Types of 3d printer extruders
3D Printer Extruder: Basic Buyer's Guide
The 3D printer extruder is a crucial piece of equipment in your 3D printer.
FDM printers work by depositing filament layer by layer to build a model. The extruder is the tool that moves, heats, and pushes the filament out of the printer. The type of extruder and hotend that you use can change the quality and style of your print, so it’s no wonder that this is considered an essential part of any 3D printer.
In this article, we’ll review the basic information you need to know about 3D printer extruders and hotends.
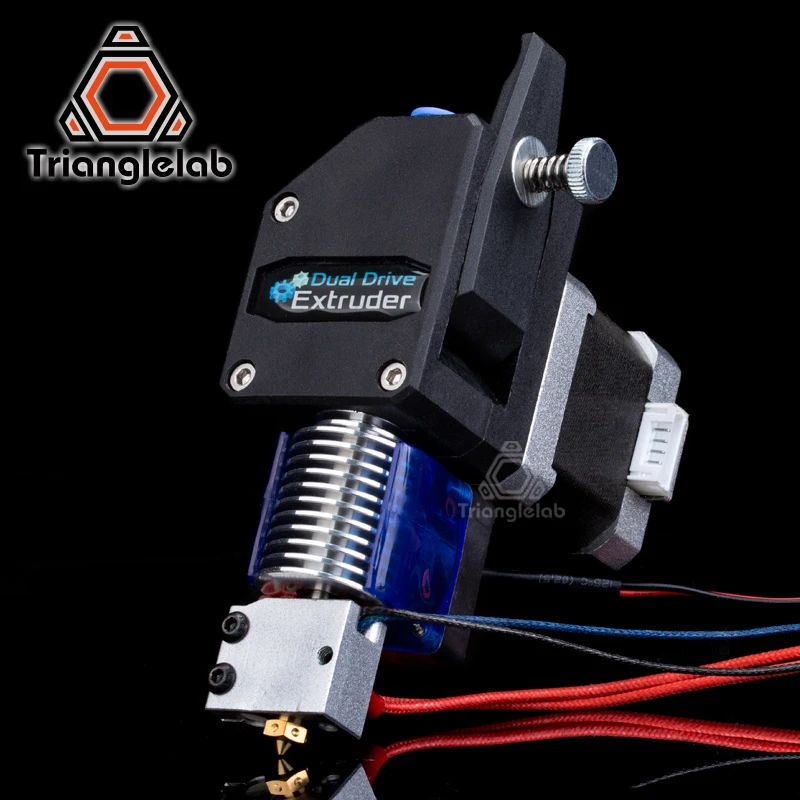
What is a 3D Printer Extruder?An extruder is the part of the 3D printer that is responsible for pushing the filament along, melting it, and placing it on the bed to build the model. A 3D printer extruder is made up of many different tools that do a combination of different jobs. Namely, there is a coldend and a hotend.
For the sake of this article, we will refer to the extruder as the entire piece of the 3D printer that moves, melts, and deposits filament – essentially, the coldend and the hotend. Others may refer to the extruder as simply the piece that moves the filament, and the hotend as the piece that melts.
- The cold end is responsible for moving the filament along to direct it to the hotend. A motor and gear work to guide filament, either through a PTFE tube or directly into the hotend. There are two different types of coldends that work a little bit differently, which we’ll review in the next section.
- The hotend heats, melts and extrudes the material layer by layer through a nozzle. Two of the most important components within the hotend are:
- The heater, which heats and melts the filament.
- The nozzle, which directs the filament as it is extruded.
There are two main types of extruders that you will find on professional 3D printers: Direct and Bowden. Some types of 3D printers also feature a dual extrusion. Let’s review the difference between all three.
Let’s review the difference between all three.
In a direct extruder, the filament runs from the cog, to the coldend, to the hotend, all in one piece. This means that the drive and the gear that moves the filament along is directly above and attached to the hotend.
Because the extruder sits directly on top of the hotend, the extruder itself is heavier and slower. However, many prefer to print flexible 3D filaments using a direct extruder. With a direct extruder, the filament has less distance to travel before getting melted and deposited. Consequently, there’s less opportunity for issues during the extrusion process.
