Baam 3d printer cost
BAAM 3D Printer In-Depth Review
ADVERTISEMENT
6.5Expert Score
BAAM 3D Printer
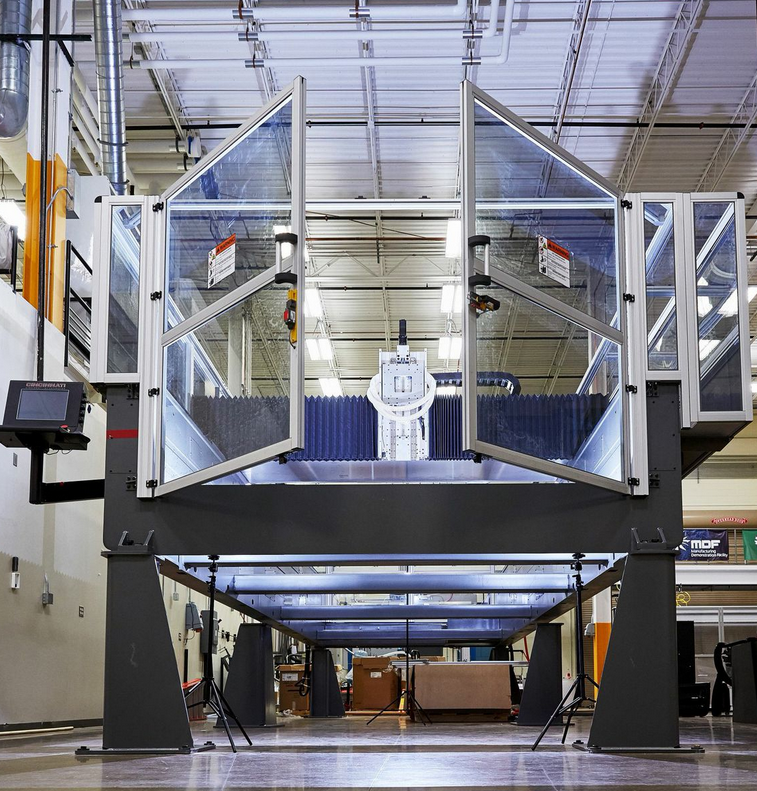
BAAM 3D printer is one of the largest machines around. And, it certainly focuses on providing better manufacturing workflow to its customers. With many amazing features, the 3D printer has stunned everyone around the world showing off its gigantic footprint.
Affordability
2
Quality
7
Speed
9
Capability
8
Practicality
7
User Expectations
6
PROS
- It is huge and can manage to print a complete car frame in one go
- Allows for open source material use
- Multiple material support
- Faster than almost every other industrial printer out there offering large model 3D printing
CONS
- Very Expensive
- Not available commercially for purchasing
- The accuracy and details may feel unsatisfactory to many
Referred to as Big Area Additive manufacturing 3D printer, it pretty much clarifies what BAAM does. The large-format 3D printer, designed for ...
Add to wishlistAdded to wishlistRemoved from wishlist 0
Add to compare
|
Table of Contents
How about we told you that a 3D printer can print 10 lbs plastic per hour? At first, this may seem a little too much. However, the BAAM 3D printer from Cincinnati has done it, effortlessly.
However, the BAAM 3D printer from Cincinnati has done it, effortlessly.
This industrial-grade 3D Printer is way too ahead of its competitors in terms of speed and size. This is an FDM 3D printer that is 10 times bigger than most of the printers out there and offers 200 times faster print speed.
While this may have not impressed you much at first. However, the fact that the printer uses affordable materials, a feedstock of plastic pellets to ensure that the printing cost pertaining to the material cost is as low as possible for large production cannot miss your attention at all.
There are many features embedded in the 3D Printer design to make this enormous project a success. And, the company has done its best to make sure that the printer is yet easy to handle as well.
FDM being the most hassle-free printing technology is easy to accomplish for most users.
Certainly, there would be a lot that the manufacturer would be planning in the coming years, however, by far, this is one of the most amazing developments that the industry has witnessed.
Proving that, one can print a complete frame of a car in one go when the 3D printer is larger than any other alternative available in the market.
Here is a comprehensive BAAM review to provide you with the many unique features that the printer flaunts and the limitations that it still is trying to fight.
