cube-like pieces that aren’t harmful.
- Ease of Print Removal: Print removal generally depends on a lot more things than the build plate, but prints are easier to remove from borosilicate glass. Due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, it won’t expand when heated.
 So as it cools, the stresses from the shrinking model make it easier to remove.
So as it cools, the stresses from the shrinking model make it easier to remove.
For more stubborn prints, you can put the build plate in a freezer to cool it faster. Borosilicate glass can survive this swing in temperature because of its resistance to thermal shocks.
Price
The price difference is not so significant, so you can really choose either and be good on price, but let’s look at which one actually comes up as cheaper.
A standard borosilicate glass bed for an Ender 3 on Amazon comes to around $15, with the Dcreate 235 x 235 x 3.8mm Borosilicate Glass Bed.
A standard tempered glass bed for an Ender 3 on Amazon comes to around $20 on Amazon, with the Creality Authentic Tempered Glass Bed, though these prices can fluctuate depending on the brand and the seller.
The prices of 3D printer beds have been getting cheaper over time, which is great for 3D printer hobbyists out there!
Overall, I’d recommend going with the Dcreate Borosilicate Glass Bed from Amazon.
You can also get yourself some professional 3D printer clamps to add onto your 3D printer to hold the glass bed into place. When I tried using the binder clips that came with my Ender 3, it was just too small for the glass bed addition.
The 4-Pack Ender 3 Stainless Steel Clamps from Amazon are a good product to keep your bed in place. They are fairly pricey but they get the job done very well.
Another option which gives you more bang for your buck is the 40 Pcs Extra Large Binder Clips from Amazon. They have a 2-inch width and has multiple practical uses outside of holding your bed in place.
Can You 3D Print Directly on Glass? Best Glass for 3D Printing – 3D Printerly
3D printing on glass is something that works really well for build plate adhesion and getting a great finish on the bottom of 3D prints, but some people can’t figure out how to do it right.
I decided to write an article about 3D printing directly on glass, answering the basic questions that should set you in the right direction to 3D print like the professionals out there!
Keep on reading to get some useful information that you can put to use straight away in your printing process.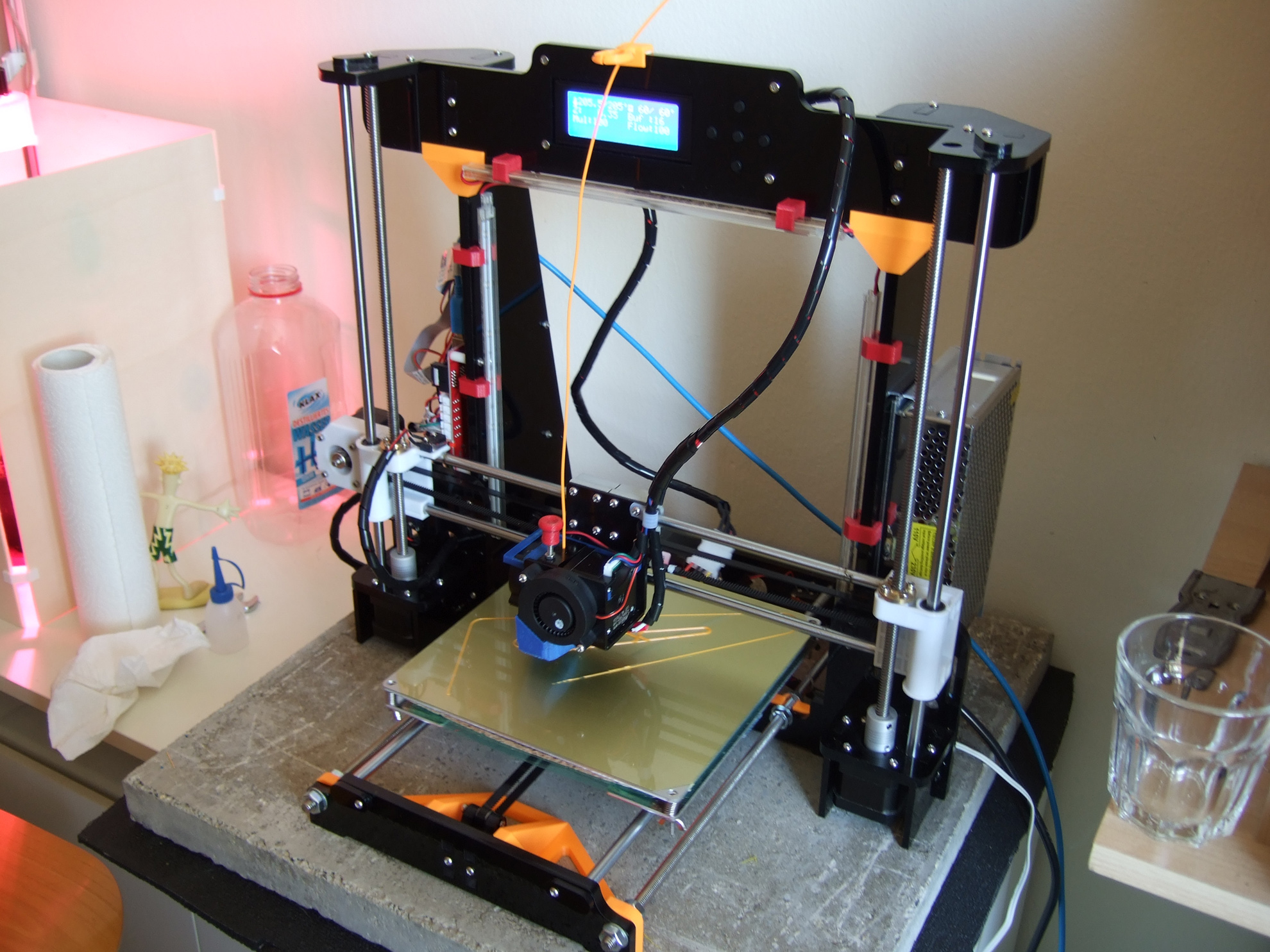
Can You 3D Print Directly on Glass?
3D printing directly on glass is possible and is popular with many users out there. Adhesion can be difficult on a glass bed, so it’s recommended that you use adhesives to help your 3D prints stick to the glass and not warp around the edges. A good bed temperature is fundamental for 3D printing on glass.
