3D printing process ppt
PPT – 3D Printing: A Beginner's Ultimate Guide PowerPoint presentation | free to download
About This Presentation
Transcript and Presenter's Notes
Title: 3D Printing: A Beginner's Ultimate Guide
1
3D Printing
- A Beginner's Ultimate Guide
2
What 3D Printing is?
- 3D printing doesnt mean three duplications of a
print. - Its mean three-dimensional printing.
- The printing is done via the automated process to
build a three-dimensional object. - The process is known as additive manufacturing.
3
How does 3D Printer Works?
- Printing is done by adding material rather than
taking it away - The additive process continues to add successive
layers until the object is created.
4
What are Major Components of 3D Printer?
- Filament A material (often plastic) used for
printing - Extruder The part of printing machine used for
melting filament - Nozzle A small hole from which melted filament
is extruded - Bed The surface where the produced object is
kept - Heated Bed A print surface kept heated for
better adhesion - Stepper Motor A motor machine used to move the
printer components
5
What are the Benefits of 3D Printing?
- It helps to customize designs and materials
- It is applied in aerospace to assemble complex
parts - It enables the producers to get rapid prototyping
of complex systems - It helps to create durable models for
architecture construction Industry - It allows the maritime experts to generate spare
parts for their equipment - It helps in printing surgical models and custom
prosthetics for medical professionals
6
In what ways, 3D Printing has Limitations?
- Everything comes with opportunities and
limitations, so the 3D printing.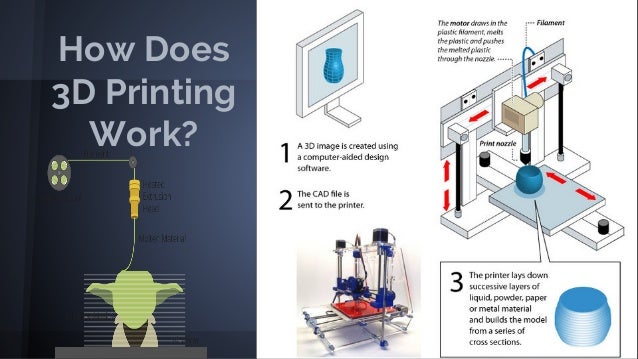
- Limitation of size, unable to create mega objects
- Restriction of Material, unable to print using
multiple materials at a time - Multi-material 3D printers do exist but not
common in use
7
What are major types of 3D Printing?
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereo-lithography (SLA)
- Selective laser sintering (SLS)
- Selective laser melting (SLM)
- Binder jetting
8
Contact Us
- XERATEK
- Phone 971 4 3997714
- Email enquiry_at_xeratekuae.com
- Website www.xeratekuae.com
About PowerShow.com
PPT – 3D Printing Materials PowerPoint presentation | free to download
About This Presentation
Transcript and Presenter's Notes
Title: 3D Printing Materials
1
3D Printing Materials
Alfa Chemistry
2
3D Printing Materials
Photosensitive resin
Ceramic materials
3D printing bioplastics
Polymer gel
Engineering plastics
