3D printer careers
9 Great 3D Printing Jobs
- 3D printing is a technology that creates a three-dimensional object using a computer-aided design (CAD).
- The 3D printing industry is rapidly growing thanks to its ability to create a wide range of versatile products in a fast, cost-effective way.
- For job seekers, the 3D printing industry offers some cool jobs on the cutting edge of the technology.
- This article is for professionals and entrepreneurs who want to work in the 3D printing industry.
President Barack Obama once said 3D printing has the “potential to revolutionize the way we make almost everything.” For that reason, the 3D printing industry was valued at $13.78 billion in 2020. And market research projections suggest it will continue its meteoric growth through 2028 – when it is expected to reach an estimated $59.65 billion.
As the 3D printing industry booms, what does it mean for job seekers? Here are 9 opportunities that will be created or get a boost from 3D printing.
What is 3D printing?
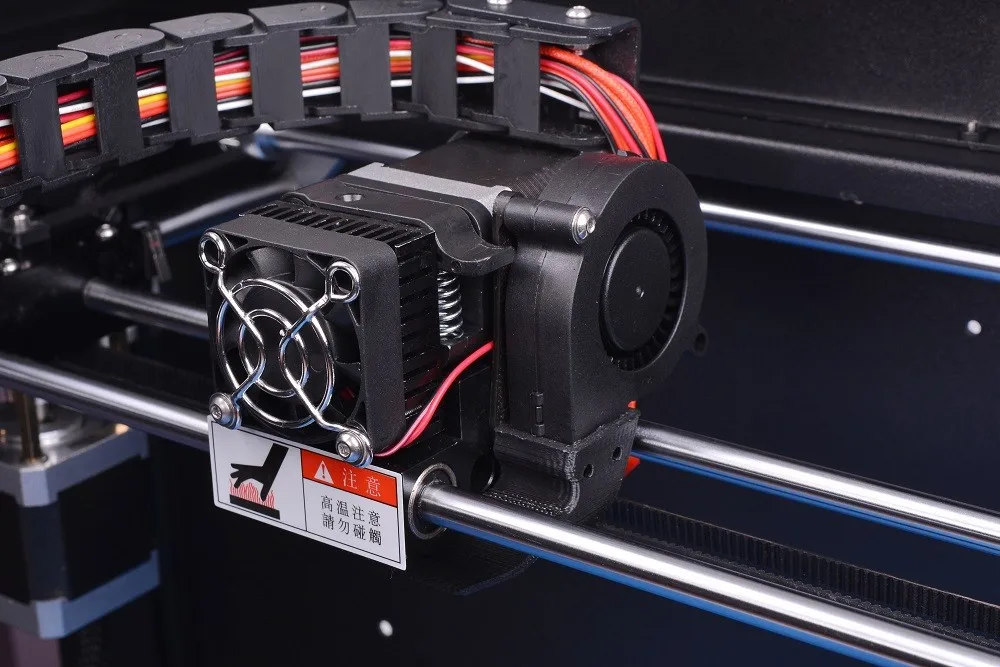
Rather than using ink and paper, a 3D printer uses materials like plastic, metal or ceramic to create a 3D model. By using computer-aided design (CAD) files as digital instructions to create an object, a 3D printer repeatedly covers a work surface with layers of material in precisely the right spots to create a structure from scratch.
While 3D printing can be used for large-scale structures, 3D printing is most useful in creating smaller, customized parts or prototype components for various uses – including automotive engineering or the medical industry. With the versatility of 3D printing, it’s a field that’s filled with opportunities. Let’s take a look at some of the areas 3D printing is being used today.
3D printing jobs
1. 3D design
3D printing relies heavily on designers who can take a product idea and bring it to life. Thanks to its growth, 3D printing will create jobs for 3D designers at 3D printing firms, in companies as part of creative teams and as freelancers.
3D printers are being used in many design disciplines – such as product design, medical device design, architectural visualization and entertainment design, said Erol Gunduz, a professor at New York University’s School of Continuing and Professional Studies (NYU-SCPS), which offers programs in 3D printing, design and modeling.
To be competitive, job seekers should gain hands-on experience in 3D technologies and stay current on how companies are using 3D printing. For instance, recent graduate student designers and researchers who are familiar with 3D printing methods have the benefit of knowing how to use the technology within their design process, Gunduz explains.