You’ll see plenty of 3D printer beds that are made out of glass because it has many characteristics which make it ideal for 3D printing. One of the main benefits is how glass tends to stay flat and not warp like other bed surfaces out there.
The bottom layer of your 3D prints also look better when printed on a glass bed, giving a smooth, shiny look. You can produce certain effects at the bottom of your 3D prints depending on what surface you use.
How Do You Make a 3D Prints Stick on Glass?
When we talk about 3D printing in general, the issue of bed adhesion arises. Often, bed adhesion can make or break your print and I remember how it feels to have a 3D print going successful for hours, then failing out of nowhere.
There are multiple ways to make your 3D print stick to the glass bed better so take these tips on and implement them in your own routine as you see fit.
The good thing is glass bed adhesion is quite easy to figure out, let’s see how.
Leveling Your Bed Surface
Leveling the bed is the foremost thing you should do before beginning your printing process. Level the bed in such a way that any point on the build plate is the same distance away from the nozzle.
It may seem minor, but it plays a critical role in glass bed adhesion and determining the quality of your print.
Ideally, you implement a strategy which means your bed doesn’t move very much in the first place. One thing I found to help reduce the need to level your bed so often are Marketty Bed Leveling Springs from Amazon.
These work so well because they are much stiffer than your stock bed springs, meaning they don’t move as much. It helps your overall stability during the printing process, and means you don’t have to level your bed all the time.
Many people who were first reluctant to change their bed springs changed over and were very happy with the results.
One user even said that after 20 prints, they still didn’t need to level the bed!
You can also get yourself an automatic bed leveling system to help correctly level your bed. The ANTCLABS BLTouch Auto Bed Leveling Sensor from Amazon is a pretty good choice for this.
It works with any kind of bed surface and is pretty easy to apply. You do need to gather up some basic information and firmware settings to get it working, but there are some great tutorials you can follow to get there properly.
Once you calibrate your Z-offset, you shouldn’t really have to level your bed in the future, and it even accounts for a warped surface (glass is usually flat so this doesn’t matter too much).
Cleaning Your Print Surface
Cleaning the bed paves way for good adhesion and a successful print. Make sure you clean the bed before printing and in between if the need arises. Often, dirt, oil, or grease can be present on your glass bed.
Often, dirt, oil, or grease can be present on your glass bed.
