3D printer freezes mid print
How to Fix 3D Printer Pausing or Freezing During Print – 3D Printerly
A 3D printer that pauses during the printing process can definitely be frustrating and can ruin the whole print. I’ve had this happen a few times so I decided to look into why this is happening and write an article to help other people.
To fix a 3D printer pausing during print, you want to ensure there aren’t mechanical issues like the extruder being clogged or a loose connection with the PTFE tube and hotend. You also want to check for heat issues that can cause clogs like heat creep, as well as connection issues with the thermistor.
There’s some more useful information that you’ll want to know so keep on reading to find out more about your 3D printer pausing during the print.
Why Does My 3D Printer Keep Pausing?
A 3D printer pausing or stopping during a print can be due to several reasons depending on your specific situation. It really comes down to narrowing what issue you are having by going through a list of checks and solutions until you find the one that works for you.
Some reasons are more common than others, but it shouldn’t be too difficult to figure out why your 3D printer keeps pausing or randomly stops.
Here is a list of reasons I could find.
Mechanical Issues
- Bad quality filament
- Extruder clogged
- Filament path issues
- PTFE tube connection with hotend loose or has a gap
- Dirty or dusty extruder gears
- Cooling fans not working properly
- Filament spring tension not set correctly
- Filament sensor error
Heat Issues
- Heat creep
- Enclosure too hot
- Incorrect temperature settings
Connection Issues
- Printing over Wi-Fi or computer connection
- Thermistor (Bad wiring connections)
- Power supply interruption
Slicer, Settings or STL File Issues
- STL file resolution too high
- Slicer not processing files properly
- Pause command in the G-code file
- Minimal layer time setting
How Do I Fix a 3D Printer That Keeps Pausing or Freezes?
In order to make this easier to fix, I’ll group some of these common reasons and fixes together so they are of a similar nature.
Mechanical Issues
The most common causes of a 3D printer that pauses or stops during the printing process is down to mechanical issues. This ranges from problems with the filament itself, to clogs or extrusion pathway issues, down to bad connections or cooling fan issues.
The first thing I would check is that your filament isn’t causing the problem. It can be down to bad quality filament that maybe has absorbed moisture over time, making it more prone to snapping, grinding, or just not printing very well.
Changing your spool for another fresher spool may fix the issue of your 3D printer pausing or shutting off mid-print.
Another thing you want to do is to make sure your filament flows through the extrusion pathway smoothly, rather than with resistance. If you have a long PTFE tube with many bends, it can make it harder for the filament to feed through the nozzle.
One issue I had, was that my spool holder was a little far from the extruder so it had to bend quite a bit to get through the extruder. I fixed this by simply moving the spool holder closer to the extruder and 3D printing a Filament Guide on my Ender 3.
I fixed this by simply moving the spool holder closer to the extruder and 3D printing a Filament Guide on my Ender 3.
Look out for any clogs in your extruder as this can start to build up and cause your 3D printer to stop extruding mid print or pausing during the print.
One lesser known fix that has worked for many is to ensure the PTFE tube connection with your hotend is properly secure and doesn’t have a gap between the tube and the nozzle
When you put together your hotend, a lot of people don’t actually push it all the way into the hotend, potentially causing printing issues and clogs.
Heat up your hotend, then remove the nozzle and pull the PTFE tube out. Check if there is residue inside the hotend, and if there is, remove it by pushing it out with a tool or object like a screwdriver/hex key.
Make sure to check the PTFE tube for any sticky residue at the bottom. If you find some, you want to cut the tube from the bottom, ideally with PTFE Tube Cutters from Amazon or something sharp so it cuts nicely.
You don’t want to use something that squeezes the tube like scissors.
Here’s a video by CHEP explaining this issue.
Try cleaning up any dusty or dirty areas like the extruder gears or the nozzle.
Check that your extruder spring tension is set correctly and isn’t too tight or loose. This is what grips your filament and helps it move through the nozzle during the printing process. I wrote an article called Simple Extruder Tension Guide for 3D Printing, so feel free to check that out.
Here is an extruder troubleshooting video to help out with some of these mechanical issues. He talks about the extruder spring tension and how it needs to be.