Bowden ExtruderIn a bowden extruder, the coldend and the hotend are separated by a PTFE tube where the filament runs along. Instead of the coldend sitting directly on top of the hotend, a tube separates the two pieces.
As opposed to a direct extruder, a bowden extruder is much lighter and faster, because the only moving part is the hotend.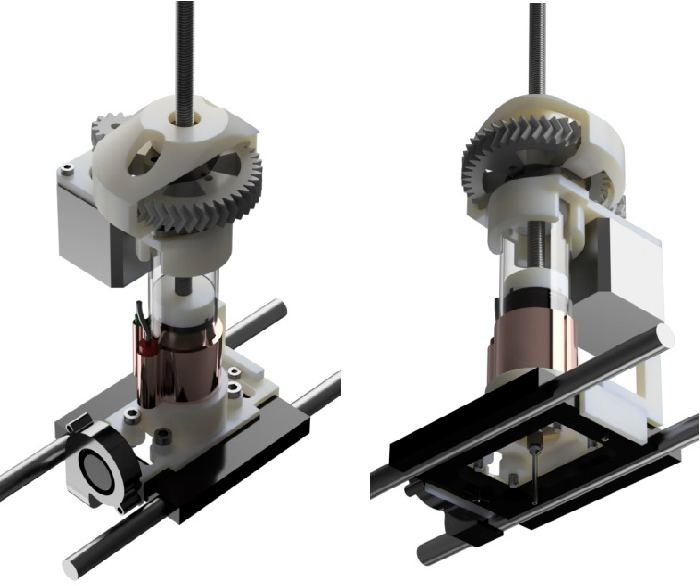 The coldend, with the drive, is positioned on a fixed point on the printer.
The coldend, with the drive, is positioned on a fixed point on the printer.
Bowden extruders print high-quality models and are great for printing models that feature long, continuous designs. It used to be said that flexible materials can’t be used with a bowden extruder, but that is an outdated thought. As long as there is no room for the filament to move or wiggle, it will be able to move just fine through the tube into the hotend.
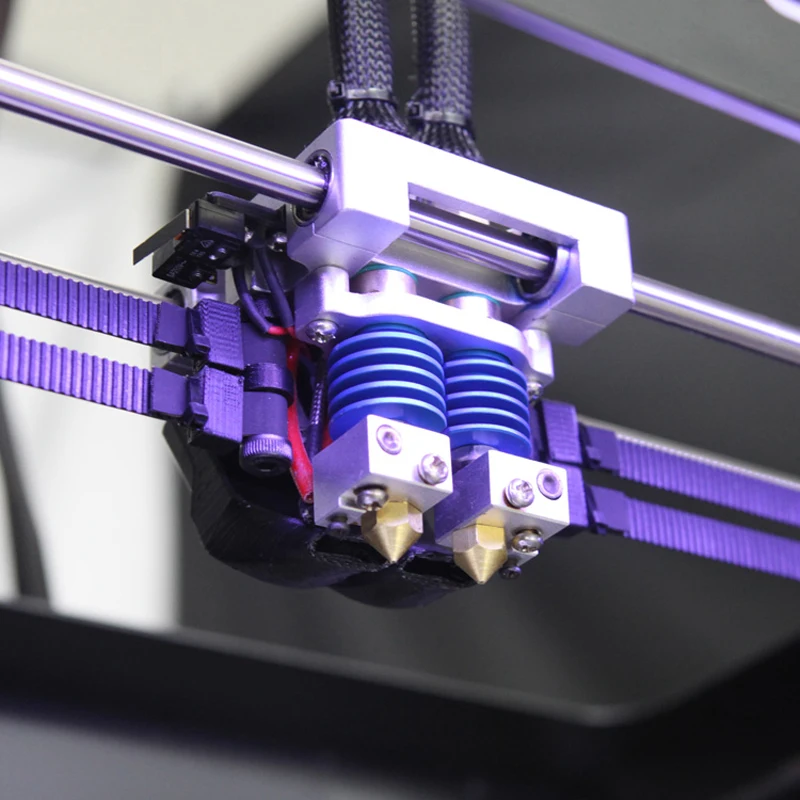
Dual ExtrudersAlong with different styles of extruders, some printers can also be equipped with two or more extruders.