ADVERTISEMENT
Features
Credit: sciencedirect.comThe manufacturer claims that the 3D printer is one of the largest machines around. And, it certainly focuses on providing better manufacturing workflow to its customers. With many amazing features, the 3D printer has stunned everyone around the world showing off its gigantic footprint.
So, here are a few features that would help you understand what this 3D printer entails for its users:
Large Build Size
As you would expect, being an industrial-grade 3D Printer, BAAM has a huge footprint. It can print car frames in one go. You can create furniture and a lot of other things without needing to connect together different parts printed using a 3D printer.
Open-Source Material
The company does not bound customers to use materials from the manufacturer itself. But, one can choose to buy material from other vendors as well.
Multiple Material Support
Unlike most of the industrial-grade 3D printer providing such huge print, volume works mostly with a few or even one material of a specific type.
However, this 3D printer allows you to print with ABS, PLA, PC, PEI, PPS, composite materials, and a lot of other options. This certainly is the ice breaker for many customers.
Print with Multiple Material
The transition between different material options is a problem with many 3D printers. And, this one isn’t ready to follow the same trend. On the contrary, it allows us to print with multiple materials at the same time.
ADVERTISEMENT
Specifications
Already stressed a lot on its size. So, let us start with the measure of this 3D printer. BAAM 3D printer is 6000 x 2300 x 1900 mm, covering a huge amount of space of a workspace.
It makes use of granular extrusion and makes printing faster than other 3D printers available. The machine weighs 18143 kgs.
Designed to serve the large scale setup, the 3D Printer is suitable for those working in huge production firms. The build rate of BAAM can reach up to 80 lbs/hour.
To connect the printer, you can use two different connectivity options. One is the network interface and the other is the USB outlet.
The machine was released in 2015 and since then, there have been many modifications made to the design.
It also has a 22 inches LCD screen for controlling the settings of the models when printing. It requires 460V of power to run.
Along with all these specifications, the 3D printer comes in handy for automotive applications.
Price
According to the sources, the manufacturer invested over $1.5 million in the designing of the BAAM 3D printer.
The cost includes the startup cost, along with the other supporting equipment charges.
Hence, you can imagine the price the company would have marked this printer with.
There is not much information available online pertaining to the cost of the 3D Printer.
And, if you are interested, you must connect with the manufacturer to find that detail out.
However, you must expect a huge cost attached to this printer.
So, only plan to get this machine installed in your workhouse if you can set aside hundreds of thousands of dollars for a 3D printer.
ADVERTISEMENT
First Impressions
Credit: sciencedirect.comYes, it is huge and you would be amazed to see how far 3D printing technology has come.
With many attractive features and occupying almost entire space at one end, the machine gives every user a beautiful shock, especially to those who have not worked with such a system before. So, you won’t be disappointed at all.
On the contrary, the entire experience is really exciting for those who can witness the printing of an entire car frame inside a machine in one go. You get every equipment with your order to support the 3D printer’s operation.
You get every equipment with your order to support the 3D printer’s operation.
Setup
Now, here you can expect to get all the help possible from the team selling you this 3D printer.
Unlike any other desktop 3D Printer and few industrial 3D printers where you can read the guide and start right away, this one requires support.
You cannot just decide to work your way through right after getting it installed at your site.
Starting from installation to the first few training sessions to maintenance, the manufacturer is going to play a very important role.
Although after training, things would seem simpler, you must take every step slowly until you are very comfortable working with this 3D printer.
Like any other 3D printer, this machine also works in the same flow. You need to have a 3D file, mostly in the STL format. Once you feed it to the machine, the slicer takes over the job.
Once the G-Code is created, the 3D printer works towards creating each layer, one at a time, to complete the entire model in one go.
ADVERTISEMENT
Printing Type/Cost
BAAM 3D printer is based on the very popular FDM 3D printing technology.
In FDM 3D printing, the material is extruder after heating the plastic above its melting point.
Every time, a layer is deposited and the bed moves downward. Later, another layer is deposited over the previous one. This process continues until the company model is prepared.
Using the same technique, the BAAM 3D printer is designed. However, to make the entire process much affordable for large production, the machine uses feedstock of plastic pallets as the material.
This is very similar to the ones used in the injection molding machines. Hence, making the process cost-efficient.
When talking about the printing cost, one must consider a lot of parameters, starting from the filament cost to the design complexity of the model.
