3D print vs injection molding
Plastic Injection Molding vs 3D Printing – Which is Better?
Among today’s manufacturers, both 3D printing and plastic injection molding are viable options for producing complex plastic parts and components. While originally considered competing technologies, these techniques are now each largely recognized as having unique advantages and can even be used together to help optimize production efficiency.
For OEMs wondering whether plastic injection molding or 3D printing is the right process for their next project, we’ll explain when to use each technique and how they can be used collectively to support one another.
When to USE 3D PRINTING AND PLASTIC INJECTION MOLDING
3D printing and plastic injection molding are both helpful processes in their own right. 3D printing has given engineers the power to create plastic designs at their desks and bring them to life in a matter of hours. Injection molding, on the other hand, is the go-to for quality and value. It is commonly used to quickly and reliably produce high-volume runs of complex plastic designs.
3D Printing is Best-Suited For:
- Quick turnaround times (1-2 weeks)
- Low volume production runs (100 parts or fewer)
- Designs with frequent changes
- Relatively small plastic parts or components
Injection Molding is Best-Suited For:
- Longer turnaround times (5-7 weeks for simple parts)
- High volume production runs (1,000+ parts per run)
- Final part design (no more prototyping)
- Parts of any size or complexity
The use of 3D printing in innovative and experimental scenarios has been grabbing recent headlines, but the reality is that the majority of today’s plastic parts are manufactured using plastic injection molding. The choice is understandable given how the process helps OEMs control quality, costs, and design complexities such as tight tolerances.
Tooling Design
Tooling design is one of the most expensive and time-consuming parts of the injection molding process.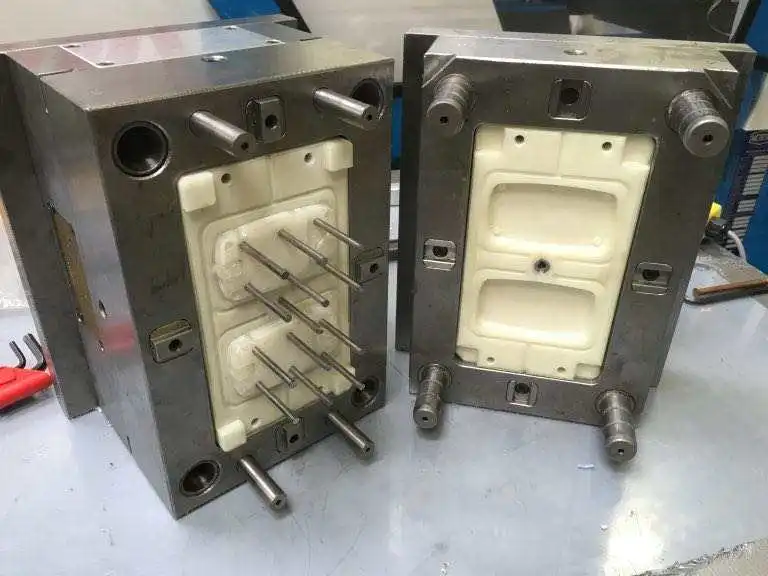 It is also an opportunity for some injection molders to leverage 3D printing to create tools during prototyping that help reduce development time and lower tooling costs. Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing, for example, can be a cost-effective alternative to metal tool fabrication, as SLA parts are fully solid and isotropic, and can withstand the pressure of low-volume molding.
It is also an opportunity for some injection molders to leverage 3D printing to create tools during prototyping that help reduce development time and lower tooling costs. Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing, for example, can be a cost-effective alternative to metal tool fabrication, as SLA parts are fully solid and isotropic, and can withstand the pressure of low-volume molding.
For larger volume production runs and more precise molds, however, traditional tooling remains the best option. Likewise, if a part requires the use of thermoplastics, metal tools are the best option to handle resins with melting temperatures at or exceeding 500°F.
Custom PLASTIC Part Design
Due to its ability to create custom plastic part designs and prototypes in a matter of hours or days, 3D printing technology has exploded in popularity. The medical industry, for example, has embraced the quick-turn technology to create custom items like prosthetics, dental products, orthopedics, exoskeletons, bones, implants, artificial heart valves, and more, with researchers even working on 3D organ printing technologies.
