3D printing needed
9 Great 3D Printing Jobs
- 3D printing is a technology that creates a three-dimensional object using a computer-aided design (CAD).
- The 3D printing industry is rapidly growing thanks to its ability to create a wide range of versatile products in a fast, cost-effective way.
- For job seekers, the 3D printing industry offers some cool jobs on the cutting edge of the technology.
- This article is for professionals and entrepreneurs who want to work in the 3D printing industry.
President Barack Obama once said 3D printing has the “potential to revolutionize the way we make almost everything.” For that reason, the 3D printing industry was valued at $13.78 billion in 2020. And market research projections suggest it will continue its meteoric growth through 2028 – when it is expected to reach an estimated $59.65 billion.
As the 3D printing industry booms, what does it mean for job seekers? Here are 9 opportunities that will be created or get a boost from 3D printing.
What is 3D printing?
Rather than using ink and paper, a 3D printer uses materials like plastic, metal or ceramic to create a 3D model. By using computer-aided design (CAD) files as digital instructions to create an object, a 3D printer repeatedly covers a work surface with layers of material in precisely the right spots to create a structure from scratch.
While 3D printing can be used for large-scale structures, 3D printing is most useful in creating smaller, customized parts or prototype components for various uses – including automotive engineering or the medical industry. With the versatility of 3D printing, it’s a field that’s filled with opportunities. Let’s take a look at some of the areas 3D printing is being used today.
3D printing jobs
1. 3D design
3D printing relies heavily on designers who can take a product idea and bring it to life. Thanks to its growth, 3D printing will create jobs for 3D designers at 3D printing firms, in companies as part of creative teams and as freelancers.
3D printers are being used in many design disciplines – such as product design, medical device design, architectural visualization and entertainment design, said Erol Gunduz, a professor at New York University’s School of Continuing and Professional Studies (NYU-SCPS), which offers programs in 3D printing, design and modeling.
To be competitive, job seekers should gain hands-on experience in 3D technologies and stay current on how companies are using 3D printing. For instance, recent graduate student designers and researchers who are familiar with 3D printing methods have the benefit of knowing how to use the technology within their design process, Gunduz explains.
“This gives them a significant advantage when looking for career opportunities within creative fields,” Gunduz said.
Did you know? 3D printers can create replacement parts for the human body, among the many things that 3D printers make.
2. 3D CAD modeling
3D printing would not be possible without CAD experts who have the skills to convert product designs into digital blueprints that the printers need. Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
“I see a lot more demand for CAD and 3D modeling jobs on the horizon because of 3D printing,” said Alex English, owner of ProtoParadigm. ProtoParadigm is a 3D printing business that also performs research and development on 3D printing hardware and new printing materials.
Although 3D CAD professionals are also needed to construct models for mass 3D printing, they are especially important for custom products.
“Bespoke manufacturing and custom prototyping both rely on the user’s ability to conceptualize the object they want and accurately create its digital representation,” English said.
Consequently, 3D CAD modeling jobs will require printing-specific modeling skills, such as feature size, geometrical constraints and knowledge of materials, English added.
3. Research and development
3D printing is all the buzz – and not just in the gadget world. Just as the 3D printing industry will require more product designers and CAD modelers, jobs will open up for forward-thinking research and development professionals who understand the intersection of tech and consumer products.
“While 3D visualization technologies have been used in the past within various fields, such as engineering and scientific agendas, many artistic and consumer product industries – such as fashion design and jewelry design – are beginning to take advantage of 3D printing systems,” Gunduz said.
Companies will need people who can find the best way to utilize 3D printing for consumer products at the lowest cost possible.
“The ability to visualize a line of fashion accessories or jewelry designs before committing to working with expensive materials affords an advantage for companies to reduce costs in development cycles,” Gunduz said.
Tip: Is your business experimenting with 3D printing research and development? Consider these tax credits that are available to companies performing cutting-edge research.
4. Biological and scientific modeling
3D printing is not limited to consumer products; it creates many products that promote medical advancement and save lives. It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
Accordingly, the 3D printing industry will need more engineers, designers and modelers who have a biomedical or scientific background to further innovate and produce highly advanced 3D-printed products.
“While all manner of designers will be able to print the things they design, there will be a high end to the market – particularly in medical, aerospace, military, and other high-precision or mission-critical applications – for those that better understand the printing technologies and how to design for their strengths and limitations,” English said.