Dual extruders allow you to print multiple materials at once, or even print two models at the same time. Dual extrusion allows you to accelerate your printing process because there are now two tools moving, melting, and depositing filament.
The dual extruders can also feature an independent dual extrusion system (IDEX). That means the extruders work independently from one another. So, even though typical dual extruders move together at the same time, IDEX extruders function freely from each other. As a result, they are opening the possibilities of increased efficiency, higher productivity, and time-saving.
As a result, they are opening the possibilities of increased efficiency, higher productivity, and time-saving.
We can’t talk about extruders without touching on the hotend. As mentioned before, hotends are the piece of the extruder that is responsible for melting and extruding the filament onto the bed.
You can customize your hotend depending on the nozzle you attach. Because the filament is pushed through the nozzle, the size and type of nozzle you choose will have a major impact on the style and effectiveness of your model.
There are many different types of nozzles you can choose and place on your 3D printers, depending on the type of material you’re printing or the design you have in mind. This topic is so extensive, that we’ve dedicated an entire article to it, which you can read here.
Should you run into troubleIf you’re experiencing difficulties regarding these printer parts, it’s most likely to be down to the most common printing issue in 3D printing: underextrusion. This pesky problem is when there’s a lack of extruded material in the printed part that presents itself as either no filament being extruded from the hotend, missing layers or spongy prints. Underextrusion occurs due to one of the following faults:
This pesky problem is when there’s a lack of extruded material in the printed part that presents itself as either no filament being extruded from the hotend, missing layers or spongy prints. Underextrusion occurs due to one of the following faults:
- outdated software
- wrong choice of material
- the state of your bowden tubes
- a lack of cooling
- issues with the hotend
- issues with the extruder board
- the extruder motor failing to push the filament properly
For more information on how to combat each of these contributing factors, have a read of this article featured on our BCN3D Knowledge Base, which is crammed full of tips and tricks to get you through the trickiest of print jobs.
How much does a 3D Printer Extruder cost?In BCN3D we offer two types of extruder motors: the Extruder Motor R and the Extruder Motor L, plus the extruder kit where both are included. Prices go from 130€ each to 180,15€ for the kit.
Prices go from 130€ each to 180,15€ for the kit.
Moreover, here you can find a wide variety of hotends and their prices.
Lastly, BCN3D offers an extruder board for the price of 15€.
Final ThoughtsNext time you look at your 3D printer, you’ll feel a little more appreciative of all the work going on in that small piece of equipment called an extruder. As with many other aspects of 3D printing, understanding this tool and its work will help you become a more efficient user and significantly improve the quality and properties of your prints.
Types of 3D extruders and Hotend
In this article we are going to talk about the types of extruders and HotEnd most common in the world of 3D printing. Before starting it should be clarified that everything cited is the result of our experience always using products from leading brands, such as the products of E3D Online, a company of high-quality 3D printer components specialized in extruders, HotEnd and nozzles. This nuance is necessary because if extruders and low quality HotEnd are used it may be the case that the characteristics that we comment below aren't met.
This nuance is necessary because if extruders and low quality HotEnd are used it may be the case that the characteristics that we comment below aren't met.
The main function of the extruder is to move the filament from the reel to the HotEnd in the most precise way and at the speed suitable for 3D printing, but there're different classifications of the extruders. In this post we will analyze the main ones.
Types of extruders depending on the drive
Within extruders there are two types depending on the type of drive: Direct and Bowden. In the direct extruder, as its name suggests, the filament runs directly from the cog of the extruder to the HotEnd. There are even systems in which these two parts are together, as in the Titan Aero.
Image 1: Titan Aero extruder. Source: E3D
In the Bowden extruders, on the contrary, the connection with the HotEnd is through a PTFE tube through which the filament passes.