That's not to diminish plastic injection molding's contributions and ongoing demand within the medical community. The value of consistently producing large quantities of defect-free, complex medical devices and components simply cannot be underestimated.
Viewing 3D printing and plastic injection molding as complementary instead of competing technologies is beneficial for OEMs and molders alike. Combining these two techniques as situations warrant can ultimately help shorten pre-production iteration cycles and allows for better testing, manufacturing, and outcomes. Interested in learning more about how the tool qualifying process helps to ensure quality outcomes? View our infographic.
You might also like...
What is the Difference Between 3D Printing and Injection Moulding?
3D printing and injection moulding are both techniques for producing plastic parts and components, but each manufacturing process has its own advantages and can be used together as complementary manufacturing methods.
3D printing technology is an additive printing process that creates objects by building up layers of material, while plastic injection moulding uses a mold that is filled with molten material that cools and hardens to produce parts and components.
Injection moulding and 3D printing can both be used for protoyping, but there are some key differences between the processes.
The Key Differences
- Injection moulding is better for high volume production with minimal material wastage
- 3D printing is a slower process, but is faster to set up and allows for frequent design changes as well as being better for complex designs
3D printing (also known as additive manufacturing) offers fast turnaround times of 1-2 week, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and for designs with frequent changes. This process is also able to produce relatively small plastic parts and components as well as being ideal for complex or intricate designs. It is, however, best suited to print parts for low production runs of 100 parts or fewer, as it can be costly in terms of time and money for larger runs.
It is, however, best suited to print parts for low production runs of 100 parts or fewer, as it can be costly in terms of time and money for larger runs.
Advantages
- 3D printing has a low entry cost. A desktop 3D printer and supply of materials is cheaper than injection moulding equipment. The proliferation of open-source software and hardware can also provide ongoing support at little or no cost
- Easy to make design changes. Since it is an additive process, 3D printing allows you to make design changes even during production, saving time and money on a run of components that may have a flaw. Being able to pause mid process and make design changes means that you do not need to start the entire production run from the start. 3D printing is also good for quick prototypes as there is little set-up required ahead of production
- Good for intricate designs. Because it produces parts layer-by-layer, 3D printing is perfect for producing complex or intricate designs with detailed infrastructures
Disadvantages
- Despite the set-up being relatively fast, 3D printing is a slow production method.
 The CAD-based, detail oriented process limits how many parts can be produced at once, with most printers only capable of building one or two items at a time
The CAD-based, detail oriented process limits how many parts can be produced at once, with most printers only capable of building one or two items at a time - 3D printing is unable to produce larger items as the process is limited by the size of the printing area. The design becomes increasingly unstable if parts hang off the edge of the printing area, so while large scale 3D printing is possible, it is not the best use of this process
- Rough finish. The finish of 3D printed parts is rough due to the layers being additively built, no matter how fine the detail is. As a result, post-build smoothing is required should you need a smooth finish
Injection moulding has long turnaround times to prepare for the creation of parts (5-7 weeks even for simple parts), which means it is not well suited to frequent design changes. However, despite the long turnaround times this process is ideal for producing parts in high volumes (1,000+ parts per run).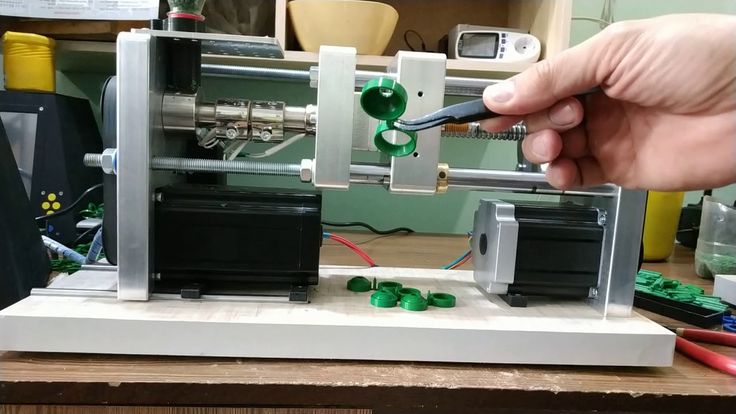 The mold tool is also fine for producing large or small components of any complexity.