There are many factors that measure the printing cost, including layer height, electricity consumption, and others. Hence, the printing cost would vary from model to model as per setting to set for the same 3D models.
Hence, the printing cost would vary from model to model as per setting to set for the same 3D models.
Print Quality
This is a big printer calling for faster manufacturing. However, the fact that the nozzle size is also bigger to make fast printing possible, the surface finish may come as a challenge to cope up with.
However, that could certainly be refined using various post-processing methods, starting from sanding to other alternatives.
Apart from that, the printer is capable of creating complex designs, overhangs, and whatever you can wish from a 3D printer.
The manufacturer does exclaim that the 3D printer is designed to offer speed by compromising a little bit on accuracy along with the details. So, one must make the decision taking everything into consideration.
ADVERTISEMENT
Software
BAAM uses special software, specially designed to meet the needs of such a huge 3D printer. It is the ORNL slicer.
The software is very capable and user friendly. The intuitive app lets users meet almost all of their slicing requirements.
The intuitive app lets users meet almost all of their slicing requirements.
Most of all, handling models of such size isn’t an easy job for the slicer. But ORNL does do its job with exemplary results.
Customer Service
Cincinnati Incorporation is very diligent when serving its customers with queries related to the BAAM 3D printer.
Understanding the need for training and installation, the company ensures to provide more than enough assistance from its side to get started.
The 3D printer is not available commercially. However, one can request the company directly for the same.
With around 900 cubic ft print volume, the 3D printer is a massive machine to deal with. Hence, the company makes sure to take over the onsite installation work and other related requirements.
Cincinnati also handles the maintenance of the printer. Overall, it offers customers a complete set of benefits to be able to work around such huge Big Area Additive Manufacturing (BAAM) 3D printer.
Parameters Influencing Buying Decision
Buying 3D printers has become a very common trend among businesses. However, when it comes to investing hundreds of thousands of dollars, one must like to find out every minute detail about the machine before making an informed decision.
Here is a gist of the entire BAAM review to help you understand the advantages as well as limitations of the 3D printer, depending on your specific needs.
3D Printer cost: A very expensive 3D printer. Because the machine is not available commercially, there isn’t any standard price related to the BAAM 3D printer. However, you can expect that to be huge. And, if interested, you must connect with the team from Cincinnati to find about the exact quote.
3D Print quality: Depending on the size of the machine, to complete printing faster, the manufacturer has used a comparatively bigger nozzle diameter. This certainly compromises the precision a little bit. And, the surface finish needs post-processing later to create a smoother finish.
And, the surface finish needs post-processing later to create a smoother finish.
3D Print speed: This is where the 3D Printer excels more than any other competitor in the market.
3D Printer capability: Being an industrial-grade 3D printer, this machine is focused on providing businesses with fast 3D printing. One can create car frames inside this machine and in a matter of hours. Doesn’t that sound like an exciting deal for automotive companies? Sure, it does.
3D Printer Practicality: BAAM has industrial use. Its application is mostly for large productions including but not limited to automotive parts.
3D Printer User expectations: Surface quality could have been better. Apart from that, it does provide users with a lot of great perks, especially the print speed.
The Verdict
Every 3D printer in the market has a certain goal connected to its design. When BAAM was proposed, the focus of the team was to create a 3D printer that could create huge models in a matter of time.
And, the professionals have done a pretty amazing job to accomplish that aim.
However, like every perk has the downside as well, this one too isn’t away from that reality. And, you may find the surface quality a bit on the rough side.
However, businesses, especially automotive companies could take huge advantage of this fast printing machine for good.
Enabling the production process takes a leap in growth and speed. The best part is that the introduction of new materials in the BAAM ecosystem is likely to strengthen the results further.
