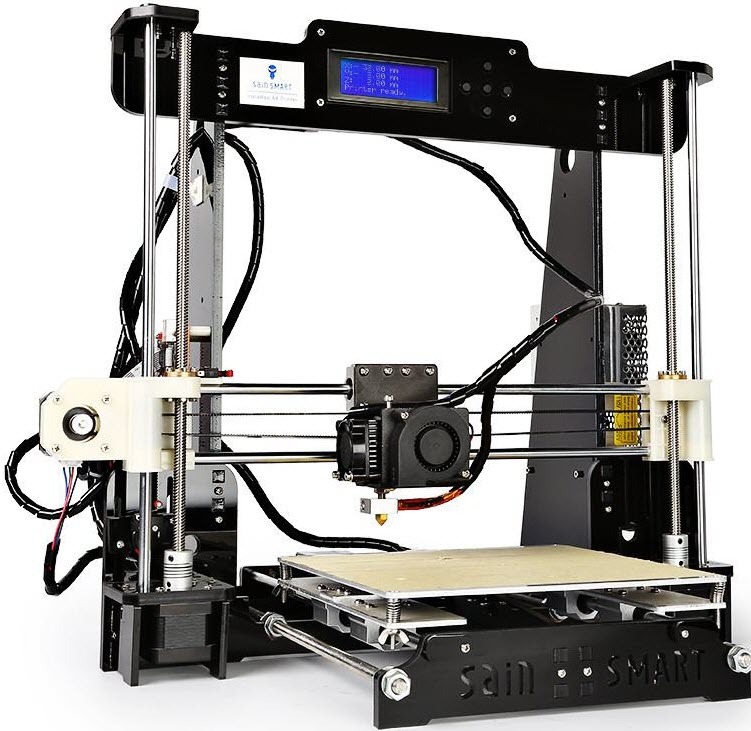
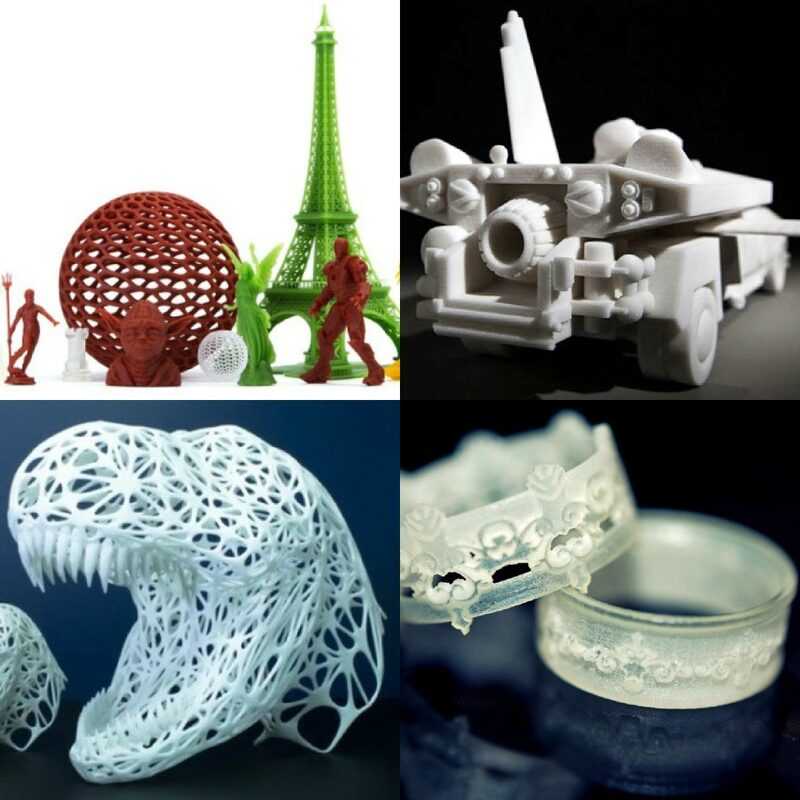
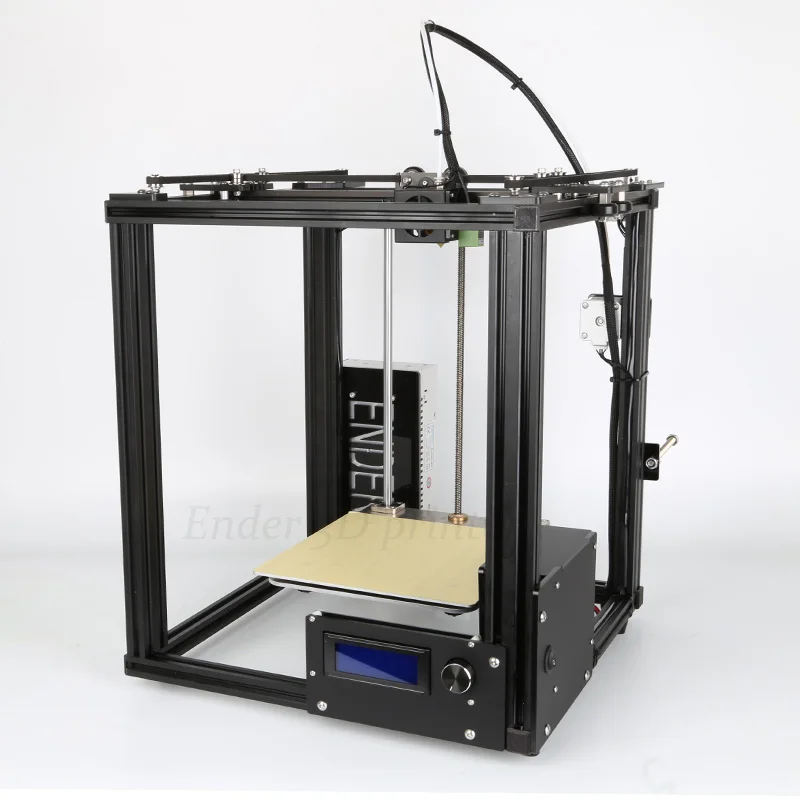
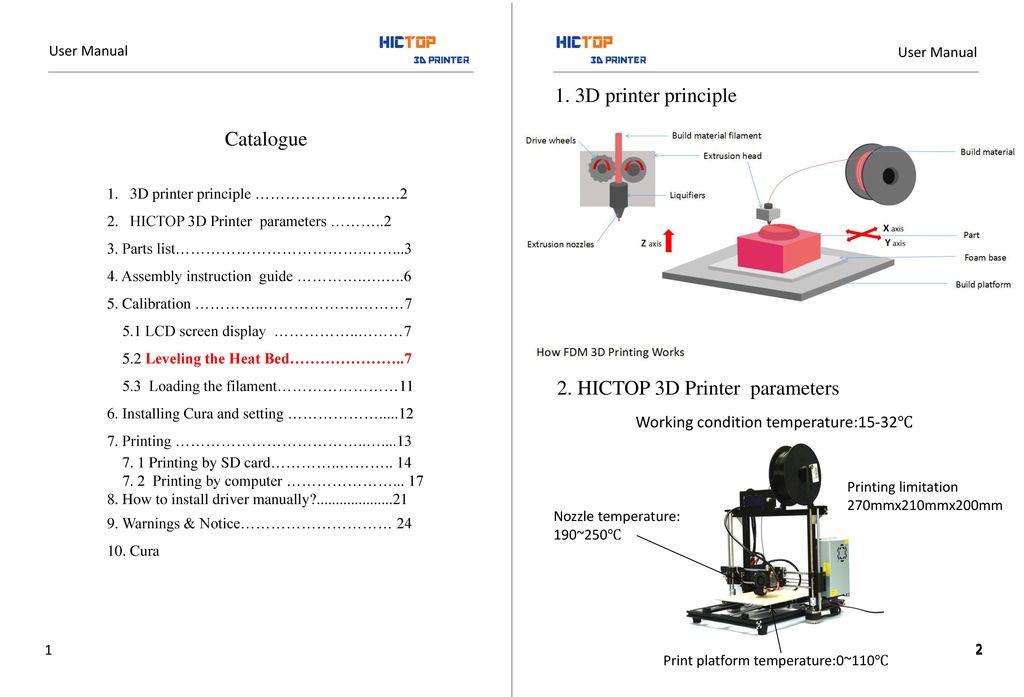
3D printer limitations
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is becoming popular with manufacturers. The demand is growing due to some of the revolutionary benefits that it can provide. Like almost all technologies it has its own drawbacks that need considering.