High-strength carbon fiber reinforced composite
Rubber materials
3D printing metal
3
Engineering plastics
ABS
PC
Engineering plastics have excellent strength,
hardness, impact resistance, resistance and
anti-aging property
Nylon-like materials
PA
4
ABS
ABS materials are the preferred engineering
plastics for 3D printing by fused deposition due
to their good hot melt property and impact
strength.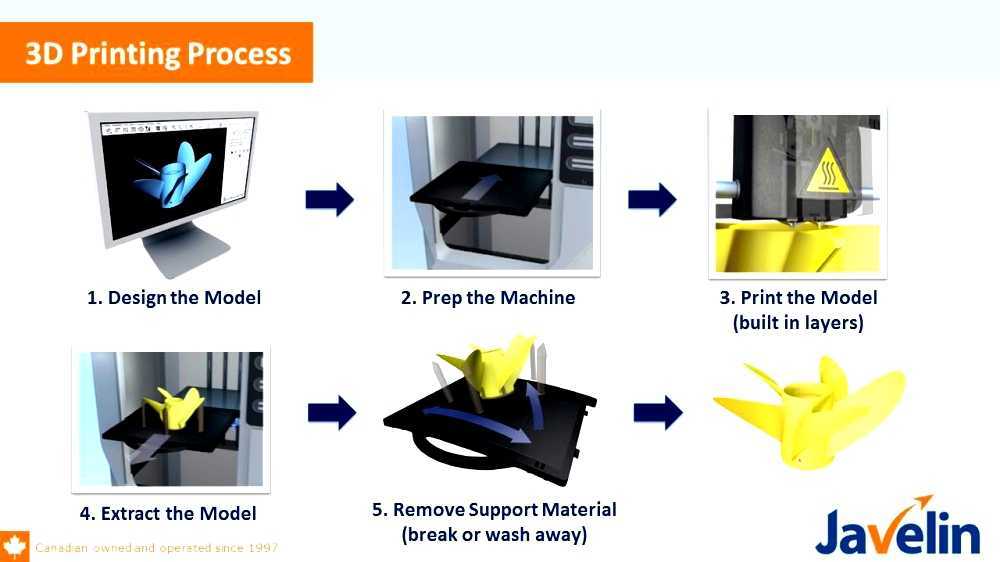
5
PA
PA has high strength and flexibility, so it can
directly use 3D printing to manufacture equipment
parts. PA carbon fiber parts manufactured by 3D
printing have high strength and toughness and can
be used for mechanical tools instead of metal
tools.
Due to the adhesiveness and powder
characteristics of PA, it can be mixed with
ceramic powder, glass powder, metal powder, and
low-temperature 3D printing of ceramic powder,
glass powder, and metal powder can be achieved by
bonding.
6
PC
PC has excellent strength, its strength is about
60 higher than ABS material, so it is suitable
for the application of super-strong engineering
products.
Engine peripheral parts
Door handle sets
Brake pedals
7
Photosensitive resin
Polymer monomer Prepolymer
Due to its good liquid flow and instant
photocuring properties, liquid photosensitive
resin is the material of choice for 3D printing
consumables for high-precision product printing.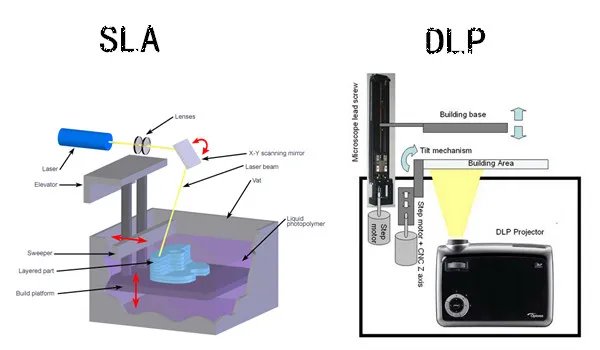
8
Rubber materials
Rubber materials possess a variety of levels of
elasticity. The hardness, elongation at break,
tear resistance and tensile strength of rubber
make them ideal for applications requiring
anti-skid or soft surfaces.
9
Ceramic materials
High strength
Low density
High hardness
Chemical stability
High temperature resistance
Corrosion resistance
10
3D printing metal
Titanium alloy
Aluminum alloy material
Cobalt-chromium alloy
Gold
Stainless steel
Silver
The metal powder used in 3D printing generally
requires high purity, good sphericity, narrow
particle size distribution and low oxygen content.
11
Polymer gel
12
High-strength carbon fiber reinforced composite
Compared to traditional extrusion or injection
molding methods, 3D printing can precisely set
its overall performance by precisely controlling
the orientation of carbon fibers and optimizing
specific mechanical, electrical and thermal
properties.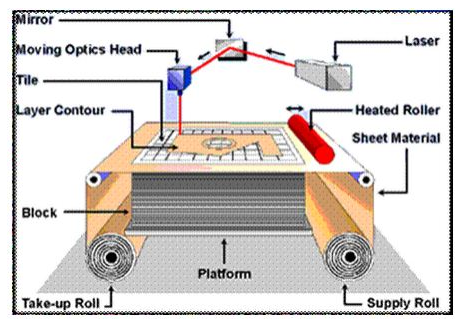 Since 3D printed composite parts can
Since 3D printed composite parts can
only be fabricated one layer at a time, each
layer can achieve any desired fiber orientation.