5. Architecture and construction modeling
3D printing will disrupt various industries, particularly those that rely heavily on blueprinting or prototyping. For the construction industry, this paradigm shift will boost the need for 3D modelers that may replace current 2D construction planning solutions.
“In the architecture, engineering and construction industries, 3D printing will redefine the production of construction documents,” said Lira Luis, chief collaboration architect at Atelier Lira Luis LLC, a Chicago-based architecture and design firm.
Instead of 2D CAD modeling on paper, 3D printing can produce true-to-life models to better represent what structures will look like.
“As the 3D printing process becomes more streamlined, it could potentially eliminate the need for construction documents and move directly to printing full-scale mock-ups prior to construction of structures,” Luis said.
6. Education
What good are these jobs if no one has the qualifications to fill them? To help fill the skills gap, schools are developing – and some have already launched – 3D printing programs at all grade levels. This will open up jobs for educators who can teach the technical and business aspects of 3D printing.
“From an educational perspective, many K-12 schools are looking to 3D printing as a point of exposure for students within the arts as well as scientific areas of study,” Gunduz said. Colleges and universities are also launching 3D printing courses and certificate programs, such as NYU-SCPS’ certificate in 3D printing rapid prototyping.
Teachers will need to have a background in the 3D printing industry. They will also need specific skill sets to teach specialized courses and stay current on the latest trends.
“For educators, having an understanding of 3D modeling and 3D printing techniques will be invaluable, as the culture of fab labs is starting to gain support as an important aspect of education,” Gunduz said. “Teachers with 3D modeling and fabrication experience have a range of opportunities open to them within educational programs looking to incorporate this new technology.”
7. Legal professionals
3D printing is not confined to the tech world. As a creative field, the industry is wide open to legal issues, prompting a need for more lawyers and legal professionals who specialize in intellectual property (IP) rights.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become more widely accessible, it will be easier for infringers to create, market, and sell products that infringe patents, copyrights, and valuable brands,” said Julie Matthews, partner at Edwards Wildman – an Am Law 100 firm with offices in the U. S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
As a result, there will be an increased need for IP enforcement actions and lawsuits, as well as expanded services to monitor for infringements, Matthews explained.
Growth areas include IP ownership, scope of rights, licensing, fair use and international rights.
8. Startup companies
Thinking of starting a new business? 3D printing offers opportunities for innovation – not only in creating products, but also for entrepreneurship. 3D printing spans across various technical and design roles, many of which make great business ideas to support companies’ 3D printing needs.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become readily accessible to home users, undoubtedly, this will lead to new business opportunities for individuals and companies offering onsite and remote 3D printing services, new product and industrial designers, and computer-aided design specialists,” Matthews said.
With 3D printing costing between $1,999 and $3,500, anyone with 3D printing knowledge can start their business.
Tip: Consider a 3D-printing-as-a-service franchise for your new business venture.
9. Administrative roles
3D printing companies don’t run on engineers and technicians alone. As the industry grows, new and established 3D printing companies will need employees to keep their business running smoothly. This includes operations and administrative staff, analysts, finance and sales professionals, and retail employees.
“The businesses that will spring up with new business models centered on 3D printing will also have a need for more common jobs that other businesses need, like marketing, clerical, shipping, etc.,” English said.
These jobs will open up in all types of 3D printing companies, including vendors, manufacturers and retail stores.