This page aims to help with the selection process. We will cover each of the advantages and disadvantages of 3D printing.
This production process offers a range of advantages compared to traditional manufacturing methods. These advantages include those related to design, time and cost, amongst others.
1. Flexible Design
3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes. More traditional processes have design restrictions which no longer apply with the use of 3D printing.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printing can manufacture parts within hours, which speeds up the prototyping process. This allows for each stage to complete faster. When compared to machining prototypes, 3D printing is inexpensive and quicker at creating parts as the part can be finished in hours, allowing for each design modification to be completed at a much more efficient rate.
3. Print on Demand
Print on demand is another advantage as it doesn’t need a lot of space to stock inventory, unlike traditional manufacturing processes. This saves space and costs as there is no need to print in bulk unless required.
The 3D design files are all stored in a virtual library as they are printed using a 3D model as either a CAD or STL file, this means they can be located and printed when needed. Edits to designs can be made at very low costs by editing individual files without wastage of out of date inventory and investing in tools.
4. Strong and Lightweight Parts
The main 3D printing material used is plastic, although some metals can also be used for 3D printing. However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
However, plastics offer advantages as they are lighter than their metal equivalents. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive and aerospace where light-weighting is an issue and can deliver greater fuel efficiency.
Also, parts can be created from tailored materials to provide specific properties such as heat resistance, higher strength or water repellency.
5. Fast Design and Production
Depending on a part’s design and complexity, 3D printing can print objects within hours, which is much faster than moulded or machined parts. It is not only the manufacture of the part that can offer time savings through 3D printing but also the design process can be very quick by creating STL or CAD files ready to be printed.
6. Minimising Waste
The production of parts only requires the materials needed for the part itself, with little or no wastage as compared to alternative methods which are cut from large chunks of non-recyclable materials. Not only does the process save on resources but it also reduces the cost of the materials being used.
7. Cost Effective
As a single step manufacturing process, 3D printing saves time and therefore costs associated with using different machines for manufacture. 3D printers can also be set up and left to get on with the job, meaning that there is no need for operators to be present the entire time. As mentioned above, this manufacturing process can also reduce costs on materials as it only uses the amount of material required for the part itself, with little or no wastage. While 3D printing equipment can be expensive to buy, you can even avoid this cost by outsourcing your project to a 3D printing service company.
8. Ease of Access
3D printers are becoming more and more accessible with more local service providers offering outsourcing services for manufacturing work. This saves time and doesn’t require expensive transport costs compared to more traditional manufacturing processes produced abroad in countries such as China.
9. Environmentally Friendly
As this technology reduces the amount of material wastage used this process is inherently environmentally friendly. However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
However, the environmental benefits are extended when you consider factors such as improved fuel efficiency from using lightweight 3D printed parts.
10. Advanced Healthcare
3D printing is being used in the medical sector to help save lives by printing organs for the human body such as livers, kidneys and hearts. Further advances and uses are being developed in the healthcare sector providing some of the biggest advances from using the technology.
Like with almost any other process there are also drawbacks of 3D printing technology which should be considered before opting to use this process.
1. Limited Materials
While 3D Printing can create items in a selection of plastics and metals the available selection of raw materials is not exhaustive. This is due to the fact that not all metals or plastics can be temperature controlled enough to allow 3D printing. In addition, many of these printable materials cannot be recycled and very few are food safe.
2. Restricted Build Size
3D printers currently have small print chambers which restrict the size of parts that can be printed. Anything bigger will need to be printed in separate parts and joined together after production. This can increase costs and time for larger parts due to the printer needing to print more parts before manual labour is used to join the parts together.