Another thing to watch out for is your filament sensor. If the switch on your filament sensor isn’t functioning properly or you have issues with the wiring, it can cause your printer to stop moving mid-print.
Either turn this off and see if it makes a difference or get a replacement if you find out this is your issue.
Mechanically check the parts of your 3D printer and make sure they are in good order. Especially the belts and idler pulley shaft. You want the printer to be able to move without any snags or unnecessary friction.
Tighten the screws around your 3D printer, especially around the extruder gear.
Check that your wires aren’t catching on anything if you find your prints are failing at the same height. Check your extruder gear for wear and replace it if they are worn out.
One user experience a misaligned idler bearing in the extruder. If that bearing is shifted, it can cause friction against the filament, preventing it from flowing easily, essentially pausing the extrusion.
As shown in the picture below, the idler bearing was misaligned due to the handle it was attached to being misaligned.
You may need to take your extruder apart, check it, then reassemble it.
Heat Issues
You could also experience pauses or 3D prints messing up half way during your 3D prints because of heat issues. If your heat is travelling too far up the heatsink, it could cause filament to be softening where it shouldn’t leading to clogs and jams in the printer.
You’d want to reduce your printing temperature in this case. Another few fixes for heat creep is to decrease your retraction length so it doesn’t pull soft filament back too far, increase the printing speed so it doesn’t heat the filament for too long, then make sure the heat sink is clean.
Ensure your cooling fans are working nicely to cool the right parts down because this can also contribute to heat creep.
Another less common fix that has worked for some people is to make sure their enclosure doesn’t get too hot. If you are printing with PLA, it is quite sensitive to temperature so if you use an enclosure, you should try opening up a small section of it to let some of the heat out.
Using an enclosure & temperature gets too hot, leave a gap in the enclosure so heat can escape. One user took the top off his cabinet enclosure and everything printed properly since doing so.
Connection Issues
Some users have experience connection issues with their 3D printer such as printing over Wi-Fi or a computer connection. It’s usually best to 3D print with a MicroSD card and USB connection inserted into the 3D printer with the G-code file.
You shouldn’t usually have issues printing over other connections, but there are reasons why it can cause a 3D printer to pause during printing. If you have a weak connection or your computer hibernates, it can stop sending data to the 3D printer and ruin the print.
If you have a weak connection or your computer hibernates, it can stop sending data to the 3D printer and ruin the print.
Printing over Wi-Fi can cause issues if you have a bad connection. It could be the baud rate on the connection or the com timeout settings in a software like OctoPrint.
You may also be experiencing wiring or connection issues with thermistor or cooling fan. If the thermistor is not fitted correctly, the printer will think it’s at a lower temperature than it actually is, causing it to increase in temperature.
This can cause printing issues which lead to your 3D print failing or your 3D printer clogging then pausing.
There is a possibility that you had a power supply interruption during the printing process, but if you have the print resume function like most 3D printers, this shouldn’t be too much of an issue.
You can simply resume from the last printing point after you turn the 3D printer back on.
Slicer, Settings or STL File Issues
The next set of issues comes from the STL file itself, the slicer, or your settings.
Your STL file could have a resolution too high, causing issues since it will have a lot of short segments and movements that the printer may not be able to handle. If your file is really large, you could try exporting it to a lower resolution.
An example would be if you have an edge of a print that has very high detail and contained 20 small movements within a very small area, it would have many instructions for movements, but the printer wouldn’t be able to keep up so well.
Slicers can usually account for this and override such instances by compiling the movements, but it may still create a pause during printing.
You can reduce polygon count by using MeshLabs. One user who repaired their STL file through Netfabb (now integrated into Fusion 360) fixed an issue with a model that kept failing at a specific area.
There could be a slicer issue where it cannot properly handle a certain model. I’d try using a different slicer and seeing if your printer still pauses.
Some users experienced their 3D printer pausing during a print due to having a minimum layer time input in the slicer. If you have some really small layers, it could create pauses to satisfy the minimum layer time.
One last thing to check is that you don’t have a pause command in the G-code file. There is an instruction that can be input into files that pause it at certain layer heights so double-check you don’t have this enabled in your slicer.
How Do You Stop or Cancel a 3D Printer?