Complex shape parts combined with reinforced
composite materials have excellent high
temperature and chemical resistance.
13
3D printing bioplastics
PLA
As an environmentally friendly plastic, PLA is
biodegradable into active compost. The
biodegradable polymer material can be molded by
3D technology to produce its PLA tissue
engineering scaffold with growth ability.
PETG
PHB
14
Suite 212, Waverly Plaza, 755 Waverly Avenue,
Holtsville, NY 11742, USA
info_at_alfa-chemistry.com
Fax 1-516-927-0118
15
Copyright 2012 - 2018 Alfa Chemistry. All
Rights Reserved.
About PowerShow.com
3D printing - online presentation
Similar presentations:
Master class on 3D printing. Picaso 3D
Picaso 3D
Possibilities of 3D technologies
Additive technologies: 3D printing
3D Printing Technologies and Trends
3D printing. Future and prospects. (Part 1)
RobotBuilder. 3D modeling programs. 3D printer
Additive technologies
3D Printing Technologies
Additive manufacturing technologies
3D printing
FABLUB BISHKEK
3D printing
Contents
01
What is 3D printing?
02
3D printing type
03
3D printing process
04
3D printer and slicer software
FABLAB BISHKEK
What is 3D printing?
An additive manufacturing process that
creates a physical object from a digital design
FABLAB BISHKEK
SLA
FDM
By charkes W. Hull
By S. Scott Crunmp
vs
Invented at 1986
Invented in 1989
Patent validity
2006
Patent validity
2012
Not a new technology!
FABLAB BISHKEK
Create complex designs
Customize each and every item
Pros
No tools or molds needed, over
low fixed costs
Speed and ease of prototyping, quick and less
risky way to market
Less waste
FABLAB BISHKEK
Higher cost for large production
Cycles
Cons
Less choice of material, color, finishing
Limited strength and endurance
Low accuracy
Fablab Bishkek
Car manufacturer
Doctor
Dentizing
Dipmate
Aerosmic companies
Aerosmes
additive manufacturing process that creates
a physical object from a digital design
FABLAB BISHKEK
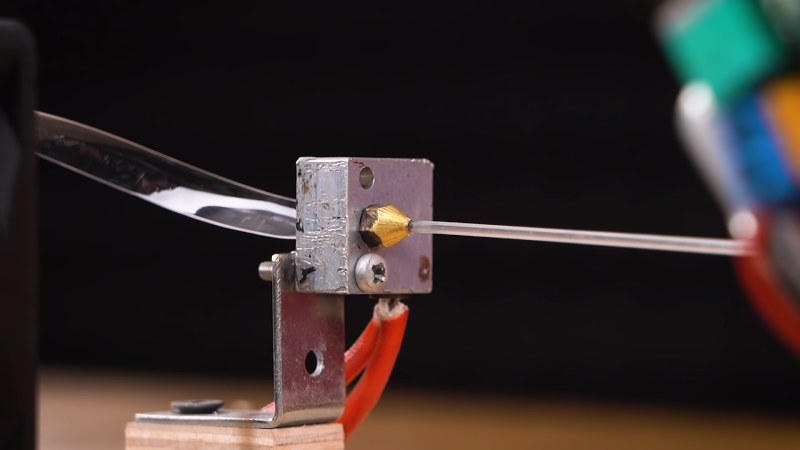
Fused extrusion
FDM
/
FFF
(Fusion Fused Modeling) / (Fused Fiber Fabrication)
FDM Technology Diagram
FABLAB BISHKEK
Photocurable
SLA / DLP
(Stereolithography Machine) / (Digital Light Processing) SLA5 FABL02 Technology Diagram BISHKEK
Sintering
SLS
(Selective Laser Sintering)
SLS Technology Diagram
FABLAB BISHKEK
Structure of the FFF type 3D Printer
l Head
l Extruder
l Fiber
l Support
l Hot table
FABLAB BISHKEK
Fiber
Granule
FABLAB BISHKEK
ABS
PLA
(Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene)
(Poly lactic acid)
general purpose plastics
Matt surface
VS
60% cornstarch
Biodegradable plastic and glossy surface
FABLAB BISHKEK
ABS
PLA
ol)
(Poly lactic acid)
Relatively soft
Can be bent
Printed at high temperature
Nozzle : 230˚C ~ 260˚C
Bedding : 90˚C ~ 110˚C
Harmful gas
Hard
Can be broken
Printed at relatively low temperature
˚C ~ 220˚C
Bedding : 20˚C ~ 70˚C
Relatively less harmful gas
Easy to complete
Difficult to complete
High shrinkage
Low shrinkage
Acetone fumigation possible
Acetone fumigation impossible
FABLAB BISHKEK
Metallic
Fiber
(Wood Fibre)
(Flexible Fibre)
Others: need to set higher temperature than ABS / PLA
FABLAB BISHKEK
The
3D printing process is an additive manufacturing process that creates a
physical object from a digital design
FABLAB BISHKEK
Starting! - 3D printing process
Concept
Have an idea for a
structure that a
manufacturer wants to make.