It will create a layer on the bed thereby not allowing the print to stick to it. By ensuring your glass bed is clean at all times, bed adhesion won’t be an issue anymore. You can use a glass cleaner or isopropyl alcohol for this purpose.
Using an alcohol-based cleaner works to break down the dirt and easily remove it from the bed. I’d recommend going with the Dynarex Alcohol Prep Pads from Amazon, which is saturated with 70% isopropyl alcohol.
Check out this video below for some great tips for making prints stick on glass just using dishwasher liquid! He says you can wash your bed every 10-20 prints and it should work well, but if the bed gets dusty it can mess with adhesion.
Add an Extra Build Surface to the Glass
Users suggest investing in a PEI (Polyetherimide) sheet if you’re aiming for large prints.
You’ll love the Gizmo Dorks PEI Sheet with Preapplied Laminated 3M Adhesive from Amazon. Thousands of users are making use of this premium bed surface for good reason.
It installs quickly onto your 3D printer with a bubble-free application, and is endlessly reuseable for multiple prints. ABS and PLA filaments can easily print directly on this PEI surface without the need of extra adhesives.
Using Adhesives
If you do want to go the adhesives route, like plenty of 3D printer hobbyists out there, then you have many options.
When using adhesives, people tend to go for products like glue sticks, hairsprays, or specialized 3D printer bed adhesives for the task.
For glue sticks, tons of people recommend the Elmer’s Purple Disappearing Glue Sticks from Amazon because they work so well. It is non-toxic, easily washable, and let’s you easily see where you applied it.
After applying, the purple marks disappear which is a really cool feature.
Figure out why plenty of people love these glue sticks and get a set from Amazon for yourself.
For hairsprays to use on your glass 3D printer bed, I’d recommend the L’Oreal Paris Advanced Control Hairspray from Amazon. It’s the hold aspect of the hairspray that provides the great adhesive plenty of people use for their bed surfaces.
Reviewers that have used this for 3D printing mention that say it is fantastic for having your 3D prints stick down with no warping. The prints even “pop out easily once your build plate cools”, and on top of all that, it’s very affordable.
One of the most popular specialized 3D printer adhesives has to be the Layerneer 3D Printer Adhesive Bed Glue from Amazon. Using glue sticks can be quite messy, as one user mentioned, but after changing over to this, he was very pleased.
The great thing about this adhesive is that you don’t need to keep on reapplying it, and one single coat can be recharged with a wet sponge to get more uses. Over time, although the price is higher, it is really cheap in the long run.
You aren’t getting any harsh smells since it is low-odor, and it’s water soluble also. The built-in foam tip makes application to your glass bed very simple, and spill-proof.
On top of all of this, you get a full 3 months or 90 days manufacturer guarantee so you can ensure that it works just as you desire.
You’ll be joining plenty of users who have transformed their 3D printing experience with the Layerneer Bed Adhesive Glue, so get yourself a bottle today.
Regulating Z-Offset
Proper distance between the nozzle and print bed is fundamental for good adhesion and successful prints. The filament won’t stick to the glass bed if the nozzle is far away.
Likewise, if the nozzle is too close to the bed, your first layer may not look so good. You want to adjust your Z-offset in a way that leaves just enough room for your printing filament to stick to the glass bed.
This can usually be solved with leveling your bed surface, but if you add a glass bed to your 3D printer, you’ll either need to move your Z-endstops or increase your Z-offset.
Adjust Your Bed Temperature
Adjusting your bed temperature can definitely improve your results when it comes to bed adhesion. When you increase your bed temperature, it usually helps with adhesion due to not letting filament cool too rapidly.
I’d recommend increasing your bed temperature in 5-10°C increments to combat bed adhesion issues.
A lot of warping issues come from quick changes in temperature, so having a more consistent bed temperature helps out.
One product that helps out with improving your bed temperature through faster heating, and keeping temperatures consistent is the HWAKUNG Heated Bed Insulation Mat from Amazon.
Print Speed and Fan Settings
Print speed can also be responsible for glass bed adhesion issues. A print speed too fast can cause ringing and under extrusion, leading to poor glass bed adhesion.
Make sure you slow down your first few layers in your slicer to give it a better success rate of sticking to your glass bed.
For your fan settings, your slicer usually defaults to having the fan off, so double-check that your fan is off during the first few layers.