Business News Daily editorial staff contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.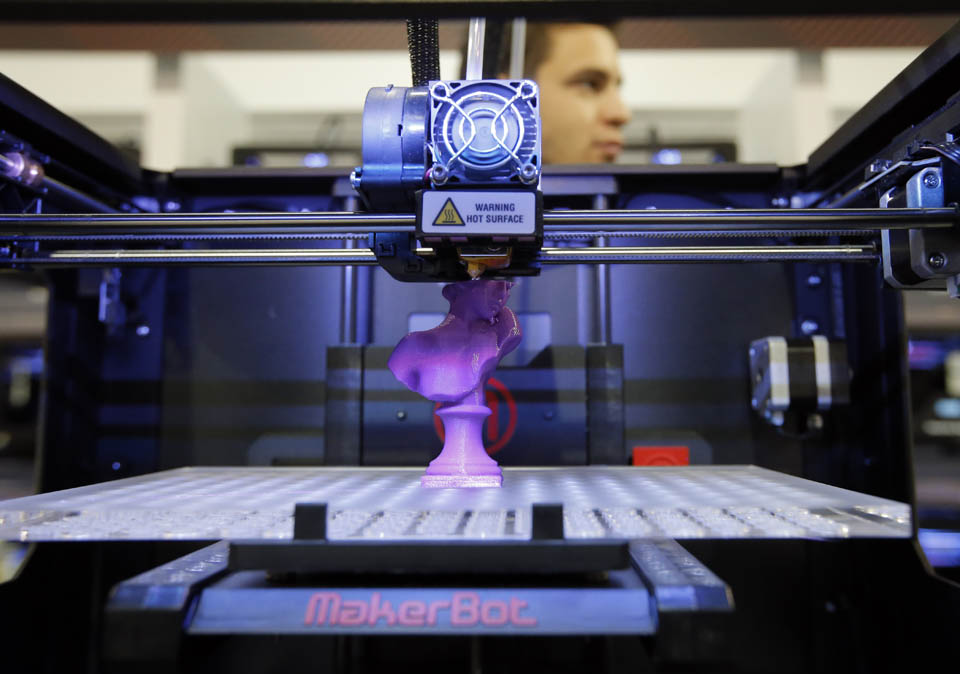
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why do we need 3D printing at school?
Today, the use of 3D printing technologies in education is only just beginning to gain momentum, but already there are amazing prospects. 3D printing can be introduced to primary and secondary schools, universities and other educational institutions. One of the reasons 3D printing has been slow to take off is the lack of awareness of the technology among education decision makers. nine0003
3D printing technology is still quite new, so the introduction of it in schools can have a significant impact on further development. At an earlier age, it is much easier to introduce new ideas and methods to a person. That is why children learn foreign languages much faster than adults. And that's why elementary and middle schools are the perfect place to introduce 3D printing courses.
Almost every subject taught in school can benefit from 3D printing – here are a few examples. nine0003
3D printing in mathematics
3D printing is already being used in teaching mathematics, in particular for the visual demonstration of graphs and mathematical models. Some students find it difficult to understand the numbers and charts they see on paper. This does not mean that they are not capable of learning - it is just a feature of the brain. 3D printing helps these students see equations, graphs, and complex mathematical models in a real-life way – and thus understand them. It is also important that 3D printing brings an element of variety to a subject that is usually quite boring. nine0003
3D printing in geography and geology
3D printing technologies can be used to show students geological formations at a scale that cannot be seen in a 2D image. We have already seen not only successful examples of the use of 3D printing in the teaching of geography and geology, but also how scientists used 3D printing to land a lander on a comet, choosing the best place to land on a 3D model. In addition, earthquake models were printed on a 3D printer for comparative analysis, as well as models of the causes and consequences of hydraulic fracturing in the development of oil and gas fields. Of course, living in a 3D world, it is best to teach geography and geology using visual 3D models. If textbook authors agree on the importance of 3D printing and want to incorporate it into lesson planning, they can include 3D printing files in each chapter. This will make the lessons more interesting and informative for both students and teachers - for example, you can print reduced models of mountain ranges, rivers, canyons and other geographical objects on a 3D printer. Thus, children will be able to observe some famous places of the world with their own eyes without leaving the classroom. nine0003
In addition, earthquake models were printed on a 3D printer for comparative analysis, as well as models of the causes and consequences of hydraulic fracturing in the development of oil and gas fields. Of course, living in a 3D world, it is best to teach geography and geology using visual 3D models. If textbook authors agree on the importance of 3D printing and want to incorporate it into lesson planning, they can include 3D printing files in each chapter. This will make the lessons more interesting and informative for both students and teachers - for example, you can print reduced models of mountain ranges, rivers, canyons and other geographical objects on a 3D printer. Thus, children will be able to observe some famous places of the world with their own eyes without leaving the classroom. nine0003
3D printing in history
It can be said that history as a subject will benefit the most from the introduction of 3D printing. Museums around the world are finally beginning to recognize the enormous potential of 3D scanning and 3D printing, not only to create replicas of ancient objects, but to give visitors the chance to literally touch them. Previously, throughout the museum there were signs "Do not touch the exhibits with your hands." Now that replicas of objects can be produced using high-precision 3D printers and scanners, museum visitors have the opportunity to touch the exhibits, many of which are virtually indistinguishable from the originals. Now imagine that in every history class, students will have the opportunity to print copies of historical objects on a 3D printer from the mass of STL files available for download. Now every school will have access to museum exhibits right in the classroom. In addition, it is much more interesting than reading chapter after chapter in a textbook, when many students cannot concentrate, are distracted and do not understand what they read. Being able to show an item from the era in question will make the lesson more fun. nine0003