Direct Extruders
Image 2: Direct Extruders
Advantages:
- Print flexible materials, both PLA Soft or TPU, and TPE (FilaFlex) in 1.
 75 mm ans 2.85 mm.
75 mm ans 2.85 mm. - Print all kinds of materials without problems, regardless of the abrasion presented by certain filaments. To print 3D abrasive materials, for example graphene, we recommend using the Olsson Ruby Nozzle, a brass nozzle with the ruby tip that has an almost infinite life.
- This system needs short retraction lengths to obtain good 3D prints, which reduces the likelihood of a jam. To know more about the retraction consult the article of the following link.
Disadvantages:
- Considerable inertia in the axis through which the extruder and the HotEnd moves. This factor is increased when you want to make 3D prints at high speeds by having to move the weight of the whole set (extruder, extruder motor and HotEnd), especially if the 3D printer has several extruders.
- Temperature problems in the electric motor of the extruder. In closed 3D printers and with a tempered chamber, temperatures in the extruder motor can be reached that affect the performance of operation.
Bowden extruders
Image 3: Bowden Extruder
Advantages:
- Low inertias in the axis of displacement of the HotEnd. In the Bowden system, since the extruder and the extruder motor are anchored to the chassis of the 3D printer, the inertias in the movement to make the impression are greatly reduced. This allows for very fast and high quality printing.
- High drag power of the filament. The majority of 3D printers that use this extruder system (BCN Sigmax, 3NTR-A2) have a set of pinions (reducer group) that increases the drag torque of the filament, thus being able to move coils larger than normal.
Disadvantages:
- Problems printing with flexible filaments with a diameter of 1.75 mm. This is due to the fact that being a flexible filament it isn't possible to keep the pressure in the filament constant along the Bowden PTFE tube until the HotEnd as it channels the filament.
 In the 2.85 mm Bowden systems, however, it's possible to print the flexible filaments at low speed.
In the 2.85 mm Bowden systems, however, it's possible to print the flexible filaments at low speed.
Types of HotEnd depending on the diameter of the material
The HotEnd is responsible for melting the filament to make the desired piece. It configures the type of HotEnd (V6 or Volcano) and the nozzle depending on the diameter of the material, depending on the type of piece, quality and finish you want to obtain. We classify the extruders in the V6 and Volcano types and then we mention the advantages and disadvantages between these two types of HotEnd.
Advantages and disadvantages of HotEnd V6
Image 4: HotEnd V6 universal 1.75mm. Source: E3D
Advantages:
- The V6 is the most versatile HotEnd on the market, valid for all types of impressions, even for flexible materials (especially with 2.85 / 3 mm filament). With the HotEnd V6 you can make all kinds of parts with an exceptional finishing quality.
Disadvantages:
- The maximum diameter of nozzle recommended for this type of extruder is 0.
 80 mm / 1 mm since for larger diameters, problems of continuity of flow usually occur.
80 mm / 1 mm since for larger diameters, problems of continuity of flow usually occur.
Advantages and disadvantages of HotEnd Volcano:
Image 5: E3D HotEnd Volcano
Advantages:
- Thanks to the parallel position of the Heater Cartridge with respect to the nozzle, a greater heated area is achieved, thus giving great control and stability over the melting of the filament. For all the above you can make 3D prints with larger diameter nozzle (1.2 mm), which leads to shorter manufacturing times and the possibility of printing with a higher layer height than in the V6.
- More resistant pieces. Thanks to making higher layers with a laminar flow (without bubbles) the joints between the chemical bonds of the material are stronger, giving more rigid and resistant parts.
Disadvantages:
- Surface finish of low detail. Due to the high layer heights, the pieces are made with steps in areas where there are curved surfaces at different heights.

Some manufacturers call the HotEnd depending on the extruder system and the filament diameter that you want to use. For example, E3D Online uses the designation "universal" for its 1.75 mm HotEnd (universal direct and universal bowden) in which the TPFE tube reaches the interior of the Heat Break, channeling the filament without interruptions to the heating block. For the 2.85 / 3 mm HotEnd simply use the designation "direct" or "bowden".
