3D printing product design
3D Printing for Product Design: Benefits and Uses
Jun 3, 2020
It’s not an exaggeration to say that, in the last few years, 3D printing has truly revolutionized the product design industry.
3D printing transforms ideas into concepts faster than any other in-house manufacturing process, allowing designers to take their ideas from their computer screens into their hands in a matter of minutes or hours.
In this article, we’ll explore the different applications of 3D printing for product design and the benefits this technology brings to the industry.
3D printing has so many different applications in product design that it would be impossible to cover them all. Here are a few of the most common uses of 3D printing for product design:
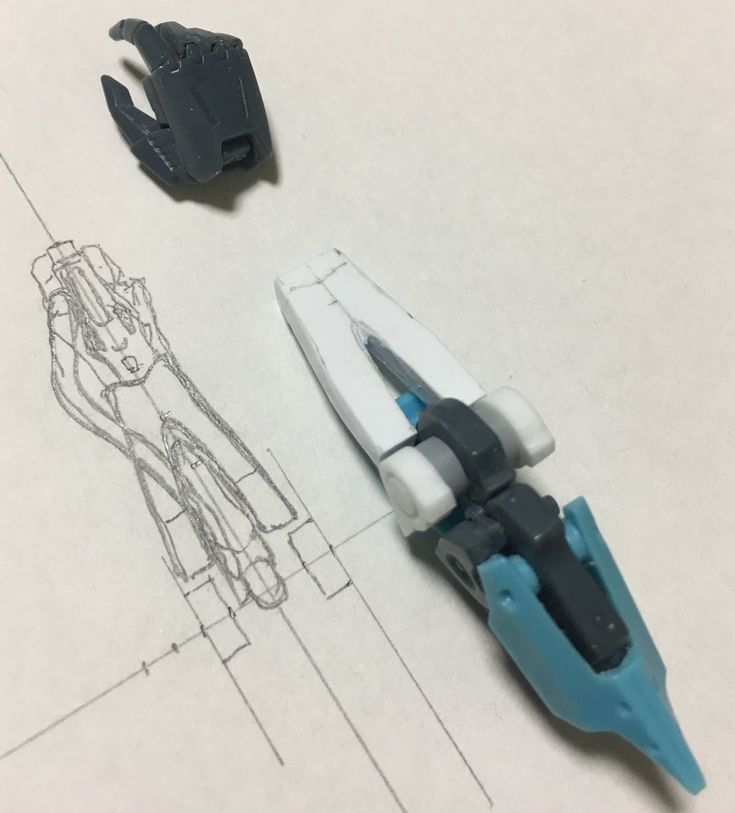
ConceptingIn the early stages of design development, it can be beneficial to have a physical model of the product to determine if this is the direction you want to go in. With a 3D printer, designers can print and visualize different design iterations quickly and at a low cost.
Physically conceptualizing an idea allows designers to compare, test, and understand the structural and visual qualities of their design. Similarly, if the product will have many different parts or features, 3D printed objects allow producers to check proportions and determine which pieces work best with each other.
PrototypingAfter conceptualizing different ideas, the next step in the design process is creating prototypes. 3D printing for product designs allows designers to create functional prototypes faster than any other prototyping process.
This benefit comes to play for many different product design purposes. From designing fashion to cars, 3D printing is a game-changer when it comes to prototyping.