The mold tool is also fine for producing large or small components of any complexity.
Advantages
- Able to mass produce a high volume of parts. Injection moulding can use a high number of molds at once, meaning that it is more cost-effective for producing a large number of objects
- Enhanced strength of objects. Injection molded parts are created using a single layer of poured material, eliminating any fissures or other areas of weakness. This process also works for dense materials, such as concrete, that would need to be diluted or modified for 3D printing
- Minimal wastage. Because injection moulding involves pouring material into a mold, it uses exactly the amount of material required for the design. This means this manufacturing method is ideal for mass producing objects cost-effectively
Disadvantages
- Limited design capabilities. The use of a mold means there are design limitations placed upon this production method.
 Right angles in the design can make it difficult to remove an object from the mod without it breaking. Injection moulding is also not well suited to creating precise and delicate designs that can stand on their own
Right angles in the design can make it difficult to remove an object from the mod without it breaking. Injection moulding is also not well suited to creating precise and delicate designs that can stand on their own - Difficult to correct mistakes or change designs. Because of the long set-up times associated with injection moulding it is difficult and expensive to rectify any mistakes in the design. The mold needs to be completely remade to change designs or fix problems, while any objects produced would need to be scrapped
- Expensive entry costs. Injection moulding machines are expensive, often costing upwards of six figures. Designed for industry, these systems are not really for hobby use as there is the cost of making molds, materials and design prototyping to take account of in addition to the original machine cost
Applications
3D Printing is best suited to:
- Small batch production, including prototyping
- Intricate designs with gaps or holes in the middle
- Design changes, even during production
Injection moulding is best suited to:
- Large batch production as you can create multiple identical objects simultaneously
- Strong, solid designs that are based on one continuous form
- Smooth finishes for parts that move against other objects.
 The ease of creating smooth parts means that there is reduced friction as compared to the rougher finish associated with 3D printed parts
The ease of creating smooth parts means that there is reduced friction as compared to the rougher finish associated with 3D printed parts
Will 3D Printing Replace Injection Moulding?
3D printing and injection moulding are often seen as competing technologies, but each has their own set of benefits and suitable uses.
While 3D printing has become more widely used in recent years, injection moulding is still used for the manufacture of the majority of plastic parts for industry. This is due to the ease with which costs and quality can be controlled while also allowing for mass production.
However, because of the cost and time consuming nature of injection moulding tooling design, 3D printing is generally seen as a better process for prototyping. The medical industry is just one area where 3D printing has been embraced for the production of custom items such as artificial heart valves, dental products or prosthetics.
Rather than seeing 3D printing as a potential replacement for injection moulding, the two technologies should be seen as complementary processes that can be used together depending upon requirements. By using the processes together, it is possible to shorten pre-production cycles before moving onto large batch production.
By using the processes together, it is possible to shorten pre-production cycles before moving onto large batch production.
Conclusion
Both processes have their benefits and drawbacks and so they should be considered as complementary rather than competing technologies. 3D printing is better for small batch, complex parts that may require frequent design changes or customisation. Injection moulding, on the other hand, is better for large volume production of less complex parts that have successfully completed the design stage.
TWI can support you with all aspects of design and manufacture related to injection moulding and 3D printing, whether that is technical support, technology acquisition, product and process development or manufacturing and production support.
You can find out more about our services and support here or contact us, by email:
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
Help with the selection process covering each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three dimensional object layer-by-layer using a computer created design.
3D Printing vs. Injection Molding - Differences & Opportunities
Industry 4.0, Automotive, Innovation May 15, 2022
The automotive industry has always strived to introduce new technologies and methods into the production process. High competition and ever-increasing user needs effectively stimulate innovation in many areas. This also applies to the production of individual components - in this context, 3D printing and injection molding are currently being used, among others. What are the features of these technologies? Can they be combined? nine0006
3D printing and injection molding in the automotive industry
These technologies can be applied to the production of both internal and external parts of a car. They are used to make parts such as bumpers, door panels, floor rails, air vents, door handles or dashboard elements. What are the features of these two technologies?
What are the features of these two technologies?