To stop a 3D printer, you simply use the control knob or the touchscreen and select the “pause print” or “stop print” option on the screen. When you click the control knob on the Ender 3, you will have the option to “pause print” by simply scrolling down on the option. The print head will move out the way.
The video below shows you what this process looks like.
3D Printer Freezes Mid Print: Troubleshooting Guide » FuturTribe
Why 3D Printer Freezes Mid Print and how to solve this problem? We will learn it in this article.
A 3D print ruined because the 3D Printer has stopped in the middle of the printing process3D Printer Freezes Mid Print: Introduction
What to do when the 3D printer freezed mid print, stopping the extrusion of plastic?
3D Printer Freezes Mid Print
At first your 3D printer works correctly and reliably, but then it stops abruptly and in the middle of 3D printing. In the following we explain the most common causes and you will get solutions for solving the most numerous problems. If your 3D printer has problems with material extrusion, please read the section on stopping the extrusion
3D Printer Freezes Mid Print: Troubleshooting
The filament is all
Granted, this problem is pretty obvious, but you should first check that there is enough filament in your 3D printer. If your spool of filament is empty, please insert a new material. In the best case, your 3D printer has a filament run-out sensor and detects a leakage of the filament, stops your 3D printing and you can insert a new spool.
If your spool of filament is empty, please insert a new material. In the best case, your 3D printer has a filament run-out sensor and detects a leakage of the filament, stops your 3D printing and you can insert a new spool.
Filament abrasion in places
During a 3D print, the extruder motor turns constantly. It conveys the filament and pushes it through a hole in the nozzle, which extrudes the liquefied plastic. If you are trying to print quickly, a lot of liquid plastic has to flow through the narrow hole. This can overload the extruder motor and drag away filament. This continues until there is no more material left for the drive wheel to grip. If the extruder motor is spinning but the filament is not being drawn in, grinding is probably the cause.
Clogged extruder
If none of the reasons mentioned above apply, the extruder is very likely blocked. Check the filament for cleanliness and make sure there is no dust on the spool or material. The large amount of dust on the filament can collect inside the nozzle and clog it. There are several other possible causes of a locked extruder.
There are several other possible causes of a locked extruder.
The extruder motor driver has overheated
The extruder motor works incredibly hard during the 3D printing process. It constantly turns back and forth to push the filament in or out. These fast movements require a lot of electricity. If the electronics of the 3D printer are not sufficiently cooled, the motor driver electronics can overheat. The motor drivers mostly have thermal shutdowns, which switch off the motor at too high temperatures. In this case, the X and Y axis motors rotate and move the extruder tool head, but the extruder motor does not move at all. The only solution to this problem is to turn off the 3D printer and let the electronics cool down. Additional ventilation of the driver also helps to solve the problem.
3D Printer Freezes Mid Print: Conclusions
We hope we helped you solve the problem for which your 3D Printer freezes mid print 🙂
If you have any question or suggestion, don’t hesitate to leave a comment below
3D printing is far from having reached its peak. Many projects and amazing achievements are waiting to be discovered. Stay up to date and follow our 3D printing blog!
Many projects and amazing achievements are waiting to be discovered. Stay up to date and follow our 3D printing blog!
Read More:
What to do if the 3D printer stops? How to continue printing
There are situations when for some reason the 3D printer has stopped printing. And for many, this is a problem, because if a couple of layers were printed, then you can start printing again and it's not expensive. But if the model was printed halfway or even more, then spending time again on a new print, wasting material again is too expensive.
There may be a number of reasons why printing has stopped:
- commonplace power outage;
- printer failure;
- clogging of the extruder nozzle;
- layer peeling and other incorrect printing problems.
Not all printers have the option to resume printing from a specific location. Moreover, they are currently in the minority. And so you have to solve all the problems yourself.
This material is devoted to this problem. We will look at Gcode and a universal way to continue printing from a specific layer. nine0003
How does 3D printing software work?