Previously, throughout the museum there were signs "Do not touch the exhibits with your hands." Now that replicas of objects can be produced using high-precision 3D printers and scanners, museum visitors have the opportunity to touch the exhibits, many of which are virtually indistinguishable from the originals. Now imagine that in every history class, students will have the opportunity to print copies of historical objects on a 3D printer from the mass of STL files available for download. Now every school will have access to museum exhibits right in the classroom. In addition, it is much more interesting than reading chapter after chapter in a textbook, when many students cannot concentrate, are distracted and do not understand what they read. Being able to show an item from the era in question will make the lesson more fun. nine0003
3D printing in art
Of course, 3D printing can be used with great success in art classes. This technology opens up a range of possibilities for teachers, such as incorporating 3D design into the curriculum. With the help of 3D printing, students can bring the models they have designed to life - this will also make the lessons more interesting. In addition, there will be no need to be limited to a two-dimensional screen to demonstrate three-dimensional models. It will be possible to carry out design projects at the national and even international level, providing other schools with open access to models for printing on a 3D printer. Schoolchildren from New York will be able to work on joint projects with their peers from India, and then both schools will be able to print the result on a 3D printer. nine0003
With the help of 3D printing, students can bring the models they have designed to life - this will also make the lessons more interesting. In addition, there will be no need to be limited to a two-dimensional screen to demonstrate three-dimensional models. It will be possible to carry out design projects at the national and even international level, providing other schools with open access to models for printing on a 3D printer. Schoolchildren from New York will be able to work on joint projects with their peers from India, and then both schools will be able to print the result on a 3D printer. nine0003
In recent years, a number of opportunities that 3D printing provides to the arts have already been shown, but this is still the smallest part of its potential. 3D printing allows you to take a fresh look at the creation of art objects. If 3D printing is available to schoolchildren around the world, it will be the next generation that will bring these technologies to all possible areas of art and ensure that their full potential is realized.
3D printing as a tool
Not only does 3D printing provide ways to explore different subjects, but it can also become the center of a new academic discipline. With due aspiration and the right approach to the implementation of this task, 3D printing can be taught as a separate subject. nine0003
We live in an era of rapid development of new technologies, and one of them is 3D printing. At the same time, schools still live in the past, having not changed the teaching methods used by previous generations for decades. It's understandable that new technologies can be intimidating, especially for the conservative old guard, but there is a need for change. The introduction of 3D printing is a change that schools around the world should be thinking about.
Already, some companies are starting to develop and popularize curricula that include 3D printing as a tool or a separate discipline – and there should be more such initiatives. It is impossible not to take into account another fact that hinders the development of technology - the insufficiency of the budget that most schools have. Also, most people just don't know much about 3D printing. nine0003
Also, most people just don't know much about 3D printing. nine0003
It is logical that when it comes to financial matters, people who are not familiar with the technology will vote against investments related to it. Given this fact, the government at the national and regional level should take on the responsibility of informing school authorities about the potential of new technologies. Particularly in the US, President Barack Obama is already taking important steps to raise awareness of 3D printing. More efforts will need to be made in this direction, with particular attention to the education sector. nine0003
What is a 3D printer and why is it needed? / Amperka
Additive technologies have been going to the masses for a long time: institutes and research centers have been closely involved in them since the 80s, and now the moment has come when you can touch high-tech and master 3D printing right at home. You don’t even have to break the bank to do this: the prices of 3D printers have caught up with average smartphones. We understand how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts!
We understand how it works and what opportunities open up for makers and DIY enthusiasts!
Everything for 3D printing ❯
Why you need a 3D printer
The printer is very useful for do-it-yourself engineers. You no longer have to look for a universal case for the project, and then drill additional holes in it. 30 minutes of design, a few hours of printing - and you already have a case that is perfect for your device. Assembly of 5 shields does not fit anywhere? Forget about such problems.