3D modeling
Using the 3
D modeling tools, create a shape for the idea.
Also, we can download the
model online.
Slicing
Using the
slicer program, cut
horizontally of the
model file
According to the specification with
nter we can install
various us
triplets
3D printing
Slicer) will print out the
result.
FABLAB BISHKEK
Getting Started! - How can I get a design for 3D printing?
- Design your own
TINKERCAD: https://www.tinkercad.com/
Autodesk FUSION 360: http://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360/overview
FABLAB BISHKEK
See I bring to your attention
- MOOC (Massive Open Online Courses)
https://www.coursera.org/
https://iversity.org/en/
https://www.edx.org/
http://www.openuped .eu/courses
https://www.udacity.com/
https://www.futurelearn.com/
https://ocw.mit.edu/index.htm
https://www.pluralsight.com/
https://www. class-central.com/
class-central.com/
https://www.skillshare.com/
http://www.digitaltutors.com/11/index.php
https://www.lynda.com/
FABLAB BISHKEK
Getting started! - How can I get a design for 3D printing?
- Find design online
Thingiverse:
3D Map:
Image Converter:
Cults:
YM(YouMagine):
Instructable:
Wevolver:
http://www.thingiverse.com/
https://touch-mapper .org/en/
http://3dp.rocks/lithophane/
https://cults3d.com/
https://www.youmagine.com/
http://www.instructables.com/
https://www.wevolver .com/
FABLAB BISHKEK
3D Printer : Sindoh 3DWOX 1
Website: https://3dprinter.sindoh.com/
FABLAB BISHKEK
Printer Specifications
Print Technology
FFF
Print Head
Single Nozzle 40 9025 Nozzle Dia. 25
Maximum assembly size
210 x 200 x 195 mm
(WxDxH)
Fiber material
PLA, ABS, ASA, PETG, etc
Connectivity
USB, Ethernet (1G), Wi-Fi
Layer thickness
0. 05 ~ 0.40 mm
05 ~ 0.40 mm
Fiber diameter
1.75mm
Size Weight
421 × 433 × 435
15kg
User Interface 5-inch Full Color Touch Screen
Leveling
Auto + Manual
Cartridge Loading
Auto
FABLAB BISHKEK
Printer Specifications
Auto Cartridge Loading Automatic Loading
Security Camera
Check print status via
WiFi
Slicer
Slicer3DWOX Desktop Slicer
Sindoh Cloud Slicer
Simplify3D input file format Ver.4.1
Operating system stl, ply, obj, G-code(RepRap)
Window 7 or above
Mac OSX 1
FABLAB BISHKEK
Slicer program
Slicer is a program that creates G-code by
cutting a simulation file into multiple layers.
FABLAB BISHKEK
Temperature
*Datasheet for reference only
- Temperature of materials.
Materials
PLA
ABS
TPU *ref.