This is the first question to be dealt with. Any 3D printer works on the same principle, regardless of the printing technology. The model is first divided into a large number of the thinnest horizontal layers parallel to each other. If printing is carried out using FDM, DLP technologies, then each layer is divided into many lines, which, as it were, are drawn by a print head or a laser. In the case of DLP technology, each layer is a bitmap, which is highlighted immediately. In this case, the line width for the FDM printer will be the diameter of the nozzle selected for printing, and the height will be set by the layer thickness. That is, a certain route is set for the extruder, so to speak, a map along which it will form a layer. This map will be presented as a specific set of commands. It is this set that is called GCode. This code is generated by special programs in automatic mode. These programs are called slicers. They cut the model into layers according to the given parameters and form the GCode. Prominent representatives of such programs are Cura, Slick3r and others. nine0003
It is this set that is called GCode. This code is generated by special programs in automatic mode. These programs are called slicers. They cut the model into layers according to the given parameters and form the GCode. Prominent representatives of such programs are Cura, Slick3r and others. nine0003
In G-code, each printhead path vector is specified by Cartesian coordinates. In addition, the code file contains a number of other information:
- movement speed;
- temperature;
- extrusion speed, etc.
Initially, GCode was developed specifically for CNC machines, so it can contain a variety of functions, commands. However, for 3D printers, GCode is much easier.
Slicers that work with 3D printers that print using SLA technologies, DLP work on a slightly different principle, and the generated code itself will contain slightly different information, since the plastic is not extruded, it is not the print head that works, but the laser controlled by projectors, galvanometers, mirrors, etc. In DLP, in general, the entire layer is illuminated at a time, that is, with a single spot. nine0003
In DLP, in general, the entire layer is illuminated at a time, that is, with a single spot. nine0003
Resuming printing with Cura slicer on FDM printers
Consider the process of resuming printing using the example of benchy, a well-known 3D model. And the first advice is that you should not move an underprinted model, since it will not work to install it in the same place with an accuracy of millimeters.
This method allows not only to resume printing from a certain place in case of failure or force majeure, but also when printing a model with one extruder, but with different materials or plastic of different colors. To do this, you first need to make GCode in manual mode, and during printing, stop the machine and change the thread. nine0003
So, the first step is to measure the height of the resulting product. To do this, you need to use a digital caliper. The more accurate the metering, the less noticeable will be the place where printing was paused.
The second step is to use the Cura slicer to find the correct layer for the height of your print. In our case, the height was 12mm. Printing was carried out at a layer thickness of 0.15 mm. So in GCode this data will correspond to layer number 80.
In our case, the height was 12mm. Printing was carried out at a layer thickness of 0.15 mm. So in GCode this data will correspond to layer number 80.
The SciTE program is used to edit sources. We use it for the next step - we open our GCode in it. This software is simple and intuitive. When opening a file with a code, be sure to select "All files".
The next step is to find layer 80 in GCode. To do this, declare a search: "Sear > Finde > LAYER:80".
The cursor is positioned at the end of layer 79. While holding SHIFT, move to the beginning of layer 1 and click on it. As a result, everything that corresponds to the already printed area will be selected. Delete the selected area. Next, you need to save the result and, if necessary, manually prescribe the resolution. nine0003
As a result of these manipulations, you get a new GCode, according to which printing will start from the layer you need. This code needs to be checked in Cura.
Slicers that are designed for printing using SLA, DLP technology, support the function of resuming printing from the right place if it is interrupted.
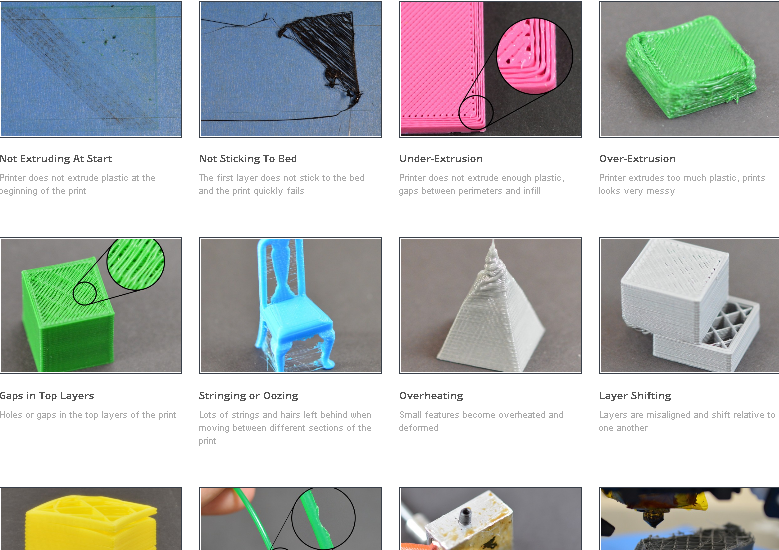
12 common 3D printing mistakes from easy to hard. How to avoid them?