The origins of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, date back to the late 1980s. Although the development of this technology has spanned several decades, it is still innovative and extremely useful - its main advantage lies in the ability to create three-dimensional tactile models that mimic digital ones. 3D printing is used in many industries, including the automotive industry, where it is used in almost every step of the production of . The technology is used, among other things, for prototyping, production of spare parts and finished components. This solution has many advantages, including the low weight of parts made using additive manufacturing technology, as well as high strength. nine0003
See also: Injection mold production in cooperation with Knauf Automotive - from design to finished product
3d printing vs injection molding - what is the difference between these technologies?
Injection molding is an alternative to 3D printing.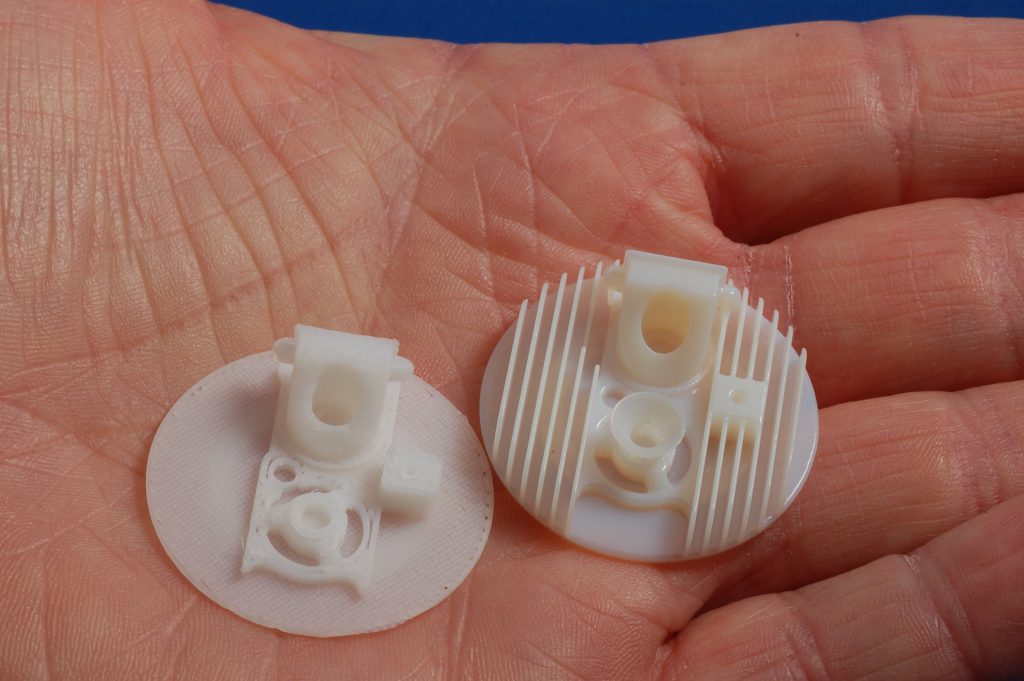 It is also well known in the automotive industry. Here, the manufacturing process involves injecting a plasticized mass of material into a mold cavity, which is then cooled to solidify the product. Here, the manufacturing process involves injecting a plasticized mass of material into a mold cavity, which is then subjected to high temperatures. The whole process must take place under a certain pressure, and after the plastic mass has solidified, the desired shape is achieved. nine0005 The differences between these methods are quite significant, since they concern not only the technology itself, the scale of production, but also the tools used. This is reflected in the cost of manufacturing elements, their durability and the speed of the whole process. However, both of these methods have their advantages - moreover, it is possible to combine the advantages of 3D printing and injection molding.
It is also well known in the automotive industry. Here, the manufacturing process involves injecting a plasticized mass of material into a mold cavity, which is then cooled to solidify the product. Here, the manufacturing process involves injecting a plasticized mass of material into a mold cavity, which is then subjected to high temperatures. The whole process must take place under a certain pressure, and after the plastic mass has solidified, the desired shape is achieved. nine0005 The differences between these methods are quite significant, since they concern not only the technology itself, the scale of production, but also the tools used. This is reflected in the cost of manufacturing elements, their durability and the speed of the whole process. However, both of these methods have their advantages - moreover, it is possible to combine the advantages of 3D printing and injection molding.