3. Post Processing
Although large parts require post-processing, as mentioned above, most 3D printed parts need some form of cleaning up to remove support material from the build and to smooth the surface to achieve the required finish. Post processing methods used include waterjetting, sanding, a chemical soak and rinse, air or heat drying, assembly and others. The amount of post processing required depends on factors including the size of the part being produced, the intended application and the type of 3D printing technology used for production. So, while 3D printing allows for the fast production of parts, the speed of manufacture can be slowed by post processing.
4. Large Volumes
3D printing is a static cost unlike more conventional techniques like injection moulding, where large volumes may be more cost effective to produce. While the initial investment for 3D printing may be lower than other manufacturing methods, once scaled up to produce large volumes for mass production, the cost per unit does not reduce as it would with injection moulding.
5. Part Structure
With 3D printing (also known as Additive Manufacturing) parts are produced layer-by-layer. Although these layers adhere together it also means that they can delaminate under certain stresses or orientations. This problem is more significant when producing items using fused deposition modelling (FDM), while polyjet and multijet parts also tend to be more brittle. In certain cases it may be better to use injection moulding as it creates homogenous parts that will not separate and break.
6. Reduction in Manufacturing Jobs
Another of the disadvantages of 3D technology is the potential reduction in human labour, since most of the production is automated and done by printers. However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
However, many third world countries rely on low skill jobs to keep their economies running, and this technology could put these manufacturing jobs at risk by cutting out the need for production abroad.
7. Design Inaccuracies
Another potential problem with 3D printing is directly related to the type of machine or process used, with some printers having lower tolerances, meaning that final parts may differ from the original design. This can be fixed in post processing, but it must be considered that this will further increase the time and cost of production.
8. Copyright Issues
As 3D printing is becoming more popular and accessible there is a greater possibility for people to create fake and counterfeit products and it will almost be impossible to tell the difference. This has evident issues around copyright as well as for quality control.
Get Further Advice On 3D Printing
Need help with determining whether 3D printing is the right process for you?
Contact our team of world-leading experts with over 20 years of experience in the additive manufacturing field.
Our technology experts help to ensure our customers apply the correct technology process depending on each individual or company requirements:
Related Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10 Limitations of 3D Printing Technology
ADVERTISEMENT
3D printing has become a trend. The thought of printing anything that you can design into CAD files is really enthralling. Apart from industrialists and entrepreneurs, a lot of enthusiasts and hobbyists are also following the trend.
The online communities are surging and the awareness is spreading like a wildfire. However, there are still a few limitations of 3D printing that make it difficult to reach masses.
With lots of things to 3D print, individuals usually feel intimidated by the way this technology works. There is a huge number of courses online, but would that knowledge justify the investment of a few hundred dollars on something that we haven’t tried for real.
There is a huge number of courses online, but would that knowledge justify the investment of a few hundred dollars on something that we haven’t tried for real.
The questions are numerous and the answers are limited. We do know that the technology is made simpler with passing time, however, have we reached that stage where we can call 3D printing technology, a technology for all?
The limitations of 3D printing can be few, but still hold a lot of importance in giving this technology ahead away into normal households.
Trying to put some light on the same side of the story, here are a few limitations that are usually not talked about a lot, but exist anyway.
ADVERTISEMENT
Limitations of 3D Printing
We have been talking about a lot of things we can accomplish by a 3D printer.
But the information wouldn’t be complete without talking about the challenges one can face when shifting the gears from traditional manufacturing to 3D printing.
Outlining 10 of the major limitations that are being worked upon by the experts would give you a better stance to decide for yourself.
Consumes a Lot of Energy for Operation
You may not have been told about this before. But you would certainly like to know about the additional cost that 3D printing would put on your shoulders.
We have been witnessing how the electricity cost has turned out against our favor from the last couple of years. With no sign to slow down, companies keep trying to implement strategies and measures to reduce the amount spent on electricity bills.