Having an in-house 3D-printer also significantly speeds up the prototyping process and even makes rapid prototyping a possibility.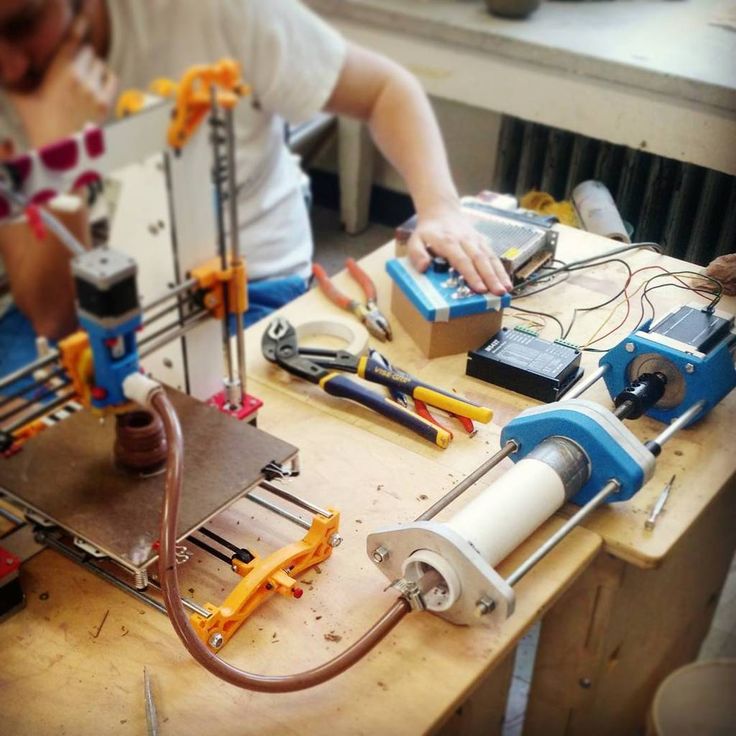 Instead of having to send design concepts to outsourced manufacturers, producers can keep their ideas in-house. 3D printers give designers the freedom to check and modify their prototypes as many times as needed and make adjustments right on the spot, without having to wait for a long period of time.
Instead of having to send design concepts to outsourced manufacturers, producers can keep their ideas in-house. 3D printers give designers the freedom to check and modify their prototypes as many times as needed and make adjustments right on the spot, without having to wait for a long period of time.
Thanks to advanced technological advancements and industrial grade materials, it is possible to use 3D printing for end-use production as well. Producers can use 3D printers to develop small batches of fully functional products and objects.
Beyond products for consumers, designers can also create tools, jigs, and support pieces that aid in the final manufacturing process for the product. Even if the final product itself is not made using 3D printing, its production can be aided by materials specifically created for its manufacturing.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Product DesignImproved WorkflowBy keeping the conception, prototyping, and even tooling processes in-house, the typical product design workflow gets drastically optimized for better designing and testing. The process is also significantly sped up. 3D printers release design departments from having to rely on an outside manufacturer and depending on their time, but instead allows designers to come up with ideas and solutions faster.
The process is also significantly sped up. 3D printers release design departments from having to rely on an outside manufacturer and depending on their time, but instead allows designers to come up with ideas and solutions faster.
A huge benefit of 3D printing in the design space is its cost-effectiveness. Creating models, prototypes, and different iterations can get very costly with traditional modeling methods or outsourcing. While a 3D printer may be an investment initially, it pays for itself in the end.
Better Testing and FreedomWith reduced costs and saved time, comes more options to create. That is to say, another benefit of 3D printing for product design is the ability to create optimized testing and real-time fixes. 3D printing for product design helps designers get a better idea of how a part or product will functionally work and thus enables them to make any iterations needed before committing to a single idea. The ability to quickly print out a new piece or form without any time or budget constraints allows manufacturers to test as many ideas and iterations as they need.
The ability to quickly print out a new piece or form without any time or budget constraints allows manufacturers to test as many ideas and iterations as they need.
3D printing is one of the best tools for the design industry. It opens up a world of possibilities in terms of building concept models and functional prototypes, cuts costs, and waiting times, and allows designers to come up with better solutions and test their designs in real-time.
How 3D Printing is Changing Product Design and Manufacturing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is having a revolutionary impact on product design and manufacturing. The technology is not only transforming how things are made, but also how things are designed, and how business is done. As the technology continues improving, the availability of materials is growing, and the cost of getting on board with the technology is going down.