The extrusion temperature
190 ~ 220 ℃
220 ~ 260 ℃
230 ~ 260 ℃
Best temperature
200 ℃
230 ℃
230 ℃
Subold temperature
50 ~ 70 ℃
80 ~ 110 ℃
40 ~ 50 ℃ 50 ℃
The temperature of the 3D printer parts.
Materials
Extrusion
Bedding
Chamber
ABS
230℃
90℃
50℃
PLA
200℃
60℃
400℃ FASH2BLK5 Examples
4005 FASH2BLK50025 source code
FABLAB BISHKEK
Thank you!
English Russian Rules
3D printing - online presentation
Similar presentations:
3D Printing Technologies and Trends
Additive technologies: 3D printing
Additive manufacturing technologies
3D printing
3D printing technologies at the enterprise "3D Techno"
Methods and technologies for prototyping products. (Lecture 7)
Control of technological processes based on computer CAD systems in mechanical engineering. (Lecture 7)
Additive manufacturing
Additive technologies in mechanical engineering
Additive technologies
3D printing
3D printer
3D printer (fabber, Rapid Prototyper) is a peripheral device that uses the
method of layer-by-layer creation of a physical object from a digital 3D model.
Charles Hull - Founder of 3D Systems Corporation
3D printing - additive manufacturing
Application:
• Prototyping (rapid prototyping),
• Finished product manufacturing (rapid manufacturing).
Printer resolution - thickness
applied layers (Z-axis) 16-200 microns.
Accuracy
printer
-
accuracy
positioning of the print head in the
horizontal plane (along the X and Y axes)
10-100 microns.
Two types of materials:
support materials.
structural
and
Method
Extrusion
Technology
Fused Deposition Modeling
(FDM or FFF)
Wireframe
Free Form Manufacturing
Electron Beam Fusing (EBFȝ)