If you have been struggling to bring your expenses down, 3D printing would make your fight even difficult.
According to the researches made on the technology, it has been found that energy consumption with 3D printing is 100 times more than the power consumed by traditional manufacturing.
We may agree to the fact that 3D printing is a step towards a greener planet by facilitating reusable materials such as plastic.
However, it would also be true to quote it as two steps backward, by consuming non-renewable energy for its operation. Hence, the only way to get past the limitation is to use 3D printing for small batch productions.
Hence, the only way to get past the limitation is to use 3D printing for small batch productions.
ADVERTISEMENT
The 3D Printer is Costly
If you are thinking of starting a manufacturing firm and have a limited budget to afford machines, to begin with, you may not like the huge cost associated with 3D printers.
Only one machine can cost you ranging from a hundred to thousands of dollars. Not just that, the software and material requirement would come as an extra cost.
That is why you may not see many businesses reaping the advantage of 3D printing even after 40 years of its invention.
There is a simple calculation to do. If you have a large order, your cost would be higher. However, for small products can be printed at a cheaper cost.
If you are up for buying a consumer 3D printer, you may get it for less money. But, why pay extra for a few items by investing in material cost and electricity bill, when you can get that at a lower cost from the market.
Unless you want to learn or want to create unique designs, you may end up repenting over your decision of buying a 3D printer.
3D Printing Requires Skilled Users for Operation
You may have read that 3D printing is easy as compared to the traditional methods which are completely true.
However, there are certain skills that must be learned before you go on printing your first 3D printed object. It may not be as user-friendly as being told or as you perceive it to be.
You must know how to work with CAD files and learn about some hardware settings of 3D printers before beginning to 3D print.
ADVERTISEMENT
Consider it Slow for Mass Production
The new 3D printers are being introduced and this limitation of 3D printer is being worked upon.
However, the fact is that mass production would eat up time when compared with traditional manufacturing.
Also, the time will depend on the complexity of the design, the size of the product and a lot of other parameters. Some 3D printing processes even require a lot of post-processing steps. If not done properly, it can even destroy the objects 3D printed.
Some 3D printing processes even require a lot of post-processing steps. If not done properly, it can even destroy the objects 3D printed.
If your 3D printing service center is too busy with orders, you may expect it to deliver yours after a week or even more.
3D Printing Can be Used for Piracy
We all know that piracy is a huge setback of businesses. Copying one design and selling it for a lower price can throw the actual manufacturer out of the business. 3D printing is making it even easier. All you need to copy design is the blueprint of the file.
Once you have the 3D design, you can print as many 3D parts as you please. And, anyone can do that. Moreover, with technology aggressively reaching more people, the cases of patent violation could become a huge problem.
The problem is deeper than one can imagine. As the blueprints are accessed through a shared repository, differentiating between the pirated ones and non-pirated ones wouldn’t be easy, hence, difficult to fight.
ADVERTISEMENT
Harmful Gases Can Cause Health Issues
We all know that plastics when melted emit fumes which is dangerous for humans if inhaled in large amounts. Aren’t 3D printers are exposing us to the harmful emissions? The 3D printers used inside the closed doors of our houses are even more dangerous.
Researchers have discovered that carcinogenic particles may be introduced in the air during additive manufacturing.
These particles can settle in the bloodstream of users and can cause congestion in their breathing system. Hence, triggering cancer and various other harmful diseases.
There are 3D printing machines that come with HEPA filter but aren’t able to completely refine 100% of the fumes. Those that aren’t compliant with HEPA filters do not help at all. All the fumes generated are circulated inside the house or affect those working close to the machine.
Long term exposure can lead to problems that are still to be realized. It is important to take precautions and include necessary measures while working with 3D printers.
The Printing Materials are Limited
The limitation of 3D printing can be directly felt when unable to choose the desired material for printing. Although the number of material choices is increasing as the demand is growing, it is still far less than the ones available with traditional manufacturing.
As of now, plastic is the most widely used 3D printing material as it is cheap and easy to manage given the lower melting point.