3D printing is beginning to touch aspects of our everyday life, sometimes in ways most of us aren’t even noticing. Those who view additive manufacturing as a kind of fringe or niche technology might be surprised to learn of the range of industries now regularly making use of it. Within the next decade, every commercial airliner is likely to be using 3D printed parts. It’s being used in the medical industry, in automobiles, industrial manufacturing, for prototyping, and for end-use parts in all manner of industries.
Those who view additive manufacturing as a kind of fringe or niche technology might be surprised to learn of the range of industries now regularly making use of it. Within the next decade, every commercial airliner is likely to be using 3D printed parts. It’s being used in the medical industry, in automobiles, industrial manufacturing, for prototyping, and for end-use parts in all manner of industries.
The increased efficiencies of additive techniques are having a transformative effect on the product design workflow. Additive manufacturing is changing how products are manufactured. It’s also changing where. 3D printing is contributing to a global economic shift, which is seeing a return of manufacturing to the United States.
Onshoring Manufacturing
It’s no secret that over the past couple of decades, U.S manufacturing has experienced a significant decline as firms move overseas to take advantage of lower labor costs. A tool made in China or Vietnam can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $50,000 less than a tool made in the U.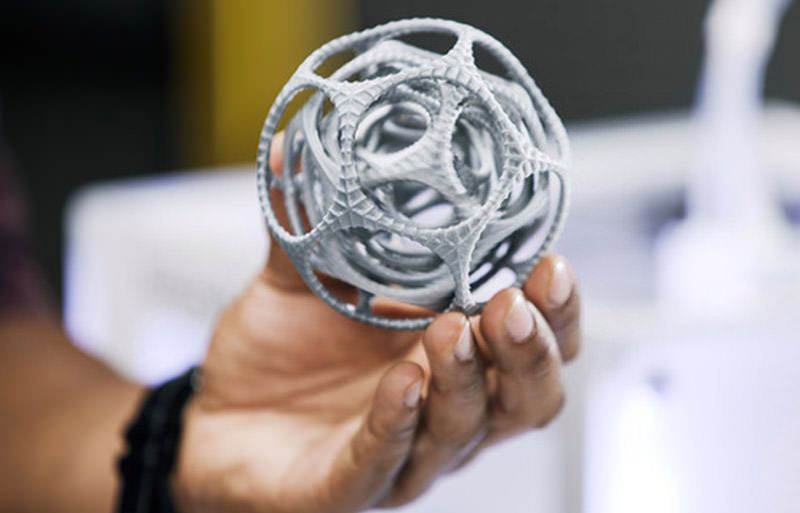 S or in other affluent nations, largely because workers are paid less.
S or in other affluent nations, largely because workers are paid less.
This has led to some challenges, though, as the increased distances involved in product development have given rise to certain complications. Long lead times, high import and export costs, shipping costs, and inventory costs combined with sole-sourced suppliers and the problem of working with manufacturers that are distant and often never seen in person have created a less than optimal context for new product design. On top of this, consumer consciousness regarding issues like climate change and a desire to support local economies have added a kind of moral incentive for companies that can produce domestically.
Additive manufacturing is emerging as a solution to many of the challenges that have cropped up in offshore manufacturing. The manufacturing landscape is changing, and the industry is moving back onshore. 3D printing is not the sole driver of this trend, but the ability to produce more complex designs, the dramatically improved lead times, and the increased efficiencies of the technology are contributing to the return of manufacturing to the U. S.
S.
The labor market is different now than it was during the manufacturing exodus. Factories now are driven more by technological innovation and engineering expertise than by human labor. Industry leaders are increasingly adopting 3D printing technologies. According to the 2015 Wohlers Report (the prominent annual report on the state of 3D printing), the use of additive manufacturing services grew almost 40% between 2013 and 2014.
This is reflective of the fact that industries are recognizing the profitable potential of 3D printing.