1. Underestimation of the importance of the first layer. 2. Don't ask the 3D printing communities for help. 3. Random entanglement of the filament. 4. Fast assembly of your 3D printer. 5. Incorrect table and nozzle height calibration. 6. Using the wrong slicer settings. 7. Using a high % infill to reinforce details instead of walls/shells. 8. Don't use support when needed. nine. Never replace worn parts. 10. Lack of 3D printing monitoring. 11. Neglect of safety rules in 3D printing. 12. Buying a bad 3D printer out of over-enthusiasm. Conclusion.
There's nothing worse than 3D printing for days, weeks, months and years only to find out you're making common mistakes.
We're sure many of you are familiar with that feeling, which is why we've written this post to get you back on the road to success by outlining some common mistakes to avoid on your 3D printing journey. nine0003
Here you will find both small errors that you did not pay attention to before, and serious errors that can lead to a complete cessation of 3D printing.
Join our research to identify the most common 3D printing mistakes, as well as simple solutions to fix them quickly.
1. Underestimation of the importance of the first layer.
Too often 3D printing fails in the middle of the process due to poor adhesion of the first layer.
Definitely keep this important factor in mind if you want a successful print. nine0087 This is a mistake that is made too often, and it causes people to chase ghosts, trying to figure out what the problem is.
All this time, the reason was the bad first layers, which did not have a strong enough connection with the working platform.
Although your first layer is held at the start of printing, adhesion decreases as the print head moves. It is likely that your print may shift or fall off after a few hours if the first layer was not well extruded. nine0003
Solution .
- Make a few test prints ahead of time and see how well the material adheres.
- Use an adhesive such as 3D Printer Varnish or at least a glue stick.
- Increase the flow rate (extrusion multiplier) for the first layer so that the material has a better chance of sticking to the printer bed.
2. Do not seek help from the 3D printing communities.
Every user of a 3D printer has encountered a problem that required some effort to fix. Some people took on entire projects just to solve a 3D printer problem, when the solution was easy to find. nine0003
3D printing communities are known for helping people solve their problems, so be sure to check out these free resources. From 3D printing forums to Facebook groups and YouTube surveys of other 3D printer users, the options are endless.
When we first started exploring 3D printing, we noticed that many people mention how helpful other 3D printer users are, so we immediately registered on all kinds of Russian and English resources, Facebook and Reddit communities and joined this space . nine0003
nine0003
In most cases, people will offer the right solution and will be happy to help you try various troubleshooting options.
Not only can they help you with troubleshooting, but they can point you to some fun projects to try, as well as some of the latest innovations in the world of 3D printing.
Solution .
- Join active Facebook groups on 3D printing and your specific 3D printer. nine0008
- Subscribe to news feeds of authoritative 3D printing resources.
- Be sure to check out YouTube 3D printing bloggers who post new and interesting content on a regular basis.
- Find groups in Viber and Telegram. This is the fastest way to get an answer to your question.
3. Random entanglement of the filament.
We have read many reviews about 3D printer materials including PLA, ABS, PETG, etc. and some of the negative reviews mention tangled filament. nine0003
Unfortunately, in most cases, the thread becomes tangled due to the fault of users.
As a general rule, when the thread is wound onto the spool, there is very little chance of tangling, much more often after you take the spool out of the package.
If you loosen the windings in the winding and then rewind the deflated windings on the spool, you could accidentally wind them unevenly and create an overlap that will ruin your prints.
Solution .
When storing the filament, make sure that the end is securely fastened and cannot be easily loosened.
If there are already tangles on the spool, unwind enough thread and wind it tightly again so that it does not cross over.