BAAM 3D Printer Gets Major Upgrade - Prints 100 lbs of Material Per Hour & More - 3DPrint.com
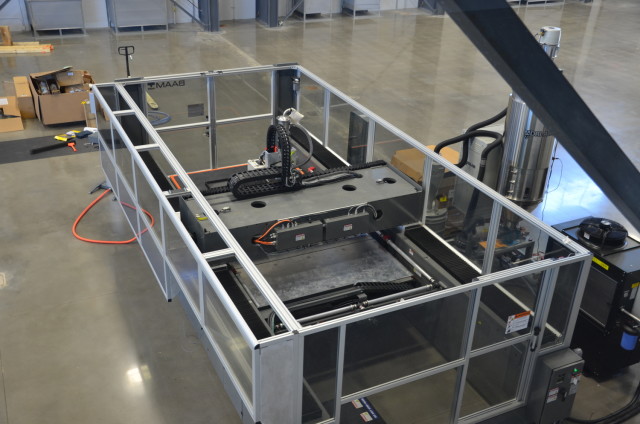
Way back in June of last year we covered an announcement by Cincinnati Inc. and the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) which revealed one of the world’s largest and most productive 3D printers, the Big Area Additive Manufacturing Machine (BAAM). Cincinnati Inc., a company which has been building manufacturing technology for over 116 years, teamed with the science and technology laboratory, managed by the US Department of Energy, because they wanted to transform the way manufacturers look at 3D printers. The BAAM machine was capable of printing a staggering 10 pounds of ABS-composite thermoplastic per hour. This compares to only a few grams that most traditional machines are able to put out each hour. Additionally, the original BAAM machine had a build envelope of approximately 6 x 12 x 3 feet, making it likely the largest FFF 3D printer in existence.
The BAAM machine was capable of printing a staggering 10 pounds of ABS-composite thermoplastic per hour. This compares to only a few grams that most traditional machines are able to put out each hour. Additionally, the original BAAM machine had a build envelope of approximately 6 x 12 x 3 feet, making it likely the largest FFF 3D printer in existence.
As a testimony to how rapidly the industry has progressed over just nine months, this printer — which has gone on to produce everything from tables and chairs to several 3D printed cars by Local Motors to a remake of a Shelby Cobra — has now been supplanted by a machine created by the very companies that produced it.
Via communications we have had with Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 3DPrint.com has been informed that they have been collaborating with Cincinnati Inc. on what is likely the fastest and largest 3D printer of its kind. There’s been a tremendous amount of research and development poured into this latest machine, which seemingly has paid off.
Their latest 3D printer, nicknamed ‘Bertha,’ is capable of printing at rates 10 times that of the original BAAM machine. Instead of outputting 10 pounds of thermoplastic an hour, ‘Bertha’ can print up to a staggering 100 pounds of ABS plastic in an hour, increasing its output by an incredible 1,000%.
“We have a new extrusion system we will likewise be implementing on it that has a production rate of 100 lb/hr,” explained Lonnie Love, Group Leader, Automation, Robotics, and Manufacturing at ORNL, to 3DPrint.com. “We are in the process of getting it completely integrated now, should be operational in a few weeks.”
If that isn’t enough to impress you, consider the fact that this latest machine has an even larger build volume, able to print in sizes up to 20 ft long x 8 ft wide x 6 ft tall.
Considering that when Local Motors used the original BAAM machine to fabricate the body of their Strati car at the International Manufacturing Technology Show back in September it took them approximately 44 hours, a quick calculation would lead us to guess that with this latest BAAM machine, that same car could theoretically be printed in under 5 hours. In fact, Local Motors plans to take delivery of a few of these machines for its microfactory in Knoxville, in close proximity to ORNL. With these machines they expect to begin 3D printing cars on-demand sometime next year.
In fact, Local Motors plans to take delivery of a few of these machines for its microfactory in Knoxville, in close proximity to ORNL. With these machines they expect to begin 3D printing cars on-demand sometime next year.
Team members at ORNL are also tinkering around 3D printing kayaks and canoes with this new machine and expect to turn their attention towards actual boats in the future. Additionally, they would like to eventually print even larger items such as blades for wind turbines.
So what else is next on the menu for Cincinnati Inc. and ORNL? How about printing with metals such as aluminum and steel? That’s exactly what they are turning their attention to next. ORNL is in the process of coming to terms on an extended 10-year collaboration agreement with Cincinnati Inc., and will look into reducing the cost and time it takes to print with metals. To do this, they must turn their attention away from the more expensive materials like titanium and instead look towards steel and aluminum. If successful they could greatly reduce the cost of industrial components for things such as buses, trucks, and aircraft.
If successful they could greatly reduce the cost of industrial components for things such as buses, trucks, and aircraft.
What this partnership is doing is greatly expanding the possible applications for 3D printing, ultimately driving manufacturing costs down, leading to savings across the board for both consumers and manufacturers alike. Let us know your thoughts on this latest 3D printer from Cincinnati Inc. and ORNL. Discuss in the BAAM 3D Printer Upgrade forum thread on 3DPB.com.