One of the most significant impacts additive manufacturing is making on product development is in the prototyping phase. With conventional manufacturing, a functional prototype that approximated the performance of the end-use product would have to be tooled. In the case of offshore manufacturers, the prototypes would then have to be shipped back to the designers. Any changes to the design would require retooling and a new production run.
3D printing changes all that. Designers can now have prototypes produced locally and immediately, without any tooling. Prototypes can be easily iterated, allowing designers to take risks and make mistakes early in the design process without incurring heavy costs or long delays in production. This new paradigm also allows designers to get feedback from customers early on. By the time the product is ready for full production, all the kinds have been worked out and fully tested.
Designers can now have prototypes produced locally and immediately, without any tooling. Prototypes can be easily iterated, allowing designers to take risks and make mistakes early in the design process without incurring heavy costs or long delays in production. This new paradigm also allows designers to get feedback from customers early on. By the time the product is ready for full production, all the kinds have been worked out and fully tested.
The adoption of additive manufacturing also represents a transition away from traditional physical product inventory towards a virtual inventory. The digital files used to generate 3D printed objects are much easier and cheaper to store than physical objects. This allows firms or designers to easily revisit earlier products and revise them. It’s no longer necessary to hold on to tools or tooling aids, freeing up inventory space and making organization that much easier.
While the costs of getting into 3D printing have been dropping considerably, the initial expense of acquiring the necessary equipment remains the largest barrier to adoption.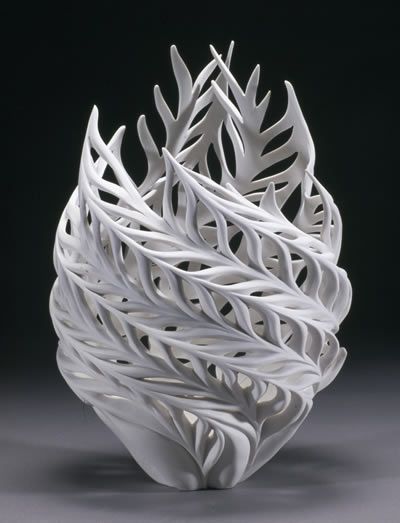 Outsourcing offers an elegant solution to that problem.
Outsourcing offers an elegant solution to that problem.
Outsourcing
The availability and capabilities of in-house additive manufacturing technology continue to expand. 3D printers capable of producing functional prototypes and end-use parts are increasingly being adopted by firms in all kinds of industries, and also by individuals and independent designers for use in their own homes or small businesses. This trend will certainly continue, as the cost of the technology keeps going down.
That said, outsourced providers are still providing a valuable service. The most obvious advantage provided by outsourced 3D printing is that it allows individuals or companies to access cutting-edge technology that might not be otherwise affordable. This is particularly valuable given the rate at which the technology is improving. Someone might invest a great deal of money into what is today a top-of-the-line system, only to see it surpassed in a few years by something even more powerful. Meanwhile, that system that they invested so heavily in is likely to be substantially less expensive a few years from now.
Meanwhile, that system that they invested so heavily in is likely to be substantially less expensive a few years from now.
For companies that specialize in providing 3D printing services, the equation is different. It makes sense to invest in the latest and greatest technology when that is the operating principal of your business. In other words, outsourcing provides a model which involves less investment risk for all parties.
An equally valuable benefit of outsourcing that is perhaps less obvious is the access it provides to expert personnel with a deep knowledge of additive manufacturing. Outsourcing is not only useful as a strategy for accessing technology, but for accessing expertise. Even firms that have the financial resources to purchase their own advanced additive systems often prefer to outsource certain tasks. This is especially true for technologies that involve more post-processing, like Laser Sintering and Direct Metal Laser Sintering. 3D printing metals requires a skilled team and sometimes additional equipment for processing that makes it difficult to implement in-house.
Sometimes outsourcing still makes sense even for firms that have invested in in-house 3D printing technologies.