Direct Laser Metal Sintering (DMLS)
Powder Fusion
Electron Beam Fusion (EBF)
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Titanium alloys, cobalt-chromium
alloys, stainless steel, aluminum
Selective thermal sintering (SHS)
Powdered thermoplastics
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
Thermoplastics, metal powders,
ceramic powders
Gypsum, plastics, metal powders,
sand mixtures
Paper, metal foil,
plastic film
Photopolymers
Photopolymers
Inkjet(3DP)
Lamination
Object Fabrication
Lamination (LOM)
Stereolithography (SLA)
Digital LED Projection (DLP)
Polymerization
Materials used
Thermoplastics (such as Polylactide
(PLA), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
, etc.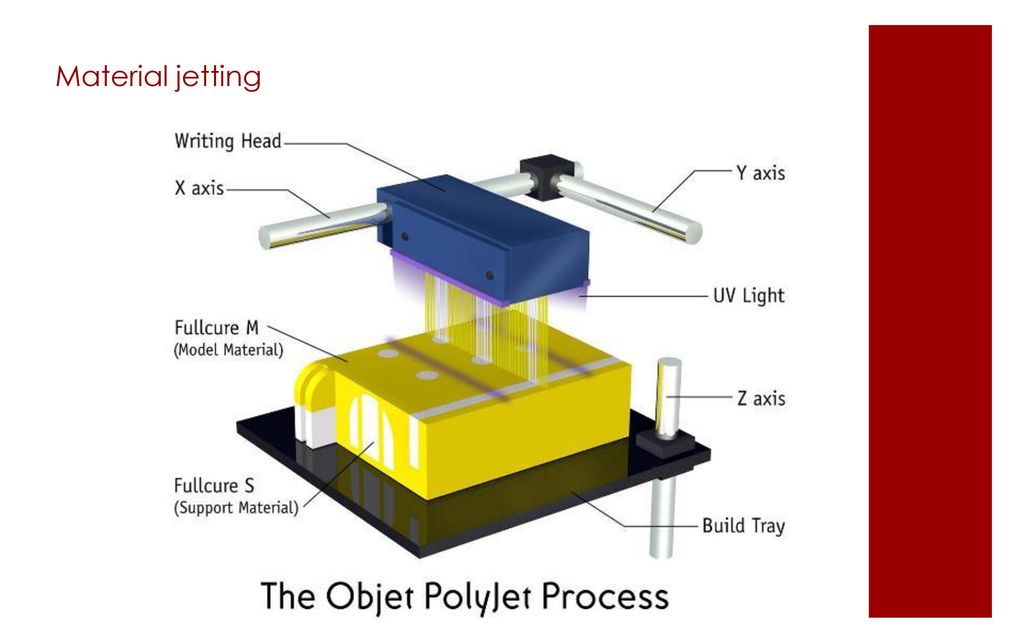 )
)
Almost any metal
alloys
Almost any metal
alloys
Titanium alloys
Layer-by-layer printing (
Depositioned 905 resin molten filament) Modeling, FDM)
FDM
technology
additive manufacturing
models, prototypes and finished products by layering melted
extruder for FFF
Printrbot printer
Electron Beam Fusion (EBFȝ)
manufacturing
Development by Karen Taminger, NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC)
FDM variation
Prototype device testing
using EBFȝ technology
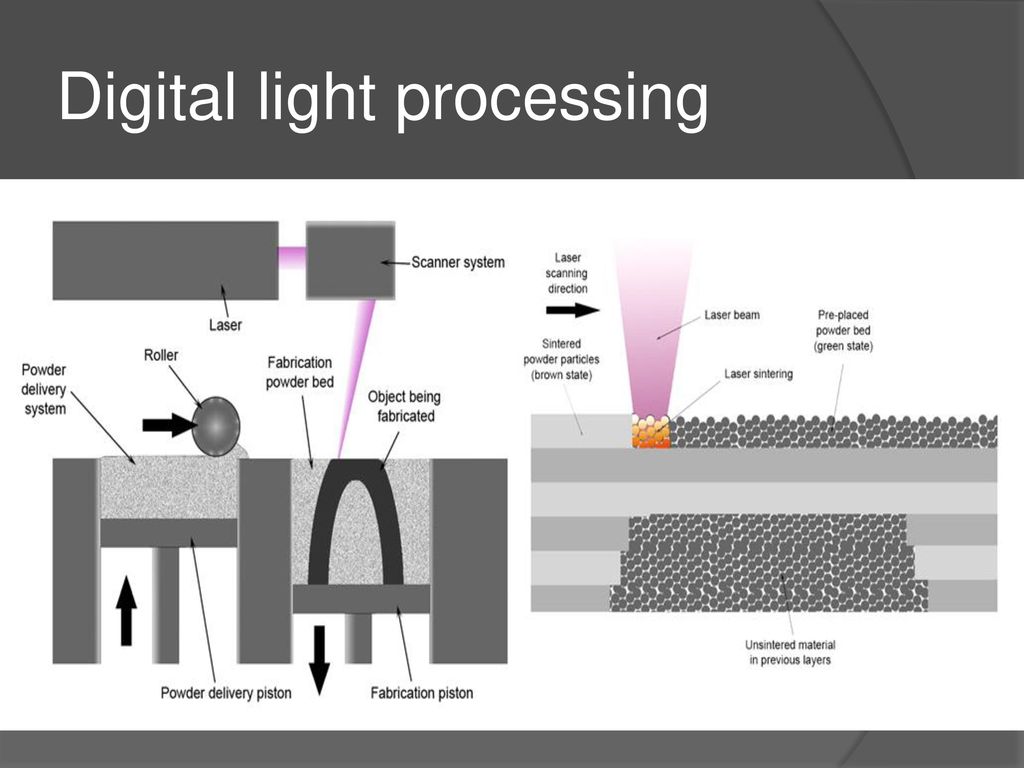
Laser sintering25 of powder materials (
Selective Laser Sintering, SLS)
SLS
technology
additive manufacturing
models, prototypes and finished products
fusible powder material
(plastic, metal) by melting it under
laser radiation.
Designed by Carl Deckard and Joseph Beeman,
University of Texas at Austin, mid-1980s.