If you are still unlucky, and you have purchased plastic of inadequate quality, during the production of which all technological cards were violated, then here is our advice: buy plastic for a 3D printer from trusted brands. The $100 price difference is infinitesimal compared to all sorts of other 3D printing costs. nine0003
However, this 100 UAH will save you not only from problems with overlaps, but also provide a stable diameter and color along the entire length, the absence of ovalities and smooth feeding.
4. Quick assembly of your 3D printer.
We were all very excited when we got our first 3D printer and it came to building it, but being overly excited can cause your 3D printer to build too quickly, resulting in poor print results.
This may not be immediately noticeable and you will get good quality prints within a few months. nine0003
What can happen gradually is wear due to incorrect assembly.
Ask yourself these questions before starting your first print.
Was your belt tight? Did you properly and securely fasten each wire? Is the Bowden tube installed correctly?
When it comes to a 3D printer, every little detail counts, so don't fall prey to 3D printing problems because of a quick and careless build.
Solution .
Find an authoritative YouTube video tutorial from an experienced 3D printer operator and follow assembly. nine0087 There are always a few little tricks they advise you to do for durability and high quality prints.
Even if you have already built your 3D printer, you can fix some things you may have missed.
The correct and high-quality assembly of a 3D printer actually leads to higher quality prints.
See also: How to set up your new 3D printer.
5. Incorrect table and nozzle height calibration.
Of all the layers in your 3D print, the first layer is the most important and it depends a lot on how well you leveled your platform and set your nozzle height. nine0003
It's not as easy as uploading a 3D model, sending it to an SD card and starting printing.
The software side of things is important, but the hardware side is just as important.
Many 3D printers come with manual platform calibration, so you have to raise or lower each corner yourself.
Your 3D printer doesn't have a perfect feedback system, which means it can't always check where the print head is.
The best he can do is use the X, Y and Z limit switches to make sure the printhead is 0. 00mm in each axis. nine0003
00mm in each axis. nine0003
What your 3D printer is very good at is extremely precise movements in the X, Y and Z axes, but if the nozzle height is not set properly at the beginning, everything falls apart.
The Z axis is height, so the nozzle must be properly adjusted so that it smoothly extrudes the filament along the surface of the build, neither too high nor too low.
Solution .
- Learn how to manually calibrate the table.
- Once your table is properly calibrated and the nozzle height adjusted, you can expect good prints. nine0008
- It might be a good idea for you to invest in an auto leveling system like BLTouch. We at our 3D printing studio in Odessa prefer manual calibration.
6. Using incorrect slicer settings.
The slicer settings you use for printing are some of the most important things when it comes to successful 3D printing.
Of the hundreds of setting changes you can make, one wrong setting is enough to ruin your print.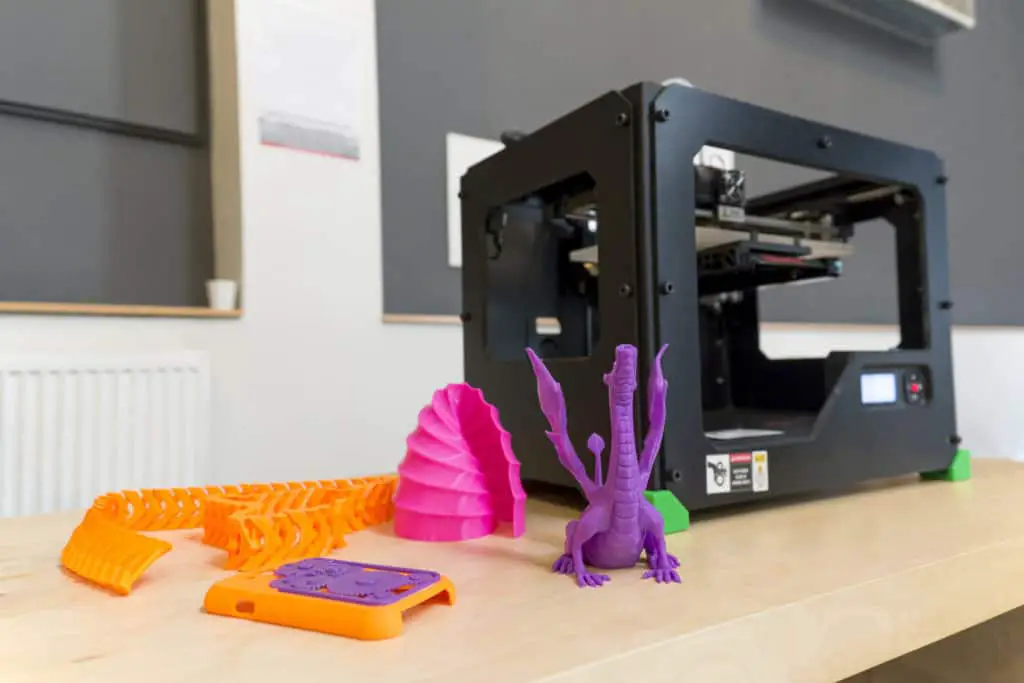 nine0003
nine0003
Fortunately, there are printer profiles and default settings that give people a basic starting point for printing.