Sometimes outsourcing still makes sense even for firms that have invested in in-house 3D printing technologies. Outsourcing will stay relevant into the future too, as additive manufacturing is increasingly used for end-use parts. Outsourcing providers have the expertise and the technology to produce the high degree of quality required for final production parts.
Expansion of Additive Manufacturing for End-Use Parts
Slowly but surely, 3D printing has been transitioning from a method of producing visual aids and prototypes to a technology that is capable of manufacturing end-use parts. While 3D printing is still viewed by some as being used primarily to produce models and trinkets, the reality is that additive manufacturing is now being used for functional parts in a variety of industries.
The widespread adoption of 3D printing is most visible in the aerospace and automotive industries. These were some of the first industries to adopt 3D printing for end-use parts in the first place, and so they have the most accumulated experience. The ability for additive technologies to produce single, lightweight pieces with complex internal geometries is particularly valuable for these industries.
These were some of the first industries to adopt 3D printing for end-use parts in the first place, and so they have the most accumulated experience. The ability for additive technologies to produce single, lightweight pieces with complex internal geometries is particularly valuable for these industries.
Technologies like Laser Sintering and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) allow for parts to be printed using materials that are nearly or completely identical to production-grade materials used in conventional manufacturing. Metal printing is one of the most exciting and highly-valued technology, and its use is expanding hugely with a great deal of applications across industries. High-temperature plastics and rubber-like materials are also in high demand for final production parts.
Carbon fiber 3D printing is expanding horizons for the automotive and aerospace industries. One of the most fascinating developments in 3D printing has been the development of bio-based materials for use in the medical industry.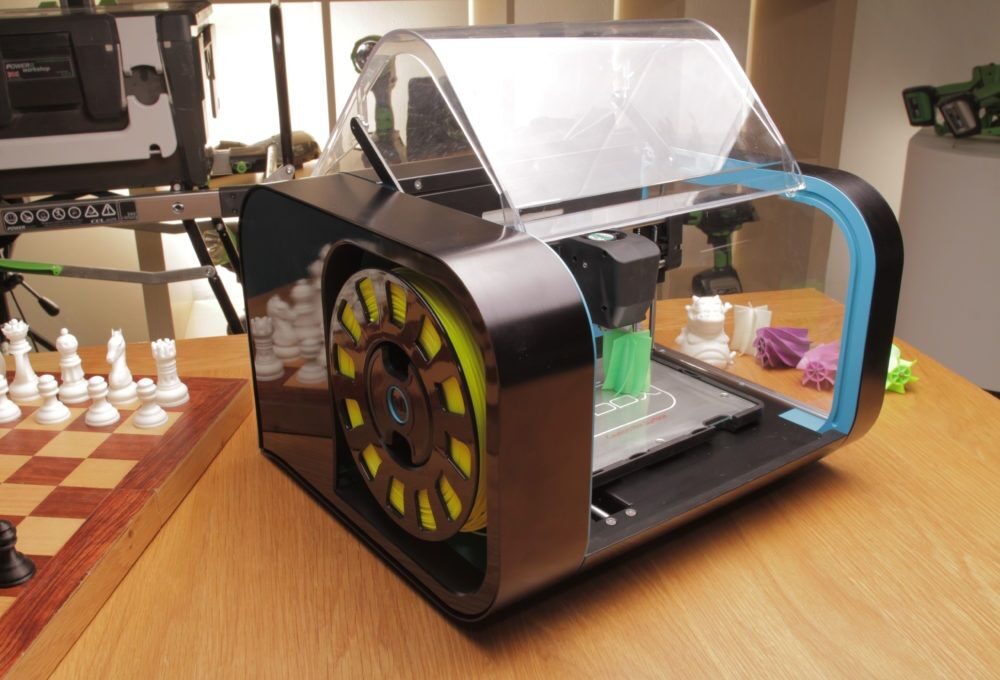 Not only can 3D printing produce FDA approved materials for medical applications, but engineers have been able to 3D print stem cells, artificial blood vessels, and even miniature organs for testing vaccines. 4D printing is also pushing the frontiers of additive technology.