Stay up-to-date on all the latest news from the 3D printing industry and receive information and offers from third party vendors.
Tagged with: BAAM • baam 3d printer • Bertha • big area additive manufacturing • cincinnati inc • fast 3d printer • huge 3d printer • large 3d printer • local motors • Oak Ridge National Laboratory • ornl
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong. In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product. nine0003
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details. nine0003
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
nine0060 -
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy. They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more. nine0003
nine0003
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
nine0021 CreatBot F160-PEEK designed to work with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model. nine0003
In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model. nine0003
Prismlab Large Area Industrial Resin Printer Family
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored. nine0003
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support. nine0003
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc. nine0003
nine0003
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model. Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.). nine0003
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder). The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype. nine0003
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale. You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model. nine0003
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin. nine0003
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull (quick release loop) for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles. nine0015
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products). nine0003
Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products). nine0003
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
nine0003
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burnout resin rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product. nine0003
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different. nine0003
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.

Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling. Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make. nine0003
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
nine0167What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer.
For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D printed model
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
If the item is only sold as an assembly. For example, a small gear broke in the mechanism, but the mechanism is sold only “assembly”. It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism. nine0003
A small batch of parts. Small batches, especially models with complex geometry, are more profitable to produce on a 3D printer than by casting or other methods.
Totals
If you need several models or a small project, sometimes it will be more expedient to outsource manufacturing.
After all, in addition to buying equipment and materials, you will have to understand the nuances of the settings and the characteristics of various materials. nine0003
Buying a 3D printer for commercial use is justified if you can fully load it with work or then it can be used for other purposes.
To print to order, you need to have several printers working on different technologies. It is better to get several devices with a smaller print area than to buy just one printer, albeit with a large working area.
How much does a 3D printer cost?
3D printing is a one-stop solution for a wide range of applications, from high-resolution model production to rapid prototyping, rapid tooling for traditional manufacturing processes, production of aids and end-use models. nine0003
However, when you consider investing in a 3D printer, the viability of a solution usually boils down to a simple question: Is it cost-effective for your business? How much does a 3D printer cost and how much time and money can it save your business?
3D printer prices range from $200 to $500,000 depending on the printing process, materials, and complexity of the solution.

In this guide, we'll break down 3D printing costs by technology, compare outsourcing versus in-house manufacturing, list factors to consider when calculating the cost of each model, and look at what else to look for when comparing different solutions. for 3D printing and other production methods. nine0003
Interactive
This interactive ROI tool will help you find out how much time and money you can save by 3D printing with a Formlabs 3D printer.
Calculate Your Costs
The three best-known plastic 3D printing technologies today are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages - take a look at the infographic:
Download this high resolution infographic here. Interested in learning more about FDM, SLA and SLS 3D printing technologies? Check out our detailed guide.
Prices for 3D printers have dropped significantly in recent years, and today all three technologies are available in compact, low cost systems.

FDM generally produces models at a lower cost if you only print relatively simple prototypes in limited numbers. SLA technology offers higher resolution and quality, as well as a wide choice of 3D printing materials at a slightly higher price. But this difference is quickly offset when you print complex designs or larger batches due to the less labor-intensive post-processing process. Finally, SLS technology is the most cost effective for medium to high volume production of high quality functional models. nine0003
Comparing the total cost of different 3D printers by price tags alone will not give you a complete picture of how the cost of a 3D printer and a printed model will compare. The cost of 3D printing materials and labor significantly affects the cost of a model, depending on the application and your production needs.
Let's look at the different factors and costs for each process.
FDM, also known as Fused Filament Manufacturing (FFF), is a printing method where the parts of a model are made by melting and extruding a thermoplastic filament, which the printer's nozzle applies layer by layer onto the model being made.
nine0003
FDM is the most popular form of consumer grade 3D printing, fueled by the proliferation of hobbyist 3D printers. However, professional and industrial FDM printers are also popular among professionals.