After a few prints, you will start experimenting with different settings such as temperature, line width, flow rate, and so on.
Some of the misapplied misconfigurations are related to changing materials.
Whether PLA or ABS or PLA of different brands and/or colors, temperature recommendations will vary. nine0003
Make sure you set them correctly.
Slicer settings can either help you or break your 3D printing, so use them wisely, preferably with some kind of guide.
In most cases, when you load a model from Thingiverse, for example, designers create a list of settings that generally work well, but don't blindly follow them and be careful.
For example, if you replaced a brass nozzle with a hardened steel nozzle, you would need to slightly increase the nozzle temperature because hardened steel does not conduct heat as well as brass. nine0003
nine0003
Another example is your work surface.
If you have added a glass substrate to your 3D printer, you should increase the table temperature to allow for the extra layer of heat transfer material.
Solution .
- Use calibration models such as speed and temperature towers for each new material.
- Spend a little more time looking at the slicer options to make sure you know what changing a setting will do. nine0008
- Repetition is the mother of learning. The more often you type, the faster you will become a pro.
Read also: The best models for 3D printing testing.
7. Using high % infill to reinforce details instead of walls/shells.
For years, most people have tried to reinforce their 3D printed parts with infill. This method definitely does the job, but there is a much more efficient method that has been proven to work much better. nine0003
Instead of wasting a lot of material and extra time printing the infill, you should use shells/walls to make the 3D printed part stronger.
In some cases, increasing the percentage of filling does not provide the necessary margin of safety, while increasing the wall thickness makes it possible to produce truly reliable and impact-resistant products.
Solution.
- Instead of adding more infill, add more shells/walls to your prints to make them stronger. nine0008
- For a functional 3D printed part requiring strength, about 4-6 walls are recommended.
8. Do not use supports when necessary.
Most people try to avoid the use of auxiliary supports to save time and material, but there are times when their use is necessary.
You can try tilting the prints in a certain way and moving them around the print bed, but sooner or later there will come a point when this approach doesn't work. nine0003
Many models are specially designed not to use support for successful printing, which is very convenient.
On the other hand, some designs are too complex to print without support.
3D printers cannot print in the air and large ridges definitely need support structures to extrude the material onto.
Most often you can do without supports on 45° or lower overhangs, but for anything higher it is recommended to use supports. nine0003
This is more of a visual skill that, with time and experience, allows you to understand when models need supports and when you can do without them.
Some slicers may not show support in preview, so you'll have to judge for yourself.
Solution.
- Make sure you don't avoid supports when they are needed, because in this case you will just lose overall. nine0008
- Use proper part orientation to ensure that your prints use as little backing material as possible.
9. Never replace worn parts.
Although the profile, power supply and stepper motors of your 3D printer are designed to last for several years, other parts are consumables.
These are parts such as belts, nozzles and bearings. Make sure you replace these parts as they wear out.
Make sure you replace these parts as they wear out.
You may notice a decrease in print quality over time, and wear and tear on certain parts can definitely be the cause, so check these consumables and replace them as needed. nine0003
If you are printing with materials such as ABS, PA12, PC or glow-in-the-dark plastics, the brass nozzles wear out much faster than when printing with traditional materials.
Switching to a hardened steel nozzle is a good idea if you want to print with abrasive materials.
The disadvantage is that it does not have the same level of thermal conductivity as brass nozzles.