Add Rafts or Brims to the Print
Within your slicer software, you can add some build plate adhesion in the form of a raft or brim to make your 3D prints stick to glass better. They are created with an air gap, so the extra material can easily be separated from your actual model.
You don’t use much plastic for rafts and brims depending on the size of your 3D print, but you can reduce how much it extends out. The default “Raft Extra Margin” in Cura is 15mm, but you can reduce this to about 5mm.
It is simply how far out the raft extends out from your model.
What Types of Glass is Used for 3D Printing?
3D printing involves printing on surfaces of various kinds, ranging from acrylic to aluminum to glass beds. Glass beds are increasingly gaining popularity among creators and 3D printing enthusiasts alike.
3D printing on glass offers plenty of advantages over its traditional counterparts. Now let’s look at the types of glass used for 3D printing.
Now let’s look at the types of glass used for 3D printing.
- Borosilicate Glass
- Tempered Glass
- Regular Glass (Mirrors, Picture Frame Glass)
Borosilicate Glass
A blend of boron trioxide and silica, Borosilicate is highly durable, has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion, and is resistant to thermal shock as well.
Unlike regular glass, Borosilicate glass does not crack under extreme and sudden temperature change, minimal to no physical changes occur during the printing process.
These properties make Borosilicate glass an optimal choice for industrial and technical applications, laboratories, and wineries, etc.
Borosilicate glass when paired with a heated bed largely helps reduce the possibility of warping, as the heated bed slows down the cooling process of the printed item.
Borosilicate glass offers an immaculate surface quality in addition to having good thermal and chemical resistance, no air bubbles, and high durability. This makes it an ideal choice for 3D printing.
This makes it an ideal choice for 3D printing.
Creators worldwide swear by Borosilicate glass, have received exceptional results consistently, and highly recommend it to users.
Tempered Glass
Tempered glass, in simple terms, is glass treated to provide better thermal stability. It means that this glass can be subjected to higher temperatures with no adverse effects to deal with. It is possible to heat tempered glass up to 240°C.
If you intend on printing with extremely high-temperature filaments like PEEK or ULTEM, tempered glass is your ideal choice.
With tempered glass, you can’t cut it to size because the way it’s manufactured means it will pop. Tempering the glass provides it with more mechanical strength, and is good protection against mechanical shocks.
Regular Glass or Mirrors
Apart from the above mentioned types of glass, users also 3D print with regular glass, mirrors, and glass used in photo frames, etc. This has more of a tendency to break since it is not treated to withstand those higher temperatures and print removal.
Some people have mentioned that they get pretty good success with them though. Many people have reported getting 3D prints sticking a little too well to these types of glass, requiring them to put it in the fridge to detatch the print.
What is the Best Glass Surface for a 3D Printer?
Borosilicate glass is the best glass surface for 3D printing. With low thermal expansion, high heat and temperature shock resistance, Borosilicate glass makes for an ideal choice for 3D printing.
Its smooth, flat, and strong surface provides consistent results with great bed adhesion and little to no warping issues.
Incredibly easy to clean and maintain, 3D printing on this glass will give you a delightful experience.
If you’re looking to invest in a glass surface that will not only give you excellent prints, immaculate surface quality, and minimal adhesion issues but also help you save money, time, and energy, Borosilicate glass is for you.
I’d recommend getting yourself the Dcreate Borosilicate Glass from Amazon for a respectable price. It comes in at a 235 x 235 x 3.8mm size and a weight of 1.1 lbs.
It comes in at a 235 x 235 x 3.8mm size and a weight of 1.1 lbs.
One user who implemented this bed had trouble at first, but with some good hairspray, they got their PLA 3D prints sticking very well.
Since these beds don’t warp, you don’t need a raft as much as with a warped 3D print bed since it doesn’t have to account for those uneven surfaces, but it can still help out if you choose to.
Rather than continuing with window glass, a reviewer said it cracked and scratched easily. Since getting theirselves a borosilicate glass bed, they noticed how thick the glass is and how it holds and distributes heat effectively.
This fits an Ender 3 just perfectly according to many people, so I’d definitely look to getting this as an upgrade to your 3D printer today.
You’re also getting an 18-month warranty and a 100% hassle-free replacement for quality issues.
glass-ceramic, borosilicate and perforated do-it-yourself
3D printers are very popular in many areas. Today, such devices are widely used in dentistry, jewelry, architecture and business. But in order for any printer to print quality parts, you should take care of choosing a surface for your desktop, taking into account the material used. Next, we will tell you how to do it right.