“This gives them a significant advantage when looking for career opportunities within creative fields,” Gunduz said.
Did you know? 3D printers can create replacement parts for the human body, among the many things that 3D printers make.
2. 3D CAD modeling
3D printing would not be possible without CAD experts who have the skills to convert product designs into digital blueprints that the printers need. Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
Along with product designers, there will be a demand for 3D CAD modelers.
“I see a lot more demand for CAD and 3D modeling jobs on the horizon because of 3D printing,” said Alex English, owner of ProtoParadigm. ProtoParadigm is a 3D printing business that also performs research and development on 3D printing hardware and new printing materials.
Although 3D CAD professionals are also needed to construct models for mass 3D printing, they are especially important for custom products.
“Bespoke manufacturing and custom prototyping both rely on the user’s ability to conceptualize the object they want and accurately create its digital representation,” English said.
Consequently, 3D CAD modeling jobs will require printing-specific modeling skills, such as feature size, geometrical constraints and knowledge of materials, English added.
3. Research and development
3D printing is all the buzz – and not just in the gadget world. Just as the 3D printing industry will require more product designers and CAD modelers, jobs will open up for forward-thinking research and development professionals who understand the intersection of tech and consumer products.
“While 3D visualization technologies have been used in the past within various fields, such as engineering and scientific agendas, many artistic and consumer product industries – such as fashion design and jewelry design – are beginning to take advantage of 3D printing systems,” Gunduz said.
Companies will need people who can find the best way to utilize 3D printing for consumer products at the lowest cost possible.
“The ability to visualize a line of fashion accessories or jewelry designs before committing to working with expensive materials affords an advantage for companies to reduce costs in development cycles,” Gunduz said.
Tip: Is your business experimenting with 3D printing research and development? Consider these tax credits that are available to companies performing cutting-edge research.
4. Biological and scientific modeling
3D printing is not limited to consumer products; it creates many products that promote medical advancement and save lives. It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
It can also create drone and defense equipment, and possibly even space food.
Accordingly, the 3D printing industry will need more engineers, designers and modelers who have a biomedical or scientific background to further innovate and produce highly advanced 3D-printed products.
“While all manner of designers will be able to print the things they design, there will be a high end to the market – particularly in medical, aerospace, military, and other high-precision or mission-critical applications – for those that better understand the printing technologies and how to design for their strengths and limitations,” English said.
5. Architecture and construction modeling
3D printing will disrupt various industries, particularly those that rely heavily on blueprinting or prototyping. For the construction industry, this paradigm shift will boost the need for 3D modelers that may replace current 2D construction planning solutions.
“In the architecture, engineering and construction industries, 3D printing will redefine the production of construction documents,” said Lira Luis, chief collaboration architect at Atelier Lira Luis LLC, a Chicago-based architecture and design firm.
Instead of 2D CAD modeling on paper, 3D printing can produce true-to-life models to better represent what structures will look like.
“As the 3D printing process becomes more streamlined, it could potentially eliminate the need for construction documents and move directly to printing full-scale mock-ups prior to construction of structures,” Luis said.
6. Education
What good are these jobs if no one has the qualifications to fill them? To help fill the skills gap, schools are developing – and some have already launched – 3D printing programs at all grade levels. This will open up jobs for educators who can teach the technical and business aspects of 3D printing.
“From an educational perspective, many K-12 schools are looking to 3D printing as a point of exposure for students within the arts as well as scientific areas of study,” Gunduz said. Colleges and universities are also launching 3D printing courses and certificate programs, such as NYU-SCPS’ certificate in 3D printing rapid prototyping.
Teachers will need to have a background in the 3D printing industry. They will also need specific skill sets to teach specialized courses and stay current on the latest trends.
“For educators, having an understanding of 3D modeling and 3D printing techniques will be invaluable, as the culture of fab labs is starting to gain support as an important aspect of education,” Gunduz said. “Teachers with 3D modeling and fabrication experience have a range of opportunities open to them within educational programs looking to incorporate this new technology.”