Not only can 3D printing produce FDA approved materials for medical applications, but engineers have been able to 3D print stem cells, artificial blood vessels, and even miniature organs for testing vaccines. 4D printing is also pushing the frontiers of additive technology.
Cad Crowd Has Freelance 3D Printing Services
If you’re interested in taking advantage of outsourcing 3D printing, Cad Crowd is the place to be. We connect you with leading U.S based manufacturers for any scale of production or prototyping. We also offer CAD design and 3D printing design services so that you can create the 3D printable files you need to bring your design to life. Learn how it works or get a free quote in under 15 minutes.
3D printing in new product prototyping / Sudo Null IT News protokot
Time to read 2 min
Views 2.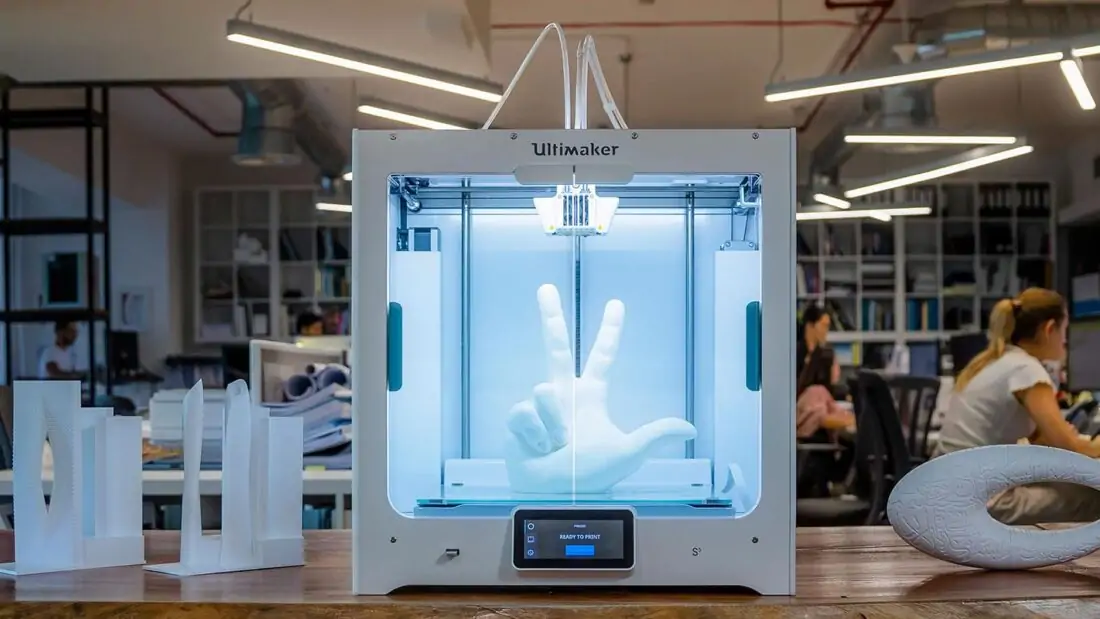 3K
3K
PROTOTYPSTER Company Blog 3D printers The future is here
Whenever a company launches a new product, it needs to review and approve its packaging design. 3D printing greatly speeds up the approval process: the prototype represents a real object, which means it will be very easy to see and identify flaws. It is also possible to make changes to the design and print the next correct prototype quickly and at no extra cost: the 3D model is quickly corrected and printed again, which takes 2 to 4 days on average.
In the case of prototyping for the food industry, we use SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) technology. Printing material - polyamide - affordable and durable, is the most suitable in such cases. The prototype can be painted in one of the colors from our catalog at the request of the customer. Polyamide is white, so in this case the body did not need to be painted, and the cover was painted black.