Limited material choice makes it difficult to employ the use of 3D printing for a greater number of applications.
If one is printing with different materials, one may have to buy different 3D printers. As every printer supports a limited number of materials. A 3D printing process printing with metal would not print with plastics and vice versa.
Moreover, some 3D printers can only print with PLA when it comes to plastics. Some have the provision to print with different plastic materials.
ADVERTISEMENT
The Textures and Color Printing Limitations
It would be incorrect to say that the multiple colors 3D printing is not possible. It sure is.
It sure is.
With new 3D printers and better technology introduction, there are many limitations of 3D printing that is being resolved with time. However, the solution hasn’t been able to impress everyone.
The textures and color options available with traditional manufacturing is still greater than what we achieve through 3D printing.
Users have to compromise in terms of color and the finished textures with 3D printing.
Or else, it must employ post-processing methods, which sometimes is too hectic and not even compatible with every 3D printing process to get the desired results.
Talking about the surface finish, one may be disappointed by the results of a few of the cheaper 3D printers. Even the costlier ones may not be able to provide the quality surface finish compared to the one achieved through other methods.
Again, printing with wood and ceramics is again a huge challenge.
The Limited Size of the 3D Printer
If you are working with a certain 3D printer, you are restricted to print objects with no larger size than allowed by the 3D printer build area.
You must confine your creativity to the size already defined for your 3D printing. These limitations of 3D Printing is highly felt within the small scale 3D printing service center.
These centers have to define the size of the orders they accept and reject those that are larger than the defined sizes.
Larger 3D printers are already at work, but not everyone can afford it. Even when able to get it by investing all the savings and loans, paying for the additional expenses would be completely impossible with limited budgets.
Although there has been a small room-sized house 3D printed by now, constructing a complex and multiple story buildings are still a challenge.
ADVERTISEMENT
3D Printing Leading to Scarcity of Jobs
As we all know that automation has always been the biggest enemy of job security and so is for the manufacturing industry as well.
Job layoffs are a serious matter and every country’s government is concerned about the problem as much as the citizens are.
With automated technology, the need for labor force is decreasing exponentially. The manufacturing industry is one of the major industries that require labor on a larger scale. Think about a 3D printer that can be operated using 3-4 technicians.
Compare it with the traditional methods and manufacturing technologies that require dozens and hundreds of workers at the same time.
You would be able to calculate the disruption 3D printing is capable of causing. The technology is no doubt is helpful in eliminating human error hugely, however, taking away jobs from labors won’t be justified either.
This can cause a universal problem if industries start implementing 3D printing technologies for all its production jobs. Ultimately leading to economic crises.
The Conclusion
As the technology starts getting into people’s ears, the hype tries to hide the problems related to it. 3D printing is no different.
The major reason why the awareness about 3D printing took so long was because of the limitation of 3D printing that, more or less, still exists.
3D printing is definitely capable of accomplishing tasks that are not possible through any other methods.
But that does not make it eligible for making the disruptions that it is capable of. Researches are heading away to tap the benefit of the technology and control the problems to its best.
We have succeeded too. In terms of reachability, cost, accessibility, awareness, etc. And, we have to cross a long way too.
However, the way the technology has succeeded in impressing the mass, the results would be out sooner.
Not just the limitations of material and color options are worked upon, but studies are being carried to make the technology safe and economical.
Companies are coming up with better and smarter 3D printing machines. Manufacturers of 3D printers are stressing on safety and ease of use.
These can bring a lot of difference in the coming future. Leaving being the limitations of 3D printing, it will take time for 3D printing to completely eliminate traditional methods of manufacturing. The clock is already ticking and the change would be seen anytime from now on.
The clock is already ticking and the change would be seen anytime from now on.
Capabilities and limitations of 3D printing
Accelerate product development, reduce costs with a digital manufacturing platform.
Get an instant quote
Upload to production in 5 min.