7. Legal professionals
3D printing is not confined to the tech world. As a creative field, the industry is wide open to legal issues, prompting a need for more lawyers and legal professionals who specialize in intellectual property (IP) rights.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become more widely accessible, it will be easier for infringers to create, market, and sell products that infringe patents, copyrights, and valuable brands,” said Julie Matthews, partner at Edwards Wildman – an Am Law 100 firm with offices in the U.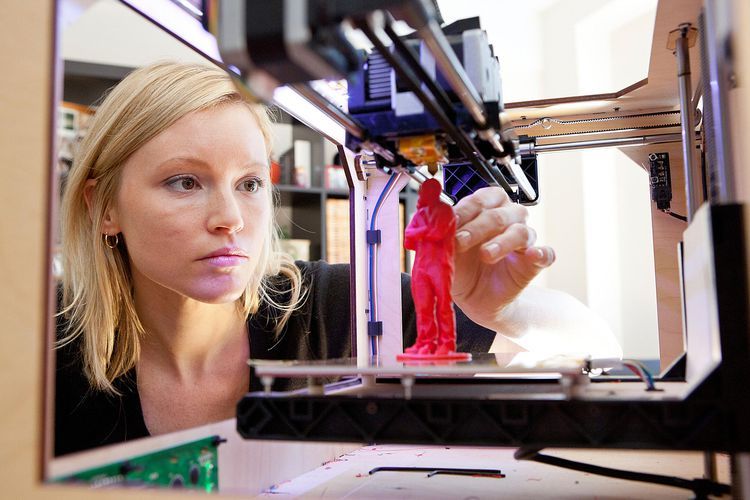 S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
S., the U.K. and Asia. “As 3D printing technologies advance, new business models will emerge in which consumer products and their component parts can be copied, modified, juxtaposed with others and produced almost anywhere.”
As a result, there will be an increased need for IP enforcement actions and lawsuits, as well as expanded services to monitor for infringements, Matthews explained.
Growth areas include IP ownership, scope of rights, licensing, fair use and international rights.
8. Startup companies
Thinking of starting a new business? 3D printing offers opportunities for innovation – not only in creating products, but also for entrepreneurship. 3D printing spans across various technical and design roles, many of which make great business ideas to support companies’ 3D printing needs.
“As 3D printing technologies advance and become readily accessible to home users, undoubtedly, this will lead to new business opportunities for individuals and companies offering onsite and remote 3D printing services, new product and industrial designers, and computer-aided design specialists,” Matthews said.
With 3D printing costing between $1,999 and $3,500, anyone with 3D printing knowledge can start their business.
Tip: Consider a 3D-printing-as-a-service franchise for your new business venture.
9. Administrative roles
3D printing companies don’t run on engineers and technicians alone. As the industry grows, new and established 3D printing companies will need employees to keep their business running smoothly. This includes operations and administrative staff, analysts, finance and sales professionals, and retail employees.
“The businesses that will spring up with new business models centered on 3D printing will also have a need for more common jobs that other businesses need, like marketing, clerical, shipping, etc.,” English said.
These jobs will open up in all types of 3D printing companies, including vendors, manufacturers and retail stores.
Business News Daily editorial staff contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.
5 amazing 3D printing careers to inspire students
We are on the cusp of the 3D printing explosion, and the careers that today’s K-8 students choose will look very different than the careers available today. Inspire the young students in your life by sharing these possibilities for their future careers.
1. 3D Chef
Out with the knives and in with the 3D printer. Using printers loaded with the most delicious food these 3D chefs will design and produce beautiful and tasty culinary masterpieces. Don’t believe me, check out Food Ink, the first ever restaurant where everything from the food to the furniture is 3D printed.
In addition to creating a luxurious and fun experience, 3D printed food offers the possibility to bring food to places in the world where it is needed most. After a natural disaster, when food is scarce, bring in a 3D printer to create nutrition dense food on the spot. The possibilities are endless.
The possibilities are endless.
2. Space Architect
Onboard the International Space Station there is an Additive Manufacturing Facility where a 3D printer produces a variety of tools and parts needed on the ISS. Could the future of 3D printing in space involve more that tools, but also printing structures?
Research suggests that it may be possible to 3D print a shelter on the moon using the moon’s surface rock as the printing material. Want to design this future moon base or maybe even one on Mars? Call yourself a future space architect.