Read also: Reverse engineering - how we use it to support our Clients. nine0006
nine0006
3D Printing vs. Injection Molding - When to Use Each Method
3D printing is most often used in situations where short production times are critical or where design is subject to frequent changes . It is also a good choice for small production runs (up to 100 parts) and relatively small items to be produced.
Injection molding, on the other hand, is a suitable option if longer production times are possible and also for high-volume production without prototyping. nine0006 This process is also flexible enough that it can be used to produce parts of any size and complexity.
As a result, 3D printing will be a good starting point for manufacturing, especially for small-scale production and prototyping.
See also: Added value in the production of automotive parts
Advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing and injection molding
3D printing (additive manufacturing) has a low cost of implementation, which can be especially important for small, growing companies . nine0005 In addition, you can easily make changes or fix design-related errors, making it ideal for the prototyping stage. However, it is worth noting that this method is not without drawbacks, the most important of which is the limited number of products that can be printed at the same time, which affects the speed of the entire production process.
nine0005 In addition, you can easily make changes or fix design-related errors, making it ideal for the prototyping stage. However, it is worth noting that this method is not without drawbacks, the most important of which is the limited number of products that can be printed at the same time, which affects the speed of the entire production process.
The main advantages of injection molding are high speed of production, exceptional strength of the final product and the ability to mass-produce defect-free parts, which greatly minimizes costs. nine0006 The disadvantages, however, are the design limitations due to the geometry of the mold, as well as the difficulty of making changes. The latter aspect, however, can be mitigated with proper project preparation. In addition, injection molding can be expensive to implement, but with large production volumes, it quickly proves to be a very cost-effective method.
See also: Automotive injection molded parts by Knauf Automotive
Is it possible to combine the advantages of these two methods?
Until recently, 3D printing and injection molding were considered two competing methods, but the automotive industry is proving that these technologies can successfully complement each other, bringing new business benefits. 3D printing is an indispensable technique primarily during the prototyping phase of an injection molding project, which must always be driven by detailed analysis to ensure that the target part fulfills its utilitarian and aesthetic functions. nine0005 Before making a decision on the implementation of the project, it is a good idea to create a prototype on a 3D printer. This will help eliminate any errors and ensure that the solution meets the customer's goals and expectations.
3D printing is an indispensable technique primarily during the prototyping phase of an injection molding project, which must always be driven by detailed analysis to ensure that the target part fulfills its utilitarian and aesthetic functions. nine0005 Before making a decision on the implementation of the project, it is a good idea to create a prototype on a 3D printer. This will help eliminate any errors and ensure that the solution meets the customer's goals and expectations.
See also: Computer Engineering in Plastic Injection Molding
Automotive Components - From Mold Design to Parts Production
Knauf Automotive is committed to innovation in the automotive industry. The combination of 3D printing and injection molding opens up significantly more possibilities and results in higher quality end components such as dashboard parts, door and window pillars, roof modules, wheel arches and grilles. nine0003
See also: Case study: Pedestrian protection module front - Renault Captur front air guides and front bumper shock absorber.
Each mold design is thoroughly analyzed to ensure that there is no room for error in the final production step. Achieving these goals is possible thanks to the 3D printing method, which is indispensable for creating prototypes. This approach allows you to make adjustments and eliminate any inconsistencies with previous specifications at an early stage. For mold design and prototyping, Knauf Automotive uses the versatile NX Siemens and Catia software. nine0003
Feel free to contact us for a more detailed offer.
Injection Molding vs 3D Printing
Injection molding and 3D printing are popular manufacturing processes for making plastic parts of varying complexity. While there is a wide range of plastics and thermoplastic materials on the market that are great for making a part in any given process, there are situations where either injection molding or 3D printing should be preferred. nine0003
In order to determine which technology to choose for your production, you should understand the advantages and disadvantages of both methods. This is what our article is about.
This is what our article is about.
Injection Molding
Injection Molding is a fast manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic or other building material into a prefabricated mold where it cools and solidifies. After the product has completely hardened, it can be removed. The casting process is repeated a thousand or tens of thousands of times. nine0003
Benefits
Low costs
Once the mold has been made, the production of the product is simple: the molten material is fed into the mold under high pressure, after which the molded product is removed and further processed if necessary.