Here is a short list of 3D printer parts that wear out over time:
- Thermal barrier;
- PTFE tube;
- Fans;
- Wires/connectors;
- Thermistors;
- Belts;
- Glass platforms;
- Bearings;
- Heating block;
- Motherboard.
You can buy accessories for 3D printers in the corresponding section of our catalog.
Solution.
- Be aware that some parts will not last forever, so check these parts from time to time and replace them as needed. nine0008
- Make sure these components are installed in a way that reduces wear.
- Keep a set of replacement parts on hand in case they fail (nozzles, belts, wiring, PTFE tubing).
- Purchase high quality parts designed for long service life.
10. No 3D printing monitoring.
Whether you have a premium or budget 3D printer, any of them can fail. They can fail within the first few minutes when the first layer is not printing well, or a few hours after printing starts. nine0003
In our practice, there have been a few cases when checking our printers after a night shift, we found a mess on the work surface and the printer continued to extrude spaghetti plastic.
Monitoring is not a panacea for all problems, but with its help you can stop the process in time and avoid waste of plastic and electricity.
It is recommended to constantly monitor your 3D printers throughout the printing process to make sure everything is in order. nine0003
What we make sure to do is monitor the first coat and then come back 15 minutes later to make sure everything is going according to plan.
After that, checking the printers every hour or so is a good idea to control your prints.
Solution.
- Check the 3D print from time to time to make sure everything goes smoothly.
- Use the camera for remote fingerprint verification in conjunction with remote power control. nine0008
- Be sure to teach others how to stop your 3D printer if necessary.
11. Neglect of safety regulations in 3D printing.
Basic safety precautions are based on burn and fire hazards, mechanical hazards, and injury from tools or melted plastic.
The risk of fire is very rare these days because 3D printers are usually equipped with overheating protection.
Pay attention to burns from hot nozzle or print bed. nine0003
We've also heard stories of injuries from the sharp edges of the printer's scraper.
This can be easily avoided if you are careful in your actions.
Removing supports is not the most pleasant and interesting thing to do, but getting cuts or scratches when cleaning parts is even worse.
It is recommended to check the wiring, bolts, belts and all moving parts from time to time so that a potential malfunction can be detected in the future. nine0003
Connectors can sometimes fail, so be sure to check these aspects to ensure the 3D printing process runs smoothly and safely.
Solution.
- Be aware of your surroundings and be safe.
- Do not put your hand too close to the nozzle.
- Do not keep your hand on the platen when taking the print.
- Provide good ventilation.
12. Buying a bad 3D printer out of over-enthusiasm.
 nine0083
nine0083 We are regularly contacted by clients who, on a wave of enthusiasm, bought a cheap 3D printer on Aliexpress or other market place, and this printer does not work.
Spontaneous cheap purchases do not give you time to analyze and compare 3D printer models. In other words, you are making your choice unconsciously.
People have experienced a number of problems, such as the SD card slot not working along with serious difficulties in transferring files over Wi-Fi.
Other options included poorly insulated wires, crooked frames and platforms. nine0003
Deformed threaded screws, cheap hot ends, broken parts, poor shipping packaging, poor assembly at the factory are also common when buying cheap "NoName" printers.
You may end up spending most of your time repairing, fixing poor print quality issues, and just getting frustrated with 3D printing.
If you've been one of those unlucky ones, you've probably learned to take your time buying a 3D printer. nine0003
nine0003
One of the most popular manufacturers of inexpensive 3D printers around the world is Creality, and their top product Ender-3 v2.
This 3D printer has been tested many times by users around the world, and its popularity proves to be the perfect combination of price and quality.
Every 3D company is a team that buys parts and builds a printer, but some do it much better than others and more consistently.
Some people who buy a bad printer either give up 3D printing, do a complete costly rebuild, or buy a better 3D printer much later. You might as well start by buying a good 3D printer! nine0003
Solution.
Choose a reliable 3D printer with a good reputation and avoid 90% of avoidable problems. We know a lot of stories about people going through the same thing, so save yourself the hassle.
We have never seen anyone call the Ender 3 Pro or the Voxelab Aquila X2 a bad first 3D printer because it really is a very good buy.