3. Body Part 3D designer and creator
Current 3D printing technology allows scientists to print skin, kidney and liver tissues, bone, and blood vessels! But, we can’t use these bio-printed tissues in humans just yet.
However, scientists researching at the cutting edge of 3D bio-printing believe the leap to human use of 3D bio-printed tissues is less than a decade away. Who will be the ones to design and create the 3D printed organs that save our lives: the K-8 students of today.
4. 3D Printing Artist
Nowhere do art and technology mix together better than in 3D printing; from armature artists to professional galleries, 3D printing technology is now a part of the art world.
And it’s just the beginning. As the technology becomes more widely available and increases in speed and capability artists will be able to visualize and create artworks that would not have been possible before 3D printing.
5. 3D Mechanic
A few cars (and buses) have already been 3D printed, but it is far from mainstream. Like the other applications of 3D printing, the automotive industry is looking to capitalize on the economic benefits of 3D printing. Now they just need 3D mechanics to design and create the cars of the future.
What about car repair or part replacement? 3D printing would allow the exact part for your exact car to be printed out, ready for your mechanic to install. What about customization? Perhaps in the future, you and the 3D design mechanic will sit down and create your perfect car in 3D design software.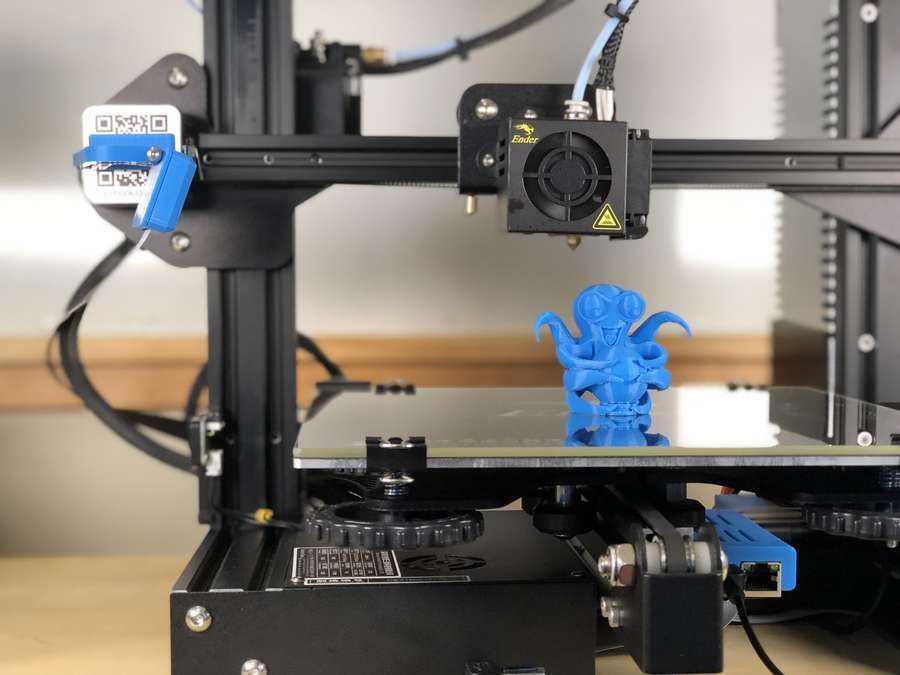
We can’t be certain what the future will hold, but it is clear that 3D printing will be there.
Now it’s your turn to let your imagination run wild. For your next 3D printing class, ask your students to create a new job for themselves that uses 3D printing and then design a device to help them do that job.