The cheapest 3D printers are FDM printers. DIY kits for FDM 3D printers start at $200. However, most of these models are more like toys or DIY projects that require a significant amount of time to build, set up and calibrate. The quality of the print largely depends on the success of these operations. In addition, machines require repairs and regular maintenance to keep them working, so they are more suitable for people with a higher engineering education who have a lot of time and patience. nine0003
Hobbyist FDM 3D printers cost between $500 and $1,500, come pre-assembled or unassembled, require less setup, but have the same disadvantages as the cheapest 3D printers. More expensive models are capable of large print volumes and work with a wide variety of materials besides low temperature ones such as PLA.

Professional 3D FDM printers start at $2,500 and large format professional FDM printers are available from $4,000. The cost of the most modern industrial FDM printers can exceed 10,000 US dollars. Most of these printers come pre-assembled and calibrated in the box, or they can be automatically calibrated. Printers in this category offer better print quality, a wider range of media, higher print volumes, improved reliability, and ease of use and maintenance. In addition, professional 3D printer manufacturers offer customer support services for troubleshooting. nine0003
Material costs for FDM 3D printing range from $50 to $150/kg for most standard and engineering filaments, and $100 to $200/kg for auxiliary materials. There are also cheaper alternatives, but they are of lower quality.
In addition, FDM printing can be very labor intensive. Successful printing of complex models requires support structures that must be removed manually or dissolved in water. To obtain a high quality surface and remove layer lines, lengthy manual post-processing of models, such as sanding, is necessary.
nine0003
SLA 3D printers use the process of photopolymerization, that is, the conversion of liquid polymers into hardened plastic using a laser. SLA is one of the most popular processes among professionals due to its high resolution, accuracy and material versatility.
Models printed on SLA printers have the highest precision, sharpest detail and smoothest surface possible of any plastic 3D printing technology. But the main advantage of the SLA method is its versatility. SLA polymers have a wide range of optical, mechanical and thermal properties that match those of standard, engineering and industrial thermoplastics. nine0003
SLA 3D printers can handle a wide range of resin materials for a wide variety of applications.
SLA used to be used only in large and complex industrial 3D printers costing over $200,000, but the process is now much more affordable. With the Formlabs Form 3+ Printer, businesses can now use industrial quality SLA printing for as little as $3,750.
With Form 3L, large format SLA printing starts at just $11,000. nine0003
Stereolithographic 3D printers will be shipped in a box assembled and calibrated. These are professional tools that are highly reliable and require virtually no maintenance. Technical support is also always available. It provides troubleshooting in a critical situation (but its probability is extremely small).
Most standard and engineered polymers for SLA technology cost between $149 and $200 per liter. nine0003
SLA printers are easy to use and many workflow steps such as rinsing and final curing can be automated to reduce labor costs. Printed models have a high quality surface immediately after printing and require only simple post-processing to remove supporting structures.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high power laser to sinter fine polymer powder particles. The unsprayed powder supports the model during printing and eliminates the need for special support structures.
This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including internal features, grooves, thin walls, and negative taper. nine0003
Models produced using SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics - their strength can be compared with the strength of injection molded parts. As a result, SLS technology is the most popular plastic 3D printing process for industrial applications.
SLS printed nylon models are ideal for a range of functional applications, from consumer product design to healthcare applications.
Like SLA, SLS was previously only available in large format, complex 3D printing systems costing $200,000 or more. With the Formlabs Fuse 1 stereolithography printer, businesses can now solve industrial-scale tasks with SLS technology starting at $18,500. The complete kit, which includes the post-processing and powder recovery system, costs $31,845.
As with SLA printers, stereolithographic printers are shipped assembled and calibrated in the box. They are reliable and can operate 24/7.
The package includes in-depth training and fast technical support. nine0003
SLS nylon print materials cost about US$100/kg. SLS does not require supporting structures and unused powder can be reused, reducing material costs.
SLS is the least labor-intensive plastic 3D printing process in the production environment, because the printed models are of high quality right away, and to remove excess powder, they simply need to be cleaned.
There are several processes for 3D printing not only plastics but also metals. nine0003
Metal FDM printers are similar in design to traditional FDM printers, but use extruded metal rods held together by a resin binder. The finished parts of the model are sintered in an oven to remove the binder.
SLM and DMLS printers are similar to SLS printers, but instead of polymer powders, they fuse metal powder particles layer by layer using a laser. 3D printers based on SLM and DMLS technologies can create strong, precise and complex metal products, making this process ideal for the aerospace, automotive and medical industries.
nine0003
Prices for metal 3D printers have also begun to decline, ranging from $100,000 to $1 million today. However, these systems are still out of reach for most businesses.