Acquired in 2001 by competing
company 3D Systems.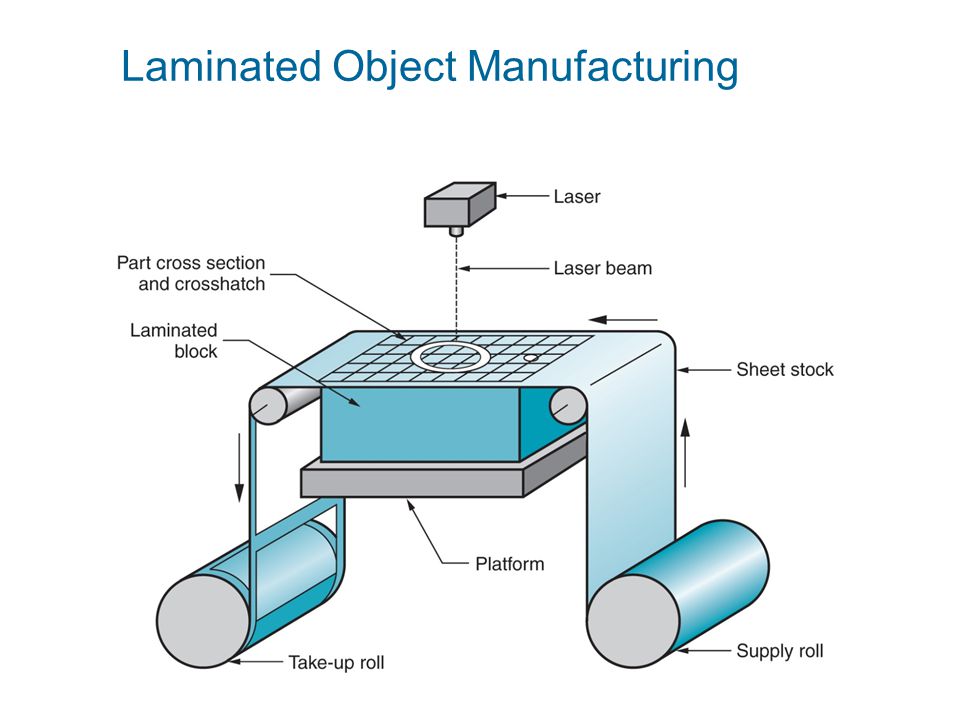
The last of the SLS
technology patents was filed on January 28, 1997,
expired on January 28, 2014, and
technology is publicly available.
Rapid Prototyping
Solutions
Five Star Plastics
New Balance Company
uses
SLS technology to create
footwear
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Developed by the Institute for Laser Technology (ILT)
Fraunhofer Society in Aachen and F&S
Stereolithographietechnik GmbH in Paderborn.
Today the technology belongs to SLM
Solutions GmbH and ReaLizer GmbH
A variation of SLS
technology The process takes place in a working chamber filled with
inert gases (argon). Oxygen free
avoids consumable oxidation
(printing with metals is possible).
Part for the J2-X rocket motor, printed
by NAS
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Developed by EOS, Munich
A variation of Selective Laser Sintering or SLS
and Selective Laser Melting Melting" or SLM).
DMLS allows the
to create solid
metal parts.
print resolution ~20 µm
DMLS installation
Rocket engine parts
Super Draco
Elon Musk, Space X Company
Material: Nickel-Chrome
Inconel Heat Resistant Alloy
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
A variation of SLS and SLM
The main difference is the use of electronic emitters instead of lasers
Titanium implant obtained using EBM
Industrial EBM machine manufactured