After the customer sent us a 3D tank model, it was checked by Prototypster engineers and prepared for printing.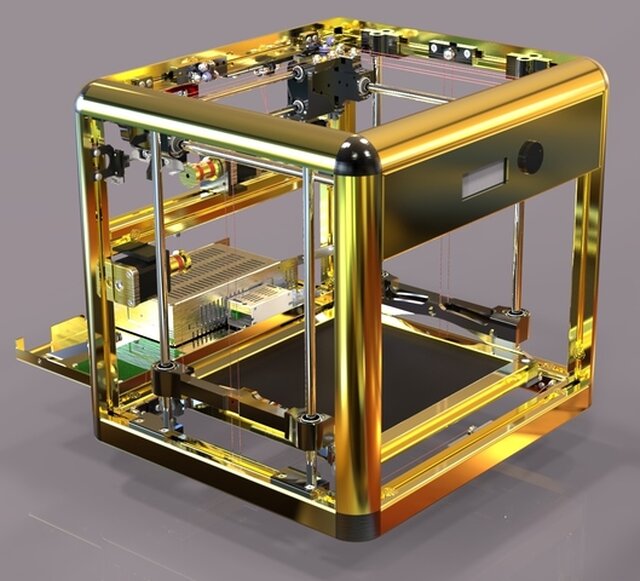 Next, the model of the vessel itself and the lid was printed, then the parts went through post-processing: cleaning, grinding and priming, alternately in several cycles. After this treatment, the product can be painted.
Next, the model of the vessel itself and the lid was printed, then the parts went through post-processing: cleaning, grinding and priming, alternately in several cycles. After this treatment, the product can be painted.
“We are launching a production of a new drink and we needed a mock-up of a bottle for an advertising photo shoot. Since it is almost impossible to produce a bottle in a single copy, we found the only solution - to contact Prototypster and print a layout on a 3D printer, says our customer. — I am satisfied with the result. Due to the design, our bottle is opaque, and the layout matched both in color and texture.”
If you need to create a product prototype for testing, demonstration, approval, use in promotional materials, then SLS technology is ideal for you. Describe your task to our specialists, and they will certainly offer solutions for the implementation of your project. Write to us at [email protected], or call the numbers listed in the contacts.
@protokot
User
Comments Comments 2
10 industries that 3D printing is starting to change
3D printing has come a long way from printing small prototype buildings out of plastic. Today, 3D printing is fulfilling its potential in a range of industries, from aerospace to apparel and footwear.
This technology not only allows you to create items with incredible precision, but also saves money.
Today, there are many materials that allow using 3D printing to produce a wide variety of objects.
Below we describe the industries in which this technology is applied.
1. Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, everything must be made with high precision. Precision plays a very important role here in the execution of every space mission, and the industry itself is extremely important for the development of mankind.
3D printing has already begun to change the industry, it is used to replace many parts that have become too expensive to produce.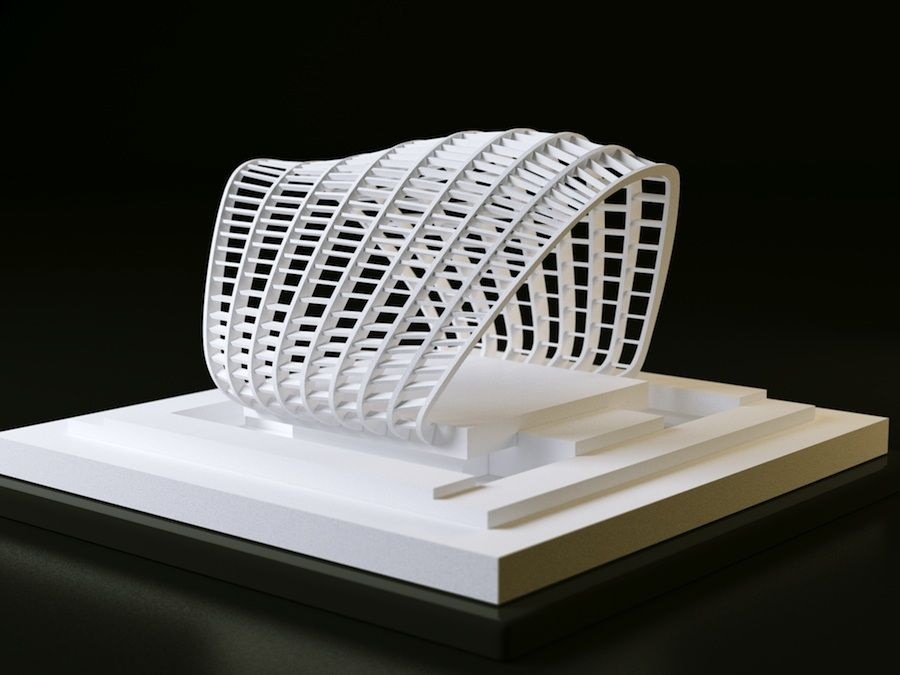 In addition, the technology is used to test prototypes.