SLA 3D printing is available as an alternative for casting workflows that allow metal models to be produced cheaper and faster than traditional methods and provide greater design freedom.
Technical report
Get design guides for 3D printing samples, see the step-by-step direct investment casting process, and study guides for indirect investment casting and sand casting.
Download white paper
Different plastic and metal 3D printing processes have unique qualities that make them suitable for different applications. Below is a comparison of different printing technologies.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Stereolithography (SLA) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Metal FDM Printing Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Metal Direct Metal Sintering (SLM) 9 (21LS9)5050DM9 Resolution ★cle ★☆ ★ opa ★ Look ★ opa ★cle ★cle ★ Look Surgery ★ opa ★ opa ☆ ★cle ☆ ★ opa Simplicity of use ★ opa ★ Look ★cle ★ opa ★ ☆☆☆☆ PROMISE 9032 Up to # 300 x 300 x 600 mm (Desktop and Workshop 3D printers)Up to ~300 x 335 x 200 mm (Desktop and Workshop 3D printers) Up to 165 x 165 x 300 mm (3D - workshop printers) Up to 300 x 200 x 200 mm Up to 400 x 400 x 400 mm Price range DIY kits for 3D printers start at $200, while hobby printers cost $500-1500. Professional 3D FDM printers start at $2,500, while large format professional FDM printers are available from $4,000.
Professional desktop printers start at $3,750, while high-volume large format desktop printers are available from $11,000. nine0533 Workshop industrial printers start at $18,500 and traditional industrial printers start at $100,000. Metal FDM printers start at $100,000, but complete solutions including an oven are much more expensive. DMLS/SLM solutions start at around $200,000. These printers require special infrastructure conditions, which can further increase costs. Cost of materials US$50-150/kg for most standard and engineering yarns and US$100-200/kg for auxiliary materials. $50-150/L for most standard and engineering polymers. $100/kg for nylon. SLS does not require supporting structures and unused powder can be reused, reducing material costs. Depends on material and technology. Significantly higher than plastic.
Depends on material and technology. Significantly higher than plastic. nine0533 Labor Manual removal of support structures (soluble support structures may be used in some cases). Long post-processing is required to obtain a high quality surface. Washing and final polymerization (both can be automated). Simple post-processing to remove supporting structures. Easy cleaning to remove excess powder. Washing and sintering (both can be automated). It is possible to use mechanical processing and other types of surface treatment. nine0533 Stress relief, support structure removal, heat treatment, and mechanical and other surface treatments. Materials Standard thermoplastics such as ABS, PLA and their various blends. Various polymers (thermosetting plastics). Standard, engineering (similar to ABS and PP, similar to silicone, flexible, heat resistant, rigid), injection molding, dental and medical (biocompatible). nine0533
Engineering thermoplastics - typically nylon and its composites (nylon 12 biocompatible + sterilizable). Stainless steel, tool steel, inconel, copper, titanium. Stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, cobalt-chromium, copper, aluminium, nickel alloys. Applications Basic experimental models, low cost rapid prototyping of simple parts. Prototypes with a high level of detail requiring close tolerances and smooth surfaces: molds, tooling, templates, medical models and functional parts. nine0533 Complex geometries, functional prototypes, low volume production or limited trial production. Robust and durable models, tools and production aids. Strong and durable models with complex geometries; ideal for the aerospace, automotive and medical industries. When calculating the cost of one model, the cost of ownership of equipment, material costs and labor costs are usually taken into account.
It is important to understand the factors that affect each of these cost components, as well as the questions to ask in order to evaluate alternative production methods and uncover hidden costs. nine0003
Hardware ownership costs are fixed costs: 3D printer price, service contracts, installation and maintenance. These amounts must be paid whether your printer is idle or produces dozens of models per week.
Add up all projected fixed costs over the lifetime of the equipment, then divide by the number of models you plan to make. As a rule, the higher the performance and efficiency of your 3D printer, the lower the cost of ownership of equipment per model. nine0003
In recent years, desktop 3D printers have shown excellent results in reducing the cost of ownership of equipment. With a price 10 to 100 times lower than traditional industrial 3D printers and the ability to produce thousands of models over a lifetime, the cost of ownership can be negligible.