What types of glasses are available for a 3D printer table?
All 3D printers have one thing in common: the desktop. It is on it that a three-dimensional product is created, the quality of which will depend on adhesion with the platform. Usually the desktop is covered with glass, but there may be other options.
Sitall glass
Sitall glass is one of the most popular adhesion methods to avoid sticking of the product to the desktop and ensure its reliable retention on the surface. The only drawback is the rather high cost of such material.
For reference. Sitall is a crystalline material with properties such as transparency, wear resistance, chemical and thermal stability.
It was first developed in the Soviet Union for use in the aviation industry.
The use of glass-ceramic glass in 3D printing allows solving a number of the following problems:
- the ability to print with different types of plastic;
- solid surface mounting;
- no deformation when printing samples even when exposed to high temperatures;
- production of quality parts;
- does not require the use of glue or other adhesive materials.
All you have to do is calibrate the height between the nozzle and the build plate and start printing your first 3D products.
Borosilicate glass
Borosilicate glass has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, making it more resistant to heat than ordinary glass. When printing 3D models on a platform equipped with a similar surface, high-quality products are obtained. This is achieved by tightly attaching the first layer to the site and ensuring good adhesion.
Borosilicate glass is made from tempered materials and is used in medicine, energy and everyday life. It is resistant to temperature extremes and chemical attack. The secret is simple - in the production of borosilicate glass, boron oxide is added to the composition and the content of air bubbles is excluded.
Even a beginner will have no problems installing the glass - it is attached to the desktop of the 3D printer with clerical clips or bolts.
Perforated glass
Special tempered glass with a perforated coating ensures that the future 3D part is firmly attached to the work platform. Another plus is that such material provides easy separation of finished products from the table after they have cooled. Perforated glass is used in a range of heated desktop 3D printers. On such devices it is easy to work with any kind of plastic.
What should I do if the glass comes off the 3D printer table?
Many buyers and beginners in 3D printing are faced with the problem of keeping the model on the desktop or dealing with surface irregularities. In these cases, glass comes to the rescue. It provides a dense fastening of the product with the surface and allows you to produce high-quality three-dimensional models. But in words, everything is easy, but in practice, a beginner may have problems not only with printing, but also with such a problem as glass peeling off the desktop. In this case, you should not panic - it is better to carefully study the possible causes, watch videos on the Internet and take possible measures:0003
In these cases, glass comes to the rescue. It provides a dense fastening of the product with the surface and allows you to produce high-quality three-dimensional models. But in words, everything is easy, but in practice, a beginner may have problems not only with printing, but also with such a problem as glass peeling off the desktop. In this case, you should not panic - it is better to carefully study the possible causes, watch videos on the Internet and take possible measures:0003
- Check table calibration settings - we recommend doing this with the bed and extruder preheated to operating temperature.
- Reduce print speed.
- Eliminate poor adhesion - glue or hairspray is suitable for this purpose, as well as alcohol, which is recommended to degrease the surface.
- Fix the glass with special clamps or screws.
How to work with glass?
If you have recently bought a 3D printer and do not yet know about all the features of this device, then most likely you will have many questions during the first and subsequent use. One of the possible options is what kind of surface to choose for the desktop and how to work with glass correctly. Here are a few helpful tips to get your 3D printing process up and running and produce quality products:
- Remove the protective film from the glass surface.
- Before placing the glass on the workbench, preheat the platform to facilitate easy removal of the protective film from the surface with minimal adhesive residue.
- Remove the sticker carefully.
- If adhesive remains on the platform, remove with acetone or thinner.
- Mount the glass on the work table using the clips.
note . Before you start printing, adjust the table height for your glass thickness and calibrate the platform.
Done right, 3D printed pieces will bring maximum comfort without the risk of them sticking to the platform. You can easily get high-quality models and avoid the risk of platform deformation when heated to high temperatures.
How to make glass with your own hands?
If you decide to save on buying glass, there is another way out - to make it yourself. This method may well become an alternative if there is not enough money to buy or there is no time to wait. We list several options for making glass with our own hands:
- Use blue tape or masking tape. One of the most effective and inexpensive ways to get the product to grip the work surface. Opt for wide rolls for quick surface coverage, and optionally use adhesive to avoid using extra heat when printing.