In addition, the technology is used to test prototypes.
ULTEM 9085 is a thermoplastic commonly used in aircraft construction that can be melted down and used in 3D printing.
2. Architecture
3D printing technology saves time in building construction.
With this technology, printing houses is as fast as printing documents.
And when creating a design, you can share it with other users by placing an object in the database.
3. Food
While 3D printing doesn't save lives, it could change the way we think about food.
Nevertheless, experts note that in the future humanity will face a shortage of food, it is already becoming increasingly difficult to feed the growing population of the planet.
However, science is looking for ways to grow meat and use alternative materials to produce food.
4. Product design
Technology allows you to design something on a computer, then print it in an hour, test it, find flaws, redesign, print a second prototype - all in just half a day.
Previously, concepts were produced, but now 3D printing technology makes it possible to get closer to an almost identical representation of products in a very short amount of time.
5. Medicine
3D printing plays an important role in almost every aspect of medicine. When it comes to prototyping, technology allows you to create ready-made models that will cost less and take less time to create, and these will be ready-made models that are completely usable.
Clarity and precision allows you to print ultra-fine lines that allow you to create the smallest tools.
In addition, 3D printing technology makes it possible to recreate parts of the human body using various materials. Scientists are constantly working to create new materials and textures.
6. Dentistry
Making dental models is very useful, but it is not always possible to make them taking into account the individual characteristics of a person.
3D printing technology allows you to make exact copies of a patient's teeth to replace them, or crowns that can last longer.
Objet Digital is a dedicated 3D printer designed for use in the field of dentistry.
He uses materials that are very similar in structure to bone to print teeth.
7. Construction
In Dubai, 3D printing is an increasingly common way to construct buildings. Cazza, a 3D printed construction company, plans to build the world's first 3D printed skyscraper.
They created special machines that can build buildings from the bottom up.
Companies around the world have expressed interest in such machines.
In addition, this method of building construction leaves less debris. During construction, environmentally friendly materials can be used.
8. Agriculture
It may seem strange to use this technology in agriculture, but it is true. Many farms need specialized tools, which cost between $8,000 and $12,000 and can take months to complete.
Many farms need specialized tools, which cost between $8,000 and $12,000 and can take months to complete.
PLA, or polylactic acid, is a material that is used for 3D printing and costs $0.25 per 1.5 cu. m. This can significantly save money and time for farmers who are looking to upgrade their machines.
9. Making clothes and shoes
So far, 3D printed clothes have not entered the mass market, but the idea of such clothes has been developed since 2013.
The idea is that in the future, customers can print clothes, which suits their individual sizes.
10. Organ Printing
3D bioprinting is a new application that is developing at a rapid pace.
Scientists have made great progress in printing ribs, but they also believe that in the future it will be possible to print hearts, kidneys, livers and other organs.
Cell Link is a company that works with products of this kind, donor organs will soon become mostly artificial.