Image 6: Types of E3D HotEnd
For our part, we recommend that each user study their particular case based on the type of parts and the speed with which they want to 3D print but always using first-class components that ensure quality in all their products.
Do you want to receive articles like this in your email?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter and you will receive every month in your email the latest news and tips on 3D printing.
* By registering you accept our privacy policy.
How to choose an extruder for a 3D printer
3DPrintStory 3D printing process How to choose an extruder for a 3D printer
Hello friends. Today we will talk about choosing an extruder.
Today we will talk about choosing an extruder.
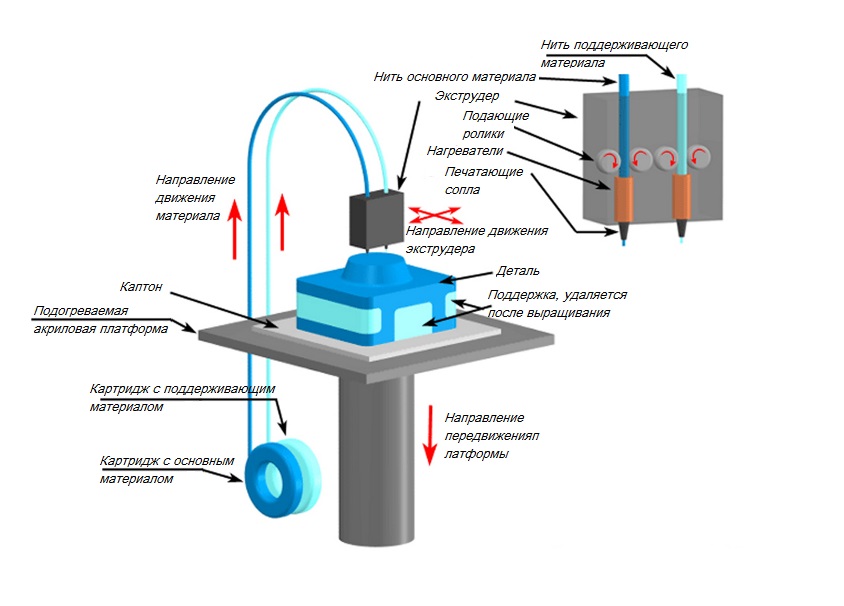
In simple terms, an extruder is a mechanism whose task is to feed molten plastic into the printing zone. It consists of a feeding mechanism and a print head.
Two types of extruders
There are two main types of extruders: bowden (bowden) - in the picture on the left and direct (direct) extruder - in the picture on the right. With a direct extruder, the plastic feed mechanism is located in close proximity to the print head. In bowden - at some distance, connected by a Teflon tube. nine0005
The main advantages and disadvantages of the two types of extruders
Both have their advantages and disadvantages.
In direct extruders, the weight of the stepper motor with the plastic feed mechanism is added to the weight of the printhead. Excess weight will increase the inertial forces when stopping and accelerating the print heads, which can adversely affect the quality of 3D printing, especially at high speeds, and also causes increased wear of the kinematics of the shafts and bearings.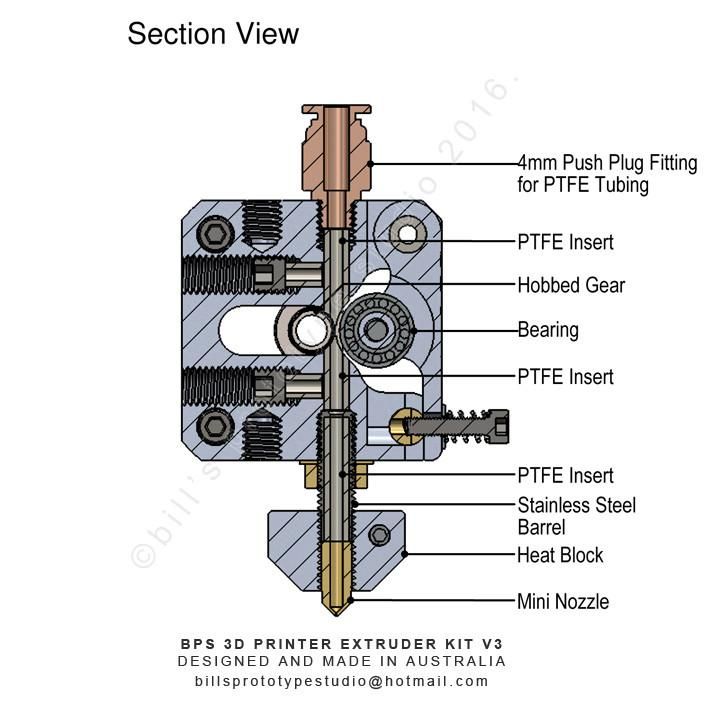 But the supply and rollback of plastic (the so-called retract) is more accurate, which makes tuning easier. nine0005
But the supply and rollback of plastic (the so-called retract) is more accurate, which makes tuning easier. nine0005
Bowden eliminates the disadvantages of direct extruders regarding extra weight, since only the print head runs along the carriage, which makes it possible to print at higher speeds. But in return, we get problems with the exact dosage of plastic, which will complicate tuning and calibration.