The printer is sure to help you repair gizmos around the house. Everyone has had a situation in life when a thing had to be thrown away, although only one plastic part was broken in it. With the help of 3D printing, you can easily replace rare plastic parts in appliances that are difficult to find separately. nine0003
Until you learn how to model plastic parts yourself, you can simply download them on the Internet. There are many sites with millions of ready-made free models that are freely exchanged by users. We devoted a separate article to the search for models.
We devoted a separate article to the search for models.
Types of 3D printers
There are several main types of 3D printers, which are fundamentally different from each other by the principle of operation.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
FDM printers are the most common type. They work due to a movable print head with a heating element. Plastic is fed into it in the form of a rod, which melts and is squeezed out in liquid form onto the printing table. At the same time, the plastic is blown by a fan and instantly freezes, and the head begins to squeeze out a new layer over the frozen one.
SLA technology (Stereolithography Apparatus)
SLA printers work on the basis of stereolithography: instead of plastic, a special photopolymer resin is used, which cures under the influence of ultraviolet rays. For printing, the resin is filled into a tray, below which there is a display with ultraviolet pixels. A drawing of the lower layer of the model is displayed on it for several seconds. In this case, the resin above the display solidifies in the form of a displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table from above. After that, the table with the first layer rises, and the next layer polymerizes in the resin. nine0003
In this case, the resin above the display solidifies in the form of a displayed pattern and then sticks to a special movable table from above. After that, the table with the first layer rises, and the next layer polymerizes in the resin. nine0003
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) Technology
SLS printers use selective laser sintering technology, which uses a special plastic powder. During the printing process, a thin layer of powder is poured, and the printer processes it with a laser so that the layer hardens according to the model. Then the next layer of powder is poured and fused with the previous one - and so on in a circle. At the end, it remains only to clean the finished part from the remnants of the powder, which can then be reused. nine0003
Technology comparison
Each type of 3D printer has its advantages and disadvantages.
- SLS printers are large and require expensive raw materials. They are often used in high-tech industries for piece parts.

- SLA printers are much more widespread. The UV display improves accuracy, but working with toxic photopolymer resin at home is difficult.
- FDM printers are the most popular among hobbyists. A plastic rod is much cheaper than a special powder or photopolymer resin. However, to print complex geometry on such a printer, you will have to take care of auxiliary support. And the print speed is on average lower than on other technologies. But FDM printers are the easiest and safest to maintain. nine0102
How to prepare a print
The process from the conception of an idea to the production of a finished plastic part is simple - a schoolboy can handle it. We've broken it down in a 3D printing guide using the Flying Bear Ghost 5 printer as an example, but here we'll show you the general principle.
Initial model
First you need to create or download a 3D model of the future part. As a rule, sources are stored in the STL format, which describes the polygonal structure of the model as a set of triangles.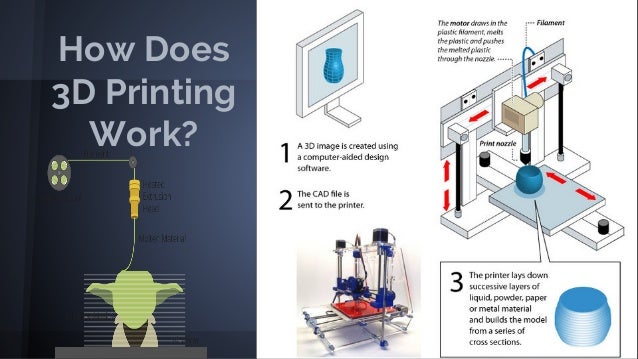 But it will not be possible to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break a detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle. nine0003
But it will not be possible to immediately send such a file to the printer: for successful printing, you first need to break a detailed 3D model into layers that the printer can handle. nine0003
Slicing
The program for cutting models (slicer) will require you to enter the model of your printer and set the print settings: layer thickness, percentage of internal filling of the part, auxiliary supports and the like. Based on this data, the slicer will automatically prepare a special code for the printer - G-Code, which describes how to move the print head, to what temperature it should be heated, and at what speed to extrude plastic in order to get the desired model layer by layer. Then it remains to load this code into a 3D printer and be patient until the end of printing. nine0003
The whole process of model preparation is clearly illustrated by the program and provided with intuitive tips for novice users. In general, slicing is not as scary as it is painted!