Plastic injection molding uses raw materials more efficiently than other manufacturing processes, leaving virtually no waste. Simplicity and repeatability make the injection molding process quite economical. And high production volumes produce the lowest unit costs. nine0003
Product quality
Injection molding products are complex designs of exceptional precision. Every millimeter of the mold is filled to prevent air bubbles or other design flaws.
Every millimeter of the mold is filled to prevent air bubbles or other design flaws.
Injection molded product is complete without the need for additional seams or assembly, so surfaces will be smooth and have functional integrity. Visually, this results in prettier and more robust parts compared to those made using 3D printing. nine0003
Speed
Depending on the type of plastic used, castings can harden in a few seconds. Many plastics do not need to be processed, which helps reduce production time. Most molds have multiple cavities, allowing more than one part to be produced at the same time and helping to increase production speed. Injection molding produces hundreds of thousands of parts per day and easily sorts products into batches.
Disadvantages
Pre-investment in the mold
A large part of the cost goes to the production of the mold. If a product has a short life cycle or low demand, investing in a durable mold can be more expensive than using a 3D printer.
Modification limits
Once a mold has been created, it cannot be modified without changing the mold design. If your product is in the process of testing, and there is no final design decision yet, then it is better to use 3D modeling. nine0003
Features
Some of the most common features of injection molding include:
- High volume production.
- Manufacture of quality plastic products that require precision and consistency in every element.
- Projects with a long lead time.
- Production of any part, from the smallest and smallest to complex and large.
3D printing
The 3D printer uses computer-aided design (CAD) files to build 3D parts layer by layer. A 3D printer uses a heated filament to create vertical layers that overlap each other to create one piece at a time.
Benefits
Low initial cost
The 3D printer does not use special dies or molds.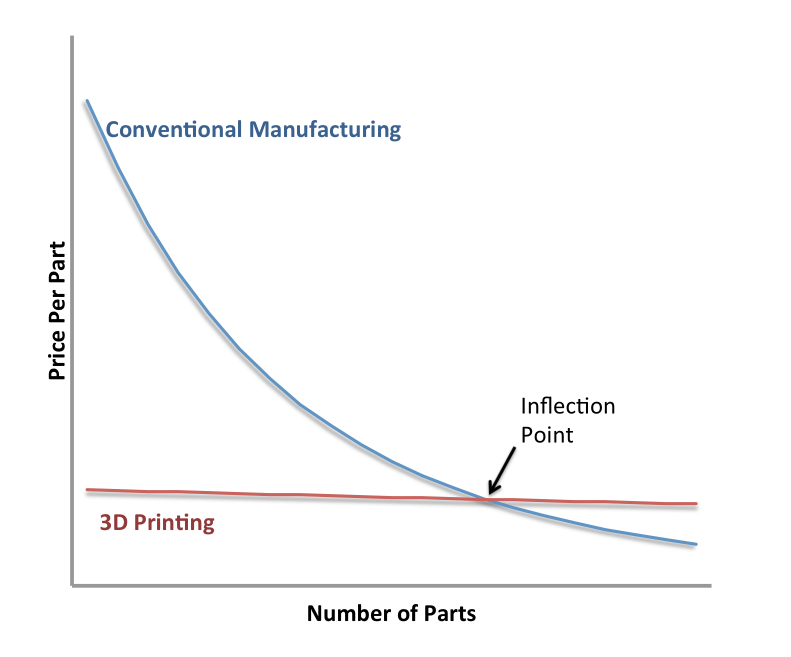 Once the product design is completed, the printer can produce one or dozens of finished parts at the same unit cost. nine0003
Once the product design is completed, the printer can produce one or dozens of finished parts at the same unit cost. nine0003
Modifiable design
Since a computer file is used instead of a mold, 3D printing can easily change the design of a product. This is ideal for prototyping while your team is still testing different options and steps.
Drawbacks
Technical details
3D printing is an evolving science. Software and hardware sometimes fail, which can lead to errors and create a low quality product. nine0003
Speed
A 3D printer creates a part layer by layer, one piece at a time. This is the most efficient way to produce orders up to 100 units.
Product Quality
3D printing can create structural manufacturing defects that are not normally found in plastic injection molding.
Features
3D printing is used for:
- Prototyping and testing.

Learn more