Extruder design
All extruder designs are similar and differ only in execution. Let's look at what the extruder consists of using the well-known e3dv6 model as an example.
These are three main nodes: cold end (cold part), hot end (hot part), which are connected by a thermal barrier. nine0005
Hot end consisting of:
- Heating element to melt plastic.
- Measuring element (thermistor) for maintaining the desired temperature.
- Aluminum heating block to house them.
- Nozzle with calibration hole from 0.1 to 0.8 millimeters.
Cold end is:
- An aluminum heatsink with a fan that serves to cool the plastic, preventing it from melting prematurely. nine0038
- Thermal barrier that serves to isolate these two elements from each other. Usually it is a stainless steel sleeve, and sometimes plain steel. Stainless steel is still preferable, since it is no worse than ordinary steel in thermal conductivity. By the way, when buying, pay attention to this! Easy to check with a magnet. With a relatively similar weight, stainless steel is not magnetic. The nozzle, on the contrary, should be made of a material that conducts heat well.
Detailed construction and features of the e3dv6 extruder
In our case, we will consider a bowden extruder based on a Chinese copy of e3dv6.
The Chinese copy works as well as the original, but costs several times cheaper. The difference is only in the quality of processing and the materials used. Please note that there is also an older version of e3dv5. They are very similar in appearance, but still have significant differences. I do not recommend taking e3dv5, since e3 dv6 is an improved version of it. The e3dv5 has a larger heatsink and a slightly different heating block. In e3dv6, the thermistor is placed closer to the nozzle than to the heater relative to e3dv5, which provides more accurate control and maintenance of temperature in the area of \u200b\u200bthe plastic, and not the heater. nine0005
They are very similar in appearance, but still have significant differences. I do not recommend taking e3dv5, since e3 dv6 is an improved version of it. The e3dv5 has a larger heatsink and a slightly different heating block. In e3dv6, the thermistor is placed closer to the nozzle than to the heater relative to e3dv5, which provides more accurate control and maintenance of temperature in the area of \u200b\u200bthe plastic, and not the heater. nine0005
There are versions for different plastic diameters. 1.75 millimeters, which most print or 3 millimeters.
To avoid traffic jams, choose a thermal barrier with a Teflon tube insert for PLA printing. It is smoother and slipperier.
Solid metal is more suitable for printing with nylon, ABS or other plastics that require a higher printing temperature, since the Teflon tube in the middle is already destroyed at a temperature of about 200 degrees. On the Internet they write that the all-metal barrier in the original prints with all types of plastic, since the hole in the middle is well polished and smooth, unlike the Chinese counterpart, in which the hole was drilled with a conventional drill without additional post-processing. nine0005
nine0005
I hope you found the information useful. Thank you for your attention, see you again in the world of 3D printing.
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
We all know that precise calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them. Many will say that it is wrong to compare them or Read more→
XYZprinting, best known for its daVinci line of desktop 3D printers, is bringing five new devices to the professional and industrial environment.