Jeanette McConnell, Ph.D. is a passionate educator with a strong scientific background. She earned a bachelor’s degree in biochemistry at San Diego State University and went on to earn a doctoral degree in chemistry at the University of NSW. Throughout her studies, she tutored her fellow students. Her experience presenting science shows and workshops to children convinced her of the value of a hands-on education. She believes Makers Empire is the way to make learning hands-on and harness the power of 3D printing technology in education.
where to study, where to work, salary
Updated
3D printing engineer is engaged in technical support, work with equipment, software, creation of 3D models. A specialist needs to have deep knowledge of engineering, programming, and mathematics. The profession is referred to the specialties of the future. By the way, the ProfGid career guidance center has recently developed an accurate career guidance test that will tell you which professions suit you, give an opinion about your personality type and intelligence. The profession is suitable for those who are interested in physics and mathematics (see. choosing a profession based on interest in school subjects). nine0005
A specialist needs to have deep knowledge of engineering, programming, and mathematics. The profession is referred to the specialties of the future. By the way, the ProfGid career guidance center has recently developed an accurate career guidance test that will tell you which professions suit you, give an opinion about your personality type and intelligence. The profession is suitable for those who are interested in physics and mathematics (see. choosing a profession based on interest in school subjects). nine0005
Content:
- Short description
- Features of the profession
- Plus and minuses
- Plus
- Minuses
- Important personal qualities
- PROMICATION 9001
- Salary
- 3d printing engineer salary as of December 2022
- Professional knowledge
- Examples of companies with 3d printing engineer vacancies
Brief description
The profession of a 3D printing engineer has appeared quite recently, but its value and social significance cannot be underestimated. With the help of 3D printing, unique products used in medicine and industry are already being created today. Mathematicians and engineers are constantly developing more advanced technologies that make it possible to create blanks, anatomical models, souvenirs, houses, prostheses using this type of printing. And printers used for printing with biomaterials make it possible to create human skin, which has become a breakthrough in the treatment of wounds, injuries, and acceleration of the rehabilitation period. nine0005
With the help of 3D printing, unique products used in medicine and industry are already being created today. Mathematicians and engineers are constantly developing more advanced technologies that make it possible to create blanks, anatomical models, souvenirs, houses, prostheses using this type of printing. And printers used for printing with biomaterials make it possible to create human skin, which has become a breakthrough in the treatment of wounds, injuries, and acceleration of the rehabilitation period. nine0005
Read also :
Complete control over 3D printing is carried out by an engineer who is an excellent programmer, technologist, biologist and even a chemist, because the profession forces him to know the composition and properties of different materials well. To work in this area, you must have a technical education, attending IT courses, lectures on modeling will be a plus. A specialist must be able to independently design a 3D model, select the necessary materials, calculate all the risks, and then print, creating products for the field of medicine, aviation, industry, etc.
Occupation specifics
3D printing engineers use different materials for their work, computer programs and industrial 3D printers. Today, medical centers, industrial, aerospace, engineering and other industries need these specialists. There are few specialists, their work cannot be called simple, because the duties of a 3D printing engineer include:
- selection of new materials, testing; nine0013 using modern software to improve and adjust 3D printer settings;
- preparation of layouts, development of raster images for subsequent printing;
- full print control;
- study of new technologies;
- knowledge of certification rules, requirements that are put forward for 3D models and finished products;
- documentation development, software debugging;
- selection of new equipment, training of other employees; nine0014
- equipment maintenance.
Responsibilities vary by location, but a 3D Printing Engineer must be a multi-skilled professional who is ready to quickly learn new technologies at any time and then successfully apply them in practice. Employers put forward strict requirements for engineers, because the wages of such specialists are solid. They must have at least 3 years of practical work experience, the obligatory knowledge of a technical foreign language is important. A 3D printing engineer must know the basics of economics and marketing, because his duties include optimizing workflows aimed at reducing the cost and speed of printing. nine0005
Employers put forward strict requirements for engineers, because the wages of such specialists are solid. They must have at least 3 years of practical work experience, the obligatory knowledge of a technical foreign language is important. A 3D printing engineer must know the basics of economics and marketing, because his duties include optimizing workflows aimed at reducing the cost and speed of printing. nine0005
Read also:
Pluses and minuses
Pluses
- An important profession that will help save millions of lives in the future, improve the environment, and allow the rational use of natural resources.
- 3D printing engineers are unique specialists today.
- Demand in various fields.
- A specialist will have no problems finding a job in megacities.
- The salary is stable and high. nine0014
- An experienced engineer will be able to open his own production for the manufacture of souvenirs or other products.

- You can study in Russia by enrolling in a technical university.
- Lack of physical activity.
Cons
- Working sedentary, but not monotonous.
- Irregular working hours, because the creation of a large product can last for more than 5 hours.