3D printing is an actively developing technology, it has a number of fundamental differences from traditional production methods. Below, we will look at the most important advantages and limitations that you need to know in order to assess the potential application and development vector of 3D printing. nine0003
Benefits of 3D printing
+ Complex geometries at no additional cost
3D printing makes it easy to produce complex shapes, many of which cannot be made using traditional methods. The additive principle of technology allows complicating the geometry of the product without changing the cost of production.
Complex structured parts optimized for 3D printing cost the same as simpler parts designed for traditional production (and sometimes even cheaper because less material is used). nine0003
nine0003
+ Low cost per piece
When casting a part, it is necessary to make a unique injection mold. In order to recoup these costs, it is necessary to produce a large circulation of products.
3D printing does not require the manufacture of special tools or tooling, so start-up costs are significantly lower. The cost of a printed part depends only on the amount of material used, the time it took the machine to print it, and post-processing if needed. nine0013
+ Inexpensive Prototyping
Prototyping is one of the main applications of 3D printing today. Prototyping is becoming an inexpensive and fast stage in product development thanks to new technology.
Parts printed on a 3D printer are usually ready within a few hours, and on industrial equipment within 5-7 working days.
The speed of prototyping greatly speeds up the design cycle. Products that would require 5-6 months of development can now be ready in as little as 8-10 weeks. nine0003
nine0003
+ Large selection of materials
The most common 3D printing materials used today are plastics. Metal 3D printing is finding an increasing number of industrial applications.
3D printed parts today can have high heat resistance, strength or stiffness, and even be biocompatible.
Composite materials used for 3D printing may contain metal, ceramic, wood, or carbon particles. Such materials allow the production of products with unique properties. nine0003
Limitations of 3D printing
- Lower strength and anisotropic properties of material
Printed parts most often have physical properties that are not uniformly distributed over the volume: since they are created in layers, the parts are more fragile by about 10-50% along one of the axes. Thus, plastic printed parts are most often used for non-functional applications (to avoid critical loads).
However, technologies such as DMLS allow the production of metal parts with superior mechanical properties. This made it possible to use the technology in areas such as the aerospace and medical industries. nine0003
This made it possible to use the technology in areas such as the aerospace and medical industries. nine0003
- Not competitive price in mass production
3D printing cannot compete with traditional manufacturing processes when it comes to mass products. The absence of special equipment leads to the fact that the cost of starting production is not high, on the other hand, this leads to the fact that the price per unit of the product decreases slightly with large runs.
In most cases, the viability of 3D printing is lost when more than 100 units are produced, depending on the material, 3D printing process, and part design. nine0003
- Restrictions on precision and manufacturing tolerances
The accuracy of 3D printing depends on the type of printing and printer settings. Generally, parts printed on a desktop FDM 3D printer have the lowest precision and will print with a tolerance of +/- 0.5mm.
Other types of 3D printing offer higher precision. For example, Industrial Material Jetting and SLA printers are capable of producing parts with an accuracy of +/- 0.01 mm.
For example, Industrial Material Jetting and SLA printers are capable of producing parts with an accuracy of +/- 0.01 mm.
Metal products printed using DMLS or SLA technology are usually CNC-machined to improve tolerances and surface quality. nine0003
- Post-processing and removal support for
Printed parts are rarely ready for use immediately after printing, usually additional post-processing is required.
Building support is required in most 3D printing processes. Support is a non-functional, auxiliary part of the product that is printed along with the part. During post-processing, the support is completely removed, but traces may remain where the support material was attached to the part. Such areas require additional operations to achieve a high surface quality (grinding, polishing, painting). nine0003
More 3D Printing Related Articles:
3D Printing Technology
3D Printing or CNC Machining
How to Reduce the Cost of 3D Printing
SLS Guide
Myths about 3D Printing and 3D Printers: Common Misconceptions
Myths about 3D printing As you know, what people are not very well versed in, over time, acquires a lot of myths and erroneous judgments. 3D printing technology is no exception. Unfortunately, in Ukraine there is an extremely low percentage of awareness about 3D technologies, which does not favor the opinion about innovative methods. Myths about 3D printing are very different, and are built on the basis of what a person has already heard about the technology. Printing on a 3D printer is a very unusual process. But most do not bother to gain deeper knowledge and are content with meager explanations about how the technology works. This is how 3D printing myths are born. nine0003
3D printing technology is no exception. Unfortunately, in Ukraine there is an extremely low percentage of awareness about 3D technologies, which does not favor the opinion about innovative methods. Myths about 3D printing are very different, and are built on the basis of what a person has already heard about the technology. Printing on a 3D printer is a very unusual process. But most do not bother to gain deeper knowledge and are content with meager explanations about how the technology works. This is how 3D printing myths are born. nine0003
In this article we will try to bring the most common myths about 3D printing and dispel them with reasoned facts. We hope this section will help you learn more about 3D technologies and better understand the process of printing with a 3D printer.