Questions:
Are there installation, training or additional initial costs other than the cost of the machine itself? nine0003
Do I need to sign a (mandatory) service contract? What does it include?
What accessories and tools are needed to make the final models?
What kind of maintenance is required for the machine to function properly? What is the expected annual maintenance cost? Will it change with an increase in production volumes?
The 3D printing raw materials and consumables you need to create models at an affordable price.
These costs largely depend on the number of models you produce. nine0003
When calculating the cost of materials, determine how much material is required to create one model, and multiply this figure by the cost of the material. Count the amount of waste and any other consumables. As production grows, the cost of ownership of equipment decreases, and the cost of 3D printing materials tends to become more balanced.
Be sure to check what materials you need to create specific models, as the cost of 3D printing consumables can vary greatly. Please note that some 3D printers only work with their proprietary materials and thus limit your ability to use third party materials. nine0003
Questions:
What is the cost of each type of 3D printing material?
How much material is required to create one particular model, including waste?
What is the shelf life of the materials?
Do I need other consumables to create models?
Can the machine work with third-party materials?
While 3D printing can replace complex traditional manufacturing methods and provide significant time savings, depending on the 3D printing technology, it can still be quite labor intensive.
nine0003
Professional desktop 3D printers are generally optimized for ease of use. DIY kits for 3D printers and hobby printers often require additional effort to adjust settings, while regular maintenance or material changes on traditional industrial machines can involve time-consuming tasks that require the assistance of a skilled operator.
Post-processing workflows vary depending on the 3D printing process, but in most cases include cleaning up models and removing support structures or excess material. However, there are solutions to automate some specific tasks. For example, Formlabs Form Wash and Form Cure simplify the wash and finish process for Formlabs SLA 3D printers, while Fuse Sift offers a turnkey post-processing and powder recovery system for the Fuse 1 SLS printer. nine0003
More complex processes such as SLA and SLS do not take long to achieve high quality models, while FDM models require lengthy manual post-processing to improve quality and remove layer lines.

Questions:
What is the whole model production workflow? What specific steps are required to set up printing, change materials, and post-process models?
nine0060How long does it take to post-process one specific model?
Are there any tools or devices available to automate some of these tasks?
Outsource production orders to 3rd party service bureaus or labs if you use 3D printing only occasionally or to make large models in non-standard materials. Typically, the bureau has several in-house 3D printing processes such as SLA, SLS, FDM, as well as metal 3D printers. They can also provide advice on a variety of materials and offer additional services such as design or improved finishes. nine0003
The main disadvantages of outsourcing are the high cost and duration of production. One of the main advantages of 3D printing is its speed compared to traditional production methods. But it is noticeably reduced if the delivery of the model produced by the involved organization takes several days or even weeks.
And as demand and capacity grow, the costs of outsourcing are rising rapidly.
Desktop 3D printers are the perfect solution for fast model production. Depending on the number of parts needed and the volume of prints, the investment in a professional 3D printer can pay for itself in just a few months. nine0003
With desktop and workshop printers, you can pay for the capacity that matches your business needs and scale your production by adding more devices as demand grows, without the heavy investment of a large format 3D printer. Using multiple 3D printers also allows you to print models from different materials at the same time. But if there is a need for the production of large parts or the use of non-standard materials, service bureaus can come to the rescue. nine0003
Investment, material and labor costs are relatively easy to calculate. But what about indirect costs and hard-to-calculate factors that affect your business? Let's look at some of the main considerations when comparing a desktop 3D printer to outsourcing or other manufacturing methods.

Save time: What if you could get products to market a few months faster? Or reduce the delivery time of your products by a few days or weeks? 3D printing simplifies traditional prototyping and manufacturing workflows, helping you save time and stay ahead of the competition. nine0003
Best results: 3D printing allows you to create more iterations, overcome failures faster and produce better end products. Troubleshooting a design early on also helps avoid costly redesign and the use of additional tools.
Interaction: Having high-quality prototypes and models allows you to communicate more effectively with customers, customers, suppliers and other stakeholders. Avoid misunderstandings and costly mistakes. nine0003
Intellectual Property Protection: Do you work with confidential information? Making your own models means you don't have to transfer intellectual property (IP) to third parties, reducing the risk of IP leakage or theft.

Learn more


 build size
build size