by the Swedish company Arcam AB
Craniofacial
implant fabricated with
EBM technology
Selective heat sintering (SHS)
A variation of SLS technology
Used for fusible materials
Desktop SHS printer - Blueprinter
Models printed using the SHS method
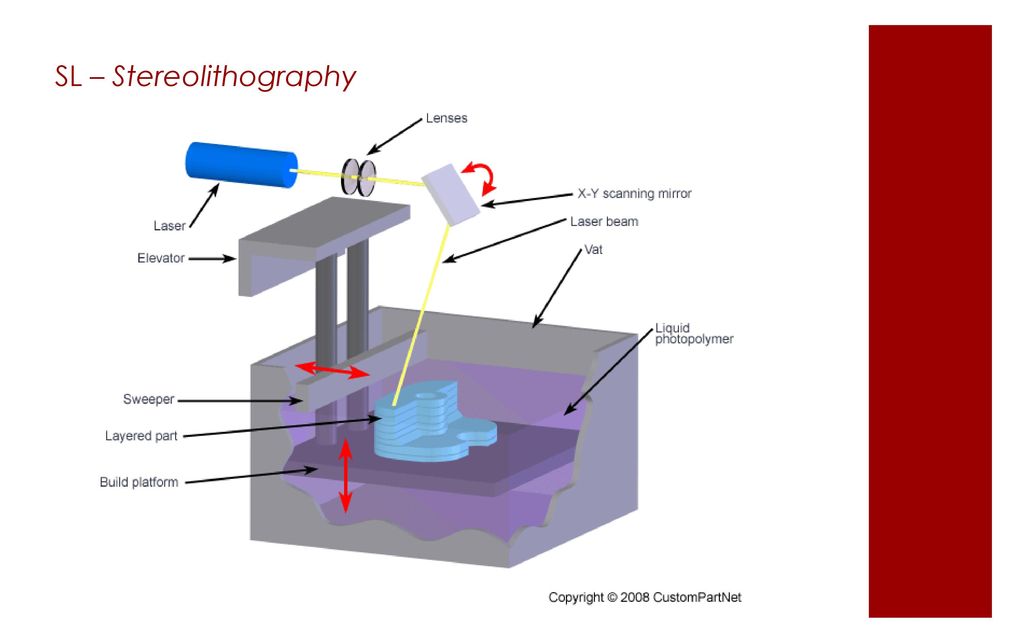
Stereolithography (Stereo Lithography
Apparatus, SLA)
Charles Hull in 1984 patent
Stereolithography
(SLA
)
additive manufacturing technology models,
prototypes
and
finished
products
from
liquid
photopolymer
resins.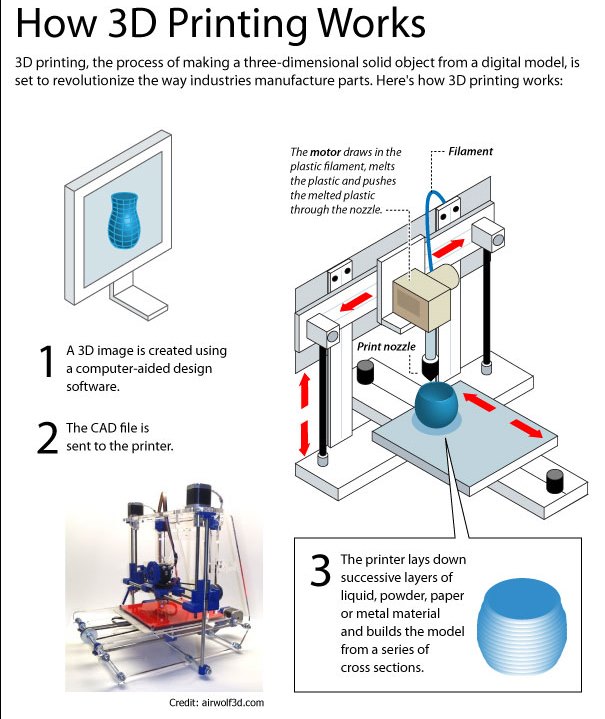
Curing
resin
occurs due to irradiation with an ultraviolet laser
Manufacturers:
• F&S Stereolithographietechnik GmbH,
• 3DSystem,
• Institute of Laser and
Information Technologies of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Resolution
down to 15 microns
Desktop
Stereolithography
OWL Printer
Nano
Digital LED Projection (DLP)
Variation of SLA technology
Difference - use of LED projector
Sheet lamination
materials (Laminated Object Manufacturing,
LOM)
Manufacturer: Helisys Inc.
LOM
-
technology
forming
layer-by-layer bonding (heating, pressure)
thin films
working material
with
cutting (using a laser beam or
cutting
tool) 90.025 corresponding contours
Mcor 3D Printer
Matrix Plus
3D Inkjet Printing (3DP)
R&D MIT
Institute (MIT), 1993
Name Variations:
• Ink Jet Modeling
• Multi-Jet Modeling, MJM,
• PolyJet,
• Drop-On-Demand-Jet,DODJet.