The most common myths about 3D printing
Let's start this section with some of the most common myths and misconceptions about 3D printing. So, what people often think about printing on a 3D printer:
1.
 It's expensive
It's expensive Myths about 3D printing are proudly led by the opinion about its cost, and this is not accidental. People are convinced that 3D printing is very expensive and out of reach for the average user. This myth is only half true. Prices for industrial installations for 3D printing are really very high. But that's why it is professional equipment used in production. The cost of desktop 3D printers is much lower and continues to decline as technology advances. The prices of consumables are also falling. Already, this makes 3D printing very accessible, and in the future, a 3D printer will become part of almost every home. nine0003
2. It's professional
Many people think that 3D printing is only suitable for a narrow range of specialized tasks or industrial applications. We can assure you that this is not the case. Of course, the prospects for 3D printing in the industry are extremely promising, but for home use, a 3D printer can be no less useful.
3.
 Can only be printed with plastic
Can only be printed with plastic Now this is a completely absurd opinion. 3D printing technology is steadily moving towards the fact that anything can be used as a material. Already today there are food 3D printers, 3D bioprinters that print with living cells, devices that print with metal, wood, silicone, rubber, clay and even glass. The method of contour construction is also actively developing, that is, 3D printing of houses. As you can see, you can print anything, almost anything. nine0003
4. 3D printing is only good for making trinkets
Contrary to the opinion that 3D printers are used professionally, there are thoughts that 3D printing is not suitable for creating serious things. A variety of functional models and final parts made on 3D printers will help to convince skeptics. Many large aerospace and automotive companies use 3D printing in their practice. For example, Airbus launched a plant that uses only additive techniques. And the creation of cars using a 3D printer has become a very common practice. nine0003
nine0003
Don't miss it, you'll love:
Myths about 3D printers
After listing the common myths about 3D printing, let's move on to the myths about 3D printers. Some exaggerate the capabilities of these devices, some downplay. But there are myths about 3D printers, and it's up to us to dispel or confirm them. So, what do ordinary people think about 3D printers?
1. This is a complex device
On the one hand, you can't argue with that. The device is really not easy, but the developers care about the maximum ease of managing 3D printers. Desktop devices are aimed at comfortable and simple work. For example, on Kickstarter, the project of the simplest 3D printer was considered. Moreover, you can assemble some printer models yourself. And if you do everything right, they will work well. Therefore, everything is not as difficult as it seems. nine0003
2. Products do not require post-processing
This is perhaps the biggest misconception. No matter how much you want, but just take it and print it will not work. Objects should definitely go through a minimal post-processing process, especially if they were printed with supports.
Objects should definitely go through a minimal post-processing process, especially if they were printed with supports.
3. Print in any color
Unfortunately, modern desktop 3D printers are not yet able to print full color samples. There are models with multiple extruders, but the maximum possible is two or three colors. On industrial printers, it is quite possible to print products in full color. However, developers are actively working to eliminate this limitation and are making significant progress. Relatively compact full color printers already exist. It remains to wait for their mass entry into the market and lower prices. nine0003
This concludes the myths about 3D printing. We hope the article was informative. And if you know even more myths and misconceptions about 3D printers and 3D printing that we have not touched on, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add them! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
Also visit our online store and choose 3D scanners, 3D printers, 3D pens, 3D plastic and accessories.