- The cost of industrial 3D printers is high, so in order to organize your own production, you need to think about starting capital or finding an investor. nine0014
- Any mistakes made by a 3D printing engineer are associated with huge financial losses.
- Difficulties with finding work in small towns and villages.
- Work at the computer leads to a decrease in vision.
Important Personal Qualities
A 3D Printing Engineer has a lot of professional knowledge, so he must be an erudite person with an excellent memory. The character of this rare specialist should contain responsibility, curiosity, and creativity. An engineer is obliged to constantly study, a craving for both the exact sciences and linguistics is welcomed, because most of the instructions, books and technical documentation are still being created mainly in foreign languages. nine0005
nine0005
See also:
3D printing engineer training
Universities
-
140,000 ₽/year
no budget places
-
4 years
220,000 ₽/year
15 budget places
-
4 years
48 500 ₽/year
12 budget places
-
36 200 ₽/year
25 budget places
See also:
Place of work
3D printing engineers will be able to work in agencies engaged in the production of consumer goods. They are in demand in architectural companies, factories, medical centers and nanolaboratories, clothing design and manufacturing agencies. 3D printing is used in all spheres of our life, so a young university graduate will be able to choose an interesting and useful direction. nine0005
nine0005
Salary
3d printing engineer salary for December 2022
Salary information is provided by hh.ru portal.
Russia 45000—100000₽
Moscow 60000—150000₽
Professional knowledge
- 3D printing technologies (SLA, FDM and others).
- 3D modeling.
- 3D printing materials (PLA, ABS and others).
- Slicers for preparing for 3D printing, working with software (Autodesk 3ds Max, SolidWorks, Autodesk 123D Design and others). nine0014
- Knowledge of the specifics of different models of equipment.
- Features of processing printed 3D models.
- English.
Read also:
Examples of companies with engineer vacancies 3D-print
Description, where to receive in Russia, prospects
Higher education in Synergy: leading university, all forms of education, star teachers
Apply
Advertising
Category: Physical and technical sciences and technologies
Promising
The profession of 3D printing engineer is relatively new in the labor market. Such specialists are engaged in maintenance of equipment designed for 3D printing of physical objects, software development, installation and adjustment of 3D printers. Also, a 3D printing engineer can be engaged in research activities in his field. nine0005
Such specialists are engaged in maintenance of equipment designed for 3D printing of physical objects, software development, installation and adjustment of 3D printers. Also, a 3D printing engineer can be engaged in research activities in his field. nine0005
Demand for the profession
The market for 3D printing services is developing unevenly. There are certain areas where such specialists are in high demand. However, as a rule, very strict requirements are imposed on applicants in terms of qualifications and professionalism. It seems that over time the need for 3D printing engineers will increase significantly. Many areas of activity, from medicine to industrial production, will attract such specialists. Prospects for the profession are wide. nine0005
Who is the profession for?
A 3D printing engineer is focused on working with complex computer equipment. Such a profession makes special demands on the personal qualities of a specialist.
The profession can be recommended to those who:
- Interested in technology, computers, programming;
- Purposeful and organized;
- Can formulate problems and build algorithms for solving them;
- Comprehensively developed, erudite, has a large vocabulary; nine0014
- Interested in innovation, easily adapts to new technologies;
- Able to work in a team.

Career
Career growth is not obvious, this profession is not yet widespread in the labor market. Such specialists work in rather specific organizations that provide narrow-profile services. However, a qualified 3D printing engineer is a highly qualified specialist in the field of programming and the use of computer systems. Such engineers will be able to achieve good positions in related professions, in large industrial and commercial structures. Most often, a young engineer is expected to occupy the position of a specialist in a scientific or industrial organization. nine0005
Responsibilities
Being a highly specialized specialist, a 3D printing engineer performs the entire range of maintenance and operation of 3D printers.
His duties include:
- Installation and adjustment of equipment for 3D printing;
- Development, installation, maintenance of 3D printer software;
- Perform routine maintenance, minor repairs of equipment;
- Adaptation of the terms of reference to the specific conditions for the manufacture of 3D printing products; nine0014
- Control of geometric and physical parameters at all stages of product manufacturing;
- Procurement of additional equipment and consumables.

Learn more