Finishing
After the model is ready, it can be further processed with sandpaper or a chemical solution. This will smooth out the unevenness between the layers, and the part will look just like the factory. There are a lot of life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look. nine0003
This will smooth out the unevenness between the layers, and the part will look just like the factory. There are a lot of life hacks on the Internet that will help minimize the flaws of the model and give it an improved look. nine0003
Printing consumables
The properties of the printed item largely depend on the raw material. As we said before, FDM 3D printers use plastic filament as a consumable, and you have a lot of room to experiment with different types of plastic.
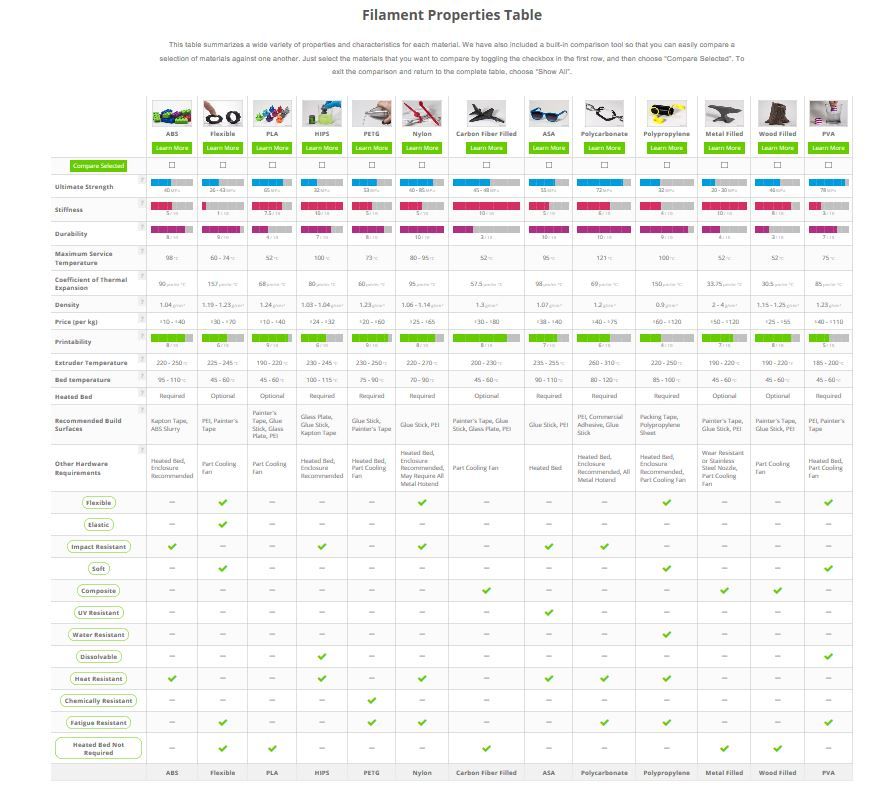
- PLA is highly extrudable and allows complex shapes to be printed at relatively low head operating temperatures as low as 190°C. The biodegradability of PLA plays into the hands of the environment, but at the same time, things from it are not very durable. nine0102
- PETG plastic is stronger than PLA, but also well suited for printers with temperatures around 200 °C. Varieties of PET plastic are well known to you from bags and plastic soda bottles.
- ABS plastic is more durable than other types.
 However, your printer will need an elevated extrusion temperature of around 250°C and a heated bed up to 120°C to print quality ABS plastic, so not every model aims to support it. nine0102
However, your printer will need an elevated extrusion temperature of around 250°C and a heated bed up to 120°C to print quality ABS plastic, so not every model aims to support it. nine0102 - HIPS plastic is similar in temperature properties to ABS, but has low caking with it and is easily removed with an organic solvent. Because of this, HIPS plastic is often used for printing composite models and supports for ABS models.
- Wood plastic is produced with the addition of wood dust. Finished models from it imitate wood not only in their appearance, but also in smell.
Plastic spools are on sale at every turn - it will not be difficult for you to choose the right consumables and combine different properties and colors of parts when printing. nine0003
In conclusion
Home 3D printing is easier than you think. With a 3D printer at hand, you can create any plastic parts you can think of: cases, mock-ups, figurines, and more. Do not forget that you have at your disposal a huge library of models that are shared on the Internet.