- Make a table with duct tape and hairspray . This method is suitable for printing with ABS plastic - spray regular hairspray on the surface of the desktop and place Kapton on top.
- Use window glass or a mirror and a sanding disc with grit 53 for the surface. This will create excellent adhesion when working with any plastic. You can fix the structure with ordinary clerical clips.

Mistakes and how to avoid them
Many beginners in 3D printing have problems, in particular with incorrect glass selection or installation. Follow these simple guidelines to avoid common mistakes:
- Select glass according to the plastic you are going to print with. It is best to give preference to glass-ceramic or borosilicate material - this option is not the most budgetary, but the most reliable.
- Before printing 3D models, make sure the desktop is properly calibrated.
- If the product sticks to the desktop surface, use additional methods of adhesion - glue or varnish.
- When making your own desktop surface, use tempered glass if possible and attach it tightly to the platform.
We hope that the first experience of 3D printing and our advice will help you to produce high-quality three-dimensional products with minimal losses!
- April 19, 2021
- 5243
Get expert advice
Install glass on the Wanhao Duplicator i3 3d printer
Many of those who decide to buy a Duplicator i3 3d printer soon after purchasing it think about installing glass on the printing platform. You can learn from the experience of many who have decided to do this, on forums and reviews on the Internet. We recommend buying borosilicate glass of the right size for your 3d printer's print platform.
You can learn from the experience of many who have decided to do this, on forums and reviews on the Internet. We recommend buying borosilicate glass of the right size for your 3d printer's print platform.
Glass comes well packaged and protected from damage. The kit includes four clips to hold it in place. Some owners of the Wanhao duplicator i3 3d printer prefer to glue the glass to the print platform, we decided to get by with clips. Please note that incorrectly installed clips can interfere with the movement of the 3D printer nozzle when printing.
First, tear off the sticker that covers the 3d printer platform. It comes off easily enough, but there is quite a lot of glue left on the platform. In order for the sticker to come off easier and less glue left, try preheating the 3d printer platform. If you bought your 3d printer a long time ago, and your Wanhao i3 is an old generation, then there are no stickers on the desktop, and you don’t need to tear anything off.
Clean the build platform of the 3d printer from adhesive residue with solvent or acetone. It will certainly take a lot of time, but the result is worth it.
Once you're done cleaning, place the glass on the 3d printer bed. Please note that in the photo the clamps are installed in a temporary position. If left as is, they will be in contact with the extruder nozzle.
Attention! Before printing, adjust the desktop height according to the thickness of the glass. Usually the height of the springs is sufficient to compensate for the increase in the level of the platform. Set the clips to a permanent position that won't interfere with the 3d printer. If necessary, experiment with clips of different sizes. You can easily find them in office supply stores. After installing the glass, we recommend that you manually disassemble and remove the shiny nickel-plated part of the clips, as it will be in contact with the printer frame.
Another simple option, you can print on the printer itself special glass holders for the Duplicator i3 3D printer. You can download the model from our website.
| Glass holder model for Duplicator i3 3D printer | Download |
More details:
What are the pros and cons of installing a printer glass.
- Installing glass on the desktop of a 3D printer greatly simplifies the process of removing the finished model. You simply remove the glass from the table and remove the model behind your workbench without fear of damaging the 3D printer table top. It also eliminates the need for frequent platform calibration.
- When the table is heated to high temperatures and large models are printed, the aluminum platform may deform and its surface becomes uneven. The glass prevents possible deformation and improves print stability and quality.
- Easy and convenient removal from the surface; glue, or other compositions to increase sticking (adhesion).
- The disadvantages include the fact that due to the thickness of the glass, for high-quality adhesion, the temperature of the table must be increased by 5-10 ° C from the standard settings.
Why is it so expensive.
- This is not ordinary, but high quality borosilicate glass, which is much more expensive to produce. Borosilicate glass is characterized by high thermal conductivity, heat resistance and structural integrity. It is stronger than ordinary glass, but under high pressure, or falling, it can break or crack. Borosilicate glass has a wide range of applications ranging from laboratory glassware to mirrors for astronomical telescopes. This glass is used to make lenses for high-quality flashlights, teapots and much more.
If I live far away, will it not break on delivery?
- The glass is wrapped in bubble wrap and as described above is significantly stronger than normal glass.